Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for how to check starter with multimeter
In today’s competitive automotive landscape, effectively diagnosing starter issues is critical for maintaining vehicle reliability and minimizing downtime. Understanding how to check a starter with a multimeter is an essential skill for professionals in the automotive supply chain, particularly for B2B buyers seeking reliable solutions. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the various methodologies for testing starters, including electrical system diagnostics and bench testing procedures, ensuring you are well-equipped to tackle common starter-related challenges.
As the global market expands, so too does the need for informed purchasing decisions. This guide addresses key considerations such as the types of starters available, their applications across different vehicle models, and supplier vetting processes to ensure quality and reliability. Additionally, we explore cost implications and value propositions, helping you to navigate the complexities of sourcing automotive components effectively.
By leveraging this resource, B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including key markets like Germany and Brazil—can enhance their procurement strategies. Ultimately, this guide empowers you to make educated choices that not only improve operational efficiency but also foster long-term partnerships with suppliers who meet international standards. Dive into the detailed sections to unlock the insights needed for successful automotive component procurement.
جدول المحتويات
- Top 5 How To Check Starter With Multimeter Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for how to check starter with multimeter
- Understanding how to check starter with multimeter Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of how to check starter with multimeter
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘how to check starter with multimeter’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for how to check starter with multimeter
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for how to check starter with multimeter
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘how to check starter with multimeter’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for how to check starter with multimeter Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing how to check starter with multimeter With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for how to check starter with multimeter
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the how to check starter with multimeter Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of how to check starter with multimeter
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for how to check starter with multimeter
- إخلاء مسؤولية هام وشروط الاستخدام
Understanding how to check starter with multimeter Types and Variations
| اسم النوع | السمات المميزة الرئيسية | التطبيقات الأساسية بين الشركات (B2B) | مزايا وعيوب موجزة للمشترين |
|---|---|---|---|
| Basic Voltage Test | Simple measurement of battery voltage at terminals. | ورش تصليح السيارات وصيانة الأساطيل. | الإيجابيات: Quick and easy; requires minimal equipment. السلبيات: قدرة تشخيصية محدودة. |
| Solenoid Current Test | Tests if the solenoid is receiving adequate power. | Auto parts suppliers, repair technicians. | الإيجابيات: Identifies power issues specifically related to the solenoid. السلبيات: May require additional tools. |
| اختبار المقعد | Involves removing the starter to test it independently. | Engine rebuilders, specialized repair shops. | الإيجابيات: Comprehensive assessment of starter functionality. السلبيات: Labor-intensive; requires technical expertise. |
| اختبار الاستمرارية | Checks for electrical continuity within starter circuits. | Electrical repair services, automotive training centers. | الإيجابيات: Detects wiring issues; ensures all components are functional. السلبيات: Requires knowledge of circuit testing. |
| اختبار الحمل | Measures how the starter performs under load conditions. | Heavy machinery maintenance, commercial vehicle servicing. | الإيجابيات: Provides realistic performance assessment. السلبيات: More complex setup; specialized equipment needed. |
What is the Basic Voltage Test and When Should It Be Used?
The Basic Voltage Test is a fundamental diagnostic method that measures the voltage present at the battery terminals. This test is essential for confirming whether the battery is providing sufficient power to the starter. It is particularly suitable for automotive repair shops and fleet maintenance operations, where quick diagnostics are crucial for efficiency. Buyers should consider that while this test is straightforward and requires minimal equipment, it offers limited diagnostic insight, potentially necessitating further testing for comprehensive troubleshooting.
How Does the Solenoid Current Test Work and Its Applications?
The Solenoid Current Test assesses whether the solenoid, which connects the battery to the starter, is receiving adequate power. This method is vital for auto parts suppliers and repair technicians who need to pinpoint electrical issues without extensive disassembly. The test is advantageous because it directly identifies power-related problems, but it may require additional tools and expertise to execute effectively. Buyers should be aware that this test is more focused than the Basic Voltage Test, making it a valuable step in troubleshooting starter issues.
What is Involved in Bench Testing a Starter?
Bench Testing involves removing the starter from the vehicle to conduct a thorough examination of its functionality. This method is commonly employed by engine rebuilders and specialized repair shops, as it allows for a comprehensive assessment of the starter’s performance. While this test is the most reliable way to determine if a starter is faulty, it requires technical expertise and is labor-intensive. Buyers should weigh the benefits of accurate diagnostics against the increased labor and time investment involved in this process.
Why is Continuity Testing Important for Starters?
Continuity Testing checks for electrical continuity within the starter’s wiring and components, ensuring all parts are functioning correctly. This method is particularly relevant for electrical repair services and automotive training centers, where understanding circuit integrity is crucial. The primary advantage of this test is its ability to detect wiring issues that may not be apparent through other tests. However, it requires a solid understanding of circuit testing, which may be a barrier for less experienced technicians.
What is Load Testing and When Should It Be Conducted?
Load Testing measures how well the starter performs under actual operating conditions, simulating the demands it will face when starting an engine. This testing method is essential for heavy machinery maintenance and commercial vehicle servicing, where reliable performance is critical. While it provides a realistic assessment of starter functionality, it involves a more complex setup and requires specialized equipment. Buyers should consider the importance of this test in high-demand applications, as it ensures that starters can handle the loads they will encounter in real-world scenarios.
Key Industrial Applications of how to check starter with multimeter
| الصناعة/القطاع | Specific Application of how to check starter with multimeter | القيمة/الفائدة للأعمال | اعتبارات التوريد الرئيسية لهذا التطبيق |
|---|---|---|---|
| إصلاح السيارات | Testing starters in vehicles for maintenance and repair | يقلل من وقت التعطل ويحسن رضا العملاء | Quality multimeters that meet international safety standards |
| الآلات الثقيلة | Checking starters in construction and agricultural equipment | ضمان الكفاءة التشغيلية وتقليل الأعطال إلى أدنى حد ممكن | Rugged multimeters suited for harsh environments |
| لوجستيات النقل والمواصلات | Verifying starter functionality in fleet vehicles | Enhances reliability and reduces operational costs | Calibration and certification for fleet maintenance tools |
| معدات صناعية | Assessing starters in generators and pumps | Prevents unexpected failures and service interruptions | Multimeters with advanced features for precise diagnostics |
| Electrical Engineering | Testing electrical systems in manufacturing setups | Improves system reliability and safety compliance | Multimeters that comply with local regulations and standards |
How is ‘how to check starter with multimeter’ utilized in automotive repair?
In the automotive repair industry, multimeters are essential tools for diagnosing starter issues in vehicles. Technicians use multimeters to test battery voltage, check electrical connections, and confirm the functionality of the starter solenoid. This process helps identify problems such as poor connections or faulty starters, enabling timely repairs. For international buyers, sourcing high-quality multimeters that comply with safety standards is crucial, as it ensures reliable diagnostics and enhances customer satisfaction through efficient service.
What role does multimeter testing play in heavy machinery maintenance?
In the heavy machinery sector, multimeters are used to check the starters of construction and agricultural equipment. These machines often operate in demanding environments, making reliable starter performance critical. By using a multimeter to diagnose starter issues, maintenance teams can prevent breakdowns and ensure that equipment is operational when needed. Buyers in this sector should consider rugged multimeters designed for harsh conditions to ensure durability and accuracy in testing.
How does multimeter testing benefit transportation logistics?
In transportation logistics, maintaining fleet vehicles is vital for operational efficiency. Multimeters are used to test starters to ensure that vehicles are ready for use and to minimize downtime caused by starter failures. Regular diagnostics can lead to significant cost savings by preventing unexpected breakdowns. B2B buyers should look for multimeters that offer calibration options, as this ensures consistent performance across a fleet of vehicles.
Why is starter testing critical in industrial equipment?
For industrial equipment, particularly generators and pumps, checking the starter functionality is essential for preventing service interruptions. Multimeters allow technicians to assess the electrical systems that power these machines, ensuring they operate smoothly. By identifying potential issues early, businesses can avoid costly downtime. Buyers should prioritize multimeters with advanced diagnostic features to enhance the reliability of their industrial operations.
What are the implications of multimeter testing in electrical engineering?
In the field of electrical engineering, multimeters are crucial for testing starters within manufacturing setups. Ensuring that electrical systems are functioning correctly is key to maintaining safety and compliance with industry standards. Multimeters help engineers verify connections and troubleshoot issues effectively. International buyers must ensure that their testing equipment meets local regulations, as this is vital for maintaining operational integrity and safety in manufacturing environments.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘how to check starter with multimeter’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Misdiagnosing Starter Issues Due to Multimeter Misuse
المشكلة: B2B buyers often encounter challenges when diagnosing starter problems due to improper use of multimeters. For instance, technicians might misinterpret voltage readings, thinking that a starter is functional when it is not. This misdiagnosis can lead to wasted time and resources, as they may replace other components unnecessarily, such as batteries or solenoids, instead of addressing the actual starter issue.
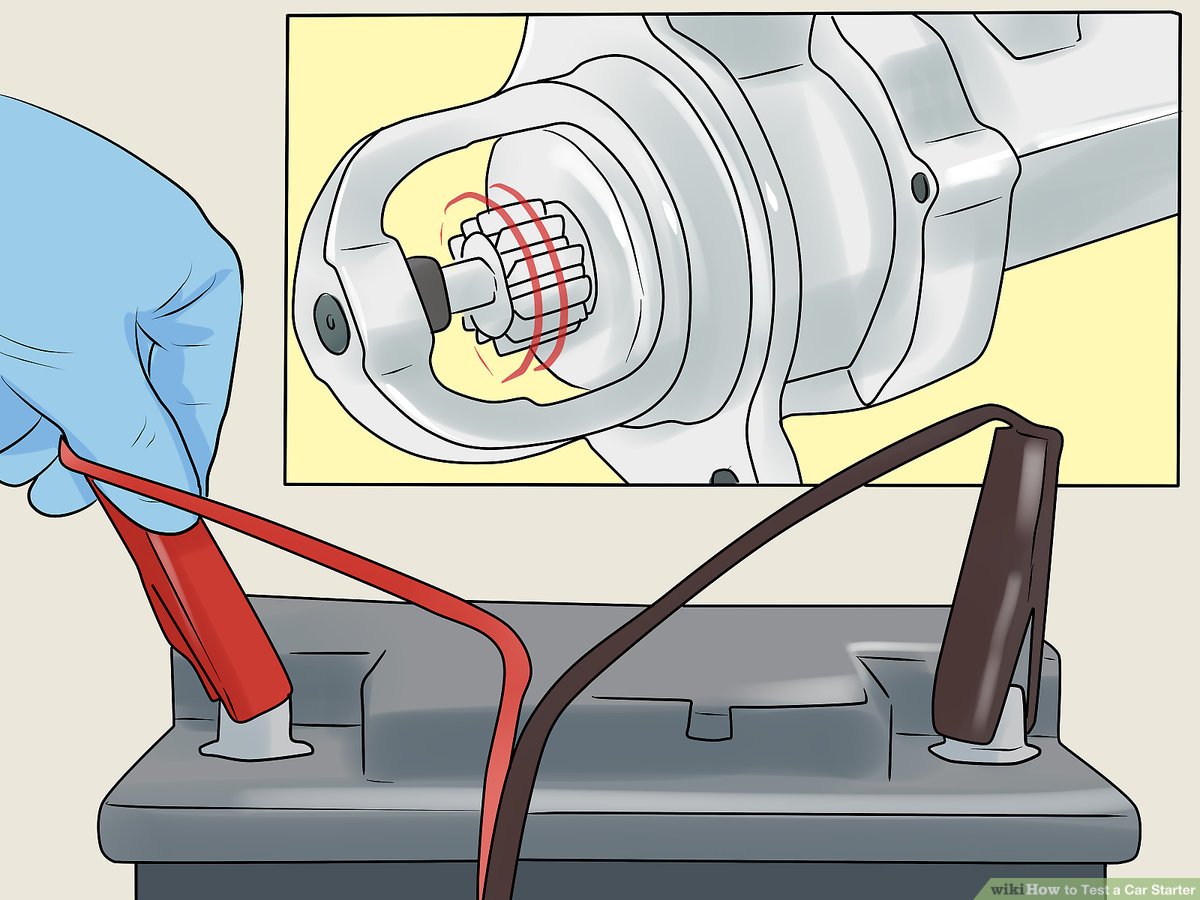
الحل: To ensure accurate readings, it’s crucial to understand the multimeter settings and the specific testing methods for starters. Start by setting the multimeter to the DC voltage range, typically 20V for automotive applications. Connect the red probe to the positive terminal of the battery and the black probe to the negative terminal. A healthy battery should read above 12.6V. If the reading is low, charge or replace the battery before proceeding. Next, test the voltage at the starter’s solenoid while someone attempts to crank the engine. A reading of 12V or more indicates that the starter is receiving adequate power. Educating technicians on these procedures can significantly enhance diagnostic accuracy, reducing misdiagnoses and unnecessary part replacements.
Scenario 2: Inconsistent Results from Bench Testing Starters
المشكلة: Another common pain point is the inconsistency in results when bench testing starters, especially in environments with varying conditions. For instance, a starter may test fine in one instance but fail in actual vehicle operation. This can lead to confusion and distrust in the diagnostic process, causing delays in repair times and potential loss of business for automotive service providers.
الحل: To achieve reliable bench testing results, it is essential to establish a controlled testing environment. Ensure that the multimeter is calibrated correctly and that the power source used for testing is stable and sufficient. When bench testing, connect the starter to a fully charged automotive battery with jumper cables. Use the multimeter to measure voltage at the starter’s terminals while activating it. A consistent reading of around 10-12 volts indicates that the starter is operational. Additionally, implementing a standardized testing protocol, including checking for mechanical issues and ensuring connections are secure, can help technicians achieve consistent and reliable results. Documenting these procedures can also provide valuable data for future diagnostics.
Scenario 3: Lack of Knowledge on Electrical System Interactions
المشكلة: Many B2B buyers, especially those in regions with less access to comprehensive automotive training, face difficulties in understanding how the starter interacts with other electrical components. This lack of knowledge can result in overlooking crucial issues, such as faulty wiring or corroded connections, which can mislead technicians into thinking the starter is the sole problem.
الحل: To overcome this challenge, it’s vital to provide thorough training on the entire electrical system related to the starter. This includes educating staff about the role of the battery, solenoid, and ignition switch in the starting process. A practical approach would be to incorporate hands-on training sessions that simulate common electrical problems. Encourage technicians to perform a systematic check of the entire starting circuit using a multimeter. Start with the battery, ensuring it has a full charge, then proceed to the solenoid and finally the starter. By fostering a holistic understanding of the system, technicians can diagnose issues more effectively, ultimately leading to faster repairs and improved service quality. Offering resources such as instructional videos and troubleshooting guides can further enhance their capabilities.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for how to check starter with multimeter
When selecting materials for components involved in checking a starter with a multimeter, it is crucial to consider properties that affect performance, durability, and compatibility with different environments. Here, we analyze four common materials used in multimeter probes and connectors, focusing on their key properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international B2B buyers.
Which Materials Are Commonly Used for Multimeter Probes and Connectors?
1. النحاس
الخصائص الرئيسية:
Copper is an excellent conductor of electricity, with low resistance and high thermal conductivity. It typically withstands temperatures up to 200°C and is resistant to corrosion when properly treated.
الإيجابيات والسلبيات:
Copper’s high conductivity makes it ideal for electrical applications, ensuring accurate readings. However, it can be prone to oxidation if exposed to moisture, which may affect performance over time. Additionally, while copper is relatively inexpensive, the cost can increase with higher purity grades.
التأثير على التطبيق:
Copper is suitable for environments where high conductivity is essential, but it may require protective coatings in humid conditions.

Illustrative image related to how to check starter with multimeter
اعتبارات للمشترين الدوليين:
Copper standards vary by region, with compliance to ASTM and DIN standards being crucial. Buyers should ensure that suppliers provide certifications confirming the purity and treatment of copper used in their products.
2. PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride)
الخصائص الرئيسية:
PVC is a versatile plastic known for its durability and resistance to chemicals and moisture. It can operate effectively in temperatures ranging from -15°C to 60°C.
الإيجابيات والسلبيات:
PVC is lightweight and cost-effective, making it a popular choice for insulation in multimeter leads. However, its flexibility can be a limitation in high-temperature applications, where it may degrade faster.
التأثير على التطبيق:
PVC is suitable for general-purpose applications, especially in environments with low to moderate thermal and chemical exposure.
اعتبارات للمشترين الدوليين:
Compliance with REACH regulations in Europe and other local standards is essential. Buyers should verify the chemical composition to avoid issues in regions with stringent environmental regulations.
3. Silicone
الخصائص الرئيسية:
Silicone is known for its excellent temperature resistance, typically ranging from -60°C to 200°C, and its flexibility. It also exhibits good electrical insulation properties.
الإيجابيات والسلبيات:
Silicone’s flexibility makes it ideal for use in applications requiring bending and movement, such as in multimeter leads. However, it is generally more expensive than PVC and may not be as durable in harsh mechanical environments.
Illustrative image related to how to check starter with multimeter
التأثير على التطبيق:
Silicone is particularly effective in high-temperature applications and environments where flexibility is crucial, such as automotive or industrial settings.
اعتبارات للمشترين الدوليين:
Buyers should look for silicone that meets international standards like ISO and ASTM. The higher cost may be justified in applications where performance and longevity are critical.
4. Stainless Steel
الخصائص الرئيسية:
Stainless steel is known for its strength, corrosion resistance, and ability to withstand high temperatures. It typically performs well in environments up to 600°C.
الإيجابيات والسلبيات:
Stainless steel is durable and resistant to corrosion, making it suitable for harsh environments. However, it is heavier and more expensive than other materials, which may not be ideal for all applications.
التأثير على التطبيق:
Stainless steel is often used in connectors and probes where durability and resistance to environmental factors are paramount.
اعتبارات للمشترين الدوليين:
International buyers should ensure compliance with standards like ASTM A240 for stainless steel grades. The choice of grade can significantly impact performance and cost.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Multimeter Applications
| المواد | Typical Use Case for how to check starter with multimeter | الميزة الرئيسية | العيب/القيود الرئيسية | التكلفة النسبية (منخفضة/متوسطة/عالية) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| النحاس | Probes and connectors for accurate electrical readings | موصلية كهربائية ممتازة | Prone to oxidation in humid environments | متوسط |
| PVC | Insulation for multimeter leads | خفيفة الوزن وفعالة من حيث التكلفة | مقاومة محدودة لدرجات الحرارة | منخفض |
| Silicone | Flexible leads for high-temperature applications | High flexibility and temperature resistance | Higher cost than PVC | عالية |
| الفولاذ المقاوم للصدأ | Durable connectors in harsh environments | Corrosion-resistant and strong | أثقل وأكثر تكلفة | عالية |
This analysis provides B2B buyers with essential insights into the materials used in multimeter applications, helping them make informed decisions that align with their operational requirements and regional standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for how to check starter with multimeter
What Are the Key Manufacturing Processes for Components Used in Multimeter Testing of Starters?
The manufacturing processes involved in producing components relevant for checking starters with a multimeter encompass several critical stages. Each stage is essential to ensure that the final product meets the necessary performance and quality standards expected by B2B buyers.
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing?
-
تحضير المواد
The process begins with selecting high-quality materials, which often include copper for wiring, durable plastics for casings, and metals like aluminum for connectors. Suppliers should ensure that the materials meet international standards for conductivity and durability. This stage often involves rigorous testing of raw materials to confirm their suitability for the intended application. -
تشكيل
Once the materials are prepared, they undergo forming processes such as stamping, machining, and injection molding. For example, the housing of the multimeter is typically produced through injection molding, allowing for precise dimensions and consistency. Each forming technique is chosen based on the component’s design requirements and the desired properties of the final product. -
الجمعية
The assembly stage involves integrating various components, such as circuit boards, displays, and battery compartments. Automated assembly lines are commonly used to enhance efficiency and precision. Workers or robots must ensure that connections are secure, especially for components that will be subjected to high electrical loads during testing. -
التشطيب
The finishing process includes surface treatments, such as coating for corrosion resistance and aesthetic enhancements. This may involve anodizing metal components or applying protective films. The goal is to not only improve durability but also to ensure that the multimeter can withstand various environmental conditions, which is particularly relevant for B2B buyers operating in diverse climates.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Multimeter Manufacturing?
Quality assurance is a crucial aspect of manufacturing, especially for B2B products that must adhere to strict performance and safety standards.
What International Standards Apply to Multimeter Manufacturing?
-
آيزو 9001
This standard outlines the requirements for a quality management system (QMS). Manufacturers must demonstrate their ability to consistently provide products that meet customer and regulatory requirements. Compliance with ISO 9001 signals to B2B buyers that the manufacturer is committed to quality and continual improvement. -
علامة CE
For products sold in Europe, CE marking signifies compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards. It assures buyers that the product has undergone rigorous testing and meets European directives. -
معايير API
For manufacturers dealing with automotive applications, adherence to API standards can be essential. These standards provide guidelines for quality assurance in products that meet the demands of automotive performance.
ما هي نقاط التحقق الرئيسية لمراقبة الجودة؟
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are integrated throughout the manufacturing process to ensure that products meet specified standards. Common checkpoints include:
-
مراقبة الجودة الواردة (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials and components before they enter the production line. Any defective materials can be identified and rejected at this stage to prevent downstream issues.
-
مراقبة الجودة أثناء الإنتاج (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, regular inspections are conducted to monitor the quality of the work in progress. This allows for immediate corrective actions if deviations from quality standards are detected.
-
مراقبة الجودة النهائية (FQC): After assembly, each multimeter undergoes thorough testing to verify its functionality and safety. This typically includes electrical testing to ensure accuracy and performance under various conditions.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used for Multimeters?
Several testing methods are employed to ensure that multimeters function correctly and meet quality standards:

Illustrative image related to how to check starter with multimeter
-
الاختبار الوظيفي: This involves testing the multimeter’s ability to measure voltage, current, and resistance accurately. It is essential for confirming that the product performs as expected in real-world applications.
-
اختبار المتانة: Multimeters are subjected to stress tests to evaluate their performance under extreme conditions, such as high temperatures, humidity, and physical shocks. This is particularly important for B2B buyers who operate in challenging environments.
-
المعايرة: Regular calibration against standardized reference instruments is crucial to maintain accuracy. This process ensures that the multimeter provides reliable measurements over time.
كيف يمكن للمشترين B2B التحقق من مراقبة جودة الموردين؟
For international B2B buyers, especially those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is vital. Here are several strategies:
-
تدقيق الموردين: Conducting on-site audits can provide insight into a supplier’s manufacturing practices and quality control measures. This firsthand observation can reveal compliance with international standards and the effectiveness of their QC processes.
-
تقارير الجودة: Requesting detailed quality reports can help buyers assess the supplier’s historical performance. Reports should include information on defect rates, corrective actions taken, and compliance with international standards.
-
عمليات التفتيش من قبل أطراف ثالثة: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased evaluation of the supplier’s quality control processes. These inspections can occur at various stages of production, offering additional assurance of product quality.
ما هي الفروق الدقيقة في مراقبة الجودة للمشترين الدوليين؟
B2B buyers operating in different international markets may encounter various challenges related to quality control:
-
الامتثال التنظيمي: Different regions have distinct regulatory requirements. Buyers must ensure that their suppliers are compliant with local standards, such as CE marking in Europe or UL certification in the U.S.
-
الاختلافات الثقافية: Understanding local manufacturing practices and cultural nuances can aid in establishing effective communication and expectations regarding quality.
-
الاعتبارات اللوجستية: Transportation and handling can impact product quality, especially for sensitive electronic components. Buyers should discuss these logistics with suppliers to ensure that quality is maintained throughout the supply chain.
In conclusion, a comprehensive understanding of manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures is essential for B2B buyers involved in the procurement of multimeters for checking starters. By ensuring suppliers adhere to international standards and maintain rigorous quality control, buyers can secure reliable products that meet their operational needs.

Illustrative image related to how to check starter with multimeter
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘how to check starter with multimeter’
مقدمة
This practical sourcing guide aims to equip B2B buyers with a structured checklist for effectively checking a starter motor using a multimeter. This process is essential for diagnosing starting issues in vehicles, which can significantly impact operational efficiency. By following this step-by-step checklist, buyers can ensure they have the right tools and knowledge to assess starter motors accurately.
الخطوة 1: Define Your Technical Requirements
Understanding the specific requirements for the starter motor and multimeter is crucial. Assess the voltage and current ratings needed for the vehicles you service, as different models may have varying specifications. This ensures that you select a multimeter capable of handling the necessary measurements without risking damage.
الخطوة 2: Select a Quality Multimeter
Investing in a reliable multimeter is key for accurate readings. Look for models that offer a range of features, such as auto-ranging, true RMS measurement, and durable construction. Ensure the multimeter is also certified for safety standards relevant to your region, which helps prevent accidents during testing.
الخطوة 3: Check Multimeter Calibration
Before performing any tests, verify that your multimeter is properly calibrated. An uncalibrated multimeter can yield inaccurate readings, leading to misdiagnosis of the starter motor. Consider using a calibration tool or sending the multimeter to a professional service to ensure its accuracy.
الخطوة 4: Gather Necessary Tools and Safety Gear
Alongside the multimeter, prepare other essential tools such as jumper cables, wire brushes, and safety goggles. Having a complete toolkit at hand allows for a thorough inspection of the starter system. Safety gear is vital to protect against electrical hazards, especially when working with live circuits.
الخطوة 5: Inspect the Starter and Electrical Connections
Begin by visually inspecting the starter motor and its connections. Check for signs of corrosion, loose wires, or physical damage that could affect performance. A thorough inspection at this stage can save time and resources by identifying obvious issues before conducting electrical tests.
الخطوة 6: Perform Voltage Tests with the Multimeter
Set the multimeter to the appropriate DC voltage setting and test the battery’s voltage first. A reading above 12 volts indicates a healthy battery. Then, proceed to check the voltage at the starter solenoid to ensure it receives adequate power when the ignition is engaged.
الخطوة 7: Analyze Results and Document Findings
After completing the tests, analyze the results to determine the condition of the starter motor. Document your findings meticulously, noting any discrepancies or issues encountered. This documentation can be invaluable for future reference, helping to track the performance of starters over time and informing decisions on repairs or replacements.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can effectively assess starter motors and ensure optimal vehicle performance, thereby enhancing their operational capabilities.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for how to check starter with multimeter Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Equipment for Checking Starters with a Multimeter?
When sourcing equipment to check starters with a multimeter, understanding the cost structure is essential for B2B buyers. The main cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margin.

Illustrative image related to how to check starter with multimeter
-
المواد: This encompasses the cost of the multimeter itself, connectors, cables, and any additional tools required for testing. High-quality materials can significantly affect the overall price, especially if the equipment is designed for heavy-duty or specialized use.
-
العمل: Labor costs include the time spent by technicians or engineers in the design, assembly, and testing of the multimeter. In regions with lower labor costs, such as parts of Africa and South America, sourcing may be more economical compared to Europe.
-
تكاليف التصنيع العامة: This refers to costs associated with the facilities and utilities needed for production. Overhead can vary greatly depending on the location of the manufacturing plant and the efficiency of the production process.
-
الأدوات: The initial setup and maintenance of tools used in manufacturing can add to the cost. This is particularly relevant for customized multimeter solutions, which may require specific tooling.
-
مراقبة الجودة (QC): Ensuring that products meet certain standards incurs additional costs. Certifications such as ISO can be a consideration for buyers, as they may warrant higher prices but ensure reliability.
-
اللوجستيات: Transporting products from manufacturers to buyers involves shipping costs, customs duties, and warehousing. Buyers should consider Incoterms, as they define the responsibilities of sellers and buyers in shipping processes, impacting overall cost.
-
الهامش: Suppliers typically add a profit margin to their costs, which can vary based on market demand and competition. This margin often reflects the perceived value of the multimeter’s features and brand reputation.
How Do Price Influencers Impact the Sourcing of Multimeters?
Several factors can influence pricing in the sourcing of multimeters for checking starters.
-
الحجم والحد الأدنى لكمية الطلب (MOQ): Larger orders often lead to discounts, reducing the per-unit cost. Understanding the MOQ from suppliers can help buyers negotiate better pricing based on projected needs.
-
المواصفات والتخصيص: Custom features, such as enhanced accuracy or additional functionalities, can increase costs. Buyers should assess whether these features are necessary for their operations to avoid overspending.
-
المواد: The choice of components, such as probes and displays, can significantly affect pricing. Higher-quality materials typically result in better performance and durability, justifying a higher initial investment.
-
الجودة والشهادات: Products with higher certifications (e.g., CE, UL) often come at a premium. While these certifications can assure reliability and safety, buyers must weigh the additional cost against their specific requirements.
-
عوامل الموردين: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can influence pricing. Established suppliers with a history of quality may command higher prices but often provide better customer service and product support.
What Are the Best Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficiency in Multimeter Sourcing?
To optimize sourcing strategies, international B2B buyers should consider the following tips:
-
التفاوض: Engage in discussions with suppliers regarding pricing and payment terms. Leverage volume purchases or long-term contracts for better rates.
-
التكلفة الإجمالية للملكية (TCO): Evaluate not just the purchase price but also the long-term costs associated with maintenance, potential repairs, and the lifespan of the equipment. A lower-priced multimeter may incur higher costs over time if it requires frequent replacements.
-
الفروق الدقيقة في الأسعار للمشترين الدوليين: Be aware of currency fluctuations, tariffs, and other trade barriers that can impact final pricing. For buyers in Africa, South America, and the Middle East, understanding local market conditions and supplier relationships can lead to better deals.
-
اعتبارات سلسلة التوريد: Assess the logistics involved in shipping and customs. Collaborating with suppliers who have efficient supply chains can minimize delays and additional costs.
In summary, a comprehensive understanding of the cost components, pricing influencers, and strategic buying tips can empower B2B buyers to make informed decisions when sourcing multimeters for checking starters. Always remember that indicative prices may vary based on market conditions and supplier negotiations.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing how to check starter with multimeter With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternative Methods for Checking Starters
When it comes to diagnosing starter issues in vehicles, various methods exist alongside using a multimeter. Each method has its own set of advantages and disadvantages depending on the specific context, available resources, and technical expertise. This section explores how the multimeter method stacks up against other viable alternatives, allowing B2B buyers to make informed decisions.
| جانب المقارنة | How To Check Starter With Multimeter | Circuit Tester Method | Bench Testing Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| الأداء | Highly accurate for voltage testing | Good for basic checks | Very thorough and reliable |
| التكلفة | Low cost for multimeter | Moderate cost for tester | Higher cost due to equipment |
| سهولة التنفيذ | يتطلب معرفة أساسية بالكهرباء | Simple, user-friendly | Requires technical skills |
| الصيانة | Low maintenance | Low maintenance | High maintenance due to equipment |
| أفضل حالة استخدام | Ideal for diagnosing electrical issues | Quick checks in the field | Comprehensive testing off the vehicle |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Using a Circuit Tester?
The circuit tester method is a straightforward approach that involves checking for power reaching the starter. It is user-friendly and typically requires minimal technical expertise. The main advantage is its simplicity; it can quickly confirm whether power is flowing without delving into detailed electrical diagnostics. However, it may not provide a complete picture of the starter’s health, especially in complex electrical systems, which may lead to incomplete diagnoses.
Why is Bench Testing a Preferred Method for Some Professionals?
Bench testing involves removing the starter from the vehicle and testing it in a controlled environment. This method is thorough, allowing technicians to assess the starter’s performance under ideal conditions. It can reveal issues that may not be apparent when the starter is installed. However, this method is time-consuming and requires a higher level of technical skill. Moreover, the need for additional equipment increases the overall cost, making it less viable for businesses with limited resources.

Illustrative image related to how to check starter with multimeter
How Should B2B Buyers Choose the Right Method?
Choosing the right method for checking a starter depends largely on the specific needs and capabilities of the business. For companies with limited technical expertise or in need of quick diagnostics, using a circuit tester may suffice. On the other hand, businesses that require detailed assessments and have skilled technicians may prefer bench testing despite the higher costs. The multimeter method strikes a balance, offering precise electrical diagnostics at a low cost, making it an excellent choice for many scenarios. Ultimately, B2B buyers should consider their operational needs, technical capabilities, and budget constraints when deciding on the best approach for their vehicle maintenance and repair services.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for how to check starter with multimeter
Understanding the essential technical properties and trade terminology related to checking a starter with a multimeter is crucial for B2B buyers in the automotive sector. This knowledge not only enhances operational efficiency but also aids in making informed purchasing decisions.
What Are the Key Technical Specifications for Checking a Starter with a Multimeter?
-
تصنيف الجهد الكهربائي
The voltage rating is a critical specification, typically measured in volts (V). When testing a car starter, a healthy battery should read above 12 volts. This specification is vital for ensuring that the starter receives adequate power to engage. Understanding voltage ratings helps businesses assess battery performance, which directly affects the starter’s efficiency. -
التيار المستهلك
Current draw, measured in amperes (A), indicates the amount of electrical current the starter requires to operate effectively. A typical starter motor draws between 100 and 200 amps during engagement. Monitoring this specification helps in identifying potential issues like a failing starter or insufficient battery capacity, which can lead to costly repairs or replacements. -
قياس المقاومة
Resistance is measured in ohms (Ω) and is crucial for evaluating the integrity of electrical connections within the starter circuit. High resistance can indicate corroded or loose connections, which can impede performance. Businesses should prioritize resistance checks to prevent operational failures and ensure reliable starter function. -
تحمل درجات الحرارة
Temperature tolerance refers to the range of temperatures within which a starter can operate effectively. Most automotive starters are designed to function within a temperature range of -40°C to +85°C. This specification is important in regions with extreme weather conditions, ensuring that the starter performs reliably regardless of external temperatures. -
Material Specifications
The materials used in a starter, such as copper for windings and steel for the housing, impact durability and performance. High-quality materials can enhance resistance to wear and corrosion, which is critical for longevity. Understanding material specifications aids buyers in selecting starters that will withstand harsh operating environments.
What Are the Common Trade Terms Relevant to Starter Testing?
-
OEM (الشركة المصنعة للمعدات الأصلية)
OEM refers to parts made by the original manufacturer of the vehicle. For buyers, sourcing OEM parts ensures compatibility and reliability in performance. It is essential for maintaining warranty coverage and ensuring that the starter meets the vehicle’s original specifications. -
MOQ (الحد الأدنى لكمية الطلب)
MOQ signifies the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is crucial for B2B buyers, as it affects inventory management and cost efficiency. Understanding MOQs helps businesses negotiate better terms with suppliers and manage their purchasing strategies effectively. -
طلب عرض أسعار (RFQ)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting price quotes for specific products or services. Utilizing RFQs enables businesses to compare pricing, quality, and delivery terms, thereby making informed purchasing decisions. This process is essential for procurement teams aiming to optimize costs. -
مصطلحات التجارة الدولية
Incoterms are international commercial terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in a transaction. Understanding Incoterms is critical for ensuring clarity in shipping, risk, and cost allocation. This knowledge helps businesses mitigate risks associated with international trade. -
قطع غيار ما بعد البيع
Aftermarket parts are components made by manufacturers other than the original equipment manufacturer. While they can offer cost savings, they may vary in quality and compatibility. Buyers should carefully evaluate aftermarket options to ensure they meet performance standards without compromising vehicle integrity.
In summary, grasping the technical specifications and industry terminology related to starter testing with a multimeter enables B2B buyers to make informed decisions. This knowledge not only enhances operational efficiency but also contributes to long-term cost savings and reliability in automotive applications.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the how to check starter with multimeter Sector
What Are the Key Trends Influencing the Market for Checking Starters with a Multimeter?
The market for automotive diagnostic tools, including multimeters for checking starters, is experiencing dynamic shifts driven by several global factors. Firstly, the increasing complexity of automotive systems necessitates advanced diagnostic tools, making multimeters essential for both DIY enthusiasts and professional mechanics. In regions such as Africa and South America, the rise of the automotive aftermarket is fostering a demand for reliable diagnostic equipment, as vehicle ownership surges and maintenance becomes more crucial. Additionally, the growing emphasis on electric vehicles (EVs) is reshaping the market landscape, with multimeters evolving to accommodate the unique requirements of hybrid and electric starter systems.
Emerging technologies such as IoT (Internet of Things) are also impacting sourcing trends. Smart multimeters, equipped with Bluetooth connectivity, allow technicians to monitor and analyze starter performance remotely, streamlining the diagnostic process. For international B2B buyers, particularly in Europe and the Middle East, investing in these advanced tools can enhance operational efficiency and service quality. Moreover, the trend towards automation in automotive workshops is driving the adoption of multimeters that integrate with existing diagnostic software, enabling seamless data collection and analysis.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impacting the Multimeter Sector?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing are becoming increasingly relevant in the multimeter market, particularly as global buyers become more conscientious about their purchasing decisions. The environmental impact of manufacturing and disposing of electronic devices, including multimeters, is significant. Manufacturers are now prioritizing eco-friendly materials and processes to reduce their carbon footprints. For B2B buyers, sourcing multimeters from companies that adhere to sustainable practices is not just a moral choice; it also reflects positively on their brand image and aligns with consumer expectations for corporate responsibility.
Additionally, certifications such as RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) and WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment) are gaining importance. These certifications ensure that products are free from harmful substances and are designed for recyclability. International buyers, particularly from regions like Germany, are increasingly demanding products that meet these standards, driving suppliers to enhance their sustainability credentials. By prioritizing ethical sourcing, companies can contribute to a circular economy while securing a competitive edge in a market that values sustainability.
What Is the Historical Context of Multimeters in Automotive Diagnostics?
The evolution of multimeters in automotive diagnostics traces back to the early 20th century when basic electrical testing tools began to emerge. Initially, these devices were rudimentary, often limited to measuring voltage and current. However, as automotive technology advanced, so did the capabilities of multimeters. By the 1970s and 1980s, digital multimeters became more prevalent, providing more accurate readings and additional functionalities that catered specifically to automotive applications.
In recent decades, the integration of microprocessor technology has revolutionized multimeters, allowing for more complex diagnostics and ease of use. This evolution has made multimeters indispensable tools in workshops globally, particularly as vehicles have become increasingly reliant on electronic systems. For B2B buyers today, understanding the historical context of these tools can provide insights into the innovations that have shaped their functionality and reliability, guiding informed purchasing decisions for the future.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of how to check starter with multimeter
1. How do I troubleshoot a starter that won’t engage using a multimeter?
To troubleshoot a starter that fails to engage, begin by checking the battery voltage with a multimeter. Set the multimeter to the DC voltage setting and connect the red probe to the positive terminal and the black probe to the negative terminal. A reading above 12 volts indicates a healthy battery. Next, test the voltage at the starter solenoid. If the voltage is present but the starter doesn’t engage, the starter motor may need to be bench tested or replaced. Always ensure proper connections and inspect for corrosion or loose wires.
2. What is the optimal multimeter setting for testing a car starter?
When testing a car starter, the optimal multimeter setting is the DC voltage setting, typically set to 20 volts. This allows you to measure the voltage coming from the battery and to the starter effectively. Ensure that your multimeter probes are correctly connected: the red probe to the positive side and the black probe to the negative side. This method helps confirm that the starter is receiving adequate voltage to function properly.
3. How can I verify the quality of the starter I’m sourcing?
To verify the quality of a starter, request detailed specifications and certifications from the supplier. Look for products that meet international standards such as ISO or equivalent automotive certifications. Additionally, ask for sample units to conduct your own multimeter tests before placing a bulk order. Engage in communication about the materials used and any warranties offered, as these factors can indicate the overall quality and reliability of the starter.
4. What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for starters in international trade?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for starters can vary significantly based on the supplier and the specific product. Typically, MOQs can range from 50 to several hundred units. When sourcing, discuss MOQs directly with potential suppliers to negotiate terms that fit your business needs. Some suppliers may offer flexibility for first-time buyers or during promotional periods, so it’s beneficial to explore options.
5. How do payment terms affect my sourcing decisions for starters?
Payment terms play a crucial role in sourcing decisions. Common arrangements include advance payments, letters of credit, or net 30/60/90 days. Favorable payment terms can improve cash flow and reduce financial risk. Always evaluate the supplier’s reliability and reputation before agreeing to any terms. Additionally, consider using escrow services for large orders to ensure that funds are released only when satisfactory delivery is confirmed.
6. What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing starters?
When importing starters, consider logistics factors such as shipping methods, customs regulations, and delivery timelines. Choose between air freight for speed or sea freight for cost-effectiveness, depending on your urgency and budget. Ensure you understand customs duties and taxes applicable in your region. Collaborating with a logistics partner familiar with automotive parts can streamline the process and help avoid delays.
7. How can I customize starters to fit specific vehicle models?
To customize starters for specific vehicle models, communicate your requirements clearly to the supplier. Provide detailed specifications such as size, voltage, and connection types. Many manufacturers offer customization options to meet specific needs, but it’s essential to discuss lead times and any additional costs involved. Engaging in a prototype phase can help ensure that the final product meets your expectations before mass production.

Illustrative image related to how to check starter with multimeter
8. What quality assurance measures should I require from my starter suppliers?
Request quality assurance measures such as third-party testing reports, production quality control protocols, and warranty policies. Ensure that the supplier conducts routine inspections throughout the manufacturing process and adheres to industry standards. Inquire about their return policy for defective items and the steps they take to rectify quality issues. This due diligence can help minimize risks associated with sourcing automotive components.
Top 5 How To Check Starter With Multimeter Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Dodge Ram – Electrical Troubleshooting Tools
المجال: reddit.com
تاريخ التسجيل: 2005 (20 عامًا)
مقدمة: 1997 Dodge Ram b2500 V8, multimeter for testing solenoid/starter, battery voltage measurement, DCV setting on multimeter, troubleshooting electrical problems.
2. WikiHow – Car Starter Testing Guide
المجال: wikihow.com
تاريخ التسجيل: 2004 (21 عامًا)
مقدمة: This article provides a comprehensive guide on how to test a car starter, including checking the pinion, testing the electrical system, and bench testing the starter. It outlines steps such as turning on the headlights to diagnose issues, inspecting battery terminals for dirt or corrosion, testing battery voltage with a multimeter, and checking the solenoid for proper connections. The article is c…
3. LinkedIn – الملف اللولبي المبدئي
المجال: linkedin.com
تاريخ التسجيل: 2002 (23 عامًا)
مقدمة: A starter solenoid is an electromagnetic switch that engages the starter motor when the ignition key is turned to the ‘start’ position. Its primary function is to control the high current needed to operate the starter motor safely, ensuring clean engagement and disengagement to reduce wear and tear. Symptoms of a bad starter solenoid include clicking noises when starting, failure to crank, difficu…
4. Ars Technica – Voltage Measurement Guide
المجال: arstechnica.com
مسجل: 1998 (27 سنة)
مقدمة: This company, Ars Technica – Voltage Measurement Guide, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
5. How a Car Works – Starter Systems Guide
المجال: howacarworks.com
مسجل: 2011 (14 سنة)
مقدمة: Inertia starter: solenoid mounted elsewhere, simple mechanical or electrical faults; Pre-engaged starter: solenoid on motor casing, checks for electrical faults with circuit tester or voltmeter; Checking starter pinion: use spanner to free if jammed, check headlights; Power input/output tests: check current to solenoid and starter; Solenoid testing: bridge terminals, listen for click; Voltmeter ch…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for how to check starter with multimeter
Understanding how to effectively check a starter with a multimeter is crucial for maintaining operational efficiency in the automotive sector. By following systematic steps—such as testing the battery voltage, inspecting electrical connections, and conducting bench tests—international B2B buyers can ensure that their machinery is functioning optimally. This not only enhances vehicle reliability but also minimizes downtime, which is particularly important in markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Strategic sourcing plays a pivotal role in this process. By partnering with reliable suppliers of high-quality multimeters and automotive components, businesses can streamline their maintenance practices and enhance their service offerings. As you look to improve your operational capabilities, consider investing in training and resources that empower your workforce to perform these critical diagnostics efficiently.
As we move forward, the demand for effective automotive solutions will continue to grow. By leveraging insights from this guide, you can position your organization to meet these challenges head-on. Engage with your suppliers today to secure the tools and knowledge necessary to keep your fleet performing at its best.
إخلاء مسؤولية هام وشروط الاستخدام
⚠️ تنويه هام
المعلومات الواردة في هذا الدليل، بما في ذلك المحتوى المتعلق بالمصنعين والمواصفات الفنية وتحليل السوق، هي لأغراض إعلامية وتعليمية فقط. ولا تشكل هذه المعلومات مشورة مهنية في مجال المشتريات أو مشورة مالية أو مشورة قانونية.
على الرغم من أننا بذلنا قصارى جهدنا لضمان دقة المعلومات وحداثتها، فإننا لا نتحمل أي مسؤولية عن أي أخطاء أو سهو أو معلومات قديمة. تخضع ظروف السوق وتفاصيل الشركة والمعايير الفنية للتغيير.
يجب على المشترين من الشركات (B2B) إجراء عمليات التحقق المستقلة والشاملة الخاصة بهم. قبل اتخاذ أي قرارات شراء. ويشمل ذلك الاتصال بالموردين مباشرة، والتحقق من الشهادات، وطلب عينات، والبحث عن استشارة مهنية. يتحمل القارئ وحده مخاطر الاعتماد على أي معلومات واردة في هذا الدليل.