Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for starter vs alternator vs battery
In the intricate landscape of automotive components, understanding the distinctions between a starter, alternator, and battery is crucial for B2B buyers aiming to optimize vehicle performance and reliability. The challenge lies in effectively sourcing these critical parts while ensuring they meet diverse operational demands across various climates and markets, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This comprehensive guide delves into the functionalities, applications, and specifications of starters, alternators, and batteries, equipping international buyers with the knowledge needed to make informed purchasing decisions.
Throughout this guide, we will explore the various types of each component, their specific applications in different vehicle models, and essential criteria for supplier vetting. Additionally, we will address cost considerations, including average pricing and factors influencing costs in different markets. By providing actionable insights and industry best practices, this resource empowers B2B buyers to navigate the global market confidently. Whether you’re in Brazil, Vietnam, or any other region, understanding these components will not only enhance your procurement strategies but also contribute to improved vehicle uptime and customer satisfaction. Embrace the opportunity to streamline your sourcing process and make knowledgeable investments in your automotive needs.
Table Of Contents
- Top 2 Starter Vs Alternator Vs Battery Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for starter vs alternator vs battery
- Understanding starter vs alternator vs battery Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of starter vs alternator vs battery
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘starter vs alternator vs battery’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for starter vs alternator vs battery
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for starter vs alternator vs battery
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘starter vs alternator vs battery’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for starter vs alternator vs battery Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing starter vs alternator vs battery With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for starter vs alternator vs battery
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the starter vs alternator vs battery Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of starter vs alternator vs battery
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for starter vs alternator vs battery
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Understanding starter vs alternator vs battery Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lead-Acid Battery | Most common type; affordable and widely available. | Automotive, commercial vehicles | Pros: Cost-effective, reliable. Cons: Limited lifespan, sensitive to temperature extremes. |
| Lithium-Ion Battery | Lightweight, high energy density, longer lifespan. | Electric vehicles, portable devices | Pros: Longer life, faster charging. Cons: Higher initial cost, requires specific charging protocols. |
| Gear Reduction Starter | Compact design, increased torque for starting engines. | Heavy machinery, performance vehicles | Pros: Enhanced performance, space-efficient. Cons: Higher cost, may require modifications for installation. |
| Brushless Alternator | Higher efficiency, reduced maintenance needs. | Industrial machinery, automotive | Pros: Greater durability, consistent output. Cons: More complex, higher upfront costs. |
| Belt-Driven Alternator | Standard in most vehicles; powered by engine belt. | Passenger vehicles, light trucks | Pros: Simple design, easy to replace. Cons: Susceptible to belt wear, can be less efficient at low RPMs. |
What are the Characteristics of Lead-Acid Batteries and Their Suitability for B2B Buyers?
Lead-acid batteries are the most prevalent type of battery used in automotive and commercial applications, primarily due to their affordability and reliability. They typically last between 3 to 5 years, making them a practical choice for businesses that require cost-effective solutions. B2B buyers should consider factors such as temperature sensitivity and replacement frequency when selecting lead-acid batteries, as extreme temperatures can significantly reduce lifespan and performance.
Why Choose Lithium-Ion Batteries for Advanced Applications?
Lithium-ion batteries stand out for their lightweight design and high energy density, allowing for longer usage times and faster charging capabilities. They are ideal for electric vehicles and portable devices, where weight and efficiency are critical. B2B buyers should weigh the higher initial investment against the long-term savings from reduced maintenance and replacement frequency, as lithium-ion batteries can last significantly longer than traditional options.
How Do Gear Reduction Starters Enhance Performance in Heavy Machinery?
Gear reduction starters are designed to provide higher torque in a compact form, making them suitable for heavy machinery and performance vehicles. Their efficiency in starting high-compression engines makes them a valuable asset in applications where reliability and performance are paramount. B2B buyers should evaluate the specific torque requirements of their machinery and consider potential installation modifications when opting for gear reduction starters.
What Advantages Do Brushless Alternators Offer for Industrial Applications?
Brushless alternators are known for their higher efficiency and lower maintenance requirements, making them ideal for industrial machinery and automotive applications. They deliver consistent power output and are more durable than traditional models. B2B buyers should consider the complexity and cost of installation, as well as the operational benefits of reduced maintenance downtime when investing in brushless alternators.
How Do Belt-Driven Alternators Function and What Are Their Limitations?
Belt-driven alternators are the standard in most passenger vehicles and light trucks, powered directly by the engine’s belt system. Their simple design facilitates easy replacement, making them a common choice for many businesses. However, B2B buyers should be aware of their susceptibility to belt wear and reduced efficiency at low RPMs, which can impact overall vehicle performance.
Key Industrial Applications of starter vs alternator vs battery
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Starter vs Alternator vs Battery | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive Manufacturing | Production line vehicles require reliable starters, alternators, and batteries to ensure efficiency in assembly processes. | Enhances production efficiency and reduces downtime. | Quality certifications, compatibility with existing systems, and local support services. |
| Agriculture | Tractors and farm equipment rely on robust batteries and starters for reliable operation in remote areas. | Increases productivity during critical farming seasons. | Durability under harsh conditions, ease of maintenance, and availability of spare parts. |
| Transportation & Logistics | Fleet vehicles depend on efficient alternators and batteries for uninterrupted operations and timely deliveries. | Minimizes operational disruptions and enhances fleet reliability. | Bulk purchasing options, warranty terms, and after-sales support. |
| Renewable Energy | Solar power systems use batteries for energy storage, while starters and alternators are crucial for hybrid systems. | Supports sustainable energy solutions and reduces reliance on fossil fuels. | Compatibility with solar technology, energy efficiency ratings, and lifecycle considerations. |
| Construction | Heavy machinery requires dependable starters and batteries for optimal performance on job sites. | Ensures equipment reliability and safety on-site. | Compliance with safety standards, performance under extreme conditions, and local availability. |
How is ‘Starter vs Alternator vs Battery’ Used in Automotive Manufacturing?
In automotive manufacturing, vehicles on production lines must start reliably to maintain efficiency. Starters engage the engine, while alternators charge the battery, ensuring all electrical systems function correctly. Any failure in these components can lead to significant downtime, affecting production schedules. Buyers must consider quality certifications and compatibility with existing assembly line systems, as well as local support for repairs and maintenance.
What Role Do Starters, Alternators, and Batteries Play in Agriculture?
Agricultural machinery, such as tractors, heavily relies on starters and batteries for reliable operation, especially in remote areas where access to power is limited. A robust battery ensures that equipment can start quickly, while a reliable alternator keeps the battery charged during operation. For B2B buyers in this sector, sourcing durable products that can withstand harsh environmental conditions and ensuring easy access to spare parts are critical for maximizing productivity during planting and harvest seasons.
How Do These Components Support Transportation and Logistics?
In the transportation and logistics sector, fleet vehicles are essential for timely deliveries. Starters, alternators, and batteries must function reliably to avoid operational disruptions. A failing battery or alternator can lead to unexpected breakdowns, affecting delivery schedules and customer satisfaction. Businesses should consider bulk purchasing options for cost efficiency, warranty terms for long-term reliability, and after-sales support to ensure quick resolution of any issues.
What Are the Applications in Renewable Energy Systems?
Renewable energy systems, particularly solar power setups, utilize batteries for energy storage, while starters and alternators are vital in hybrid systems. These components ensure that energy is efficiently stored and can be utilized when needed. For international buyers, especially in developing regions, compatibility with existing solar technology and a focus on energy efficiency ratings are essential for optimizing system performance and sustainability.
How Are Starters, Alternators, and Batteries Used in Construction?
Heavy machinery used in construction relies on dependable starters and batteries to ensure optimal performance on job sites. Any failure can lead to project delays and safety hazards. B2B buyers in construction must prioritize compliance with safety standards, the ability of equipment to perform under extreme conditions, and the local availability of these components to minimize downtime and maintain project timelines.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘starter vs alternator vs battery’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty Diagnosing Electrical Issues in Vehicles
The Problem: B2B buyers in the automotive sector often face challenges in diagnosing issues related to starter, alternator, or battery failures. The interconnected nature of these components makes it difficult to pinpoint the exact cause of a vehicle not starting. This uncertainty can lead to unnecessary downtime, increased repair costs, and customer dissatisfaction, especially for fleet operators who rely on their vehicles for business operations. Without a clear understanding of which component is at fault, companies may end up replacing parts that are still functional, further escalating expenses.
The Solution: To tackle this diagnostic challenge, B2B buyers should invest in advanced diagnostic tools that can accurately assess the performance of starters, alternators, and batteries. Tools like multimeters, battery testers, and even onboard diagnostic (OBD) scanners can provide critical data on voltage levels and component performance. Additionally, implementing a systematic troubleshooting protocol can streamline the diagnosis process. For instance, begin with a jump-start test: if the vehicle starts, the battery is likely the issue; if it doesn’t, focus on the starter. Providing training for technicians on these diagnostic methods can enhance their skills and confidence, leading to quicker and more accurate repairs, thus minimizing vehicle downtime.
Scenario 2: Managing Inventory of Critical Components
The Problem: B2B buyers in automotive repair shops or fleet management often struggle with maintaining an optimal inventory of starters, alternators, and batteries. Excessive stock can tie up capital and increase storage costs, while insufficient stock can lead to delays in repairs and lost business opportunities. This balancing act is compounded by the varying lifespans and failure rates of these components, influenced by environmental factors and usage patterns.
The Solution: To optimize inventory management, companies should utilize data analytics and inventory management software to track usage patterns and predict demand. Conducting regular audits of vehicle performance and failure rates can provide insights into the specific needs of the fleet or repair operations. Establishing partnerships with reliable suppliers can also ensure a steady flow of components without overstocking. Implementing a just-in-time (JIT) inventory strategy can help reduce excess stock while ensuring that critical components are available when needed. Additionally, training staff to understand the typical lifespan and failure symptoms of starters, alternators, and batteries can lead to more informed purchasing decisions.
Scenario 3: Understanding Component Lifespan and Environmental Impact
The Problem: For B2B buyers, particularly those operating in regions with extreme temperatures or harsh conditions, understanding the lifespan and performance impact of starters, alternators, and batteries is crucial. Components may fail sooner than expected due to environmental factors such as humidity, extreme heat, or cold, leading to unexpected maintenance costs and service interruptions. Buyers often feel overwhelmed by the need to choose the right products that can withstand these conditions.
The Solution: To ensure component longevity, B2B buyers should prioritize sourcing high-quality products specifically designed for their operational environment. Investing in batteries with better heat resistance or starters and alternators with enhanced sealing against moisture can significantly extend the lifespan of these components. Moreover, providing training for technicians on the effects of environmental factors on component performance can lead to better maintenance practices. Regular inspections and preventive maintenance schedules tailored to the specific conditions faced by the fleet can also help identify potential issues before they lead to failure. By aligning product specifications with environmental needs, companies can reduce costs and improve reliability, ultimately enhancing customer satisfaction.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for starter vs alternator vs battery
What Materials Are Commonly Used in Starters, Alternators, and Batteries?
When selecting materials for starters, alternators, and batteries, B2B buyers must consider various factors, including performance properties, cost, and regional compliance standards. Below, we analyze four common materials used in these components: copper, aluminum, lead, and plastic.
How Does Copper Perform in Starters and Alternators?
Copper is widely used in electrical connections due to its excellent conductivity and thermal properties. It has a high melting point (approximately 1,984°F or 1,085°C) and can withstand significant electrical loads without degrading.
Pros: Copper’s superior conductivity ensures efficient energy transfer, which is essential for starters and alternators that require quick and reliable power delivery. It is also highly durable and resistant to corrosion, making it suitable for various environmental conditions.
Cons: The primary downside of copper is its cost, which is higher compared to alternatives like aluminum. Manufacturing processes can also be complex, especially when forming intricate shapes for specific applications.
Impact on Application: In regions with high humidity or corrosive environments, the corrosion resistance of copper is a significant advantage. However, buyers must ensure proper insulation to prevent short circuits.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards such as ASTM B170 (for copper wire) is crucial. Buyers from Africa and South America should also consider local sourcing to mitigate costs.

Illustrative image related to starter vs alternator vs battery
What Role Does Aluminum Play in Alternators?
Aluminum is often used in alternator housings and components due to its lightweight and good conductivity. With a melting point of about 1,221°F (660.3°C), aluminum can handle moderate thermal stress.
Pros: The lightweight nature of aluminum reduces overall vehicle weight, which can improve fuel efficiency. It is also more cost-effective than copper, making it a popular choice for manufacturers.
Cons: While aluminum has decent conductivity, it is not as efficient as copper. Additionally, it can be more susceptible to corrosion, particularly in salty or humid environments.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is suitable for applications where weight reduction is critical, but buyers must consider protective coatings to enhance corrosion resistance.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in Europe and the Middle East should be aware of compliance with standards such as DIN 1725 for aluminum alloys. Local market preferences may also influence material selection.
Why Is Lead Important for Batteries?
Lead is the traditional material used in lead-acid batteries, which are commonly found in vehicles. Lead has a melting point of approximately 621°F (327.5°C) and provides excellent electrochemical properties.
Pros: The primary advantage of lead is its high energy density, which allows for substantial power storage in a compact form. It is also relatively inexpensive and readily available.
Cons: Lead is heavy and poses environmental hazards if not disposed of properly. Additionally, lead-acid batteries require regular maintenance to ensure longevity.

Illustrative image related to starter vs alternator vs battery
Impact on Application: In regions where battery weight is less of a concern, lead remains a reliable choice. However, buyers must consider recycling regulations and environmental compliance.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards such as JIS C 8702 for lead-acid batteries is essential. Buyers from Africa and South America should also be aware of local regulations regarding lead disposal.
How Does Plastic Factor Into Battery and Starter Design?
Plastic is commonly used for battery casings and starter housings due to its lightweight and insulating properties. It can withstand temperatures up to 200°F (93°C) and offers good chemical resistance.
Pros: The use of plastic reduces overall weight and provides excellent insulation, minimizing the risk of electrical shorts. It is also cost-effective and can be molded into complex shapes.
Cons: While plastic is durable, it can be less resistant to extreme temperatures compared to metals. Over time, exposure to UV light can degrade some plastics, affecting their structural integrity.
Impact on Application: Plastic is ideal for applications where weight savings and insulation are critical. However, buyers should consider the specific type of plastic used to ensure compatibility with battery acids and other chemicals.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards like ASTM D638 for plastic materials is crucial. Buyers should also consider local preferences for materials, especially in regions with strict environmental regulations.
Summary Table of Material Selection
| Material | Typical Use Case for starter vs alternator vs battery | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Copper | Electrical connections in starters and alternators | Excellent conductivity | High cost and complex manufacturing | High |
| Aluminum | Alternator housings and components | Lightweight and cost-effective | Lower conductivity and corrosion susceptibility | Medium |
| Lead | Lead-acid batteries | High energy density and reliability | Heavy and environmental hazards | Low |
| Plastic | Battery casings and starter housings | Lightweight and insulating | Less resistance to extreme temperatures | Medium |
This analysis provides B2B buyers with actionable insights into material selection for starters, alternators, and batteries, emphasizing the importance of performance properties, cost, and compliance with regional standards.

Illustrative image related to starter vs alternator vs battery
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for starter vs alternator vs battery
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Starters, Alternators, and Batteries?
The manufacturing processes for starters, alternators, and batteries are complex and involve several critical stages. Understanding these stages can help B2B buyers assess the quality and reliability of components they are sourcing.
1. Material Preparation
The first step in the manufacturing process involves selecting and preparing the raw materials. For starters and alternators, key materials include high-grade steel, copper wire, and various plastics for insulation. Batteries typically require lead, sulfuric acid, and plastic casings. Suppliers must ensure that materials meet international standards for quality and safety. Rigorous testing for material integrity and compliance with standards such as ISO 9001 is essential at this stage.
2. Forming
In this stage, the prepared materials are shaped into the required components. For starters, this includes forming the housing and producing the armature. Alternators undergo a similar process where the rotor and stator are fabricated. Battery manufacturing involves the creation of lead plates and separators. Advanced techniques such as precision machining, stamping, and injection molding are often employed. The accuracy of forming processes is critical, as any defects can lead to component failure.
3. Assembly
The assembly stage is where various components are brought together. For starters, this involves assembling the motor, solenoid, and gears. In alternators, the assembly includes the rotor, stator, and rectifier components. Battery assembly consists of stacking the lead plates, inserting separators, and filling the cells with electrolyte. Quality control is crucial during this phase; ensuring correct alignment and connections can significantly affect performance and longevity.
4. Finishing
Finishing processes involve surface treatments, such as coating and insulation, to enhance durability and performance. For starters and alternators, this may include applying protective coatings to prevent corrosion. Battery casings are sealed to prevent leakage and ensure safety. This stage often includes final inspections to verify that the components meet the required specifications.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Typically Implemented?
Quality assurance is vital throughout the manufacturing process to ensure that starters, alternators, and batteries are reliable and perform as expected. Various international and industry-specific standards guide these measures.
Relevant International Standards
The ISO 9001 standard is a widely recognized quality management system that ensures consistent quality across manufacturing processes. Compliance with ISO 9001 can provide B2B buyers with confidence in a supplier’s quality management practices. Additionally, specific certifications such as CE (Conformité Européenne) for electrical components or API (American Petroleum Institute) for automotive applications may also be relevant, depending on the market.
QC Checkpoints: What Are They?
Quality control checkpoints are integrated at various stages of the manufacturing process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during the manufacturing process helps identify any defects early, reducing the risk of larger issues later on.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): This stage includes comprehensive testing of finished products to ensure they perform according to specifications. Common tests include electrical performance, load testing, and environmental tests for durability.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers need to conduct thorough due diligence when selecting suppliers for starters, alternators, and batteries. Here are some actionable steps to verify the quality control practices of potential suppliers:
1. Conduct Supplier Audits
Regular audits of suppliers can help verify their manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures. Audits should assess compliance with international standards, the effectiveness of their quality management systems, and adherence to best practices.
2. Request Quality Reports
Buyers should ask suppliers for detailed quality control reports, including data on defect rates, compliance with standards, and results from quality tests. This information can help buyers gauge the reliability of the components they are sourcing.
3. Utilize Third-Party Inspection Services
Engaging third-party inspection agencies can provide an impartial assessment of the supplier’s manufacturing and quality assurance practices. These agencies can perform on-site inspections and testing, ensuring that the products meet the required specifications.
What Are the Quality Control and Certification Nuances for International Buyers?
International buyers, especially those from diverse regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, must consider several nuances regarding quality control and certification:

Illustrative image related to starter vs alternator vs battery
1. Regional Standards and Compliance
Different regions may have specific regulations and standards that apply to automotive components. Buyers should familiarize themselves with local compliance requirements to ensure that the products meet not only international standards but also regional ones.
2. Variability in Quality Standards
Quality standards can vary significantly between suppliers from different countries. Buyers should assess the reliability and reputation of suppliers in their specific region, as well as their ability to consistently meet quality standards.
3. Language and Cultural Barriers
When dealing with international suppliers, language and cultural differences may pose challenges in communication. It is crucial to establish clear lines of communication and ensure that all quality expectations are well understood.
Conclusion
Understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for starters, alternators, and batteries is essential for B2B buyers looking to source reliable automotive components. By focusing on material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing, and ensuring compliance with relevant quality standards, buyers can make informed decisions that enhance their supply chain reliability and performance.

Illustrative image related to starter vs alternator vs battery
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘starter vs alternator vs battery’
Introduction
Navigating the procurement of starters, alternators, and batteries is critical for B2B buyers in the automotive and heavy machinery sectors. This checklist will guide you through essential steps to ensure you select the right components for your needs while minimizing risks associated with quality and supplier reliability. By following this structured approach, you can make informed decisions that enhance operational efficiency and reduce downtime.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outline your requirements for starters, alternators, and batteries. This includes understanding the voltage, size, and capacity needed for your specific applications. By establishing these parameters, you ensure that you only consider products that fit your operational needs, reducing the likelihood of costly mismatches.
- Identify the make and model of the vehicles or machinery.
- Determine the environmental conditions, such as temperature extremes, that may affect performance.
Step 2: Research Market Trends and Technologies
Stay informed about the latest advancements in automotive electrical components. Understanding emerging technologies and trends can help you identify high-quality products that offer better performance and longevity. This knowledge will also empower you to ask the right questions when engaging with suppliers.
- Look for innovations in battery technology, such as lithium-ion versus lead-acid options.
- Evaluate the benefits of high-efficiency alternators and starters that consume less energy.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough due diligence on potential suppliers. A reliable supplier can significantly influence the quality and performance of the products you procure. Review company profiles, certifications, and customer testimonials to gauge their credibility and reliability in the market.
- Request references from other businesses in your industry.
- Check for industry certifications, such as ISO or TS16949, that demonstrate quality management standards.
Step 4: Compare Pricing and Terms
Analyze pricing structures and payment terms from multiple suppliers. While cost is an essential factor, it should not be the only consideration. Ensure that the pricing reflects the quality and reliability of the components offered.
- Look for bulk purchase discounts or loyalty programs.
- Clarify warranty and return policies to safeguard your investment.
Step 5: Test Samples and Request Technical Support
Before finalizing your order, request samples for testing. This step allows you to evaluate the quality and performance of the products in real-world conditions. Additionally, assess the level of technical support offered by the supplier.
- Conduct performance tests to ensure compatibility with your systems.
- Ensure the supplier provides adequate technical documentation and support.
Step 6: Finalize Your Order with Clear Specifications
Clearly communicate your specifications and expectations when placing your order. This includes delivery timelines, quantities, and quality assurance measures. A well-defined order can prevent misunderstandings and ensure timely delivery of the right products.

Illustrative image related to starter vs alternator vs battery
- Use a standardized order form to document all specifications.
- Confirm all details with the supplier before finalizing the transaction.
Step 7: Establish a Long-term Relationship with Suppliers
Consider building long-term partnerships with reliable suppliers. Strong relationships can lead to better pricing, priority service, and improved communication in future transactions. Regularly assess supplier performance to ensure they continue to meet your evolving needs.
- Schedule regular check-ins to discuss performance and any necessary adjustments.
- Share feedback to foster a collaborative relationship that benefits both parties.
By following this practical sourcing checklist, B2B buyers can streamline their procurement process for starters, alternators, and batteries, ultimately enhancing operational efficiency and reducing potential disruptions.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for starter vs alternator vs battery Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Starters, Alternators, and Batteries?
When considering the sourcing of starters, alternators, and batteries, understanding the various cost components is crucial for B2B buyers. Each component incurs distinct costs that contribute to the final price.
-
Materials: The primary materials used in starters, alternators, and batteries include metals like copper and aluminum, as well as plastics and rubber. The quality and sourcing of these materials can significantly affect costs. For instance, high-purity copper used in wiring may lead to higher costs but offers improved conductivity and durability.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region and can affect the overall pricing structure. In regions with higher labor rates, such as Europe, the manufacturing costs may be more substantial than in countries with lower labor costs, such as those in parts of Africa or South America.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to facility operations, utilities, and administrative expenses. Efficient manufacturing processes can minimize overhead, impacting the final pricing favorably.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in tooling for specific designs or customizations can be significant. B2B buyers should consider whether they require standard products or customized solutions, as the latter will typically incur higher tooling costs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing rigorous QC processes ensures that components meet required standards, but it also adds to the cost. Buyers should evaluate the trade-off between quality assurance and pricing, especially when sourcing from suppliers with varying reputations.
-
Logistics: Shipping and transportation costs can fluctuate based on distance, shipping methods, and Incoterms. Understanding these costs is vital, particularly for international transactions where tariffs and customs duties may apply.
-
Margin: Suppliers will include a profit margin in their pricing, which can vary widely based on market conditions and competition. Buyers should conduct market research to understand typical margins in their specific region.
What Influences Pricing for Starters, Alternators, and Batteries?
Several factors influence the pricing of automotive components, and understanding these can help buyers make informed decisions.
-
Volume/MOQ: Bulk purchasing often leads to lower prices per unit. Buyers should negotiate for better pricing based on their order volume, which can significantly impact overall costs.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized components tailored to specific vehicle models may incur higher costs compared to off-the-shelf products. Buyers need to balance the need for customization with budget constraints.
-
Quality and Certifications: Components that meet international quality standards or certifications (e.g., ISO, CE) may command higher prices but provide assurance of reliability and performance.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers play a crucial role in pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium for their proven track record, while newer entrants might offer lower prices to gain market share.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the terms of delivery (e.g., FOB, CIF) is essential for calculating the total landed cost. This includes not just the price of the goods but also shipping, insurance, and duties.
How Can Buyers Optimize Costs and Enhance Value?
To achieve cost efficiency in sourcing starters, alternators, and batteries, B2B buyers should consider the following tips:
-
Negotiate Terms: Engage suppliers in discussions about pricing, payment terms, and delivery schedules. Establishing a good relationship can lead to better deals and flexibility.
-
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Look beyond the initial purchase price. Consider factors like warranty, maintenance, and performance over the product’s lifecycle to assess the true cost.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances for International Transactions: Different regions may have unique pricing structures influenced by local economies, tariffs, and exchange rates. Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should conduct thorough market analysis to avoid unexpected costs.
-
Conduct Supplier Audits: Regularly assess supplier performance and quality. This can help maintain standards and ensure that costs are kept in line with expectations.
Conclusion
Navigating the cost structure and pricing dynamics of starters, alternators, and batteries requires a strategic approach. By understanding cost components, pricing influencers, and optimization strategies, international B2B buyers can make informed purchasing decisions that align with their operational needs and budgetary constraints. Always remember that prices can fluctuate based on market conditions, so continuous monitoring and negotiation are essential for maintaining competitive sourcing.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing starter vs alternator vs battery With Other Solutions
Introduction
In the automotive industry, the synergy between the starter, alternator, and battery is essential for vehicle performance. However, as technology advances, alternative solutions are emerging that can either complement or replace these traditional components. Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of both the conventional trio and alternative technologies can help B2B buyers make informed purchasing decisions that align with their operational needs and budget constraints.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Starter Vs Alternator Vs Battery | Alternative 1: Lithium-Ion Battery | Alternative 2: Capacitor Start Systems |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Reliable but can fail under extreme conditions | High energy density, quick charging | Quick discharge for high power demands |
| Cost | Moderate initial cost, short lifespan | Higher upfront cost, longer lifespan | Lower initial cost, but limited to specific applications |
| Ease of Implementation | Standard installation in most vehicles | Requires specialized installation | More complex; needs additional circuitry |
| Maintenance | Regular checks required; moderate maintenance | Minimal maintenance; long life | Requires periodic checks; less frequent |
| Best Use Case | General automotive use | Electric vehicles, hybrid systems | High-performance applications needing rapid energy release |
Detailed Breakdown
Alternative 1: Lithium-Ion Battery
Lithium-ion batteries are gaining traction in the automotive sector, especially with the rise of electric and hybrid vehicles. Their high energy density allows for longer ranges and faster charging times compared to traditional lead-acid batteries. However, they come with a higher initial cost, making them less accessible for some buyers. Furthermore, the installation requires specialized knowledge, which can add to labor costs. The longevity and minimal maintenance needs of lithium-ion batteries make them a favorable option for companies looking to invest in sustainable technologies.
Alternative 2: Capacitor Start Systems
Capacitor start systems provide a unique approach to automotive starting mechanisms. These systems can discharge energy rapidly, making them suitable for high-performance applications where immediate power is necessary, such as in racing. While they are generally less expensive than traditional starter and battery setups, they require more complex installation and additional circuitry. Maintenance is less frequent, but users must ensure periodic checks to maintain optimal performance. Capacitor systems are ideal for niche markets, but their limited applications may not meet the needs of all buyers.
Conclusion
When considering the right solution for automotive needs, B2B buyers must evaluate their specific requirements, including performance expectations, budget constraints, and ease of implementation. The traditional starter, alternator, and battery trio remains a reliable choice for general automotive applications, but alternatives like lithium-ion batteries and capacitor start systems present compelling advantages for specialized uses. By weighing the pros and cons of each option, buyers can make strategic decisions that enhance their operational efficiency and align with technological advancements in the automotive sector.

Illustrative image related to starter vs alternator vs battery
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for starter vs alternator vs battery
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Starters, Alternators, and Batteries?
Understanding the essential technical properties of starters, alternators, and batteries is crucial for B2B buyers, particularly those involved in automotive procurement or repair services. Here are some critical specifications to consider:
1. Material Grade
The materials used in the construction of starters, alternators, and batteries significantly impact their durability and performance. For instance, copper is often used in windings due to its high conductivity, while aluminum may be used in housings for weight reduction. Selecting components with appropriate material grades ensures longevity and efficiency, which is essential for reducing overall maintenance costs in fleet operations.
2. Voltage Rating
Voltage rating indicates the electrical potential the component can handle. For automotive applications, batteries typically range from 12V to 24V. Understanding voltage ratings is crucial for ensuring compatibility between components, as mismatched voltage can lead to system failures or reduced performance.
3. Current Capacity (Amperage)
Current capacity, measured in Amperes (A), indicates the maximum current a battery can deliver. This specification is vital for starters, as they require a significant initial current to engage the engine. For B2B buyers, selecting a starter with an adequate current capacity can prevent operational failures and ensure reliable vehicle performance.
4. Cycle Life
Cycle life refers to the number of complete charge and discharge cycles a battery can undergo before its capacity significantly diminishes. Batteries with a higher cycle life are more desirable for commercial applications, as they offer better value over time, reducing the need for frequent replacements.
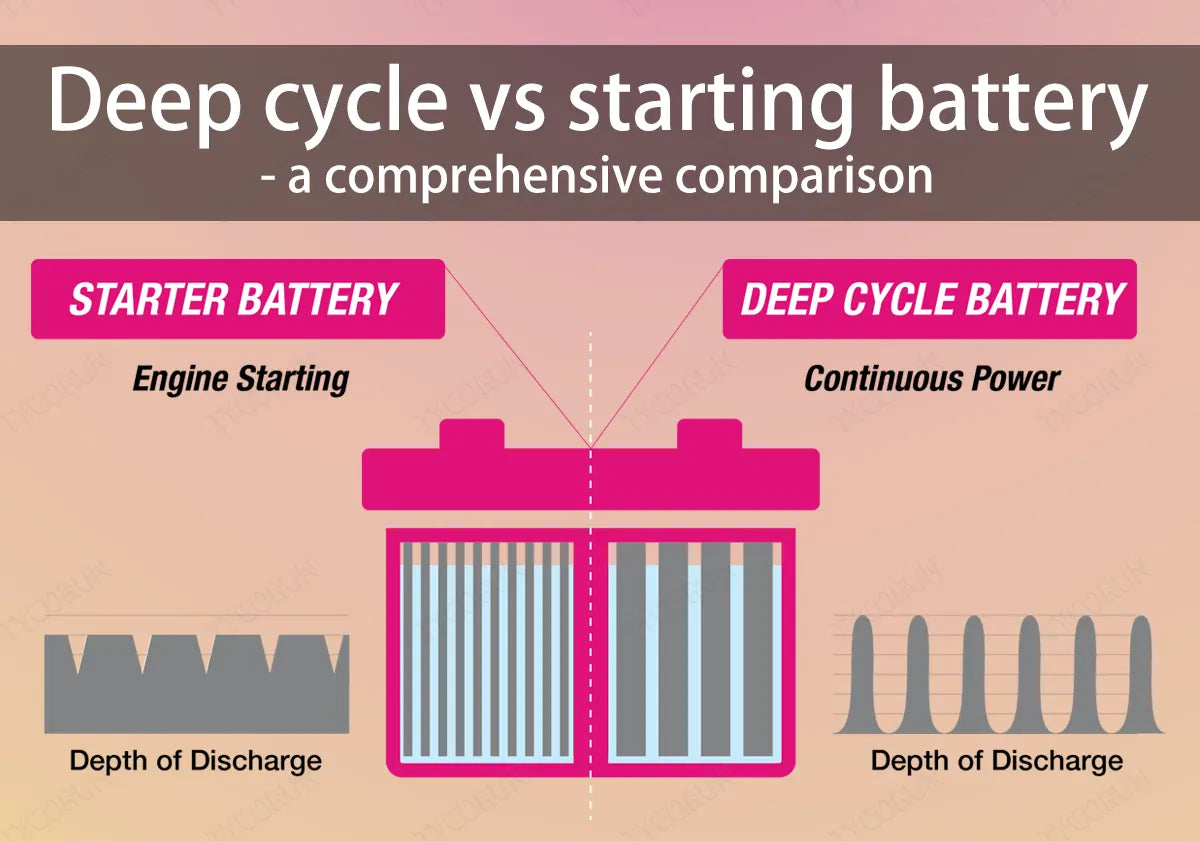
Illustrative image related to starter vs alternator vs battery
5. Temperature Tolerance
Temperature tolerance specifies the range of environmental temperatures in which a component can operate effectively. Starters and batteries may degrade faster in extreme conditions. B2B buyers should consider the operating environment when selecting components, as this can greatly influence their performance and lifespan.
6. Size and Weight Specifications
The physical dimensions and weight of starters, alternators, and batteries can impact vehicle design and efficiency. For instance, lighter components can improve fuel efficiency in vehicles. Understanding size and weight specifications helps buyers ensure compatibility with vehicle designs and performance requirements.
What Are Common Trade Terms in the Automotive Component Industry?
In the automotive component sector, familiarity with trade terminology can streamline procurement and enhance communication. Here are some key terms:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to parts made by the manufacturer of the vehicle or component, ensuring compatibility and quality. For B2B buyers, opting for OEM parts can lead to improved reliability, as they meet the original specifications set by the vehicle manufacturer.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is vital for B2B buyers to manage inventory effectively and ensure they are purchasing sufficient quantities to meet demand without overstocking.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to request pricing and terms for specific products. For B2B buyers, crafting a clear RFQ can lead to better pricing and terms, enabling informed purchasing decisions.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international trade, particularly regarding shipping and delivery. Familiarity with these terms helps B2B buyers negotiate better contracts and understand their obligations in global transactions.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the amount of time it takes from placing an order until the goods are received. Understanding lead times is essential for B2B buyers to manage supply chain logistics effectively and ensure timely availability of components.

Illustrative image related to starter vs alternator vs battery
6. Warranty Period
The warranty period indicates the duration for which a manufacturer guarantees the performance of their product. A longer warranty period may reflect higher quality and reliability, making it an important consideration for B2B buyers aiming to minimize long-term costs.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions when procuring starters, alternators, and batteries, ultimately enhancing operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the starter vs alternator vs battery Sector
What Are the Key Drivers Influencing the Starter, Alternator, and Battery Market?
The global market for starters, alternators, and batteries is influenced by several key drivers, particularly as the automotive industry evolves. One of the primary factors is the increasing demand for electric and hybrid vehicles, which require advanced battery technologies and more efficient starters and alternators. According to industry reports, the global electric vehicle market is projected to grow significantly, particularly in regions such as Europe and South America, where governments are implementing stricter emissions regulations and providing incentives for electric vehicle adoption.
Emerging technologies are also reshaping sourcing trends. The shift towards smart batteries and integrated power management systems enhances vehicle performance and efficiency, prompting manufacturers to invest in innovative solutions. Additionally, the trend towards automation and digitization in supply chains is making it easier for B2B buyers to source components globally. For international buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, this means access to a broader range of suppliers and potentially lower costs, as companies leverage technology for more efficient logistics and inventory management.
Moreover, the ongoing global supply chain disruptions, exacerbated by geopolitical tensions and the COVID-19 pandemic, have highlighted the need for resilience. Buyers are increasingly focusing on diversifying their supplier base to mitigate risks associated with single-source dependency. This trend is particularly relevant for B2B buyers in emerging markets, where establishing local partnerships can enhance supply chain stability.
How Is Sustainability Shaping Sourcing Strategies in the Starter, Alternator, and Battery Sector?
Sustainability is becoming a central theme in the sourcing strategies for starters, alternators, and batteries. As environmental concerns grow, manufacturers and B2B buyers are increasingly prioritizing products that minimize ecological impact. This includes sourcing materials that are recyclable or made from sustainable practices, reducing reliance on finite resources, and decreasing carbon footprints throughout the supply chain.
Ethical sourcing has also gained traction, with buyers seeking suppliers who adhere to fair labor practices and environmentally responsible manufacturing processes. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and ISO 50001 (Energy Management) are becoming essential criteria for B2B buyers looking to ensure that their suppliers meet high environmental and ethical standards.

Illustrative image related to starter vs alternator vs battery
In addition, the push for “green” technologies is leading to innovations in battery technology, such as lithium-ion and solid-state batteries, which offer improved performance and lower environmental impact compared to traditional lead-acid batteries. B2B buyers are encouraged to look for suppliers who invest in research and development to create more sustainable products, as this not only aligns with corporate social responsibility goals but can also enhance brand reputation and customer loyalty.
What Is the Historical Context of Starters, Alternators, and Batteries in the Automotive Industry?
The evolution of starters, alternators, and batteries has been closely linked to advancements in automotive technology. Initially, vehicles relied on hand-cranked engines and simple electrical systems. The introduction of the electric starter in the early 20th century revolutionized vehicle operation, allowing for easier engine ignition and reducing the physical strain on drivers.
As automotive technology progressed, so did the need for more efficient and reliable power systems. The development of the alternator in the 1960s provided a significant upgrade over generators, allowing for better charging of batteries and supporting the increasing electrical demands of modern vehicles. This shift laid the groundwork for the sophisticated electrical systems found in today’s vehicles, which incorporate various electronic components and rely heavily on the synergy between starters, alternators, and batteries.

Illustrative image related to starter vs alternator vs battery
In recent years, the focus has shifted towards enhancing battery technology, particularly with the rise of electric and hybrid vehicles. As manufacturers invest in research and development, the historical context of these components continues to shape the future landscape of the automotive industry, influencing both design and sourcing strategies for B2B buyers.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of starter vs alternator vs battery
-
How do I identify whether the starter, alternator, or battery is causing my vehicle’s issues?
To diagnose the problem, start by checking the battery, which is the most common culprit for starting issues and typically lasts 3-5 years. Look for signs like dim lights, slow cranking, or a swollen battery case. If the battery is functioning well, test the alternator by monitoring the voltage gauge and listening for unusual sounds. Finally, if the starter is suspected, listen for clicking noises or check if the dashboard lights up without the engine cranking. Conducting a jump-start test can also help narrow down the faulty component. -
What is the best battery type for vehicles used in extreme climates?
For vehicles operating in extreme climates, opt for maintenance-free lead-acid batteries or AGM (Absorbent Glass Mat) batteries. These batteries are designed to withstand harsh temperature fluctuations and provide reliable performance. In hot climates, look for batteries with high heat resistance, while in cold climates, ensure the battery has a high cold cranking amp (CCA) rating. Always consult with suppliers about specific performance ratings to match your regional climate needs. -
What are the critical factors to consider when sourcing starters, alternators, or batteries?
When sourcing these components, prioritize quality, compatibility, and supplier reliability. Look for products that meet international standards and certifications, ensuring they are suitable for your vehicle types. Assess the supplier’s reputation through reviews and their experience in the industry. Additionally, inquire about warranties and return policies, as these can protect your investment in case of defects or incompatibility. -
How can I ensure the quality of starters and alternators from international suppliers?
To ensure quality, request samples or certifications before placing larger orders. Conduct factory audits if possible, or rely on third-party quality assurance services that can verify production processes and standards. Establish clear quality control measures, such as inspections during production and pre-shipment checks. It’s also beneficial to build relationships with suppliers who have a proven track record in quality management. -
What customization options are available for batteries and starters?
Many manufacturers offer customization options for batteries and starters, including size, capacity, and terminal configurations to fit specific vehicle models. Discuss your requirements with suppliers to see if they can accommodate your needs, such as branding or unique specifications. It’s crucial to communicate any special requirements upfront to avoid compatibility issues later on. -
What are common minimum order quantities (MOQs) for starters, alternators, and batteries?
MOQs can vary significantly by supplier and product type. Generally, for starters and alternators, MOQs may range from 50 to 200 units, while batteries might require a higher MOQ due to shipping and storage considerations. Always clarify MOQs before engaging in negotiations, as some suppliers may offer flexibility based on your business needs or offer tiered pricing based on order volume. -
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing automotive components internationally?
Payment terms can vary widely based on supplier policies and the buyer’s negotiation power. Common terms include payment in advance, a letter of credit, or 30-60 days net after delivery. It’s essential to discuss payment options upfront to ensure they align with your cash flow needs. Consider using escrow services for high-value transactions to protect against fraud. -
How can I efficiently manage logistics for international shipments of automotive parts?
To manage logistics effectively, partner with experienced freight forwarders familiar with automotive parts shipping. Ensure they understand customs regulations in your destination country to avoid delays. Utilize tracking systems for real-time updates on your shipment status. It’s also wise to maintain open communication with suppliers regarding shipping schedules and any potential issues, allowing for proactive problem-solving.
Top 2 Starter Vs Alternator Vs Battery Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Honda Civic – Starting Issues Diagnosis
Domain: mechanics.stackexchange.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: 2006 Honda Civic EX 1.8L 4 Cylinder; symptoms include weak cranking, failure to start, and a single click when attempting to start; potential issues with starter or alternator; new battery installed; previous battery tested good; starter failure when hot; voltage drop test suggested for diagnosis.
2. Champion Auto Parts – Batteries & Alternators
Domain: championautoparts.com
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
Introduction: Battery: Typically lasts 3-5 years, easiest and cheapest to replace, essential for starter function. Symptoms of a dead battery include inability to start the car. Alternator: Lasts 8-12 years, charges the battery and powers electrical systems. Symptoms of a bad alternator include a dead battery. Starter: Responsible for starting the engine, draws power from the battery. Symptoms of a bad starter …
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for starter vs alternator vs battery
In navigating the intricate landscape of automotive components, understanding the interplay between starters, alternators, and batteries is crucial for international B2B buyers. Each component plays a pivotal role in vehicle operation, and their mutual dependency underscores the importance of strategic sourcing. By identifying quality suppliers and maintaining robust inventory levels, businesses can minimize downtime and enhance customer satisfaction.
Key takeaways include the need for regular maintenance checks to extend the lifespan of these components, as well as the significance of sourcing high-quality parts to ensure reliability. Additionally, being aware of the common failure signs can empower buyers to make informed decisions, whether in procurement or maintenance practices.
As the automotive market continues to evolve, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, there is a growing demand for efficient and durable automotive parts. Suppliers who prioritize quality and customer service will have a competitive edge. Moving forward, international buyers should leverage data-driven sourcing strategies and foster partnerships with reputable manufacturers to secure a sustainable supply chain. Embrace this opportunity to enhance your operations and position your business for future growth in the automotive industry.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.