Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for how to test a starter
In today’s fast-paced global market, understanding how to test a starter is crucial for businesses looking to maintain operational efficiency and reduce unnecessary costs. Many international B2B buyers, particularly in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, face challenges in sourcing reliable components for their machinery and vehicles. A faulty starter can lead to significant downtime, impacting productivity and profitability. This comprehensive guide aims to equip you with the knowledge and tools necessary to effectively assess starter performance, thereby empowering informed purchasing decisions.
Throughout this guide, we will delve into various types of starters, their applications across different industries, and the essential steps for testing their functionality. Additionally, we will explore supplier vetting strategies to ensure you partner with reputable manufacturers and distributors, as well as provide insights into cost considerations to help you budget effectively. By arming yourself with this information, you can navigate the complexities of the global market with confidence, ensuring that your organization minimizes risks associated with faulty components.
Whether you are based in Saudi Arabia, Nigeria, or elsewhere, this guide serves as an invaluable resource, allowing you to make strategic decisions that enhance your operational capabilities and ultimately drive your business forward.
جدول المحتويات
- Top 3 How To Test A Starter Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for how to test a starter
- Understanding how to test a starter Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of how to test a starter
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘how to test a starter’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for how to test a starter
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for how to test a starter
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘how to test a starter’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for how to test a starter Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing how to test a starter With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for how to test a starter
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the how to test a starter Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of how to test a starter
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for how to test a starter
- إخلاء مسؤولية هام وشروط الاستخدام
Understanding how to test a starter Types and Variations
| اسم النوع | السمات المميزة الرئيسية | التطبيقات الأساسية بين الشركات (B2B) | مزايا وعيوب موجزة للمشترين |
|---|---|---|---|
| اختبار المقعد | Involves removing the starter and testing it independently. | ورش تصليح السيارات وموردي قطع الغيار | الإيجابيات: Accurate results, isolates issues. السلبيات: Time-consuming and requires specialized equipment. |
| اختبار انخفاض الجهد | Measures voltage drop across the starter circuit during operation. | Electrical diagnostics, fleet maintenance | الإيجابيات: Quick and non-invasive. السلبيات: Requires access to diagnostic tools and trained personnel. |
| اختبار السحب الحالي | Assesses the amount of current the starter draws when engaged. | Fleet management, automotive service centers | الإيجابيات: Identifies potential electrical issues. السلبيات: May require additional tools and expertise. |
| Inductive Ammeter Test | Uses an inductive ammeter to measure current flow without direct contact. | Electrical repair services, automotive workshops | الإيجابيات: Safe and efficient. السلبيات: Limited availability of equipment and requires skilled operators. |
| الفحص البصري | Involves a thorough visual check for signs of wear, corrosion, or damage. | Maintenance teams, automotive retailers | الإيجابيات: Cost-effective and quick. السلبيات: May overlook internal failures not visible externally. |
What Are the Characteristics of Bench Testing for Starters?
Bench testing is a method where the starter is removed from the vehicle and tested independently using specialized equipment. This process allows for a comprehensive evaluation of the starter’s functionality, including checking the motor, solenoid, and other components. It’s particularly suitable for automotive repair shops and parts suppliers that need to ensure the reliability of the starter before installation. However, this method can be time-consuming and may require investment in diagnostic equipment, making it less feasible for smaller operations.
How Does Voltage Drop Testing Work in Diagnosing Starters?
Voltage drop testing involves measuring the voltage across the starter circuit while the engine is being cranked. This method helps identify any resistance in the wiring or connections that could affect performance. It’s particularly beneficial for electrical diagnostics and fleet maintenance, where quick checks are essential for minimizing downtime. While voltage drop tests are relatively quick and non-invasive, they require access to diagnostic tools and trained personnel to interpret the results accurately.
Why Use Current Draw Testing for Starters?
Current draw testing measures the amount of electrical current the starter consumes when engaged. This test is vital for fleet management and automotive service centers, as it can reveal underlying electrical issues that may not be evident through visual inspection. The benefits of this method include quick identification of problems, but it may necessitate additional tools and expertise to conduct effectively, which can be a barrier for some businesses.
What Are the Advantages of Using an Inductive Ammeter Test?
Inductive ammeter testing employs an inductive ammeter to assess current flow without needing direct contact with the electrical circuit. This method is popular among electrical repair services and automotive workshops due to its safety and efficiency. While it provides valuable insights into the starter’s performance, the availability of the necessary equipment and the requirement for skilled operators can limit its widespread use.
How Effective is Visual Inspection in Starter Diagnostics?
Visual inspection is the simplest method, involving a thorough check for visible signs of wear, corrosion, or damage on the starter and its connections. This method is cost-effective and can be performed quickly, making it suitable for maintenance teams and automotive retailers. However, while it can identify obvious external issues, it may overlook internal failures, necessitating further testing for a complete diagnosis.
Key Industrial Applications of how to test a starter
| الصناعة/القطاع | Specific Application of how to test a starter | القيمة/الفائدة للأعمال | اعتبارات التوريد الرئيسية لهذا التطبيق |
|---|---|---|---|
| إصلاح السيارات | Diagnosing starter issues in vehicles during maintenance services | Reduces downtime and repair costs | توافر أدوات التشخيص والفنيين المهرة |
| المعدات الثقيلة | Testing starters in construction and agricultural machinery | يضمن الكفاءة التشغيلية والسلامة | Access to specialized testing equipment and parts |
| النقل واللوجستيات | Ensuring reliable starter function in fleet vehicles | Minimizes disruptions and enhances fleet reliability | Supplier relationships for quick access to replacement parts |
| التعدين | Verifying starter performance in mining equipment | Enhances productivity and reduces equipment failure | Compliance with local regulations and sourcing reliability |
| Marine & Offshore | Testing starters in marine engines and equipment | Increases safety and operational readiness | Availability of marine-grade components and expertise |
How is ‘how to test a starter’ used in Automotive Repair?
In the automotive repair industry, testing a starter is crucial for diagnosing electrical issues in vehicles. This process involves checking the current draw, inspecting connections, and ensuring the starter engages properly. For international buyers, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, the availability of local repair shops equipped with the necessary diagnostic tools is essential. Proper testing can prevent costly repairs and ensure vehicles are safe and reliable, thereby enhancing customer satisfaction and loyalty.
What are the implications of starter testing in Heavy Equipment?
In heavy equipment sectors, such as construction and agriculture, starters play a pivotal role in ensuring machinery operates efficiently. Testing starters helps identify potential failures that could lead to machinery downtime, which is costly in these industries. Buyers must consider sourcing equipment that can handle the harsh conditions often found on job sites. Additionally, having access to skilled technicians who understand the specific requirements of heavy machinery is critical for effective maintenance and operation.
How does starter testing impact Transportation & Logistics?
For businesses in transportation and logistics, ensuring that fleet vehicles start reliably is paramount. Regular starter testing can prevent unexpected breakdowns that disrupt operations and lead to financial losses. Companies should prioritize partnerships with suppliers who can provide timely access to replacement parts and diagnostic tools. In regions with challenging supply chains, establishing strong supplier relationships is vital for maintaining fleet reliability and ensuring timely deliveries.
Why is starter testing crucial in Mining operations?
In the mining industry, equipment reliability is directly linked to productivity. Testing starters in mining machinery ensures that equipment is operational when needed, reducing the risk of costly delays. Buyers should focus on sourcing components that meet local regulations and environmental standards. Additionally, understanding the specific operational challenges faced in different mining environments can help businesses select the right testing solutions to enhance operational efficiency.
How does starter testing contribute to Marine & Offshore applications?
In marine and offshore operations, the reliability of starters in engines and equipment is critical for safety and efficiency. Regular testing helps prevent failures that could lead to hazardous situations at sea. Buyers in this sector must ensure they have access to marine-grade components and expertise in starter testing. Additionally, compliance with maritime regulations is essential, making it important for businesses to partner with suppliers who understand these specific industry requirements.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘how to test a starter’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Misdiagnosis Leading to Unnecessary Repairs
المشكلة: One of the most common challenges B2B buyers face when testing a starter is the risk of misdiagnosis. Many businesses rely on external mechanics for starter testing, and the lack of clarity in communication can lead to unnecessary repairs. For instance, a company might be quoted for a complete starter replacement when the issue could simply be a faulty battery connection or a defective relay. This not only results in wasted resources but also affects operational efficiency and budget allocation.
الحل: To mitigate this issue, businesses should invest in training personnel or acquiring diagnostic tools for basic starter testing. Understanding how to conduct simple tests, such as measuring voltage at the starter with a multimeter or checking for draw using an ammeter, can significantly reduce reliance on external mechanics. Additionally, businesses can establish a clear communication protocol with service providers, requiring detailed diagnostic reports before approving repairs. This ensures that any proposed solutions are backed by evidence, ultimately saving costs and improving maintenance strategies.
Illustrative image related to how to test a starter
السيناريو 2: نقص المعرفة التقنية بين الموظفين
المشكلة: A significant pain point for many organizations is the gap in technical knowledge regarding starter systems among staff. Employees may lack the skills or understanding to perform essential tests, leading to delays in troubleshooting and increased downtime. This is particularly problematic in industries where vehicles or machinery are critical to operations, as any delay can have a cascading effect on productivity and profitability.
الحل: Organizations should consider implementing a structured training program focused on electrical systems and starter testing procedures. This could involve hands-on workshops led by experienced technicians or partnerships with vocational schools to provide ongoing education. Furthermore, businesses can create easy-to-follow manuals or video tutorials that outline testing procedures for starters. By empowering staff with the necessary knowledge, companies can enhance their operational efficiency and reduce dependency on external service providers.
Scenario 3: Inconsistent Testing Equipment and Practices
المشكلة: Inconsistent testing practices and equipment can lead to unreliable results when diagnosing starter issues. Many businesses operate with varying levels of equipment quality, which can result in discrepancies in testing outcomes. For example, using outdated or faulty multimeters can lead to incorrect voltage readings, further complicating the diagnosis and potentially resulting in unnecessary replacement of parts.
الحل: To address this inconsistency, organizations should standardize their testing equipment and procedures across all service locations. This includes investing in high-quality, reliable diagnostic tools that are regularly calibrated and maintained. Additionally, businesses should develop a set of best practices for testing starters, including step-by-step guidelines that all technicians must follow. Implementing a quality control process where results are cross-verified by multiple technicians can also help ensure accuracy. By standardizing equipment and practices, organizations can improve diagnostic reliability and reduce the likelihood of costly errors in starter testing.
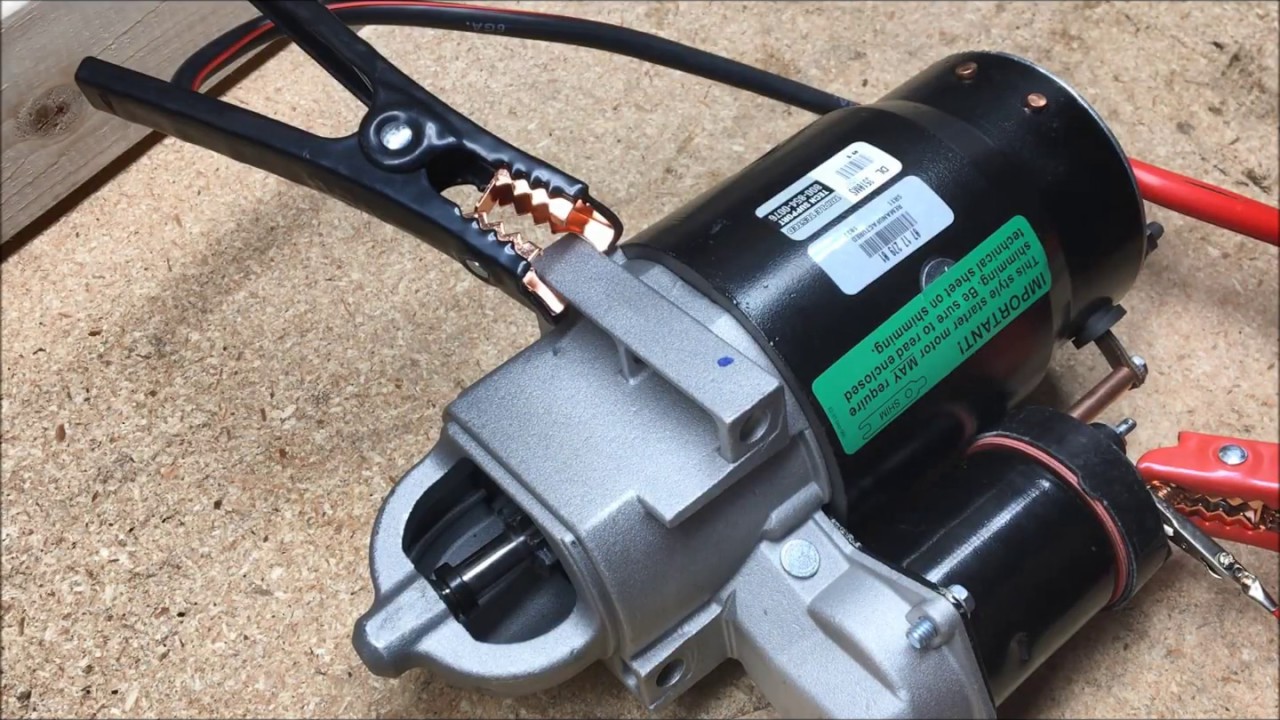
Strategic Material Selection Guide for how to test a starter
When selecting materials for testing a starter, it is essential to consider the specific properties, advantages, and limitations of each material. This analysis focuses on four common materials: copper, aluminum, steel, and plastic. Each of these materials has unique characteristics that can significantly impact the performance and reliability of starter testing tools and equipment.

Illustrative image related to how to test a starter
What are the Key Properties of Copper in Starter Testing?
Copper is widely recognized for its excellent electrical conductivity and thermal properties, making it a preferred choice for wiring and connectors in starter testing applications. It can handle high temperatures and provides low resistance, which is crucial for accurate testing results. However, copper is susceptible to corrosion, especially in humid environments, which can lead to degradation over time.
الإيجابيات: High conductivity, excellent thermal properties, and ease of soldering.
سلبيات: Prone to corrosion, higher cost compared to aluminum.
For international buyers, especially in regions like Africa and the Middle East, it is vital to consider the local climate when using copper components. Corrosion-resistant coatings may be necessary to ensure longevity.
How Does Aluminum Compare for Testing Starters?
Aluminum is another popular choice due to its lightweight nature and good conductivity, although it is not as conductive as copper. It offers excellent resistance to corrosion, making it suitable for various environments, including those with high humidity or salt exposure. Aluminum components are often more cost-effective than copper, which can be advantageous for budget-conscious buyers.
الإيجابيات: Lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and cost-effective.
سلبيات: Lower conductivity than copper and potential for galvanic corrosion when in contact with other metals.
For B2B buyers in South America and Europe, aluminum’s compliance with various international standards (such as ASTM) can simplify procurement processes. Additionally, its lightweight nature can reduce shipping costs.
What Role Does Steel Play in Starter Testing Applications?
Steel is frequently used in structural components of testing equipment due to its strength and durability. It can withstand high pressures and temperatures, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications. However, steel is prone to rust and corrosion, particularly if not properly treated or coated.
الإيجابيات: High strength, durability, and cost-effective for structural applications.
سلبيات: Susceptible to rust and corrosion, heavier than aluminum and copper.
International buyers should be aware of the need for protective coatings or treatments to prevent corrosion, especially in regions with high moisture levels, such as Nigeria and parts of Europe.
Why is Plastic a Viable Option for Testing Starters?
Plastic materials are often used for non-conductive components in starter testing equipment. They are lightweight, resistant to corrosion, and can be manufactured in various shapes and sizes. However, plastics may have lower temperature resistance compared to metals and can degrade over time when exposed to certain chemicals.
الإيجابيات: Lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and versatile in design.
سلبيات: Lower temperature resistance and potential chemical degradation.
For buyers in the Middle East and Africa, selecting high-quality plastics that comply with local standards can enhance product reliability and performance.
جدول تلخيصي لاختيار المواد لاختبار المبتدئين
| المواد | Typical Use Case for how to test a starter | الميزة الرئيسية | العيب/القيود الرئيسية | التكلفة النسبية (منخفضة/متوسطة/عالية) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| النحاس | الأسلاك والموصلات | موصلية كهربائية عالية | عرضة للتآكل | عالية |
| الألومنيوم | Lightweight structural components | Corrosion-resistant | موصلية أقل من النحاس | متوسط |
| الصلب | المكونات الهيكلية | قوة ومتانة عالية | عرضة للصدأ | منخفض |
| بلاستيك | Non-conductive parts | خفيفة الوزن ومتعددة الاستخدامات | مقاومة درجات الحرارة المنخفضة | متوسط |
This analysis provides a comprehensive overview of material selection for testing starters, emphasizing the importance of understanding each material’s properties, advantages, and limitations. For international B2B buyers, aligning material choices with local conditions and compliance standards is crucial for ensuring product reliability and performance.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for how to test a starter
ما هي المراحل الرئيسية في عملية تصنيع البادئات؟
The manufacturing of starters involves several critical stages, each of which plays a vital role in ensuring the final product’s reliability and performance. Understanding these stages can provide B2B buyers with insights into the quality and durability of the starters they intend to procure.
تحضير المواد: ما هي المواد المستخدمة في تصنيع البادئ؟
The first stage in the manufacturing process is material preparation. Starters typically consist of various components, including the housing, armature, field coils, and solenoid. Common materials used include high-strength steel for the housing, copper for electrical components, and durable plastics for insulation. Suppliers often procure these materials from certified vendors to ensure they meet specific mechanical and electrical standards. Buyers should inquire about the sourcing of materials, as this directly impacts the longevity and reliability of the starter.
كيف تتم عملية التشكيل للمبتدئين؟
The forming process involves shaping and assembling the various components. Techniques such as stamping, machining, and molding are common. For instance, the housing is often stamped from sheets of steel, while the armature is machined to precise specifications to ensure proper fit and function. Advanced manufacturing technologies, such as CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining, are frequently employed to enhance accuracy and reduce waste. B2B buyers should consider suppliers that utilize these technologies, as they typically yield higher-quality products with fewer defects.
ما الذي تنطوي عليه عملية التجميع؟
Once the components are formed, the assembly process begins. This stage involves fitting the armature into the housing, connecting the field coils, and integrating the solenoid. Automated assembly lines are commonly used to enhance efficiency and consistency. However, manual inspections are still essential at this stage to ensure that all components are correctly aligned and securely fastened. Buyers should request information on the assembly methods used by their suppliers, as a robust assembly process can significantly affect the starter’s performance.
How Is the Finishing Process Carried Out?
The finishing stage involves several treatments, such as painting, coating, or plating, to enhance corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal. For starters, a protective coating is essential to prevent rust and deterioration, especially in environments with high humidity or exposure to corrosive elements. B2B buyers should verify that their suppliers apply industry-standard finishing techniques, as this can prolong the life of the starter and reduce maintenance costs.
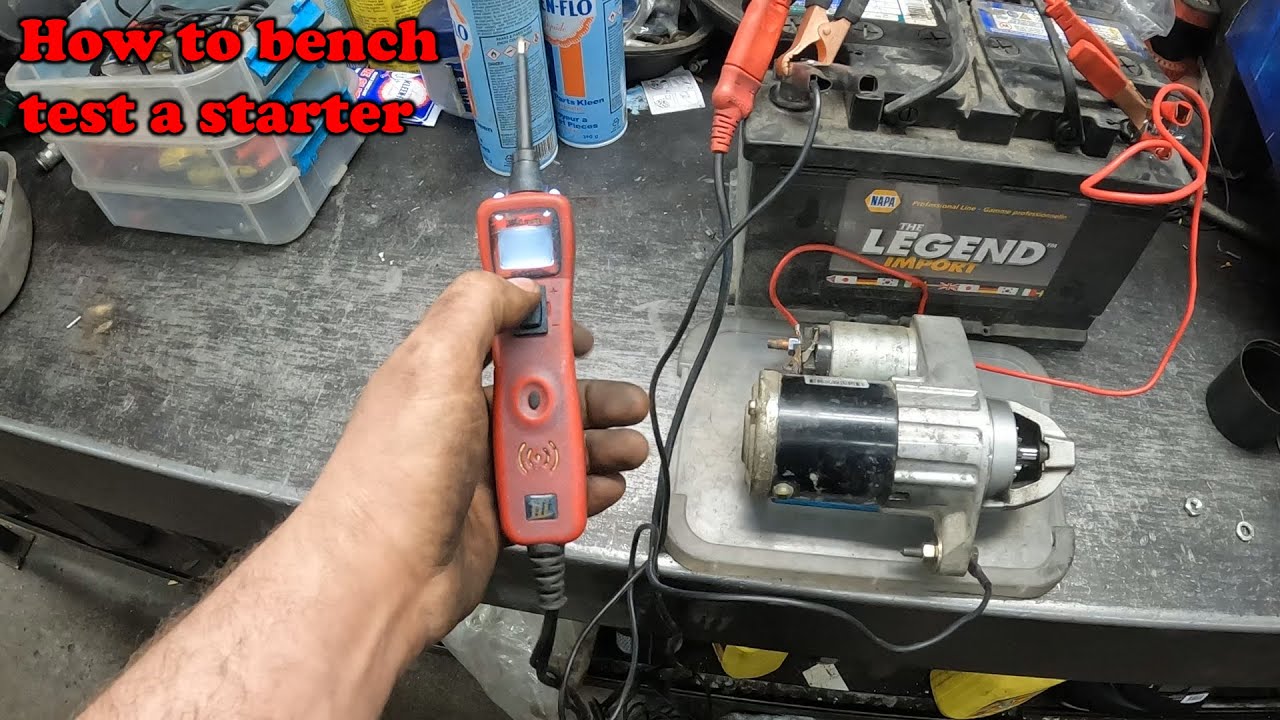
ما هي تدابير مراقبة الجودة المطبقة في تصنيع البادئ؟
Quality control (QC) is a crucial aspect of the manufacturing process, ensuring that starters meet specific performance and safety standards. Various international and industry-specific standards govern these QC measures.

Illustrative image related to how to test a starter
Which International Standards Apply to Starter Manufacturing?
ISO 9001 is a widely recognized international standard that outlines criteria for quality management systems. Manufacturers aiming for ISO 9001 certification demonstrate their commitment to consistent quality and customer satisfaction. Additionally, industry-specific certifications, such as CE marking for compliance with European health, safety, and environmental protection standards, and API standards for petroleum and natural gas equipment, may also apply. B2B buyers should seek suppliers with these certifications, as they indicate adherence to rigorous quality standards.
What Are the Key QC Checkpoints During the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control checkpoints are established throughout the manufacturing process, including Incoming Quality Control (IQC), In-Process Quality Control (IPQC), and Final Quality Control (FQC).
- IQC involves inspecting raw materials and components upon arrival to ensure they meet specifications.
- IPQC monitors the manufacturing process, checking for defects or deviations in real-time.
- FQC is the final inspection stage, where finished products are tested for functionality, performance, and safety.
Implementing these checkpoints helps identify and rectify issues early in the production process, reducing the risk of defective products reaching the market.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used to Validate Starter Performance?
Testing methods are critical in validating the performance and reliability of starters. Common tests include:
- Bench Testing: Involves running the starter on a testing rig to assess its functionality under load.
- Inductive Ammeter Testing: Measures the current draw when the starter is engaged to ensure it operates within specified limits.
- اختبار المتانة: Simulates extended use to identify potential failure points over time.
B2B buyers should inquire about the specific testing methods employed by suppliers to ensure that the starters meet performance expectations.
كيف يمكن للمشترين B2B التحقق من ممارسات مراقبة الجودة لدى الموردين؟
For international B2B buyers, verifying the quality control practices of potential suppliers is essential. Here are several effective strategies:
-
عمليات التدقيق: Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to assess the manufacturing processes and quality control measures firsthand. This can include reviewing documentation and observing operations.
-
تقارير الجودة: Requesting detailed quality reports can provide insights into the supplier’s QC history, including defect rates, testing results, and corrective actions taken.
-
عمليات التفتيش من طرف ثالث: Engaging third-party inspection services can offer an unbiased evaluation of the supplier’s quality management practices and product reliability.
ما هي الفروق الدقيقة في مراقبة الجودة والاعتماد للمشترين الدوليين بين الشركات؟
International buyers should also be aware of specific nuances regarding quality control and certification, particularly when sourcing from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Regulatory requirements may differ significantly between regions, and understanding local standards is vital for compliance.
For instance, while CE marking is critical for European markets, products sold in African and South American markets may need to meet different local regulations. Buyers should ensure that their suppliers are well-versed in these regulations and can provide the necessary documentation to demonstrate compliance.
By focusing on these manufacturing and quality assurance aspects, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing starters, ultimately enhancing their operational reliability and reducing costs associated with product failures.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘how to test a starter’
مقدمة
In the realm of automotive maintenance, testing a starter is a critical task that can save time and resources for businesses involved in vehicle servicing and parts procurement. This guide offers a systematic approach to understanding how to test a starter effectively, ensuring you can make informed decisions when sourcing necessary components or services.
الخطوة 1: Understand the Starter Functionality
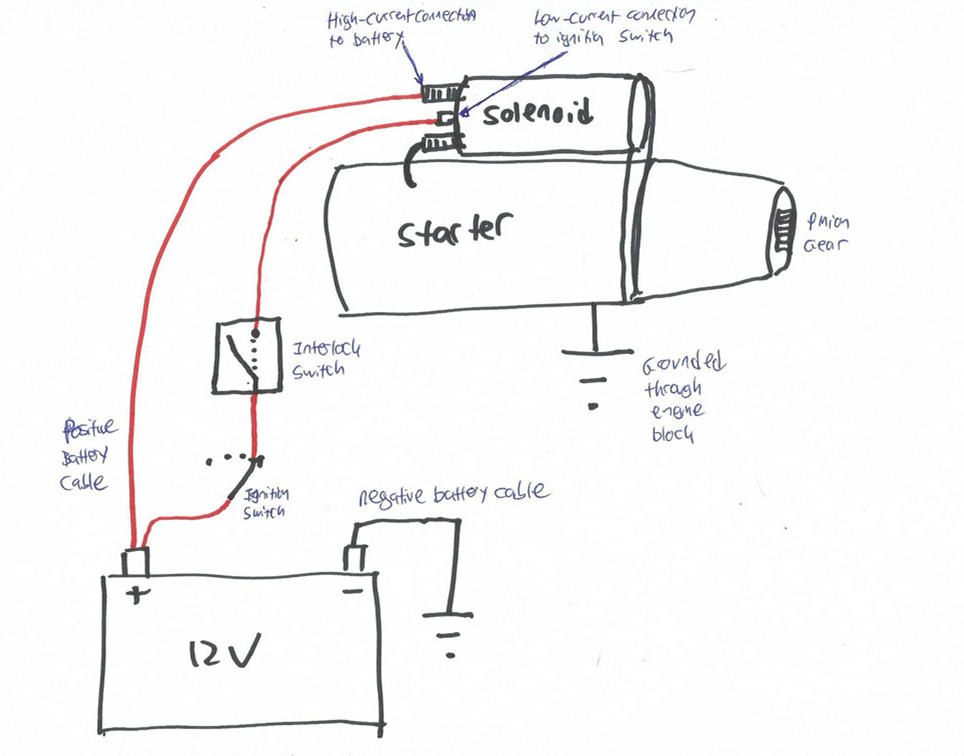
Grasping how a starter operates is essential for any testing process. The starter’s primary role is to crank the engine, initiating the combustion process. Familiarize yourself with the components involved—such as the solenoid, the battery connections, and the starter motor itself—to identify potential failure points during testing.
الخطوة 2: Gather Required Tools and Equipment
Before starting any testing procedure, ensure you have the necessary tools at hand. Common tools include:
– Multimeter: For checking voltage and continuity.
– Jumper Cables: To provide direct power to the starter.
– Inductive Ammeter: To measure the current draw when the starter is engaged.
Having these tools ready will streamline the testing process and help diagnose issues accurately.
الخطوة 3: إجراء فحص بصري
Conducting a thorough visual inspection of the starter and its connections is a crucial first step. Look for signs of wear, corrosion, or damage to wires and terminals. A clean and secure connection is vital for proper starter function. If any components appear burnt or melted, it may indicate a more serious electrical issue.
الخطوة 4: Test the Voltage at the Starter
Using a multimeter, check the voltage at the starter while someone attempts to crank the engine. Ideally, you should see at least 12.4 volts. If the voltage is significantly lower, it may indicate a problem with the battery or the wiring. This step helps pinpoint whether the issue lies within the starter itself or in the electrical supply leading to it.
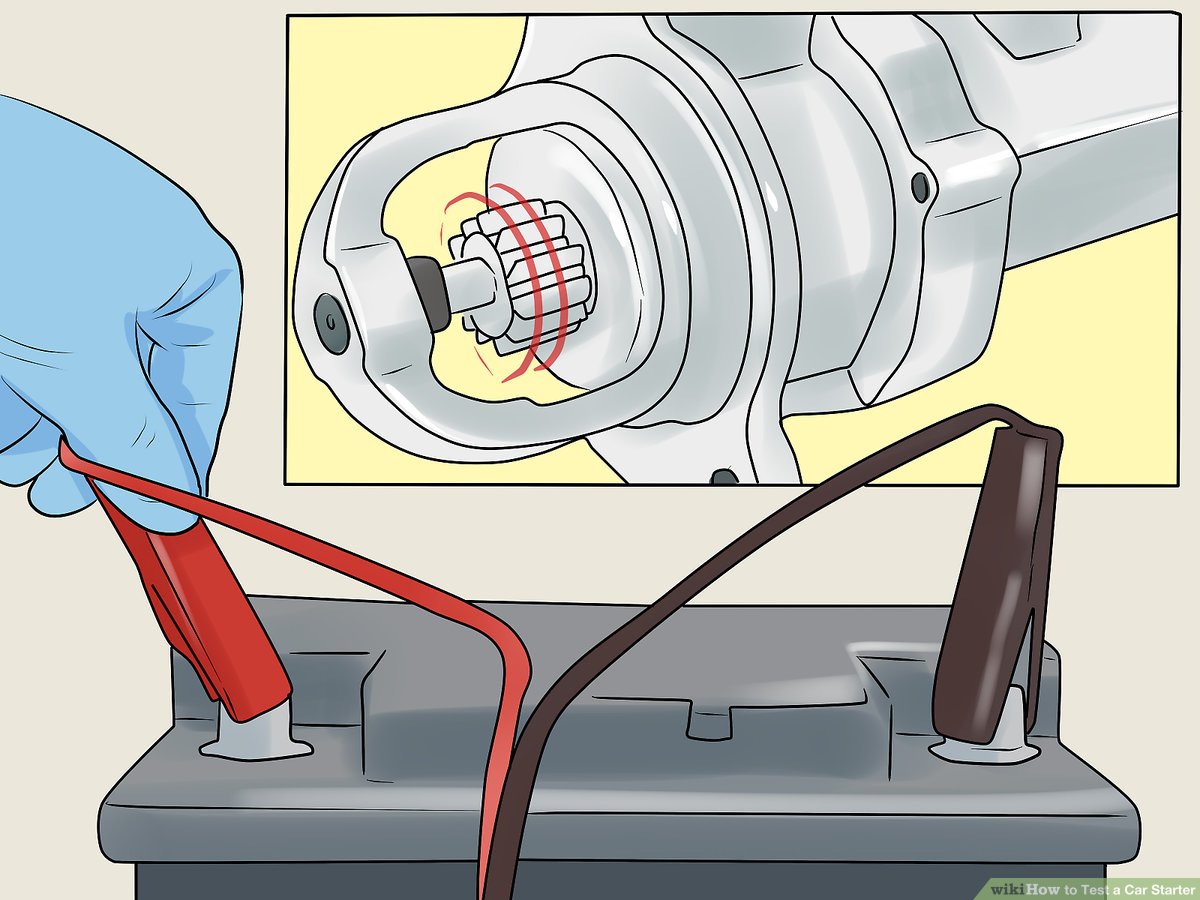
الخطوة 5: Bench Test the Starter
If the starter is removed, perform a bench test to verify its functionality. Connect the starter to a battery using jumper cables and activate it briefly. Observe if the starter engages and the bendix extends. If it does not operate as expected or emits a burnt smell, replacement may be necessary.
الخطوة 6: Evaluate Current Draw
While conducting the bench test, use an inductive ammeter to measure the current draw. A typical starter should draw between 150 to 200 amps. If the current exceeds this range, it may indicate internal issues such as shorted windings or excessive friction. Understanding current draw is crucial for assessing the starter’s health.
الخطوة 7: Consult with Professionals if Needed
If the testing process yields inconclusive results or if you lack the expertise to interpret the findings, consider consulting with automotive professionals or specialized shops. These experts can provide advanced diagnostics and repair services, ensuring that your starter issues are resolved effectively and efficiently.
By following these steps, B2B buyers can ensure they are well-equipped to test starters accurately, leading to better procurement decisions and enhanced operational efficiency in their automotive services.
Illustrative image related to how to test a starter
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for how to test a starter Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Testing a Starter?
When considering the cost structure for testing a starter, several critical components come into play. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margins.
-
المواد: The essential materials for testing a starter typically include electrical components such as wiring, connectors, and testing equipment like ammeters and multimeters. These materials are vital for accurate diagnostics and can vary in cost based on quality and sourcing.
-
العمل: Labor costs can significantly influence the total expense. Skilled technicians are required to perform diagnostic tests, which may involve disassembling the starter and conducting electrical tests. Labor rates can vary widely depending on geographic location and expertise, often ranging from $50 to $150 per hour.
-
تكاليف التصنيع العامة: This includes costs associated with the facilities and equipment used for testing starters. Overhead can be a fixed cost that impacts pricing regardless of the volume of starters being tested.
-
الأدوات: Specialized tools required for testing starters can add to the initial setup costs. These tools may include diagnostic machines and testing rigs, which can be costly but are essential for efficient operations.
-
مراقبة الجودة (QC): Ensuring that the testing process meets industry standards requires a robust QC system. Implementing QC measures may involve additional costs but ultimately leads to more reliable outcomes, which can reduce return rates and enhance customer satisfaction.
-
اللوجستيات: The transportation of starters to and from testing facilities also contributes to the overall cost structure. Efficient logistics management can help minimize these expenses.
-
الهامش: Finally, profit margins must be factored in. Suppliers typically aim for a margin that reflects the quality of service and expertise provided, which can range from 15% to 30% depending on market conditions.
How Do Price Influencers Affect the Cost of Testing a Starter?
Several factors can influence pricing for testing starters, particularly for international buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
-
الحجم/الحد الأدنى لكمية الطلب: Higher volumes can lead to reduced per-unit costs. Suppliers often offer discounts for bulk orders, which can significantly lower the overall price for buyers.
-
المواصفات والتخصيص: Custom specifications may drive up costs. Buyers should carefully assess whether customization is necessary or if standard testing solutions will suffice.
-
شهادات المواد والجودة: The quality of materials used in testing equipment can vary. Suppliers that offer certified equipment may charge a premium, but this can provide assurance of reliability and compliance with international standards.
-
عوامل الموردين: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can affect pricing. Established suppliers with a proven track record may charge more but offer better service and support.
-
مصطلحات التجارة الدولية: Understanding the terms of sale is crucial. Incoterms dictate shipping responsibilities and costs, which can vary significantly based on the chosen terms (e.g., FOB, CIF). This understanding is essential for accurate budgeting.
What Are Essential Buyer Tips for Negotiating Costs?
B2B buyers can implement several strategies to optimize costs when testing starters:
-
التفاوض: Engage suppliers in discussions about pricing, particularly for larger orders. Leveraging your purchasing power can result in better deals.
-
الفعالية من حيث التكلفة: Evaluate the total cost of ownership rather than just the upfront price. Consider factors such as durability, maintenance, and the potential for future repairs.
-
الفروق الدقيقة في الأسعار للمشترين الدوليين: Be aware of potential additional costs such as tariffs, taxes, and shipping fees when importing equipment. Understanding local regulations can also help avoid unexpected expenses.
-
البحث والمقارنة: Investigate multiple suppliers and compare their offerings. This research can uncover competitive pricing and superior service options.
إخلاء المسؤولية بشأن الأسعار
Prices for testing starters can fluctuate based on market conditions, supplier policies, and geographic factors. It is essential for buyers to conduct thorough research and obtain multiple quotes to ensure they are getting the best value for their investment.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing how to test a starter With Other Solutions
Introduction to Alternative Solutions for Testing Starters
When it comes to diagnosing starter issues in vehicles, businesses often seek efficient and cost-effective methods. While traditional starter testing methods have their benefits, exploring alternative solutions can provide additional insights and potentially save time and money. This section compares the conventional approach of testing a starter against two viable alternatives: using a professional electrical diagnostics service and employing an inductive ammeter for current draw analysis.
جدول المقارنة
| جانب المقارنة | How To Test A Starter | Electrical Diagnostics Service | Inductive Ammeter Testing |
|---|---|---|---|
| الأداء | Reliable for initial tests | Comprehensive and accurate | Quick and effective |
| التكلفة | Low (DIY tools) | High (service fees apply) | Moderate (purchase of meter) |
| سهولة التنفيذ | Moderate (requires tools) | Easy (leave it to professionals) | Easy (requires minimal training) |
| الصيانة | Low (occasional use) | N/A | Low (durable tool) |
| أفضل حالة استخدام | DIY enthusiasts and basic checks | Complex electrical issues | Quick checks of starter draw |
تفصيل البدائل
Electrical Diagnostics Service
Utilizing a professional electrical diagnostics service is an excellent alternative for businesses that prefer to outsource vehicle maintenance tasks. These services provide a comprehensive analysis of the starter and associated electrical systems, ensuring that all potential issues are identified. The primary advantage is the accuracy of the diagnostics, as professionals use advanced tools and have the expertise to interpret results correctly. However, the downside is the cost, which can be significant, especially for small businesses or individual buyers. This method is best used for complex issues where multiple components may be involved.
Inductive Ammeter Testing
An inductive ammeter offers a quick and efficient way to assess the current draw of the starter without removing it from the vehicle. By simply clamping the meter around the battery cable, technicians can determine if the starter is drawing the appropriate amount of current during operation. This method is relatively low-cost and requires minimal training, making it accessible for businesses looking to enhance their diagnostic capabilities. However, while it provides quick insights, it may not uncover deeper electrical issues that a full diagnostic service might catch. This alternative is ideal for routine checks or when immediate troubleshooting is needed.
الخلاصة: اختيار الحل المناسب لاختبار احتياجاتك
Selecting the appropriate method for testing a starter depends on your specific business requirements and resources. For companies with technical expertise and a focus on cost savings, the DIY approach of testing a starter may be sufficient. However, for those facing complex electrical problems, investing in a professional electrical diagnostics service can provide peace of mind through comprehensive analysis. Meanwhile, the inductive ammeter serves as an excellent middle ground, enabling quick assessments that can streamline troubleshooting processes. Evaluating the trade-offs of each option will help B2B buyers make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and budget constraints.

Illustrative image related to how to test a starter
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for how to test a starter
What Are the Essential Technical Properties for Testing a Starter?
When testing a starter, understanding its technical properties is crucial for accurate diagnostics and effective decision-making. Here are the key specifications you should be aware of:
-
التيار المستهلك
The starter motor typically requires a specific amount of electrical current to operate effectively, usually measured in amperes (amps). A healthy starter draws between 100 to 200 amps during operation. If the current draw is significantly higher or lower, it may indicate a fault, such as a short circuit or internal damage. Monitoring the current draw can help identify issues before they lead to complete failure. -
Resistance
The electrical resistance of the starter windings is another critical property. Measured in ohms, resistance should fall within manufacturer specifications. High resistance can indicate wear or damage, which can lead to overheating and eventual failure. Testing for resistance ensures the starter can handle the electrical load without excessive heat generation. -
تصنيف عزم الدوران
Torque is the measure of rotational force produced by the starter motor, typically expressed in inch-pounds or Newton-meters. Each starter has a specified torque rating necessary to crank the engine. Understanding this specification is essential, as insufficient torque may result in failure to start the engine, while excessive torque can damage the starter or the engine itself. -
تركيب المواد
Starters are often constructed from various materials, including metals like copper for electrical components and durable plastics for housing. The material grade affects the starter’s longevity and performance. B2B buyers should ensure that they are sourcing starters made from high-quality materials, as this impacts reliability and warranty considerations. -
نطاق درجة حرارة التشغيل
Starters must operate efficiently across a range of temperatures. This specification indicates the environmental conditions in which the starter can function without failure. Understanding the operating temperature range is vital, especially for businesses operating in extreme climates, ensuring that the starter will perform reliably.
Which Trade Terms Should You Know When Testing a Starter?
Familiarity with industry jargon can streamline communication and improve procurement processes. Here are some essential trade terms:
-
OEM (الشركة المصنعة للمعدات الأصلية)
This term refers to parts made by the original manufacturer of the vehicle. OEM starters are typically more reliable and are designed to fit and function precisely as intended. Understanding the difference between OEM and aftermarket parts is crucial for ensuring quality and compatibility. -
MOQ (الحد الأدنى لكمية الطلب)
MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ is important for B2B buyers to manage inventory effectively and to negotiate better terms, especially when considering bulk purchases. -
طلب عرض أسعار (RFQ)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and availability for specific products, such as starters. This process helps buyers compare options and negotiate better deals, ensuring they receive competitive pricing and favorable terms. -
مصطلحات التجارة الدولية
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) are a set of rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international trade. Understanding these terms is vital for B2B transactions, as they clarify who is responsible for shipping, insurance, and tariffs, reducing the risk of misunderstandings. -
اختبار المقعد
Bench testing involves removing the starter from the vehicle and testing it independently to assess its performance. This method allows for a thorough evaluation of the starter’s functionality, identifying issues that may not be apparent when the starter is installed. -
Solenoid
The solenoid is an electromagnetic switch that engages the starter motor when the ignition key is turned. Understanding the role of the solenoid is essential for diagnosing starting issues, as a faulty solenoid can prevent the starter from operating even if the motor itself is in good condition.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, international B2B buyers can enhance their decision-making process, ensuring they select the right starters for their needs while optimizing procurement strategies.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the how to test a starter Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics for Testing Starters in the Automotive Sector?
The global market for automotive components, including starter testing equipment, is significantly influenced by technological advancements and evolving consumer expectations. One of the primary drivers is the increasing complexity of vehicles, which incorporates more electronic components and systems. This trend necessitates sophisticated diagnostic tools that can accurately assess the functionality of starters and other electrical components. For international B2B buyers, particularly those in emerging markets like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these dynamics is crucial for making informed sourcing decisions.
Additionally, the rise of electric vehicles (EVs) is reshaping the market landscape. As more manufacturers pivot towards electric drivetrains, the demand for conventional starter testing equipment may decline, while testing technologies for EV components gain prominence. B2B buyers should be aware of the shift towards integrated diagnostic solutions that cater to both traditional and electric vehicles. Furthermore, as regulatory pressures increase regarding vehicle emissions and safety, the need for reliable testing equipment becomes paramount.
Emerging technologies, such as IoT and AI, are also playing a vital role in the automotive sector. These technologies allow for real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance, which can enhance the reliability of starters and reduce downtime. Buyers should consider suppliers who invest in these technologies, as they will be better positioned to meet future demands and offer competitive advantages.
How Can B2B Buyers Ensure Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing for Starter Testing Equipment?
In today’s market, sustainability and ethical sourcing are not just optional; they are essential for maintaining a competitive edge. The automotive sector’s environmental impact is substantial, with traditional starter manufacturing processes contributing to resource depletion and pollution. B2B buyers should prioritize suppliers who adopt sustainable practices in their manufacturing processes, such as utilizing recycled materials and minimizing waste.
Moreover, buyers should look for certifications that indicate adherence to environmental standards, such as ISO 14001 for environmental management systems or certifications related to green manufacturing. These certifications assure buyers that their suppliers are committed to reducing their ecological footprint and promoting sustainability.
Ethical sourcing extends beyond environmental concerns. B2B buyers must ensure that their suppliers uphold fair labor practices and provide safe working conditions. This is particularly relevant in regions where labor laws may be less stringent. By choosing suppliers who are transparent about their supply chains and demonstrate a commitment to ethical practices, buyers can enhance their brand reputation and align with growing consumer expectations for corporate responsibility.
What Is the Evolution of Testing Technologies for Starters in the Automotive Industry?
The evolution of testing technologies for starters reflects broader changes in the automotive industry. Initially, starter testing involved basic mechanical checks and manual methods, which often lacked accuracy and reliability. As vehicles became more sophisticated, so did the testing equipment. The introduction of electrical testing devices allowed for more precise diagnostics, reducing the guesswork involved in identifying starter issues.
In recent years, advancements in digital technology have revolutionized starter testing. Modern diagnostic tools incorporate software that can analyze performance metrics and provide detailed reports on starter functionality. This shift not only enhances accuracy but also streamlines the testing process, making it more efficient for technicians and reducing labor costs.
The future of starter testing is likely to be dominated by smart technologies that leverage data analytics and machine learning. These innovations will enable predictive maintenance, allowing businesses to anticipate starter failures before they occur, thus minimizing downtime and improving overall vehicle reliability. As a result, B2B buyers must stay informed about these technological advancements to ensure they invest in the most effective and forward-thinking solutions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of how to test a starter
-
How do I diagnose a faulty starter in a vehicle?
To diagnose a faulty starter, start by checking the battery voltage and connections. Ensure the battery is charged and that the terminals are clean and tight. Next, use a multimeter to measure voltage at the starter when the ignition is turned on; if there’s no voltage, the ignition switch or relay may be faulty. Remove the starter and connect it directly to a power source using jumper cables. The starter should engage and turn the motor; if it doesn’t, it may need replacing. Always consult a service manual for specific vehicle guidance. -
What equipment do I need to test a starter effectively?
To effectively test a starter, you will need a multimeter to measure voltage, an inductive ammeter to check current draw, and jumper cables for direct testing. It’s also helpful to have a service manual for your vehicle, which provides wiring diagrams and troubleshooting steps. In some cases, a specialized starter tester can provide detailed diagnostics. Ensuring you have these tools will streamline the testing process and help you accurately identify issues. -
What are common symptoms of a bad starter?
Common symptoms of a bad starter include a clicking noise when turning the ignition, the engine not cranking, or intermittent starting issues. Additionally, you may notice dimming lights when attempting to start the vehicle or a burning smell from the starter area. If you experience these symptoms, it’s crucial to perform diagnostics as soon as possible to prevent further damage to the vehicle’s electrical system. -
How can I ensure I’m sourcing a reliable starter supplier?
To ensure you’re sourcing a reliable starter supplier, begin by researching potential vendors and reading reviews from other B2B buyers. Check their certifications and industry experience, particularly in your region (Africa, South America, Middle East, or Europe). Request samples to assess product quality and verify their compliance with international standards. Establish communication to gauge their responsiveness and willingness to address your concerns or customization needs. -
What is the typical minimum order quantity (MOQ) for starters?
Minimum order quantities (MOQ) for starters can vary significantly based on the supplier and the specific product. Typically, MOQs range from 50 to 500 units for bulk orders. However, some suppliers may offer lower MOQs for first-time buyers or sample orders. It’s advisable to discuss your requirements with potential suppliers to negotiate MOQs that align with your purchasing strategy. -
What payment terms should I consider when sourcing starters internationally?
When sourcing starters internationally, consider payment terms that ensure security and flexibility. Common options include letters of credit, advance payments, and payment upon delivery. It’s essential to negotiate terms that protect both parties, especially if dealing with new suppliers. Always document agreements clearly and consider using escrow services for larger transactions to mitigate risks associated with international trade. -
How can I customize starters to fit specific vehicle models?
To customize starters for specific vehicle models, communicate your requirements clearly with your supplier. Provide detailed specifications, including dimensions, voltage, and any unique features required for compatibility. Some suppliers may offer customization options, while others may have ready-made solutions for common vehicle models. Ensure you discuss lead times and any additional costs associated with customization during the procurement process. -
What quality assurance measures should I implement when testing starters?
Implementing quality assurance measures when testing starters involves several steps. First, ensure that all testing equipment is calibrated and functioning correctly. Create a standardized testing protocol that includes voltage checks, current draw measurements, and physical inspections of the starter. Document all test results for traceability and future reference. Additionally, consider engaging third-party quality control services to validate the performance of the starters before finalizing large orders.
Top 3 How To Test A Starter Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Reddit – Starter Testing Guide
المجال: reddit.com
تاريخ التسجيل: 2005 (20 عامًا)
مقدمة: To check if your starter is working correctly on your car, you can use a multimeter or jumper cables. A multimeter can help diagnose electrical issues, while jumper cables can be used for a bench test if you remove the starter from the car. Additionally, tapping on the starter while a friend turns the key may help if the starter is stuck.
2. Farmall BN – 6 Volt Starter
المجال: forums.yesterdaystractors.com
تاريخ التسجيل: 1997 (28 عامًا)
مقدمة: Starter for Farmall BN, 6 volt system, can be tested with a battery or battery charger. Caution advised when using 12 volts on a 6 volt starter to avoid overspeeding. Recommendations include visual inspection for wear, checking connections, and load testing under real conditions. Starters can often be repaired without special tools.
3. Elevate Auto – Starter Motor Bench Testing
المجال: elevateauto.com.au
مقدمة: This company, Elevate Auto – Starter Motor Bench Testing, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for how to test a starter
In conclusion, effectively testing a starter is crucial for maintaining operational efficiency and ensuring reliability in your vehicles. By understanding the diagnostic processes—such as checking current draw with an inductive ammeter, verifying voltage at different system points, and utilizing manual or professional services—you can make informed decisions that save time and money.
Strategic sourcing plays a vital role in this process. By selecting suppliers who provide quality parts and reliable diagnostic services, you can enhance your operational capabilities and reduce the risk of unnecessary repairs. This approach not only improves your bottom line but also strengthens relationships with trustworthy partners in the automotive supply chain.
As you navigate the complexities of sourcing and testing starters, consider the unique demands of your market, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Engage with local experts and leverage international networks to ensure you are equipped with the best tools and knowledge. By prioritizing strategic sourcing, you position your business for success in an increasingly competitive landscape. Take action today to optimize your sourcing strategies and ensure your fleet’s performance remains uncompromised.
إخلاء مسؤولية هام وشروط الاستخدام
⚠️ تنويه هام
المعلومات الواردة في هذا الدليل، بما في ذلك المحتوى المتعلق بالمصنعين والمواصفات الفنية وتحليل السوق، هي لأغراض إعلامية وتعليمية فقط. ولا تشكل هذه المعلومات مشورة مهنية في مجال المشتريات أو مشورة مالية أو مشورة قانونية.
على الرغم من أننا بذلنا قصارى جهدنا لضمان دقة المعلومات وحداثتها، فإننا لا نتحمل أي مسؤولية عن أي أخطاء أو سهو أو معلومات قديمة. تخضع ظروف السوق وتفاصيل الشركة والمعايير الفنية للتغيير.
يجب على المشترين من الشركات (B2B) إجراء عمليات التحقق المستقلة والشاملة الخاصة بهم. قبل اتخاذ أي قرارات شراء. ويشمل ذلك الاتصال بالموردين مباشرة، والتحقق من الشهادات، وطلب عينات، والبحث عن استشارة مهنية. يتحمل القارئ وحده مخاطر الاعتماد على أي معلومات واردة في هذا الدليل.