Introdução: Navegar no mercado global para saber como ligar um veículo com um motor de arranque avariado
Ao lidar com as complexidades da manutenção de veículos, um dos desafios mais prementes enfrentados pelas empresas de vários sectores é como pôr em funcionamento um veículo com um mau motor de arranque. Este problema não só perturba as operações, como também pode implicar custos significativos se não for tratado de forma eficiente. Neste guia abrangente, pretendemos fornecer aos compradores B2B internacionais informações práticas sobre como diagnosticar problemas de arranque, explorar soluções temporárias e compreender quando procurar ajuda profissional.
O nosso guia abrange um vasto leque de tópicos relevantes, incluindo os vários tipos de motores de arranque, as suas aplicações em diferentes modelos de veículos e as ferramentas essenciais necessárias para a resolução de problemas. Além disso, aprofundamos as estratégias de verificação de fornecedores, considerações de custos e melhores práticas para o fornecimento de peças de substituição. Ao equipar os compradores de regiões como África, América do Sul, Médio Oriente e Europa com este conhecimento, capacitamo-los a tomar decisões de compra informadas que aumentam a sua resiliência operacional.
Compreender as nuances de como lidar com questões de arranque não só simplifica os processos de manutenção, como também protege contra potenciais períodos de inatividade. Este guia foi concebido para servir como um recurso valioso, garantindo que as empresas possam navegar eficazmente no mercado global, minimizando as interrupções e maximizando a produtividade.
Índice
- Lista dos 3 principais fabricantes e fornecedores de como ligar um veículo com um mau arranque
- Introdução: Navegar no mercado global para saber como ligar um veículo com um motor de arranque avariado
- Compreender como arrancar um veículo com um mau arranque Tipos e variações
- Principais aplicações industriais de como arrancar um veículo com um motor de arranque avariado
- 3 Pontos de dor comuns dos utilizadores para ‘como arrancar um veículo com um mau arranque’ e as suas soluções
- Guia de seleção de materiais estratégicos para o arranque de um veículo com um motor de arranque avariado
- Análise aprofundada: Processos de fabrico e garantia de qualidade para saber como arrancar um veículo com um mau arrancador
- Guia prático de abastecimento: Uma lista de verificação passo-a-passo para ‘como arrancar um veículo com um mau arranque’
- Análise exaustiva dos custos e dos preços para saber como arrancar um veículo com um mau arranque Sourcing
- Análise de alternativas: Comparação de como arrancar um veículo com um mau arranque com outras soluções
- Propriedades técnicas essenciais e terminologia comercial para saber como arrancar um veículo com um motor de arranque avariado
- Como navegar na dinâmica do mercado e nas tendências de abastecimento no sector do arranque de um veículo com um mau arranque
- Perguntas frequentes (FAQs) para compradores B2B sobre como arrancar um veículo com um mau motor de arranque
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusão e perspectivas sobre como arrancar um veículo com um motor de arranque avariado
- Aviso legal importante e termos de utilização
Compreender como arrancar um veículo com um mau arranque Tipos e variações
| Nome do tipo | Principais características distintivas | Aplicações B2B primárias | Breves prós e contras para compradores |
|---|---|---|---|
| Reparação da ligação da bateria | Envolve a limpeza e a fixação dos terminais da bateria. | Oficinas mecânicas, serviços de frota. | Prós: Solução de baixo custo; solução rápida. Contras: Só é eficaz se houver problemas com a bateria. |
| Técnica de tapping para iniciantes | Bater ligeiramente no motor de arranque para libertar os componentes presos. | Prestadores de serviços de bricolage para automóveis. | Prós: Método simples; não são necessárias ferramentas especiais. Contras: Solução temporária; risco de danos adicionais. |
| Inspeção do solenoide | Verificação e limpeza das ligações do solenoide. | Manutenção de veículos comerciais. | Prós: Resolve um ponto de falha comum; melhora a fiabilidade. Contras: Requer conhecimentos técnicos; consome muito tempo. |
| Método de arranque por pressão | Fazer rolar o veículo e acionar a embraiagem para arrancar manualmente. | Utilizado principalmente em veículos com transmissão manual. | Prós: Eficaz para automóveis manuais; não são necessárias ferramentas. Contras: Não é adequado para veículos automáticos; requer assistência. |
| Arranque rápido | Utilizar cabos de ligação em ponte para fornecer energia a partir de outro veículo. | Prestadores de serviços no sector automóvel, assistência rodoviária. | Prós: Rápido e fácil; pode resolver problemas relacionados com a bateria. Contras: Ineficaz se o motor de arranque for o principal problema. |
Quais são as principais caraterísticas da reparação da ligação da bateria?
A reparação da ligação da bateria é uma abordagem fundamental que se concentra em garantir que os terminais da bateria estão limpos e ligados de forma segura. Este método é particularmente adequado para oficinas de reparação automóvel e serviços de frotas onde os veículos têm frequentemente problemas de arranque. Os compradores devem ter em consideração a relação custo-eficácia desta solução, uma vez que resolve frequentemente os problemas sem a necessidade de peças dispendiosas. No entanto, apenas resolve problemas relacionados com as ligações da bateria, o que torna essencial o diagnóstico exato da causa principal.
Como é que a técnica de tapping de arranque funciona?
A técnica de bater no motor de arranque envolve bater suavemente no motor de arranque com um martelo ou objeto semelhante para desalojar os componentes presos. Este método é ideal para os prestadores de serviços de bricolage no sector automóvel e pode ser executado com o mínimo de ferramentas. Embora seja uma abordagem simples que pode produzir resultados imediatos, é essencial que os compradores reconheçam que se trata de uma solução temporária. A utilização excessiva pode provocar mais danos, exigindo uma solução mais permanente.
Porque é que a inspeção do solenoide é importante?
A inspeção do solenoide é crucial, uma vez que este desempenha um papel significativo no sistema de arranque, convertendo a corrente baixa do interrutor de ignição em corrente alta para o motor de arranque. Este método é particularmente aplicável na manutenção de veículos comerciais, onde a fiabilidade é fundamental. Os compradores devem estar cientes de que, embora esta inspeção possa melhorar o desempenho do veículo, requer um certo nível de conhecimentos técnicos e pode ser demorada, com impacto nos custos de mão de obra.
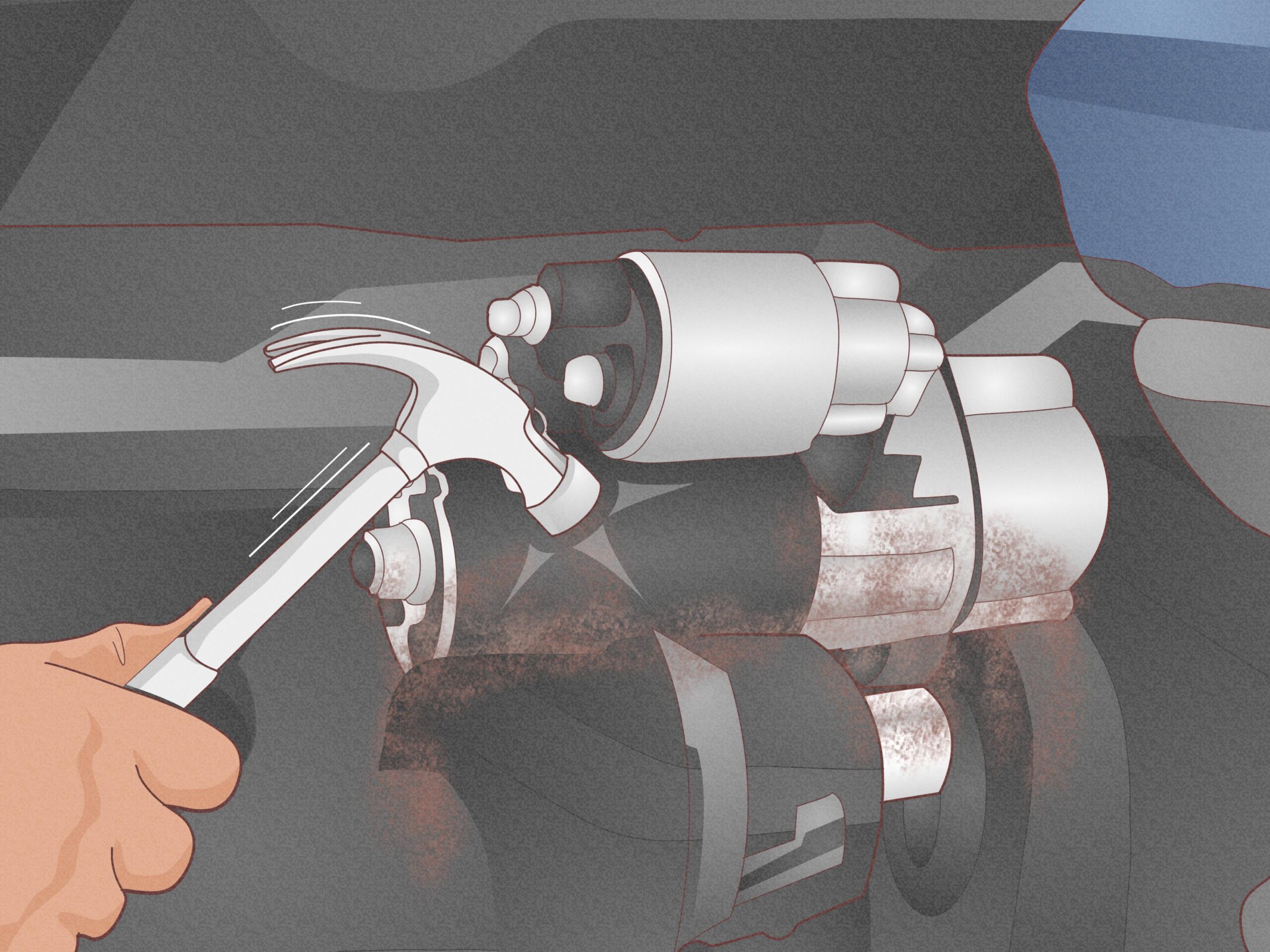
Imagem ilustrativa relacionada com o arranque de um veículo com um mau arranque
Quando é que o Push Starting é uma opção viável?
O método de arranque por pressão é uma solução prática para os veículos de transmissão manual, permitindo aos utilizadores contornar os problemas do motor de arranque rodando o veículo e accionando a embraiagem. Esta técnica é especialmente útil para entusiastas de automóveis ou em situações em que a assistência está prontamente disponível. No entanto, é fundamental que os compradores tenham em atenção que este método não é aplicável a veículos automáticos e requer uma equipa para ajudar no processo, o que pode limitar a sua praticabilidade em determinados cenários.
Como é que o arranque assistido pode ajudar nesta situação?
O arranque com bateria fornece uma solução rápida para problemas de arranque, especialmente quando a tensão baixa da bateria é o problema subjacente. Este método é amplamente utilizado por prestadores de serviços automóveis e equipas de assistência na estrada. Embora possa resolver eficazmente os problemas relacionados com a bateria, os compradores devem compreender que, se o motor de arranque for a principal preocupação, o arranque com bateria não proporcionará uma solução duradoura. Esta distinção é vital para tomar decisões de compra informadas relativamente aos serviços de manutenção de veículos.
Principais aplicações industriais de como arrancar um veículo com um motor de arranque avariado
| Indústria/Setor | Aplicação específica de como arrancar um veículo com um motor de arranque avariado | Valor/benefício para a empresa | Considerações importantes sobre o fornecimento para esta aplicação |
|---|---|---|---|
| Oficinas de reparação automóvel | Utilização de correcções temporárias para arrancar veículos para diagnóstico | Minimiza o tempo de inatividade, permitindo uma resposta mais rápida ao serviço | Necessidade de ferramentas e peças fiáveis; formação para técnicos |
| Logística e transporte de mercadorias | Assegurar que os veículos de entrega podem arrancar apesar de problemas com o motor de arranque | Mantém a eficiência operacional e as entregas atempadas | Acesso a ferramentas e peças portáteis; consideração pelos serviços de reparação locais |
| Gestão de frotas | Implementação de correcções rápidas para veículos da frota com problemas no motor de arranque | Reduz os custos de manutenção e aumenta a fiabilidade da frota | Aquisição de ferramentas a granel; parcerias com mecânicos locais |
| Equipamento agrícola | Arranque de veículos agrícolas com motores de arranque defeituosos | Assegura o funcionamento contínuo durante as épocas críticas de plantação | Disponibilidade de ferramentas robustas; suporte para diversos tipos de veículos |
| Serviços de emergência | Soluções rápidas para veículos de emergência | Melhora a prontidão e os tempos de resposta em situações críticas | Acesso a ferramentas especializadas; formação do pessoal de emergência |
Como é que as oficinas de reparação automóvel beneficiam com o arranque de veículos com um mau arranque?
As oficinas de reparação automóvel encontram frequentemente veículos que apresentam problemas com o motor de arranque. Ao utilizar soluções temporárias, como a limpeza das ligações da bateria ou a utilização de um martelo no motor de arranque, os técnicos podem diagnosticar e resolver rapidamente os problemas. Esta abordagem minimiza o tempo de inatividade do veículo, permitindo um serviço mais rápido e uma maior satisfação do cliente. As oficinas de reparação devem adquirir ferramentas e componentes fiáveis, assegurando que os seus técnicos têm formação para lidar eficazmente com vários problemas relacionados com o motor de arranque.
Que vantagens obtêm as empresas de logística e de transporte de mercadorias com a resolução de problemas de arranque?
As empresas de logística e de transporte de mercadorias dependem fortemente dos seus veículos de entrega. Quando confrontadas com um mau arranque, a implementação de soluções rápidas pode ajudar a manter a eficiência operacional e garantir entregas atempadas. Isto é crucial em mercados competitivos, onde os atrasos podem resultar na perda de negócios. As empresas devem considerar a aquisição de ferramentas portáteis e estabelecer ligações com serviços de reparação locais para resolver problemas de arranque de forma rápida e eficaz.
Como é que a gestão de frotas melhora a fiabilidade com soluções de arranque temporário?
As operações de gestão de frotas lidam frequentemente com vários veículos, tornando os problemas de arranque uma preocupação significativa. As reparações rápidas permitem que os gestores de frotas resolvam os problemas prontamente, reduzindo os custos de manutenção e melhorando a fiabilidade geral da sua frota. Isto é especialmente importante em sectores onde a disponibilidade dos veículos é crítica. Os gestores de frotas devem concentrar-se na compra a granel das ferramentas necessárias e considerar parcerias com mecânicos locais para um apoio eficiente.
Porque é que é importante que o equipamento agrícola arranque apesar dos problemas com o motor de arranque?
Na agricultura, a capacidade de arranque de máquinas como tractores e ceifeiras é vital, especialmente durante as épocas de plantação e colheita. Soluções temporárias, como a limpeza de ligações ou a utilização de um martelo para bater no motor de arranque, podem garantir que estes veículos essenciais permanecem operacionais. Os agricultores precisam de adquirir ferramentas robustas que possam suportar condições adversas e garantir o suporte de vários tipos de maquinaria agrícola.
Como é que os serviços de emergência beneficiam de soluções rápidas para problemas de arranque?
Os serviços de emergência têm de estar preparados para responder a qualquer momento, tornando crítica a capacidade de arrancar veículos com motores de arranque avariados. Soluções rápidas, como o arranque rápido ou a verificação das ligações dos solenóides, podem melhorar a prontidão e os tempos de resposta em situações de emergência. As agências devem considerar a aquisição de ferramentas especializadas e fornecer formação ao pessoal para garantir que podem gerir eficazmente os problemas do motor de arranque em situações de alta pressão.
3 Pontos de dor comuns dos utilizadores para ‘como arrancar um veículo com um mau arranque’ e as suas soluções
Cenário 1: Diagnosticar problemas de arranque em frotas comerciais
O problema:
Para os gestores de frotas que supervisionam vários veículos, surge um desafio comum quando um ou vários veículos não arrancam devido a problemas suspeitos com o motor de arranque. A incapacidade de diagnosticar rapidamente se o motor de arranque está de facto avariado - ou se o problema está noutro lado, como uma bateria fraca ou uma falha na ignição - pode levar a tempos de inatividade dispendiosos. Com ferramentas de diagnóstico limitadas e um orçamento operacional apertado, os gestores de frotas sentem-se frequentemente sobrecarregados quando tentam resolver estes problemas de forma eficiente, minimizando a perturbação das operações diárias.
A solução:
Os gestores de frotas devem investir em ferramentas de diagnóstico abrangentes que incluam voltímetros e testadores de bateria. Estas ferramentas permitem uma abordagem sistemática à resolução de problemas. Comece por verificar a tensão da bateria; uma leitura inferior a 12,5 volts indica uma bateria fraca que pode necessitar de um arranque rápido ou de substituição. Se a bateria estiver a funcionar corretamente, inspeccione as ligações do motor de arranque quanto a corrosão ou folga, que são frequentemente os culpados em situações de não arranque. Sessões de formação regulares para o pessoal sobre a utilização de equipamento de diagnóstico também podem capacitar as equipas para resolverem estes problemas rapidamente, reduzindo a dependência de mecânicos externos e garantindo que os veículos regressam rapidamente à estrada.
Cenário 2: Gestão da manutenção em locais remotos
O problema:
Para as empresas que operam em zonas remotas, lidar com veículos que têm um mau arranque pode ser particularmente difícil. O acesso limitado a instalações de reparação e peças pode levar a um tempo de inatividade prolongado do veículo, afectando a prestação de serviços e a eficiência operacional. Este cenário deixa muitas vezes os proprietários de empresas à procura de soluções rápidas, apenas para descobrirem que não têm as ferramentas ou os conhecimentos necessários para executar reparações temporárias eficazes.
A solução:
Para atenuar este problema, as empresas devem equipar os seus veículos com ferramentas e materiais essenciais para reparações no local. Isto inclui cabos de ligação, ferramentas manuais básicas e um arrancador de baterias portátil. A elaboração de um guia simples de resolução de problemas para os condutores também pode ser benéfica. Este guia deve incluir os passos para verificar as ligações da bateria, dar o arranque ao veículo e, se aplicável, efetuar uma reparação temporária batendo no motor de arranque com um martelo para potencialmente desalojar quaisquer componentes presos. A formação dos condutores sobre estes procedimentos permitir-lhes-á resolver rapidamente problemas menores, minimizando o tempo de inatividade e mantendo o fluxo operacional, mesmo em locais remotos.
Cenário 3: O custo de falhas frequentes do arrancador
O problema:
As empresas que dependem fortemente de veículos podem registar falhas frequentes nos motores de arranque, o que leva a um aumento dos custos de manutenção e a ineficiências operacionais. Este problema recorrente pode causar frustração entre os condutores e a direção, especialmente se os veículos forem essenciais para a entrega de bens ou serviços. O desafio reside não só em resolver o problema imediato do motor de arranque, mas também em compreender as causas subjacentes para evitar falhas futuras.
A solução:
A realização de uma análise minuciosa dos sistemas eléctricos dos veículos pode ajudar a identificar as causas das frequentes falhas do motor de arranque. Isto inclui examinar a qualidade das ligações da bateria, o estado do sistema de ignição e o estado geral do motor de arranque. Investir em motores de arranque de qualidade superior com uma vida útil mais longa também pode ser uma estratégia económica a longo prazo. Além disso, o estabelecimento de um calendário de manutenção regular que inclua inspecções dos componentes eléctricos pode ajudar a detetar problemas antes que estes conduzam a falhas do motor de arranque. Educar os condutores sobre o funcionamento correto do veículo - tal como evitar o arranque excessivo - pode prolongar ainda mais a vida útil dos motores de arranque e reduzir os custos associados a substituições e reparações.
Guia de seleção de materiais estratégicos para o arranque de um veículo com um motor de arranque avariado
Ao enfrentar os desafios do arranque de um veículo com um mau arranque, a seleção de materiais para ferramentas e componentes é crucial. Segue-se uma análise dos materiais mais comuns utilizados neste contexto, focando as suas propriedades, vantagens, desvantagens e considerações para os compradores internacionais B2B.
Quais são as principais propriedades dos materiais comuns utilizados nas ferramentas de reparação de arrancadores?
1. Aço
O aço é um material muito utilizado em ferramentas como chaves, martelos e cabos de para-choques.
- Propriedades principais: Elevada resistência à tração, durabilidade e resistência à deformação sob tensão. As ferramentas de aço podem suportar temperaturas e pressões elevadas, o que as torna adequadas para aplicações no sector automóvel.
- Prós e contras: As ferramentas de aço são geralmente económicas e muito duráveis. No entanto, podem ser propensas à corrosão se não forem devidamente mantidas, especialmente em ambientes húmidos ou salinos.
- Impacto na aplicação: A resistência do aço torna-o ideal para aplicações pesadas, mas a sua suscetibilidade à ferrugem pode limitar o seu tempo de vida em ambientes agressivos.
- Considerações para compradores internacionais: A conformidade com as normas internacionais, tais como ASTM e ISO, é essencial. Os compradores em regiões húmidas como partes de África e da América do Sul devem considerar revestimentos resistentes à corrosão.
2. Cobre
O cobre é frequentemente utilizado em componentes eléctricos, incluindo cabos de ligação e conectores.
- Propriedades principais: Excelente condutividade eléctrica e resistência à corrosão. O cobre pode suportar cargas de corrente elevadas, o que o torna ideal para aplicações eléctricas.
- Prós e contras: A condutividade superior do cobre melhora o desempenho das ligações eléctricas. No entanto, é mais caro do que outros materiais e pode ficar manchado com o tempo, afectando potencialmente o desempenho.
- Impacto na aplicação: O cobre é fundamental para garantir ligações eléctricas fiáveis nos sistemas de arranque, especialmente em veículos com necessidades eléctricas complexas.
- Considerações para compradores internacionais: Os compradores devem garantir a conformidade com as normas eléctricas e considerar o impacto das condições ambientais locais na longevidade do cobre.
3. Alumínio
O alumínio é frequentemente utilizado para ferramentas e componentes mais leves devido às suas propriedades favoráveis.
- Propriedades principais: Leve, boa resistência à corrosão e uma boa relação resistência/peso. O alumínio pode suportar temperaturas moderadas e é frequentemente utilizado em componentes como martelos leves ou carcaças de ferramentas.
- Prós e contras: As ferramentas de alumínio são fáceis de manusear e transportar, reduzindo a fadiga durante a utilização. No entanto, podem não ser tão duráveis como as de aço e podem deformar-se sob tensão elevada.
- Impacto na aplicação: O alumínio é adequado para aplicações que requerem ferramentas leves, mas pode não resistir a uma utilização pesada.
- Considerações para compradores internacionais: Os compradores devem procurar produtos de alumínio que cumpram as normas de qualidade locais e internacionais, especialmente em regiões onde se prevê uma utilização intensiva.
4. Compósitos plásticos
Os compósitos plásticos são cada vez mais utilizados em ferramentas e equipamentos de proteção não condutores.
- Propriedades principais: Leve, resistente à corrosão e não condutor. Estes materiais podem suportar uma gama de temperaturas e são frequentemente utilizados em equipamentos de segurança.
- Prós e contras: Os compósitos plásticos são económicos e podem ser moldados em formas complexas. No entanto, podem não oferecer o mesmo nível de durabilidade que os metais e podem degradar-se sob exposição aos raios UV.
- Impacto na aplicação: Ideal para equipamento de proteção e ferramentas não condutoras, os compósitos plásticos podem aumentar a segurança durante as reparações.
- Considerações para compradores internacionais: O cumprimento das normas de segurança é fundamental e os compradores devem certificar-se de que os materiais plásticos são adequados às condições ambientais específicas das suas regiões.
Tabela de resumo da seleção de materiais para arrancar um veículo com um mau arranque
| Material | Caso de utilização típico para saber como arrancar um veículo com um motor de arranque avariado | Vantagem principal | Principal desvantagem/limitação | Custo relativo (baixo/médio/alto) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aço | Chaves, martelos, cabos de ligação | Alta durabilidade e resistência | Suscetível à corrosão | Médio |
| Cobre | Cabos de ligação, conectores eléctricos | Excelente condutividade | Custo mais elevado, mancha-se com o tempo | Alto |
| Alumínio | Ferramentas leves, invólucros | Leve e fácil de manusear | Menos durável sob forte tensão | Médio |
| Compósitos plásticos | Ferramentas não condutoras, equipamento de proteção | Económica e resistente à corrosão | Menos durável do que os metais | Baixo |
Este guia estratégico de seleção de materiais fornece informações essenciais para compradores B2B em regiões como África, América do Sul, Médio Oriente e Europa, garantindo que tomam decisões informadas que se alinham com as suas necessidades operacionais e condições ambientais.
Análise aprofundada: Processos de fabrico e garantia de qualidade para saber como arrancar um veículo com um mau arrancador
Quais são as principais fases dos processos de fabrico dos componentes envolvidos no arranque de um veículo com um mau arranque?
Os processos de fabrico envolvidos na produção de componentes relacionados com os motores de arranque dos veículos exigem precisão e cumprimento de normas de qualidade. Normalmente, estes processos podem ser divididos em quatro fases principais: preparação do material, moldagem, montagem e acabamento.
Como é que o material é preparado para os componentes de arranque?
O primeiro passo no processo de fabrico é a preparação do material, que envolve a seleção de materiais de alta qualidade adequados para os componentes específicos do sistema de arranque. Os materiais comuns incluem metais como o aço e o alumínio para maior durabilidade e condutividade eléctrica. Durante esta fase, as matérias-primas são inspeccionadas quanto a defeitos e as suas propriedades são testadas para garantir que cumprem as normas da indústria.
Uma vez adquiridos os materiais, estes são submetidos a uma série de tratamentos, como o tratamento térmico ou o revestimento de superfícies, para melhorar as suas caraterísticas de desempenho. Por exemplo, a aplicação de revestimentos resistentes à corrosão pode prolongar significativamente a vida útil dos componentes expostos a ambientes agressivos, o que é particularmente relevante para os mercados em África e na América do Sul, onde as condições meteorológicas podem ser extremas.
Que técnicas são utilizadas na formação de componentes de arranque?
A fase de conformação consiste em moldar os materiais preparados em componentes específicos. São normalmente utilizadas técnicas como a estampagem, a maquinagem e a fundição injetada. A estampagem é utilizada para criar componentes planos, enquanto a maquinagem permite a moldagem precisa de peças com tolerâncias mais apertadas. A fundição sob pressão é particularmente útil para produzir formas complexas com um elevado grau de precisão, o que é essencial para peças como a caixa do motor de arranque.
Cada técnica tem as suas vantagens e é selecionada com base na complexidade do componente, nos requisitos de volume e nas propriedades do material. As tecnologias de fabrico avançadas, como a maquinagem por controlo numérico computorizado (CNC), permitem aos fabricantes obter uma elevada precisão e repetibilidade, cruciais para garantir a compatibilidade e o desempenho dos sistemas de arranque.
Como é que os componentes são montados para os sistemas de arranque?
Uma vez formados os componentes individuais, inicia-se a fase de montagem. Este processo envolve normalmente várias sub-etapas, incluindo a integração de componentes eléctricos como solenóides e escovas no motor de arranque. As linhas de montagem automatizadas podem ser utilizadas para aumentar a eficiência, onde robots ou maquinaria especializada montam peças com o mínimo de intervenção humana.
A garantia de qualidade é fundamental durante a montagem, uma vez que mesmo pequenos erros podem levar a problemas de desempenho significativos. Os fabricantes implementam frequentemente técnicas à prova de erros, como os sistemas poka-yoke, para minimizar os erros de montagem. Isto é especialmente importante nos mercados internacionais, onde o custo de uma falha pode ser elevado devido a pedidos de garantia e danos à reputação.
Quais são os processos de garantia de qualidade para componentes de arranque?
A garantia de qualidade (GQ) é uma parte integrante do processo de fabrico, assegurando que todos os componentes cumprem as normas regulamentares e as expectativas dos clientes. Várias normas internacionais e específicas do sector orientam estes processos de GQ.
Quais normas internacionais são relevantes para a garantia da qualidade?
A ISO 9001 é uma das normas internacionais mais reconhecidas para sistemas de gestão da qualidade. Fornece uma estrutura que ajuda as organizações a garantir que cumprem os requisitos regulamentares e do cliente de forma consistente. Para os fabricantes de componentes de arranque, a adesão à ISO 9001 pode aumentar a sua credibilidade nos mercados globais.
Para além das normas ISO, outras certificações como a marcação CE (para produtos vendidos no Espaço Económico Europeu) e API (para componentes automóveis) são cruciais. Estas certificações indicam a conformidade com as normas de segurança e desempenho, o que pode afetar significativamente o processo de decisão de um comprador, especialmente em regiões com ambientes regulamentares rigorosos.
Quais são os principais pontos de verificação do controlo de qualidade no processo de fabrico?
Os pontos de controlo de qualidade (CQ) estão estrategicamente colocados ao longo do processo de fabrico para garantir que os defeitos são detectados precocemente. Os pontos de controlo comuns incluem:

Imagem ilustrativa relacionada com o arranque de um veículo com um mau arranque
-
Controlo de Qualidade de Entrada (IQC): Isto implica a inspeção das matérias-primas antes de entrarem no processo de produção. Os fornecedores devem fornecer documentação de garantia de qualidade para verificar a conformidade do material.
-
Controlo de qualidade em processo (IPQC): Durante as fases de fabrico, são efectuadas inspecções contínuas para controlar os processos e identificar quaisquer desvios em relação às normas de qualidade.
-
Controlo de Qualidade Final (FQC): Esta fase envolve testes rigorosos dos produtos acabados para garantir que cumprem as especificações. Os métodos de teste comuns incluem testes funcionais, testes de resistência e testes eléctricos.
Como os compradores B2B podem verificar o controlo de qualidade dos fornecedores?
Os compradores B2B podem tomar várias medidas para verificar os processos de controlo de qualidade dos potenciais fornecedores:
-
Auditorias: A realização de auditorias no local permite aos compradores avaliar as instalações de fabrico, os processos e a adesão às normas de qualidade. Isto é particularmente importante para os compradores internacionais que podem não ter uma supervisão direta.
-
Relatórios de qualidade: A solicitação de relatórios de qualidade detalhados pode fornecer informações sobre as práticas de gestão da qualidade do fornecedor, incluindo taxas de defeitos e medidas corretivas tomadas.
-
Inspeções por terceiros: A contratação de serviços de inspeção por terceiros pode oferecer uma avaliação imparcial dos processos e produtos do fornecedor. Isto é especialmente benéfico para compradores em regiões onde as práticas locais de garantia de qualidade podem variar.
Quais são os métodos de teste comuns utilizados na garantia de qualidade para componentes de arrancadores?
Os métodos de ensaio são essenciais para garantir que os componentes do arrancador funcionem de forma fiável em condições reais. Os métodos mais comuns incluem:
-
Testes elétricos: Isto verifica a funcionalidade dos componentes eléctricos, tais como solenóides e ligações de cabos. Os compradores devem certificar-se de que os fabricantes realizam testes eléctricos completos para evitar falhas no terreno.
-
Teste de durabilidade: Os componentes são submetidos a testes de esforço para simular uma utilização a longo prazo. Isto é vital para garantir que as peças podem suportar os rigores da operação diária, particularmente em ambientes desafiantes.
-
Teste de desempenho: A avaliação do funcionamento do motor de arranque em várias condições garante que este cumpre as especificações do fabricante. Isto inclui testar o tempo de resposta e a potência de saída.
Como é que as nuances do controlo de qualidade afectam os compradores internacionais B2B?
Para os compradores B2B internacionais, é essencial compreender as nuances do controlo de qualidade. As variações nas normas de qualidade entre regiões podem afetar a fiabilidade do produto e a conformidade com os regulamentos locais. Por exemplo, os fabricantes na Europa podem ter de cumprir normas de emissões mais rigorosas em comparação com os de outras regiões.
Além disso, as diferenças culturais nas práticas de fabrico podem afetar a forma como a qualidade é percebida e implementada. Os compradores devem estar preparados para adaptar as suas expectativas de qualidade com base na localização do fornecedor e nas normas da indústria.
Em conclusão, compreender os processos de fabrico e as medidas de garantia de qualidade dos componentes de arranque é crucial para os compradores B2B nos mercados internacionais. Ao concentrarem-se na qualidade, na conformidade e nos métodos de verificação, os compradores podem tomar decisões informadas que melhoram a sua eficiência operacional e a satisfação do cliente.
Guia prático de abastecimento: Uma lista de verificação passo-a-passo para ‘como arrancar um veículo com um mau arranque’
Para ajudar os compradores B2B internacionais a navegar pelas complexidades do arranque de um veículo com um mau arranque, este guia oferece uma lista de verificação prática. Centra-se nos passos essenciais para garantir que dispõe das ferramentas, conhecimentos e ligações corretas para gerir este desafio de forma eficaz.
Passo 1: Identificar os sintomas de um mau arrancador
Reconhecer os sinais de um mau arranque é crucial antes de avançar com qualquer solução. Os indicadores comuns incluem um único clique ao rodar a chave, nenhum ruído ou um clique rápido. O diagnóstico exato do problema ajuda a evitar reparações e custos desnecessários.
Passo 2: Reunir ferramentas essenciais para a resolução de problemas
Ter à mão as ferramentas corretas é fundamental para resolver os problemas dos arrancadores. As principais ferramentas incluem:
– Cabos de ligação em ponte: Para testar a viabilidade da bateria.
– Marreta ou martelo: Para bater suavemente no motor de arranque e libertar eventuais componentes presos.
– Voltímetro: Para verificar a tensão da bateria e excluir problemas relacionados com a bateria.
Estas ferramentas facilitam a resolução eficaz de problemas e garantem a implementação de soluções imediatas.
Passo 3: Avaliar as ligações da bateria
Antes de assumir que o motor de arranque está avariado, inspeccione as ligações da bateria. A corrosão ou cabos soltos podem prejudicar o desempenho. Limpe os terminais positivo e negativo com uma escova de arame e certifique-se de que estão bem ligados. Este simples passo pode muitas vezes resolver problemas de arranque sem intervenção adicional.
Passo 4: Avaliar o motor de arranque e o solenoide
Verifique se o motor de arranque apresenta danos físicos ou desgaste. Se o seu veículo tiver um solenoide externo, inspeccione os fios quanto a corrosão ou ligações soltas. Um solenoide avariado pode impedir que o motor de arranque receba a corrente necessária, pelo que é essencial garantir que todas as ligações estão limpas e intactas.
Passo 5: Considerar soluções temporárias
Se a reparação imediata não for uma opção, explore soluções temporárias, tais como:
– Bater no motor de arranque: Por vezes, um toque suave pode restabelecer a funcionalidade.
– Veículos manuais de arranque por pressão: Se aplicável, este método pode contornar temporariamente os problemas do arrancador.
Estas tácticas podem constituir uma medida provisória enquanto se espera por uma solução mais permanente.
Passo 6: Estabelecer relações com fornecedores fiáveis
Ao adquirir peças ou ferramentas, é vital estabelecer parcerias com fornecedores de confiança. Procure aqueles com reputação estabelecida no sector automóvel, especialmente na sua região. Avalie a qualidade dos seus produtos, o serviço de apoio ao cliente e os prazos de entrega para garantir que conseguem satisfazer as suas necessidades de forma eficaz.
Passo 7: Programar verificações de manutenção regulares
A manutenção preventiva pode reduzir significativamente a probabilidade de problemas com o motor de arranque. Programe verificações regulares do estado da bateria, do estado do motor de arranque e das ligações eléctricas. O estabelecimento de um calendário de manutenção de rotina garante que os problemas são identificados atempadamente e resolvidos antes de se agravarem.
Ao seguir estes passos, os compradores B2B podem gerir eficazmente os desafios associados ao arranque de um veículo com um mau arranque, garantindo a eficiência operacional e minimizando o tempo de inatividade.
Análise exaustiva dos custos e dos preços para saber como arrancar um veículo com um mau arranque Sourcing
Quais são os principais componentes de custo para ligar um veículo com um mau arranque?
Ao considerar a estrutura de custos para pôr em funcionamento um veículo com um motor de arranque avariado, entram em jogo vários componentes-chave.

Imagem ilustrativa relacionada com o arranque de um veículo com um mau arranque
-
Materiais: Os principais materiais envolvidos incluem cabos de ligação, marretas ou martelos, chaves, voltímetros e material de limpeza, como escovas de arame. A qualidade destes materiais pode afetar significativamente o custo total. Por exemplo, os cabos de ligação resistentes são mais caros, mas oferecem um melhor desempenho.
-
Trabalho: Os custos de mão de obra variam consoante a tarefa seja executada internamente ou subcontratada a um prestador de serviços. Os técnicos especializados podem exigir taxas mais elevadas, mas a sua experiência pode reduzir o tempo gasto no diagnóstico e na resolução do problema.
-
Custos indiretos de produção: Inclui custos relacionados com instalações, serviços públicos e despesas administrativas associadas à produção de quaisquer peças necessárias para reparações ou substituições do motor de arranque.
-
Ferramentas: As ferramentas especializadas para reparações de arranque podem aumentar os custos iniciais. Se uma empresa efectua frequentemente este tipo de reparações, o investimento em ferramentas de alta qualidade pode conduzir a poupanças a longo prazo.
-
Controlo de Qualidade (QC): Assegurar que todos os componentes cumprem as normas de qualidade pode implicar custos adicionais. No entanto, o investimento no controlo de qualidade pode reduzir os pedidos de garantia futuros e aumentar a satisfação do cliente.
-
Logística: Os custos associados ao transporte de materiais e ferramentas para o local de reparação podem variar muito em função de factores geográficos. Isto é especialmente pertinente para os compradores internacionais, onde as tarifas de importação e as taxas de envio podem afetar significativamente os custos globais.
-
Margem: As empresas devem ter em conta a margem de lucro que pretendem obter quando fixam os preços dos serviços ou produtos relacionados com problemas de arranque de veículos. Esta margem varia consoante a concorrência e a procura no mercado.
Como é que os influenciadores de preços afectam as decisões de aprovisionamento?
Vários factores podem influenciar o preço quando se procura materiais ou serviços para pôr em marcha um veículo com um mau arranque:
-
Volume/MOQ: As quantidades mínimas de encomenda (MOQ) e os descontos por volume podem afetar significativamente os preços. As compras em massa reduzem normalmente os custos por unidade, o que pode ser vantajoso para as empresas com elevadas taxas de rotação.
-
Especificações e personalização: As soluções personalizadas adaptadas a tipos de veículos específicos ou a necessidades de reparação podem aumentar os custos. Os compradores devem avaliar se as soluções genéricas podem satisfazer as suas necessidades sem incorrer em despesas adicionais.
-
Qualidade dos materiais e certificações: Os materiais de qualidade superior têm muitas vezes um preço mais elevado, mas podem conduzir a um melhor desempenho e durabilidade. As certificações também podem influenciar o preço; os fornecedores com certificações de qualidade reconhecidas podem cobrar mais pelos seus produtos.
-
Fatores relacionados ao fornecedor: A fiabilidade e a reputação dos fornecedores podem afetar os custos. Os fornecedores estabelecidos podem oferecer melhores condições, mas a um preço mais elevado, devido à sua reputação de qualidade e serviço.
-
Incoterms: Compreender os Incoterms é crucial para os compradores internacionais, uma vez que estes definem as responsabilidades dos compradores e dos vendedores no transporte. Estes termos podem ter um impacto significativo nos custos relacionados com o transporte, o seguro e os direitos aduaneiros.
Quais são as melhores dicas do comprador para uma boa relação custo-eficácia?
Para maximizar a eficiência de custos ao procurar soluções para ligar um veículo com um mau arranque, considere as seguintes sugestões:
-
Negociação: Negoceie sempre os preços com os fornecedores. Muitos fornecedores estão dispostos a oferecer descontos, especialmente para encomendas em massa ou contratos a longo prazo.
-
Custo total de propriedade (TCO): Avalie não só o preço de compra inicial mas também o custo total de propriedade, que inclui a manutenção, a durabilidade e o potencial valor de revenda das ferramentas e dos materiais.
-
Compreender as nuances dos preços: Os compradores internacionais devem ter em conta as flutuações cambiais, os impostos de importação e os direitos aduaneiros que podem afetar os custos finais. Este conhecimento pode ajudar na orçamentação e na negociação de melhores negócios.
-
Investigação e comparação: Efetuar uma pesquisa exaustiva e comparar vários fornecedores para encontrar a melhor combinação de preço e qualidade. As plataformas em linha e as feiras comerciais podem fornecer informações sobre as taxas de mercado e a fiabilidade dos fornecedores.
Isenção de responsabilidade sobre preços indicativos
Os preços podem variar significativamente com base na localização geográfica, nas condições de mercado e nos requisitos específicos do comprador. É essencial que as empresas efectuem as devidas diligências e obtenham vários orçamentos para garantir que estão a tomar decisões de compra informadas.

Imagem ilustrativa relacionada com o arranque de um veículo com um mau arranque
Análise de alternativas: Comparação de como arrancar um veículo com um mau arranque com outras soluções
Explorando alternativas para ligar um veículo com um mau arranque
Quando confrontado com o desafio de ligar um veículo com um mau arranque, é essencial considerar várias alternativas que podem alcançar resultados semelhantes. Cada solução tem as suas próprias vantagens e desvantagens, especialmente quando se tem em conta aspectos como o desempenho, o custo, a facilidade de implementação e a manutenção. Esta análise tem como objetivo ajudar os compradores B2B a tomar decisões informadas e adaptadas às suas necessidades operacionais específicas.
| Aspecto comparativo | Como ligar um veículo com um mau arranque | Alternativa 1: Arranque rápido | Alternativa 2: Arranque por impulso |
|---|---|---|---|
| Desempenho | Correção temporária; pode não funcionar de forma consistente | Fiável se a bateria estiver fraca | Eficaz para veículos manuais |
| Custo | Baixo (as ferramentas necessárias são mínimas) | Baixo (requer cabos de ligação) | Sem custos (não necessita de ferramentas) |
| Facilidade de implementação | Moderado; requer alguma perícia mecânica | Fácil; pode ser feito por qualquer pessoa | Moderado; necessita de assistência |
| Manutenção | Mínimo; requer controlos ocasionais | Nenhum; depende do estado da bateria | Nenhuma; ação única |
| Melhor caso de uso | Solução rápida para utilização imediata | O melhor para problemas de bateria fraca | Adequado para veículos manuais |
Quais são os prós e os contras de um arranque rápido como alternativa?
O arranque com bateria é um método simples que pode ser utilizado quando o problema está principalmente relacionado com uma bateria fraca e não com um motor de arranque avariado. O processo envolve a ligação de cabos de ligação de uma bateria em funcionamento à bateria descarregada do veículo que não arranca.
Prós:
– Fiabilidade: Se o motor de arranque estiver a funcionar, este método permite normalmente pôr o veículo a funcionar.
– Facilidade de utilização: A maioria das pessoas pode realizá-lo com um mínimo de formação, o que o torna acessível.
Contras:
– Dependência da saúde da bateria: Se o problema principal for o motor de arranque, este método não resolverá o problema.
– Equipamento necessário: Este método requer a existência de cabos de ligação e o acesso a outro veículo, o que pode nem sempre estar disponível.
Como é que o Push Starting funciona e quais são os seus benefícios?
O arranque por impulso, ou arranque por solavanco, é uma técnica aplicável principalmente a veículos com transmissão manual. Este método consiste em fazer rolar o veículo para ganhar impulso e, em seguida, engatar o motor com a mudança engrenada.
Prós:
– Sem custos: Este método não requer ferramentas ou equipamentos especiais, o que o torna económico.
– Simplicidade: É uma técnica simples que pode ser executada com a ajuda de poucas pessoas.
Contras:
– Aplicação limitada: Este método só é viável para veículos com transmissão manual, deixando os proprietários de veículos automáticos sem opção.
– Esforço físico necessário: Exige mais esforço físico e coordenação de vários indivíduos, o que pode nem sempre ser viável.
Como é que os compradores B2B devem escolher a solução certa para as suas necessidades?
A seleção do método adequado para pôr em funcionamento um veículo com um mau arranque depende de vários factores. Os compradores B2B devem avaliar o tipo de veículo com que estão a lidar, os recursos à sua disposição e a urgência da situação. Por exemplo, se for necessária uma ação imediata e o veículo tiver uma transmissão manual, o arranque por pressão pode ser a melhor opção. Por outro lado, se o problema puder ser causado por uma bateria fraca, o arranque por saltos seria mais adequado. Em última análise, a compreensão do contexto e dos requisitos específicos orientará os compradores para a solução mais eficaz.
Propriedades técnicas essenciais e terminologia comercial para saber como arrancar um veículo com um motor de arranque avariado
Quais são as caraterísticas técnicas essenciais para ligar um veículo com um mau arranque?
Compreender as especificações técnicas relacionadas com os motores de arranque para automóveis é crucial para os compradores B2B, especialmente os envolvidos na reparação e manutenção de veículos. Eis algumas especificações críticas a considerar:
1. Grau de material dos componentes do arrancador
O tipo de material dos componentes, como a caixa do motor de arranque, as engrenagens e as ligações eléctricas, influencia grandemente a durabilidade e o desempenho. Os materiais comuns incluem alumínio para aplicações leves e vários tipos de aço para resistência. Os compradores B2B devem dar prioridade a materiais de alta qualidade que resistam às condições ambientais, especialmente em regiões com temperaturas ou humidade extremas, o que é vital para a fiabilidade a longo prazo.

Imagem ilustrativa relacionada com o arranque de um veículo com um mau arranque
2. Tensão nominal
A maioria dos motores de arranque dos veículos funciona com uma tensão normal de 12V. É crucial garantir que o motor de arranque consegue suportar flutuações de tensão sem falhar. Um motor de arranque com uma maior tolerância às variações de tensão pode melhorar o desempenho, particularmente em regiões onde os sistemas eléctricos podem ser instáveis. Esta especificação é essencial para a aquisição, uma vez que afecta a compatibilidade com diferentes modelos de veículos.
3. Saída de binário
O binário de saída é uma medida da capacidade do motor de arranque para virar o motor. Uma classificação de binário mais elevada indica um melhor desempenho no arranque de veículos, especialmente aqueles com motores maiores. Os compradores devem avaliar os requisitos de binário para modelos de veículos específicos para garantir que os motores de arranque que adquirem satisfazem as expectativas de desempenho, especialmente em aplicações de elevada exigência.
4. Durabilidade e tolerância à temperatura
A durabilidade é frequentemente definida pelo número de ciclos que um motor de arranque pode completar antes de falhar. Isto é especialmente relevante para os compradores B2B que se concentram na gestão de frotas ou em aplicações comerciais. Além disso, a tolerância à temperatura indica o desempenho do motor de arranque em condições de calor ou frio extremos, o que pode ser uma preocupação em vários mercados globais.

Imagem ilustrativa relacionada com o arranque de um veículo com um mau arranque
5. Especificações de peso e tamanho
As dimensões físicas e o peso do motor de arranque são significativos, particularmente para a adaptação de veículos mais antigos ou para aplicações de desempenho em que a redução de peso é crítica. Os compradores devem certificar-se de que o motor de arranque cabe no espaço designado no compartimento do motor, satisfazendo simultaneamente os requisitos de peso para aplicações específicas.
Quais são os termos comerciais comuns relacionados com os arrancadores?
A familiaridade com o jargão da indústria é essencial para uma comunicação e negociação eficazes no mercado das peças automóveis. Aqui estão alguns termos comuns relevantes para os iniciantes:
1. OEM (Fabricante de Equipamento Original)
OEM refere-se a peças fabricadas pelo fabricante do veículo. Estas peças são frequentemente mais caras, mas têm a garantia de cumprir as especificações exactas necessárias para o desempenho e a fiabilidade. Os compradores B2B podem escolher peças OEM para assegurar a compatibilidade e manter a cobertura da garantia dos veículos.
2. MOQ (Quantidade mínima de encomenda)
O MOQ é a quantidade mais pequena de um produto que um fornecedor está disposto a vender. Compreender o MOQ é crucial para os compradores, uma vez que tem impacto na gestão do inventário e no fluxo de caixa. Os compradores devem negociar MOQs que estejam de acordo com o seu poder de compra e capacidades de armazenamento.
3. RFQ (Pedido de Orçamento)
Um pedido de cotação é um documento enviado aos fornecedores solicitando preços e condições para produtos ou serviços específicos. Este termo é essencial para os processos de aquisição, uma vez que ajuda os compradores a comparar opções e a tomar decisões informadas relativamente aos fornecedores a contratar.
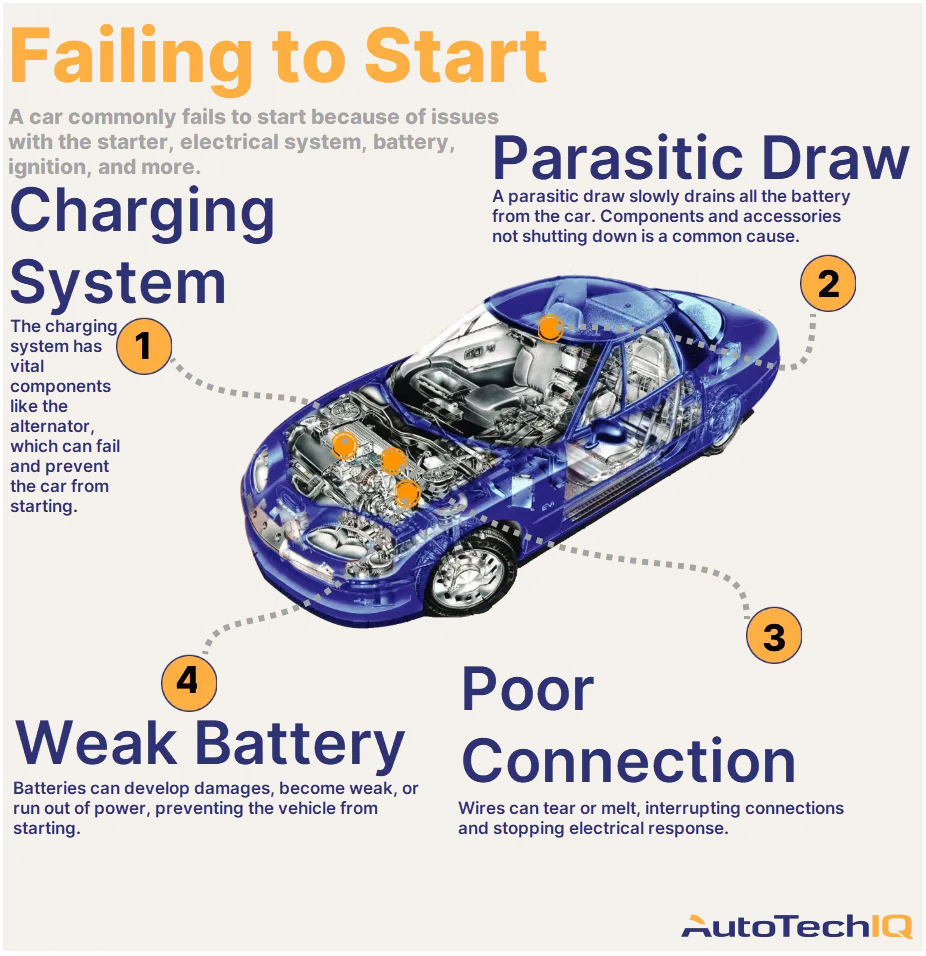
Imagem ilustrativa relacionada com o arranque de um veículo com um mau arranque
4. Incoterms (Termos Comerciais Internacionais)
Os Incoterms definem as responsabilidades dos compradores e vendedores no comércio internacional, incluindo quem é responsável pelo envio, seguro e tarifas. A compreensão destes termos é vital para as transacções B2B, especialmente para os compradores que importam entradas de diferentes países.
5. Mercado pós-venda
O mercado de reposição refere-se a peças e acessórios que não são fornecidos pelo fabricante original. Estas peças podem oferecer poupanças de custos e alternativas aos compradores, mas podem variar em termos de qualidade e compatibilidade. Os compradores devem avaliar cuidadosamente as opções do mercado pós-venda para garantir que cumprem os requisitos de desempenho.
6. Termos da garantia
Os termos da garantia especificam o período durante o qual uma peça pode ser substituída ou reparada devido a defeitos. Compreender as condições de garantia é crucial para os compradores B2B para garantir que recebem valor e proteção contra falhas de fabrico, que podem ter um impacto significativo nos custos operacionais.
Ao compreender estas propriedades técnicas e termos comerciais, os compradores internacionais B2B podem tomar decisões informadas sobre o fornecimento e manutenção de motores de arranque de veículos, melhorando assim a eficiência operacional e a fiabilidade do veículo.
Como navegar na dinâmica do mercado e nas tendências de abastecimento no sector do arranque de um veículo com um mau arranque
Quais são as actuais dinâmicas de mercado que afectam o sector ‘Como arrancar um veículo com um mau arranque’?
O sector da reparação e manutenção automóvel está a assistir a transformações significativas impulsionadas pelos avanços tecnológicos, pela alteração das preferências dos consumidores e por factores económicos. As principais tendências incluem a crescente dependência de ferramentas digitais para diagnósticos e reparações, o que aumenta a eficiência e a precisão. Para os compradores B2B internacionais, particularmente em regiões como África, América do Sul, Médio Oriente e Europa, a procura de soluções inovadoras para resolver problemas comuns dos veículos, como um mau arranque, é crítica.
As tecnologias emergentes, como as aplicações móveis que oferecem orientação para a resolução de problemas e soluções de reparação, estão a remodelar o panorama do mercado. Além disso, o aumento das plataformas de comércio eletrónico está a facilitar o acesso a peças e ferramentas para automóveis, permitindo aos compradores obter os componentes necessários de forma rápida e económica. Além disso, a ênfase crescente nas soluções de gestão e manutenção de frotas está a impulsionar a procura de produtos fiáveis que garantam o tempo de atividade e a eficiência operacional dos veículos.
A dinâmica do mercado é também influenciada pelas condições económicas regionais, onde os diferentes níveis de infra-estruturas e capacidades de serviço automóvel podem ter impacto nos tipos de soluções mais procurados. Nos mercados em desenvolvimento, por exemplo, as soluções económicas e fáceis de utilizar para o arranque de veículos com um mau arranque são particularmente valiosas, uma vez que enfrentam frequentemente desafios relacionados com a disponibilidade de serviços e a escassez de mão de obra especializada.
Como é que a sustentabilidade e o fornecimento ético estão a ter impacto no sector da reparação automóvel?
A sustentabilidade está a tornar-se uma consideração fundamental para os compradores B2B no sector da reparação automóvel. O impacto ambiental da manutenção automóvel, particularmente em termos de produção de resíduos e consumo de recursos, está a levar as empresas a procurar práticas sustentáveis. Por exemplo, a aquisição de componentes e ferramentas produzidos de forma ética não só minimiza a pegada ecológica, como também satisfaz a crescente procura dos consumidores por produtos ambientalmente responsáveis.
Os compradores estão a procurar cada vez mais fornecedores que possam fornecer certificações ‘verdes’ para os seus produtos, tais como materiais recicláveis ou ferramentas energeticamente eficientes. Além disso, as empresas estão a centrar-se no ciclo de vida completo das peças para automóveis, desde a produção até à eliminação, para garantir que as suas decisões de abastecimento apoiam os objectivos de sustentabilidade. Esta mudança é particularmente relevante em regiões onde os quadros regulamentares relativos à proteção ambiental estão a tornar-se mais rigorosos.
As cadeias de abastecimento éticas também estão a ganhar força, uma vez que as empresas reconhecem a importância de práticas de abastecimento responsáveis. Ao estabelecer parcerias com fornecedores comprometidos com práticas de trabalho justas e responsabilidade social, os compradores B2B podem melhorar a reputação da sua marca e, ao mesmo tempo, contribuir positivamente para as comunidades locais. Este foco no fornecimento ético alinha-se com as tendências globais de transparência e responsabilidade nas cadeias de fornecimento.
Como é que o sector da reparação automóvel evoluiu ao longo do tempo?
A evolução do sector da reparação automóvel, em especial no que diz respeito ao arranque de veículos com motores de arranque avariados, reflecte os avanços tecnológicos mais amplos e a evolução das necessidades dos consumidores. Inicialmente, a manutenção dos veículos dependia muito do diagnóstico manual e de ferramentas rudimentares. No entanto, à medida que os veículos se tornaram mais complexos, a indústria assistiu à introdução de ferramentas de diagnóstico eletrónico e de técnicas de reparação avançadas.
Nas últimas duas décadas, a proliferação da tecnologia digital revolucionou a forma como as reparações automóveis são efectuadas. O advento dos smartphones e das aplicações móveis permitiu que os mecânicos e os proprietários de veículos acedessem a guias de resolução de problemas e a tutoriais de reparação na ponta dos dedos. Esta mudança não só permite que os indivíduos resolvam os problemas de arranque de forma mais eficiente, como também melhora a prestação global de serviços no mercado da reparação automóvel.
Além disso, a globalização das cadeias de abastecimento permitiu um maior acesso a peças e ferramentas automóveis de qualidade, facilitando às empresas das regiões em desenvolvimento a manutenção eficaz dos seus veículos. Como resultado, o sector continua a evoluir, com a sustentabilidade e as considerações éticas a moldarem cada vez mais as estratégias operacionais e de aprovisionamento.
Perguntas frequentes (FAQs) para compradores B2B sobre como arrancar um veículo com um mau motor de arranque
-
Como é que posso diagnosticar um mau arranque no meu veículo?
O diagnóstico de um mau motor de arranque envolve vários passos. Primeiro, rode a chave da ignição; se ouvir um estalido rápido, isso pode indicar uma bateria fraca em vez de um problema no motor de arranque. Se o motor se virar mas não arrancar, considere outros componentes como o sistema de ignição ou o fornecimento de combustível. A ausência de ruído ou um único clique ao rodar a chave aponta frequentemente para um mau arranque. Verificar se os terminais da bateria apresentam corrosão e garantir ligações seguras também pode ajudar a excluir problemas eléctricos. Utilize um voltímetro para verificar a tensão da bateria; qualquer valor abaixo de 12,5 volts sugere uma bateria fraca. -
Que soluções temporárias posso utilizar para pôr a funcionar um veículo com um motor de arranque avariado?
Se estiver perante um motor de arranque avariado, existem várias soluções temporárias que pode tentar. Limpar as ligações da bateria pode, por vezes, restabelecer a funcionalidade. Bater suavemente no motor de arranque com um martelo pode libertar componentes presos. Se o seu veículo tiver uma transmissão manual, um arranque por pressão pode contornar o problema do motor de arranque. Para garantir a segurança, peça a ajuda de duas pessoas e evite estradas movimentadas. Estes métodos podem ser soluções eficazes a curto prazo, mas é essencial agendar reparações profissionais o mais rapidamente possível para evitar mais complicações. -
De que ferramentas necessito para solucionar um mau arranque?
Para resolver o problema de um mau arranque, reúna algumas ferramentas essenciais. Os cabos de ligação são cruciais para testar os problemas da bateria, enquanto uma chave inglesa ou um conjunto de tomadas ajuda a desligar os terminais da bateria em segurança. Um martelo ou martelo pode ser utilizado para bater suavemente no motor de arranque e um voltímetro é útil para verificar a tensão da bateria. Uma lanterna ajudará na visibilidade sob o capô. Ferramentas opcionais, como um relé de arranque ou testadores de fusíveis, podem ajudar a diagnosticar problemas eléctricos, e equipamento de proteção, como luvas e óculos de proteção, garante a segurança durante o processo. -
Como posso encontrar fornecedores fiáveis de peças de substituição para o motor de arranque?
Encontrar fornecedores fiáveis de peças de substituição para motores de arranque implica uma pesquisa minuciosa. Procure fornecedores com uma forte reputação na indústria automóvel, de preferência com experiência internacional. Verifique as críticas e os testemunhos online de outros compradores B2B da sua região. Participe em feiras comerciais ou conferências do sector para conhecer os fornecedores e avaliar as suas ofertas. Além disso, considere os fornecedores que fornecem especificações detalhadas dos produtos e garantias para assegurar a qualidade. O estabelecimento de relações de longo prazo com fornecedores de renome pode melhorar o seu processo de aquisição e garantir uma qualidade consistente. -
Quais são as condições de pagamento comuns para transacções B2B no sector das peças para automóveis?
As condições de pagamento comuns para transacções B2B na indústria de peças automóveis variam consoante o fornecedor e a região. As condições típicas incluem 30 líquidos, 60 líquidos ou pagamento aquando da entrega. Alguns fornecedores podem oferecer descontos para pagamentos antecipados ou exigir um depósito antecipado para grandes encomendas. É essencial esclarecer as condições de pagamento antes de finalizar uma transação para evitar mal-entendidos. Além disso, considere a utilização de métodos de pagamento seguros que ofereçam proteção contra a fraude. O estabelecimento de acordos claros sobre as condições de pagamento pode facilitar as transacções e promover a confiança entre compradores e fornecedores. -
Qual é a quantidade mínima de encomenda (MOQ) para peças de arranque?
A quantidade mínima de encomenda (MOQ) para peças de arranque pode variar significativamente entre fornecedores. Alguns podem ter uma MOQ de uma unidade para pequenas empresas, enquanto outros podem exigir encomendas maiores para compensar os custos de fabrico. Ao adquirir peças, informe-se antecipadamente sobre as quantidades mínimas de encomenda e considere a possibilidade de negociar termos que se adaptem às necessidades da sua empresa. Além disso, não se esqueça de que encomendar a granel pode muitas vezes levar a descontos e melhores preços. Compreender os MOQs ajuda a planear o inventário e a gerir eficazmente o fluxo de caixa. -
Como posso assegurar a garantia de qualidade das peças de arranque fornecidas a nível internacional?
Assegurar a garantia de qualidade para peças de arranque de origem internacional envolve a implementação de um processo de verificação robusto. Comece por exigir que os fornecedores forneçam certificações e documentação de controlo de qualidade. Efectue auditorias à fábrica ou solicite amostras para avaliar a qualidade do produto antes de efetuar encomendas maiores. Estabeleça normas e especificações de qualidade claras para comunicar eficazmente as suas expectativas. Além disso, considere a possibilidade de trabalhar com serviços de inspeção de terceiros para verificar a qualidade do produto antes da expedição. A criação de fortes canais de comunicação com os fornecedores também pode facilitar uma melhor gestão da qualidade ao longo do processo de aquisição. -
Que considerações logísticas devo ter em conta ao importar peças de arranque?
Ao importar peças de arranque, são cruciais várias considerações logísticas. Em primeiro lugar, avalie os métodos de envio e os prazos para garantir uma entrega atempada. Compreender os regulamentos e direitos aduaneiros aplicáveis no seu país para evitar custos inesperados. Colabore com transitários experientes que possam navegar pelas complexidades do transporte internacional. Certifique-se de que os seus fornecedores estão cientes dos requisitos de embalagem para evitar danos durante o transporte. Por fim, mantenha uma comunicação clara com todas as partes envolvidas na cadeia de fornecimento para resolver quaisquer problemas de forma rápida e eficiente.
Lista dos 3 principais fabricantes e fornecedores de como ligar um veículo com um mau arranque
1. Honda - Problema com o motor de arranque do Accord 2003
Domínio: reddit.com
Registado: 2005 (20 anos)
Introdução: Honda Accord 2003, motor de arranque avariado, bateria cheia, faróis acesos, ruído de clique do motor de arranque, transmissão automática.
2. WikiHow - Ligando um carro com um motor de arranque ruim
Domínio: wikihow.com
Registado: 2004 (21 anos)
Introdução: O artigo fornece soluções para o arranque de um automóvel com um mau arranque, incluindo bater no arranque com um martelo ou madeira, empurrar o arranque de um veículo com transmissão manual e fazer saltar a bateria. É dada ênfase à verificação da bateria em primeiro lugar, uma vez que esta é frequentemente a causa dos problemas de arranque. O motor de arranque é descrito como um dispositivo que puxa a carga da bateria para ligar o motor e os sintomas de um mau arranque...
3. Automóvel - Problemas de arranque
Domínio: mechanics.stackexchange.com
Registado: 2009 (16 anos)
Introdução: O automóvel tem uma bateria nova e potente (com 1 semana). Os sintomas incluem: o automóvel não arranca, nem sequer faz um clique, mas todas as luzes funcionam corretamente. Os possíveis problemas identificados incluem: ligações soltas da bateria, problemas no interrutor de ignição, mau arranque, mau solenoide, má ligação à terra e má ligação do motor de arranque. As etapas de resolução de problemas sugeridas incluem a verificação dos terminais da bateria, o arranque do carro e a inspec...
Strategic Sourcing Conclusão e perspectivas sobre como arrancar um veículo com um motor de arranque avariado
Em conclusão, a resolução eficaz dos problemas de arranque de um veículo, particularmente os que resultam de um motor de arranque defeituoso, sublinha a importância do aprovisionamento estratégico no sector automóvel. As principais conclusões incluem a necessidade de um diagnóstico correto - distinguindo entre problemas de bateria e falhas no motor de arranque - bem como a implementação de soluções temporárias, tais como a limpeza de ligações e a utilização de métodos físicos para ligar o motor de arranque. Para os compradores B2B, a compreensão destas nuances não só melhora a eficiência operacional, como também reduz o tempo de inatividade, conduzindo, em última análise, a poupanças de custos.
À medida que os mercados internacionais em África, na América do Sul, no Médio Oriente e na Europa continuam a evoluir, a procura de soluções fiáveis para o sector automóvel irá aumentar. As parcerias estratégicas com fornecedores e fabricantes de renome podem garantir o acesso a componentes e ferramentas de alta qualidade, facilitando as reparações e a manutenção atempadas.
No futuro, encorajamos os compradores B2B a investirem em formação e recursos abrangentes que capacitem as suas equipas para resolverem eficazmente as questões relacionadas com o arranque. Ao fazê-lo, as organizações podem manter a fiabilidade e o desempenho das suas frotas, abrindo caminho para um crescimento sustentável e para a satisfação dos clientes num cenário cada vez mais competitivo.
Aviso legal importante e termos de utilização
⚠️ Aviso importante
As informações fornecidas neste guia, incluindo conteúdo sobre fabricantes, especificações técnicas e análises de mercado, têm fins meramente informativos e educativos. Não constituem aconselhamento profissional sobre aquisições, aconselhamento financeiro ou aconselhamento jurídico.
Embora tenhamos envidado todos os esforços para garantir a precisão e atualidade das informações, não nos responsabilizamos por quaisquer erros, omissões ou informações desatualizadas. As condições de mercado, os detalhes da empresa e os padrões técnicos estão sujeitos a alterações.

Imagem ilustrativa relacionada com o arranque de um veículo com um mau arranque
Os compradores B2B devem realizar a sua própria diligência prévia independente e minuciosa. antes de tomar qualquer decisão de compra. Isso inclui entrar em contacto diretamente com os fornecedores, verificar certificações, solicitar amostras e procurar aconselhamento profissional. O risco de confiar em qualquer informação contida neste guia é assumido exclusivamente pelo leitor.