Introdução: Navegando no mercado global de quanto custa consertar um alternador
Navegar pelas complexidades das reparações automóveis, em particular compreender quanto custa a reparação de um alternador, pode ser um desafio significativo para os compradores B2B internacionais. Este guia tem como objetivo desmistificar os vários aspectos da reparação e substituição de alternadores, oferecendo informações essenciais para tomar decisões de compra informadas. Desde os tipos de alternadores disponíveis e as suas aplicações específicas até aos factores críticos que influenciam os custos, forneceremos uma visão geral abrangente adaptada às necessidades das empresas em diversas regiões, incluindo África, América do Sul, Médio Oriente e Europa.
Para os compradores B2B em mercados como o Brasil e a Arábia Saudita, a procura de fornecedores fiáveis e a compreensão das nuances dos preços dos alternadores são fundamentais. Este guia irá aprofundar os meandros da verificação de fornecedores, assegurando que pode identificar peças de qualidade que se adequam às especificações do seu veículo sem comprometer o desempenho. Além disso, iremos explorar os sinais comuns de falha do alternador, ajudando-o a antecipar potenciais reparações antes que estas se transformem em problemas dispendiosos.
Ao equipá-lo com os conhecimentos necessários para navegar neste mercado global, damos-lhe a possibilidade de tomar decisões estratégicas que se alinham com os seus objectivos operacionais. Quer esteja a gerir uma frota de veículos ou a supervisionar reparações automóveis, compreender quanto custa a reparação de um alternador irá, em última análise, melhorar a eficiência e os resultados da sua empresa.
Índice
- Lista dos 4 principais fabricantes e fornecedores de Quanto custa a reparação de um alternador
- Introdução: Navegando no mercado global de quanto custa consertar um alternador
- Para saber quanto custa a reparação de um alternador Tipos e variações
- Principais aplicações industriais de quanto custa a reparação de um alternador
- 3 Pontos de dor comuns dos utilizadores para ‘quanto custa a reparação de um alternador’ e as suas soluções
- Guia de seleção de material estratégico para quanto custa a reparação de um alternador
- Análise aprofundada: Processos de fabrico e garantia de qualidade para quanto custa a reparação de um alternador
- Guia prático de abastecimento: Uma lista de verificação passo-a-passo para ‘quanto custa reparar um alternador’
- Análise exaustiva de custos e preços para quanto custa a reparação de um alternador Sourcing
- Análise de alternativas: Comparação do custo da reparação de um alternador com outras soluções
- Propriedades técnicas essenciais e terminologia comercial para quanto custa a reparação de um alternador
- Navegar na dinâmica do mercado e nas tendências de aprovisionamento no sector de quanto custa a reparação de um alternador
- Perguntas frequentes (FAQs) para compradores B2B de quanto custa a reparação de um alternador
- Conclusão e perspectivas do aprovisionamento estratégico para quanto custa a reparação de um alternador
- Aviso legal importante e termos de utilização
Para saber quanto custa a reparação de um alternador Tipos e variações
| Nome do tipo | Principais características distintivas | Aplicações B2B primárias | Breves prós e contras para compradores |
|---|---|---|---|
| Substituição do alternador OEM | Qualidade do equipamento original, concebido para modelos específicos | Concessionários de automóveis, serviços de frota | Prós: Compatibilidade e qualidade garantidas. Contras: Custo mais elevado em comparação com as opções do mercado pós-venda. |
| Alternador de substituição | Alternativas económicas, de qualidade variável | Oficinas de reparação independentes, frotas regionais | Prós: Mais acessível, maior disponibilidade. Contras: A qualidade pode variar; risco de falha prematura. |
| Alternador Remanufacturado | Reconstruído de acordo com as especificações originais, muitas vezes com garantia | Retalhistas de peças para automóveis, garagens | Prós: Opção económica e ecológica. Contras: Pode não corresponder à fiabilidade OEM; garantia limitada. |
| Alternador de alta potência | Maior amperagem para sistemas eléctricos de elevada exigência | Veículos de desempenho, frotas comerciais | Prós: Suporta maiores exigências eléctricas. Contras: Investimento inicial mais elevado; pode exigir modificações. |
| Alternador reparado | As lojas de reparação locais reparam as unidades existentes | Pequenas garagens, entusiastas da bricolage | Prós: Económica para problemas menores. Contras: Risco de problemas recorrentes; duração de vida limitada. |
Quais são as caraterísticas de uma substituição de alternador OEM?
Os alternadores OEM (Fabricante de Equipamento Original) são concebidos especificamente para a marca e modelo de um veículo, assegurando uma adaptação e funcionalidade perfeitas. São fabricados de acordo com as mesmas normas que as peças originais, proporcionando fiabilidade e longevidade. Os compradores B2B, especialmente os concessionários de automóveis e os serviços de frotas, beneficiam da oferta de substituições OEM, uma vez que garantem a compatibilidade e o desempenho. No entanto, o custo é normalmente mais elevado do que as opções pós-venda, o que pode dissuadir alguns compradores.
Porquê escolher alternadores do mercado de substituição para aplicações B2B?
Os alternadores do mercado de substituição constituem uma alternativa económica para as empresas que procuram minimizar as despesas de reparação. Estas peças são produzidas por fabricantes terceiros e podem variar significativamente em termos de qualidade. As oficinas de reparação independentes e as frotas regionais optam frequentemente por estas peças devido à sua acessibilidade e disponibilidade. No entanto, as empresas devem ter cuidado, uma vez que a qualidade pode ser inconsistente, levando potencialmente a falhas prematuras.
Quais são as vantagens dos alternadores remanufaturados?
Os alternadores remanufacturados são reconstruídos para cumprir ou exceder as especificações originais, muitas vezes com garantia. São uma opção amiga do ambiente, uma vez que reciclam peças existentes. Os retalhistas e as oficinas de peças automóveis utilizam frequentemente estes componentes devido ao seu equilíbrio entre custo e fiabilidade. Embora ofereçam um bom compromisso entre preço e qualidade, podem existir preocupações quanto ao desempenho a longo prazo em comparação com as peças OEM.
Quando é que as empresas devem considerar os alternadores de alto rendimento?
Os alternadores de alto rendimento são concebidos para veículos que requerem mais potência eléctrica, como os veículos de desempenho ou comerciais. Estes alternadores fornecem uma maior amperagem para suportar acessórios e sistemas eléctricos adicionais. As aplicações B2B incluem oficinas de automóveis de desempenho e frotas comerciais que necessitam de alimentar vários dispositivos em simultâneo. O investimento inicial é mais elevado e a instalação pode exigir modificações, mas são essenciais para cenários de elevada procura.
Quais são os benefícios da reparação de um alternador?
A reparação de um alternador pode ser uma opção viável para as empresas que pretendem reduzir os custos. As oficinas de reparação locais oferecem frequentemente este serviço, que pode ser eficaz para problemas menores. Esta abordagem atrai as pequenas oficinas e os entusiastas da bricolage que procuram soluções económicas. No entanto, a desvantagem é o risco de problemas recorrentes, uma vez que as unidades reparadas podem não ter o mesmo tempo de vida útil ou fiabilidade que as alternativas novas ou remanufacturadas.
Principais aplicações industriais de quanto custa a reparação de um alternador
| Indústria/Setor | Aplicação específica de quanto custa a reparação de um alternador | Valor/benefício para a empresa | Considerações importantes sobre o fornecimento para esta aplicação |
|---|---|---|---|
| Reparação automóvel | Estimativa de custos para reparações de alternadores em oficinas | Preços informados ajudam a manter a vantagem competitiva | Qualidade das peças, opções de garantia e custos de mão de obra |
| Transporte | Orçamentação da manutenção dos veículos da frota | Reduz o tempo de inatividade e aumenta a eficiência operacional | Disponibilidade de peças, compatibilidade com vários modelos |
| Agricultura | Manutenção de máquinas e veículos agrícolas | Garante a fiabilidade durante os períodos críticos de colheita | Fornecimento de peças duradouras adequadas a ambientes agressivos |
| Construção | Reparação de máquinas e veículos pesados | Minimiza os atrasos nos projectos e melhora a produtividade | Acesso a peças OEM e pós-venda, capacidades de serviço |
| Logística e entrega | Assegurar que os camiões de entrega estão operacionais | Aumenta a satisfação do cliente através de entregas atempadas | Compreender as regulamentações locais e obter peças de qualidade |
Como é que as oficinas de reparação automóvel podem beneficiar da compreensão dos custos de reparação do alternador?
As oficinas de reparação automóvel devem ter um conhecimento claro dos custos de reparação do alternador para fornecer estimativas exactas aos clientes. Esta transparência promove a confiança e aumenta a fidelidade do cliente. Ao adquirirem peças de alta qualidade, as oficinas podem evitar regressos frequentes, melhorando assim a sua reputação e rentabilidade. Além disso, a oferta de preços competitivos pode atrair mais clientes, especialmente em regiões onde a sensibilidade ao preço é elevada, como em partes de África e da América do Sul.
Porque é que a gestão de custos é fundamental para as frotas de transportes?
Para as empresas de transportes, saber o custo da reparação de alternadores é crucial para uma gestão eficaz da frota. A orçamentação exacta da manutenção pode reduzir significativamente o tempo de inatividade dos veículos, o que tem um impacto direto na prestação de serviços e na eficiência operacional. Em regiões como o Médio Oriente, onde a logística é vital para o comércio, garantir que os veículos estão sempre operacionais pode aumentar a fiabilidade do serviço e a satisfação do cliente. As empresas devem também considerar a disponibilidade de peças compatíveis para evitar atrasos nas reparações.
Imagem ilustrativa relacionada com quanto custa a reparação de um alternador
Como é que as empresas agrícolas garantem a fiabilidade da maquinaria?
Na agricultura, a fiabilidade das máquinas é fundamental durante as épocas de colheita. Compreender os custos associados à reparação de alternadores em tractores e outros veículos permite aos agricultores fazer um orçamento eficaz e evitar avarias inesperadas. Isto é particularmente importante em regiões como o Brasil, onde a produção agrícola está fortemente dependente de operações atempadas. Os compradores deste sector devem dar prioridade ao fornecimento de peças de alternador duradouras que possam suportar condições de trabalho difíceis.
Quais são as implicações das reparações de alternadores na construção?
No sector da construção, a eficiência operacional da maquinaria pesada é fundamental. Conhecer os custos de reparação de alternadores pode ajudar as empresas de construção a minimizar os atrasos nos projectos causados por falhas no equipamento. Com projectos frequentemente com prazos apertados, é essencial ter acesso fiável a peças e mão de obra especializada. As empresas devem ponderar as vantagens das peças OEM em relação às opções do mercado pós-venda para garantir que estão a tomar decisões rentáveis sem comprometer a qualidade.
Como é que a compreensão dos custos do alternador afecta a logística e a entrega?
Para as empresas de logística, o estado operacional dos camiões de entrega é vital para manter os horários e a satisfação dos clientes. Compreender os custos associados às reparações de alternadores ajuda estas empresas a gerir eficazmente os seus orçamentos de manutenção. Na Europa, onde os regulamentos podem ditar normas para os veículos, as empresas de logística têm de garantir a conformidade e, ao mesmo tempo, obter peças de qualidade que cumpram essas normas. Este conhecimento não só ajuda nas reparações imediatas, como também facilita o planeamento estratégico para a gestão da frota a longo prazo.
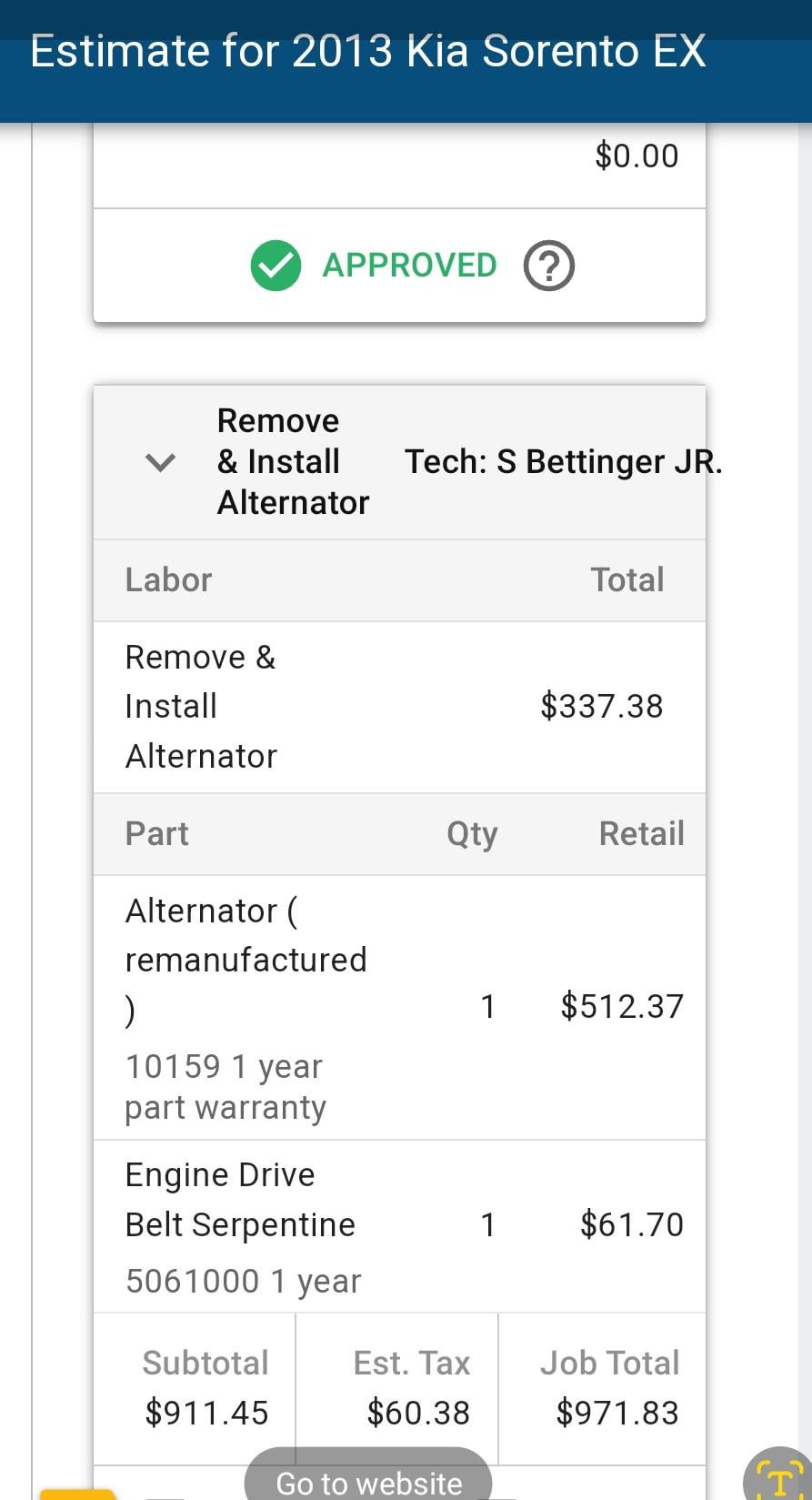
Imagem ilustrativa relacionada com quanto custa a reparação de um alternador
3 Pontos de dor comuns dos utilizadores para ‘quanto custa a reparação de um alternador’ e as suas soluções
Cenário 1: Confusão sobre a variabilidade dos custos em diferentes mercados
O problema: Os compradores B2B, especialmente os que se encontram em mercados internacionais como África ou América do Sul, enfrentam frequentemente uma grande confusão relativamente aos custos flutuantes associados às reparações e substituições de alternadores. Factores como as taxas de mão de obra locais, a disponibilidade de peças e até as flutuações da moeda podem levar a discrepâncias nos custos previstos. Esta incerteza pode complicar a orçamentação e a previsão financeira das empresas que dependem de uma frota de veículos, levando a potenciais interrupções nas operações.
A solução: Para lidar eficazmente com esta questão, os compradores B2B devem efetuar uma pesquisa de mercado exaustiva para compreender os custos médios das reparações de alternadores na sua região específica. O contacto com fornecedores locais de serviços automóveis pode fornecer informações sobre as taxas de mão de obra e a disponibilidade de peças. Além disso, o recurso à tecnologia através de plataformas online que agregam dados de preços pode ajudar a identificar preços competitivos. Os compradores devem também considerar o estabelecimento de parcerias com fornecedores fiáveis que ofereçam acordos de preços fixos, mitigando assim os riscos associados às flutuações de preços. A revisão e atualização regulares destes acordos garantem que as empresas se mantêm informadas sobre as tendências do mercado e podem ajustar os seus orçamentos em conformidade.
Cenário 2: Preocupações de qualidade com peças de reposição
O problema: Muitos compradores B2B são frequentemente apanhados num dilema quando se trata de adquirir alternadores. Embora as peças do mercado de substituição possam ser significativamente mais baratas, existe um receio prevalecente de comprometer a qualidade. As peças de qualidade inferior podem levar a reparações frequentes, a um aumento do tempo de inatividade e, em última análise, a custos mais elevados a longo prazo. Esta preocupação é exacerbada em mercados onde as garantias e as políticas de devolução podem não ser tão robustas, deixando os compradores em desvantagem.
A solução: Para resolver os problemas de qualidade, os compradores B2B devem concentrar-se no fornecimento de alternadores de fabricantes reputados que ofereçam garantias e certificações para os seus produtos. Realizar a devida diligência nos fornecedores, verificando as críticas, classificações da indústria e testemunhos, também pode ajudar a tomar decisões informadas. Os compradores podem optar por peças OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) sempre que possível, uma vez que estas garantem geralmente a compatibilidade e o desempenho. O estabelecimento de relações com fornecedores de confiança pode proporcionar acesso a programas de garantia de qualidade e descontos em compras em massa, ajudando as empresas a manter um equilíbrio entre custo e fiabilidade.
Cenário 3: Falta de compreensão dos prazos e custos das reparações
O problema: Um ponto problemático comum para os compradores B2B é a falta de clareza relativamente aos prazos e custos associados às reparações de alternadores. Muitas empresas não têm uma noção clara de quanto tempo demorará o processo de reparação e de como estes custos podem afetar a sua eficiência operacional. Esta incerteza pode levar a calendários mal geridos e a encargos financeiros inesperados, especialmente para as empresas que dependem fortemente do transporte.
A solução: Para mitigar estes desafios, os compradores B2B devem dar prioridade à manutenção proactiva e às inspecções regulares dos sistemas eléctricos dos seus veículos, incluindo o alternador. O desenvolvimento de um calendário de manutenção abrangente pode ajudar a identificar potenciais problemas antes que estes se transformem em reparações dispendiosas. Além disso, os compradores devem obter orçamentos detalhados dos prestadores de serviços que descrevam o âmbito do trabalho, as peças necessárias e os prazos estimados para a conclusão. Esta transparência ajudará a um melhor planeamento financeiro e à afetação de recursos. A contratação de fornecedores de serviços que ofereçam serviços de reparação móvel também pode minimizar o tempo de inatividade, permitindo que as empresas mantenham a eficiência operacional durante os períodos de reparação.
Guia de seleção de material estratégico para quanto custa a reparação de um alternador
Quais são os principais materiais para os custos de reparação do alternador?
Ao avaliar os custos associados à reparação de um alternador, os materiais utilizados na sua construção desempenham um papel fundamental na determinação do desempenho e do preço. Abaixo, analisamos vários materiais comuns que são parte integrante da funcionalidade do alternador, concentrando-nos nas suas propriedades, vantagens e desvantagens, e considerações para os compradores B2B internacionais.
Quais são as principais propriedades do cobre nos alternadores?
O cobre é muito utilizado nos alternadores devido à sua excelente condutividade eléctrica. Apresenta normalmente uma classificação de alta temperatura, tornando-o adequado para o calor gerado durante o funcionamento. Além disso, o cobre é resistente à corrosão, o que é essencial para a longevidade em vários ambientes.

Imagem ilustrativa relacionada com quanto custa a reparação de um alternador
Prós e contras: A elevada condutividade do cobre garante uma produção eficiente de energia, mas é relativamente cara em comparação com outros materiais. A complexidade de fabrico é moderada, uma vez que requer técnicas especializadas de enrolamento e ligação. No entanto, a sua adequação a aplicações de elevado desempenho torna-o uma escolha preferencial.
Impacto na aplicação: A compatibilidade do cobre com os sistemas eléctricos é fundamental, uma vez que afecta diretamente a eficiência do alternador. Em regiões como a África e a América do Sul, onde as infra-estruturas eléctricas podem ser menos estáveis, a fiabilidade do cobre pode melhorar significativamente o desempenho.
Considerações internacionais: Os compradores devem garantir a conformidade com as normas internacionais, como a ASTM B170, para o fio de cobre. Em regiões com elevada humidade ou ambientes corrosivos, como partes do Médio Oriente, a seleção de cobre com revestimentos protectores pode aumentar a durabilidade.
Como é que o alumínio se compara aos componentes do alternador?
O alumínio é frequentemente utilizado em caixas de alternadores e alguns componentes internos devido à sua natureza leve e condutividade decente. Tem uma boa classificação de temperatura, mas é menos condutor do que o cobre.
Prós e contras: A principal vantagem do alumínio é o seu baixo custo e peso, o que pode reduzir o peso total do veículo e melhorar a eficiência do combustível. No entanto, a sua menor condutividade pode levar a uma diminuição da eficiência na produção de energia em comparação com o cobre. A complexidade de fabrico é menor, o que facilita a moldagem e a modelação.
Impacto na aplicação: A natureza leve do alumínio pode ser benéfica em aplicações onde a poupança de peso é crítica. No entanto, a sua baixa condutividade pode não ser ideal para veículos de alto desempenho que exijam uma potência eléctrica máxima.
Considerações internacionais: Para os compradores internacionais, a conformidade com normas como a DIN 1725 para ligas de alumínio é crucial. Em regiões como a Europa, onde as normas para automóveis são rigorosas, garantir que os componentes de alumínio cumprem estas especificações pode evitar recolhas dispendiosas.

Imagem ilustrativa relacionada com quanto custa a reparação de um alternador
Qual é o papel do plástico na caixa do alternador?
Os materiais plásticos são frequentemente utilizados em caixas e isoladores de alternadores devido às suas propriedades de leveza e resistência à corrosão. Normalmente, têm uma classificação de temperatura moderada, adequada para a maioria das aplicações automóveis.
Prós e contras: A principal vantagem do plástico é o seu baixo custo e a facilidade de fabrico. No entanto, a sua durabilidade pode ser uma preocupação, especialmente sob calor elevado ou stress mecânico. Embora possa não ser adequado para componentes de suporte de carga, funciona bem para peças não estruturais.
Impacto na aplicação: O plástico pode ajudar a reduzir o peso total do alternador, o que é benéfico para a eficiência do combustível. No entanto, em condições extremas, como temperaturas elevadas ou exposição a produtos químicos, os componentes de plástico podem degradar-se mais rapidamente do que os componentes metálicos.
Considerações internacionais: Os compradores B2B devem estar cientes dos regulamentos relativos aos materiais plásticos, particularmente na Europa, onde a conformidade com o REACH pode afetar a seleção de materiais. Em regiões como o Brasil, onde as variações de temperatura podem ser significativas, a seleção de plásticos de alta qualidade pode melhorar o desempenho.
Qual a importância do aço na construção de alternadores?
O aço é frequentemente utilizado para os componentes estruturais dos alternadores, como as estruturas do rotor e do estator, devido à sua resistência e durabilidade. Tem uma classificação de alta temperatura e é resistente ao desgaste.

Imagem ilustrativa relacionada com quanto custa a reparação de um alternador
Prós e contras: A principal vantagem do aço é a sua resistência, que confere integridade estrutural ao alternador. No entanto, é mais pesado do que o alumínio ou o plástico, o que pode afetar negativamente o desempenho do veículo. A complexidade de fabrico é mais elevada devido à necessidade de maquinagem e soldadura.
Impacto na aplicação: A robustez do aço torna-o adequado para aplicações pesadas, particularmente em veículos comerciais. No entanto, o seu peso pode ser uma desvantagem em veículos orientados para o desempenho, onde cada quilograma conta.
Considerações internacionais: Os compradores devem certificar-se de que o aço utilizado está em conformidade com normas como ASTM A36 ou JIS G3101. Em regiões com elevada humidade, como as regiões do Médio Oriente, a escolha de um aço resistente à corrosão pode prolongar a vida útil do alternador.

Imagem ilustrativa relacionada com quanto custa a reparação de um alternador
Tabela de resumo dos materiais para os custos de reparação do alternador
| Material | Caso de utilização típico para quanto custa a reparação de um alternador | Vantagem principal | Principal desvantagem/limitação | Custo relativo (baixo/médio/alto) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cobre | Enrolamentos elétricos e ligações | Excelente condutividade | Custo elevado | Alto |
| Alumínio | Caixas e alguns componentes internos | Leve e económico | Condutividade inferior | Médio |
| Plástico | Componentes não-estruturais e isolamento | Baixo custo e fácil de fabricar | Preocupações com a durabilidade sob tensão | Baixo |
| Aço | Componentes estruturais como estruturas do rotor e do estator | Alta resistência e durabilidade | Mais pesado do que as alternativas | Médio |
Este guia estratégico de seleção de materiais fornece aos compradores B2B informações essenciais sobre os materiais utilizados na reparação de alternadores, permitindo decisões de compra informadas que se alinham com as normas regionais e as necessidades operacionais.
Análise aprofundada: Processos de fabrico e garantia de qualidade para quanto custa a reparação de um alternador
Quais são as principais fases do processo de fabrico dos alternadores?
O fabrico de um alternador envolve várias fases críticas que garantem que o produto final cumpre as normas de qualidade e desempenho. As principais fases incluem a preparação do material, a moldagem, a montagem e o acabamento.
Como é que o material é preparado para o fabrico de alternadores?
O processo de fabrico começa com a preparação do material, que envolve o fornecimento de matérias-primas de alta qualidade, como o cobre para os enrolamentos, o aço para a caixa e outras ligas para vários componentes. Os fornecedores devem assegurar que os materiais cumprem as normas específicas da indústria para garantir a durabilidade e o desempenho. Esta fase pode também incluir processos de pré-tratamento, como a limpeza e o revestimento, para aumentar a resistência à corrosão.
Que técnicas são utilizadas na formação de componentes?
Após a preparação do material, são utilizadas técnicas de moldagem para criar componentes individuais do alternador. Os métodos mais comuns incluem:
- Estampagem: Utilizado para peças metálicas, em que as folhas de metal são cortadas e moldadas com recurso a matrizes.
- Elenco: Esta técnica é frequentemente utilizada para a carcaça do alternador e consiste em verter metal fundido em moldes para obter a forma desejada.
- Maquinação: Os processos de maquinação de precisão, como o torneamento e a fresagem, são aplicados para obter tolerâncias apertadas em componentes críticos como o rotor e o estator.
Estas técnicas são vitais, pois têm um impacto direto na eficácia e na duração de vida do alternador.
Como é conduzido o processo de montagem?
A fase de montagem é a fase em que todos os componentes individuais se juntam para formar o alternador. Este processo envolve normalmente:
- Bobinagem do estator: Os fios de cobre são enrolados à volta de um núcleo para criar o campo magnético necessário à produção de eletricidade.
- Montagem do rotor: O rotor é colocado dentro do estator e os rolamentos são instalados para permitir uma rotação suave.
- Ligação de componentes eléctricos: Os díodos, os reguladores de tensão e outros componentes eléctricos estão integrados para garantir a funcionalidade adequada.
As verificações de controlo de qualidade são cruciais durante a montagem para verificar se todos os componentes se encaixam corretamente e funcionam como pretendido.
Que processos de acabamento são aplicados aos alternadores?
A fase de acabamento envolve vários tratamentos que melhoram o desempenho e a longevidade do alternador. Isto pode incluir:
- Tratamento de superfície: São aplicados revestimentos de proteção para evitar a corrosão e o desgaste.
- Testes: Cada alternador é submetido a testes rigorosos para garantir que cumpre as especificações de desempenho elétrico e mecânico.
Os processos de acabamento são essenciais para garantir que o alternador resista às diferentes condições de funcionamento.
Que práticas de garantia de qualidade são essenciais no fabrico de alternadores?
A garantia de qualidade (QA) é uma pedra angular do processo de fabrico, assegurando que os alternadores cumprem as normas internacionais e específicas da indústria.
Que normas internacionais devem os compradores B2B considerar?
As normas internacionais, como a ISO 9001, desempenham um papel crucial na garantia da existência de sistemas de gestão da qualidade. A conformidade com estas normas indica que o fabricante mantém uma qualidade consistente nos seus processos. Além disso, certificações como a CE (Conformité Européenne) e a API (American Petroleum Institute) são importantes para mercados específicos, especialmente para compradores na Europa e no Médio Oriente.

Imagem ilustrativa relacionada com quanto custa a reparação de um alternador
Quais são os principais pontos de verificação do controlo de qualidade?
Os pontos de controlo de qualidade (CQ) estão estrategicamente integrados em todo o processo de fabrico, incluindo:
- Controlo de Qualidade de Entrada (IQC): Inspecciona as matérias-primas à chegada para garantir que cumprem as especificações.
- Controlo de qualidade em processo (IPQC): Monitoriza o processo de produção para identificar defeitos numa fase inicial.
- Controlo de Qualidade Final (FQC): Efectua testes exaustivos ao produto acabado antes de este sair da fábrica.
Estes pontos de controlo ajudam a evitar que produtos defeituosos cheguem ao mercado, protegendo os compradores B2B de potenciais perdas.
Que métodos de ensaio são normalmente utilizados para os alternadores?
Os métodos de ensaio para alternadores incluem:
- Testes elétricos: Verifica a saída de tensão e a capacidade de corrente.
- Testes mecânicos: Avalia a durabilidade dos componentes sob tensão.
- Teste de desempenho: Simula condições de funcionamento para garantir que o alternador funciona como esperado.
Estes testes fornecem dados valiosos que podem ser utilizados para melhorar os processos de fabrico e garantir a fiabilidade do produto.
Como os compradores B2B podem verificar o controlo de qualidade dos fornecedores?
Para os compradores B2B internacionais, particularmente os de África, América do Sul, Médio Oriente e Europa, a verificação do controlo de qualidade do fornecedor é essencial para mitigar os riscos.
Que práticas de auditoria devem os compradores implementar?
Os compradores devem considerar a realização de auditorias aos fornecedores para avaliar a conformidade com as normas de qualidade. Isto pode envolver:

Imagem ilustrativa relacionada com quanto custa a reparação de um alternador
- Inspecções no local: Visita às instalações de fabrico para avaliar processos e práticas.
- Revisão da documentação de controlo de qualidade: Analisar relatórios relacionados com o IQC, IPQC e FQC para compreender o compromisso do fornecedor para com a qualidade.
Estas auditorias podem revelar potenciais problemas antes de efetuar encomendas significativas.
Qual a importância das inspecções por terceiros?
As inspecções por terceiros são outra forma eficaz de verificar o controlo de qualidade. A contratação de organizações independentes para realizar inspecções fornece uma avaliação imparcial das capacidades do fornecedor. Isto pode ser particularmente valioso para os compradores B2B que podem não ter os recursos para efetuar auditorias internas abrangentes.
Quais são as nuances do controlo de qualidade para os compradores internacionais?
Os compradores internacionais devem estar cientes das nuances do controlo de qualidade que podem variar consoante a região. Por exemplo, certas certificações podem ter mais peso em mercados específicos, afectando a qualidade percebida do produto. Além disso, é fundamental conhecer os regulamentos e normas locais para garantir a conformidade e facilitar a importação.
Ao concentrarem-se nestas práticas de garantia de qualidade e nos processos de fabrico, os compradores B2B podem tomar decisões informadas sobre o fornecimento de alternadores, garantindo que investem em produtos fiáveis que satisfazem as suas necessidades operacionais.
Guia prático de abastecimento: Uma lista de verificação passo-a-passo para ‘quanto custa reparar um alternador’
Introdução
Este guia serve como uma lista de verificação prática para compradores B2B que procuram compreender os custos associados à reparação ou substituição de um alternador. Dado o papel vital que os alternadores desempenham na funcionalidade do veículo, avaliar com exatidão os custos envolvidos é essencial para tomar decisões de aquisição informadas. Esta lista de controlo ajudará a simplificar o processo de aquisição e a garantir que recebe o melhor valor pelo seu investimento.
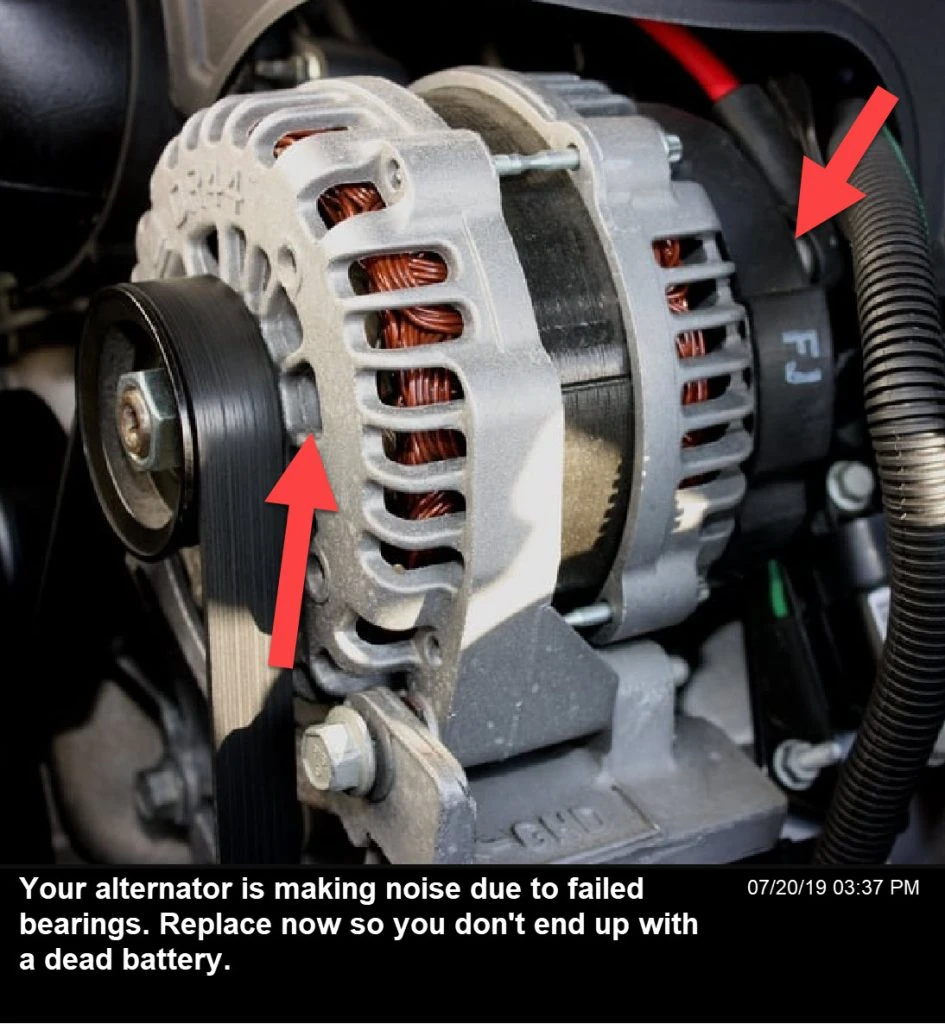
Imagem ilustrativa relacionada com quanto custa a reparação de um alternador
Passo 1: Defina as suas especificações técnicas
É fundamental estabelecer especificações técnicas claras para o alternador. Considere factores como o ano, a marca, o modelo e o tamanho do motor do veículo para garantir a compatibilidade. Isto ajudará a evitar erros dispendiosos e a garantir que o alternador satisfaz as necessidades eléctricas do veículo.
- Requisitos de amperagem: Identificar a amperagem necessária com base na carga eléctrica do veículo.
- Estilo de montagem: Verifique o estilo de montagem para garantir um ajuste perfeito.
Passo 2: Pesquisar preços de mercado
Efectue uma pesquisa de mercado exaustiva para compreender a gama de preços das substituições de alternadores. Os preços podem variar significativamente consoante o fornecedor, a qualidade das peças e a localização geográfica.
- Comparar fornecedores: Procure vários fornecedores, tanto a nível local como internacional, para avaliar a competitividade dos preços.
- Considerar a qualidade versus o custo: Equilibre o custo com a qualidade dos alternadores, uma vez que as opções mais baratas podem levar a despesas mais elevadas a longo prazo devido a problemas de fiabilidade.
Passo 3: Avalie potenciais fornecedores
Antes de efetuar uma compra, examine minuciosamente os potenciais fornecedores. Procure empresas estabelecidas com um historial comprovado na indústria de peças para automóveis.
- Solicitar documentação: Peça certificações, garantias e referências de clientes.
- Verificar comentários: As críticas e os testemunhos em linha podem fornecer informações sobre a fiabilidade e o serviço ao cliente do fornecedor.
Passo 4: Avaliar as políticas de garantia e devolução
Compreender a garantia e as políticas de devolução é essencial para a gestão de riscos. Uma garantia robusta pode proporcionar paz de espírito, especialmente se o alternador falhar pouco tempo depois da instalação.
- Duração da garantia: Procure garantias que cubram pelo menos um ano, com opções de cobertura alargada.
- Processo de devolução: Certifique-se de que o fornecedor dispõe de um processo de devolução simples em caso de defeito ou incompatibilidade.
Passo 5: Analisar os custos de instalação
Tenha em conta os custos de mão de obra associados à instalação do alternador, uma vez que isso pode afetar significativamente a despesa global.
- Taxas de trabalho: Pesquise as taxas de mão de obra locais e considere se vai utilizar técnicos internos ou subcontratar a instalação.
- Estimativas de tempo: Solicite estimativas sobre o tempo de instalação, pois isso influenciará os custos de mão de obra.
Passo 6: Planear reparações adicionais
Esteja preparado para potenciais reparações adicionais que possam surgir durante o processo de substituição do alternador.
- Componentes relacionados: Avaliar o estado dos componentes relacionados, como as correias e a cablagem, que também podem necessitar de atenção.
- Serviços de diagnóstico: Considere investir em serviços de diagnóstico para garantir que todo o sistema elétrico está a funcionar corretamente.
Passo 7: Finalizar a sua estratégia de aprovisionamento
Depois de ter reunido todas as informações necessárias, finalize a sua estratégia de aquisição estabelecendo um orçamento e selecionando o fornecedor mais adequado com base na sua pesquisa.
- Dotação orçamental: Certifique-se de que o seu orçamento tem em conta os custos do alternador e da instalação.
- Negociação com fornecedores: Esteja aberto à negociação de termos e preços com o fornecedor escolhido para maximizar o valor.
Seguindo esta lista de verificação, estará bem equipado para tomar decisões informadas sobre a aquisição de alternadores, garantindo a qualidade e a rentabilidade da sua estratégia de aprovisionamento.
Análise exaustiva de custos e preços para quanto custa a reparação de um alternador Sourcing
Quais são os principais componentes de custo na reparação de um alternador?
Ao avaliar os custos associados à reparação de um alternador, é essencial considerar vários componentes de custo que contribuem para a despesa global. Estes incluem:

Imagem ilustrativa relacionada com quanto custa a reparação de um alternador
-
Materiais: O custo do material principal deriva do próprio alternador, que pode variar em função de especificações como a amperagem e a compatibilidade com diferentes modelos de veículos. A gama de preços dos alternadores pode situar-se entre $100 e $1.000, consoante se opte por peças novas, remanufacturadas ou de substituição.
-
Trabalho: Os custos de mão de obra para a substituição de um alternador variam normalmente entre $120 e $200, dependendo da complexidade do trabalho e da região. Isto pode variar significativamente com base nas taxas de mão de obra locais e no facto de o serviço ser realizado por um concessionário ou por um mecânico independente.
-
Custos indiretos de produção: Inclui os custos indirectos associados à produção do alternador, incluindo as operações da fábrica, os serviços públicos e as despesas administrativas. Estes custos estão geralmente incluídos no preço do alternador.
-
Ferramentas e controlo de qualidade (QC): Podem ser necessárias ferramentas especializadas para a instalação ou reparação de um alternador. Além disso, as medidas de controlo de qualidade garantem que os alternadores cumprem as normas de desempenho e segurança, o que pode aumentar ligeiramente os custos.
-
Logística: O transporte e o manuseamento das peças podem afetar os preços, especialmente para os compradores internacionais. Os custos podem variar consoante os métodos de envio, as distâncias e as tarifas regionais.
-
Margem: Os fornecedores incluem normalmente uma margem de lucro nos seus preços, que pode ser influenciada pela concorrência, procura e factores da cadeia de fornecimento.
O que influencia o preço das reparações de alternadores?
O preço das reparações de alternadores pode ser influenciado por vários factores:
-
Volume e quantidade mínima de encomenda (MOQ): Os compradores B2B podem beneficiar das compras por grosso. Os volumes de encomendas mais elevados podem dar origem a descontos, reduzindo significativamente o custo por unidade.
-
Especificações e personalização: Os alternadores personalizados concebidos para modelos de veículos específicos podem implicar custos adicionais. Assegurar-se de que as especificações correspondem aos requisitos do veículo para evitar problemas de compatibilidade.
-
Qualidade dos materiais e certificações: Optar por peças OEM (Fabricante de Equipamento Original) tem normalmente um preço mais elevado. No entanto, as peças pós-venda de alta qualidade com certificações podem oferecer um equilíbrio entre custo e fiabilidade.
-
Fatores relacionados ao fornecedor: A escolha do fornecedor desempenha um papel crucial. Os fornecedores estabelecidos com uma boa reputação podem cobrar mais, mas muitas vezes oferecem uma melhor garantia de qualidade e serviço ao cliente.
-
Incoterms: A compreensão das condições de envio é vital para as transacções internacionais. Termos como FOB (Free on Board) ou CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) podem afetar o custo total dos alternadores.
Quais são as melhores dicas para os compradores que procuram eficiência de custos?
Para os compradores B2B, particularmente em regiões como África, América do Sul, Médio Oriente e Europa, várias estratégias podem melhorar a eficiência dos custos:
-
Negociar termos: Iniciar sempre negociações com os fornecedores. Aproveitar os compromissos de volume para garantir melhores preços ou condições de pagamento favoráveis.
-
Avalie o custo total de propriedade (TCO): Considere não apenas o preço de compra inicial, mas também a longevidade e a garantia do alternador. Um custo inicial ligeiramente mais elevado pode levar a poupanças a longo prazo devido a menos substituições.
-
Esteja ciente das nuances dos preços: Os compradores internacionais devem ter em atenção as flutuações cambiais, os impostos locais e os direitos de importação, que podem afetar significativamente o custo global.
-
Pesquisar e comparar fornecedores: Reserve algum tempo para avaliar vários fornecedores. Procure aqueles que oferecem garantias abrangentes, apoio ao cliente e qualidade consistente.
-
Planear futuras reparações: Compreender o tempo de vida útil dos alternadores (normalmente 40.000 a 100.000 milhas) pode ajudar a orçamentar futuras reparações ou substituições, permitindo um melhor planeamento financeiro.
Isenção de responsabilidade
Os preços mencionados nesta análise são indicativos e podem variar em função de múltiplos factores, incluindo a localização, o fornecedor e as condições de mercado. Consulte sempre os profissionais locais para obter as informações mais exactas e actualizadas sobre os preços.
Análise de alternativas: Comparação do custo da reparação de um alternador com outras soluções
Explorando alternativas para consertar um alternador
Na indústria automóvel, manter o desempenho do veículo é fundamental para a eficiência operacional. Quando um alternador avaria, as empresas devem pesar o custo e as implicações da reparação em relação a soluções alternativas que possam satisfazer as suas necessidades. Aqui, comparamos os custos e a eficácia da reparação de um alternador com duas alternativas viáveis: a substituição da bateria do veículo e a utilização de uma fonte de alimentação externa.
| Aspecto comparativo | Quanto custa a reparação de um alternador | Substituição da bateria do veículo | Utilizar uma fonte de alimentação externa |
|---|---|---|---|
| Desempenho | Restabelece o pleno funcionamento do sistema elétrico; dura normalmente 7 a 10 anos. | Melhora o arranque e o desempenho elétrico, mas não resolve os problemas do alternador. | Fornece energia imediata; não é uma solução a longo prazo. |
| Custo | Normalmente, varia entre $100 e $1.000. | Geralmente custa entre $50 e $200. | Varia muito; os geradores portáteis podem custar mais de $200, mas podem necessitar de combustível. |
| Facilidade de implementação | Requer instalação profissional; normalmente demora 2-3 horas. | Pode muitas vezes ser um projeto de bricolage; a instalação é simples. | Requer configuração e pode necessitar de uma operação especializada. |
| Manutenção | Mínimo; uma vez substituído, deve durar vários anos. | São necessárias verificações regulares; as baterias duram normalmente 3-5 anos. | Requer combustível e manutenção; os custos correntes podem acumular-se. |
| Melhor caso de uso | Ideal para a fiabilidade e o desempenho do veículo a longo prazo. | O melhor para problemas imediatos da bateria, sem ter em conta as falhas do alternador. | Adequado para necessidades temporárias de energia, como assistência na estrada. |
Análise aprofundada das alternativas
Substituição da bateria do veículo
A substituição da bateria de um veículo pode aliviar temporariamente os sintomas associados a uma falha do alternador, como a dificuldade em arrancar com o veículo ou o escurecimento das luzes. Esta solução é económica, com preços que geralmente variam entre $50 e $200, o que a torna uma opção atractiva para as empresas que procuram minimizar as despesas. No entanto, não resolve a questão subjacente se o alternador for a causa principal do problema. Além disso, embora a substituição da bateria seja muitas vezes um processo simples que pode ser efectuado internamente, é normalmente uma solução a curto prazo e pode levar a mais complicações se o alternador não for resolvido.
Utilizar uma fonte de alimentação externa
A utilização de uma fonte de energia externa, como um gerador portátil ou um conjunto de baterias, pode fornecer energia imediata a um veículo ou equipamento em caso de falha do alternador. Este método pode ser benéfico para empresas que necessitam de energia em movimento, especialmente em locais remotos. No entanto, o investimento inicial pode ser significativo, muitas vezes superior a $200 para geradores de qualidade, e os custos contínuos de combustível podem aumentar ainda mais as despesas. Além disso, esta solução não substitui um alternador em funcionamento e serve apenas como medida temporária, levando potencialmente a um aumento do tempo de inatividade e da ineficiência operacional.
Fazer a escolha certa para a sua empresa
Ao considerar como resolver os problemas do alternador, os compradores B2B devem avaliar as suas necessidades específicas e contextos operacionais. Para as empresas que se concentram na fiabilidade do veículo a longo prazo, a reparação ou substituição do alternador é frequentemente a escolha mais prudente, apesar do custo inicial mais elevado. Por outro lado, se as restrições orçamentais imediatas forem fundamentais e o veículo puder funcionar temporariamente, a substituição da bateria ou a utilização de uma fonte de energia externa pode ser suficiente. Em última análise, a decisão deve estar alinhada com as prioridades operacionais da organização, as restrições orçamentais e a longevidade esperada do veículo em questão.
Propriedades técnicas essenciais e terminologia comercial para quanto custa a reparação de um alternador
Quais são as principais propriedades técnicas a ter em conta na reparação de um alternador?
Ao avaliar o custo de reparação ou substituição de um alternador, várias propriedades técnicas são fundamentais para os compradores B2B compreenderem. Estas propriedades não só afectam o preço, como também têm impacto no desempenho e na longevidade do alternador em várias aplicações de veículos.
-
Classificação de amperagem
- A classificação da amperagem indica a quantidade de corrente eléctrica que o alternador pode produzir. Os alternadores de amperagem mais elevada são frequentemente necessários para veículos com sistemas eléctricos extensos, como os que possuem sistemas avançados de info-entretenimento ou iluminação adicional. Compreender as necessidades específicas de amperagem de um veículo ajuda os compradores a selecionar o alternador certo, garantindo um desempenho ótimo e evitando falhas eléctricas. -
Estilo de montagem
- Diferentes veículos têm requisitos de montagem distintos para alternadores, que podem incluir variações no design e orientação dos suportes. É fundamental que os compradores B2B identifiquem o estilo de montagem correto para evitar problemas de compatibilidade. Um ajuste incorreto pode levar a desafios de instalação e custos adicionais, tornando esta especificação vital nas decisões de aquisição. -
Composição do material
- Os materiais utilizados na construção de um alternador, como o cobre para os enrolamentos e o alumínio para a caixa, afectam significativamente a durabilidade e a eficiência. Materiais de qualidade superior podem levar a um melhor desempenho e a uma vida útil mais longa, o que pode traduzir-se em custos totais mais baixos ao longo do tempo. Os compradores devem considerar o compromisso entre o preço de compra inicial e o valor a longo prazo quando avaliam a qualidade do material. -
Período de garantia
- O período de garantia oferecido pelos fabricantes pode servir como um indicador da fiabilidade do produto e da confiança do fabricante. Os alternadores com garantias alargadas reflectem frequentemente uma maior qualidade e durabilidade. Os compradores B2B devem ponderar o custo de um produto em relação aos seus termos de garantia, uma vez que uma garantia mais longa pode reduzir as despesas futuras relacionadas com reparações ou substituições. -
Tipo de ligações eléctricas
- Os alternadores podem ter diferentes tipos de ligações eléctricas, tais como configurações de 1 ou 3 fios. A complexidade das ligações eléctricas pode influenciar o processo de instalação e o custo global. A compreensão destas especificações garante que os compradores selecionam um alternador que se alinha com o sistema elétrico do seu veículo, minimizando as complicações durante a instalação.
Quais são os termos comerciais comuns relacionados com os custos do alternador?
Navegar no mundo da aquisição de peças para automóveis requer familiaridade com termos comerciais específicos que podem influenciar as decisões de compra. Aqui estão alguns termos essenciais que os compradores B2B devem conhecer:
-
OEM (Fabricante de Equipamento Original)
- As peças OEM são fabricadas pelo mesmo fabricante que produziu os componentes originais do veículo. Embora sejam normalmente mais caras, as peças OEM são muitas vezes vistas como um investimento mais seguro devido à sua compatibilidade e qualidade garantidas. -
MOQ (Quantidade mínima de encomenda)
- O MOQ refere-se à quantidade mais pequena de um produto que um fornecedor está disposto a vender. Compreender o MOQ é crucial para que os compradores B2B possam gerir eficazmente os custos de inventário e garantir que estão a comprar unidades suficientes para satisfazer a procura sem comprometer demasiado os recursos. -
RFQ (Pedido de Orçamento)
- Uma solicitação de cotação é um processo comercial padrão no qual um comprador solicita informações sobre preços aos fornecedores. Este processo ajuda as empresas a comparar custos e a tomar decisões de compra informadas. Os compradores B2B devem utilizar RFQs para negociar melhores condições e garantir preços competitivos. -
Incoterms (Termos Comerciais Internacionais)
- Os Incoterms são um conjunto de regras internacionais que definem as responsabilidades dos compradores e vendedores relativamente à entrega de mercadorias. A familiaridade com estes termos ajuda os compradores B2B a compreender as responsabilidades de envio, a atribuição de custos e a gestão de riscos nas transacções internacionais. -
Peças de reposição
- As peças de substituição são fabricadas por outras empresas que não o fabricante original. Embora possam oferecer poupanças de custos, os compradores devem ter cuidado para garantir que a qualidade e a compatibilidade destas peças cumprem as suas normas operacionais. -
Carga de base
- Uma taxa de núcleo é uma taxa adicionada ao preço de compra de um novo alternador, que é reembolsada quando o alternador antigo (o “núcleo”) é devolvido. Compreender os encargos do núcleo pode ajudar os compradores B2B a gerir os custos globais e a tomar decisões informadas sobre a substituição de peças.
Ao compreenderem estas propriedades técnicas e terminologias comerciais, os compradores B2B podem tomar decisões mais informadas relativamente a reparações e substituições de alternadores, conduzindo, em última análise, a melhores resultados de aquisição e gestão de custos.
Navegar na dinâmica do mercado e nas tendências de aprovisionamento no sector de quanto custa a reparação de um alternador
Quais são as principais dinâmicas de mercado que afectam os custos de reparação do alternador?
O mercado global de reparações e substituições de alternadores é influenciado por vários factores que os compradores B2B internacionais têm de compreender. Em primeiro lugar, a crescente complexidade dos sistemas eléctricos dos veículos devido aos avanços tecnológicos aumentou a procura de alternadores de alta qualidade. Os veículos modernos estão equipados com numerosos componentes electrónicos, o que faz do alternador um componente crítico para um desempenho consistente. Esta tendência é particularmente evidente em regiões como a Europa, onde os veículos eléctricos e híbridos estão a ganhar força, levando a um aumento da procura de alternadores especializados.
Além disso, os factores económicos regionais desempenham um papel significativo no preço das reparações de alternadores. Nos mercados emergentes, como o Brasil e a Arábia Saudita, a flutuação dos valores da moeda e a variação das tarifas de importação podem afetar o custo das peças importadas, o que pode levar à volatilidade dos preços. Para além disso, as perturbações na cadeia de fornecimento - exacerbadas por eventos globais - levaram os compradores a procurar fornecedores locais para mitigar os riscos e reduzir os prazos de entrega. Esta mudança para o fornecimento local está a tornar-se cada vez mais comum entre os compradores B2B que procuram soluções rentáveis sem comprometer a qualidade.
As tecnologias emergentes, como as plataformas em linha para o fornecimento de peças, também estão a remodelar o mercado. Estas plataformas permitem aos compradores comparar rapidamente preços e especificações, possibilitando decisões de compra informadas. Consequentemente, as empresas estão a tornar-se mais estratégicas em relação aos seus processos de aprovisionamento, privilegiando a qualidade e a fiabilidade em detrimento da mera redução de custos.
Como é que a sustentabilidade está a moldar o sector da reparação de alternadores?
A sustentabilidade e o fornecimento ético estão a tornar-se considerações críticas na indústria de reparação de alternadores. Com o aumento da consciencialização global para as questões ambientais, os compradores B2B estão a dar cada vez mais prioridade aos fornecedores que aderem a práticas sustentáveis. O fabrico de alternadores envolve normalmente materiais como o cobre e o alumínio, que têm impactos ambientais substanciais quando são extraídos e processados. Por conseguinte, os fornecedores que utilizam materiais reciclados ou processos de fabrico sustentáveis estão a ganhar terreno entre os compradores conscienciosos.
Além disso, a procura de certificações ‘verdes’ está a aumentar. Os fornecedores que podem fornecer provas de práticas de abastecimento sustentáveis ou certificações são susceptíveis de atrair mais negócios. Esta tendência não só reflecte um compromisso com a responsabilidade ambiental, como também se alinha com os valores dos consumidores e das empresas que dão prioridade à sustentabilidade nas suas operações.
O conceito de economia circular também é relevante. Os alternadores remanufacturados podem ser uma alternativa económica e ecológica às unidades novas. Ao escolher peças remanufacturadas, os compradores podem reduzir o desperdício e contribuir para uma cadeia de fornecimento mais sustentável. Esta mudança não só apoia os objectivos ambientais, como também pode levar a poupanças de custos significativas, tornando-a vantajosa para os compradores B2B em diversos mercados.
Qual é o contexto histórico do desenvolvimento do alternador?
O alternador evoluiu significativamente desde a sua introdução no início do século XX. Inicialmente, os veículos utilizavam geradores para produzir eletricidade, que eram menos eficientes e frequentemente exigiam mais manutenção. A transição para os alternadores nos anos 60 marcou um momento crucial, uma vez que estes dispositivos proporcionaram maior eficiência e fiabilidade, permitindo a alimentação de sistemas eléctricos cada vez mais sofisticados nos veículos.
Ao longo das décadas, os avanços nos materiais e nos processos de fabrico conduziram ao desenvolvimento de alternadores mais compactos e potentes. Os alternadores actuais não só cumprem a função básica de carregar a bateria, como também gerem a carga eléctrica de uma vasta gama de componentes, desde sistemas de informação e entretenimento a sistemas avançados de assistência ao condutor (ADAS). Esta evolução fez com que o alternador se tornasse parte integrante do desempenho e da fiabilidade do veículo, sublinhando a sua importância nas discussões sobre manutenção e reparação para os compradores B2B internacionais.
À medida que o panorama automóvel continua a mudar, compreender o contexto histórico dos alternadores pode ajudar os compradores a tomar decisões informadas sobre o abastecimento, os preços e a adoção de tecnologia.

Imagem ilustrativa relacionada com quanto custa a reparação de um alternador
Perguntas frequentes (FAQs) para compradores B2B de quanto custa a reparação de um alternador
-
Como posso determinar o custo de reparação de um alternador?
Para avaliar o custo da reparação de um alternador, considere factores como a marca e o modelo do veículo, o tipo de alternador necessário (novo ou remanufacturado) e os custos de mão de obra na sua região. Os custos médios variam normalmente entre $100 e $1.000, incluindo peças e mão de obra. Para os compradores B2B, é crucial obter cotações de vários fornecedores, tendo em conta o transporte e quaisquer tarifas potenciais, especialmente quando se trata de mercados internacionais. -
Quais são os principais factores que influenciam o preço da substituição de um alternador?
Vários factores influenciam o preço da substituição de um alternador, incluindo o ano, a marca e o modelo do veículo, bem como a amperagem do alternador e o estilo de montagem. A garantia oferecida no alternador também afecta o custo; uma garantia mais longa significa geralmente um preço inicial mais elevado. Além disso, as condições do mercado local e as estratégias de preços dos fornecedores podem levar a variações de custos em diferentes regiões, especialmente em África, na América do Sul e no Médio Oriente. -
Qual é o melhor tipo de alternador para o meu veículo?
O melhor tipo de alternador para o seu veículo depende das suas necessidades eléctricas específicas e da compatibilidade. As peças do Fabricante de Equipamento Original (OEM) são frequentemente recomendadas pela sua fiabilidade, mas as opções do mercado pós-venda de alta qualidade também podem proporcionar poupanças significativas. Considere factores como a amperagem do alternador, a garantia e a reputação do fornecedor. A pesquisa e a comparação de especificações garantirão a escolha do alternador mais adequado para um desempenho ótimo. -
Como é que posso verificar os fornecedores de peças para alternadores?
Ao examinar os fornecedores de peças para alternadores, avalie a sua reputação, as opiniões dos clientes e a experiência no sector. Verifique as suas certificações e processos de controlo de qualidade para garantir a conformidade com as normas internacionais. Solicite amostras ou referências de clientes anteriores para avaliar a qualidade e fiabilidade do produto. Além disso, considere as suas capacidades logísticas, incluindo tempos e custos de envio, especialmente para transacções internacionais. -
Quais são as quantidades mínimas de encomenda (MOQs) para peças de alternadores?
As quantidades mínimas de encomenda (MOQs) para peças de alternadores variam consoante o fornecedor e dependem das suas capacidades de produção e níveis de inventário. Normalmente, os fabricantes maiores podem ter MOQs mais elevados, enquanto os fornecedores mais pequenos ou especializados podem oferecer termos mais flexíveis. É essencial negociar MOQs que se alinham com as suas necessidades de compra e estratégias de gestão de inventário, especialmente quando se abastece em diferentes regiões como África ou América do Sul. -
Que condições de pagamento devo esperar quando forneço alternadores a nível internacional?
As condições de pagamento podem variar significativamente consoante o fornecedor e a região. As condições mais comuns incluem pagamentos adiantados, cartas de crédito ou pagamento aquando da entrega. É aconselhável estabelecer termos claros que protejam os seus interesses, tais como pagamentos parciais aquando da confirmação da encomenda e o restante aquando da entrega. Além disso, considere factores como taxas de câmbio e taxas de transação ao planear o seu orçamento para compras internacionais. -
Como posso assegurar a garantia de qualidade das peças do alternador?
Para assegurar a garantia de qualidade das peças do alternador, solicite documentação dos processos de controlo de qualidade do fornecedor, incluindo certificações como a ISO 9001. Realize inspecções periódicas das expedições e estabeleça referências de qualidade que se alinhem com as suas normas operacionais. Além disso, considere a possibilidade de trabalhar com fornecedores que ofereçam garantias sobre os seus produtos, proporcionando-lhe um recurso caso surjam problemas após a compra. -
Que considerações logísticas devo ter em conta aquando da importação de alternadores?
Ao importar alternadores, considere aspectos logísticos como métodos de envio, desalfandegamento e potenciais tarifas. Avalie a fiabilidade do transitário que escolheu e certifique-se de que este tem experiência com peças automóveis. Além disso, tenha em conta os prazos de entrega e o impacto dos regulamentos regionais nos processos de importação. Ser proactivo nestas áreas minimizará os atrasos e garantirá que as suas peças de alternador chegam dentro do prazo e em boas condições.
Lista dos 4 principais fabricantes e fornecedores de Quanto custa a reparação de um alternador
1. Toyota - RAV4 Substituição do Alternador
Domínio: reddit.com
Registado: 2005 (20 anos)
Introdução: Substituição do alternador do Toyota RAV4 2006, custo total de $450 incluindo mão de obra.
2. Facebook - Acessórios para veículos
Domínio: facebook.com
Registado: 1997 (28 anos)
Introdução: Esta empresa, Facebook - Acessórios para veículos, é uma entidade notável no mercado. Para obter informações específicas sobre os produtos, recomenda-se a visita direta ao seu sítio Web.
3. Car Talk - Custos de substituição do alternador
Domínio: cartalk.com
Registrado: 1995 (30 anos)
Introdução: O custo de substituição de um alternador varia entre $600 e $1.500. Um alternador é um componente crítico que converte a força mecânica em energia eléctrica, alimentando o motor, as luzes e carregando a bateria. Os sintomas de uma avaria do alternador incluem uma luz de verificação do motor, faróis a escurecer e a necessidade de arranques rápidos. Os alternadores podem falhar devido a desgaste mecânico ou falha de componentes eléctricos. ...
4. J.D. Power - Custos de substituição do alternador
Domínio: jdpower.com
Registrado: 1995 (30 anos)
Introdução: Os custos de substituição do alternador variam entre $100 e $700, dependendo do modelo do veículo, com custos médios entre $350 e $400 para a substituição. Os modelos de luxo podem exigir custos mais elevados. Se a correia serpentina precisar de ser substituída, acrescente $20 a $50. Os custos totais para a substituição do alternador podem variar entre $350 e $900. Os alternadores reconstruídos estão disponíveis e devem corresponder ou exceder a capacidade de amperagem do original....
Conclusão e perspectivas do aprovisionamento estratégico para quanto custa a reparação de um alternador
Em conclusão, compreender os custos associados à reparação de um alternador é vital para os compradores B2B internacionais que navegam no panorama da reparação automóvel. O custo de substituição pode variar entre $100 e $1.000, influenciado por factores como a marca do veículo, o modelo e as especificações específicas do alternador. Esta variabilidade sublinha a importância do aprovisionamento estratégico, permitindo às empresas assegurar peças de qualidade a preços competitivos, garantindo simultaneamente a compatibilidade e a fiabilidade.
Investir em componentes de qualidade, quer sejam novos ou remanufacturados, pode trazer benefícios a longo prazo, incluindo a redução do tempo de inatividade e um melhor desempenho do veículo. Além disso, à medida que o mercado automóvel global evolui, será crucial manter-se informado sobre os fornecedores e as tendências de preços em regiões como África, América do Sul, Médio Oriente e Europa.
Ao olhar para o futuro, considere estabelecer parcerias com fornecedores de renome que possam fornecer não só soluções rentáveis, mas também conhecimentos sobre tecnologias emergentes e melhores práticas na manutenção de alternadores. Ao dar prioridade ao aprovisionamento estratégico, pode posicionar a sua empresa para o sucesso num mercado cada vez mais competitivo. Contacte hoje mesmo os seus fornecedores para garantir que está preparado para as necessidades e desafios futuros da reparação automóvel.
Aviso legal importante e termos de utilização
⚠️ Aviso importante
As informações fornecidas neste guia, incluindo conteúdo sobre fabricantes, especificações técnicas e análises de mercado, têm fins meramente informativos e educativos. Não constituem aconselhamento profissional sobre aquisições, aconselhamento financeiro ou aconselhamento jurídico.
Embora tenhamos envidado todos os esforços para garantir a precisão e atualidade das informações, não nos responsabilizamos por quaisquer erros, omissões ou informações desatualizadas. As condições de mercado, os detalhes da empresa e os padrões técnicos estão sujeitos a alterações.
Os compradores B2B devem realizar a sua própria diligência prévia independente e minuciosa. antes de tomar qualquer decisão de compra. Isso inclui entrar em contacto diretamente com os fornecedores, verificar certificações, solicitar amostras e procurar aconselhamento profissional. O risco de confiar em qualquer informação contida neste guia é assumido exclusivamente pelo leitor.