Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for what does a bad alternator look like
Navigating the complexities of automotive maintenance requires a keen understanding of critical components, such as the alternator. For international B2B buyers, particularly those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, recognizing the signs of a bad alternator is vital for ensuring vehicle reliability and minimizing downtime. This guide delves into the multifaceted world of alternators, exploring the types, common symptoms of failure, and their implications for various applications within the automotive industry.
As you source components and services, understanding what constitutes a malfunctioning alternator will empower you to make informed purchasing decisions. We will cover the essential features to look for when evaluating suppliers, the cost implications of alternator repairs or replacements, and strategies for mitigating risks associated with faulty electrical systems.
By equipping yourself with this knowledge, you can streamline your procurement processes and enhance operational efficiency. Whether you’re managing a fleet of vehicles or overseeing automotive maintenance in your business, this comprehensive guide serves as a valuable resource for navigating the global market, ensuring that you are well-prepared to tackle any challenges related to alternator issues. With a clear understanding of what to watch for, you can safeguard your investments and maintain optimal performance across your automotive assets.
Table Of Contents
- Top 3 What Does A Bad Alternator Look Like Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for what does a bad alternator look like
- Understanding what does a bad alternator look like Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of what does a bad alternator look like
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘what does a bad alternator look like’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for what does a bad alternator look like
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for what does a bad alternator look like
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘what does a bad alternator look like’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for what does a bad alternator look like Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing what does a bad alternator look like With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for what does a bad alternator look like
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the what does a bad alternator look like Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of what does a bad alternator look like
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for what does a bad alternator look like
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Understanding what does a bad alternator look like Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electrical Failure | Flickering lights, electrical glitches, dashboard warning lights. | Automotive repair shops, fleet maintenance. | Pros: Easy to diagnose; Cons: Can lead to complete failure if ignored. |
| Mechanical Wear | Whirring or buzzing noises, worn bearings. | Heavy machinery, automotive manufacturing. | Pros: Often repairable; Cons: May require specialized tools for repairs. |
| Battery Charging Issues | Frequent dead batteries, difficulty starting the engine. | Transportation services, logistics companies. | Pros: Directly impacts operational efficiency; Cons: Can disrupt service schedules. |
| Electrical Overload | Random electrical malfunctions, short-circuits. | Commercial fleets, public transportation. | Pros: Identifies broader electrical system issues; Cons: May require comprehensive system checks. |
| Physical Damage | Visible signs of wear, corrosion, or burnt components. | Auto parts suppliers, vehicle refurbishers. | Pros: Easy to identify; Cons: Replacement may be costly depending on vehicle type. |
How to Identify Electrical Failure in Alternators for B2B Applications
Electrical failure in alternators is often characterized by symptoms such as flickering lights, erratic electrical behavior, and dashboard warning lights indicating battery or alternator issues. For businesses operating automotive repair shops or managing fleet maintenance, recognizing these signs early can prevent costly downtime. Buyers should consider investing in diagnostic tools that can accurately assess electrical systems to improve service efficiency.
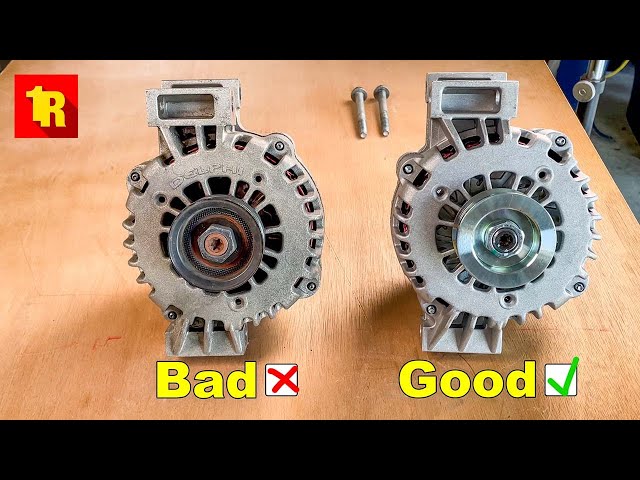

Illustrative image related to what does a bad alternator look like
What to Look for in Mechanical Wear of Alternators
Mechanical wear manifests through unusual sounds, such as whirring or buzzing noises, typically stemming from worn bearings within the alternator. This type of failure is common in heavy machinery and automotive manufacturing settings. B2B buyers should prioritize regular maintenance and inspections to extend the lifespan of alternators and reduce the likelihood of unexpected failures that could halt production or service operations.
Understanding Battery Charging Issues Related to Alternators
Frequent dead batteries and difficulties in starting engines are clear indicators of battery charging issues linked to the alternator. For businesses in transportation services or logistics, these problems can disrupt schedules and lead to financial losses. It’s crucial for B2B buyers to establish a preventive maintenance program that includes regular checks of the alternator’s performance to ensure operational reliability.
Recognizing Electrical Overload Symptoms
Electrical overload in an alternator can cause random malfunctions, such as short-circuits or other electrical failures. This is particularly relevant for commercial fleets and public transportation systems, where reliability is paramount. Buyers should consider investing in comprehensive electrical system assessments to identify and mitigate potential overload issues before they escalate into major failures.
Identifying Physical Damage in Alternators
Physical damage to alternators can often be spotted through visible signs like corrosion, wear, or burnt components. This issue is significant for auto parts suppliers and vehicle refurbishers, as it directly impacts the quality of the components they provide. B2B buyers should ensure thorough inspections of alternators during procurement to avoid costly replacements and maintain high standards in their offerings.
Key Industrial Applications of what does a bad alternator look like
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of what does a bad alternator look like | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive Repair | Diagnostic services for electrical issues related to alternators | Enhanced customer satisfaction through timely and accurate repairs | Expertise in alternator diagnostics; availability of parts and tools |
| Transportation & Logistics | Fleet maintenance to ensure vehicle reliability | Reduced downtime and operational costs through proactive maintenance | Access to quality alternator parts; skilled technicians for repairs |
| Mining & Construction | Heavy machinery maintenance and repair | Increased equipment uptime and productivity | Quality assurance for parts; ability to handle rugged operating conditions |
| Agricultural Machinery | Maintenance of agricultural vehicles and equipment | Maximized efficiency and minimized crop loss | Availability of specialized alternator components for diverse machinery |
| Renewable Energy | Maintenance of electric vehicles and hybrid systems | Sustainability through reliable electric systems | Understanding of specific alternator needs for electric and hybrid models |
How is ‘What Does a Bad Alternator Look Like’ Used in Automotive Repair?
In the automotive repair industry, identifying the signs of a faulty alternator is crucial for providing effective diagnostic services. Technicians rely on symptoms such as dimming lights, unusual noises, and battery warning lights to pinpoint alternator issues. By addressing these problems promptly, repair shops can enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty, reducing the likelihood of vehicle breakdowns. For international B2B buyers, sourcing high-quality diagnostic tools and training for technicians can significantly improve service outcomes.
What Role Does Alternator Maintenance Play in Transportation and Logistics?
In the transportation and logistics sector, maintaining a fleet of vehicles is essential for operational efficiency. A bad alternator can lead to unexpected breakdowns, affecting delivery schedules and increasing costs. By implementing routine checks and maintenance focused on alternator health, businesses can minimize downtime and enhance overall fleet reliability. B2B buyers should consider suppliers that offer comprehensive maintenance solutions and high-quality alternator components to ensure fleet longevity and performance.
Why is Alternator Functionality Important in Mining and Construction?
Heavy machinery used in mining and construction relies heavily on electrical systems powered by alternators. A malfunctioning alternator can lead to equipment failure, resulting in costly delays and reduced productivity. Regular maintenance checks to identify alternator issues can help companies maintain optimal equipment performance. Buyers in this sector should prioritize sourcing durable and reliable alternator parts that can withstand harsh operating conditions and ensure the longevity of their machinery.
How Does Agricultural Machinery Benefit from Understanding Alternator Issues?
In agriculture, the reliability of vehicles and machinery is paramount for efficient operations. A faulty alternator can disrupt the functionality of essential equipment, leading to potential crop loss. By recognizing the signs of a bad alternator, farmers can schedule timely maintenance and avoid costly downtime. B2B buyers in this industry should focus on sourcing specialized alternator components that cater to a variety of agricultural machinery, ensuring they meet the unique demands of farming operations.

Illustrative image related to what does a bad alternator look like
What is the Importance of Alternator Maintenance in Renewable Energy?
With the rise of electric vehicles and hybrid systems, understanding alternator functionality is vital in the renewable energy sector. A failing alternator can compromise the efficiency of electric systems, impacting sustainability efforts. Regular inspections and maintenance can help ensure these systems operate effectively. International B2B buyers should seek suppliers who understand the specific alternator requirements for electric and hybrid vehicles, ensuring reliable performance and adherence to environmental standards.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘what does a bad alternator look like’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Unexplained Electrical Failures in Fleet Vehicles
The Problem: For fleet operators, unexpected electrical issues can lead to significant downtime and loss of productivity. Imagine a delivery service that relies on multiple vehicles for timely operations. If one vehicle starts showing signs of electrical malfunctions—like flickering lights or erratic dashboard indicators—this could indicate a failing alternator. The challenge lies in quickly diagnosing the problem before it escalates, especially when each vehicle is critical to maintaining service levels. Delays in repairs not only impact schedules but can also lead to customer dissatisfaction and potential loss of contracts.
The Solution: To mitigate this issue, fleet managers should implement a regular maintenance schedule that includes alternator inspections. Utilizing diagnostic tools that can read the vehicle’s onboard computer will help identify faults early. Additionally, training your maintenance team to recognize common symptoms of alternator failure—such as unusual noises or dimming lights—can facilitate quicker repairs. When sourcing parts, consider partnering with reputable suppliers who can provide quality alternators and components. This proactive approach not only minimizes downtime but also ensures that your fleet remains reliable and efficient.
Scenario 2: Costly Repairs Due to Misdiagnosed Battery Issues
The Problem: Many businesses face the problem of misdiagnosing electrical issues, often assuming that a dead battery is the sole culprit. This misunderstanding can lead to repeated battery replacements without addressing the underlying issue of a faulty alternator. For example, a construction company relying on multiple vehicles may find that their trucks frequently fail to start, resulting in delays and added expenses. If the alternator is not producing enough power to recharge the battery, simply replacing the battery will not resolve the issue, leading to unnecessary costs and operational interruptions.
The Solution: To avoid this pitfall, businesses should adopt a comprehensive diagnostic approach when dealing with electrical failures. Implementing a standard operating procedure that includes testing both the battery and alternator can provide a clearer picture of the issue at hand. When sourcing batteries, always inquire about their compatibility with your alternators and the expected lifespan based on your vehicle’s usage. Additionally, consider investing in training for your technicians on identifying and resolving alternator-related issues. This ensures that problems are correctly diagnosed and resolved, ultimately saving money and improving efficiency.
Scenario 3: Increased Maintenance Costs Due to Alternator Failure
The Problem: A manufacturing company that relies on heavy machinery often experiences increased operational costs due to alternator failures in their equipment. These failures may not be immediately noticeable, leading to sudden breakdowns that halt production. When machinery stops functioning, not only does it incur repair costs, but it also affects the entire production line, leading to delays and increased labor costs. Such incidents can severely impact profitability, especially in industries where time is money.
The Solution: To combat this issue, manufacturers should implement a predictive maintenance program that utilizes data analytics to monitor the health of their alternators and other critical components. By analyzing performance data and identifying patterns that precede alternator failures, businesses can schedule maintenance before a breakdown occurs. Additionally, sourcing high-quality alternators and ensuring that staff are trained in proper installation and maintenance techniques can further reduce the likelihood of unexpected failures. By adopting a proactive approach to equipment maintenance, companies can significantly lower their operational costs and enhance productivity.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for what does a bad alternator look like
What Materials Are Commonly Used in Alternators and How Do They Affect Performance?
When assessing what a bad alternator looks like, understanding the materials used in its construction can provide valuable insights into performance, longevity, and potential failure modes. Here, we analyze several common materials used in alternators, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for international B2B buyers.
1. Copper
Key Properties: Copper is known for its excellent electrical conductivity, with a conductivity rating of around 59.6% IACS (International Annealed Copper Standard). It also has good corrosion resistance, especially when coated.
Pros & Cons: Copper’s high conductivity makes it ideal for windings in alternators, enhancing efficiency. However, it is relatively expensive compared to alternatives like aluminum. Additionally, copper is prone to oxidation, which can affect performance if not properly treated.
Impact on Application: Copper’s compatibility with various electrical systems makes it suitable for high-performance applications. However, in regions with high humidity or corrosive environments, additional protective coatings may be necessary.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards such as ASTM B170 for copper wire is crucial. Buyers from regions like Europe and South America may prefer copper for its reliability, while those in cost-sensitive markets might lean towards alternatives.
2. Aluminum
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight and has good corrosion resistance, with a density approximately one-third that of copper. Its thermal conductivity is lower than that of copper but sufficient for many applications.
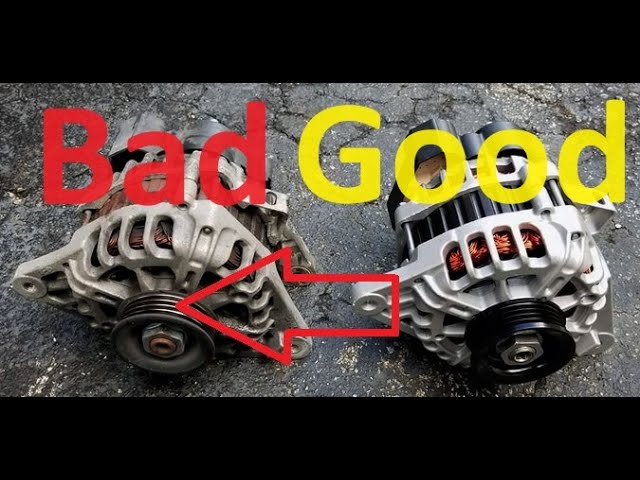

Illustrative image related to what does a bad alternator look like
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of aluminum is its lower cost and weight, which can improve fuel efficiency in vehicles. However, its electrical conductivity is only about 61% of copper’s, which can lead to reduced efficiency in high-load applications.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is often used in the casing and some internal components of alternators. While it offers adequate performance for standard vehicles, it may not be suitable for high-performance applications where efficiency is paramount.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with standards like DIN EN 573 for aluminum alloys. In markets like Africa and the Middle East, where cost and weight are significant factors, aluminum is often favored.
3. Steel
Key Properties: Steel is known for its strength and durability, with high tensile strength and resistance to deformation. It is less conductive than copper and aluminum but is often used for structural components.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of steel is its robustness, making it ideal for housing and mounting components of alternators. However, its weight can be a disadvantage, potentially affecting vehicle performance.
Impact on Application: Steel’s strength makes it suitable for high-stress applications, but its lower conductivity limits its use in electrical components. It is often used in conjunction with other materials to balance performance and durability.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM A36 for structural steel is important. In Europe, buyers may prioritize steel with specific corrosion-resistant coatings, especially in coastal regions.
4. Plastic Composites
Key Properties: Plastic composites are lightweight and resistant to corrosion and moisture. They can be molded into complex shapes, allowing for design flexibility.
Pros & Cons: The lightweight nature of plastic composites can reduce overall alternator weight, improving efficiency. However, they may not withstand high temperatures and mechanical stresses as well as metals.
Impact on Application: Plastic composites are often used for non-structural components like covers and insulators. Their performance can be adequate for standard applications but may fall short in high-performance scenarios.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider compliance with standards like ISO 9001 for quality management. In regions like South America, where environmental conditions can be harsh, durable plastic composites are often preferred.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for what does a bad alternator look like | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Copper | Windings and electrical connections | Excellent conductivity | High cost, oxidation potential | High |
| Aluminum | Casing and some internal components | Lightweight and cost-effective | Lower conductivity than copper | Medium |
| Steel | Structural components and housings | High strength and durability | Heavier, less conductive | Medium |
| Plastic Composites | Non-structural components like covers | Lightweight, corrosion-resistant | Limited temperature resistance | Low |
This analysis provides B2B buyers with a comprehensive understanding of the materials used in alternators, enabling informed decisions based on performance, cost, and regional considerations.

Illustrative image related to what does a bad alternator look like
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for what does a bad alternator look like
What Are the Main Stages of Alternator Manufacturing?
Manufacturing an alternator involves several crucial stages, each designed to ensure the quality and reliability of the final product. Understanding these stages can help B2B buyers make informed decisions when sourcing alternators for their operations.
How Is Material Prepared for Alternator Production?
The first step in alternator manufacturing is the preparation of raw materials. High-quality materials such as aluminum for the housing, copper for windings, and steel for the rotor are selected based on their electrical and thermal conductivity properties. Material preparation involves cutting, shaping, and treating these materials to enhance their durability. Processes like anodizing aluminum and insulating copper wires are common to ensure that the components can withstand the operational stresses and environmental conditions they will face.
What Forming Techniques Are Used in Alternator Manufacturing?
Once the materials are prepared, the next step is forming the various components. This includes die-casting the alternator housing, stamping the rotor and stator, and winding the copper wires. Techniques such as precision die casting and CNC machining are often employed to achieve the required specifications and tolerances. Each component must fit perfectly to ensure efficient power generation and minimize mechanical wear during operation.
How Are Alternators Assembled?
Assembly is a critical phase where individual components are brought together. The stator is placed into the housing, followed by the rotor, which is secured with bearings. The assembly process typically involves automated machinery to ensure consistency and speed, but skilled technicians oversee the assembly to catch any potential errors. Proper alignment and secure connections are essential to prevent premature failure, which is a common issue in faulty alternators.
What Finishing Processes Are Applied to Alternators?
After assembly, alternators undergo various finishing processes to enhance their performance and longevity. These may include surface treatments to prevent corrosion, such as powder coating or painting, and the application of insulation to electrical components. Finishing also involves thorough cleaning to remove any residues from manufacturing processes, which can adversely affect performance.
What Quality Control Measures Are Essential for Alternators?
Quality control (QC) is a vital aspect of alternator manufacturing that ensures each unit meets industry standards and customer expectations. For B2B buyers, understanding the QC processes can provide confidence in the reliability of their purchases.
Which International Standards Are Relevant for Alternator Quality Control?
International standards such as ISO 9001 play a pivotal role in ensuring quality throughout the manufacturing process. ISO 9001 outlines requirements for a quality management system, focusing on continuous improvement and customer satisfaction. Other industry-specific certifications, such as CE marking for compliance with European safety standards and API standards for automotive components, are also crucial for ensuring that alternators are safe and reliable.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Alternator Manufacturing?
Quality control is integrated into the manufacturing process through several key checkpoints:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial inspection ensures that raw materials meet specified standards before production begins.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, random samples of components are tested for dimensional accuracy and electrical performance to catch any defects early.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): After assembly, each alternator undergoes rigorous testing to verify its performance under load conditions. This may include checks for electrical output, noise levels, and thermal performance.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used to Ensure Alternator Quality?
Testing methods are critical in validating the functionality and reliability of alternators. Common techniques include:
- Electrical Testing: This verifies that the alternator produces the correct voltage and current output, ensuring it meets the required specifications.
- Load Testing: Alternators are subjected to various loads to simulate real-world conditions, checking for performance stability and overheating.
- Visual Inspections: Trained technicians examine the alternator for any signs of physical defects, such as improper assembly or surface imperfections.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
For international buyers, especially those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying supplier quality control practices is essential to ensure they receive reliable products.
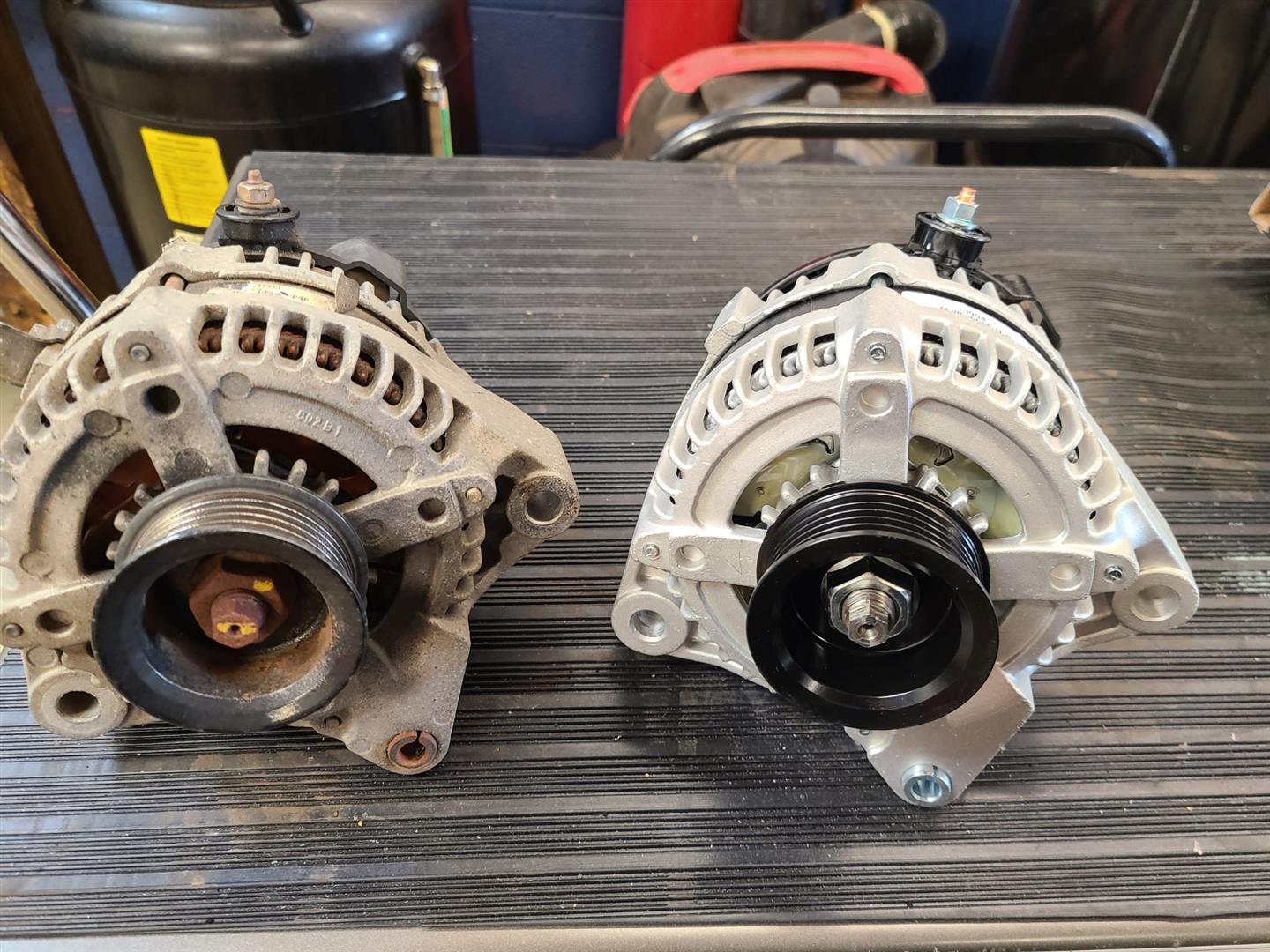

Illustrative image related to what does a bad alternator look like
What Steps Can Buyers Take to Audit Supplier QC Processes?
- Request Documentation: Buyers should ask for detailed quality assurance documentation, including ISO certifications, test reports, and compliance certificates.
- Conduct On-Site Audits: Whenever possible, visiting the manufacturing facility allows buyers to assess the QC processes firsthand and engage with the production team.
- Utilize Third-Party Inspections: Employing independent inspection services can provide an unbiased evaluation of the supplier’s quality assurance practices.
What Are the QC Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International buyers must navigate various regulatory environments and standards. It is crucial to understand the specific requirements in their target markets, such as CE marking in Europe or compliance with local automotive standards in South America. Buyers should also consider the implications of tariffs and import regulations that may affect the overall cost and feasibility of sourcing alternators from international suppliers.
Conclusion
Understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures associated with alternators is vital for B2B buyers looking to source reliable automotive components. By familiarizing themselves with material preparation, forming techniques, assembly, and finishing processes, buyers can make informed decisions. Additionally, being aware of international standards and quality control checkpoints enables buyers to ensure the products they purchase meet their operational needs and quality expectations.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘what does a bad alternator look like’
Introduction
This guide serves as a practical checklist for B2B buyers seeking to understand the signs of a bad alternator. Recognizing these signs is crucial for effective procurement and maintenance strategies, especially for businesses that rely on a fleet of vehicles or automotive parts. By following this checklist, you can ensure that you are sourcing parts that meet your operational needs and maintain the integrity of your vehicles.
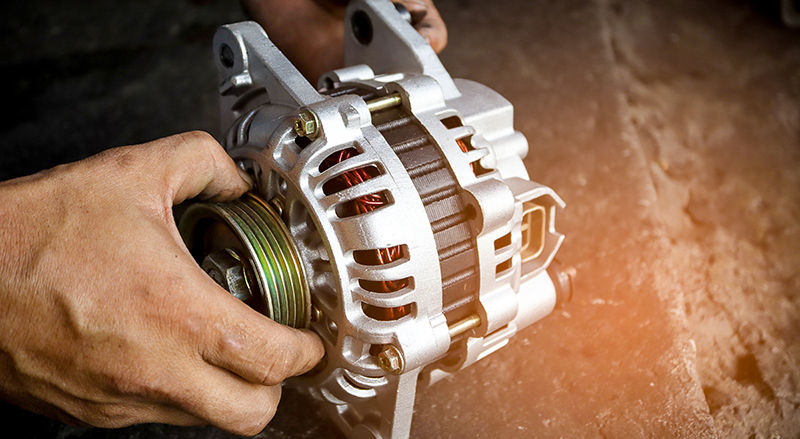

Illustrative image related to what does a bad alternator look like
1. Identify Common Symptoms of Alternator Failure
Understanding the typical signs of a failing alternator is essential. Common symptoms include dimming or flickering lights, unusual electrical malfunctions, and persistent battery issues. Recognizing these indicators early can prevent more extensive damage and costly repairs.
- Dimming lights: If your vehicle’s headlights or dashboard lights appear unusually dim, this could indicate insufficient power supply from the alternator.
- Electrical malfunctions: Look for erratic behavior in electronic systems, such as windows that operate slowly or air conditioning that fails to function properly.
2. Evaluate the Importance of Regular Maintenance
Regular maintenance of the alternator can significantly extend its lifespan. Routine checks can help identify issues like wear and tear before they escalate into serious problems. Establish a maintenance schedule to ensure timely inspections and necessary repairs.
- Scheduled inspections: Implementing a regular inspection routine helps detect early signs of alternator failure.
- Documentation: Keep records of all maintenance activities to track the performance and reliability of your alternators over time.
3. Understand the Role of the Alternator in Vehicle Systems
A thorough understanding of how the alternator functions within a vehicle’s electrical system is critical for effective sourcing. The alternator converts mechanical energy into electrical energy, which powers essential systems and recharges the battery. Knowing its role helps in recognizing the impact of a failing alternator.
- Electrical supply: The alternator supplies power to the battery and electrical components, ensuring that systems operate efficiently.
- Impact on performance: A malfunctioning alternator can lead to broader electrical failures, affecting vehicle safety and functionality.
4. Research Supplier Capabilities and Experience
When sourcing alternators, it’s vital to evaluate potential suppliers for their expertise and reliability. Investigate their history in the industry, customer reviews, and case studies. This will give you confidence in their ability to provide quality products.
- Supplier reputation: Look for suppliers with a proven track record in providing reliable alternators and excellent customer service.
- Technical support: Ensure the supplier offers robust technical support and warranty options for their products.
5. Request Product Specifications and Certifications
Before making a purchase, request detailed product specifications and any relevant certifications. This ensures that the alternators meet industry standards and are suitable for your specific vehicle types.
- Industry standards: Check for compliance with international automotive standards, which indicate quality and reliability.
- Detailed specifications: Understanding the specifications allows you to match the alternator with your vehicle’s requirements effectively.
6. Analyze Total Cost of Ownership
Consider the total cost of ownership when evaluating alternators, which includes purchase price, installation costs, and long-term maintenance. A cheaper alternator might lead to higher costs in the long run if it requires frequent replacements or repairs.
- Lifecycle costs: Assess the longevity and reliability of the alternators you are considering to avoid unexpected expenses.
- Installation and maintenance: Factor in the costs associated with installation and ongoing maintenance to get a clearer picture of the investment required.
7. Establish a Clear Procurement Process
Develop a structured procurement process to streamline the sourcing of alternators. This should include steps for evaluation, approval, and purchase to ensure that you are making informed decisions.
- Approval workflow: Create a clear approval process that involves relevant stakeholders in the decision-making.
- Documentation: Maintain records of all procurement activities to facilitate future sourcing and ensure compliance with company policies.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for what does a bad alternator look like Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Sourcing Alternators?
When evaluating the cost structure for sourcing alternators, various components contribute to the final price. These include:
-
Materials: The primary materials used in alternator manufacturing are copper, aluminum, and various plastics and composites. The quality of these materials directly affects performance and durability, influencing the overall cost.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary significantly depending on geographic location and the skill level required. Regions with higher wages, such as parts of Europe, may see increased labor costs compared to regions in Africa or South America, where labor may be more affordable.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with factory maintenance, utilities, and administrative expenses. Efficient manufacturing processes can help reduce overhead costs, which can be beneficial for pricing.
-
Tooling: Initial tooling costs can be significant, especially for custom alternators. These costs are amortized over production volumes, so higher volume orders can lead to lower per-unit costs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Investing in QC is crucial, particularly for alternators that must meet specific performance standards. Higher QC standards may lead to increased costs but can result in fewer failures and warranty claims.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs, especially for international shipments, are a critical factor in the total cost. Incoterms will dictate responsibilities for transport costs and risks, which can significantly affect pricing.
-
Margin: Suppliers will add a margin to cover their operational costs and profit. This margin can vary widely based on market conditions and the competitive landscape.
What Influences the Pricing of Alternators in the B2B Market?
Several factors can impact the pricing of alternators, especially in international B2B contexts:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Suppliers often provide better pricing for larger orders. Understanding the MOQ can help buyers negotiate better terms and reduce costs.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom alternators tailored to specific vehicle models or performance requirements can lead to higher costs. Buyers should assess whether they need customization or if standard models suffice.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher-quality materials and certifications (like ISO) can increase costs but may also enhance reliability and reduce long-term expenses.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their proven track record, while emerging suppliers might offer competitive prices to gain market share.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the responsibilities laid out in Incoterms is vital for calculating total costs. Terms like FOB (Free On Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) will affect the final price and who bears the shipping risk.
What Should Buyers Consider for Cost-Efficiency When Sourcing Alternators?
International B2B buyers should employ strategic approaches to enhance cost-efficiency:
-
Negotiation: Engage suppliers in discussions about pricing, especially for bulk orders. Emphasizing long-term partnerships can lead to favorable terms.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider not just the purchase price but also potential long-term costs, such as maintenance, warranty claims, and performance reliability. A cheaper alternator may lead to higher TCO if it fails frequently.
-
Pricing Nuances for Different Regions: Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should understand regional pricing differences influenced by local economic conditions, import tariffs, and logistical challenges.
-
Market Research: Conduct thorough research on suppliers and market rates to ensure competitive pricing. Leverage industry connections and forums to gain insights into pricing trends.
Disclaimer on Pricing
Prices for alternators can vary widely based on numerous factors, including model, specifications, and market conditions. The figures mentioned in this analysis are indicative and should be verified with suppliers for the most accurate pricing.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing what does a bad alternator look like With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to ‘What Does a Bad Alternator Look Like’
In the automotive sector, diagnosing issues with vehicle components is crucial for maintaining efficiency and safety. While understanding the signs of a failing alternator is essential, exploring alternative solutions can provide B2B buyers with a broader perspective on managing vehicle maintenance and repairs. Here, we will compare the symptoms of a bad alternator against two alternative solutions: battery management systems and hybrid/electric vehicle technologies.
| Comparison Aspect | What Does A Bad Alternator Look Like | Battery Management System | Hybrid/Electric Vehicle Technologies |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Inconsistent electrical supply, dim lights, frequent dead batteries | Ensures optimal battery life and performance | Provides efficient energy management and reduces dependency on alternators |
| Cost | Replacement costs can range from $250 to $800 | Initial investment varies, often between $100 to $500 | Higher upfront costs ($20,000+) but savings on fuel and maintenance |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires professional diagnostics and potential replacement | Can be integrated into existing systems, but may require training | Requires specialized knowledge for installation and maintenance |
| Maintenance | Regular checks recommended; costly if neglected | Low maintenance; periodic software updates may be needed | Requires regular servicing and software updates |
| Best Use Case | Traditional vehicles with conventional engines | Fleets relying on lead-acid or lithium batteries | Electric or hybrid fleets aiming for sustainability and efficiency |
What Are the Benefits and Drawbacks of Battery Management Systems?
Battery management systems (BMS) serve as a crucial alternative for monitoring battery health and performance in various vehicles. These systems ensure batteries are charged efficiently, extending their lifespan and maintaining optimal performance. The primary advantage of a BMS is its ability to prevent overcharging and deep discharging, which can enhance battery reliability and reduce maintenance costs. However, the initial investment may deter some businesses, particularly those with a limited budget for vehicle technology upgrades.
How Do Hybrid and Electric Vehicle Technologies Compare?
Hybrid and electric vehicle technologies represent a significant shift in the automotive landscape, reducing reliance on traditional alternators. These vehicles utilize advanced energy management systems that optimize power usage and battery performance. The key benefits include lower fuel costs and reduced emissions, appealing to environmentally-conscious businesses. However, the higher initial costs and the need for specialized maintenance can be barriers for some B2B buyers, especially in regions where electric infrastructure is still developing.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Business
When evaluating the best approach for managing vehicle electrical systems, B2B buyers should consider the specific needs of their fleet. For companies operating traditional vehicles, understanding the symptoms of a bad alternator is critical to avoid costly breakdowns. Conversely, investing in battery management systems or transitioning to hybrid/electric technologies may offer long-term savings and sustainability benefits. Ultimately, the decision should be guided by factors such as cost, ease of implementation, and the operational demands of the business. By weighing these alternatives, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their strategic goals.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for what does a bad alternator look like
What Are the Key Technical Properties of a Bad Alternator?
Understanding the technical specifications of alternators is crucial for B2B buyers, particularly when assessing quality and compatibility for automotive applications. Here are some critical properties to consider:
-
Material Grade
The materials used in an alternator, such as aluminum or high-grade steel, affect durability and performance. High-quality materials resist corrosion and wear, which is essential for vehicles operating in diverse climates, particularly in regions like Africa and South America. Choosing alternators made from robust materials can lead to longer life and reduced maintenance costs. -
Tolerance Levels
Tolerance refers to the allowable deviation from specified dimensions in alternator components. High precision in manufacturing tolerances ensures better fitment and performance. A tighter tolerance in the rotor and stator alignment can enhance energy conversion efficiency, which is critical for maintaining battery health and overall vehicle performance. -
Output Voltage and Current Rating
Alternators are rated for specific output voltages (typically 12V) and current (measured in amperes). Understanding these ratings is vital for ensuring that the alternator can meet the electrical demands of the vehicle’s systems. For businesses sourcing alternators, matching these specifications with the vehicle’s requirements is essential to avoid electrical failures and ensure reliable operation. -
Bearing Type
The type of bearings used in the alternator impacts its operational noise and lifespan. Ball bearings tend to offer better performance and longevity compared to sleeve bearings, especially in high-load applications. Buyers should consider the bearing type when evaluating the durability and noise level of the alternator, as this can affect customer satisfaction and service intervals. -
Cooling Mechanism
Effective cooling is essential for alternators to prevent overheating, especially in heavy-duty applications. Alternators may utilize air-cooled or liquid-cooled systems. Knowing the cooling method can help buyers assess performance in high-temperature environments, ensuring the alternator operates efficiently without risking failure. -
Weight
The weight of the alternator can influence installation and overall vehicle performance. Lighter alternators may offer better fuel efficiency, while heavier models may provide enhanced durability. Understanding weight specifications can assist in making informed decisions based on vehicle design and intended use.
What Are the Common Trade Terms Related to Alternators?
Familiarity with industry jargon is important for B2B buyers to navigate procurement processes effectively. Here are some key terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to parts made by the same manufacturer that produced the original components for the vehicle. Sourcing OEM alternators ensures compatibility and quality, which is crucial for maintaining vehicle warranties and performance standards. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is important for businesses looking to optimize inventory levels and cost-effectiveness when purchasing alternators in bulk. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for specific products. By issuing an RFQ for alternators, businesses can compare prices, delivery times, and terms, ensuring they secure the best deal for their needs. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international shipping. They clarify who is responsible for shipping costs, insurance, and risks. Understanding Incoterms is essential for B2B transactions involving alternators, particularly when dealing with international suppliers. -
Warranty Period
The warranty period refers to the timeframe during which the manufacturer guarantees the alternator’s performance. Knowledge of warranty terms can influence purchasing decisions, as longer warranty periods often indicate higher confidence in product reliability. -
Aftermarket Parts
Aftermarket parts are components made by manufacturers other than the OEM. While often more affordable, their quality can vary significantly. Understanding the difference between OEM and aftermarket parts is crucial for businesses aiming to balance cost with reliability and performance.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing alternators, ensuring they meet their operational needs while managing costs effectively.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the what does a bad alternator look like Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends in the Alternator Sector
The global automotive alternator market is experiencing significant shifts influenced by various factors, including technological advancements, changing consumer preferences, and regulatory pressures. One major driver is the increasing reliance on advanced electrical systems in vehicles, including infotainment systems, navigation aids, and safety features. As vehicles become more electrified, particularly with the rise of electric and hybrid models, the demand for high-performance alternators that can efficiently manage power distribution is soaring.
International B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, are witnessing a rise in sourcing trends that emphasize quality and reliability. Buyers are increasingly looking for suppliers who can provide detailed product specifications, including performance metrics and warranty information. Additionally, there’s a growing trend towards the adoption of smart technology in alternators, such as those equipped with integrated sensors for real-time monitoring of performance. This is particularly appealing in markets like Germany, where precision engineering is paramount.
Moreover, the market is becoming more competitive, with suppliers expanding their offerings to include customizable solutions that meet specific regional demands. For instance, buyers from Brazil may prioritize alternators designed for high-temperature environments, while those in Europe might focus on energy-efficient models that comply with stringent emissions regulations. As a result, international buyers must navigate a complex landscape of suppliers while ensuring they align with their operational needs and regulatory requirements.
How Is Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing Impacting the Alternator Market?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing are becoming pivotal considerations for international B2B buyers in the alternator sector. The environmental impact of automotive components, including alternators, has come under scrutiny, prompting buyers to seek suppliers who prioritize eco-friendly manufacturing processes. This includes the use of recycled materials and adherence to stringent waste management practices.
The demand for ‘green’ certifications is also on the rise. Suppliers who can demonstrate compliance with international environmental standards, such as ISO 14001, are more likely to attract buyers concerned about their carbon footprint. Additionally, ethical sourcing practices, including fair labor conditions and transparent supply chains, are increasingly influencing purchasing decisions. Buyers are becoming more discerning, often favoring suppliers who can provide evidence of their ethical practices.

Illustrative image related to what does a bad alternator look like
Incorporating sustainability into sourcing strategies not only meets regulatory requirements but also enhances brand reputation. Companies that prioritize sustainable practices can market themselves as responsible and forward-thinking, appealing to a growing segment of eco-conscious consumers. This trend is particularly relevant in Europe, where consumers are increasingly aware of the environmental impact of their purchases, thus influencing B2B buying behaviors.
What Is the Evolution of the Alternator in the Automotive Industry?
The alternator has undergone significant evolution since its inception in the early 20th century. Originally designed to generate electrical power for basic vehicle functions, modern alternators are now sophisticated components that integrate seamlessly with advanced automotive electrical systems. Early models were primarily mechanical, relying on direct drive from the engine, but advancements in technology have led to the development of more efficient, compact, and lightweight designs.
The transition from mechanical to electronic systems has also transformed alternator functionality. Today’s alternators not only charge the battery but also manage the electrical load of various components, enhancing overall vehicle performance. Innovations such as smart alternators, which adjust output based on real-time power demands, have become increasingly common, especially in high-performance and electric vehicles.
As the automotive industry moves towards electrification, the role of the alternator is set to evolve further. The shift towards hybrid and electric vehicles necessitates new designs and functionalities, making it essential for B2B buyers to stay informed about the latest technological advancements and sourcing options. Understanding this evolution allows buyers to make informed decisions when selecting alternators that align with current and future market demands.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of what does a bad alternator look like
-
1. How can I identify a bad alternator in a vehicle?
Identifying a bad alternator involves observing several symptoms. Look for dashboard warning lights indicating battery or alternator issues, flickering or dimming lights, and unusual electrical malfunctions like windows or air conditioning not operating correctly. Additionally, listen for any unusual whirring or buzzing noises from the engine, which may suggest worn bearings. If the vehicle struggles to start or frequently has a dead battery, these are strong indicators of alternator failure. Regular maintenance checks can help catch these issues early. -
2. What is the most common cause of alternator failure?
The most common causes of alternator failure include wear and tear due to age, exposure to extreme temperatures, and poor electrical connections. Over time, internal components like bearings and diodes can degrade, leading to inefficiencies or complete failure. Contaminants such as dirt and debris can also obstruct the alternator’s functionality. Ensuring regular maintenance and inspections can mitigate these risks and prolong the life of the alternator. -
3. How do I choose the right alternator supplier for my business?
When selecting an alternator supplier, prioritize factors such as reputation, product quality, and reliability. Look for suppliers with certifications and positive reviews from previous clients. Assess their ability to provide customization options that meet your specific needs, such as size and power output. Additionally, consider their logistics capabilities, including shipping times and costs, especially if you operate in regions like Africa or South America where logistics can be challenging. -
4. What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for alternators?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for alternators can vary significantly depending on the supplier and the type of alternator. Generally, MOQs can range from 50 to several hundred units for bulk orders. When sourcing, inquire about MOQs upfront and consider negotiating smaller quantities for initial orders to test product quality. Suppliers may be willing to accommodate smaller orders if you establish a long-term relationship or demonstrate potential for larger future orders. -
5. What payment terms should I expect when sourcing alternators internationally?
Payment terms for international transactions typically include options such as letter of credit, advance payment, or net payment terms (e.g., 30, 60, or 90 days after delivery). Each supplier may have different preferences based on their risk tolerance and relationship with you. Ensure that you clarify these terms before finalizing agreements, and consider using escrow services for larger transactions to protect both parties. Understanding local regulations and currency exchange rates is also crucial in international dealings. -
6. How can I ensure quality assurance (QA) for the alternators I purchase?
To ensure quality assurance for purchased alternators, request detailed product specifications and certifications from the supplier. Conduct audits of the manufacturing process if possible, and consider third-party inspections before shipment. Implement a quality control process upon receiving the products, including testing for functionality and compliance with your specifications. Establishing a clear return policy for defective units is also essential for managing quality issues effectively. -
7. What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing alternators?
When sourcing alternators, logistics considerations include shipping methods, lead times, and customs regulations. Choose a supplier with reliable shipping partners to ensure timely delivery. Be aware of import duties and taxes that may apply to your region, particularly in areas with complex customs processes like Africa and the Middle East. It’s advisable to work with logistics experts to navigate these challenges and ensure smooth transportation of your products. -
8. How can I customize alternators to fit my specific business needs?
Customization of alternators can involve altering specifications such as voltage, amperage, size, or additional features like built-in regulators or connectors. Discuss your requirements with potential suppliers to explore available options. Some manufacturers may offer tailored solutions, while others may have standard models that can be modified. Providing detailed specifications and collaborating closely with the supplier will help ensure that the customized alternators meet your operational requirements effectively.
Top 3 What Does A Bad Alternator Look Like Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Nationwide – Alternator and Battery Insights
Domain: blog.nationwide.com
Registered: 1994 (31 years)
Introduction: Alternator: Powers the car when the engine is running, charges the battery, lasts the lifetime of the car but can wear out. Signs of a bad alternator include dim interior lights, dim or overly bright headlights, growling noises, and burning smells. Battery: Stores power, starts the engine, delivers electricity to the ignition system, works with the alternator, regulates voltage. Signs of a bad bat…
2. Alternator Replacement – Cost Overview
Domain: rac.co.uk
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Alternator replacement cost in the UK ranges from £250 to £800, with an average price of around £535.05 for parts and labor. Replacement costs vary by manufacturer: Audi £628.59, BMW £603.37, Citroen £629.99, Ford £494.90, Mercedes £614.57, MINI £549.36, Nissan £482.06, Peugeot £663.06, Renault £587.78, Toyota £477.93, Vauxhall £477.93, Volkswagen £507.07, Volvo £539.62. RAC Mobile Mechanics offer…
3. TDI Club – Alternator Insights
Domain: forums.tdiclub.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Alternator cost: around $200; Common symptoms of a bad alternator: battery light on, slow starting, dead battery; Recommended testing method: use a digital voltmeter to check voltage (should be over 13.8 volts with engine running); Possible replacement part: voltage regulator; Common failure point: diodes inside the alternator; Replacement options: 120 Amp alternator from Kragen for $165 with limi…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for what does a bad alternator look like
In conclusion, understanding the signs of a bad alternator is essential for international B2B buyers in the automotive industry. The key indicators—such as unusual electrical issues, warning lights, and dimming lights—serve as critical signals that can help prevent more extensive damage and costly repairs. A strategic sourcing approach not only ensures access to high-quality alternators but also fosters relationships with reliable suppliers who can provide timely support and maintenance services.
Illustrative image related to what does a bad alternator look like
As markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe continue to evolve, the demand for efficient and durable automotive components will only grow. By prioritizing quality and reliability in sourcing practices, businesses can enhance their operational efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Looking ahead, it is imperative for B2B buyers to stay informed about the latest advancements in automotive technology and supplier capabilities. Engage with your suppliers proactively, and consider implementing regular maintenance checks to mitigate risks associated with alternator failures. This approach will not only safeguard your fleet but also position your business for sustainable growth in a competitive landscape.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Illustrative image related to what does a bad alternator look like