مقدمة: الإبحار في السوق العالمية لما هو الفرق بين المولد والمولد المتردد
في إطار البحث عن حلول موثوقة للطاقة، يعد فهم الفرق بين المولد والمولد المولد أمرًا بالغ الأهمية بالنسبة للمشترين الدوليين في مجال الأعمال التجارية. هذان الجهازان، على الرغم من أن كلاهما ضروريان في تحويل الطاقة الميكانيكية إلى طاقة كهربائية، إلا أنهما يخدمان أغراضًا مختلفة ويظهران كفاءات ومخرجات مختلفة. بالنسبة للشركات في جميع أنحاء أفريقيا وأمريكا الجنوبية والشرق الأوسط وأوروبا، يمكن أن يشكل الحصول على المعدات المناسبة تحديًا، خاصةً عند التعامل مع تعقيدات المواصفات والتطبيقات وموثوقية الموردين.
يهدف هذا الدليل الشامل إلى إزالة الغموض عن الفروق الدقيقة بين المولدات ومولدات التيار المتردد، حيث يغطي أنواعها وآليات تشغيلها وتطبيقاتها والعوامل الحاسمة مثل التكلفة وفحص الموردين. من خلال الخوض في الاختلافات الهيكلية وكفاءة الطاقة وحالات الاستخدام النموذجية - بدءًا من تطبيقات السيارات إلى إنتاج الكهرباء على نطاق واسع - سيحصل المشترون على رؤى قيمة تسترشد بها قرارات الشراء.
لا يساعد فهم هذه الاختلافات في اتخاذ خيارات مستنيرة فحسب، بل يعزز أيضًا الكفاءة التشغيلية وفعالية التكلفة. يعمل هذا الدليل على تمكين صانعي القرار من خلال توفير المعرفة القابلة للتنفيذ، مما يضمن قدرة الشركات على التعامل بثقة مع الموردين والاستثمار في التكنولوجيا المناسبة المصممة خصيصًا لتلبية احتياجاتها الخاصة من الطاقة. سواء كنت تتطلع إلى تشغيل العمليات عن بُعد أو تعزيز قدرات التصنيع لديك، فإن هذا المورد سيكون بمثابة أداة محورية في التنقل في السوق العالمية للمولدات ومولدات الطاقة المتجددة.
جدول المحتويات
- أعلى 3 ما هو الفرق بين المولد والمولد قائمة المصنعين والموردين 3
- مقدمة: الإبحار في السوق العالمية لما هو الفرق بين المولد والمولد المتردد
- فهم ما هو الفرق بين أنواع المولدات والمولدات وأنواع المولدات واختلافاتها
- التطبيقات الصناعية الرئيسية لما هو الفرق بين المولد ومولد التيار المتردد
- 3 نقاط ألم شائعة لدى المستخدمين حول ‘ما الفرق بين المولد والمولد المتردد’ وحلولها
- دليل اختيار المواد الاستراتيجية لما هو الفرق بين المولد والمولد المتردد
- نظرة متعمقة: عمليات التصنيع وضمان الجودة لمعرفة الفرق بين المولد والمولد المتردد
- دليل عملي للمصادر: قائمة تدقيق خطوة بخطوة لـ ‘ما الفرق بين المولد والمولد المتردد’
- تحليل شامل للتكلفة والتسعير لما هو الفرق بين المولد والمولد المولد المولد المولد
- تحليل البدائل: مقارنة ما هو الفرق بين المولد والمولد المولد مع الحلول الأخرى
- الخصائص التقنية الأساسية والمصطلحات التجارية لما هو الفرق بين المولد والمولد المتردد
- الإبحار في ديناميكيات السوق واتجاهات التوريد في قطاع ما هو الفرق بين قطاع المولدات والمولدات الكهربائية
- الأسئلة المتداولة (FAQs) لمشتري B2B عن الفرق بين المولد والمولد المتردد
- استنتاج المصادر الاستراتيجية والتوقعات لما هو الفرق بين المولد والمولد المتردد
- إخلاء مسؤولية هام وشروط الاستخدام
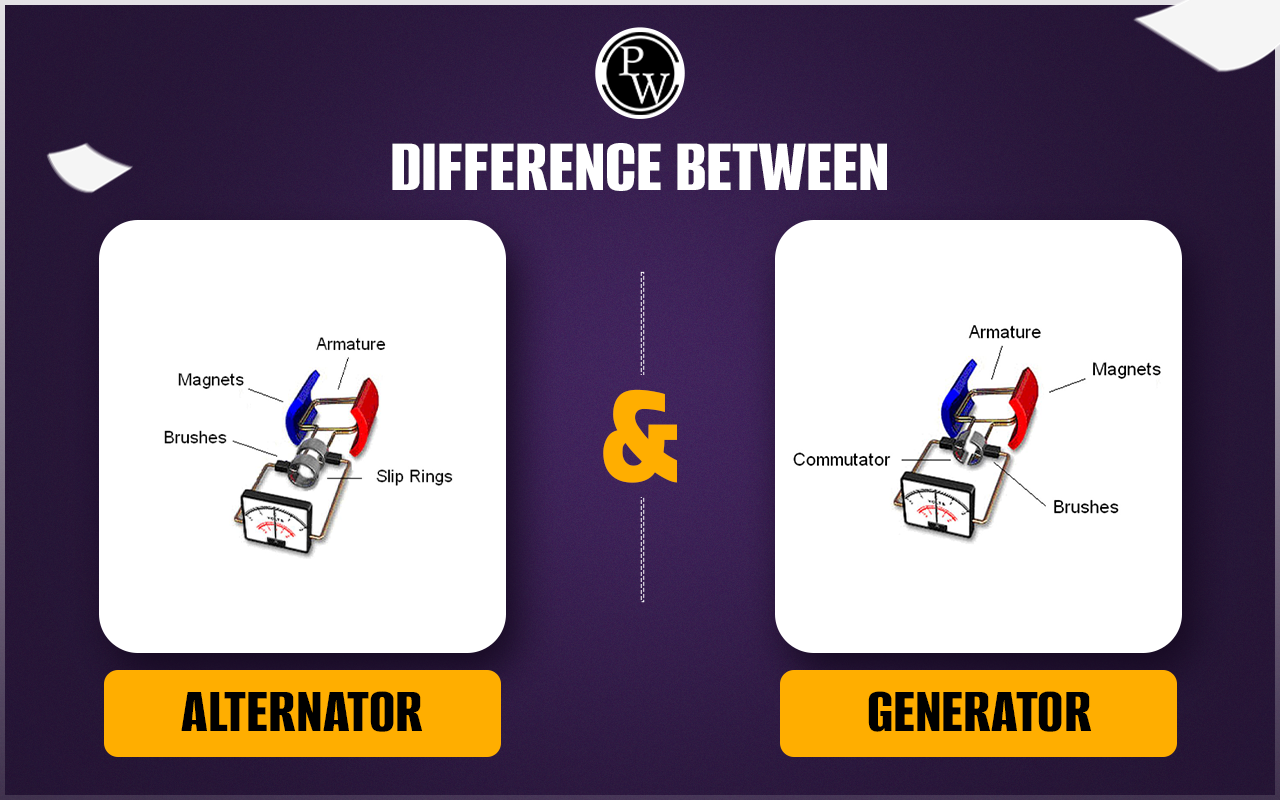
فهم ما هو الفرق بين أنواع المولدات والمولدات وأنواع المولدات واختلافاتها
| اسم النوع | السمات المميزة الرئيسية | التطبيقات الأساسية بين الشركات (B2B) | مزايا وعيوب موجزة للمشترين |
|---|---|---|---|
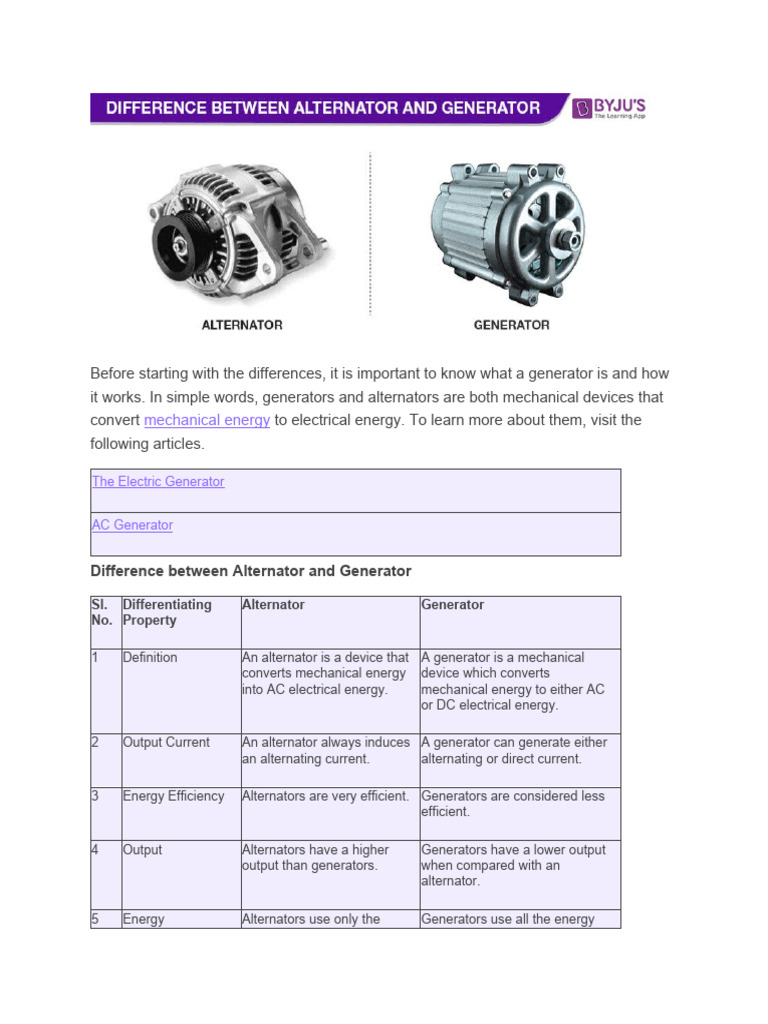
| المولد | يحول الطاقة الميكانيكية إلى تيار متردد؛ محرك ثابت؛ كفاءة عالية | السيارات، أنظمة الطاقة المتجددة | الإيجابيات: موفرة للطاقة ومدمجة ومنخفضة الصيانة. السلبيات: لا يمكن شحن البطاريات الفارغة بالكامل. |
| مولد التيار المستمر | يحول الطاقة الميكانيكية إلى تيار مستمر؛ محرك دوار؛ يستخدم مقوم تيار مستمر | التطبيقات الصناعية، شحن البطاريات | الإيجابيات: مناسبة لشحن البطاريات، وإخراج ثابت. السلبيات: أقل كفاءة من المولدات المترددة. |
| مولد تيار متردد | يحول الطاقة الميكانيكية إلى تيار متردد؛ محرك دوار؛ يستخدم حلقات الانزلاق | محطات الطاقة، ومواقع الإنشاءات | الإيجابيات: قدرة إنتاج عالية وموثوقة للكهرباء على نطاق واسع. السلبيات: أكبر حجماً وأكثر تعقيداً. |
| مولد كهربائي محمول | مدمجة ومتنقلة؛ يمكن تشغيلها بالغاز أو الديزل؛ متعددة الاستخدامات | البناء، والفعاليات الخارجية، والدعم الاحتياطي في حالات الطوارئ | الإيجابيات: سهولة التنقل وسهولة الاستخدام وإمدادات الطاقة الفورية. السلبيات: ضوضاء ووقت تشغيل محدود للوقود. |
| المولدات العاكسة | تحويل التيار المستمر إلى تيار متردد؛ تشغيل أكثر هدوءاً؛ خرج طاقة مستقر | الإلكترونيات الحساسة، الاستخدام الترفيهي | الإيجابيات: طاقة نظيفة وموفرة للوقود وأكثر هدوءاً. السلبيات: تكلفة أولية أعلى، وإنتاج طاقة أقل مقارنة بالمولدات القياسية. |
ما هي الخصائص الرئيسية للمولد في تطبيقات B2B؟
تُستخدم المولدات في المقام الأول في صناعة السيارات وأنظمة الطاقة المتجددة. فهي تقوم بتحويل الطاقة الميكانيكية إلى تيار متردد (AC) بكفاءة، مع وجود محرك ثابت يقلل من البلى، مما يؤدي إلى انخفاض تكاليف الصيانة. بالنسبة لمشتري B2B، فإن الحجم الصغير وكفاءة الطاقة تجعل من المولدات خيارًا عمليًا، خاصة في البيئات التي تكون فيها المساحة والحفاظ على الطاقة أمرًا بالغ الأهمية. ومع ذلك، لا يمكنها شحن البطاريات المستنزفة بالكامل، وهو ما يمكن أن يكون قيدًا على بعض التطبيقات.
كيف يختلف مولد التيار المستمر عن الأنواع الأخرى في سياقات العمل؟
تقوم مولدات التيار المستمر بتحويل الطاقة الميكانيكية إلى تيار مباشر (DC) وتستخدم عادة في التطبيقات الصناعية وشحن البطاريات. وتتميز هذه المولدات بمحرك دوّار وتستخدم مقوم تيار للحفاظ على ثبات الخرج. بالنسبة للشركات، فإن القدرة على شحن البطاريات باستمرار تجعل مولدات التيار المستمر ضرورية في القطاعات التي تحتاج إلى إمدادات طاقة موثوقة. ومع ذلك، فهي أقل كفاءة من مولدات التيار المتردد، مما قد يدفع المشترين إلى التفكير في خيارات بديلة حسب احتياجاتهم من الطاقة.
ما هي مزايا استخدام مولد التيار المتردد في العمليات الكبيرة؟
تُستخدم مولدات التيار المتردد على نطاق واسع في محطات توليد الطاقة ومواقع الإنشاءات نظرًا لقدرتها على تحويل الطاقة الميكانيكية إلى تيار متردد. وتتميز هذه المولدات بمحور دوّار وحلقات انزلاق، مما يسمح بمستويات إنتاج عالية مناسبة لتوليد الكهرباء على نطاق واسع. وتستفيد الشركات من موثوقيتها وقدرتها على الإنتاج، مما يجعلها مثالية للعمليات الواسعة النطاق. ومع ذلك، قد يتطلب حجمها الأكبر وتعقيدها مساحة أكبر واستثماراً أكبر، وهو ما يجب على المشترين مراعاته.
لماذا اختيار مولد محمول لتلبية احتياجات الطاقة أثناء التنقل؟
المولدات المحمولة مصممة للتنقل وتعدد الاستخدامات، وغالباً ما تعمل بالغاز أو الديزل. وهي مثالية لمواقع البناء والفعاليات الخارجية والطاقة الاحتياطية في حالات الطوارئ. يسمح تصميمها المدمج للشركات بنقلها بسهولة، مما يوفر إمدادات الطاقة الفورية عند الحاجة. ومع ذلك، يجب على المشترين المحتملين أن يكونوا على دراية بمستويات الضوضاء ووقت تشغيلها المحدود بالوقود، مما قد يؤثر على ملاءمتها لبيئات معينة.
ما الذي يجعل المولدات العاكسة الخيار المفضل للإلكترونيات الحساسة؟
تقوم المولدات العاكسة بتحويل التيار المستمر إلى تيار متردد، وهي معروفة بتشغيلها الهادئ ومخرجات الطاقة المستقرة. وهي مناسبة بشكل خاص لتشغيل الإلكترونيات الحساسة، مما يجعلها خيارًا شائعًا في الأماكن الترفيهية والخارجية. إن الطاقة النظيفة والكفاءة في استهلاك الوقود للمولدات العاكسة تجذب الشركات التي تتطلع إلى تقليل تأثيرها على البيئة. ومع ذلك، قد تكون التكلفة الأولية الأعلى ومخرجات الطاقة المنخفضة مقارنةً بالمولدات القياسية عائقًا لبعض المشترين.
التطبيقات الصناعية الرئيسية لما هو الفرق بين المولد ومولد التيار المتردد
| الصناعة/القطاع | تطبيق محدد لما هو الفرق بين المولد والمولد المتردد | القيمة/الفائدة للأعمال | اعتبارات التوريد الرئيسية لهذا التطبيق |
|---|---|---|---|
| الطاقة وتوليد الطاقة | فهم الفروق في الكفاءة لتحسين عمليات إنتاج الطاقة. | يؤدي تعزيز كفاءة الطاقة إلى خفض التكاليف التشغيلية. | تقييم قدرة الإخراج، ونوع الطاقة (تيار متردد/ تيار مستمر)، واحتياجات الصيانة. |
| السيارات | استخدام المولدات الكهربائية لأنظمة شحن بطارية السيارة. | تحسين عمر البطارية وموثوقية السيارة. | التركيز على الحجم والوزن والتوافق مع طرازات المركبات. |
| البناء والتعدين | تنفيذ مولدات لإمداد الطاقة المحمولة في المواقع النائية. | يزيد مصدر الطاقة الموثوق به من الإنتاجية والسلامة. | قم بتقييم نوع الوقود ومخرجات الطاقة وميزات التنقل. |
| الاتصالات السلكية واللاسلكية | استخدام مولدات احتياطية للخدمة غير المنقطعة أثناء انقطاع التيار الكهربائي. | يضمن التواصل المستمر وسلامة البيانات. | ضع في اعتبارك وقت التشغيل ومستويات الضوضاء والامتثال التنظيمي. |
| الزراعة | استخدام مولدات كهربائية لأنظمة الري في المناطق التي لا يمكن الاعتماد عليها في الشبكة. | إمدادات المياه المتسقة تعزز من إنتاجية المحاصيل وجودتها. | فحص كفاءة الوقود، ومتطلبات الصيانة، والقدرة الإنتاجية. |
كيف يتم تطبيق معرفة الفرق بين المولدات والمولدات الكهربائية في توليد الطاقة والطاقة المتجددة؟
في قطاع الطاقة، يعد فهم الاختلافات بين المولدات ومولدات التيار المتردد أمرًا بالغ الأهمية لتحسين عمليات إنتاج الطاقة. غالبًا ما تستخدم المولدات، التي يمكن أن تنتج طاقة التيار المتردد والتيار المستمر على حد سواء، لتوليد الكهرباء على نطاق واسع. وعلى النقيض من ذلك، يفضل استخدام المولدات في التطبيقات التي تكون فيها الكفاءة والحفاظ على الطاقة أمرًا بالغ الأهمية. من خلال اختيار الجهاز المناسب بناءً على متطلباتها التشغيلية، يمكن للشركات تقليل تكاليف الطاقة بشكل كبير وتحسين كفاءة النظام بشكل عام. يجب أن يركز المشترون على قدرة الإنتاج واحتياجات الصيانة للأنظمة التي يدرسونها.
ما الدور الذي تلعبه المولدات في صناعة السيارات؟
في صناعة السيارات، تُعد المولدات جزءًا لا يتجزأ من أنظمة شحن بطارية السيارة. فهي تقوم بتحويل الطاقة الميكانيكية من المحرك إلى طاقة كهربائية، مما يضمن بقاء البطاريات مشحونة وعاملة. وتُترجم هذه الكفاءة بشكل مباشر إلى تحسين موثوقية السيارة وعمر البطارية. بالنسبة للمشترين الدوليين، لا سيما في المناطق ذات المعايير المختلفة للسيارات، من الضروري مراعاة حجم المولدات وتوافقها مع طرازات السيارات المختلفة، مما يضمن أنها تلبي اللوائح المحلية وتوقعات الأداء.
كيف تدعم المولدات الكهربائية عمليات البناء والتعدين؟
تُعد المولدات الكهربائية حيوية في الإنشاءات والتعدين، حيث توفر الطاقة المحمولة في المواقع النائية حيث يكون الوصول إلى الشبكة محدودًا. فهي تتيح تشغيل الآلات الثقيلة والإضاءة والمعدات الأساسية الأخرى، مما يؤثر بشكل مباشر على الإنتاجية والسلامة. يساعد فهم الفرق بين المولدات ومولدات التيار المتردد الشركات على اختيار المعدات المناسبة لتلبية احتياجاتها من الطاقة. يجب على المشترين تقييم عوامل مثل نوع الوقود ومخرجات الطاقة وميزات التنقل لضمان قدرة المولدات المختارة على تحمل الظروف الصعبة المعتادة في هذه الصناعات.
لماذا تعتبر المولدات الاحتياطية ضرورية للاتصالات السلكية واللاسلكية؟
تعتمد شركات الاتصالات السلكية واللاسلكية على المولدات الاحتياطية للحفاظ على استمرارية الخدمة أثناء انقطاع التيار الكهربائي. تضمن هذه المولدات استمرار عمل أنظمة الاتصالات، مما يحافظ على سلامة البيانات ورضا العملاء. يساعد فهم الاختلافات بين المولدات ومولدات الطاقة الاحتياطية الشركات على اختيار أنظمة الطاقة الاحتياطية المناسبة والمصممة خصيصًا لتلبية احتياجاتها الخاصة. تشمل الاعتبارات الرئيسية وقت التشغيل ومستويات الضوضاء والامتثال للوائح المحلية، وكلها يمكن أن تؤثر على الكفاءة التشغيلية والعلاقات المجتمعية.
كيف تعزز المولدات الكهربائية العمليات الزراعية؟
وفي مجال الزراعة، تعتبر المولدات ضرورية لتشغيل أنظمة الري، لا سيما في المناطق التي لا يمكن الاعتماد فيها على إمدادات الكهرباء. فهي تضمن إمدادات مياه ثابتة، مما يؤثر بشكل مباشر على إنتاجية المحاصيل وجودتها. من خلال فهم الاختلافات بين المولدات والمولدات الكهربائية، يمكن للشركات الزراعية اتخاذ قرارات مستنيرة تعزز إنتاجيتها. يجب أن يركز المشترون على كفاءة الوقود ومتطلبات الصيانة والقدرة الإنتاجية لاختيار المولدات الأكثر ملاءمة لاحتياجاتهم من الري، خاصة في المناطق ذات التحديات المناخية والتشغيلية المتنوعة.
3 نقاط ألم شائعة لدى المستخدمين حول ‘ما الفرق بين المولد والمولد المتردد’ وحلولها
السيناريو 1: الارتباك بشأن احتياجات العمليات من الطاقة
المشكلة: يتطلع مصنع في البرازيل إلى تعزيز إمدادات الطاقة لدعم الآلات الجديدة. ومع ذلك، فإن فريق المشتريات في حيرة من أمره بشأن الاستثمار في مولد أو مولد كهربائي. تتطلب متطلباتهم التشغيلية مصدر طاقة موثوقًا وفعالًا، ولكن الاختلافات بين الجهازين غير واضحة. وهم يخشون القيام باستثمار خاطئ، مما قد يؤدي إلى عدم الكفاءة التشغيلية وزيادة التكاليف.
الحل: لمواجهة هذا التحدي، من الضروري إجراء تقييم شامل للاحتياجات قبل إجراء عملية الشراء. يجب على مشتري B2B تحليل متطلباتهم التشغيلية، مثل نوع الماكينات المستخدمة، واستهلاك الطاقة، وما إذا كانوا بحاجة إلى طاقة تيار متردد أو تيار مستمر. إذا كانت عملياتهم تتطلب في المقام الأول طاقة تيار متردد، فسيكون المولد هو الخيار الأفضل نظرًا لكفاءته الأعلى وقدرته على الحفاظ على الطاقة. وعلى العكس من ذلك، إذا كان التطبيق يتطلب طاقة تيار مستمر، فإن المولد ضروري. يمكن أن يساعد التعامل مع مورد واسع الاطلاع يمكنه تقديم مواصفات تفصيلية ونصائح تشغيلية استنادًا إلى الآلات المحددة وعبء العمل على ضمان اتخاذ القرار الصحيح.
السيناريو 2: سوء فهم متطلبات الصيانة
المشكلة: تستخدم إحدى شركات الإنشاءات في جنوب أفريقيا مولدًا لتلبية احتياجاتها من الطاقة ولكنها تواجه أعطالًا متكررة وإصلاحات مكلفة. لا يدرك الفريق أن متطلبات صيانة المولدات تختلف اختلافًا كبيرًا عن متطلبات صيانة المولدات الكهربائية، مما يؤدي إلى زيادة وقت التعطل والضغوط المالية. وهم يشعرون بالإحباط بسبب عدم وضوح كيفية صيانة هذه الأجهزة بشكل صحيح.
الحل: يجب على المشترين تثقيف أنفسهم حول احتياجات الصيانة المحددة للمولدات مقابل المولدات الكهربائية. يمكن أن تكون المولدات، التي تتطلب استقطابًا منتظمًا وغالبًا ما تحتوي على أجزاء متحركة أكثر، أكثر تطلبًا من حيث الصيانة. في المقابل، تميل مولدات التوليد، مع محركها الثابت وفرشها التي تدوم لفترة أطول، إلى أن تتطلب صيانة أقل تكرارًا. يجب على الشركات إنشاء جدول صيانة يتماشى مع متطلبات التشغيل ونوع المعدات المستخدمة. بالإضافة إلى ذلك، فإن إقامة شراكات مع مقدمي الخدمات المتخصصين في المولدات أو المولدات المترددة يمكن أن يضمن تنفيذ ممارسات الصيانة الصحيحة، مما يقلل من وقت التعطل وتكاليف الإصلاح.
السيناريو 3: التحديات في التحجيم والكفاءة
المشكلة: تقوم شركة زراعية في فيتنام بتوسيع عملياتها وتحتاج إلى تركيب نظام جديد لإمداد الطاقة. ومع ذلك، فإنها تواجه صعوبة في تحديد الحجم المناسب ونوع المعدات. فهم ليسوا متأكدين من كيفية تأثير حجم المولد أو المولد على الكفاءة والإنتاج، مما يؤدي إلى احتمال الإفراط في الشراء أو نقصان الحجم، وكلاهما قد يكون ضارًا.
الحل: ولمعالجة هذه المشكلة، يجب على المشترين إجراء تحليل مفصل لمتطلباتهم من الطاقة، مع الأخذ في الاعتبار الأحمال في أوقات الذروة والطلبات التشغيلية العادية. يمكن أن يساعد استخدام أدوات تحليل الأحمال في تحديد السعة اللازمة بدقة. إذا اختارت الشركة استخدام مولد كهربائي، فيجب أن تستفيد من قدرته على توليد الطاقة عند الحاجة إليها فقط، مما قد يعزز الكفاءة بشكل كبير. وعلى العكس من ذلك، إذا كان المولد ضرورياً، يجب على المشترين التأكد من عدم زيادة حجم المولد عن الحاجة، لأن ذلك قد يؤدي إلى إهدار الطاقة وزيادة التكاليف التشغيلية. إن العمل مع المهندسين أو الاستشاريين الكهربائيين ذوي الخبرة الذين يمكنهم المساعدة في تحديد حجم المعدات المناسبة واختيارها بناءً على تقييمات شاملة للأحمال سيساعد في اتخاذ قرارات مستنيرة تعمل على تحسين كفاءة الطاقة وفعالية التكلفة.
دليل اختيار المواد الاستراتيجية لما هو الفرق بين المولد والمولد المتردد
ما هي المواد المستخدمة عادة في المولدات والمولدات الكهربائية؟
عند النظر في الاختلافات بين المولدات والمولدات الكهربائية، فإن المواد المستخدمة في بنائها تلعب دورًا حاسمًا في الأداء والمتانة والكفاءة. فيما يلي، نحلل أدناه العديد من المواد الشائعة المستخدمة في هذه الأجهزة، مع التركيز على خصائصها ومزاياها وعيوبها والآثار المترتبة على المشترين الدوليين من الشركات.
1. النحاس
الخصائص الرئيسية: يتميز النحاس بتوصيل كهربائي ممتاز، وتوصيل حراري ومقاومة للتآكل. ويمكن أن تصل درجة حرارته إلى 200 درجة مئوية، مما يجعله مناسبًا للتطبيقات عالية الأداء.
إيجابيات وسلبيات: الميزة الأساسية للنحاس هي موصلية النحاس الفائقة، مما يعزز كفاءة كل من المولدات ومولدات التيار المتردد. ومع ذلك، فإن النحاس مكلف نسبياً مقارنة ببدائل مثل الألومنيوم، ويمكن أن يكون وزنه عيباً في التطبيقات التي يكون فيها تقليل الكتلة أمراً بالغ الأهمية.
التأثير على التطبيق: النحاس مناسب بشكل خاص للتطبيقات التي تتطلب كفاءة وموثوقية عالية، كما هو الحال في مولدات السيارات والمولدات الصناعية. كما أن توافقه مع مختلف الوسائط يجعله خياراً متعدد الاستخدامات.
اعتبارات للمشترين الدوليين: يجب على المشترين في مناطق مثل أفريقيا وأمريكا الجنوبية مراعاة توافر النحاس وتقلبات التكلفة. ومن الضروري الامتثال للمعايير الدولية، مثل ASTM B170 للنحاس، لضمان الجودة.
2. الألومنيوم
الخصائص الرئيسية: يتميز الألومنيوم بخفة وزنه ومقاومته للتآكل، كما أن درجة انصهاره أقل (حوالي 660 درجة مئوية) مقارنةً بالنحاس. وتبلغ موصلية الألومنيوم الكهربائية حوالي 60% من النحاس.
إيجابيات وسلبيات: تتمثل الميزة الرئيسية للألومنيوم في طبيعته الخفيفة الوزن، مما يقلل من الوزن الإجمالي للمعدات ويحسن من قابلية النقل. ومع ذلك، فهو أقل توصيلاً من النحاس، مما قد يؤدي إلى فقدان الكفاءة في بعض التطبيقات.
التأثير على التطبيق: غالبًا ما يستخدم الألومنيوم في بناء علب المولدات ومكوناتها حيث يكون الوزن عاملًا حاسمًا. كما أن مقاومته للتآكل تجعله مناسبًا للتطبيقات الخارجية في البيئات القاسية.
اعتبارات للمشترين الدوليين: يجب على المشترين التأكد من أن مكونات الألومنيوم تتوافق مع معايير مثل ASTM B221. في المناطق ذات الرطوبة العالية أو التعرض للملح، يمكن أن تكون مقاومة الألومنيوم للتآكل ميزة كبيرة.
3. الفولاذ
الخصائص الرئيسية: يشتهر الفولاذ بقوته ومتانته، مع درجة حرارة عالية (تصل إلى 600 درجة مئوية). وغالباً ما يستخدم في المكونات الهيكلية للمولدات والمولدات الكهربائية.
إيجابيات وسلبيات: الميزة الأساسية للفولاذ هي متانته، مما يجعله مثاليًا للتطبيقات الشاقة. ومع ذلك، فهو أثقل من كل من النحاس والألومنيوم، وهو ما يمكن أن يكون عيباً في التطبيقات المحمولة.
التأثير على التطبيق: يشيع استخدام الفولاذ في الإطارات والأغلفة والمكونات الدوارة في المولدات والمولدات الكهربائية. وقوته ضرورية للتطبيقات التي تتطلب ثباتاً ميكانيكياً عالياً.
اعتبارات للمشترين الدوليين: يجب أن تفي مكونات الصلب بمعايير مثل ASTM A36. يجب على المشترين أيضًا مراعاة تأثير الظروف البيئية المحلية على مقاومة الفولاذ للتآكل، مما قد يستلزم طلاءات أو معالجات إضافية.
4. المواد المركبة
الخصائص الرئيسية: توفر المواد المركبة، التي غالبًا ما تكون مصنوعة من مزيج من الألياف والراتنجات، مزيجًا فريدًا من الخصائص خفيفة الوزن والقوة. ويمكنها تحمل مجموعة واسعة من درجات الحرارة ومقاومة للتآكل.
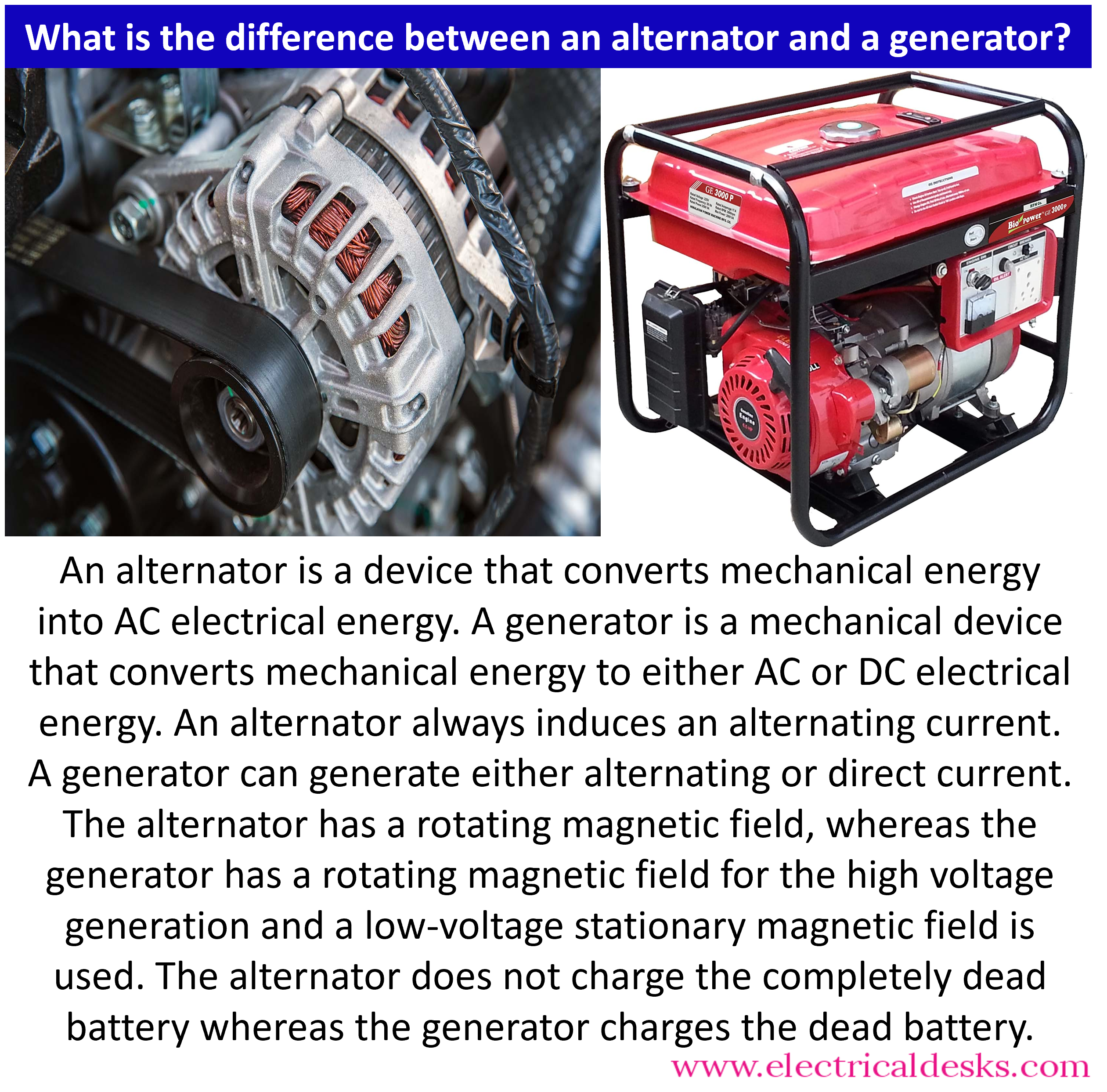
صورة توضيحية تتعلق بالفرق بين المولد ومولد التيار المتردد
إيجابيات وسلبيات: الميزة الأساسية للمركبات هي قدرتها على تقليل الوزن مع الحفاظ على السلامة الهيكلية. غير أن تصنيعها قد يكون أكثر تكلفة وقد يتطلب تقنيات متخصصة للتجميع.
التأثير على التطبيق: يتم استخدام المواد المركبة بشكل متزايد في التطبيقات عالية الأداء، كما هو الحال في مجال الفضاء ومولدات السيارات المتقدمة، حيث يكون توفير الوزن أمرًا بالغ الأهمية.
اعتبارات للمشترين الدوليين: يجب على المشترين أن يكونوا على دراية بالمعايير المحددة للمواد المركبة في منطقتهم، مثل ISO 9001 لنظم إدارة الجودة. يمكن أن يختلف توافر المواد المركبة بشكل كبير حسب المنطقة، مما يؤثر على لوجستيات سلسلة التوريد.
جدول ملخص
| المواد | حالة الاستخدام النموذجية لما هو الفرق بين المولد والمولد المتردد | الميزة الرئيسية | العيب/القيود الرئيسية | التكلفة النسبية (منخفضة/متوسطة/عالية) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| النحاس | اللفات في المولدات والمولدات | توصيلية فائقة | التكلفة العالية والوزن الثقيل | عالية |
| الألومنيوم | المبيت والمكونات خفيفة الوزن في المولدات | خفيف الوزن ومقاوم للتآكل | موصلية أقل من النحاس | متوسط |
| الصلب | الإطارات الهيكلية ومكونات الدوار | قوة ومتانة عالية | أثقل من المواد الأخرى | متوسط |
| المواد المركبة | التطبيقات المتقدمة للسيارات والفضاء المتقدمة | خفيف الوزن مع قوة جيدة | تعقيد التصنيع العالي | عالية |
يقدم هذا التحليل نظرة عامة شاملة عن اختيار المواد اللازمة للمولدات ومولدات التيار المتردد، مع التأكيد على أهمية فهم خصائص كل نوع من المواد والآثار المترتبة على كل نوع من المواد لاتخاذ قرارات شراء فعالة في مجال B2B.
صورة توضيحية تتعلق بالفرق بين المولد ومولد التيار المتردد
نظرة متعمقة: عمليات التصنيع وضمان الجودة لمعرفة الفرق بين المولد والمولد المتردد
ما هي عمليات التصنيع النموذجية للمولدات والمولدات الكهربائية؟
يُعد فهم عمليات تصنيع المولدات ومولدات التيار المتردد أمرًا بالغ الأهمية بالنسبة للمشترين بين الشركات الذين يهدفون إلى شراء معدات عالية الجودة. يتضمن إنتاج هذه الأجهزة عدة مراحل رئيسية، بما في ذلك إعداد المواد والتشكيل والتجميع والتشطيب. تستخدم كل مرحلة تقنيات محددة لضمان استيفاء المنتجات النهائية لمعايير الأداء والسلامة.
ما هي المواد المستخدمة عادة في تصنيع المولدات والمولدات الكهربائية؟
يبدأ تصنيع المولدات ومولدات التيار المتردد عادةً باختيار المواد المناسبة. وتشمل المواد الرئيسية ما يلي:
- النحاس: يستخدم للملفات بسبب توصيله الكهربائي الممتاز.
- الفولاذ: غالباً ما تستخدم في قلب الدوار والجزء الثابت، مما يوفر القوة والمتانة.
- ألومنيوم: يستخدم أحياناً كبديل خفيف الوزن للنحاس في اللفات.
- المواد العازلة: يتم استخدام مواد عازلة مختلفة لمنع حدوث ماس كهربائي وتعزيز السلامة.
كيف يتم تشكيل وتجميع المولدات والمولدات الكهربائية؟
ما التقنيات المستخدمة في تشكيل المكونات؟
تتضمن مرحلة التشكيل تقنيات مختلفة مصممة خصيصًا للمكونات المحددة للمولدات ومولدات التيار المتردد:
- الختم: يتم ختم الصفائح المعدنية في أشكال محددة للقلب الدوار والجزء الثابت.
- اللف: يتم لف أسلاك النحاس أو الألومنيوم في لفائف، وهي ضرورية للأداء الكهربائي للجهاز. تُستخدم آلات اللف الآلية عادةً لتحقيق الدقة.
- الصب والتشكيل: يمكن إنتاج المكونات التي تتطلب قوة ومتانة عالية، مثل المبيت والإطار، من خلال عمليات الصب أو التشكيل.
كيف يتم التجميع في عملية التصنيع؟
بمجرد تشكيل المكونات الفردية، تبدأ عملية التجميع:
- تكامل المكونات: يتم وضع الدوار داخل الجزء الثابت، مما يضمن تفاعل المجال المغناطيسي بفعالية.
- التوصيلات الكهربائية: يتم توصيل الأسلاك بأطراف الخرج، وغالباً ما يتم ذلك باستخدام تقنيات اللحام أو العقص.
- الاختبار والمعايرة: قبل التجميع النهائي، غالبًا ما يتم اختبار المكونات للتأكد من وظيفتها. وقد يشمل ذلك فحص المقاومة الكهربائية والاستمرارية.
ما هي عمليات التشطيب المتضمنة في التصنيع؟
تضمن عمليات التشطيب أن تكون المنتجات جاهزة للسوق وقادرة على تحمل الضغوط التشغيلية:
- الطلاء والطلاء: يتم استخدام الطلاءات الواقية لمنع التآكل وتعزيز المظهر الجمالي. ويُعد طلاء الإيبوكسي ومسحوق الطلاء من الخيارات الشائعة.
- التجميع النهائي: يتم تركيب مكونات إضافية، مثل الفرش والمحامل. قد تتضمن هذه المرحلة أيضًا تركيب المولد أو المولد في مبيت.
- الاختبار النهائي: يتم إجراء اختبارات شاملة لضمان استيفاء كل وحدة لمواصفات الأداء. ويشمل ذلك الاختبارات التشغيلية تحت ظروف التحميل.
كيف تتم إدارة ضمان الجودة في إنتاج المولدات والمولدات الكهربائية؟
يعد ضمان الجودة أمرًا بالغ الأهمية في تصنيع المولدات ومولدات التيار المتردد لضمان الموثوقية والأداء. توجه العديد من المعايير الدولية والشهادات الخاصة بالصناعة عمليات ضمان الجودة.
ما هي المعايير الدولية التي يجب أن يكون المشترون من الشركات على دراية بها؟
يجب على المشترين بين الشركات البحث عن الشركات المصنعة التي تلتزم بمعايير الجودة العالمية، مثل:
- ISO 9001: يركز هذا المعيار على أنظمة إدارة الجودة وهو أمر بالغ الأهمية لضمان اتساق الجودة في عمليات التصنيع.
- علامة CE: بالنسبة للمنتجات التي تباع في الاتحاد الأوروبي، تشير علامة CE إلى الامتثال لمعايير الصحة والسلامة وحماية البيئة.
- شهادة API: بالنسبة للمصنعين الذين ينتجون معدات لقطاع النفط والغاز، تعتبر معايير معهد البترول الأمريكي (API) ذات صلة.
ما هي نقاط التحقق الرئيسية لمراقبة الجودة في التصنيع؟
يتم دمج نقاط فحص مراقبة الجودة (QC) في مراحل مختلفة من عملية التصنيع:
- مراقبة الجودة الواردة (IQC): يتم فحص المواد الخام عند وصولها للتأكد من مطابقتها للمواصفات.
- مراقبة الجودة أثناء الإنتاج (IPQC): أثناء التصنيع، يتم إجراء العديد من الاختبارات، بما في ذلك فحوصات الأبعاد واختبارات المقاومة الكهربائية.
- مراقبة الجودة النهائية (FQC): تخضع المنتجات النهائية لاختبارات شاملة للتحقق من الأداء والسلامة قبل الشحن.
ما هي طرق الاختبار الشائعة المستخدمة للمولدات والمولدات الكهربائية؟
تعتبر طرق الاختبار ضرورية لضمان أداء المولدات ومولدات التيار المتردد كما هو متوقع. وتشمل الطرق الشائعة ما يلي:
- اختبار الحمل: يتم اختبار الوحدات في ظروف الحمل الفعلي لتقييم الأداء.
- اختبار مقاومة العزل: تتحقق هذه الطريقة من وجود أي أعطال في العزل قد تؤدي إلى حدوث ماس كهربائي.
- اختبار الاهتزازات: يضمن تشغيل المعدات بسلاسة دون اهتزازات مفرطة، مما قد يؤدي إلى عطل ميكانيكي.
كيف يمكن للمشترين B2B التحقق من مراقبة جودة الموردين؟
يجب على المشترين بين الشركات اتخاذ خطوات استباقية للتحقق من تدابير مراقبة الجودة لدى مورديهم:
- عمليات تدقيق الموردين: يمكن أن يوفر إجراء عمليات التدقيق للموردين رؤى حول عمليات التصنيع والالتزام بمعايير الجودة.
- تقارير الجودة: يمكن أن يساعد طلب تقارير مراقبة الجودة في تقييم أداء المورد وامتثاله للمعايير ذات الصلة.
- عمليات التفتيش من طرف ثالث: يمكن أن يوفر إشراك خدمات الفحص من طرف ثالث تقييمًا غير متحيز لجودة المنتج قبل الشحن.
ما هي الفروق الدقيقة في مراقبة الجودة التي يجب على المشترين الدوليين بين الشركات أخذها بعين الاعتبار؟
يجب أن يكون المشترون الدوليون بين الشركات، لا سيما من مناطق مثل أفريقيا وأمريكا الجنوبية والشرق الأوسط وأوروبا، على دراية بالعديد من الفروق الدقيقة:
- الامتثال التنظيمي: قد يكون للمناطق المختلفة متطلبات تنظيمية محددة يجب الوفاء بها. من الضروري فهم اللوائح المحلية.
- شفافية سلسلة التوريد: يجب على المشترين التأكد من أن الموردين يحافظون على الشفافية في جميع مراحل سلسلة التوريد، خاصة فيما يتعلق بمصادر المواد وممارسات التصنيع.
- الاعتبارات الثقافية: قد يكون للمناطق المختلفة توقعات مختلفة فيما يتعلق بمعايير الجودة وأساليب التواصل. ويمكن أن يساعد إنشاء قنوات اتصال واضحة في الحد من سوء الفهم.
الخلاصة
خلاصة القول، إن فهم عمليات التصنيع ومقاييس ضمان الجودة للمولدات ومولدات التيار المتردد أمر ضروري للمشترين بين الشركات. من خلال إيلاء اهتمام وثيق لاختيار المواد وتقنيات التصنيع ومعايير الجودة وطرق الاختبار، يمكن للمشترين اتخاذ قرارات مستنيرة تؤدي إلى مشتريات ناجحة وشراكات طويلة الأجل. تزود هذه المعرفة الشاملة المشترين بالقدرة على التعامل مع تعقيدات التوريد الدولي بفعالية.
صورة توضيحية تتعلق بالفرق بين المولد ومولد التيار المتردد
دليل عملي للمصادر: قائمة تدقيق خطوة بخطوة لـ ‘ما الفرق بين المولد والمولد المتردد’
مقدمة
يُعد فهم الاختلافات بين المولدات ومولدات التيار المتردد أمرًا بالغ الأهمية بالنسبة للمشترين من الشركات الذين يشاركون في شراء المعدات الكهربائية. يوفر هذا الدليل قائمة مراجعة عملية تحدد الخطوات الأساسية لضمان اتخاذ قرارات مستنيرة عند شراء أي من الجهازين. من خلال اتباع هذه الخطوات، يمكنك تقييم احتياجاتك بفعالية واختيار المعدات المناسبة واختيار الموردين الموثوق بهم.
الخطوة 1: حدد المواصفات الفنية الخاصة بك
قبل البدء في عملية الشراء، حدد بوضوح متطلباتك الفنية. ضع في اعتبارك عوامل مثل نوع التيار المطلوب (تيار متردد أو تيار مستمر)، وجهد الخرج، وتقييمات الكفاءة. هذه الخطوة ضرورية لضمان توافق المعدات مع احتياجاتك التشغيلية ومعايير الصناعة.
- متطلبات الجهد: تحديد مستويات الجهد المطلوب لتطبيقاتك.
- احتياجات الكفاءة: تحديد مستويات الكفاءة اللازمة لفعالية التكلفة التشغيلية الخاصة بك.
الخطوة 2: ملاءمة التطبيق البحثي
تحقق من التطبيقات المحددة التي تحتاج من أجلها إلى مولد أو مولد كهربائي. غالبًا ما تستخدم المولدات لإنتاج الكهرباء على نطاق واسع، في حين أن المولدات تناسب أكثر استخدامات السيارات والاستخدامات الأصغر حجمًا. سيساعدك فهم هذه الفروق في اختيار المعدات المناسبة لاحتياجاتك.
- حالات الاستخدام: حدد ما إذا كان مشروعك يتطلب إمداداً مستمراً للطاقة أو استخداماً متقطعاً.
- معايير الصناعة: ابحث عن الامتثال للمعايير المحلية والدولية ذات الصلة بمجال عملك.
الخطوة 3: تقييم شهادات الموردين
من الضروري التحقق من أن الموردين المحتملين يحملون الشهادات اللازمة ويلتزمون بمعايير الصناعة. تشير الشهادات مثل ISO و CE إلى الالتزام بالجودة والسلامة. هذه الخطوة ضرورية للتخفيف من المخاطر المرتبطة بفشل المعدات وعدم الامتثال.
صورة توضيحية تتعلق بالفرق بين المولد ومولد التيار المتردد
- ضمان الجودة: التحقق من شهادات إدارة الجودة.
- معايير السلامة: ضمان الامتثال للوائح السلامة ذات الصلة بمنطقتك.
الخطوة 4: مقارنة مقاييس الأداء
اجمع مقاييس الأداء من مختلف الموردين لكل من المولدات ومولدات التيار المتردد. تتضمن المقاييس الرئيسية تقييمات الكفاءة وسعة الإخراج ومتطلبات الصيانة. ستساعدك مقارنة هذه المقاييس على تحديد المنتج الذي يلبي مواصفاتك وميزانيتك على أفضل وجه.
- تقييمات الكفاءة: البحث عن مقاييس كفاءة الطاقة لتقييم التكاليف التشغيلية على المدى الطويل.
- سعة الإخراج: تأكد من توافق سعة الإخراج مع متطلبات مشروعك.
الخطوة 5: طلب عروض توضيحية للمنتجات
قبل الانتهاء من عملية الشراء، اطلب عروضاً توضيحية للمنتج أو عينات إن أمكن. يتيح لك ذلك تقييم أداء المعدات في سيناريو واقعي. يمكن أن توفر العروض العملية رؤى قيمة حول موثوقية المعدات وسهولة تشغيلها.
- شروط الاختبار: تأكد من أن العرض التوضيحي يعكس بيئتك التشغيلية.
- آراء المستخدمين: جمع المدخلات من الموظفين الفنيين الذين سيقومون بتشغيل المعدات.
الخطوة 6: التفاوض على الشروط والأحكام
بمجرد اختيار المورّد، تفاوض على الشروط التي تفيد الطرفين. ناقش جوانب مثل فترات الضمان واتفاقيات الصيانة وشروط الدفع. يمكن أن يؤدي التفاوض الفعال إلى صفقة شاملة أفضل وشراكة أقوى مع المورد.
- تغطية الضمان: التأكد من أن شروط الضمان تغطي الأعطال التشغيلية المحتملة.
- دعم الصيانة: مناقشة خيارات الدعم والخدمات المستمرة.
الخطوة 7: مراجعة دعم ما بعد البيع
تقييم دعم ما بعد البيع الذي يقدمه المورد الخاص بك. يمكن أن تؤثر خدمة العملاء الموثوقة ودعم الصيانة بشكل كبير على طول عمر معداتك وكفاءتها. يمكن أن يساعدك المورد الذي يتمتع بدعم قوي لما بعد البيع في حل المشكلات بسرعة وكفاءة.
- الدعم الفني: تأكيد توافر المساعدة الفنية بعد الشراء.
- فرص التدريب: استفسر عن تدريب موظفيك على تشغيل المعدات وصيانتها.
من خلال اتباع قائمة المراجعة هذه، يمكن للمشترين بين الشركات التعامل مع تعقيدات الحصول على المولدات ومولدات التيار المتردد بثقة أكبر، مما يضمن اختيار المعدات الأنسب لاحتياجاتهم.
تحليل شامل للتكلفة والتسعير لما هو الفرق بين المولد والمولد المولد المولد المولد
ما هي مكونات التكلفة الرئيسية في توريد المولدات الكهربائية مقابل المولدات الكهربائية؟
عند تقييم مصادر توريد المولدات ومولدات التيار المتردد، فإن فهم هيكل التكلفة أمر بالغ الأهمية بالنسبة للمشترين بين الشركات. تشمل مكونات التكلفة الأساسية المواد والعمالة ونفقات التصنيع العامة والأدوات ومراقبة الجودة والخدمات اللوجستية وهوامش الربح.
-
المواد: يؤثر اختيار المواد بشكل كبير على التكلفة. وغالباً ما تتطلب المولدات الكهربائية مكونات أكثر قوة للتعامل مع أنواع مختلفة من الخرج (تيار متردد أو تيار مستمر)، مما قد يرفع تكاليف المواد. وقد تستخدم المولدات، لكونها أكثر كفاءة وأصغر حجماً عادة، مواد أخف وزناً ولكنها لا تزال تتطلب مكونات كهربائية عالية الجودة لضمان الأداء.
-
العمل: يمكن أن تختلف تكاليف العمالة حسب مدى تعقيد عملية التجميع. فقد تتطلب المولدات الكهربائية عمالة متخصصة للتجميع والاختبار، خاصة عندما يتعلق الأمر بمواصفات مخصصة. وعلى العكس من ذلك، قد ينطوي تصنيع المولدات على عمالة أقل بسبب بساطة تصميمها.
-
تكاليف التصنيع العامة: يشمل ذلك التكاليف المتعلقة بالمرافق وصيانة المعدات وعمليات المصنع. واعتمادًا على موقع المورد، يمكن أن تتقلب هذه التكاليف. على سبيل المثال، قد يقوم المصنعون في المناطق التي ترتفع فيها تكاليف الطاقة بتمرير هذه النفقات إلى المشترين.
-
الأدوات: يمكن أن تكون الأدوات المخصصة ذات تكلفة مسبقة كبيرة، خاصةً بالنسبة للمولدات أو المولدات المتخصصة. يجب على المشترين الاستفسار عن تكاليف الأدوات إذا كانوا يحتاجون إلى تكوينات أو تعديلات محددة، حيث يمكن أن يؤثر ذلك على السعر الإجمالي.
-
مراقبة الجودة: ينطوي ضمان استيفاء المنتجات للمعايير الدولية على تكاليف إضافية. ويمكن لشهادات ضمان الجودة أن تضيف إلى السعر ولكنها ضرورية للموثوقية التشغيلية، خاصة في الصناعات التي تكون فيها السلامة أمراً بالغ الأهمية.
-
اللوجستيات: يمكن أن تختلف تكاليف الشحن اختلافاً كبيراً تبعاً لمنشأ المنتجات ووجهتها. وتؤدي شروط التجارة الدولية دوراً حاسماً في تحديد من يتحمل هذه التكاليف. وينبغي على المشترين أن يأخذوا في الحسبان التعريفات والضرائب وتكلفة الشحن المحتملة عند المقارنة بين الموردين.
-
الهامش: يمكن أن تختلف هوامش الموردين بناءً على طلب السوق والمنافسة وسمعة العلامة التجارية. ويمكن أن يساعد فهم هيكل الهامش المشترين على التفاوض على أسعار أفضل.
ما الذي يؤثر على تسعير المولدات والمولدات الكهربائية؟
هناك عدة عوامل تؤثر على تسعير المولدات ومولدات التيار المتردد بخلاف مكونات التكلفة الأساسية.
-
الحجم والحد الأدنى لكمية الطلب (MOQ): غالباً ما تؤدي المشتريات بالجملة إلى انخفاض أسعار الوحدة الواحدة. وينبغي للمشترين مناقشة خصومات الحجم مع الموردين لتعزيز كفاءة التكلفة.
-
المواصفات والتخصيص: عادة ما تكون المنتجات المخصصة حسب الطلب مرتفعة الثمن. ويجب على المشترين تحديد متطلباتهم بوضوح مقدماً لتجنب التكاليف غير المتوقعة في وقت لاحق من عملية الشراء.
-
شهادات المواد والجودة: يمكن أن تؤثر جودة المواد وتوافر الشهادات بشكل كبير على الأسعار. فالمنتجات التي تتمتع بتصنيفات جودة أعلى أو شهادات إضافية قد تفرض أسعاراً أعلى ولكنها قد تؤدي إلى انخفاض تكاليف الصيانة على المدى الطويل.
-
عوامل الموردين: يمكن أن تؤثر سمعة المورد وموثوقيته أيضًا على الأسعار. فقد يتقاضى الموردون الراسخون رسوماً أعلى ولكنهم يقدمون دعماً وضمانات ومستويات خدمة أفضل.
-
مصطلحات التجارة الدولية: إن فهم الآثار المترتبة على شروط التجارة الدولية أمر بالغ الأهمية بالنسبة للمشترين الدوليين. فهي تحدد مسؤوليات المشترين والبائعين في الشحن والخدمات اللوجستية، مما يؤثر على التكاليف الإجمالية.
كيف يمكن للمشترين التفاوض على أسعار أفضل؟
يمكن لاستراتيجيات التفاوض الفعالة أن تساعد المشترين على تأمين أسعار مناسبة للمولدات ومولدات التيار المتردد.
-
حجم الرافعة المالية: من خلال الالتزام بطلبات أكبر، يمكن للمشترين التفاوض على خصومات وشروط أفضل.
-
مقارنة الموردين المتعددين: يساعد جمع عروض الأسعار من موردين مختلفين على إنشاء مشهد تنافسي، مما يسمح للمشترين بالاستفادة من العروض المقدمة من بعضهم البعض.
-
التركيز على التكلفة الإجمالية للملكية (TCO): بدلاً من التكلفة الأولية فقط، ضع في اعتبارك التكاليف التشغيلية على المدى الطويل، بما في ذلك الصيانة وكفاءة الطاقة ووقت التعطل المحتمل.
-
التحلي بالشفافية بشأن المتطلبات: التواصل الواضح فيما يتعلق بالمواصفات ومعايير الجودة يمكن أن يقلل من سوء الفهم ويؤدي إلى تسعير أكثر دقة.
-
التوقيت وظروف السوق: أن تكون على دراية باتجاهات السوق والتغيرات الموسمية يمكن أن يوفر لك ميزة في المفاوضات.
ما الذي يجب أن يضعه المشترون الدوليون في الاعتبار؟
بالنسبة للمشترين الدوليين بين الشركات، لا سيما من أفريقيا وأمريكا الجنوبية والشرق الأوسط وأوروبا، فإن فهم الديناميكيات الإقليمية أمر ضروري. يمكن لعوامل مثل اللوائح المحلية وتقلبات العملة والظروف الجيوسياسية أن تؤثر على استراتيجيات التسعير والتوريد. يجب على المشترين إجراء بحث شامل للسوق لتحديد أفضل الموردين والتفاوض على الشروط التي تعكس ظروف السوق المحلية.
إخلاء المسؤولية: يمكن أن تختلف أسعار المولدات ومولدات التيار المتردد اختلافًا كبيرًا بناءً على المواصفات والحجم وظروف السوق. يُنصح بإجراء بحث شامل للسوق وتقييمات شاملة للموردين للحصول على أسعار دقيقة وضمان أفضل قيمة لاستثمارك.
صورة توضيحية تتعلق بالفرق بين المولد ومولد التيار المتردد
تحليل البدائل: مقارنة ما هو الفرق بين المولد والمولد المولد مع الحلول الأخرى
استكشاف البدائل: مقارنة بين المولدات والمولدات والمولدات الأخرى
في إطار السعي لتحويل الطاقة بشكل موثوق به، يعد فهم الاختلافات بين المولدات ومولدات الطاقة المترددة أمرًا بالغ الأهمية لمشتري الأعمال التجارية الذين يبحثون عن الحلول المثلى. ومع ذلك، توجد بدائل مختلفة يمكنها أيضًا تلبية احتياجات توليد الطاقة، ولكل منها مجموعة من المزايا والتحديات الخاصة بها. يقارن هذا القسم بين المولدات ومولدات المولدات مقابل بديلين قابلين للتطبيق: أنظمة الطاقة الشمسية وحلول تخزين البطاريات.
جدول المقارنة
| جانب المقارنة | ما هو الفرق بين المولد والمولد والمولد المولد | أنظمة الطاقة الشمسية | حلول تخزين البطاريات |
|---|---|---|---|
| الأداء | كفاءة أعلى في تحويل الطاقة، خرج تيار متردد فقط | تعتمد على ضوء الشمس؛ يمكن أن تنتج تيار متردد أو تيار مستمر | يوفر طاقة ثابتة، ولكنه يعتمد على مصادر الشحن |
| التكلفة | تكلفة أولية أقل بشكل عام، ولكن التكاليف التشغيلية تتفاوت | استثمار أولي مرتفع، ولكن تكاليف تشغيلية منخفضة | تكاليف متوسطة المدى؛ تتطلب استثمارًا أوليًا للبطاريات والتركيب |
| سهولة التنفيذ | يحتاج إلى عمالة ماهرة للتركيب؛ يحتاج إلى صيانة | قد تكون عملية التركيب معقدة، وتعتمد على الموقع؛ وقد تكون التصاريح مطلوبة | التثبيت بسيط نسبياً، ولكنه يتطلب التكامل مع الأنظمة الحالية |
| الصيانة | صيانة معتدلة؛ تتآكل الفرش مع مرور الوقت | الحد الأدنى من الصيانة؛ الحاجة إلى تنظيف الألواح | الفحوصات المنتظمة مطلوبة؛ يختلف عمر البطارية حسب الاستخدام |
| أفضل حالة استخدام | مثالية للمناطق النائية التي تحتاج إلى كهرباء موثوقة | الأفضل للمناطق ذات أشعة الشمس الوافرة؛ صديقة للبيئة | مناسبة لتطبيقات الطاقة الاحتياطية وتخزين الطاقة |
تفصيل البدائل
أنظمة الطاقة الشمسية
تعمل أنظمة الطاقة الشمسية على تسخير ضوء الشمس لتوليد الكهرباء، مما يجعلها بديلاً جذاباً للمولدات والمولدات التقليدية. وتتمثل الميزة الأساسية للطاقة الشمسية في استدامتها وانخفاض تكاليفها التشغيلية بمجرد تركيبها. ومع ذلك، يمكن أن يكون الاستثمار الأولي كبيراً، ويعتمد الأداء بشكل كبير على الموقع الجغرافي والظروف الجوية. في المناطق ذات أشعة الشمس الثابتة، يمكن أن توفر أنظمة الطاقة الشمسية مصدراً موثوقاً للطاقة، ولكنها قد تتطلب تركيبات وتصاريح معقدة، مما قد يعيق بعض الشركات.
حلول تخزين البطاريات
تعمل أنظمة تخزين البطاريات كتقنية تكميلية لكل من المولدات ومولدات التيار المتردد. فهي تخزن الطاقة لاستخدامها في وقت لاحق، مما يوفر إمدادات طاقة ثابتة بغض النظر عن مصدر الطاقة. هذه الحلول ذات قيمة خاصة في التطبيقات التي تتطلب طاقة احتياطية أو للشركات التي تتطلع إلى تحسين استهلاك الطاقة. وعلى الرغم من أنها توفر الراحة والمرونة، إلا أن أنظمة البطاريات لها عيوبها أيضاً، بما في ذلك الحاجة إلى الصيانة الدورية والعمر الافتراضي المحدود للبطاريات. يمكن أن يكون الاستثمار الأولي معتدلاً، مما يجعلها خياراً ممكناً للعديد من الشركات.
الخاتمة: اختيار حل الطاقة المناسب لاحتياجاتك
عند اختيار حل الطاقة الأنسب، يجب على المشترين بين الشركات النظر في احتياجاتهم التشغيلية المحددة وقيود الميزانية والعوامل البيئية. تظل المولدات والمولدات الكهربائية خيارات موثوقة لتلبية الاحتياجات الفورية للطاقة، خاصة في المناطق النائية. ومع ذلك، يمكن أن يؤدي استكشاف بدائل مثل أنظمة الطاقة الشمسية وتخزين البطاريات إلى تحقيق وفورات واستدامة طويلة الأجل. من خلال تقييم الأداء والتكاليف وسهولة التنفيذ والصيانة وأفضل حالات الاستخدام لكل خيار، يمكن للمشترين اتخاذ قرارات مستنيرة تتماشى مع أهدافهم الاستراتيجية ومتطلباتهم التشغيلية.
الخصائص التقنية الأساسية والمصطلحات التجارية لما هو الفرق بين المولد والمولد المتردد
ما هي الخصائص التقنية الرئيسية التي تميز بين المولدات والمولدات الكهربائية؟
عند الاختيار بين مولد ومولد كهربائي، فإن فهم مواصفاتهما الفنية أمر بالغ الأهمية لاتخاذ قرارات شراء مستنيرة. إليك العديد من المواصفات الهامة التي يجب أخذها في الاعتبار:
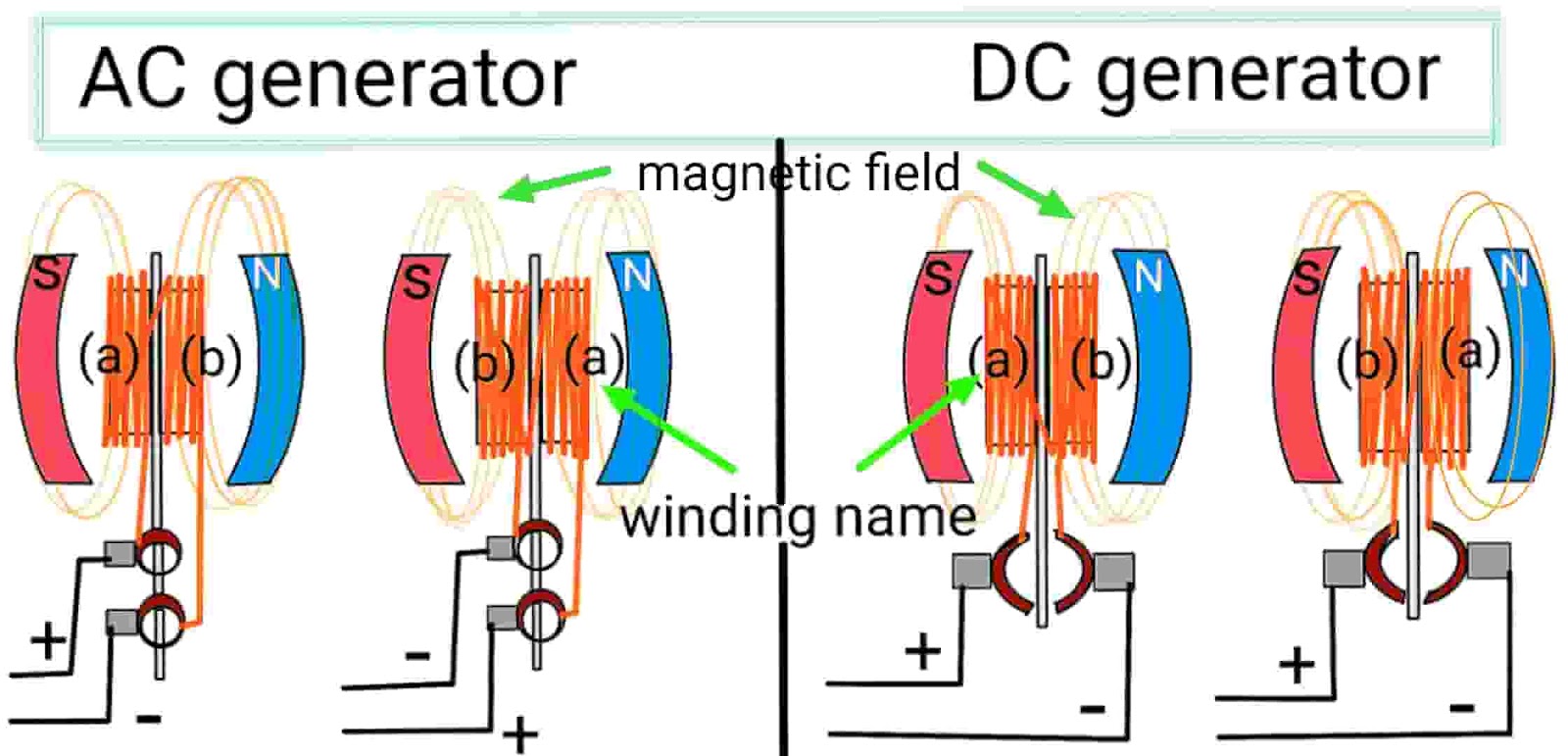
1. نوع الإخراج: تيار متردد مقابل تيار مستمر
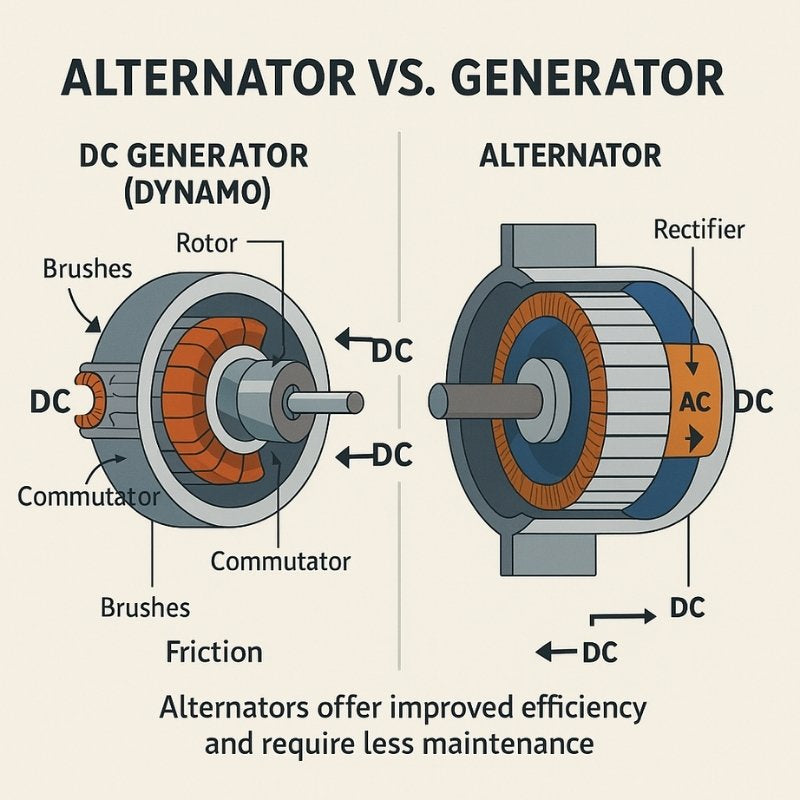
- التعريف: يمكن للمولدات أن تنتج تيارًا مترددًا (AC) وتيارًا مباشرًا (DC)، بينما تنتج المولدات على وجه التحديد تيارًا مترددًا.
- الأهمية: هذا التمييز أمر حيوي للمشترين، لأنه يحدد مدى ملاءمة التطبيق. على سبيل المثال، يفضل استخدام المولدات في الإعدادات التي تتطلب تياراً مستمراً لشحن البطارية، بينما تعتبر المولدات مثالية للتطبيقات مثل أنظمة السيارات حيث يكون التيار المتردد كافياً.
2. تصنيف الكفاءة
- التعريف: تشير الكفاءة إلى نسبة الناتج الكهربائي المفيد إلى طاقة الإدخال الميكانيكية.
- الأهمية: تعد المولدات أكثر كفاءة بشكل عام من المولدات، حيث تقوم بتحويل نسبة أعلى من الطاقة الميكانيكية إلى طاقة كهربائية. ويمكن أن تؤدي هذه الكفاءة إلى انخفاض التكاليف التشغيلية والحفاظ على الطاقة، مما يجعل المولدات خياراً أفضل للصناعات التي تركز على الاستدامة.
3. مواصفات الحجم والوزن
- التعريف: الأبعاد المادية للجهاز ووزنه.
- الأهمية: عادةً ما تكون المولدات أصغر وأخف وزنًا من المولدات. ويمكن أن يكون هذا عاملاً حاسماً في التطبيقات ذات المساحة المحدودة، كما هو الحال في المركبات أو حلول الطاقة المحمولة، حيث يؤثر الوزن والحجم بشكل مباشر على الأداء وسهولة الاستخدام.
4. متطلبات الصيانة
- التعريف: تواتر وتعقيد الصيانة اللازمة لضمان التشغيل الأمثل.
- الأهمية: غالبًا ما تتطلب المولدات صيانة أقل نظرًا لتصميمها الثابت، مما يقلل من البلى والتلف. وبالنسبة لمشتري B2B، فإن انخفاض الصيانة يعني انخفاض وقت التعطل والتكاليف التشغيلية.
5. نطاق RPM (عدد الدورات في الدقيقة)
- التعريف: نطاق السرعة التشغيلية التي يمكن للجهاز عندها توليد خرج كهربائي بكفاءة.
- الأهمية: تعمل المولدات بفعالية على نطاق واسع من عدد الدورات في الدقيقة، مما يتيح مرونة أكبر في مختلف التطبيقات. وعلى النقيض من ذلك، فإن المولدات عادةً ما يكون نطاق عدد الدورات في الدقيقة أقل، مما قد يحد من استخدامها في التطبيقات عالية السرعة.
6. احتياجات الاستقطاب
- التعريف: عملية إنشاء مجال مغناطيسي في المولد.
- الأهمية: تحتاج المولدات إلى الاستقطاب بعد التركيب، بينما لا تحتاج المولدات إلى الاستقطاب بعد التركيب، بينما لا تحتاج المولدات إلى ذلك. يمكن أن يؤثر هذا الاختلاف على وقت التركيب وتعقيده، مما يجعل المولدات خياراً أكثر وضوحاً للمستخدمين الذين يسعون إلى الإعداد السريع.
ما هي المصطلحات التجارية الشائعة المتعلقة بالمولدات والمولدات الكهربائية؟
يعد فهم المصطلحات الخاصة بالصناعة أمرًا ضروريًا للمشترين بين الشركات عند التنقل في عمليات الشراء. فيما يلي بعض المصطلحات الشائعة المرتبطة بالمولدات ومولدات التيار المتردد:
صورة توضيحية تتعلق بالفرق بين المولد ومولد التيار المتردد
1. OEM (الشركة المصنعة للمعدات الأصلية)
- التعريف: شركة تنتج قطع غيار أو معدات قد يتم تسويقها من قبل مصنع آخر.
- الأهمية: يجب على المشترين أن يكونوا على دراية بحالة صانعي المعدات الأصلية عند الحصول على قطع غيار المولدات أو المولدات الكهربائية، حيث إنها غالبًا ما تشير إلى الجودة والتوافق مع الأنظمة الحالية.
2. MOQ (الحد الأدنى لكمية الطلب)
- التعريف: أصغر كمية من منتج يرغب المورد في بيعها.
- الأهمية: يساعد فهم موك المشترين على إدارة المخزون وقيود الميزانية، مما يضمن طلب الكميات التي تتماشى مع الاحتياجات التشغيلية دون تكبد تكاليف زائدة.
3. طلب عرض أسعار (RFQ)
- التعريف: وثيقة تصدرها الجهة المشترية لدعوة الموردين لتقديم عطاءات على منتجات أو خدمات محددة.
- الأهمية: يمكن أن يؤدي تقديم طلب عرض أسعار إلى الحصول على أسعار تنافسية وشروط أفضل، وهو أمر بالغ الأهمية لشراء مولدات أو مولدات كهربائية على نطاق واسع.
4. شروط التجارة الدولية (Incoterms)
- التعريف: مجموعة من القواعد الدولية المحددة مسبقاً التي توضح مسؤوليات المشترين والبائعين في المعاملات الدولية.
- الأهمية: الإلمام بشروط التجارة الدولية أمر حيوي للمشترين بين الشركات لفهم تكاليف الشحن ومسؤوليات التسليم وإدارة المخاطر عند استيراد المولدات أو المولدات الكهربائية.
5. KVA (كيلو فولت أمبير)
- التعريف: وحدة للطاقة الظاهرية في الدائرة الكهربائية، تُستخدم لقياس قدرة المولدات ومولدات التيار المتردد.
- الأهمية: تساعد تصنيفات KVA المشترين على تحديد حجم المعدات المناسب لمتطلباتهم من الطاقة، مما يضمن اختيار مولد أو مولد كهربائي يلبي احتياجاتهم من الطاقة.
6. عامل التحميل
- التعريف: مقياس لكفاءة الاستخدام الكهربائي، ويُحسب كنسبة الناتج الفعلي إلى أقصى ناتج ممكن خلال فترة محددة.
- الأهمية: يساعد فهم عوامل الحمولة المشترين في اختيار المولدات أو المولدات التي يمكنها التعامل بكفاءة مع الأحمال التشغيلية الخاصة بهم، مما يؤدي إلى تحسين استهلاك الطاقة والتكاليف.
من خلال فهم هذه الخصائص التقنية والمصطلحات التجارية، يمكن للمشترين بين الشركات اتخاذ قرارات مستنيرة بشكل أفضل عند الاختيار بين المولدات والمولدات المترددة، مما يؤدي في النهاية إلى عمليات أكثر كفاءة وفعالية من حيث التكلفة.
الإبحار في ديناميكيات السوق واتجاهات التوريد في قطاع ما هو الفرق بين قطاع المولدات والمولدات الكهربائية
ما هي ديناميكيات السوق الرئيسية التي تؤثر على قطاع المولدات والمولدات الكهربائية؟
تتشكل السوق العالمية للمولدات ومولدات الطاقة المتجددة من خلال مجموعة من العوامل بما في ذلك الطلب المتزايد على الطاقة، والتقدم التكنولوجي، والتطورات الاقتصادية الإقليمية. ومع سعي الدول إلى تحقيق الاستقلالية في مجال الطاقة، هناك تحول متزايد نحو أنظمة الطاقة اللامركزية، لا سيما في الأسواق الناشئة في أفريقيا وأمريكا الجنوبية. على سبيل المثال، تكتسب حلول الطاقة الشمسية خارج الشبكة زخمًا متزايدًا، حيث يمكن إقران مولدات الطاقة الشمسية بمولدات الطاقة المترددة لتوفير طاقة موثوقة في المناطق النائية.
تؤثر التقنيات الناشئة، مثل الشبكات الذكية والأجهزة التي تدعم إنترنت الأشياء، على اتجاهات التوريد. يبحث المشترون من الشركات بشكل متزايد عن مولدات ومولدات كهربائية يمكن أن تتكامل مع هذه التقنيات لتعزيز الكفاءة ومراقبة الأداء. في أوروبا، تدفع اللوائح الصارمة المتعلقة بكفاءة الطاقة الشركات المُصنِّعة إلى الابتكار، مما يؤدي إلى إنتاج مولدات كهربائية توفر إنتاجًا أعلى مع استهلاك أقل للطاقة.
صورة توضيحية تتعلق بالفرق بين المولد ومولد التيار المتردد
وبالإضافة إلى ذلك، ومع سعي المشترين الدوليين إلى تحسين سلاسل التوريد الخاصة بهم، هناك اتجاه ملحوظ نحو إقامة شراكات مع المصنعين المحليين في مناطق مثل فيتنام والبرازيل. ولا تقتصر هذه الشراكات على تقليل تكاليف النقل فحسب، بل تضمن أيضًا أوقات استجابة أسرع لمتطلبات السوق. على هذا النحو، يصبح فهم الفروق الدقيقة بين المولدات ومولدات التيار المتردد - خاصةً فيما يتعلق بتطبيقاتها وكفاءتها - أمرًا بالغ الأهمية بالنسبة للمشترين بين الشركات الذين يتطلعون إلى اتخاذ قرارات شراء مستنيرة.
كيف تؤثر الاستدامة والمصادر الأخلاقية على صناعة المولدات والمولدات الكهربائية؟
أصبحت الاستدامة مصدر قلق بالغ الأهمية بالنسبة للمشترين من الشركات في قطاع المولدات ومولدات التيار المتردد. فمع تزايد الوعي العالمي بتغير المناخ والتدهور البيئي، تتعرض الشركات لضغوط لتبني ممارسات أكثر مراعاة للبيئة. ويشمل ذلك الحصول على المواد من الموردين الذين يلتزمون بمعايير الإنتاج الأخلاقية ويظهرون التزامهم بالحد من بصمتهم الكربونية.
على سبيل المثال، غالبًا ما يتم إعطاء الأولوية للمصنعين الذين ينتجون مولدات ومولدات موفرة للطاقة من قبل المشترين الذين يسعون إلى التوافق مع الممارسات المستدامة. تشير الشهادات الخضراء، مثل ISO 14001، إلى الالتزام بتقليل الأثر البيئي إلى الحد الأدنى، وهو ما يمكن أن يكون عامل تمييز مهم في السوق. وعلاوة على ذلك، يهتم المشترون بشكل متزايد بتقييمات دورة الحياة لفهم الآثار البيئية المترتبة على مشترياتهم، بدءًا من الإنتاج وحتى التخلص منها.
كما يؤدي التحول نحو مصادر الطاقة المتجددة إلى زيادة الطلب على المولدات التي يمكن أن تعمل جنبًا إلى جنب مع أنظمة الطاقة البديلة. ويتضح هذا الاتجاه بشكل خاص في مناطق مثل الشرق الأوسط، حيث يوجد توجه كبير نحو الطاقة الشمسية وطاقة الرياح. إن المشترين من الشركات الذين يعطون الأولوية للتوريد المستدام والأخلاقي لا يعززون فقط ملفاتهم الخاصة بالمسؤولية الاجتماعية للشركات، بل يضعون أنفسهم في موقع تنافسي في سوق يقدّر الاستدامة بشكل متزايد.
ما هو السياق التاريخي للمولدات الكهربائية والمولدات الكهربائية في التوريد بين الشركات؟
كان لتطور المولدات ومولدات التيار المتردد دور محوري في تشكيل حلول الطاقة الحديثة. في البداية، كانت المولدات تُستخدم في المقام الأول لإنتاج الكهرباء بالتيار المباشر (DC)، مما حد من استخداماتها. ومع ذلك، أحدث ظهور المولدات في أوائل القرن العشرين ثورة في توليد الكهرباء من خلال تمكين إنتاج التيار المتردد (AC). وسمح هذا التحول بنقل الطاقة بكفاءة أكبر لمسافات طويلة وفتح إمكانيات جديدة للتطبيقات الكهربائية.
ومع تطور الصناعات، تطورت كذلك التكنولوجيا الكامنة وراء هذه الأجهزة. وقد أدى إدخال تصميمات أكثر كفاءة، مثل الأذرع الثابتة والمجالات المغناطيسية الدوارة إلى تعزيز كفاءة الطاقة وتقليل احتياجات الصيانة. بالنسبة للمشترين بين الشركات، يعد فهم هذا السياق التاريخي أمرًا ضروريًا، حيث إنه يُعلم القدرات التكنولوجية الحالية وتطبيقات المولدات ومولدات التيار المتردد. تتيح هذه المعرفة اتخاذ قرارات مستنيرة بشأن التوريد التي تتماشى مع كل من الاحتياجات التشغيلية وأهداف الاستدامة.
الأسئلة المتداولة (FAQs) لمشتري B2B عن الفرق بين المولد والمولد المتردد
-
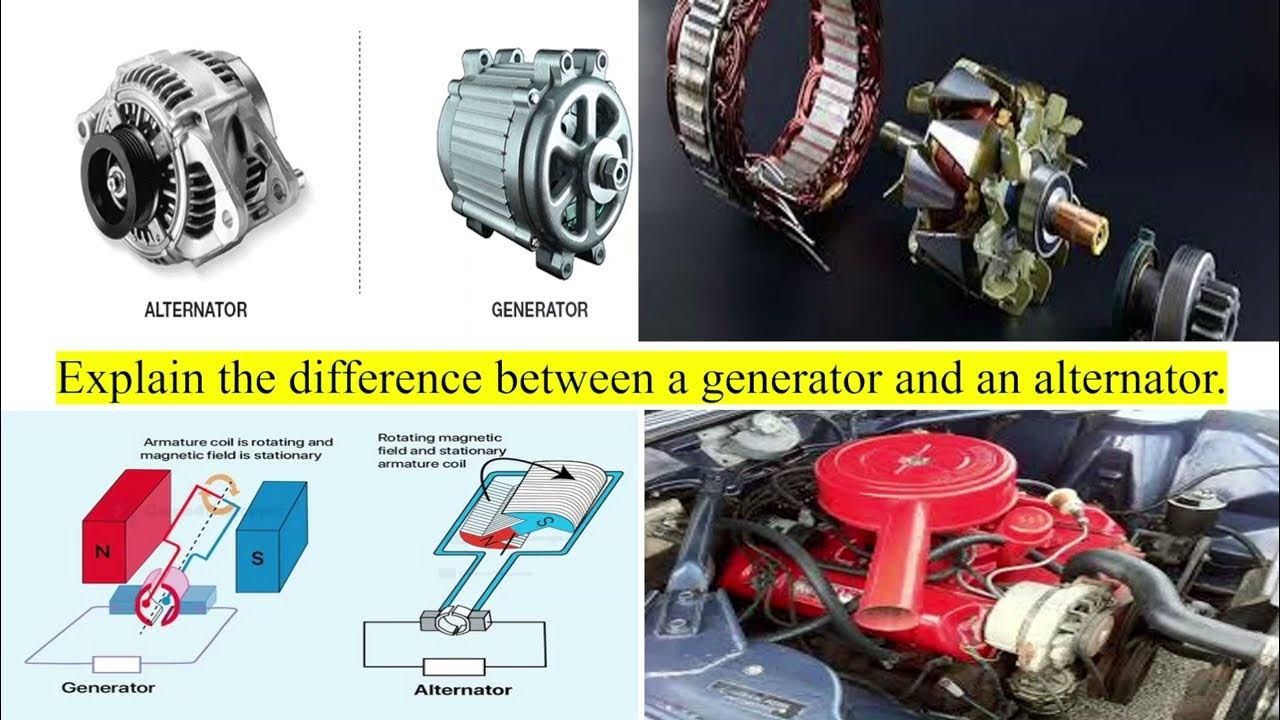
ما هي الاختلافات الرئيسية بين المولد ومولد التيار المتردد؟
يحول كل من المولدات والمولدات المترددة الطاقة الميكانيكية إلى طاقة كهربائية، لكنهما يختلفان في تشغيلهما ومخرجاتهما. يمكن للمولد أن ينتج إما تيارًا مترددًا (AC) أو تيارًا مباشرًا (DC)، بينما المولد يولد تيارًا مترددًا فقط. بالإضافة إلى ذلك، تكون المولدات أكثر كفاءة في استخدام الطاقة وعادةً ما يكون ناتجها أعلى من المولدات. يظل المحرك في المولد ثابتًا، مع دوران المجال المغناطيسي حوله، بينما في المولد، يدور المحرك داخل مجال مغناطيسي ثابت. يمكن أن يساعد فهم هذه الاختلافات مشتري B2B على اتخاذ قرارات مستنيرة بناءً على احتياجاتهم من الطاقة. -
كيف يمكنني تحديد أيهما أفضل للتطبيق الصناعي الخاص بي: مولد أو مولد التيار المتردد؟
يعتمد الاختيار بين المولد والمولد المولد على متطلباتك المحددة من الطاقة. بالنسبة للتطبيقات التي تحتاج إلى طاقة تيار متردد متسقة وفعالة، كما هو الحال في أنظمة السيارات، فإن المولد المولد هو الأفضل. وعلى العكس من ذلك، إذا كان التشغيل الخاص بك يتطلب طاقة تيار متردد وطاقة تيار مستمر أو إذا كنت بحاجة إلى شحن البطاريات الفارغة، فسيكون المولد أكثر ملاءمة. قم بتقييم احتياجاتك من الطاقة ومتطلبات الكفاءة وقدرات الصيانة لاتخاذ أفضل قرار لعملياتك. -
ما الذي يجب أن أضعه في الاعتبار عند الحصول على مولدات ومولدات التيار المتردد من الموردين الدوليين؟
عند التوريد من موردين دوليين، ضع في اعتبارك عوامل مثل سمعة المورد، والامتثال لمعايير الجودة الدولية، وخبرته في الصناعة. ومن الضروري أيضاً تقييم قدرتهم الإنتاجية، ومهل الإنتاج، وتوافر الدعم الفني. بالإضافة إلى ذلك، يمكن أن يساعدك فهم اللوائح المحلية ورسوم الاستيراد في تقييم التكاليف الإجمالية. إن إقامة تواصل واضح والتأكد من قدرة المورد على تلبية متطلبات التخصيص الخاصة بك أمر بالغ الأهمية لنجاح عملية الشراء. -
هل يوجد حد أدنى لكميات الطلبات (MOQs) لشراء المولدات ومولدات التيار المتردد؟
العديد من الموردين لديهم حد أدنى لكميات الطلبات التي يمكن أن تختلف بشكل كبير بناءً على نوع المعدات وقدرات المورد الإنتاجية. عادة، بالنسبة للمعدات الصناعية كبيرة الحجم مثل المولدات والمولدات الكهربائية، قد تتراوح الكميات المطلوبة من بضع وحدات إلى عدة عشرات. يمكن أن تؤدي مناقشة احتياجاتك المحددة وإمكانية الطلبات المستقبلية في بعض الأحيان إلى شروط أكثر ملاءمة. قم دائمًا بتوضيح هذه التفاصيل قبل تقديم الطلب لتجنب التكاليف غير المتوقعة أو التحديات اللوجستية. -
ما هي شروط الدفع التي يقدمها عادةً مورّدو المولدات الكهربائية ومولدات التيار المتردد؟
يمكن أن تختلف شروط الدفع اختلافًا كبيرًا بين الموردين، وتتأثر بعوامل مثل حجم الطلبية والجدارة الائتمانية للمشتري وسياسات المورد. تشمل الشروط الشائعة إيداع مبلغ مقدمًا (غالبًا ما يكون 30-50%)، مع استحقاق الرصيد عند التسليم أو قبل الشحن. قد يقدم بعض الموردين خيارات تمويل أو خطط دفع ممتدة للطلبات الكبيرة. من الضروري التفاوض على الشروط التي تتماشى مع التدفق النقدي والجداول الزمنية للمشروع مع ضمان فهمك للآثار المترتبة على كل هيكل دفع. -
كيف يمكنني التأكد من جودة المولدات ومولدات التيار المتردد من المورد الخاص بي؟
لضمان الجودة، اطلب من مورديك الحصول على شهادات مثل ISO 9001 أو غيرها من معايير الصناعة ذات الصلة. من المفيد أيضًا طلب عينات من المنتج أو إجراء زيارات للمصنع إن أمكن. يمكن أن يساعد إنشاء عملية واضحة لضمان الجودة تشمل عمليات الفحص والاختبار قبل الشحن في الحد من المخاطر. بالإضافة إلى ذلك، يمكن أن توفر مراجعة ملاحظات العملاء السابقين وشهاداتهم رؤى حول موثوقية المورد وجودة المنتج. -
ما هي الاعتبارات اللوجستية التي يجب أن أضعها في اعتباري عند استيراد المولدات ومولدات التيار المتردد؟
تشمل الاعتبارات اللوجستية طرق الشحن والتخليص الجمركي والجداول الزمنية للتسليم. اختر شريك شحن موثوق به من ذوي الخبرة في التعامل مع الآلات الثقيلة لتجنب التأخير. تأكد من فهمك للوائح الاستيراد والرسوم الجمركية في بلدك، حيث يمكن أن تؤثر بشكل كبير على التكاليف الإجمالية. بالإضافة إلى ذلك، ضع في اعتبارك خيارات التخزين إذا كان التسليم الفوري غير ممكن، وضع خطة اتصال واضحة مع المورد الخاص بك لمراقبة تقدم الشحن. -
هل يمكن تخصيص المولدات ومولدات التيار المتردد لتلبية احتياجات العمل المحددة؟
نعم، يقدم العديد من الموردين خيارات تخصيص للمولدات ومولدات المولدات لتلبية متطلبات العمل المحددة. يمكن أن تشمل التخصيصات تعديلات على خرج الجهد ومواصفات الحجم والميزات الإضافية مثل إمكانيات المراقبة عن بُعد. عند مناقشة التخصيص، قدم المواصفات التفصيلية وحالات الاستخدام لضمان فهم المورد لاحتياجاتك بشكل كامل. يمكن أن يؤدي التعاون الوثيق أثناء مرحلة التصميم إلى حلول تعزز الكفاءة والأداء لعملياتك.
أعلى 3 ما هو الفرق بين المولد والمولد قائمة المصنعين والموردين 3
1. ريديت - شرح المولدات والمولدات الكهربائية
المجال: reddit.com
تاريخ التسجيل: 2005 (20 عامًا)
مقدمة: المولدات ومولدات التيار المتردد كلاهما جهازان يولدان الكهرباء، لكنهما يعملان بشكل مختلف. المولد هو نوع من المولدات التي تنتج تيارًا مترددًا (AC) على وجه التحديد، في حين أن مصطلح ‘المولد’ يمكن أن يشير إلى الأجهزة التي تنتج إما تيارًا مترددًا أو تيارًا مباشرًا (DC). تستخدم المولدات بشكل شائع في السيارات لتشغيل الأنظمة الكهربائية وشحن البطارية. وهي مزودة بمولدات...
2. بيجو - المولدات الكهربائية والمولدات الكهربائية
المجال: byjus.com
مسجل: 2013 (12 سنة)
مقدمة: 1. التعريف: يحوِّل المولِّد الطاقة الميكانيكية إلى طاقة كهربائية تيار متردد، بينما يحوِّل المولِّد الطاقة الميكانيكية إلى طاقة كهربائية تيار متردد أو تيار مستمر. 2. التيار الناتج: تستحث المولدات دائمًا تيارًا متناوبًا؛ أما المولدات فيمكنها توليد تيار متناوب أو تيار مباشر. 3. كفاءة الطاقة: المولدات أكثر كفاءة من المولدات. 4. الناتج: تتمتع المولدات بمخرجات أعلى...
3. سبيدواي موتورز - المولدات مقابل المولدات الكهربائية
المجال: سبيدواي موتورز
تاريخ التسجيل: 1996 (29 عامًا)
مقدمة: Alternator vs Generator: Both convert mechanical energy into electrical energy to charge a car’s battery. Generators use a rotating armature inside static magnets, while alternators rotate the magnetic field inside the conductor. Generators are less efficient and struggle to provide adequate current for modern electrical demands, especially at low speeds. Alternators, introduced in the early 60s, …
استنتاج المصادر الاستراتيجية والتوقعات لما هو الفرق بين المولد والمولد المتردد
In summary, understanding the differences between generators and alternators is crucial for international B2B buyers aiming to make informed decisions in their sourcing strategies. While both devices convert mechanical energy into electrical energy, their operational mechanics, output types, efficiency levels, and applications diverge significantly. Generators can produce both AC and DC power, making them versatile for various large-scale applications, while alternators are optimized for efficiency and primarily generate AC power, ideal for automotive and smaller applications.
For businesses in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, strategic sourcing of these power generation solutions can lead to improved operational efficiency and reduced energy costs. By carefully evaluating the specific energy needs and applications, companies can leverage the strengths of each device to enhance productivity and reliability.
صورة توضيحية تتعلق بالفرق بين المولد ومولد التيار المتردد
As the global energy landscape evolves, consider how innovative energy solutions can contribute to your operational strategy. Engage with trusted suppliers who understand your unique market demands and can provide tailored advice on the best equipment for your needs. The right choice today can pave the way for sustainable growth tomorrow.
إخلاء مسؤولية هام وشروط الاستخدام
⚠️ تنويه هام
المعلومات الواردة في هذا الدليل، بما في ذلك المحتوى المتعلق بالمصنعين والمواصفات الفنية وتحليل السوق، هي لأغراض إعلامية وتعليمية فقط. ولا تشكل هذه المعلومات مشورة مهنية في مجال المشتريات أو مشورة مالية أو مشورة قانونية.
على الرغم من أننا بذلنا قصارى جهدنا لضمان دقة المعلومات وحداثتها، فإننا لا نتحمل أي مسؤولية عن أي أخطاء أو سهو أو معلومات قديمة. تخضع ظروف السوق وتفاصيل الشركة والمعايير الفنية للتغيير.
يجب على المشترين من الشركات (B2B) إجراء عمليات التحقق المستقلة والشاملة الخاصة بهم. قبل اتخاذ أي قرارات شراء. ويشمل ذلك الاتصال بالموردين مباشرة، والتحقق من الشهادات، وطلب عينات، والبحث عن استشارة مهنية. يتحمل القارئ وحده مخاطر الاعتماد على أي معلومات واردة في هذا الدليل.