Introdução: Navegar no mercado global para saber como testar o solenoide com um multímetro
No mercado global atual, compreender como testar um solenoide com um multímetro é uma competência essencial para os compradores B2B, especialmente para os que adquirem componentes para máquinas complexas em sectores que vão desde o automóvel à automação industrial. Os solenóides desempenham um papel vital em várias aplicações, mas a sua eficiência e fiabilidade podem ser comprometidas sem um teste adequado. Este guia oferece uma visão geral abrangente das técnicas de teste de solenóides, incluindo a utilização de um multímetro para avaliar a resistência eléctrica, a continuidade e a funcionalidade geral.
Para os compradores internacionais em regiões como África, América do Sul, Médio Oriente e Europa, a capacidade de avaliar o desempenho dos solenóides não só assegura a eficiência operacional como também reduz os riscos associados à falha do equipamento. Ao delinear métodos de teste essenciais, processos de verificação de fornecedores e considerações de custo, este guia equipa os decisores com o conhecimento necessário para tomar decisões de compra informadas.
Compreender as nuances dos testes de solenóides permite às empresas melhorar as suas estratégias de aquisição, garantindo que selecionam componentes de alta qualidade que satisfazem as suas exigências operacionais específicas. Com conhecimentos práticos adaptados aos desafios únicos enfrentados pelos compradores globais, este guia serve como um recurso vital para otimizar o desempenho dos solenóides e, em última análise, o sucesso operacional.
Índice
- Lista dos 2 principais fabricantes e fornecedores de Como testar o solenoide com multímetro
- Introdução: Navegar no mercado global para saber como testar o solenoide com um multímetro
- Compreender como testar o solenoide com um multímetro Tipos e variações
- Principais aplicações industriais de como testar o solenoide com um multímetro
- 3 Pontos de dor comuns do utilizador para ‘como testar o solenoide com um multímetro’ e as suas soluções
- Guia de Seleção de Material Estratégico para saber como testar o solenoide com um multímetro
- Análise aprofundada: Processos de fabrico e garantia de qualidade para saber como testar o solenoide com um multímetro
- Guia prático de abastecimento: Uma lista de verificação passo-a-passo para ‘como testar o solenoide com um multímetro’
- Análise abrangente de custos e preços para como testar solenoide com multímetro Sourcing
- Análise de alternativas: Comparação de como testar o solenoide com multímetro com outras soluções
- Propriedades técnicas essenciais e terminologia comercial para saber como testar o solenoide com um multímetro
- Como navegar na dinâmica do mercado e nas tendências de aprovisionamento no sector do teste de solenoide com multímetro
- Perguntas frequentes (FAQs) para compradores B2B de como testar o solenoide com um multímetro
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for how to test solenoid with multimeter
- Aviso legal importante e termos de utilização
Compreender como testar o solenoide com um multímetro Tipos e variações
| Nome do tipo | Principais características distintivas | Aplicações B2B primárias | Breves prós e contras para compradores |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ensaios de resistência | Mede a resistência da bobina para determinar a funcionalidade | Automóvel, máquinas industriais | Prós: Configuração simples; eficaz para o diagnóstico de avarias. Contras: Requer conhecimento dos valores de resistência aceitáveis. |
| Teste de continuidade | Verifica se o circuito elétrico está completo | Sistemas eléctricos, painéis de controlo | Prós: Rápido e direto; confirma a integridade operacional. Contras: Pode não identificar falhas intermitentes. |
| Teste de tensão | Mede a tensão entre os terminais do solenoide | Sistemas HVAC, robótica | Prós: Fornece informações sobre problemas de alimentação eléctrica. Contras: Requer acesso a circuitos sob tensão; riscos de segurança envolvidos. |
| Testes em bancada | Envolve a alimentação externa do solenoide | Fabrico, prototipagem | Prós: Avaliação exaustiva do desempenho mecânico e elétrico. Contras: Requer equipamento adicional e tempo de preparação. |
| Teste de carga | Avalia o desempenho em condições operacionais | Máquinas pesadas, aplicações automóveis | Prós: Avaliação do desempenho no mundo real; identifica potenciais falhas operacionais. Contras: Mais complexo; pode necessitar de equipamento especializado. |
O que é o teste de resistência e a sua adequação para compradores B2B?
O ensaio de resistência é um método fundamental para avaliar a funcionalidade dos solenóides através da medição da resistência eléctrica da bobina. Este tipo de ensaio é particularmente adequado para indústrias como a automóvel e a maquinaria industrial, onde os solenóides desempenham um papel fundamental em sistemas como os motores de arranque e os actuadores. Os compradores devem ter em conta os valores de resistência especificados para o solenoide, uma vez que os desvios podem indicar falhas. Este método é simples e requer um equipamento mínimo, o que o torna uma escolha económica para a manutenção de rotina.
Como é que os testes de continuidade beneficiam as aplicações B2B?
O teste de continuidade assegura que um circuito elétrico está completo, confirmando a integridade operacional do solenoide. Este método é amplamente aplicável em sistemas eléctricos e painéis de controlo em várias indústrias. É particularmente vantajoso para os compradores B2B que procuram um diagnóstico rápido. Embora seja fácil de efetuar, os compradores devem estar cientes de que o teste de continuidade pode não revelar problemas intermitentes, o que pode levar a futuros problemas operacionais.
Porque é que o teste de tensão é importante para os solenóides?
O teste de tensão envolve a medição da tensão nos terminais do solenoide para avaliar se este está a receber a fonte de alimentação correta. Este método é crucial nos sistemas HVAC e na robótica, onde os solenóides são parte integrante da funcionalidade. Para os compradores B2B, o teste de tensão pode ajudar a identificar rapidamente problemas de alimentação eléctrica. No entanto, requer o acesso a circuitos eléctricos, o que exige precauções de segurança e pode complicar o processo de teste.
Quais são as vantagens de testar solenóides em banco de ensaio?
O teste em banco de ensaio permite uma avaliação completa do desempenho elétrico e mecânico de um solenoide, alimentando-o externamente. Este método é especialmente relevante em ambientes de fabrico e prototipagem, onde os solenóides têm de ser verificados antes da integração nos sistemas. Embora forneça uma avaliação abrangente, os compradores devem ter em atenção que o ensaio em bancada requer equipamento adicional e tempo de configuração, o que pode afetar a eficiência operacional.
Como é que o teste de carga melhora a avaliação do desempenho do solenoide?
O teste de carga avalia o desempenho de um solenoide em condições operacionais reais, tornando-o inestimável em maquinaria pesada e aplicações automóveis. Ao simular as exigências do mundo real, este método de ensaio ajuda a identificar potenciais falhas antes de estas ocorrerem. Para os compradores B2B, o teste de carga oferece uma avaliação detalhada do desempenho, embora seja mais complexo e possa necessitar de equipamento especializado, tornando-o menos acessível para verificações de rotina.
Principais aplicações industriais de como testar o solenoide com um multímetro
| Indústria/Setor | Aplicação específica de como testar o solenoide com um multímetro | Valor/benefício para a empresa | Considerações importantes sobre o fornecimento para esta aplicação |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotivo | Ensaio de solenóides em motores de arranque e injectores de combustível | Assegura um desempenho fiável do veículo e reduz as avarias | Qualidade dos multímetros, disponibilidade de apoio técnico e serviços de calibração |
| Fabricação | Ensaio de solenóides em máquinas automatizadas e linhas de montagem | Aumenta a eficiência operacional e minimiza o tempo de inatividade | Compatibilidade com o equipamento existente, custo de manutenção e fiabilidade do fornecedor |
| Sistemas HVAC | Ensaio de solenóides em válvulas e actuadores para controlo da temperatura | Aumenta a fiabilidade do sistema e a eficiência energética | Especificações para as classificações de tensão, resistência ambiental e serviço pós-venda |
| Equipamento agrícola | Ensaio de solenóides em sistemas e máquinas de irrigação | Assegura um rendimento ótimo das culturas e a gestão dos recursos | Conformidade com a regulamentação local, abastecimento de fabricantes de confiança e eficácia de custos |
| Petróleo e gás | Ensaio de solenóides em sistemas de perfuração e de controlo | Aumenta a segurança e a eficiência operacional em ambientes perigosos | Cumprimento das normas da indústria, certificações de fornecedores e durabilidade em condições extremas |
Como é que ‘como testar o solenoide com um multímetro’ é utilizado no sector automóvel?
Na indústria automóvel, testar solenóides com um multímetro é fundamental para diagnosticar problemas relacionados com motores de arranque e injectores de combustível. Ao medir a resistência e verificar a continuidade, os técnicos automóveis podem garantir que os solenóides estão a funcionar corretamente, o que tem um impacto direto na fiabilidade do veículo. Isto é particularmente importante em regiões como África e América do Sul, onde o desempenho dos veículos pode afetar significativamente as actividades económicas. Os compradores devem considerar a qualidade e a calibração dos multímetros para garantir diagnósticos precisos.
Que papel desempenha o teste de solenóides na produção?
No fabrico, os solenóides são parte integrante da maquinaria automatizada e das linhas de montagem. Testar estes componentes com um multímetro garante que funcionam corretamente, o que minimiza o tempo de inatividade e aumenta a eficiência global. Dada a natureza competitiva da produção, especialmente na Europa e no Médio Oriente, as empresas beneficiam do investimento em equipamento de teste fiável. Os compradores devem concentrar-se em adquirir multímetros que sejam compatíveis com vários sistemas e que ofereçam um suporte técnico robusto para lidar com quaisquer desafios operacionais.
Porque é que o teste dos solenóides é crítico nos sistemas AVAC?
Nos sistemas AVAC, os solenóides controlam as válvulas e os actuadores, tornando o seu bom funcionamento essencial para uma regulação eficaz da temperatura. Testar estes solenóides com um multímetro ajuda a manter a fiabilidade do sistema e a eficiência energética, crucial tanto em ambientes comerciais como residenciais. Para os compradores internacionais, especialmente em regiões que enfrentam condições climatéricas extremas, é vital adquirir equipamento que possa resistir aos desafios ambientais. Os compradores devem dar prioridade às especificações que se alinham com os requisitos do seu sistema e considerar o serviço pós-venda para apoio contínuo.
Qual o impacto do ensaio de solenóides no equipamento agrícola?
O equipamento agrícola depende frequentemente de solenóides para sistemas de irrigação e operações de maquinaria. O teste destes componentes garante uma funcionalidade óptima, que é fundamental para maximizar o rendimento das colheitas e gerir os recursos de forma eficaz. Nas regiões em desenvolvimento, como a África e a América do Sul, onde a agricultura é o principal motor económico, a realização de testes fiáveis pode evitar falhas dispendiosas. Os compradores devem procurar multímetros que cumpram a conformidade regulamentar local e que sejam fornecidos por fabricantes com um historial comprovado em aplicações agrícolas.

Imagem ilustrativa relacionada com a forma de testar o solenoide com um multímetro
Qual é a importância do teste de solenóides na indústria do petróleo e do gás?
No sector do petróleo e do gás, os solenóides são utilizados em sistemas de perfuração e controlo onde a segurança e a eficiência são fundamentais. Testar estes componentes com um multímetro ajuda a identificar potenciais falhas antes que estas conduzam a problemas operacionais significativos. Tendo em conta os ambientes perigosos típicos desta indústria, é crucial adquirir equipamento que cumpra as rigorosas normas da indústria. Os compradores devem considerar fornecedores que forneçam produtos certificados e demonstrem durabilidade em condições extremas para garantir a segurança operacional.
3 Pontos de dor comuns do utilizador para ‘como testar o solenoide com um multímetro’ e as suas soluções
Cenário 1: Dificuldade em identificar as especificações do solenoide para teste
O problema: Muitos compradores B2B deparam-se com desafios quando tentam identificar as especificações corretas dos solenóides para testar com um multímetro. Isto surge frequentemente quando se lida com vários tipos de solenóides em várias aplicações, o que leva a confusão sobre os valores de resistência e as classificações de tensão. Sem informações precisas, os compradores podem arriscar-se a testar as definições erradas dos solenóides, danificando potencialmente os componentes ou levando a avaliações incorrectas da funcionalidade.
A solução: Para enfrentar eficazmente este desafio, os compradores devem dar prioridade ao fornecimento de documentação abrangente do produto para cada tipo de solenoide. Isto inclui manuais do utilizador, folhas de dados técnicos e especificações do fabricante que descrevem os valores de resistência e os requisitos de tensão. Ao preparar-se para testar um solenoide, certifique-se de que faz uma referência cruzada das especificações com as definições do multímetro. Além disso, estabeleça uma base de dados centralizada ou um guia de referência que consolide esta informação para um acesso rápido. Ao criar uma abordagem sistemática para catalogar as especificações do solenoide, as equipas podem simplificar os procedimentos de teste e minimizar os erros.
Cenário 2: Resultados de testes inconsistentes que conduzem a um diagnóstico incorreto
O problema: Os compradores B2B enfrentam frequentemente problemas com leituras inconsistentes do multímetro ao testar solenóides, o que pode levar a um diagnóstico incorreto do estado de um solenoide. Factores como pontos de ligação deficientes, problemas de calibração do multímetro ou condições ambientais podem contribuir para leituras flutuantes. Esta inconsistência pode resultar em substituições ou reparações desnecessárias, afectando, em última análise, a eficiência operacional e aumentando os custos.
A solução: Para mitigar resultados de teste inconsistentes, é essencial implementar um protocolo de teste padrão. Comece por se certificar de que o multímetro está corretamente calibrado antes de cada utilização. Inspeccione e limpe regularmente todos os pontos de ligação para garantir que estão livres de corrosão e seguros. Além disso, considere a realização de testes num ambiente controlado para limitar as influências externas, como a temperatura e a humidade. Documente os resultados meticulosamente para identificar padrões que possam indicar problemas subjacentes com o solenoide ou com o processo de teste. Estes dados podem ser valiosos para melhorar a precisão de futuros testes e tomadas de decisão.
Cenário 3: Falta de formação adequada sobre a utilização do multímetro
O problema: Um ponto de dor comum para os compradores B2B é a falta de formação adequada entre os técnicos e o pessoal sobre como utilizar corretamente um multímetro para testar solenóides. Sem o conhecimento adequado, os funcionários podem ter dificuldade em interpretar as leituras, o que leva a erros no diagnóstico da funcionalidade do solenoide. Isto não só afecta a fiabilidade do processo de teste, como também pode levar a riscos de segurança no local de trabalho.
A solução: Para colmatar esta lacuna de conhecimentos, as organizações devem investir em programas de formação abrangentes centrados na utilização de multímetros e no teste de solenóides. Isto pode incluir workshops práticos, módulos de formação online e o desenvolvimento de guias de instrução que descrevam as melhores práticas. Incentive uma cultura de aprendizagem contínua, fornecendo recursos para que o pessoal se mantenha atualizado sobre as mais recentes técnicas e tecnologias de teste. Além disso, considere a possibilidade de criar um programa de mentoria em que os técnicos experientes possam orientar os funcionários mais novos no processo de teste. Esta abordagem não só melhora os níveis de competências, como também promove um ambiente de trabalho mais seguro e eficiente.
Ao abordar estes pontos problemáticos comuns com soluções específicas, os compradores B2B podem melhorar os seus processos de teste e garantir a fiabilidade das suas aplicações de solenóides.
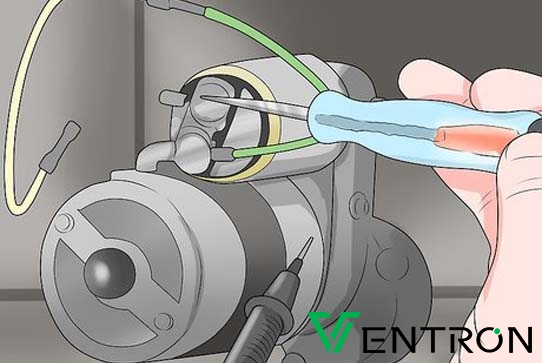
Imagem ilustrativa relacionada com a forma de testar o solenoide com um multímetro
Guia de Seleção de Material Estratégico para saber como testar o solenoide com um multímetro
Que materiais são normalmente utilizados para testar solenóides com um multímetro?
Quando se trata de testar solenóides com um multímetro, a escolha dos materiais utilizados na construção do solenoide e no equipamento de teste pode afetar significativamente o desempenho e a fiabilidade. Abaixo encontram-se análises de materiais comuns relevantes para esta aplicação.
1. Cobre
Principais propriedades:
O cobre é altamente condutor, o que o torna ideal para aplicações eléctricas. Tem um ponto de fusão de 1.984°F (1.085°C) e uma excelente resistência à corrosão, especialmente quando ligado a outros elementos.
Prós e contras:
A elevada condutividade do cobre assegura uma perda mínima de energia, aumentando a eficiência do funcionamento do solenoide. No entanto, pode ser mais caro do que alternativas como o alumínio, e a sua suscetibilidade à oxidação pode exigir revestimentos protectores para manter o desempenho.
Impacto na aplicação:
O cobre é compatível com uma vasta gama de meios, o que o torna adequado para várias aplicações de solenóides, incluindo utilizações automóveis e industriais. As suas propriedades térmicas permitem-lhe suportar temperaturas elevadas sem se degradar.

Imagem ilustrativa relacionada com a forma de testar o solenoide com um multímetro
Considerações para compradores internacionais:
Os compradores em regiões como África e América do Sul devem garantir que os componentes de cobre cumprem as normas locais de condutividade e resistência à corrosão. Na Europa e no Médio Oriente, espera-se frequentemente o cumprimento das normas ASTM.
2. Alumínio
Principais propriedades:
O alumínio é leve e tem um ponto de fusão de 660,3°C (1.221°F). Oferece boa resistência à corrosão, especialmente quando anodizado.
Prós e contras:
O baixo peso do alumínio facilita o manuseamento e a instalação, reduzindo os custos globais. No entanto, a sua menor condutividade em comparação com o cobre pode levar a maiores perdas de energia em aplicações eléctricas, o que pode afetar o desempenho.
Impacto na aplicação:
O alumínio é adequado para aplicações em que o peso é um fator crítico, como nas indústrias aeroespacial e automóvel. A sua resistência à corrosão é benéfica em ambientes húmidos ou costeiros.

Imagem ilustrativa relacionada com a forma de testar o solenoide com um multímetro
Considerações para compradores internacionais:
Em regiões com regulamentações rigorosas, como a Europa, os componentes de alumínio devem estar em conformidade com as normas DIN. Os compradores devem considerar o impacto ambiental da produção e reciclagem do alumínio, o que pode afetar as decisões de aquisição.
3. Aço inoxidável
Principais propriedades:
O aço inoxidável é conhecido pela sua elevada resistência e excelente resistência à corrosão, com um ponto de fusão de cerca de 1.370°C (2.500°F). É frequentemente utilizado em ambientes agressivos.
Prós e contras:
Embora o aço inoxidável ofereça uma durabilidade e resistência à corrosão superiores, é mais pesado e mais caro do que o cobre e o alumínio. A sua complexidade de fabrico pode também aumentar os prazos de entrega.
Impacto na aplicação:
O aço inoxidável é ideal para aplicações expostas a ambientes corrosivos, como a indústria marítima ou química. A sua resistência garante um desempenho duradouro, reduzindo a necessidade de substituições frequentes.

Imagem ilustrativa relacionada com a forma de testar o solenoide com um multímetro
Considerações para compradores internacionais:
Os compradores devem verificar se os componentes de aço inoxidável cumprem as normas internacionais específicas (por exemplo, JIS no Japão, ASTM nos EUA) para garantir a compatibilidade e a qualidade. Compreender as condições de corrosão locais é essencial para selecionar o tipo certo.
4. Compósitos plásticos
Principais propriedades:
Os compósitos de plástico podem ser concebidos para obter propriedades específicas, incluindo resistência à temperatura e isolamento elétrico. Normalmente, têm uma condutividade térmica mais baixa e podem suportar temperaturas até 300°F (149°C).
Prós e contras:
Estes materiais são leves e resistentes à corrosão, o que os torna adequados para várias aplicações. No entanto, podem não ter um bom desempenho sob altas temperaturas ou cargas mecânicas pesadas, limitando a sua utilização em algumas aplicações de solenóides.
Impacto na aplicação:
Os compósitos plásticos são frequentemente utilizados em ambientes onde o isolamento elétrico é fundamental, como na eletrónica de consumo. A sua versatilidade permite a personalização com base nas necessidades específicas da aplicação.
Considerações para compradores internacionais:
Os compradores devem certificar-se de que os materiais compósitos de plástico cumprem as normas de segurança e desempenho relevantes na sua região. Compreender o clima local e as condições ambientais pode ajudar a selecionar o material compósito adequado.

Imagem ilustrativa relacionada com a forma de testar o solenoide com um multímetro
Tabela de resumo da seleção de materiais para testar solenóides com um multímetro
| Material | Caso de utilização típico de como testar o solenoide com um multímetro | Vantagem principal | Principal desvantagem/limitação | Custo relativo (baixo/médio/alto) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cobre | Ligações eléctricas no ensaio de solenóides | Alta condutividade | Suscetível à oxidação | Alto |
| Alumínio | Aplicações de solenóides leves | Baixo peso | Condutividade inferior | Médio |
| Aço inoxidável | Aplicações de solenóides em ambientes agressivos | Excelente resistência à corrosão | Mais pesado e mais caro | Alto |
| Compósitos plásticos | Componentes isolantes no ensaio de solenóides | Leve e resistente à corrosão | Desempenho térmico limitado | Baixo |
Este guia estratégico de seleção de materiais fornece informações valiosas aos compradores B2B, ajudando-os a tomar decisões informadas ao selecionar materiais para testar solenóides com um multímetro.
Análise aprofundada: Processos de fabrico e garantia de qualidade para saber como testar o solenoide com um multímetro
Quais são as principais etapas do processo de fabrico de solenóides?
O processo de fabrico de solenóides envolve várias fases críticas que garantem que o produto final cumpre as especificações exigidas em termos de funcionalidade e durabilidade. Compreender estas fases é vital para os compradores B2B, particularmente aqueles que se abastecem em regiões como África, América do Sul, Médio Oriente e Europa.
1. Preparação do material: Que materiais são utilizados no fabrico de solenóides?
O primeiro passo no fabrico de solenóides é a seleção dos materiais adequados. Normalmente, os solenóides são feitos de materiais que possuem uma elevada condutividade eléctrica e permeabilidade magnética. Os materiais comuns incluem:
- Cobre: Utilizado para enrolar a bobina devido à sua excelente condutividade eléctrica.
- Aço ou ferro: Frequentemente utilizado no invólucro e no núcleo do solenoide, proporcionando resistência e propriedades magnéticas.
- Materiais plásticos ou compósitos: Utilizado para o isolamento e a proteção da habitação contra factores ambientais.
A qualidade do material é fundamental, uma vez que materiais de qualidade inferior podem levar à falha do solenoide, afectando o desempenho em aplicações como a indústria automóvel, maquinaria industrial e eletrónica de consumo.
2. Conformação: Como é que os solenóides são moldados e montados?
Depois de preparados, os materiais são submetidos a várias técnicas de moldagem:
- Enrolamento: O fio de cobre é enrolado à volta de um núcleo para criar a bobina do solenoide. O número de voltas e o calibre do fio são fundamentais para obter as propriedades electromagnéticas desejadas.
- Maquinação: Os componentes da caixa são maquinados com dimensões precisas, assegurando que as peças se encaixam corretamente e funcionam como pretendido.
- Moldagem: No caso dos componentes de plástico, a moldagem por injeção é frequentemente utilizada para criar formas complexas que satisfaçam as especificações do projeto.
O processo de conformação deve ser controlado de perto para manter as tolerâncias e assegurar que as caraterísticas electromagnéticas do solenoide são preservadas.
3. Montagem: O que é que está envolvido na montagem de um solenoide?
A montagem envolve a junção de todos os componentes numa unidade funcional. As principais etapas incluem:
- Inserção da bobina: A bobina enrolada é cuidadosamente colocada no interior da caixa.
- Ligação: As ligações eléctricas são feitas, assegurando que a bobina pode ser energizada corretamente.
- Vedação: O solenoide pode ser selado para o proteger do pó, da humidade e de outros factores ambientais.
As práticas de montagem eficazes são fundamentais para garantir a fiabilidade e a longevidade no terreno.
4. Acabamento: Quais são os retoques finais no fabrico de solenóides?
Os processos de acabamento aumentam a durabilidade e o desempenho do solenoide. As técnicas de acabamento mais comuns incluem:
- Revestimento: Aplicação de revestimentos de proteção para evitar a corrosão e o desgaste.
- Testes: Os testes funcionais iniciais são realizados para verificar se o solenoide funciona corretamente nas condições especificadas.
A fase de acabamento é essencial para garantir que o solenoide possa suportar as exigências da sua aplicação.
Como é que a garantia de qualidade é implementada no fabrico de solenóides?
A garantia de qualidade (QA) é um aspeto crucial do fabrico de solenóides, particularmente para os compradores B2B que exigem fiabilidade e conformidade com as normas internacionais.
Que normas internacionais regem a qualidade do fabrico de solenóides?
Muitas normas internacionais aplicam-se ao fabrico e ensaio de solenóides, incluindo:
- ISO 9001: Uma norma mundialmente reconhecida para sistemas de gestão da qualidade (QMS). Garante que os fabricantes fornecem consistentemente produtos que cumprem os requisitos regulamentares e do cliente.
- Marcação CE: Exigido para produtos vendidos no Espaço Económico Europeu (EEE), indicando a conformidade com as normas de saúde, segurança e proteção ambiental.
- Padrões API: Particularmente relevante na indústria do petróleo e do gás, garantindo que componentes como os solenóides cumprem os rigorosos requisitos de desempenho e segurança.
A conformidade com estas normas é vital para o comércio internacional e para a confiança dos clientes.
Quais são os principais pontos de controlo de qualidade na fabricação de solenóides?
Os processos de controlo de qualidade (CQ) envolvem normalmente vários pontos de controlo:
- Controlo de Qualidade de Entrada (IQC): As matérias-primas e os componentes são inspeccionados à chegada para garantir que cumprem as normas especificadas.
- Controlo de qualidade em processo (IPQC): A monitorização contínua durante o processo de fabrico ajuda a detetar defeitos precocemente. Isto inclui a verificação das dimensões, da resistência eléctrica e de outros parâmetros críticos.
- Controlo de Qualidade Final (FQC): Os solenóides acabados são submetidos a testes exaustivos para confirmar que cumprem as especificações de desempenho. Isto pode incluir testes eléctricos, testes de durabilidade mecânica e simulações ambientais.
Estes pontos de controlo ajudam a garantir que quaisquer defeitos são identificados e rectificados antes de o produto chegar ao cliente.
Que métodos de ensaio são normalmente utilizados para solenóides?
São utilizados vários métodos de teste para garantir que os solenóides funcionam corretamente:
- Ensaios de resistência: Utilizar um multímetro para medir a resistência eléctrica da bobina do solenoide. Isto ajuda a verificar se a bobina está intacta e a funcionar corretamente.
- Teste de continuidade: Assegura-se de que não há interrupções no percurso elétrico do solenoide.
- Testes funcionais: Avaliação do desempenho do solenoide em condições reais de funcionamento, incluindo frequentemente um teste de clique para verificar a atuação.
Estes ensaios são essenciais para confirmar a fiabilidade dos solenóides nas suas aplicações previstas.
Como os compradores B2B podem verificar o controlo de qualidade dos fornecedores?
Para os compradores B2B, especialmente os que se encontram em regiões com normas de fabrico variáveis, é crucial verificar as práticas de controlo de qualidade dos fornecedores. Eis alguns métodos:
- Auditorias a fornecedores: A realização de auditorias no local permite que os compradores avaliem os processos de fabrico e as práticas de CQ em primeira mão.
- Relatórios de qualidade: A solicitação de relatórios detalhados de controlo de qualidade pode fornecer informações sobre os métodos de ensaio do fornecedor e a conformidade com as normas relevantes.
- Inspeções por terceiros: A contratação de serviços de inspeção por terceiros pode proporcionar uma avaliação imparcial da qualidade do produto antes da expedição.
Estes passos podem ajudar a reduzir os riscos associados à aquisição de produtos a fornecedores internacionais, garantindo que os produtos cumprem as especificações e normas exigidas.
Quais são as nuances do controlo de qualidade para compradores B2B internacionais?
Os compradores B2B internacionais devem estar cientes das nuances específicas do controlo de qualidade ao adquirirem solenóides:
Imagem ilustrativa relacionada com a forma de testar o solenoide com um multímetro
- Compreender as normas locais: Os diferentes países podem ter normas e certificações únicas, pelo que é essencial compreender os requisitos locais e garantir a conformidade.
- Factores culturais: Os estilos de comunicação e negociação podem variar, afectando o processo de aquisição. A criação de relações fortes com os fornecedores pode facilitar um melhor controlo da qualidade e uma maior capacidade de resposta.
- Considerações logísticas: O transporte marítimo internacional pode introduzir riscos, pelo que é vital garantir a manutenção da qualidade ao longo de toda a cadeia de abastecimento.
Ao concentrarem-se nestas áreas, os compradores B2B podem melhorar os seus processos de aquisição e garantir que recebem solenóides de alta qualidade que satisfazem as suas necessidades operacionais.
Guia prático de abastecimento: Uma lista de verificação passo-a-passo para ‘como testar o solenoide com um multímetro’
Introdução
Este guia prático de fornecimento fornece aos compradores B2B internacionais uma lista de verificação passo a passo para testar eficazmente os solenóides com um multímetro. Compreender como testar com precisão os solenóides é essencial para garantir um desempenho ótimo em várias aplicações, desde a indústria automóvel à maquinaria industrial. Este guia irá fornecer-lhe os passos necessários para obter as ferramentas e os conhecimentos corretos para um ensaio eficaz de solenóides.
Passo 1: Definir os requisitos de teste
Identifique as aplicações específicas e os tipos de solenóides que irá testar. Saber se está a lidar com solenóides automóveis, válvulas solenóides industriais ou outros tipos irá ajudá-lo a determinar as especificações necessárias do multímetro e as técnicas de teste. Esta clareza garante que adquire equipamento adequado e evita problemas de compatibilidade.
Passo 2: Selecionar um multímetro adequado
Escolha um multímetro que cumpra as especificações necessárias para o seu teste de solenoide. Procure caraterísticas como capacidades de medição de resistência, teste de continuidade e medição de tensão. Certifique-se de que o multímetro tem um visor nítido e uma interface de fácil utilização, uma vez que isso irá aumentar a precisão e a facilidade de utilização durante o teste.
Passo 3: Garantir a conformidade com as normas de segurança
Antes de comprar equipamento de teste, verifique se está em conformidade com as normas de segurança relevantes. Verifique se existem certificações como a marcação CE na Europa ou a certificação UL nos Estados Unidos. Isto é crucial para garantir a segurança do seu pessoal e a fiabilidade dos seus procedimentos de teste, especialmente em regiões com regulamentos rigorosos.
Passo 4: Verificar as certificações dos fornecedores
Efetuar verificações completas dos antecedentes de potenciais fornecedores de multímetros e equipamento de teste. Solicite documentação que comprove as suas certificações e sistemas de gestão de qualidade, como a ISO 9001. Este passo é vital para garantir que se está a abastecer junto de fornecedores reputados que fornecem ferramentas de teste fiáveis e precisas.
Passo 5: Avaliar o suporte técnico e os recursos
Avalie o nível de suporte técnico e os recursos oferecidos pelo fornecedor. Procure fornecedores que forneçam manuais abrangentes, tutoriais online e um serviço de apoio ao cliente reativo. Este apoio é importante para a resolução de problemas e para garantir que a sua equipa pode utilizar eficazmente o multímetro para o teste de solenóides.
Passo 6: Solicitar demonstrações ou amostras de produtos
Antes de finalizar a sua encomenda, peça demonstrações de produtos ou amostras dos multímetros que está a considerar. Isto permite à sua equipa avaliar a usabilidade e funcionalidade do equipamento em primeira mão. Observar o multímetro em ação pode ajudar a confirmar que este cumpre os seus requisitos de teste e fornece a precisão necessária.
Passo 7: Estabelecer suporte e garantia pós-compra
Confirmar a garantia e o apoio pós-compra fornecidos pelo fornecedor. Uma garantia sólida pode proteger o seu investimento e assegurar que recebe apoio em caso de falha do equipamento. Compreender as condições de serviço e assistência também pode ajudá-lo a planear futuras manutenções e reparações, o que é essencial para uma eficiência operacional a longo prazo.
Seguindo estes passos, os compradores B2B podem tomar decisões informadas ao adquirirem as ferramentas necessárias para testar eficazmente os solenóides com um multímetro, garantindo a fiabilidade e o desempenho nas suas aplicações.
Análise abrangente de custos e preços para como testar solenoide com multímetro Sourcing
Quais são os principais componentes de custo para testar solenóides com um multímetro?
Ao analisar os custos associados ao teste de solenóides usando um multímetro, vários componentes de custo entram em jogo. Estes incluem materiais, mão de obra, despesas gerais de fabrico, ferramentas, controlo de qualidade (CQ), logística e margem.
-
Materiais: Os principais materiais envolvidos são o próprio multímetro e os componentes do solenoide. Dependendo da complexidade e das especificações do solenoide, os custos podem variar significativamente. Os multímetros de alta qualidade podem variar entre $20 e mais de $200, enquanto os preços dos solenóides podem variar com base no tipo e nas especificações, situando-se normalmente entre $30 e $250.
-
Trabalho: Os custos de mão de obra englobam o tempo que os técnicos ou engenheiros passam a testar os solenóides. Estes custos podem variar muito com base nos padrões salariais locais, com a mão de obra qualificada na Europa a custar potencialmente mais do que em regiões como África ou América do Sul.
-
Custos indiretos de produção: Inclui os custos relacionados com as operações da fábrica, tais como os serviços públicos, a manutenção do equipamento e a conservação das instalações. Dependendo do volume de produção e da eficiência do processo de fabrico, as despesas gerais podem influenciar significativamente o custo global.
-
Ferramentas: Se forem necessárias ferramentas especializadas para os testes, isso pode aumentar o custo. As despesas com ferramentas são muitas vezes amortizadas ao longo das séries de produção, afectando o custo unitário.
-
Controlo de Qualidade (QC): É essencial garantir que os solenóides cumprem as normas de qualidade. Os custos de controlo de qualidade podem incluir equipamento de teste, pessoal e processos para verificar o desempenho, aumentando a despesa total.
-
Logística: Os custos associados ao transporte de solenóides e equipamento de teste para o local de teste ou para as instalações do cliente podem variar significativamente com base na distância, nos métodos de envio e nos direitos aduaneiros internacionais.
-
Margem: Os fornecedores normalmente incluem uma margem de lucro para cobrir as suas despesas e gerar lucro. Esta margem pode variar em função da concorrência e da procura no mercado.
Como é que os influenciadores de preços afectam o custo do teste de solenóides?
Vários factores podem influenciar o preço dos serviços de ensaio de solenóides, especialmente para os compradores internacionais B2B.
-
Volume/MOQ: As compras a granel conduzem frequentemente a descontos. Os fornecedores podem oferecer melhores preços para encomendas maiores, o que pode reduzir significativamente o custo por unidade.
-
Especificações e personalização: Solenóides personalizados ou requisitos de teste específicos podem aumentar os custos. Os compradores devem comunicar claramente as suas necessidades para evitar despesas inesperadas.
-
Materiais e certificações de qualidade: Os materiais de alta qualidade e as certificações (como a ISO) podem aumentar os custos. Os compradores devem ponderar a importância da certificação em função do seu orçamento e das necessidades da aplicação.
-
Fatores relacionados ao fornecedor: A reputação, a fiabilidade e a localização do fornecedor podem afetar os preços. Os fornecedores estabelecidos com bons antecedentes podem cobrar um prémio.
-
Incoterms: Compreender os Incoterms é crucial para a gestão de custos em transacções internacionais. Estas condições ditam as responsabilidades em matéria de transporte, seguro e tarifas, afectando os custos globais.
Que dicas do comprador podem ajudar a otimizar os custos de teste de solenóides?
Os compradores B2B internacionais podem otimizar os seus custos através de várias estratégias:
-
Negociação: Envolva os fornecedores em discussões sobre preços, especialmente se tiver planos de compras a longo prazo. Aproveite as cotações competitivas para negociar melhores negócios.
-
Relação custo-benefício: Avaliar o custo total de propriedade (TCO), incluindo não apenas o preço de compra, mas também os custos de manutenção e operacionais ao longo do tempo. A escolha de solenóides de alta qualidade pode levar a custos mais baixos a longo prazo.
-
Nuances de preços para compradores internacionais: Tenha em atenção as flutuações cambiais e o seu impacto nos preços. Além disso, considere os regulamentos e tarifas locais que podem influenciar o custo total da importação de solenóides.
-
Compreender os prazos de entrega: Alinhe a sua estratégia de compras com os calendários de produção para evitar custos de envio urgente, que podem acrescentar despesas significativas.
-
Relações com fornecedores: O estabelecimento de relações duradouras com os fornecedores pode conduzir a melhores condições e preços. A comunicação e o feedback regulares podem melhorar o serviço e reduzir os custos.
Isenção de responsabilidade para preços indicativos
O preço dos solenóides de teste e do equipamento associado pode variar com base em inúmeros factores, incluindo as condições de mercado, as estratégias de preços dos fornecedores e as influências económicas regionais. Os preços mencionados neste guia são indicativos e podem flutuar; os compradores devem efetuar uma pesquisa de mercado exaustiva e comparações de fornecedores para obterem preços exactos e actuais.

Imagem ilustrativa relacionada com a forma de testar o solenoide com um multímetro
Análise de alternativas: Comparação de como testar o solenoide com multímetro com outras soluções
Compreender os métodos alternativos de ensaio de solenóides
Quando se trata de testar solenóides, existem vários métodos disponíveis, cada um com vantagens e limitações únicas. Para os compradores B2B internacionais, particularmente em regiões como África, América do Sul, Médio Oriente e Europa, compreender estas alternativas é crucial para tomar decisões informadas que se alinhem com as necessidades operacionais e restrições orçamentais. Abaixo, comparamos o método convencional de utilização de um multímetro com duas alternativas viáveis: o teste de clique e o teste de bancada com uma bateria.
| Aspecto comparativo | Como testar o solenoide com um multímetro | Clique em Testar | Teste de bancada com bateria |
|---|---|---|---|
| Desempenho | Elevada precisão na medição da resistência e da continuidade | Verificação da funcionalidade básica; confirmação audível | Bom para verificar o estado operacional, mas menos preciso |
| Custo | Moderado (custo do multímetro) | Baixo (são necessárias ferramentas mínimas) | Moderado (custo da bateria e das ferramentas básicas) |
| Facilidade de implementação | Requer conhecimentos de utilização de multímetros | Muito fácil; não são necessárias ferramentas especiais | Requer alguma configuração e conhecimentos de ligações eléctricas |
| Manutenção | Baixos; os multímetros são duráveis | Nenhum; não há equipamento para manter | Baixo; as pilhas podem ser substituídas facilmente |
| Melhor caso de uso | Diagnóstico detalhado e resolução de problemas | Controlos rápidos em ambientes de baixo risco | Confirmação da funcionalidade antes da instalação ou manutenção |
Quais são os prós e os contras do teste de clique para o teste de solenóides?
O teste de clique é um dos métodos mais simples para verificar a funcionalidade de um solenoide. Aplicando energia e ouvindo um som de clique, os utilizadores podem verificar rapidamente se o solenoide está a engatar. Este método é económico e requer ferramentas mínimas, tornando-o acessível a vários utilizadores. No entanto, o teste de clique não fornece informações detalhadas sobre o estado interno do solenoide, tais como problemas de resistência ou continuidade. Por conseguinte, embora seja uma solução rápida para verificações básicas, não tem a profundidade necessária para um diagnóstico completo.
Como é que o teste de bancada com uma bateria se compara à utilização de um multímetro?
O teste de bancada com uma bateria envolve a ligação do solenoide a uma fonte de alimentação para observar o seu funcionamento. Este método permite aos utilizadores confirmar visualmente que o solenoide está a engatar, tornando-o útil para verificações iniciais de funcionalidade antes da instalação. A configuração é simples e requer ferramentas básicas, mas não mede propriedades eléctricas como a resistência. Consequentemente, embora possa confirmar eficazmente o estado operacional, pode não detetar problemas subjacentes que podem afetar o desempenho ao longo do tempo.
Fazendo a escolha certa para as suas necessidades de teste de solenoide
Ao decidir qual o melhor método para testar solenóides, os compradores B2B devem considerar factores como a aplicação específica, o nível de detalhe exigido no diagnóstico e as restrições orçamentais. Para uma análise eléctrica detalhada, é aconselhável utilizar um multímetro, especialmente para sistemas críticos em que a precisão é fundamental. Por outro lado, para verificações rápidas ou ambientes de baixo risco, o teste de clique pode ser suficiente. Os testes de bancada constituem um meio-termo, oferecendo um equilíbrio entre a verificação da funcionalidade e a facilidade de utilização. Ao avaliar estas alternativas em função das suas necessidades operacionais, os compradores podem selecionar a solução mais eficaz para os seus requisitos.
Propriedades técnicas essenciais e terminologia comercial para saber como testar o solenoide com um multímetro
Quais são as propriedades técnicas essenciais a considerar ao testar um solenoide com um multímetro?
Compreender as propriedades técnicas dos solenóides é crucial para os compradores B2B, particularmente quando se trata de garantir a fiabilidade e o desempenho em várias aplicações. Aqui estão algumas especificações críticas a considerar:
-
Valor da resistência (Ohms)
A resistência de uma bobina de solenoide é uma especificação chave medida em ohms (Ω). Este valor indica a resistência eléctrica que a bobina apresenta à corrente. Os compradores B2B devem consultar as especificações do fabricante para determinar o intervalo de resistência aceitável para o seu solenoide específico. Uma leitura fora deste intervalo pode indicar uma falha, como um curto-circuito ou uma bobina aberta. -
Classificação da tensão (Volts)
Cada solenoide é concebido para funcionar com uma tensão específica. É essencial testar os solenóides à sua tensão nominal para garantir um funcionamento correto. Utilizando um multímetro, os compradores podem verificar se o solenoide está a receber a tensão correta e diagnosticar problemas nos sistemas eléctricos. A compreensão das classificações de tensão pode ajudar a evitar danos nos solenóides e no equipamento associado. -
Consumo de corrente (Amperes)
O consumo de corrente indica a quantidade de corrente que o solenoide consome quando está ligado. Esta especificação é importante para avaliar se a fonte de alimentação pode suportar a carga. A monitorização da corrente também pode ajudar a detetar problemas como o sobreaquecimento, que pode levar a uma falha prematura. -
Ciclo de trabalho
O ciclo de funcionamento é a relação entre o tempo que um solenoide pode ser ativado e o tempo que deve permanecer desligado para evitar o sobreaquecimento. Esta especificação é vital para aplicações em que os solenóides são frequentemente activados. Os compradores devem considerar o ciclo de funcionamento para garantir que o solenoide pode funcionar eficazmente na aplicação pretendida sem correr o risco de sofrer danos. -
Dimensões físicas
O tamanho e o peso do solenoide podem afetar a instalação e a compatibilidade com os sistemas existentes. Os compradores devem certificar-se de que as dimensões do solenoide correspondem às especificações da sua aplicação, particularmente em espaços confinados ou equipamento especializado.
Quais são os termos comerciais comuns relacionados com o teste de solenóides com um multímetro?
A familiaridade com o jargão do sector pode simplificar a comunicação e as transacções dos compradores B2B. Aqui estão alguns termos essenciais:
-
OEM (Fabricante de Equipamento Original)
Os OEM produzem componentes que são utilizados na montagem final de um produto. Perceber se um solenoide é proveniente de um OEM pode ajudar os compradores a avaliar a qualidade e a fiabilidade. Os componentes OEM cumprem frequentemente normas de fabrico rigorosas, garantindo a compatibilidade e o desempenho. -
MOQ (Quantidade mínima de encomenda)
O MOQ refere-se à quantidade mais pequena de um produto que um fornecedor está disposto a vender. Este termo é particularmente relevante para os compradores B2B que podem precisar de comprar a granel. Conhecer o MOQ pode ajudar as empresas a planear o seu inventário e a gerir os custos de forma eficaz. -
RFQ (Pedido de Orçamento)
Um pedido de cotação é um documento formal enviado aos fornecedores solicitando preços e condições para produtos ou serviços específicos. Os compradores B2B devem utilizar RFQs para obter preços competitivos para solenóides, permitindo uma melhor orçamentação e tomada de decisões. -
Incoterms (Termos Comerciais Internacionais)
Os Incoterms são um conjunto de regras que definem as responsabilidades de compradores e vendedores em transacções internacionais. A compreensão destes termos é crucial para os compradores B2B internacionais, uma vez que esclarecem quem é responsável pelo envio, seguro e tarifas, afectando o custo global e a logística da aquisição de solenóides. -
Teste de continuidade
Um teste de continuidade verifica se um circuito elétrico está completo, indicando que a corrente pode fluir. No caso dos solenóides, a realização de um teste de continuidade com um multímetro garante que não existem rupturas na bobina. Isto é essencial para diagnosticar problemas antes da instalação. -
Testes em bancada
O teste em banco de ensaio refere-se à avaliação da funcionalidade de um solenoide num ambiente controlado antes da instalação. Este processo ajuda a identificar quaisquer defeitos ou problemas de desempenho numa fase inicial, reduzindo, em última análise, o tempo de inatividade e os custos de reparação em ambientes operacionais.
Ao compreender estas propriedades técnicas e termos comerciais, os compradores B2B podem tomar decisões informadas, garantindo que os solenóides que adquirem cumprem os seus requisitos e normas operacionais.
Como navegar na dinâmica do mercado e nas tendências de aprovisionamento no sector do teste de solenoide com multímetro
Quais são as principais tendências de mercado que influenciam o teste de solenóides com multímetros?
O mercado global de solenóides e das suas metodologias de ensaio é atualmente moldado por várias tendências dinâmicas. O aumento da automatização em todas as indústrias está a impulsionar a procura de uma funcionalidade fiável dos solenóides, o que torna essencial a realização de testes eficazes. Em regiões como a África, a América do Sul, o Médio Oriente e a Europa, há uma ênfase crescente na manutenção preventiva e na otimização do sistema, o que leva a um maior interesse em soluções de teste. Além disso, o aumento das tecnologias inteligentes está a levar os fabricantes a integrar capacidades de diagnóstico avançadas, incluindo sistemas de teste automatizados que utilizam multímetros para monitorização e resolução de problemas em tempo real.
As novas tendências tecnológicas B2B mostram uma mudança para soluções digitais. O advento dos dispositivos IoT (Internet das Coisas) está a facilitar a monitorização remota dos solenóides, permitindo uma manutenção proactiva em vez de reparações reactivas. Os compradores procuram cada vez mais fornecedores que ofereçam não só solenóides, mas também equipamento de teste abrangente, incluindo multímetros equipados com interfaces digitais e compatibilidade móvel. Esta evolução aumenta a eficiência, reduz o tempo de inatividade e, em última análise, diminui os custos operacionais, o que a torna uma área fundamental de foco para os compradores internacionais.
Além disso, a procura de solenóides duráveis e de alta qualidade está a levar os fornecedores a adotar medidas rigorosas de controlo de qualidade. Os compradores de mercados emergentes, como a Nigéria e o Vietname, estão particularmente concentrados no fornecimento de componentes fiáveis que possam suportar diversas condições ambientais, o que é crucial para aplicações em climas e ambientes industriais variados.
Como é que a sustentabilidade e o fornecimento ético estão a afetar o teste de solenóides com multímetros?
A sustentabilidade está a tornar-se uma pedra angular das estratégias de aquisição B2B, particularmente no contexto do fornecimento de componentes como solenóides e equipamento de teste. Os compradores estão cada vez mais preocupados com o impacto ambiental dos processos de fabrico e com o ciclo de vida dos produtos. Isto levou a uma procura de fornecedores que dão prioridade a práticas sustentáveis, tais como a utilização de materiais amigos do ambiente e a redução de resíduos durante a produção.
O abastecimento ético é igualmente importante. Os compradores internacionais estão à procura de fabricantes que respeitem práticas laborais justas e mantenham a transparência nas suas cadeias de abastecimento. Certificações como a ISO 14001 para a gestão ambiental e a ISO 9001 para a gestão da qualidade estão a tornar-se critérios essenciais para a seleção de fornecedores. Estas certificações não só reflectem um compromisso com a sustentabilidade, como também asseguram aos compradores a qualidade e a fiabilidade dos produtos que adquirem.
Além disso, a utilização de materiais ‘verdes’ na produção de solenóides e equipamento de teste associado está a ganhar força. Os fornecedores que consigam demonstrar a utilização de materiais recicláveis ou que contribuam para a eficiência energética nos seus produtos são susceptíveis de ganhar uma vantagem competitiva no mercado. Esta tendência alinha-se com o impulso global no sentido de reduzir as pegadas de carbono e promover práticas de fabrico responsáveis, tornando-a uma consideração significativa para os compradores B2B em diversas regiões.
Qual é o contexto histórico das práticas de teste de solenóides?
A evolução das práticas de teste de solenóides tem sido marcada por avanços tecnológicos e mudanças nos padrões da indústria. Inicialmente, os métodos de teste eram rudimentares, baseando-se fortemente em técnicas manuais e ferramentas básicas. À medida que as indústrias cresciam e a procura de fiabilidade aumentava, o mesmo acontecia com a complexidade dos métodos de teste. A introdução dos multímetros revolucionou a forma como os solenóides eram testados, permitindo medições precisas da resistência eléctrica e da continuidade.
No final do século XX, à medida que a automação começou a ser implementada em vários sectores, o foco passou a ser o desenvolvimento de protocolos de teste mais sofisticados. Isto incluiu a integração de multímetros digitais capazes de fornecer feedback instantâneo e capacidades de registo de dados. Atualmente, o teste de solenóides com multímetros não é apenas uma prática padrão, mas também um componente crítico das estratégias de manutenção destinadas a garantir a eficiência operacional e a minimizar o tempo de inatividade.
A evolução contínua das práticas de ensaio reflecte as tendências mais amplas dos sectores industrial e de fabrico, onde a precisão, a fiabilidade e a sustentabilidade se tornaram fundamentais. Atualmente, os compradores B2B beneficiam de uma riqueza de conhecimentos e de ferramentas avançadas que melhoram a sua capacidade de garantir o desempenho ideal dos solenóides em diversas aplicações.
Perguntas frequentes (FAQs) para compradores B2B de como testar o solenoide com um multímetro
-
Como testar um solenoide com um multímetro?
Para testar um solenoide com um multímetro, comece por se certificar de que a alimentação está desligada. Defina o seu multímetro para a definição de resistência (ohms) e ligue as sondas aos terminais do solenoide. Um solenoide em funcionamento apresenta normalmente um valor de resistência entre 10 e 100 ohms, dependendo do modelo. Se a leitura for significativamente inferior ou apresentar uma resistência infinita, o solenoide pode estar avariado. Além disso, pode verificar a continuidade mudando o multímetro para a definição de continuidade e verificando se o circuito está completo quando o solenoide é ativado. -
Que problemas comuns podem ser identificados por um multímetro nos solenóides?
Um multímetro pode ajudar a identificar vários problemas nos solenóides, incluindo circuitos abertos, curtos-circuitos e níveis de resistência incorrectos. Um circuito aberto indica uma rutura na bobina, enquanto um curto-circuito sugere que o enrolamento se fundiu. Valores de resistência incorrectos podem indicar deterioração ou falha do solenoide. Ao diagnosticar estes problemas atempadamente, as empresas podem evitar tempos de inatividade dispendiosos e garantir que os seus sistemas funcionam de forma fiável. -
Como é que posso verificar as especificações de um solenoide antes de o comprar?
Ao adquirir solenóides, é crucial verificar especificações como tensão, resistência e dimensões físicas. Solicite fichas de dados técnicos aos fornecedores para confirmar estes pormenores. Além disso, considere a possibilidade de pedir amostras para testar a compatibilidade com os seus sistemas. A discussão com o fornecedor sobre os seus requisitos específicos irá garantir que recebe um produto que satisfaz as suas necessidades operacionais. -
Quais são as quantidades mínimas de encomenda (MOQs) típicas para solenóides no comércio internacional?
As quantidades mínimas de encomenda (MOQs) para solenóides podem variar muito consoante o fornecedor e a complexidade do produto. Normalmente, as MOQs podem variar de 50 a várias centenas de unidades. Para compradores internacionais, é aconselhável negociar MOQs com os fornecedores, especialmente se estiver a testar uma nova linha de produtos ou a entrar num novo mercado. O estabelecimento de uma boa relação com o seu fornecedor pode conduzir a condições mais favoráveis. -
Que condições de pagamento são normalmente aceites para compras internacionais de solenóides?
As condições de pagamento comuns no comércio internacional de solenóides incluem cartas de crédito, transferências electrónicas e pagamento contra entrega. Alguns fornecedores podem oferecer condições líquidas 30 ou líquidas 60, permitindo-lhe pagar após a receção das mercadorias. É essencial discutir as opções de pagamento antecipadamente para garantir que estão alinhadas com o seu fluxo de caixa e estratégias orçamentais. Considere a possibilidade de utilizar serviços de caução para transacções maiores para proteger ambas as partes. -
Como posso assegurar a garantia de qualidade (QA) para solenóides fornecidos internacionalmente?
Para assegurar a garantia de qualidade dos solenóides de origem internacional, estabeleça normas de controlo de qualidade claras com o seu fornecedor. Solicite certificações como a ISO 9001 para verificar os seus processos de fabrico. Além disso, considere a realização de inspecções no local ou a contratação de serviços de QA de terceiros para avaliar os produtos antes do envio. A comunicação regular com o fornecedor relativamente às expectativas de qualidade também pode ajudar a reduzir os riscos. -
Que considerações logísticas devo ter em conta ao importar solenóides?
Ao importar solenóides, considere factores logísticos como os métodos de envio, os regulamentos aduaneiros e os prazos de entrega. Escolha entre frete aéreo e marítimo com base na urgência e na relação custo-benefício. Familiarize-se com as tarifas e os direitos de importação que podem ser aplicados à sua encomenda. Também é benéfico trabalhar com um transitário que possa navegar pelas complexidades do transporte internacional e do desalfandegamento para um processo mais suave. -
Como posso personalizar os solenóides para se adaptarem às minhas aplicações específicas?
A personalização de solenóides é frequentemente possível, dependendo das capacidades do fornecedor. Ao discutir os seus requisitos, forneça especificações detalhadas relativamente ao tamanho, tensão e caraterísticas funcionais. Muitos fornecedores estão dispostos a colaborar em modificações de design para garantir que os seus produtos satisfazem as suas necessidades exclusivas. Certifique-se de que solicita protótipos ou amostras para testar os solenóides personalizados antes de se comprometer com encomendas maiores.
Lista dos 2 principais fabricantes e fornecedores de Como testar o solenoide com multímetro
1. Ford - Guia de Teste do Solenoide da TDF
Domínio: tractorbynet.com
Registado: 1999 (26 anos)
Introdução: Solenoide para a tomada de força de um trator Ford 3000 de 1965; o valor de resistência esperado para um bom solenoide é de 15-30 ohms; um solenoide de 12 V com um consumo de 4 A tem uma resistência de 3 ohms; se estiver a queimar um fusível de 10 A, a resistência pode ser de 1,2 ohms ou menos; o procedimento de teste inclui a verificação da resistência com um multímetro e a utilização de fios de ligação de uma fonte de 12 V para verificar a funcionalidade.
2. Elektroda - Teste da bobina da válvula solenoide
Domínio: elektroda.com
Registado: 2002 (23 anos)
Introdução: Para testar as bobinas das válvulas solenóides utilizando um multímetro digital (DMM), é necessário definir o DMM para a definição de ohms e colocá-lo entre os dois terminais da bobina. Uma bobina em bom estado deve apresentar uma leitura de ohm, enquanto uma leitura ‘OL’ (acima do limite) indica uma bobina defeituosa que necessita de ser substituída. A bobina deve ser desligada do circuito para evitar danificar o DMM. Os métodos de teste alternativos incluem a medição...
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for how to test solenoid with multimeter
Em conclusão, testar eficazmente os solenóides com um multímetro é uma prática crucial para garantir a fiabilidade operacional em várias aplicações. Ao compreender os valores de resistência específicos e as verificações de continuidade, os compradores B2B podem evitar tempos de inatividade dispendiosos e melhorar o desempenho do sistema. Este processo não só salvaguarda os investimentos em maquinaria e equipamento, como também se alinha com os princípios do aprovisionamento estratégico, ao enfatizar a qualidade e a fiabilidade na seleção de componentes.
Para os compradores internacionais de regiões como África, América do Sul, Médio Oriente e Europa, a utilização de métodos de teste de alta qualidade pode levar a uma maior eficiência operacional e a custos de manutenção reduzidos. À medida que as indústrias evoluem, a importância de solenóides fiáveis em sistemas de automação e controlo não pode ser exagerada.
Olhando para o futuro, encorajamos os compradores B2B a dar prioridade à aquisição de componentes de qualidade e a adotar protocolos de teste abrangentes. Ao fazê-lo, pode garantir que as suas operações se mantêm competitivas e respondem às exigências do mercado. Explore parcerias com fornecedores de confiança e invista em formação para melhorar a experiência da sua equipa em testes e manutenção de solenóides. Esta abordagem proactiva não só reforçará as suas capacidades operacionais, como também posicionará a sua empresa para o crescimento e sucesso futuros.

Imagem ilustrativa relacionada com a forma de testar o solenoide com um multímetro
Aviso legal importante e termos de utilização
⚠️ Aviso importante
As informações fornecidas neste guia, incluindo conteúdo sobre fabricantes, especificações técnicas e análises de mercado, têm fins meramente informativos e educativos. Não constituem aconselhamento profissional sobre aquisições, aconselhamento financeiro ou aconselhamento jurídico.
Embora tenhamos envidado todos os esforços para garantir a precisão e atualidade das informações, não nos responsabilizamos por quaisquer erros, omissões ou informações desatualizadas. As condições de mercado, os detalhes da empresa e os padrões técnicos estão sujeitos a alterações.
Os compradores B2B devem realizar a sua própria diligência prévia independente e minuciosa. antes de tomar qualquer decisão de compra. Isso inclui entrar em contacto diretamente com os fornecedores, verificar certificações, solicitar amostras e procurar aconselhamento profissional. O risco de confiar em qualquer informação contida neste guia é assumido exclusivamente pelo leitor.

Imagem ilustrativa relacionada com a forma de testar o solenoide com um multímetro