Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for starter vs alternator vs battery
When sourcing components like starters, alternators, and batteries, international B2B buyers face a multifaceted challenge. These critical automotive parts not only ensure vehicle functionality but also significantly influence operational efficiency and maintenance costs. Understanding the distinctions between these components is essential for making informed purchasing decisions that can impact supply chain reliability and customer satisfaction. This guide offers a comprehensive exploration of starters, alternators, and batteries, detailing their types, applications, and the nuances of performance in various environmental conditions.
For businesses operating in diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including key markets like Saudi Arabia and Nigeria—navigating the complexities of sourcing these components is crucial. This guide empowers buyers by providing actionable insights into supplier vetting processes, cost considerations, and the latest market trends. By understanding the interplay between these parts and their respective roles in vehicle performance, you can optimize your procurement strategy, enhance operational resilience, and ensure compliance with regional standards.
Ultimately, our goal is to equip you with the knowledge to make strategic purchasing decisions that not only meet your immediate needs but also contribute to long-term success in the competitive automotive sector. Whether you are looking to enhance fleet performance or streamline your supply chain, this guide serves as your essential resource.
Table Of Contents
- Top 2 Starter Vs Alternator Vs Battery Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for starter vs alternator vs battery
- Understanding starter vs alternator vs battery Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of starter vs alternator vs battery
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘starter vs alternator vs battery’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for starter vs alternator vs battery
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for starter vs alternator vs battery
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘starter vs alternator vs battery’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for starter vs alternator vs battery Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing starter vs alternator vs battery With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for starter vs alternator vs battery
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the starter vs alternator vs battery Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of starter vs alternator vs battery
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for starter vs alternator vs battery
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Understanding starter vs alternator vs battery Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lead-Acid Battery | Traditional design, affordable, widely used | Automotive, industrial machinery | Pros: Cost-effective, easily sourced. Cons: Limited lifespan, sensitive to temperature. |
| Lithium-Ion Battery | Lightweight, high energy density, longer lifespan | Electric vehicles, portable electronics | Pros: Longer life, fast charging. Cons: Higher initial cost, requires specialized handling. |
| Starter Motor | Converts electrical energy into mechanical energy to start engines | Automotive, marine applications | Pros: Essential for engine ignition. Cons: Can fail due to wear, often requires professional installation. |
| Alternator | Generates electricity while the engine runs, charges the battery | Automotive, heavy machinery | Pros: Provides continuous power, durable. Cons: Can be costly to replace, requires precise alignment. |
| High-Performance Battery | Designed for enhanced power output and durability | Racing, high-demand applications | Pros: Superior performance, optimized for extreme conditions. Cons: Expensive, may require specific vehicle compatibility. |
What Are the Key Features of Lead-Acid Batteries for B2B Buyers?
Lead-acid batteries are the most common type used in automotive applications due to their cost-effectiveness and widespread availability. These batteries typically last between three to five years, making them a reliable choice for many businesses. However, they are sensitive to extreme temperatures and can suffer from reduced performance if not maintained properly. For B2B buyers, understanding the environment in which these batteries will operate is crucial, as it can influence longevity and performance.
How Do Lithium-Ion Batteries Compare in Terms of Suitability?
Lithium-ion batteries have gained popularity in various industries due to their lightweight design and high energy density. They are particularly suitable for electric vehicles and portable electronics, where space and weight are critical factors. While they offer a longer lifespan and faster charging capabilities compared to lead-acid batteries, their higher initial cost and the need for specialized handling can be a barrier for some businesses. Buyers should consider the total cost of ownership when evaluating lithium-ion options.
What Role Does the Starter Motor Play in Automotive Applications?
The starter motor is an essential component in the automotive sector, responsible for initiating engine operation. It converts electrical energy from the battery into mechanical energy, enabling the engine to start. While generally reliable, starters can fail due to wear over time, necessitating professional installation and replacement. Businesses should evaluate the durability and compatibility of starter motors with their vehicle fleets to ensure efficient operations.
Why Is the Alternator Critical for Vehicle Performance?
The alternator plays a vital role in maintaining the electrical system of a vehicle by generating electricity while the engine is running. It charges the battery and powers the vehicle’s electrical components. Alternators typically have a longer lifespan than batteries but can be costly to replace if they fail. B2B buyers should assess the power requirements of their vehicles and consider the quality and reliability of alternators when making purchasing decisions.
What Are the Advantages of High-Performance Batteries for Specialized Applications?
High-performance batteries are specifically designed to deliver enhanced power output and durability, making them ideal for racing and other high-demand applications. These batteries can withstand extreme conditions and provide superior performance compared to standard options. However, they come with a higher price tag and may require specific compatibility with vehicles. Businesses in competitive industries should weigh the benefits of performance against the costs when selecting these batteries.
Key Industrial Applications of starter vs alternator vs battery
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of starter vs alternator vs battery | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive Manufacturing | Quality control in assembly lines for vehicle components | Ensures reliable vehicle performance and reduces recalls | Sourcing high-quality, durable components; compliance with international standards |
| Construction | Powering heavy machinery and equipment | Enhances operational efficiency and reduces downtime | Availability of robust batteries and starters; local support for maintenance |
| Transportation | Fleet management for commercial vehicles | Improves fleet reliability and minimizes operational costs | Bulk purchasing agreements; compatibility with various vehicle models |
| Agriculture | Starting and powering agricultural machinery | Increases productivity and ensures timely operations | Access to agricultural-grade batteries; understanding of environmental impacts |
| Renewable Energy | Backup power systems for solar and wind installations | Provides energy reliability and supports sustainability goals | Sourcing high-capacity batteries; understanding local regulations and incentives |
How Is ‘Starter vs Alternator vs Battery’ Used in Automotive Manufacturing?
In automotive manufacturing, starters, alternators, and batteries are integral to the assembly and quality control processes. These components are tested to ensure they meet performance standards before installation in vehicles. The reliability of these parts directly impacts vehicle performance and customer satisfaction. Buyers should prioritize sourcing components that comply with international quality standards, ensuring long-term reliability and reduced recalls.
What Role Do These Components Play in Construction?
Heavy machinery in the construction sector relies heavily on robust batteries and starters to ensure consistent power supply. These components help start engines and maintain electrical systems, which are critical for operational efficiency. For buyers in this sector, it’s essential to consider sourcing durable products that can withstand harsh environments and provide local maintenance support to minimize downtime.
How Do They Impact Fleet Management in Transportation?
In the transportation industry, fleet management systems utilize starters, alternators, and batteries to maintain the reliability of commercial vehicles. These components are vital for starting engines and powering onboard systems. Businesses benefit from improved reliability and reduced operational costs by ensuring these parts are functioning optimally. Buyers should explore bulk purchasing agreements and ensure compatibility across various vehicle models to streamline operations.
Why Are These Components Essential in Agriculture?
Agricultural machinery, such as tractors and harvesters, relies on effective starters and batteries to operate efficiently. These components help initiate machinery and maintain electrical systems essential for productivity. Buyers should focus on sourcing agricultural-grade batteries that can withstand environmental challenges, ensuring timely operations during critical seasons.
What Is the Importance of These Components in Renewable Energy?
In renewable energy applications, especially solar and wind installations, batteries serve as backup power systems to ensure energy reliability. Starters and alternators are crucial for maintenance and operation of equipment. Businesses can enhance sustainability by investing in high-capacity batteries that meet local regulations. Understanding regional incentives can also guide sourcing decisions to optimize investments in renewable energy solutions.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘starter vs alternator vs battery’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Diagnosing Vehicle Start Issues in Remote Areas
The Problem: Many businesses operating in remote regions, such as mining companies in Nigeria or agriculture suppliers in rural South America, face significant downtime when vehicles won’t start. This can be due to a faulty battery, alternator, or starter. The challenge intensifies in locations where access to professional automotive services is limited. With unreliable transportation, businesses risk delays in operations, increased costs, and loss of productivity. Identifying the root cause of the problem quickly is essential to resume operations and maintain supply chain efficiency.
The Solution: To effectively diagnose the issue, businesses should invest in portable diagnostic tools that can test the battery, alternator, and starter. These tools can help pinpoint the failure without needing immediate access to a mechanic. Additionally, it’s advisable to train staff on basic troubleshooting techniques. For instance, if a vehicle won’t start, they can check for common symptoms: a dead battery often presents as dim lights or slow cranking, while a failing alternator might show flickering lights or electrical malfunctions. Having a reliable source for replacement parts that can be shipped quickly is crucial, ensuring that repairs can be made without lengthy delays. Establishing relationships with local suppliers or international parts distributors can streamline this process.
Scenario 2: Maintaining Fleet Vehicles in Harsh Environments
The Problem: Companies that operate fleets, such as logistics firms in the Middle East or delivery services in Europe, often face the challenge of maintaining vehicle performance in extreme temperatures. High heat can lead to battery failure or damage to the alternator and starter, resulting in unexpected breakdowns. This can be particularly problematic in regions where vehicles are exposed to harsh weather conditions, leading to increased maintenance costs and operational inefficiencies.
The Solution: To mitigate these issues, businesses should implement a proactive maintenance schedule tailored to their specific operating environment. Regularly inspecting battery health, including checking for corrosion and ensuring proper fluid levels, can extend battery life. For alternators and starters, using heat-resistant components and ensuring proper installation can prevent premature failure. Moreover, investing in temperature-resistant batteries can provide added durability. Consider collaborating with suppliers who specialize in heavy-duty automotive components, ensuring that the right products are utilized for extreme conditions. Additionally, training drivers to recognize early signs of electrical issues can lead to timely interventions before they escalate into more significant problems.
Scenario 3: Understanding the Interdependence of Starter, Alternator, and Battery
The Problem: International buyers, particularly those new to the automotive parts industry, often struggle with understanding how the starter, alternator, and battery interact. Misdiagnosing one component for another can lead to unnecessary costs and prolonged vehicle downtime. This lack of knowledge can hinder effective decision-making when sourcing replacements or repairs, impacting the overall efficiency of their operations.
The Solution: To address this knowledge gap, companies should invest in comprehensive training for their procurement and maintenance teams. Workshops or online courses focusing on the functionality and interdependence of these components can empower staff to make informed decisions. Providing easy-to-understand documentation or reference guides that outline how to troubleshoot issues based on symptoms can also be beneficial. Furthermore, collaborating with manufacturers who offer educational resources, such as webinars or detailed product manuals, can enhance understanding. Encouraging a culture of continuous learning within the organization will lead to better maintenance practices, ultimately reducing costs and improving operational efficiency.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for starter vs alternator vs battery
What Are the Key Materials Used in Starters, Alternators, and Batteries?
When selecting materials for starters, alternators, and batteries, understanding the properties, advantages, and limitations of each material is crucial for B2B buyers. This section analyzes common materials used in these components, focusing on their performance characteristics, manufacturing complexities, and suitability for various applications.
What are the Common Materials Used in Starters?
Copper
Copper is widely used in starter motors due to its excellent electrical conductivity and thermal properties. It can withstand high temperatures and has a good resistance to corrosion, which is vital for longevity in automotive applications. The primary advantage of copper is its high conductivity, allowing for efficient power transfer. However, it is relatively expensive compared to alternatives like aluminum and can be prone to oxidation over time, which may affect performance.
Aluminum
Aluminum is often used in starter housings and components due to its lightweight nature and resistance to corrosion. It is less expensive than copper and easier to manufacture, making it a popular choice for many automotive applications. However, aluminum has lower electrical conductivity than copper, which can impact performance in high-load situations. For international buyers, aluminum components must comply with relevant standards to ensure quality and performance.
What Materials Are Commonly Found in Alternators?
Steel
Steel is commonly used for alternator housings and internal components due to its strength and durability. It can withstand high mechanical stress and is resistant to wear and tear. The main disadvantage is that steel is heavier than other materials, which can impact overall vehicle weight. Buyers from regions with high humidity or corrosive environments should consider steel alloys with protective coatings to enhance corrosion resistance.
Plastic Composites
Plastic composites are increasingly used in alternators for non-load-bearing components due to their lightweight and corrosion-resistant properties. They can be molded into complex shapes, allowing for design flexibility. However, they may not withstand high temperatures as well as metals, which could limit their application in high-performance environments. Compliance with international standards for plastics, such as ASTM, is essential for ensuring quality.
What Materials Are Typically Used in Batteries?
Lead
Lead is the traditional material used in lead-acid batteries, which are common in automotive applications. Lead provides good conductivity and can handle high discharge rates. However, lead is heavy, and its environmental impact is a concern, especially in regions with strict regulations. Buyers should ensure that lead-acid batteries comply with local environmental standards to avoid penalties.
Lithium
Lithium is becoming increasingly popular in automotive batteries due to its lightweight and high energy density. Lithium batteries can provide longer life cycles and faster charging times compared to lead-acid batteries. However, they are more expensive and require careful handling to prevent thermal runaway. International buyers should be aware of the specific regulations regarding lithium battery transport and disposal.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Starters, Alternators, and Batteries
| Material | Typical Use Case for starter vs alternator vs battery | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Copper | Starter windings and connectors | Excellent electrical conductivity | High cost, prone to oxidation | High |
| Aluminum | Starter housings and components | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Lower conductivity than copper | Medium |
| Steel | Alternator housings and internal components | Strong and durable | Heavier, may require corrosion protection | Medium |
| Plastic Composites | Non-load-bearing alternator components | Lightweight and design flexibility | Limited temperature tolerance | Low |
| Lead | Lead-acid batteries | Good conductivity and high discharge rates | Heavy, environmental concerns | Medium |
| Lithium | Modern automotive batteries | Lightweight, high energy density | Expensive, requires careful handling | High |
This strategic material selection guide provides valuable insights for international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, ensuring they make informed decisions based on performance, cost, and compliance considerations.

Illustrative image related to starter vs alternator vs battery
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for starter vs alternator vs battery
What Are the Main Manufacturing Processes for Starters, Alternators, and Batteries?
The manufacturing processes for starters, alternators, and batteries involve several critical stages, each designed to ensure efficiency, reliability, and performance. Understanding these processes allows B2B buyers to make informed decisions when sourcing these components.
How Are Materials Prepared for Starters, Alternators, and Batteries?
Material preparation is the first step in the manufacturing process. For starters and alternators, common materials include high-grade steel, copper windings, and various plastics for housing. Batteries primarily use lead, sulfuric acid, and other chemical compounds.
The quality of materials is crucial; B2B buyers should ensure that suppliers source raw materials that meet international standards, such as ASTM or ISO certifications. This guarantees that the components will withstand the rigors of automotive applications, especially in diverse climates across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
What Forming Techniques Are Used in the Production of Starters, Alternators, and Batteries?
Forming techniques vary depending on the component:
-
Starters: The production involves stamping and machining processes to create the housing and internal components. Precision engineering is critical here to ensure that parts fit together seamlessly.
-
Alternators: These components undergo die-casting for the housing and winding processes for the copper wires. The winding must be done with precision to ensure optimal electromagnetic performance.
-
Batteries: The lead plates are cast and then assembled into cells. The paste formation process is essential here, as it directly influences the battery’s performance and lifespan.
Using advanced forming techniques, such as CNC machining and automated assembly lines, can significantly enhance production efficiency and reduce costs, which is particularly beneficial for international B2B buyers looking for competitive pricing.
How Are Starters, Alternators, and Batteries Assembled?
Assembly is a critical stage where precision and quality control are paramount. Each component is carefully assembled to ensure functionality:

Illustrative image related to starter vs alternator vs battery
-
Starters: The assembly includes fitting the armature and field coils into the housing, followed by the installation of the solenoid and other electrical connections.
-
Alternators: Similar to starters, alternators require the integration of various components such as the rotor, stator, and rectifier. Ensuring proper alignment during assembly is crucial to prevent future failures.
-
Batteries: The assembly involves connecting multiple cells, ensuring proper sealing, and filling with electrolyte. Quality assurance during this stage is vital to prevent leaks and ensure longevity.
B2B buyers should look for suppliers that utilize automated assembly processes, as these can reduce human error and improve consistency across production runs.
What Finishing Techniques Are Applied to Starters, Alternators, and Batteries?
Finishing techniques enhance the durability and appearance of the components. Common finishing processes include:
-
Coatings: Applying protective coatings to prevent corrosion, especially for starters and alternators, which are often exposed to harsh conditions.
-
Testing: After assembly, components undergo rigorous testing to ensure they meet performance standards. This includes electrical testing for starters and alternators and capacity testing for batteries.
Finishing processes can significantly affect the product’s lifespan, making it essential for buyers to inquire about the specific techniques employed by their suppliers.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Essential for Starters, Alternators, and Batteries?
Quality assurance (QA) is critical in ensuring that starters, alternators, and batteries meet performance and safety standards. Understanding the QA measures can help B2B buyers choose reliable suppliers.
Which International Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
International standards such as ISO 9001 are fundamental in establishing a quality management system. This standard ensures that manufacturers maintain consistent quality in their processes. Additionally, certifications like CE mark for Europe and API for automotive products are essential indicators of quality and compliance.
For B2B buyers in regions like Africa and South America, being aware of regional certifications can also be beneficial. For example, SABS certification in South Africa or INMETRO in Brazil can ensure that products meet local regulatory requirements.
What Are the Key QC Checkpoints in the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control checkpoints include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials and components upon arrival to ensure they meet specifications.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Ongoing inspections during manufacturing ensure that processes adhere to established standards. This might include dimensional checks and functional testing.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After assembly, final inspections assess the product’s overall quality, including performance testing and safety checks.
These checkpoints are essential for ensuring that any defects are caught early in the manufacturing process, reducing the likelihood of failures in the field.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
Verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is crucial for B2B buyers. Here are some actionable steps:
-
Audits: Conducting regular audits of suppliers can provide insights into their quality management systems. This can include reviewing their manufacturing processes and quality control measures.
-
Reports: Requesting quality assurance reports from suppliers can provide detailed information on their compliance with international standards and internal QA processes.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control systems and product quality.
For international buyers, understanding the nuances of QC certification in different regions can help mitigate risks associated with sourcing from various markets.
What Are the Common Testing Methods for Starters, Alternators, and Batteries?
Testing methods vary by component but typically include:
-
Electrical Testing: For starters and alternators, this involves checking voltage output, current draw, and overall functionality.
-
Cycle Testing: Batteries undergo cycle testing to assess their charge and discharge capabilities, simulating real-world usage.
-
Environmental Testing: Components are subjected to extreme conditions (temperature, humidity) to ensure they can withstand varied environments.
By understanding these testing methods, B2B buyers can better assess the reliability and performance of the components they source, ensuring they meet their operational requirements.
Illustrative image related to starter vs alternator vs battery
In summary, the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for starters, alternators, and batteries are complex and essential for ensuring the reliability and performance of these critical automotive components. B2B buyers should prioritize suppliers that adhere to international standards and demonstrate robust quality control practices to ensure a dependable supply chain.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘starter vs alternator vs battery’
Introduction
Navigating the procurement of automotive components such as starters, alternators, and batteries can be complex, especially for B2B buyers. This guide aims to streamline your sourcing process by providing actionable steps to help you make informed decisions. Understanding the nuances of each component and their interdependence will enhance your purchasing strategy, ensuring that you acquire high-quality products that meet your operational needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is critical before initiating your search for starters, alternators, or batteries. Consider factors such as voltage, amperage, size, and compatibility with existing systems. This will help ensure that the components you source are suitable for the vehicles or equipment you manage.
Step 2: Research Market Trends and Requirements
Stay informed about current market trends and regulatory requirements in your target regions, such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Understanding regional preferences, environmental regulations, and technological advancements will guide your sourcing decisions and help you align with local standards.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a supplier, conduct thorough evaluations. Look for suppliers with established reputations in the industry and request company profiles, case studies, and references from other B2B buyers. Additionally, assess their experience with international shipping and support for your specific geographic markets.
- Check for certifications: Ensure suppliers hold relevant certifications, such as ISO or local quality standards, which can indicate reliability and adherence to quality practices.
Step 4: Request Samples and Specifications
Once you have shortlisted potential suppliers, request samples of their products along with detailed specifications. Testing samples allows you to assess quality firsthand and determine if the products meet your requirements. Pay attention to the build quality, materials used, and performance under typical conditions.
Step 5: Compare Pricing and Terms
Analyze the pricing structures and payment terms from different suppliers. Look beyond just the upfront costs—consider shipping fees, lead times, and warranty conditions. A slightly higher price may be justified by better service or longer-lasting products, so weigh total ownership costs rather than focusing solely on initial expenses.
Step 6: Understand After-Sales Support and Warranty
Evaluate the after-sales support offered by suppliers, as this can significantly impact your operational efficiency. Ensure that they provide adequate warranty coverage and support services for installation and maintenance. A responsive support team can save you time and reduce downtime in case of product issues.
Step 7: Establish a Long-Term Relationship
Once you have selected a supplier, focus on building a long-term relationship. Effective communication, regular feedback, and collaboration can lead to better pricing, priority service, and insights into new product developments. A reliable partnership can enhance your supply chain resilience and responsiveness.
By following these steps, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing starters, alternators, and batteries with greater confidence, ensuring they make informed decisions that align with their operational goals.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for starter vs alternator vs battery Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Sourcing Starters, Alternators, and Batteries?
When sourcing automotive components like starters, alternators, and batteries, understanding the cost structure is essential. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margin.
-
Materials: The cost of raw materials is a significant part of the overall expense. For starters and alternators, key materials include copper, steel, and various plastics. Batteries typically require lead, acid, and separators. Fluctuations in global commodity prices can directly impact sourcing costs.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary based on the region and the complexity of the manufacturing process. For instance, regions with higher labor costs, such as Europe, may have more expensive components compared to those sourced from regions like South America or Africa.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes indirect costs such as utilities, rent, and administrative expenses associated with production facilities. Overhead can significantly affect pricing, particularly if the supplier operates in a high-cost region.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling for specialized components adds to the initial investment. For buyers requiring specific designs or modifications, this cost needs to be factored into the total pricing.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that products meet quality standards is critical, especially for components like batteries that affect vehicle safety. QC processes can increase costs but are necessary for maintaining reliability and compliance with industry regulations.
-
Logistics: Transportation and handling costs can vary widely, especially for international shipments. Factors such as distance, mode of transport, and local customs can influence these expenses.
-
Margin: Suppliers will add a profit margin to cover their operational risks and ensure sustainability. This margin can differ based on the supplier’s market position and the competitive landscape.
What Price Influencers Should Buyers Consider?
Several factors can influence pricing beyond the basic cost structure:
-
Volume/MOQ: Higher order volumes often lead to lower per-unit costs. Buyers should negotiate minimum order quantities (MOQ) to achieve cost savings.
-
Specifications/Customization: Customized components may incur higher costs due to specialized manufacturing processes. Clear communication regarding specifications can help manage expectations and pricing.
-
Material Quality/Certifications: Higher quality materials and certifications (e.g., ISO, CE) can raise costs but also enhance product reliability and safety. Buyers should weigh the benefits of quality against budget constraints.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reputation, reliability, and location can impact pricing. Established suppliers with a proven track record may command higher prices due to their reliability.
-
Incoterms: The choice of Incoterms affects logistics costs and responsibilities. Understanding terms like FOB (Free on Board) and CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) is crucial for calculating total landed costs.
What Are Essential Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficiency?
-
Negotiation: Engage in discussions with multiple suppliers to compare quotes and negotiate better terms. Leverage your purchasing power to secure favorable pricing.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate the TCO, which includes not just the purchase price but also installation, maintenance, and potential downtime costs. This holistic view can uncover hidden savings.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, and the Middle East should be aware of currency fluctuations, import duties, and local taxes that may affect the overall cost.
-
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices: It’s important to note that pricing can vary significantly based on the factors mentioned above. Always seek updated quotes and terms from suppliers to ensure accuracy.
In conclusion, a comprehensive understanding of the cost components, price influencers, and strategic negotiation techniques can empower international B2B buyers to make informed decisions when sourcing starters, alternators, and batteries.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing starter vs alternator vs battery With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Starter, Alternator, and Battery Solutions
In the automotive industry, the traditional components of the starter, alternator, and battery form the core of a vehicle’s electrical system, ensuring it starts and runs efficiently. However, various alternative technologies and methods can achieve similar results, offering potential advantages depending on the specific requirements of businesses, especially in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This analysis explores viable alternatives, comparing them against the conventional starter, alternator, and battery setup.
| Comparison Aspect | Starter Vs Alternator Vs Battery | Alternative 1 Name: Lithium-Ion Battery Systems | Alternative 2 Name: Supercapacitors |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Reliable for conventional engines | Higher energy density, faster charging | Rapid charge/discharge capabilities |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment | Higher upfront costs, but decreasing over time | Lower initial costs, depending on application |
| Ease of Implementation | Standardized installation | Requires specialized installation | Simple integration with existing systems |
| Maintenance | Periodic checks and replacements | Low maintenance after installation | Minimal maintenance, long lifespan |
| Best Use Case | Traditional combustion engines | Electric vehicles, hybrid systems | Applications requiring quick bursts of energy |
In-Depth Analysis of Alternatives
What are Lithium-Ion Battery Systems, and How Do They Compare?
Lithium-ion battery systems are increasingly popular in electric and hybrid vehicles due to their high energy density and efficiency. They can charge faster than traditional lead-acid batteries and provide a longer lifespan. While they require a higher initial investment, their decreasing costs and efficiency make them a compelling option for businesses transitioning to electric fleets or hybrid systems. However, they necessitate specialized installation and management to maximize their performance and safety.

Illustrative image related to starter vs alternator vs battery
How Do Supercapacitors Work and What Are Their Benefits?
Supercapacitors are energy storage devices that excel in applications requiring rapid energy discharge and recharge. They offer a significant advantage over traditional batteries in scenarios where quick bursts of power are essential, such as in regenerative braking systems. Their minimal maintenance requirements and long operational lifespan make them an attractive alternative for specific applications. However, their energy density is lower than that of lithium-ion batteries, which can limit their use in long-range electric vehicles.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Needs
For B2B buyers, the decision to opt for traditional starter, alternator, and battery systems versus alternative technologies like lithium-ion batteries or supercapacitors should hinge on specific operational needs and cost considerations. Businesses focused on sustainability and efficiency may find lithium-ion systems advantageous, particularly for electric and hybrid vehicles. Meanwhile, for applications requiring rapid energy bursts, supercapacitors might provide the necessary performance benefits. Evaluating these factors will enable buyers to select the most suitable solution for their operational demands, ensuring reliability and efficiency in their vehicle fleets.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for starter vs alternator vs battery
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Starters, Alternators, and Batteries?
Understanding the technical properties of starters, alternators, and batteries is crucial for B2B buyers in the automotive industry. Below are some essential specifications that influence purchasing decisions.
What Are the Material Grades and Specifications?
-
Battery Composition: Most automotive batteries are lead-acid, but lithium-ion batteries are gaining popularity due to their higher energy density and lighter weight. Buyers should assess the composition to ensure compatibility with vehicle specifications and longevity, especially in varying climates prevalent in regions like Africa and the Middle East.
-
Alternator Output (Amperage): This specification indicates the maximum electrical current the alternator can produce. A higher output is essential for vehicles with advanced electrical systems, such as those equipped with multiple infotainment systems or electric windows. Understanding the amperage helps buyers select the appropriate alternator to avoid electrical failures.
-
Starter Torque Rating: This is the measure of the starter’s ability to turn the engine over and is typically expressed in Newton-meters (Nm). A higher torque rating is crucial for larger engines or those in cold climates where additional power is needed to start the engine.
-
Temperature Tolerance: This property refers to the operational range of each component. Batteries, starters, and alternators have varying tolerances to heat and cold, impacting their lifespan and performance. For instance, batteries may fail prematurely in extreme temperatures, making this a vital consideration for international buyers.
-
Cycle Life: This refers to the number of charge and discharge cycles a battery can undergo before its capacity significantly decreases. A higher cycle life translates to lower replacement costs over time, making it an important specification for fleet operators and businesses relying on vehicle uptime.
What Trade Terminology Should Buyers Know?
Familiarizing oneself with industry jargon can significantly streamline the purchasing process. Here are some common terms that B2B buyers should understand:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer): This term refers to components made by the same manufacturer that produced the original parts for the vehicle. OEM parts are often preferred for their guaranteed compatibility and quality, which can be a selling point for businesses seeking reliable performance.
-
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): This is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is essential for budget planning and inventory management, particularly for businesses looking to maintain a steady supply of components.
-
RFQ (Request for Quotation): An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for a specific quantity of goods. This process is vital for ensuring competitive pricing and establishing supplier relationships, especially in markets where cost-effectiveness is critical.
-
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms): These are standardized terms used in international trade to clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Knowledge of Incoterms can help buyers navigate complex logistics and reduce the risk of unexpected costs.
-
Aftermarket: This term refers to parts and accessories that are not sourced from the original vehicle manufacturer. Aftermarket products can often be less expensive and are a popular choice for businesses looking to save on maintenance costs without sacrificing quality.
-
Warranty Period: This refers to the time frame during which a manufacturer guarantees the performance of their products. A longer warranty period can indicate confidence in the product’s durability and can be a crucial factor for B2B buyers when evaluating options.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terminologies, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they select the most suitable components for their automotive needs.

Illustrative image related to starter vs alternator vs battery
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the starter vs alternator vs battery Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics and Trends in the Starter, Alternator, and Battery Sector?
The starter, alternator, and battery market is witnessing significant transformations driven by technological advancements, changing consumer preferences, and a growing emphasis on sustainability. Globally, the automotive sector is increasingly adopting electric and hybrid vehicles, which has led to a surge in demand for high-performance batteries and alternators. In regions like Africa and South America, where the automotive market is expanding rapidly, international B2B buyers are focusing on sourcing reliable components that can withstand diverse climatic conditions. The Middle East and Europe are seeing a shift towards premium products with enhanced longevity and efficiency, as consumers become more discerning about quality.
Emerging technologies such as advanced battery management systems (BMS) and smart alternators are reshaping how these components are designed and manufactured. B2B buyers are increasingly looking for suppliers who can provide integrated solutions that include not just parts, but also the technology to monitor and optimize performance. Additionally, the rise of e-commerce platforms and digital marketplaces is making it easier for international buyers to source components from diverse suppliers, increasing competition and driving down prices.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impacting the Starter, Alternator, and Battery Market?
Sustainability is becoming a cornerstone of the starter, alternator, and battery industry. The environmental impact of battery production, particularly in terms of lithium extraction, has raised significant concerns. As a result, B2B buyers are increasingly prioritizing ethical sourcing practices that ensure minimal environmental degradation. Suppliers who can demonstrate compliance with international sustainability standards and offer products with certifications such as ISO 14001 are more likely to gain the trust of international buyers.
The importance of an ethical supply chain cannot be overstated. Businesses that engage in responsible sourcing not only enhance their brand reputation but also mitigate risks associated with supply chain disruptions. Furthermore, the demand for “green” materials is on the rise. Buyers are seeking alternatives such as recyclable batteries and sustainably sourced components, which can help reduce the overall carbon footprint of their operations. Companies that invest in research and development to create innovative, eco-friendly products will be better positioned to capture market share in this evolving landscape.
What Is the Historical Context of the Starter, Alternator, and Battery Industry?
The starter, alternator, and battery industry has evolved significantly since the advent of the internal combustion engine. Initially, vehicles relied on simple battery systems to start engines, which were later complemented by mechanical alternators for recharging. The introduction of advanced materials and technologies in the late 20th century led to the development of more efficient batteries, including lead-acid and lithium-ion variants.
As consumer preferences shifted towards more reliable and high-performing vehicles, the industry responded with innovations such as smart alternators and high-capacity batteries. This evolution has been further accelerated by the increasing adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) in the 21st century, which has reshaped the market dynamics. International B2B buyers today benefit from a rich history of innovation, enabling them to source cutting-edge components that meet the demands of modern automotive applications.
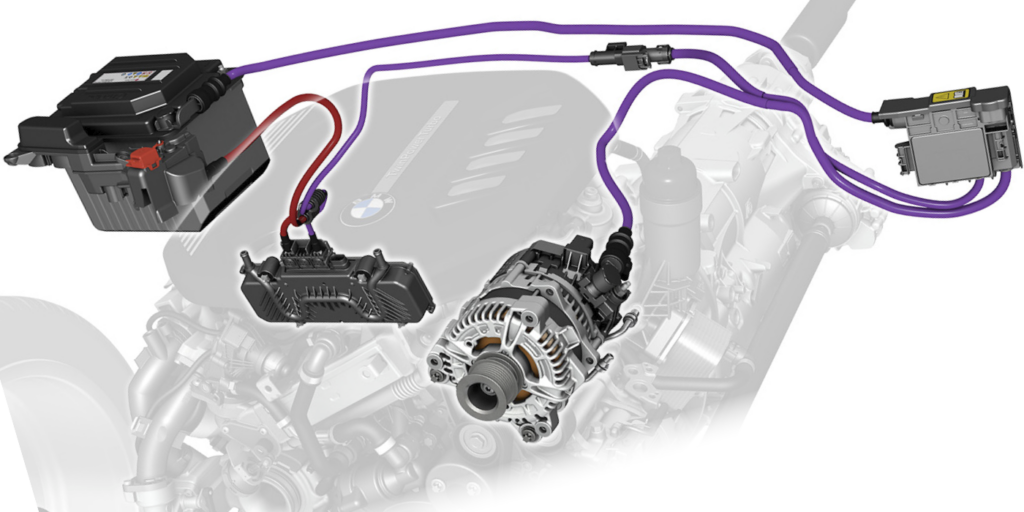
Illustrative image related to starter vs alternator vs battery
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of starter vs alternator vs battery
-
How do I identify whether the issue lies with the battery, alternator, or starter?
To diagnose the problem, start with the battery, as it is the most common culprit. Check for symptoms like slow engine cranking, dim lights, or a bloated battery case. If the battery seems fine, test the alternator by observing if the battery holds a charge after jump-starting. If the vehicle starts but dies shortly after disconnecting the jumper cables, the alternator is likely at fault. Lastly, listen for unusual sounds when trying to start the engine; grinding or clicking noises can indicate starter failure. -
What is the best battery type for commercial vehicles?
For commercial vehicles, opt for heavy-duty lead-acid batteries or AGM (Absorbent Glass Mat) batteries. Lead-acid batteries are cost-effective and widely available, suitable for standard applications. AGM batteries, on the other hand, provide superior performance in extreme conditions and have a longer lifespan, making them ideal for regions with fluctuating temperatures. Consider factors like vehicle load, operating conditions, and maintenance requirements when selecting the best battery type for your fleet. -
What are the key factors to consider when sourcing alternators for bulk purchase?
When sourcing alternators, prioritize quality, compatibility, and warranty terms. Assess the manufacturer’s reputation and look for certifications that ensure product reliability. Understand the technical specifications, such as voltage and amperage ratings, to ensure compatibility with your vehicles. Additionally, inquire about the supplier’s minimum order quantities (MOQ) and lead times, as well as their ability to provide after-sales support and replacement parts. -
How do I vet suppliers for starters, alternators, and batteries?
Begin by researching potential suppliers’ backgrounds, focusing on their experience in the industry and customer reviews. Request samples to evaluate product quality firsthand. Verify their certifications, such as ISO or other relevant standards. Establish communication to gauge their responsiveness and willingness to accommodate your needs, including customization options. Lastly, seek references from other businesses that have sourced similar products from them to validate their reliability. -
What are the payment terms typically offered by suppliers in the automotive parts industry?
Payment terms can vary widely, but common arrangements include net 30, net 60, or payment upon receipt. Some suppliers may offer discounts for early payment or require a deposit for large orders. Ensure you clarify payment methods accepted, such as bank transfers, credit cards, or letters of credit, especially for international transactions. It’s advisable to negotiate terms that align with your cash flow needs while ensuring the supplier’s security. -
What logistics considerations should I be aware of when importing automotive components?
When importing starters, alternators, and batteries, consider shipping methods, customs regulations, and potential tariffs or duties. Assess the total landed cost, including shipping, insurance, and customs fees. Ensure compliance with international shipping regulations, particularly for batteries, which may be classified as hazardous materials. Partnering with a reliable freight forwarder can help navigate the complexities of international logistics and ensure timely delivery. -
How can I ensure quality assurance for automotive parts sourced internationally?
Implement a robust quality assurance (QA) process that includes pre-shipment inspections and testing. Define quality standards in your supplier agreements and request documentation of compliance with these standards. Consider third-party inspection services to verify product quality before shipment. Establish a return policy for defective products to safeguard your investment and maintain good relationships with suppliers. -
Can I customize automotive components for my specific needs?
Many suppliers offer customization options for starters, alternators, and batteries based on your specifications. This may include modifications in size, power ratings, or specific features tailored to your fleet’s requirements. Discuss your needs with potential suppliers during the sourcing process to understand their capabilities and any additional costs or lead times associated with custom orders.
Top 2 Starter Vs Alternator Vs Battery Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Champion Auto Parts – Batteries & Alternators
Domain: championautoparts.com
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
Introduction: Battery: Typically lasts 3-5 years; easiest and cheapest to replace; essential for starter operation. Symptoms of a dead battery include inability to start the car. Alternator: Lasts 8-12 years; charges the battery and powers the electrical system; a dead battery may indicate a failing alternator. Symptoms of a bad alternator include battery not holding charge. Starter: Responsible for starting th…
2. Honda – Civic Starting Issues
Domain: mechanics.stackexchange.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: 2006 Honda Civic EX 1.8L 4 Cylinder; issues with starting; symptoms include weak cranking, clicking noise, and failure to start even with a new battery; potential problems identified: bad starter, bad alternator, or issues with battery cables; troubleshooting methods suggested include checking battery voltage, performing a voltage drop test on cables, and using a voltmeter to assess starter perfor…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for starter vs alternator vs battery
In summary, understanding the distinct roles and interactions of the starter, alternator, and battery is essential for effective vehicle management and maintenance. Each component plays a vital role in the automotive electrical system, and their performance can significantly impact operational efficiency. Strategic sourcing of high-quality parts can ensure reliability and longevity, ultimately reducing downtime and repair costs for businesses that rely on a fleet or automotive services.
For international B2B buyers, particularly those operating in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, investing in reliable suppliers who prioritize quality and performance can yield long-term benefits. As markets evolve and vehicle technology advances, staying informed about the latest developments in automotive components will be crucial for maintaining competitive advantage.
Consider establishing partnerships with manufacturers and distributors who understand regional challenges and can provide tailored solutions. By doing so, businesses can enhance their operational resilience and ensure optimal performance of their vehicles. Embrace this opportunity to innovate your sourcing strategies and drive success in your automotive endeavors.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.

Illustrative image related to starter vs alternator vs battery