Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for difference between relay and solenoid
Understanding the difference between relay and solenoid is crucial for international B2B buyers looking to enhance their operational efficiency. Sourcing the right electromechanical components can be a daunting task, especially when considering varying applications across diverse industries. This comprehensive guide aims to demystify the functionalities, applications, and key distinctions between relays and solenoids, empowering you to make informed purchasing decisions tailored to your specific needs.
The guide explores various types of relays and solenoids, their unique operational mechanisms, and the contexts in which they excel. We will also delve into supplier vetting strategies to ensure quality and reliability, alongside cost considerations that can impact your overall procurement strategy. By presenting a detailed comparison, this resource equips B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including markets like Vietnam and Brazil—with the insights needed to optimize their sourcing processes.
Navigating the global market for these components requires a strategic approach, and this guide serves as your roadmap. With a clear understanding of the capabilities and applications of relays and solenoids, you can confidently select the right products to drive your business success in an increasingly competitive landscape.
Índice
- Top 4 Difference Between Relay And Solenoid Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for difference between relay and solenoid
- Understanding difference between relay and solenoid Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of difference between relay and solenoid
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘difference between relay and solenoid’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for difference between relay and solenoid
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for difference between relay and solenoid
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘difference between relay and solenoid’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for difference between relay and solenoid Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing difference between relay and solenoid With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for difference between relay and solenoid
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the difference between relay and solenoid Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of difference between relay and solenoid
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for difference between relay and solenoid
- Aviso legal importante e termos de utilização
Understanding difference between relay and solenoid Types and Variations
| Nome do tipo | Principais características distintivas | Aplicações B2B primárias | Breves prós e contras para compradores |
|---|---|---|---|
| Relé eletromecânico | Uses electromagnetic coils to open/close contacts; can have multiple contact configurations. | Automation systems, industrial machinery, automotive applications. | Prós: Versatile, can handle high currents. Contras: Slower switching times compared to solid-state alternatives. |
| Relé de estado sólido | Utilizes semiconductor devices for switching; no moving parts, leading to faster operation. | HVAC systems, medical equipment, and process control. | Prós: High reliability, faster switching, longer lifespan. Contras: Typically more expensive, limited current capacity. |
| Linear Solenoid | Converts electrical energy into linear motion; typically features a plunger mechanism. | Door locks, automotive starters, and industrial automation. | Prós: Simple design, effective for linear actuation. Contras: Limited to specific motion types, may require additional components for certain applications. |
| Rotary Solenoid | Generates rotary motion instead of linear; ideal for applications requiring rotational force. | Automotive door locks, camera shutters, and vending machines. | Prós: Efficient for rotational tasks. Contras: More complex design, may not fit all applications. |
| Relé de bloqueio | Maintains its position without continuous power; ideal for power-saving applications. | Smart home devices, industrial control panels, and security systems. | Prós: Energy-efficient, maintains state without power. Contras: More complex circuitry, potential for mechanical wear over time. |
Quais são as principais caraterísticas dos relés eletromecânicos?
Electromechanical relays are widely used in B2B applications due to their ability to control high-power circuits with low-power signals. They feature a coil that generates a magnetic field to open or close contacts, allowing for various configurations, including normally open or normally closed setups. Buyers should consider their specific current handling needs, as these relays can manage significant loads, making them suitable for automation systems and industrial machinery.
How Do Solid-State Relays Differ in Functionality?
Solid-state relays (SSRs) utilize semiconductor technology to perform switching without moving parts, resulting in faster operation and increased reliability. They are ideal for applications where rapid switching is crucial, such as in HVAC systems or medical equipment. While their initial cost may be higher than traditional relays, their longevity and reduced maintenance make them a smart investment for businesses looking to minimize downtime.
What Applications Benefit from Linear Solenoids?
Linear solenoids are designed to convert electrical energy into direct linear motion, making them suitable for applications like door locks and automotive starters. Their simple construction allows for effective mechanical actuation in various industrial automation tasks. When purchasing, businesses should assess the required stroke length and power specifications to ensure compatibility with their systems.
Why Choose Rotary Solenoids for Specific Tasks?
Rotary solenoids provide rotational movement, which is beneficial for applications like automotive door locks and camera shutters. Their design allows for efficient torque delivery in a compact form factor. However, potential buyers should evaluate the complexity of integration and ensure that the solenoid’s specifications align with their operational requirements.
What Advantages Do Latching Relays Offer?
Latching relays are particularly advantageous in applications that require power efficiency, as they maintain their state without needing continuous power. This feature is beneficial for smart home devices and industrial control panels. Buyers should consider the complexity of the circuitry involved and the potential for mechanical wear, as these factors can influence long-term performance and reliability.
Key Industrial Applications of difference between relay and solenoid
| Indústria/Setor | Specific Application of difference between relay and solenoid | Valor/benefício para a empresa | Considerações importantes sobre o fornecimento para esta aplicação |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotivo | Engine starting systems using solenoids and relays for control circuits | Enhanced reliability in starting mechanisms and circuit control | Quality certifications, compatibility with existing systems, local regulations |
| Automação industrial | Control panels utilizing relays for circuit isolation and solenoids for actuation | Improved safety and efficiency in operational processes | Voltage ratings, load capacity, environmental resistance |
| Sistemas HVAC | Solenoids in valve control and relays for fan operation | Energy efficiency and improved climate control | Energy ratings, compliance with local HVAC standards, size specifications |
| Home Appliances | Relays in washing machines for motor control and solenoids in door locks | Increased functionality and user safety | Durability standards, ease of integration, cost-effectiveness |
| Agricultura | Solenoids for irrigation control and relays for automation systems | Optimized resource usage and labor savings | Weatherproofing, response time, compatibility with irrigation systems |
How Are Solenoids and Relays Used in the Automotive Sector?
In the automotive industry, solenoids are critical for engine starting systems, where they engage the flywheel to initiate combustion. Relays, on the other hand, manage various control circuits, ensuring that low-power signals can safely activate high-power components. For international buyers, particularly in emerging markets, sourcing high-quality solenoids and relays is essential for maintaining vehicle reliability and performance. Buyers should focus on quality certifications and compatibility with existing automotive systems to avoid operational failures.
What Role Do Solenoids and Relays Play in Industrial Automation?
In industrial automation, relays are utilized for circuit isolation, allowing low-power control signals to manage high-power equipment safely. Solenoids provide necessary actuation for various mechanical operations, such as opening and closing valves. This combination enhances operational efficiency and safety. Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should consider sourcing components that meet local environmental standards and have robust load capacities to withstand demanding industrial applications.
How Are Solenoids and Relays Applied in HVAC Systems?
In HVAC systems, solenoids control valve operations for refrigerant flow, while relays manage the operation of fans and compressors. This dual functionality leads to improved energy efficiency and climate control. Buyers should prioritize sourcing products that comply with local HVAC regulations and standards, as well as ensure that components are rated for the specific voltage and environmental conditions they will face.
What Are the Applications of Solenoids and Relays in Home Appliances?
Home appliances, such as washing machines and security systems, leverage relays for motor control and solenoids for locking mechanisms. This integration enhances appliance functionality and user safety. International B2B buyers should focus on durability and ease of integration when sourcing these components, as well as consider cost-effectiveness to ensure competitive pricing in their markets.
How Are Solenoids and Relays Used in Agriculture?
In agriculture, solenoids are often employed in irrigation systems to control water flow, while relays automate various agricultural processes, from machinery operation to environmental monitoring. This leads to optimized resource usage and significant labor savings. Buyers in the agricultural sector should look for weatherproof components with fast response times and compatibility with existing systems to enhance efficiency and reliability in their operations.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘difference between relay and solenoid’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Confusion Over Application Suitability of Relays and Solenoids
O problema: B2B buyers often struggle to determine whether a relay or a solenoid is appropriate for their specific application. For instance, a manufacturer in Brazil may be designing an automated assembly line and needs to decide between using solenoids for linear actuation or relays for circuit control. This confusion can lead to improper component selection, resulting in inefficiencies, increased costs, and potential delays in production.
A solução: To address this challenge, buyers should start by clearly defining the requirements of their application. Create a detailed list of the operational needs, such as the required movement (linear vs. switching) and current handling capabilities. Next, consult with suppliers or technical experts who can provide insights into the strengths and weaknesses of each component. For instance, solenoids are ideal for applications requiring direct mechanical movement, such as locking mechanisms or valve control, while relays excel in circuit isolation and control for high-power applications. By matching the component’s characteristics with application needs, buyers can make informed decisions that enhance efficiency and reduce downtime.
Scenario 2: Difficulty in Sourcing Quality Components
O problema: International buyers, especially from regions like Africa and the Middle East, often face challenges in sourcing high-quality relays and solenoids. They may encounter suppliers offering subpar products that do not meet industry standards, leading to operational failures and financial losses. This is particularly critical in sectors like automotive and manufacturing, where reliability is paramount.
A solução: To effectively source quality components, buyers should prioritize working with established suppliers who have a proven track record in the industry. Conduct thorough due diligence by reviewing supplier certifications, customer testimonials, and product specifications. Additionally, consider utilizing online platforms that aggregate multiple suppliers, allowing for price comparison and quality assessment. Establishing direct lines of communication with manufacturers can also facilitate better understanding and assurance of product quality. By investing time in the sourcing process and leveraging trustworthy suppliers, buyers can secure reliable components that will uphold their operational integrity.
Scenario 3: Understanding Technical Specifications and Testing Procedures
O problema: Buyers often find themselves at a loss when it comes to understanding the technical specifications of relays and solenoids, as well as the proper testing procedures to ensure they function correctly. For instance, a buyer in Europe may purchase a solenoid without knowing the necessary voltage ratings or how to test its operational efficiency. This can lead to incorrect installations and operational failures, incurring additional costs for troubleshooting and replacements.
A solução: To mitigate this issue, buyers should invest in training or resources that cover the technical aspects of relays and solenoids. This includes understanding key specifications such as voltage ratings, current capacity, and mechanical movement parameters. Additionally, buyers should familiarize themselves with testing procedures, such as using multimeters to check coil resistance and continuity for relays, or assessing plunger movement in solenoids. Collaborating with suppliers who offer technical support and documentation can further enhance understanding and operational success. Utilizing these resources will empower buyers to make informed choices, leading to improved reliability and performance in their applications.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for difference between relay and solenoid
What Materials Are Commonly Used in Relays and Solenoids?
When selecting materials for relays and solenoids, it is crucial to consider their properties and how they affect performance in various applications. Here, we analyze four common materials used in the construction of these electromechanical devices: copper, steel, plastic, and aluminum.
How Does Copper Influence Performance in Relays and Solenoids?
Copper is widely used for electrical contacts and windings in both relays and solenoids due to its excellent electrical conductivity. Key properties include high thermal and electrical conductivity, allowing for efficient current flow and minimal energy loss.
Prós: Copper’s high conductivity ensures reliable performance, particularly in applications requiring rapid switching. Its durability and resistance to corrosion in many environments also enhance the lifespan of the device.
Contras: However, copper can be relatively expensive compared to other conductive materials, and its weight can be a disadvantage in portable applications. Additionally, copper is prone to oxidation, which can affect performance if not properly treated.
Impacto na aplicação: Copper is suitable for high-current applications, making it ideal for automotive and industrial uses. However, it may not be compatible with certain corrosive environments unless adequately protected.
Considerações para compradores internacionais: Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should ensure compliance with local standards regarding electrical conductivity and corrosion resistance, such as ASTM or JIS specifications.
What Role Does Steel Play in the Construction of Relays and Solenoids?
Steel is primarily used for the housing and core components of solenoids and relays. Its key properties include high tensile strength and magnetic permeability, which enhance the device’s performance.
Prós: Steel’s strength provides structural integrity, making it suitable for demanding applications. Its magnetic properties are beneficial for solenoids, as they help in efficiently converting electrical energy into mechanical motion.
Contras: On the downside, steel can be susceptible to corrosion, which necessitates protective coatings or treatments. Additionally, its weight can be a drawback in applications where weight reduction is critical.
Impacto na aplicação: Steel is ideal for heavy-duty applications, such as industrial machinery. However, its corrosion susceptibility may limit its use in outdoor or humid environments without adequate protection.
Considerações para compradores internacionais: Buyers in the Middle East and Europe should be aware of regional standards for corrosion resistance and mechanical properties, ensuring that the steel used meets local regulations.
How Does Plastic Contribute to the Functionality of Relays and Solenoids?
Plastics are often used for insulation and housing in relays and solenoids due to their lightweight and non-conductive properties. Common types include polycarbonate and nylon.
Prós: Plastics offer excellent electrical insulation, reducing the risk of short circuits. They are also lightweight, which can be advantageous in portable applications.
Contras: However, plastics may have lower thermal and mechanical strength compared to metals, potentially limiting their use in high-temperature or high-stress environments. They can also degrade over time when exposed to UV light or certain chemicals.
Impacto na aplicação: Plastic components are suitable for consumer electronics and applications where weight is a concern. However, their limitations in extreme conditions should be considered.
Considerações para compradores internacionais: Buyers should verify that the plastics used comply with international safety and environmental standards, particularly in markets with stringent regulations like Europe.
What Advantages Does Aluminum Offer in Relay and Solenoid Design?
Aluminum is increasingly used in the construction of relay and solenoid housings due to its favorable properties, including lightweight and good corrosion resistance.
Prós: Aluminum’s lightweight nature makes it ideal for applications where weight savings are essential. Its natural corrosion resistance reduces the need for additional protective coatings, simplifying manufacturing processes.
Contras: However, aluminum can be less durable than steel and may not withstand high mechanical stresses as effectively. Its thermal conductivity is also lower than that of copper, which may impact performance in certain applications.
Impacto na aplicação: Aluminum is well-suited for automotive and aerospace applications where weight is critical. However, its lower strength may limit its use in heavy-duty industrial applications.
Considerações para compradores internacionais: Buyers from regions like South America should consider aluminum’s compliance with local standards for mechanical properties and corrosion resistance, ensuring suitability for their specific applications.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Relays and Solenoids
| Material | Typical Use Case for difference between relay and solenoid | Vantagem principal | Principal desvantagem/limitação | Custo relativo (baixo/médio/alto) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cobre | Electrical contacts and windings in relays and solenoids | Excelente condutividade elétrica | Prone to oxidation and relatively expensive | Alto |
| Aço | Core components and housing for solenoids and relays | High tensile strength and magnetic permeability | Suscetível à corrosão | Médio |
| Plástico | Insulation and housing for lightweight applications | Lightweight and excellent electrical insulation | Lower thermal and mechanical strength | Baixo |
| Alumínio | Housings in automotive and aerospace applications | Leve e com boa resistência à corrosão | Menor durabilidade em comparação com o aço | Médio |
This strategic material selection guide provides international B2B buyers with essential insights into the materials used in relays and solenoids, facilitating informed purchasing decisions that align with their specific application needs.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for difference between relay and solenoid
What Are the Key Manufacturing Processes for Relays and Solenoids?
Understanding the manufacturing processes for relays and solenoids is crucial for B2B buyers looking to source these components. Both devices have distinct manufacturing requirements due to their different functionalities. Here’s a detailed breakdown of the main stages involved in their production.
What Materials Are Used in Manufacturing Relays and Solenoids?
Preparação do material:
The selection of materials is vital in the manufacturing of relays and solenoids. Common materials include:
- Fio de cobre: Used for coil winding due to its excellent conductivity.
- Ferromagnetic Materials: Such as iron or steel, which are used in the core of solenoids to enhance magnetic fields.
- Plastic or Metal Casings: These provide structural integrity and protect the internal components from environmental factors.
Key Techniques in Material Preparation:
Precision cutting and shaping of materials are performed using laser cutting or CNC machining to ensure that all parts fit together seamlessly.
How Are Relays and Solenoids Formed?
Forming Processes:
The forming stage involves transforming raw materials into functional components. The key processes include:
- Coil Winding: For both relays and solenoids, copper wire is wound around a core to create the electromagnetic coil. This is done using automatic winding machines to ensure uniformity and precision.
- Core Formation: The core is shaped and treated to optimize its magnetic properties. Techniques such as heat treatment may be employed to enhance durability.
Assembly Techniques:
The assembly process varies slightly between relays and solenoids but generally includes:
- Mechanical Assembly: Components such as the plunger in solenoids or the armature in relays are assembled with precision to ensure proper alignment and functionality.
- Soldering and Welding: Electrical connections are made using soldering techniques or laser welding to ensure reliable electrical conductivity.
What Finishing Processes Are Involved in Relay and Solenoid Manufacturing?
Finishing Stages:
Finishing processes enhance the performance and longevity of both devices. Common techniques include:
- Revestimento: Applying protective coatings to prevent corrosion and wear. Solenoids may receive a layer of zinc or epoxy, while relays might have a protective enamel coating.
- Testing and Quality Control: Before final packaging, components undergo rigorous testing to ensure they meet performance standards.
What Quality Assurance Standards Are Relevant for Relays and Solenoids?
Quality assurance is a critical aspect of manufacturing relays and solenoids. International standards help ensure that products are reliable and safe for end-users.
Which International Standards Should Buyers Be Aware Of?
ISO 9001 Certification:
This standard focuses on quality management systems and is crucial for manufacturers to demonstrate their commitment to quality. B2B buyers should prioritize suppliers with this certification.
Marcação CE:
For products sold in Europe, CE marking indicates compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
Padrões API:
For applications in the oil and gas sector, API standards may be relevant, ensuring that components meet industry-specific requirements.
Quais são os principais pontos de controlo de qualidade na produção?
Quality control checkpoints ensure that products meet specified standards throughout the manufacturing process. Here are the main checkpoints:
What Are the Stages of Quality Control in Relay and Solenoid Manufacturing?
-
Controlo de Qualidade de Entrada (IQC):
This stage involves inspecting raw materials upon delivery. Buyers should verify that suppliers conduct IQC to prevent defects from entering the production line. -
Controlo de qualidade em processo (IPQC):
During manufacturing, IPQC monitors processes at various stages. This includes checking the winding of coils and the assembly of components to catch defects early. -
Controlo de Qualidade Final (FQC):
Before products are shipped, FQC involves comprehensive testing to ensure that relays and solenoids function correctly under specified conditions. Testing methods might include: -
Testes elétricos: Ensuring that electrical characteristics such as resistance and current capacity meet specifications.
- Testes mecânicos: Assessing the movement of plungers in solenoids or contact performance in relays.
Como os compradores B2B podem verificar o controlo de qualidade dos fornecedores?
B2B buyers should adopt a proactive approach to verify the quality control processes of their suppliers. Here are effective strategies:
What Are Effective Strategies for Verifying Supplier QC?
-
Auditorias:
Conducting regular audits of suppliers can help buyers assess compliance with quality standards. This includes reviewing manufacturing practices and quality documentation. -
Relatórios de qualidade:
Requesting quality assurance reports can provide insights into the supplier’s performance and adherence to standards over time. This documentation should detail testing results and any corrective actions taken. -
Inspeções por terceiros:
Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased evaluation of the supplier’s manufacturing and quality assurance processes. This is particularly important for international transactions where buyers may not have direct oversight.
What Nuances in Quality Control Should International B2B Buyers Consider?
When sourcing relays and solenoids from international suppliers, particularly in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, certain nuances must be considered:
How Do Regional Differences Impact Quality Assurance?
-
Conformidade regulamentar:
Different regions may have varying regulatory requirements. Buyers should familiarize themselves with local standards and ensure that suppliers comply with them. -
Factores culturais:
Understanding the cultural context can impact communication and expectations regarding quality. Clear specifications and open communication lines can mitigate misunderstandings. -
Desafios logísticos:
International shipping can introduce risks related to product integrity. It is advisable for buyers to confirm that suppliers have robust packaging and handling procedures to protect products during transit.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for relays and solenoids, B2B buyers can make informed decisions and select reliable suppliers who meet their operational needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘difference between relay and solenoid’
To assist B2B buyers in understanding the differences between relays and solenoids and making informed purchasing decisions, this practical sourcing guide outlines essential steps to consider during the procurement process. Each step is crucial for ensuring that the selected components meet operational requirements and deliver reliability in applications.
Passo 1: Defina as suas especificações técnicas
Before initiating the procurement process, clearly outline the technical specifications for both relays and solenoids. Consider the required voltage, current ratings, and intended applications. This step is vital because mismatched specifications can lead to component failure and operational inefficiencies.
- Valores nominais de tensão e corrente: Ensure these align with your system requirements to avoid overheating or underperformance.
- Application Needs: Identify whether you require a solenoid for mechanical actuation or a relay for electrical switching.
Passo 2: Research Manufacturer Reputation
Investigate the reputation of potential manufacturers. A reliable supplier will have a history of producing quality components that meet industry standards. This research helps mitigate risks associated with performance and reliability.
- Comentários de clientes: Look for testimonials or case studies from previous customers.
- Certificações do sector: Ensure the manufacturer adheres to relevant quality standards, such as ISO 9001.
Passo 3: Avalie potenciais fornecedores
Before committing to a supplier, it’s crucial to vet them thoroughly. This evaluation should include requesting company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in a similar industry or region.
- Histórico do fornecedor: Assess their experience in the market and their specialization in relays and solenoids.
- Serviços de apoio: Check if they provide technical support and after-sales service.
Passo 4: Solicitar amostras para teste
Always request samples of relays and solenoids before making a bulk purchase. Testing samples allows you to verify performance and compatibility with your existing systems.
- Testes funcionais: Evaluate the samples under real operating conditions to assess their reliability and performance.
- Quality Checks: Inspect for any physical defects or inconsistencies in manufacturing.
Passo 5: Comparar preços e valores
While pricing is a significant factor, it should not be the sole consideration. Compare the overall value offered by different suppliers, including warranty terms, support, and delivery timelines.
- Custo total de propriedade: Factor in potential maintenance costs and the lifespan of the components.
- Descontos para compras em massa: Inquire about discounts for larger orders, which can significantly affect your budget.
Passo 6: Verify Compliance with Regional Standards
Ensure that the components comply with the regulatory standards of the regions where they will be used. This is particularly important for international buyers who may face varying standards across countries.
- Certification Documentation: Request compliance certificates relevant to your industry and location.
- Regulamentos locais: Stay updated on any changes in regulations that may affect your procurement process.
Passo 7: Establish Clear Terms of Agreement
Once you have chosen a supplier, ensure that the terms of agreement are clear and comprehensive. This includes payment terms, delivery schedules, and return policies.
- Revisão do contrato: Have legal counsel review the contract to protect your interests.
- Communication Protocols: Set expectations for communication during the order process to prevent misunderstandings.
By following this sourcing checklist, B2B buyers can confidently navigate the complexities of procuring relays and solenoids, ensuring they select the best components for their specific needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for difference between relay and solenoid Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components When Sourcing Relays and Solenoids?
When considering the sourcing of relays and solenoids, it is essential to understand the various cost components involved. These typically include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and the supplier’s margin.
-
Materiais: The choice of materials significantly impacts the cost. For solenoids, high-quality copper wire and ferromagnetic cores are essential, whereas relays may require specialized contacts and insulating materials. The price of raw materials can fluctuate based on market demand and availability, which can affect overall pricing.
-
Trabalho: Labor costs vary by region. In countries with higher labor costs, such as those in Europe, the manufacturing cost will typically be higher compared to regions like Southeast Asia or parts of Africa. Understanding local labor dynamics is crucial for accurate cost assessments.
-
Custos indiretos de produção: This includes the indirect costs associated with production, such as utilities, rent, and equipment depreciation. Efficient manufacturing processes can help reduce overhead costs, which may be reflected in the pricing.
-
Ferramentas: Custom tooling for specialized applications can be a significant upfront cost. For solenoids and relays with unique specifications, investing in tailored tooling may be necessary, but it can lead to higher initial costs.
-
Controlo de Qualidade (QC): Ensuring product quality through rigorous QC processes can add to the overall cost. Buyers should evaluate the QC measures in place, as well as any certifications that may be required, such as ISO standards, which can influence the price.
-
Logística: Shipping costs can vary greatly depending on the mode of transport, distance, and Incoterms. International buyers should factor in customs duties and taxes, which can add to the total cost.
-
Margem: Suppliers typically include a profit margin in their pricing. This margin can vary based on competition, brand reputation, and the complexity of the product.
What Influences the Pricing of Relays and Solenoids?
Several factors can influence the pricing of relays and solenoids, which buyers should consider:
-
Volume/MOQ (Quantidade mínima de encomenda): Suppliers often offer better pricing for larger orders. Buyers should assess their needs and consider negotiating terms that allow for bulk purchasing to reduce unit costs.
-
Especificações e personalização: Custom specifications can lead to increased costs due to the need for specialized materials or manufacturing processes. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid unexpected costs.
-
Materiais e certificações de qualidade: Higher quality materials and additional certifications can drive up costs but may offer better performance and reliability. Buyers should weigh the benefits of investing in higher-quality products against budget constraints.
-
Fatores relacionados ao fornecedor: The supplier’s reputation, experience, and location can influence pricing. Established suppliers with strong quality assurance processes may command higher prices but offer better reliability.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the implications of different Incoterms is crucial for international buyers. Terms like FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) can significantly affect the total landed cost.
What Tips Can Help Buyers Negotiate Better Prices for Relays and Solenoids?
To ensure cost efficiency, international buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should consider the following tips:
-
Negociar termos: Don’t hesitate to negotiate pricing and payment terms. Suppliers may be willing to offer discounts or better terms for larger orders or long-term contracts.
-
Foco no custo total de propriedade: Evaluate the total cost of ownership rather than just the initial purchase price. Consider factors such as durability, maintenance costs, and energy efficiency to make informed decisions.
-
Leverage Local Knowledge: Utilize local representatives or agents who understand the market dynamics and can help navigate negotiations with suppliers.
-
Mantenha-se informado sobre as tendências do mercado: Keeping abreast of market trends and material costs can empower buyers to make timely purchasing decisions, especially when prices are favorable.
-
Considerar fornecedores alternativos: Exploring multiple suppliers can provide leverage in negotiations and help identify competitive pricing structures.
Isenção de responsabilidade sobre preços indicativos
It is important to note that prices for relays and solenoids can vary widely based on the aforementioned factors. Buyers should conduct thorough market research and obtain multiple quotes to ensure they are receiving competitive pricing tailored to their specific needs.
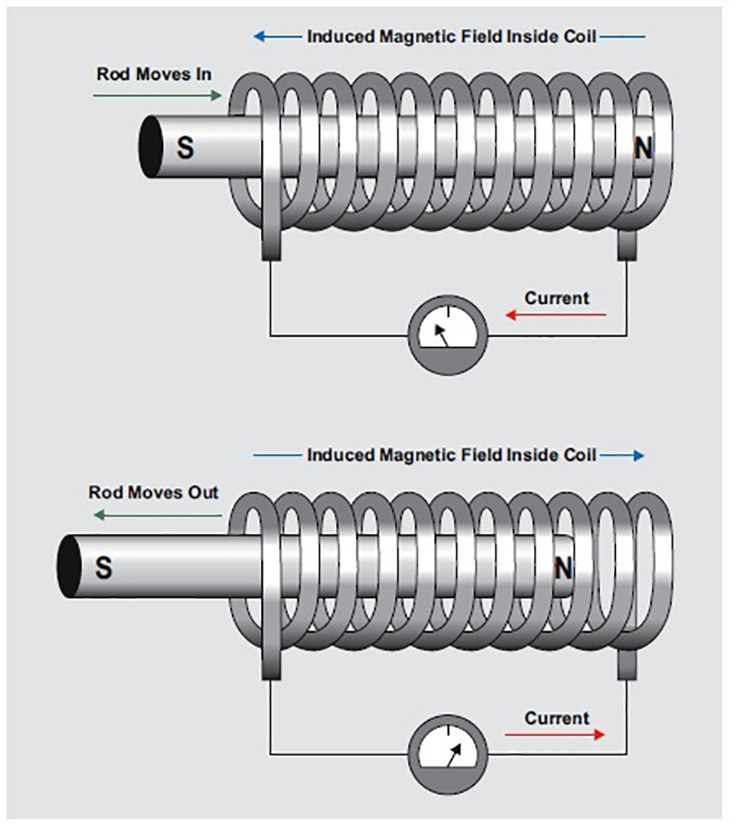
Illustrative image related to difference between relay and solenoid
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing difference between relay and solenoid With Other Solutions
Introduction to Alternatives in Electromechanical Devices
When evaluating the functionalities of relays and solenoids, it’s essential to consider viable alternatives that may provide similar solutions depending on specific application needs. Various technologies offer unique advantages and drawbacks, which can significantly impact operational efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and ease of implementation for international B2B buyers. This analysis compares relays and solenoids against two notable alternatives: contactors and actuators.
Tabela comparativa
| Aspecto comparativo | Difference Between Relay and Solenoid | Contactor | Actuator |
|---|---|---|---|
| Desempenho | Limited to low-current applications | Handles high currents | Provides precise movement |
| Custo | Generally low cost | Higher than relays | Varies widely |
| Facilidade de implementação | Simple wiring | More complex | May require integration |
| Manutenção | Manutenção mínima necessária | Necessidade de controlos regulares | Maintenance depends on type |
| Melhor caso de uso | Low-power control circuits | Industrial machinery | Robotics and automation |
Discriminação detalhada das alternativas
What Are Contactors and How Do They Compare?
Contactors are electromechanical switches specifically designed to control high-power applications, such as motors and lighting systems. They can handle larger currents than relays and are ideal for industrial environments where robust performance is necessary. While contactors generally have a higher upfront cost compared to relays, they provide superior durability and reliability for high-load applications. However, their complexity in wiring and installation may pose challenges for some users, especially in smaller-scale operations.
How Do Actuators Function and What Are Their Benefits?
Actuators are devices that convert energy into motion, providing precise control over mechanical movements. They can be pneumatic, hydraulic, or electric, offering a wide range of functionalities from simple linear movements to complex, programmable actions. While actuators can be more expensive than both relays and solenoids, they excel in applications requiring high precision and repeatability, such as robotics and automated systems. The trade-off includes potentially higher maintenance needs, especially in hydraulic or pneumatic systems, which may require regular checks for leaks and pressure levels.
Conclusão: escolhendo a solução certa para as suas necessidades
In selecting between relays, solenoids, contactors, and actuators, B2B buyers should assess their specific application requirements, including current handling capacity, cost constraints, and maintenance capabilities. For basic control of low-power circuits, relays or solenoids may suffice. However, for high-load operations or applications demanding precision, contactors or actuators could be the optimal choice. Understanding these distinctions will empower buyers to make informed decisions that align with their operational goals and budget considerations, ultimately enhancing their system’s efficiency and effectiveness.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for difference between relay and solenoid
What Are the Key Technical Properties That Differentiate Relays and Solenoids?
Understanding the technical properties of relays and solenoids is crucial for B2B buyers, especially when selecting the right component for specific applications. Here are some critical specifications to consider:
-
Actuation Type
– Definição: This refers to the method by which the device initiates action. Solenoids typically provide linear motion, while relays function as switches that open or close electrical contacts.
– Importância do B2B: Knowing the actuation type helps buyers choose the right device based on the required application, such as mechanical movement or electrical control. -
Classificação atual
– Definição: The maximum amount of electrical current that a device can handle safely. Solenoids are designed for higher current applications, while relays usually manage lower currents.
– Importância do B2B: Selecting components with appropriate current ratings is critical for ensuring system reliability and preventing damage to other parts of the circuit. -
Tensão da bobina
– Definição: This specifies the voltage required to energize the coil in both solenoids and relays. Common voltages include 12V, 24V, and 120V.
– Importância do B2B: Understanding coil voltage is essential for compatibility with existing systems and power supplies, ensuring optimal performance and energy efficiency. -
Tempo de resposta
– Definição: The time it takes for the device to actuate once power is applied. Relays generally have a slower response time compared to solenoids.
– Importância do B2B: In applications requiring quick operation, such as automotive systems or robotics, knowing the response time can impact overall system performance and efficiency. -
Mechanical Life Cycle
– Definição: This refers to the number of operations a solenoid or relay can perform before mechanical failure. Solenoids often have a limited cycle life compared to relays.
– Importância do B2B: A higher mechanical life cycle translates to lower maintenance costs and longer operational periods, which is a key consideration for budget-conscious businesses. -
Size and Form Factor
– Definição: The physical dimensions and design of the device can vary significantly between solenoids and relays.
– Importância do B2B: For integration into compact systems or equipment, understanding the size and form factor ensures that the selected components fit within design constraints.
What Are the Common Trade Terms Relevant to Relays and Solenoids?
Navigating the procurement process for relays and solenoids involves familiarity with industry terminology. Here are several key terms that B2B buyers should understand:
-
OEM (Fabricante de Equipamento Original)
– Definição: Uma empresa que produz peças ou equipamentos que podem ser comercializados por outro fabricante.
– Importância: Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify the original source of parts, ensuring quality and compatibility with existing systems. -
MOQ (Quantidade mínima de encomenda)
– Definição: A menor quantidade de um produto que um fornecedor está disposto a vender.
– Importância: Knowing the MOQ is essential for budgeting and planning inventory, particularly for businesses looking to scale production. -
RFQ (Pedido de Orçamento)
– Definição: A document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for specific products or services.
– Importância: An RFQ helps buyers compare prices and terms across different suppliers, facilitating informed purchasing decisions. -
Incoterms (Termos Comerciais Internacionais)
– Definição: A set of predefined international rules that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in the shipping process.
– Importância: Familiarity with Incoterms is vital for managing shipping costs and risks, particularly in international transactions. -
Prazo de entrega
– Definição: The amount of time between the initiation of a process and its completion, particularly concerning the delivery of products.
– Importância: Understanding lead times is crucial for project planning and ensuring that components are available when needed. -
Normas de certificação
– Definição: Compliance with industry standards (e.g., ISO, CE) that ensure safety, reliability, and performance.
– Importância: Buyers must verify certification standards to ensure that components meet regulatory requirements and quality expectations.
By familiarizing themselves with these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance operational efficiency and product reliability.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the difference between relay and solenoid Sector
What Are the Global Drivers Influencing the Relay and Solenoid Market?
The global market for relays and solenoids is witnessing significant growth driven by advancements in automation and the increasing demand for smart devices. Industries such as automotive, consumer electronics, and industrial automation are key sectors propelling this demand. In regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, there’s a marked shift towards integrating these devices into smart systems, which enhances operational efficiency and reduces energy consumption. Additionally, the rise of electric vehicles (EVs) in Europe and Asia is creating new opportunities for solenoid and relay applications, particularly in engine management and control systems.
Emerging trends in B2B sourcing emphasize the importance of technology integration. Buyers are increasingly seeking suppliers that offer not just components but also integrated solutions, such as smart relays with IoT capabilities. Furthermore, the shift towards digital procurement processes is transforming how businesses source these components, enabling more streamlined operations and better price negotiations. As international buyers navigate this dynamic landscape, understanding these trends can help them make informed decisions.
How Is Sustainability Shaping the Sourcing of Relays and Solenoids?
Sustainability is becoming a cornerstone of B2B sourcing strategies, particularly in the relay and solenoid sector. Buyers are increasingly aware of the environmental impact associated with manufacturing processes, prompting a shift towards more sustainable practices. This includes sourcing from suppliers who prioritize ethical supply chains and utilize eco-friendly materials. For instance, manufacturers are adopting recyclable components and reducing waste through lean production techniques.
The demand for ‘green’ certifications is also on the rise. Certifications such as ISO 14001 can provide assurance to buyers that suppliers adhere to environmental management standards. Moreover, the use of low-impact materials in the production of relays and solenoids is gaining traction, aligning with global initiatives to reduce carbon footprints. By prioritizing sustainable sourcing, businesses not only enhance their brand reputation but also align with the values of environmentally-conscious consumers and partners.
What Is the Historical Context of Relays and Solenoids in the B2B Sector?
The history of relays and solenoids dates back to the late 19th century, when early electrical engineers first harnessed the principles of electromagnetism. Relays were developed to control circuits remotely, allowing for safer and more efficient operation of electrical devices. Solenoids followed, providing mechanical movement for various applications, from door locks to automotive starters.
As technology evolved, both devices became integral to the development of modern electronics. The introduction of solid-state technology in the late 20th century further transformed these components, enhancing their reliability and performance. Today, relays and solenoids are essential in numerous applications, from industrial automation to consumer electronics, highlighting their enduring significance in the B2B landscape. Understanding this evolution helps buyers appreciate the capabilities and innovations available in today’s market.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of difference between relay and solenoid
-
How do I determine whether to use a relay or a solenoid in my application?
To choose between a relay and a solenoid, first assess the function you need. Relays are best for switching electrical circuits, providing isolation and control, while solenoids are ideal for mechanical movement applications, such as locking mechanisms or valve control. Consider the current load: relays handle low-power control signals to switch high-power circuits, whereas solenoids operate under higher current loads for direct mechanical action. Evaluating the specific requirements of your application will help you make the right choice. -
What are the key differences between relays and solenoids regarding functionality?
Relays serve as electrically controlled switches that open or close contacts in response to low current signals, ideal for circuit isolation and logic control. In contrast, solenoids convert electrical energy into linear mechanical motion, operating devices like locks or valves. The choice depends on whether you require electrical circuit control (relay) or mechanical actuation (solenoid). Understanding these functionalities will streamline your sourcing decision. -
What factors should I consider when sourcing relays and solenoids internationally?
When sourcing internationally, evaluate the supplier’s reputation, quality certifications, and compliance with international standards. Research their experience in your industry and check for customer testimonials. Additionally, consider the supplier’s ability to provide customization options, minimum order quantities (MOQ), and payment terms that suit your financial planning. Logistics capabilities, including shipping times and costs, are also critical to ensure timely delivery. -
How can I ensure the quality of relays and solenoids from suppliers?
To ensure quality, request detailed product specifications and certifications from your suppliers. Conduct audits and ask for samples before placing bulk orders. Implement quality assurance protocols by establishing clear standards for testing and inspection. It’s also beneficial to partner with suppliers who have a robust return policy and warranty, as this provides an additional layer of security regarding product quality. -
What are common applications for relays and solenoids in various industries?
Relays are commonly used in automotive, telecommunications, and industrial automation for circuit control and isolation. They can also be found in home appliances for switching operations. Solenoids, on the other hand, are prevalent in automotive starter motors, door locks, and fuel injection systems in engines. Understanding these applications can help you identify potential suppliers who specialize in your industry. -
What customization options should I look for when sourcing relays and solenoids?
Customization options can include variations in voltage ratings, coil resistance, size, and housing materials. Depending on your specific application, you may require custom wiring configurations or specialized actuating forces for solenoids. Discuss your requirements with potential suppliers and request prototypes to evaluate their capabilities. Customization can significantly enhance the performance of the components in your specific applications. -
What payment terms are common in international B2B transactions for electrical components?
Common payment terms include Letter of Credit (LC), Telegraphic Transfer (TT), and PayPal for smaller orders. Negotiate terms based on order size, supplier trustworthiness, and your cash flow needs. For larger orders, a partial payment upfront with the balance upon delivery is often standard. Ensure to clarify any additional costs, such as tariffs or shipping fees, to avoid unexpected expenses. -
How do logistics impact the sourcing of relays and solenoids from international suppliers?
Logistics play a crucial role in the timely delivery of your components. Assess the supplier’s shipping capabilities, including options for air or sea freight, and their ability to handle customs clearance efficiently. Consider lead times, especially if you’re working on a tight schedule. Additionally, inquire about tracking systems to monitor your shipment’s progress and ensure you can plan your inventory management accordingly.
Top 4 Difference Between Relay And Solenoid Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. EDN – Solenoids
Domínio: edn.com
Registado: 1997 (28 anos)
Introdução: Solenoids are electromechanical devices that act as electromagnets created by applying current to a coil of wire. They are used in various applications such as engaging engine starting motors, power door locks, and moving valves. The solenoid’s operation involves two forces: the initial force to move the armature and the holding force to keep it in place, often assisted by a spring. Relays are a t…
2. Dotheton - Relés e Solenóides
Domínio: dotheton.com
Registado: 2007 (18 anos)
Introdução: Relays and solenoids are both electro-mechanical devices used for switching electricity. A relay is an electrically controlled switch, while a solenoid is an electrically controlled plunger. Solenoids typically handle higher current loads than relays, with relays usually rated for 10A to 50A and solenoids capable of handling up to 600A in automotive applications. Starter solenoids and starter rela…
3. Agriculture.com – Relays, Solenoids, and Servos
Domínio: agriculture.com
Registrado: 1995 (30 anos)
Introdução: Relays, solenoids, and servos are essential devices in agricultural machinery. Relays control high electrical loads remotely, allowing for efficient operation without the need for heavy wiring. Common issues with relays include low energize voltage, high resistance in the solenoid winding, burned contacts, and corroded connections. Solenoids evoke action rather than transferring current, connectin…
4. Overland Bound – Relay and Solenoid Solutions
Domínio: overlandbound.com
Registado: 2011 (14 anos)
Introdução: Relay: 120 amp capacity, used for low current applications like fog lights and horns. Solenoid: Generally used for higher current applications (40a and above), such as winches. High current solenoids can be rated up to 500 amps for dual battery setups. Smart solenoids prevent battery combining until after the vehicle starts, triggered by voltage readings or timers. DC-DC chargers are recommended f…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for difference between relay and solenoid
How Can Understanding the Differences Between Relays and Solenoids Enhance Your Sourcing Strategy?
In conclusion, grasping the distinctions between relays and solenoids is vital for international B2B buyers seeking to optimize their procurement processes. Relays serve as essential components for circuit control and isolation, suitable for low-current applications, while solenoids provide powerful linear motion for mechanical tasks. Understanding these functionalities allows buyers to make informed decisions that align with their project requirements and industry standards.
Illustrative image related to difference between relay and solenoid
Strategic sourcing in this context means not only selecting the right components but also ensuring that suppliers can provide high-quality, reliable products that meet operational needs. This is particularly crucial for markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where sourcing challenges can vary significantly.
As you navigate your purchasing journey, consider leveraging partnerships with reputable suppliers who can offer insights into product specifications and applications. Embrace the opportunity to enhance your supply chain efficiency by selecting the appropriate electromechanical devices that drive your projects forward. Engage with your suppliers today to explore tailored solutions that will empower your business for future success.
Aviso legal importante e termos de utilização
⚠️ Aviso importante
As informações fornecidas neste guia, incluindo conteúdo sobre fabricantes, especificações técnicas e análises de mercado, têm fins meramente informativos e educativos. Não constituem aconselhamento profissional sobre aquisições, aconselhamento financeiro ou aconselhamento jurídico.
Embora tenhamos envidado todos os esforços para garantir a precisão e atualidade das informações, não nos responsabilizamos por quaisquer erros, omissões ou informações desatualizadas. As condições de mercado, os detalhes da empresa e os padrões técnicos estão sujeitos a alterações.
Os compradores B2B devem realizar a sua própria diligência prévia independente e minuciosa. antes de tomar qualquer decisão de compra. Isso inclui entrar em contacto diretamente com os fornecedores, verificar certificações, solicitar amostras e procurar aconselhamento profissional. O risco de confiar em qualquer informação contida neste guia é assumido exclusivamente pelo leitor.