Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for how much does it cost to rebuild an alternator
In today’s competitive automotive landscape, understanding how much it costs to rebuild an alternator is essential for international B2B buyers. As businesses navigate varying market conditions across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the challenge lies not only in sourcing quality components but also in managing costs effectively. This guide addresses these challenges by providing a comprehensive analysis of the alternator rebuilding process, detailing the types of alternators available, their applications across different vehicle models, and crucial insights into supplier vetting.
With an emphasis on cost breakdowns, potential savings, and the importance of high-quality parts, this guide equips buyers with the knowledge needed to make informed purchasing decisions. We delve into the intricacies of rebuilding versus replacing an alternator, highlighting the advantages of each option in terms of performance and cost-effectiveness. Furthermore, we explore the nuances of global supply chains and the best practices for sourcing reliable suppliers in diverse regions, ensuring that businesses can confidently navigate the complexities of the automotive parts market.
By leveraging the insights contained within this guide, B2B buyers can enhance their procurement strategies, optimize their operational efficiency, and ultimately drive profitability in their automotive ventures. Whether you are in Vietnam or Brazil, the information provided here will serve as a valuable resource in your quest for reliable alternator solutions.
Table Of Contents
- Top 4 How Much Does It Cost To Rebuild An Alternator Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for how much does it cost to rebuild an alternator
- Understanding how much does it cost to rebuild an alternator Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of how much does it cost to rebuild an alternator
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘how much does it cost to rebuild an alternator’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for how much does it cost to rebuild an alternator
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for how much does it cost to rebuild an alternator
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘how much does it cost to rebuild an alternator’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for how much does it cost to rebuild an alternator Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing how much does it cost to rebuild an alternator With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for how much does it cost to rebuild an alternator
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the how much does it cost to rebuild an alternator Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of how much does it cost to rebuild an alternator
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for how much does it cost to rebuild an alternator
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Understanding how much does it cost to rebuild an alternator Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| DIY Rebuild Kit | Contains essential components for rebuilding; cost-effective. | Small repair shops, individual mechanics. | Pros: Low cost, hands-on experience. Cons: Requires skill and time; potential for errors. |
| Professional Rebuild Service | Performed by certified technicians; includes comprehensive testing. | Larger auto repair businesses, fleet operators. | Pros: High reliability, professional quality. Cons: Higher cost, potential for longer turnaround time. |
| Remanufactured Alternator | Factory-refurbished; meets OEM standards; warranty included. | Automotive retailers, service centers. | Pros: Guaranteed quality, often cheaper than new. Cons: May not be available for all models; quality can vary by manufacturer. |
| Custom Rebuild | Tailored rebuilds for specific vehicle models; specialized parts. | Specialty auto shops, performance vehicle markets. | Pros: Optimized performance, unique solutions. Cons: Higher costs, longer lead times. |
| Used Alternator | Salvaged units from other vehicles; lower cost. | Budget-conscious repair shops, DIY enthusiasts. | Pros: Very low cost, immediate availability. Cons: Uncertain lifespan, potential hidden issues. |
What are the Characteristics of a DIY Rebuild Kit for Alternators?
DIY rebuild kits are ideal for mechanics with experience in automotive repairs. They typically include components such as bearings, brushes, and voltage regulators, allowing users to replace damaged parts and restore functionality. This option is particularly suitable for small repair shops or individual mechanics looking to save costs. B2B buyers should consider the skill level required and the time investment, as improper assembly can lead to further issues.
How Does a Professional Rebuild Service Compare?
A professional rebuild service offers a comprehensive solution where certified technicians conduct thorough inspections and repairs. This option is favored by larger auto repair businesses and fleet operators that require reliability and efficiency. Buyers should weigh the benefits of guaranteed quality and service against the higher costs and potential longer turnaround times, especially when managing multiple vehicles.
Why Choose a Remanufactured Alternator?
Remanufactured alternators are factory-refurbished units that adhere to OEM standards, often including a warranty. This option is popular among automotive retailers and service centers as it combines quality assurance with a cost-effective alternative to new parts. Buyers must ensure they source from reputable manufacturers to avoid discrepancies in quality and availability, particularly for specific vehicle models.
What are the Advantages of Custom Rebuilds?
Custom rebuilds cater to specific vehicle models or performance needs, making them ideal for specialty auto shops and performance vehicle markets. This tailored approach can optimize performance and extend the lifespan of the alternator. However, B2B buyers should consider the higher costs and longer lead times associated with sourcing specialized parts.
When Should You Consider a Used Alternator?
Used alternators are salvaged from vehicles and offer a budget-friendly option for repair shops and DIY enthusiasts. While their low cost and immediate availability can be appealing, buyers should be cautious of the uncertain lifespan and potential hidden issues that may arise from previous usage. This option is best suited for temporary fixes or projects with limited budgets.
Key Industrial Applications of how much does it cost to rebuild an alternator
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of how much does it cost to rebuild an alternator | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive Repair | Rebuilding alternators for fleet vehicles | Reduces downtime and costs associated with purchasing new units | Availability of quality rebuild kits and skilled technicians |
| Construction Equipment | Maintaining heavy machinery by rebuilding alternators | Extends equipment lifespan and minimizes operational disruptions | Access to specialized parts and expertise in heavy machinery |
| Transportation | Rebuilding alternators in commercial transport vehicles | Enhances reliability and efficiency of transport fleets | Sourcing reliable components and understanding vehicle specifications |
| Renewable Energy | Servicing wind turbines with rebuilt alternators | Improves energy efficiency and reduces maintenance costs | Understanding of specific alternator requirements for renewable systems |
| Mining | Rebuilding alternators for mining equipment to ensure operational reliability | Minimizes equipment failure and ensures continuous operation | Access to durable parts and expertise in heavy-duty applications |
How is Rebuilding Alternators Beneficial in Automotive Repair?
In the automotive repair industry, rebuilding alternators for fleet vehicles is a common practice. Businesses can significantly reduce costs by opting to rebuild rather than replace, leading to lower operational expenses. This approach also minimizes vehicle downtime, allowing fleets to remain operational. International B2B buyers should consider the availability of quality rebuild kits and the expertise of local technicians to ensure that repairs meet industry standards.
Why is Rebuilding Alternators Important for Construction Equipment?
For construction companies, maintaining heavy machinery is crucial for project timelines. Rebuilding alternators helps extend the lifespan of expensive equipment, thus minimizing the need for new purchases. This practice can prevent operational disruptions that might arise from equipment failure. Buyers in this sector should focus on sourcing specialized parts and skilled technicians familiar with heavy machinery to ensure effective repairs.
How Does Rebuilding Alternators Impact Transportation?
In the transportation sector, rebuilding alternators in commercial vehicles enhances reliability and efficiency. A well-functioning alternator ensures that vehicles remain operational, which is essential for timely deliveries and services. B2B buyers must be aware of the specific requirements for their vehicle types and ensure they source reliable components to maintain optimal performance.
What Role Does Rebuilding Alternators Play in Renewable Energy?
In the renewable energy sector, particularly with wind turbines, the efficiency of alternators is critical for energy production. Rebuilding these components can lead to improved energy efficiency and reduced maintenance costs, making it a financially viable option. Buyers should understand the specific requirements for alternators used in renewable systems to ensure compatibility and performance.
How Can Mining Operations Benefit from Rebuilding Alternators?
In mining operations, the reliability of equipment is paramount. Rebuilding alternators for mining machinery minimizes the risk of equipment failure, ensuring continuous operation in challenging environments. This not only enhances productivity but also reduces the costs associated with unexpected repairs. Buyers should prioritize access to durable parts and expertise in heavy-duty applications to support their operational needs.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘how much does it cost to rebuild an alternator’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Unforeseen Costs During Alternator Rebuild Projects
The Problem: B2B buyers often face unexpected costs when rebuilding alternators due to a lack of comprehensive knowledge about the specific components that might need replacement. When a buyer purchases a rebuild kit for $25 to $60, they may overlook additional expenses such as labor, diagnostic testing, or specialized tools required for the rebuild process. This oversight can lead to budget overruns, which can be particularly challenging for businesses operating with tight margins or in competitive markets.
The Solution: To mitigate these unforeseen costs, it is crucial for buyers to conduct thorough preliminary assessments before purchasing parts. Engage a qualified technician to perform an initial diagnostic test on the alternator to identify all potential issues. This can include checking the condition of the rotor, stator, diodes, and brushes. By understanding the full scope of repairs needed, buyers can budget more accurately and avoid surprise expenses. Additionally, they should consider investing in quality rebuild kits from reputable suppliers who provide detailed documentation on what is included and any additional components that might be necessary. This proactive approach not only enhances cost management but also ensures that the rebuilt alternator will perform reliably.
Scenario 2: Difficulty in Finding Quality Rebuild Kits and Components
The Problem: Another significant pain point for international B2B buyers is sourcing high-quality rebuild kits and components for alternators. Many suppliers offer kits, but the quality can vary dramatically, leading to concerns about reliability and performance. This is especially critical in regions where automotive service standards are paramount, as subpar components can lead to failures that compromise customer satisfaction and brand reputation.
The Solution: Buyers should establish relationships with trusted suppliers who specialize in automotive parts and have a track record of providing high-quality rebuild kits. It’s advisable to request samples or product specifications before making large purchases to ensure quality meets required standards. Additionally, participating in industry trade shows or automotive expos can provide opportunities to meet suppliers in person, allowing for discussions about quality assurance practices. Implementing a rigorous vetting process for suppliers, including checking reviews and certifications, can significantly enhance the quality of the parts sourced, thereby ensuring the longevity and reliability of the rebuilt alternators.
Scenario 3: Navigating Technical Complexity of Alternator Rebuilding
The Problem: The technical complexity involved in rebuilding alternators can be a daunting challenge for B2B buyers, particularly those who may not have in-depth mechanical knowledge. Understanding the intricate details of the alternator’s electrical components, such as the voltage regulator, diode assembly, and the correct reassembly of the unit, can be overwhelming. This complexity can lead to improper rebuilds, resulting in additional costs and time delays.
The Solution: To address this issue, buyers should invest in training programs for their technicians or staff involved in the rebuilding process. Online courses, workshops, or certifications focused on alternator repair and electrical systems can equip the team with the necessary skills and knowledge. Furthermore, leveraging video tutorials and step-by-step guides from reliable sources can demystify the rebuilding process. Implementing a mentorship program where experienced technicians guide novices through the rebuilding process can also foster knowledge transfer and improve overall team competency. By enhancing technical proficiency, businesses can streamline their operations, reduce rebuild errors, and ultimately save costs associated with repeated repairs or replacements.
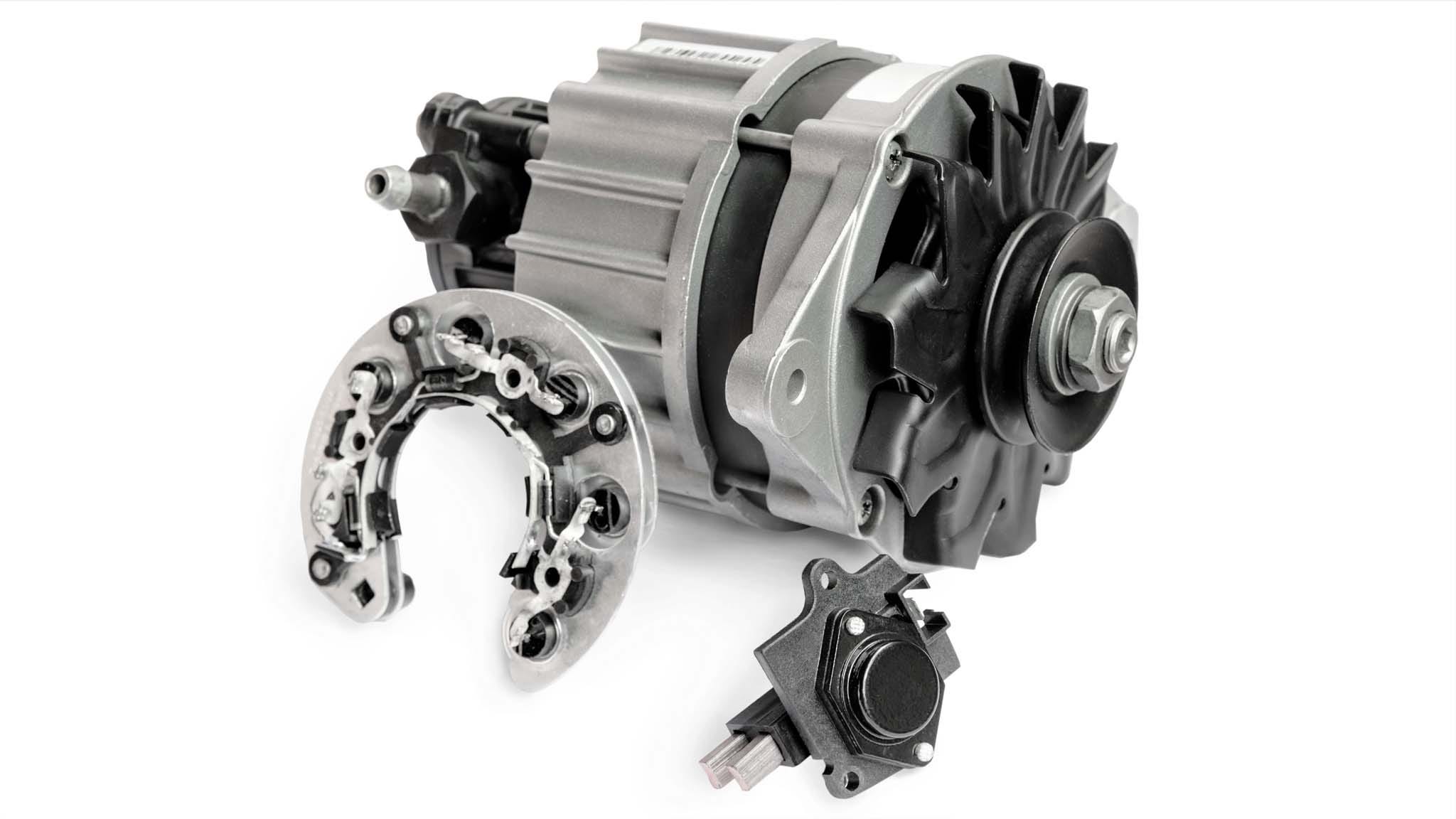

Illustrative image related to how much does it cost to rebuild an alternator
Strategic Material Selection Guide for how much does it cost to rebuild an alternator
What Materials Are Commonly Used in Alternator Rebuilding?
When considering the cost of rebuilding an alternator, the selection of materials plays a crucial role in determining performance, longevity, and overall effectiveness. Here, we analyze four common materials used in alternator components, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for international B2B buyers.
What Are the Key Properties of Copper in Alternator Rebuilding?
Copper is widely used for windings and electrical connections in alternators due to its excellent electrical conductivity. It can withstand high temperatures, making it suitable for the heat generated during operation. Additionally, copper has a good resistance to corrosion, especially when coated.
Pros and Cons:
Copper’s primary advantage is its superior conductivity, which enhances the efficiency of the alternator. However, it is relatively expensive compared to other materials, which can increase the overall cost of rebuilding. Manufacturing complexity is moderate, as copper components can be easily shaped and soldered.
Impact on Application:
Copper’s high conductivity ensures effective energy transfer, critical for applications requiring reliable electrical performance. However, in humid or corrosive environments, additional protective coatings may be necessary to prevent degradation.
Considerations for International Buyers:
In regions like Africa and South America, where the electrical infrastructure may vary, understanding local standards for copper quality (e.g., ASTM B170) is essential. Buyers should ensure compliance with local regulations regarding material sourcing and electrical safety.
How Does Aluminum Compare as a Material for Alternator Components?
Aluminum is often used for housings and some internal components due to its lightweight and good corrosion resistance. It can handle moderate temperatures but may not perform as well as copper in terms of conductivity.
Pros and Cons:
The lightweight nature of aluminum reduces the overall weight of the alternator, which can improve fuel efficiency in vehicles. However, its lower conductivity compared to copper can lead to reduced performance in high-demand applications. Manufacturing processes for aluminum can be complex, requiring specialized techniques like die-casting.
Impact on Application:
Aluminum’s corrosion resistance makes it suitable for environments with high moisture levels, but its lower thermal conductivity may limit its use in high-performance applications.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers in Europe and the Middle East should be aware of the relevant standards for aluminum (e.g., EN 573) to ensure compliance. Additionally, sourcing aluminum from reputable suppliers is crucial to avoid quality issues.
What Role Does Steel Play in Alternator Rebuilding?
Steel is commonly used in the structural components of alternators, such as the frame and some internal parts. It offers high strength and durability, making it suitable for high-stress applications.
Pros and Cons:
Steel’s strength is a significant advantage, providing durability and resistance to mechanical failure. However, it is heavier than aluminum and can be susceptible to corrosion if not properly treated. Manufacturing complexity can be high due to the need for precise machining.
Impact on Application:
Steel’s robustness makes it ideal for heavy-duty applications, but its weight can affect overall vehicle performance. Proper coatings or treatments are necessary to enhance corrosion resistance.
Considerations for International Buyers:
In regions with high humidity or corrosive environments, such as coastal areas in Brazil or the Middle East, buyers should consider steel grades with enhanced corrosion resistance (e.g., ASTM A36). Compliance with local manufacturing standards is also critical.
How Important Is Plastic in Alternator Rebuilding?
Plastic is often used for non-structural components, such as insulation and covers. It is lightweight and can be molded into complex shapes, making it versatile for various applications.
Pros and Cons:
Plastic’s lightweight nature and resistance to corrosion are significant advantages. However, it may not withstand high temperatures as well as metals, and its mechanical properties can be inferior. Manufacturing complexity is low, as plastic can be easily molded.
Impact on Application:
Plastic components can help reduce the overall weight of the alternator, but care must be taken to ensure they are suitable for the operational environment, especially concerning temperature and chemical exposure.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should ensure that the plastics used comply with relevant standards (e.g., ISO 9001) to guarantee quality. In regions like Africa, where UV exposure may be high, selecting UV-resistant plastics is advisable.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Alternator Rebuilding
| Material | Typical Use Case for how much does it cost to rebuild an alternator | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Copper | Windings and electrical connections | Superior conductivity | High cost | High |
| Aluminum | Housings and internal components | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Lower conductivity | Medium |
| Steel | Structural components and frames | High strength and durability | Susceptible to corrosion | Medium |
| Plastic | Insulation and non-structural covers | Lightweight and moldable | Limited temperature resistance | Low |
This analysis provides a comprehensive overview of the materials involved in alternator rebuilding, offering valuable insights for B2B buyers navigating the complexities of material selection in different international markets.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for how much does it cost to rebuild an alternator
What Are the Main Stages of the Manufacturing Process for Rebuilding an Alternator?
The manufacturing process for rebuilding an alternator involves several critical stages, each designed to ensure the final product meets stringent quality and performance standards. Here’s a breakdown of the key stages involved:
1. Material Preparation: How Are Raw Materials Selected and Processed?
The first step in the alternator rebuilding process is the selection and preparation of raw materials. High-quality metals, such as aluminum for the casing and copper for the windings, are typically sourced from reputable suppliers. These materials undergo rigorous inspections to ensure they meet industry standards.
Once the materials are received, they are processed to remove any impurities and prepare them for forming. This may involve cutting, machining, or treating the materials to enhance their durability and conductivity. Proper material preparation is essential, as the performance and longevity of the rebuilt alternator depend heavily on the quality of these raw materials.
2. Forming: What Techniques Are Used to Shape Components?
Forming is the next stage, where the prepared materials are shaped into the various components of the alternator. Techniques such as die casting, machining, and stamping are commonly employed.
-
Die Casting: This process is often used for the alternator housing, allowing for precise shapes and reduced waste. High-pressure die casting ensures a smooth finish and tight tolerances.
-
Machining: Components like the rotor and stator may be machined to achieve the necessary specifications. This process involves removing material to create the desired shape, which is critical for ensuring a proper fit and function.
-
Stamping: This method is used for creating flat components such as brackets and mounts. It involves placing sheets of metal into a stamping press, which shapes them into the required form.
The forming stage is vital as it lays the groundwork for the assembly and functionality of the alternator.
3. Assembly: How Are Components Assembled for Optimal Performance?
During the assembly stage, the individual components are brought together to form the complete alternator. This process typically involves:
-
Component Inspection: Each part is inspected for defects before assembly. This includes checking for proper dimensions and ensuring that there are no visible flaws.
-
Assembly Techniques: Skilled technicians use specific assembly techniques, such as soldering or mechanical fastening, to join components securely. The alternator’s internal wiring, including the brushes and diodes, is carefully arranged to ensure optimal electrical performance.
-
Testing During Assembly: Some manufacturers conduct preliminary testing at this stage to ensure that components function correctly when assembled. This might include checking the electrical connections and the mechanical integrity of the assembled unit.
4. Finishing: What Processes Ensure Quality and Aesthetic Appeal?
The finishing stage involves treating the alternator to enhance its durability and appearance. Common processes include:
-
Surface Treatment: Techniques such as anodizing or powder coating are used to protect the alternator from corrosion and wear. This is particularly important for alternators that will be exposed to harsh environments.
-
Final Inspection: After finishing, the alternator undergoes a comprehensive inspection to ensure it meets all quality standards. This final quality check is crucial for identifying any defects that may have occurred during manufacturing.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Implemented During the Rebuilding Process?
Quality assurance is critical in the alternator rebuilding process to ensure that the final product meets international standards and customer expectations. Here are the key quality control measures:
1. What International Standards Should B2B Buyers Look For?
International standards such as ISO 9001 are essential for ensuring that manufacturers adhere to quality management principles. This certification indicates that the manufacturer has established a quality management system that consistently meets customer and regulatory requirements.
Additionally, industry-specific certifications like CE (Conformité Européenne) or API (American Petroleum Institute) may also apply, particularly for alternators used in specialized applications. These certifications demonstrate compliance with specific safety and performance standards.
2. What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control checkpoints are critical in the manufacturing process to catch defects early and ensure quality throughout. These typically include:
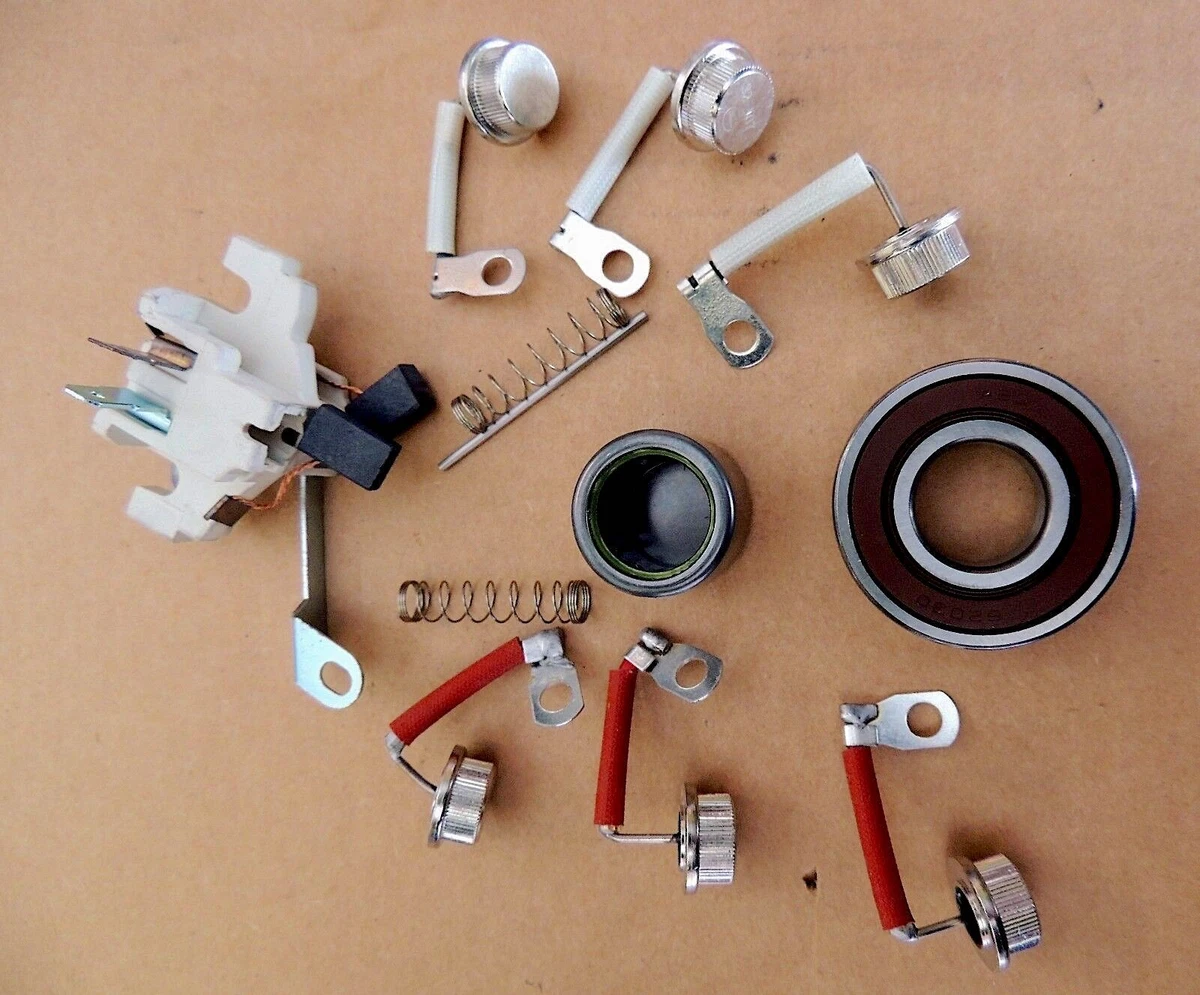

Illustrative image related to how much does it cost to rebuild an alternator
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial stage involves inspecting raw materials upon receipt to ensure they meet specified standards before they enter the manufacturing process.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, various checkpoints are established to monitor the quality of components at different stages. This helps identify and address issues in real-time.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once the alternator is fully assembled, it undergoes final testing and inspection. This includes functional tests to ensure it operates within specified parameters and visual inspections to check for any cosmetic defects.
3. How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers can take several steps to verify the quality control practices of their suppliers:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting regular audits of suppliers can provide insights into their quality management systems, manufacturing processes, and adherence to international standards.
-
Quality Reports: Requesting quality assurance reports can help buyers understand the results of previous inspections and tests, providing evidence of a supplier’s commitment to quality.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can offer an unbiased evaluation of a supplier’s quality control practices. These inspections can be conducted at various stages of the manufacturing process, providing additional assurance.
What Are the QC and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers must navigate specific challenges regarding quality control and certification when sourcing rebuilt alternators from different regions:
-
Regional Standards: Different countries may have varying quality standards and certifications. Buyers should be aware of the specific requirements in their region, such as EU regulations for products sold in Europe or local compliance standards in Africa and South America.
-
Documentation and Traceability: Ensuring that suppliers provide comprehensive documentation, including certificates of compliance and traceability for materials used, is essential. This helps verify that the alternators meet the required standards.
-
Cultural and Language Barriers: Communication challenges may arise when dealing with suppliers from different countries. Buyers should establish clear lines of communication and possibly engage local representatives to facilitate understanding and compliance with quality expectations.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures involved in rebuilding alternators, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing these critical components for their operations.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘how much does it cost to rebuild an alternator’
Introduction
In the competitive landscape of automotive repair, understanding the costs associated with rebuilding alternators is essential for B2B buyers. This guide provides a structured checklist to help you navigate the sourcing process effectively, ensuring you make informed decisions that align with your business needs and budget constraints.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before engaging suppliers, clearly outline the technical specifications required for the alternator rebuild. This includes the make and model of the vehicle, the type of alternator, and any specific parts that may need replacement.
– Why it’s important: Having precise specifications ensures compatibility and helps avoid costly errors down the line.
– What to look for: Check manufacturer guidelines and consider the amperage requirements based on any additional electronic components you may have installed.

Illustrative image related to how much does it cost to rebuild an alternator
Step 2: Research Cost Estimates for Rebuilding
Investigate the average costs associated with rebuilding alternators in your target market regions, such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
– Why it’s important: Understanding cost variations can help you budget appropriately and identify competitive pricing.
– What to look for: Gather data from multiple sources, including industry reports, supplier quotes, and local market trends to get a comprehensive view.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing, it’s crucial to vet suppliers thoroughly. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in a similar industry or region.
– Why it’s important: A reliable supplier can significantly impact the quality and cost-effectiveness of your alternator rebuilds.
– What to look for: Focus on suppliers with a proven track record in automotive parts and those who can provide warranties on their rebuild kits.
Step 4: Verify Supplier Certifications and Quality Standards
Ensure that potential suppliers comply with industry standards and possess relevant certifications.
– Why it’s important: Compliance with quality standards (like ISO certifications) indicates that the supplier adheres to rigorous quality control processes.
– What to look for: Check for certifications that relate to automotive parts manufacturing and rebuilding processes.
Step 5: Request Detailed Quotations
Once you have shortlisted potential suppliers, request detailed quotations that break down costs associated with the rebuilding process.
– Why it’s important: Detailed quotes help in understanding the cost structure and any hidden fees that may arise.
– What to look for: Ensure quotations include costs for parts, labor, shipping, and any warranty or after-sales support.
Step 6: Assess Lead Times and Availability
Inquire about the lead times for parts and the overall rebuilding process from each supplier.
– Why it’s important: Timeliness can affect your operational efficiency and customer satisfaction.
– What to look for: Ask suppliers for their estimated turnaround times and their capacity to handle large orders.
Step 7: Consider After-Sales Support and Warranty Terms
Evaluate the after-sales support and warranty terms offered by suppliers on the rebuilt alternators.
– Why it’s important: Strong after-sales support can minimize downtime and enhance customer satisfaction.
– What to look for: Look for warranties that cover defects and a responsive customer service team for troubleshooting.
By following this practical sourcing checklist, B2B buyers can confidently navigate the complexities of procuring alternator rebuilding services, ultimately leading to more informed purchasing decisions.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for how much does it cost to rebuild an alternator Sourcing
Analyzing the costs associated with rebuilding an alternator is crucial for B2B buyers looking to maximize their investment and ensure quality sourcing. Understanding the various cost components, price influencers, and strategic buyer tips can significantly impact procurement decisions, especially for international markets.
What Are the Key Cost Components in Rebuilding an Alternator?
-
Materials: The primary materials required for rebuilding an alternator include the alternator rebuild kit, which typically costs between $25 and $60. This kit generally contains essential components like bearings, voltage regulators, diodes, and brushes. Quality materials are critical as they directly influence the longevity and performance of the rebuilt alternator.
-
Labor: Labor costs can vary based on the complexity of the alternator design and the expertise required for the rebuild. Skilled technicians are necessary for proper disassembly, inspection, and reassembly, which can lead to significant labor expenses. Depending on the region, labor rates can range from $20 to $100 per hour.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes indirect costs associated with the rebuilding process, such as utilities, facility costs, and administrative expenses. A thorough understanding of these costs can help buyers evaluate suppliers more effectively.
-
Tooling: Specialized tools may be needed for certain alternator models, which can add to the initial setup costs. Investing in quality tools can improve efficiency and reduce labor time.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing rigorous QC processes is essential for ensuring the rebuilt alternator meets industry standards. This involves additional costs for testing equipment and inspection protocols.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs, particularly for international buyers, can significantly impact the overall cost. Understanding Incoterms is vital for accurately assessing these expenses.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically apply a margin on top of their costs to ensure profitability. This margin can vary widely based on supplier reputation, market demand, and the specific agreements negotiated.
What Price Influencers Should B2B Buyers Consider?
-
Volume/MOQ: The quantity of alternators being sourced can influence pricing. Larger orders often lead to bulk discounts, making it essential to assess minimum order quantities (MOQs) when negotiating prices.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom specifications may increase costs due to additional engineering and material requirements. Buyers should clearly communicate their needs to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher-quality materials and certifications can lead to increased costs but may be worth the investment for improved performance and reliability.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s location, reputation, and production capabilities can affect pricing. Established suppliers may command higher prices due to their reliability and quality assurance processes.
-
Incoterms: Familiarity with Incoterms can help buyers understand their responsibilities regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs, ultimately impacting the total cost.
What Are Some Effective Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficiency?
-
Negotiate Terms: Always negotiate pricing and payment terms with suppliers. Establishing long-term relationships can lead to better deals and more favorable terms over time.
-
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider not only the upfront costs but also the long-term implications of sourcing decisions. A lower initial price may lead to higher maintenance and operational costs.
-
Research and Compare Suppliers: Conduct thorough research on potential suppliers, comparing their pricing, quality, and service levels. Look for reviews and case studies from other buyers in similar markets.
-
Be Aware of Pricing Nuances: International buyers should consider currency fluctuations, import duties, and regional market dynamics that can influence pricing.
-
Plan for Contingencies: Always have contingency plans for potential delays in logistics or unexpected increases in material costs to avoid disruptions in your supply chain.
Disclaimer
The prices and cost structures discussed herein are indicative and can vary significantly based on specific project requirements, geographic location, and supplier capabilities. Always conduct comprehensive market research and engage in direct negotiations to obtain the most accurate pricing for your needs.

Illustrative image related to how much does it cost to rebuild an alternator
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing how much does it cost to rebuild an alternator With Other Solutions
When faced with a malfunctioning alternator, businesses have several options to consider. Rebuilding an alternator is one potential solution, but it’s essential to evaluate it against other alternatives such as outright replacement with a new alternator or opting for a remanufactured unit. Understanding the costs and implications of each option can help international B2B buyers make informed decisions that align with their operational needs.
| Comparison Aspect | How Much Does It Cost To Rebuild An Alternator | New Alternator Replacement | Remanufactured Alternator |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Generally restores original performance; depends on quality of components used. | New units offer optimal performance with guaranteed specifications. | Restored to factory specifications but may not match new performance entirely. |
| Cost | $25 to $60 for rebuild kit; total may vary based on labor and parts replaced. | $100 to $600 depending on vehicle make and model. | Typically $50 to $300, depending on brand and warranty. |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires technical skills; labor-intensive if done in-house. | Quick and straightforward; installation can be done by a professional or DIY. | Easier than rebuilding; still requires installation skills but less complex than a full rebuild. |
| Maintenance | May require ongoing monitoring; quality of rebuild varies. | Minimal maintenance; generally higher reliability. | May need more attention than a new unit; quality can vary by remanufacturer. |
| Best Use Case | Cost-effective for DIY enthusiasts with technical skills; ideal for older vehicles. | Best for those needing immediate, reliable performance; suitable for newer vehicles. | Great for budget-conscious buyers who want a balance of performance and cost without the risks of used parts. |
What Are the Pros and Cons of Rebuilding an Alternator?
Rebuilding an alternator can be a cost-effective solution, especially for businesses with skilled technicians. The primary advantage is the low cost of parts, which can range from $25 to $60 for a rebuild kit. However, the process can be labor-intensive and may lead to inconsistent performance depending on the quality of the components used. Additionally, businesses must weigh the potential risks of using a rebuilt alternator, as the longevity and reliability can vary significantly.
How Does a New Alternator Replacement Compare?
Opting for a new alternator replacement is generally the simplest and most reliable choice. The costs range from $100 to $600, depending on the vehicle type. New alternators come with a warranty and guaranteed performance, reducing the risk of failure. However, this option can be more expensive upfront, making it less appealing for businesses with tight budgets. Additionally, the installation may require a professional mechanic unless the buyer has the necessary skills.
What Are the Benefits of Choosing a Remanufactured Alternator?
Remanufactured alternators offer a middle ground between rebuilding and buying new. Priced between $50 and $300, they provide a balance of performance and cost. These units undergo rigorous factory processes to restore them to original specifications, which can offer peace of mind for businesses. However, potential downsides include variability in quality depending on the remanufacturer and the possibility of needing more maintenance compared to new units.
How Can B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution?
When choosing the right solution for an alternator issue, B2B buyers should consider their operational needs, budget constraints, and technical capabilities. If cost-saving is a priority and skilled labor is available, rebuilding may be the best route. For those requiring reliability and warranty support, investing in a new alternator might be worthwhile. Lastly, remanufactured units can serve as a practical compromise for budget-conscious businesses seeking dependable performance. Each option has its merits, and careful evaluation will lead to the best decision for the organization’s specific requirements.

Illustrative image related to how much does it cost to rebuild an alternator
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for how much does it cost to rebuild an alternator
What Are the Key Technical Properties to Consider When Rebuilding an Alternator?
Understanding the essential technical specifications related to alternator rebuilding can significantly influence decision-making for B2B buyers. Here are several critical specs to consider:
-
Material Grade
– The materials used in alternator components, such as copper for windings and aluminum for housings, are crucial for durability and efficiency. Higher-grade materials often translate to better conductivity and resistance to wear, which can extend the lifespan of the rebuilt alternator. B2B buyers should prioritize suppliers that use high-quality materials to ensure reliability. -
Electrical Tolerance
– This refers to the acceptable range of electrical characteristics such as voltage output and current capacity. For instance, an alternator typically operates within a voltage range of 13 to 14.5 volts. Ensuring that rebuilt alternators meet these tolerances is vital for the performance of the vehicle’s electrical system. Buyers should verify tolerance specifications to avoid future failures. -
Amperage Rating
– This is the maximum amount of electrical current the alternator can provide, typically measured in amps. Alternators with higher amperage ratings can support additional electrical loads, such as upgraded sound systems or additional lighting. B2B buyers should assess the amperage requirements based on the specific application to prevent overloading and potential damage. -
Thermal Resistance
– Alternators generate heat during operation, and components must withstand high temperatures without degrading. Thermal resistance is essential for maintaining performance and preventing premature failure. Buyers should inquire about the thermal ratings of rebuilt alternators to ensure they can operate effectively under varying conditions. -
Fitment and Compatibility
– The rebuilt alternator must be compatible with specific vehicle models, which includes dimensions, mounting points, and connector types. Understanding the fitment specifications is critical for ensuring a seamless installation. Buyers should reference OEM specifications to confirm compatibility with their vehicle fleet.
What Are Common Trade Terms Relevant to Alternator Rebuilding?
Familiarity with industry jargon can aid B2B buyers in navigating the complexities of alternator rebuilding. Here are some essential terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Refers to the company that originally manufactured the parts for a vehicle. When sourcing rebuilt alternators, buyers should consider OEM standards to ensure quality and compatibility. OEM parts often come with warranties and are designed to meet specific performance criteria. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– This term denotes the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is crucial for buyers, particularly those operating on tight budgets or with limited storage capacity. It allows for better inventory management and cost control. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– A formal process where buyers solicit price quotes from suppliers for specific products or services. An RFQ can include detailed specifications, quantities, and delivery timelines. For alternator rebuilding, submitting an RFQ helps ensure accurate pricing and terms tailored to the buyer’s needs. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– These are standardized trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Familiarity with Incoterms is essential for international transactions, ensuring clarity on who bears the risk at different stages of the shipping process. -
Warranty Period
– The duration during which the supplier guarantees the alternator against defects in material or workmanship. A robust warranty period indicates the supplier’s confidence in their product’s quality. B2B buyers should evaluate warranty terms to mitigate risks associated with potential failures.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when considering the cost and implications of rebuilding an alternator. This knowledge is essential in ensuring that the chosen solution meets operational requirements and budget constraints effectively.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the how much does it cost to rebuild an alternator Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics Influencing the Cost to Rebuild an Alternator?
The alternator rebuilding sector is experiencing a significant transformation driven by several global factors. One of the primary drivers is the rising cost of new automotive parts and the increased focus on cost efficiency among international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This economic landscape is compelling businesses to consider rebuilding as a viable alternative to purchasing new or remanufactured alternators, which can range from $100 to $600.
Emerging technologies are also shaping the market dynamics. The introduction of advanced diagnostic tools and automated testing equipment has streamlined the rebuilding process, reducing labor costs and turnaround times. Additionally, an increase in online platforms for sourcing parts is enhancing access to alternator rebuild kits, which typically range from $25 to $60. This accessibility allows smaller businesses to compete effectively by offering competitive pricing and faster service.
Furthermore, as the automotive industry shifts towards electric vehicles (EVs), there is a growing demand for hybrid alternators. This shift not only affects the components used in traditional alternators but also opens up new avenues for innovation and sourcing in the rebuilding sector. B2B buyers must stay informed about these trends to make strategic sourcing decisions that align with their business goals.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impacting the Alternator Rebuilding Market?
Sustainability has emerged as a critical consideration in the alternator rebuilding sector. The environmental impact of automotive waste is prompting businesses to adopt more sustainable practices. Rebuilding alternators not only conserves resources but also minimizes landfill contributions by extending the life of existing components. For B2B buyers, emphasizing sustainability can enhance brand reputation and align with the growing consumer demand for environmentally responsible practices.
Ethical sourcing plays a pivotal role in this context. Businesses are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who adhere to ethical labor practices and environmental standards. Certifications that indicate adherence to green practices, such as ISO 14001, are becoming essential in procurement processes. B2B buyers should seek suppliers that provide transparency in their supply chains, ensuring that the materials used in rebuilding alternators are sourced responsibly.
Incorporating “green” materials, such as eco-friendly lubricants and recyclable components, can further enhance the sustainability of the rebuilding process. As businesses strive to meet regulatory requirements and consumer expectations, integrating sustainability into the sourcing strategy will not only mitigate environmental impact but also foster long-term profitability.
What Is the Historical Context of Alternator Rebuilding in the Automotive Industry?
The practice of rebuilding alternators has its roots in the early automotive industry, where the focus was primarily on repair and maintenance rather than replacement. As vehicles became more complex and the demand for reliable electrical systems grew, the alternator’s role evolved. The introduction of mass production techniques in the mid-20th century made it easier and cheaper to produce new alternators, which initially led to a decline in rebuilding practices.
However, as the automotive landscape shifted in the late 20th and early 21st centuries, economic pressures and environmental concerns reignited interest in rebuilding as a cost-effective and sustainable alternative. Today, the alternator rebuilding sector is characterized by a blend of traditional craftsmanship and modern technology, allowing for high-quality repairs that can meet the demands of contemporary vehicles. This evolution not only underscores the resilience of the rebuilding process but also highlights its relevance in the current market, where cost efficiency and sustainability are paramount.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of how much does it cost to rebuild an alternator
-
How much does it typically cost to rebuild an alternator?
The cost to rebuild an alternator can vary widely based on the parts required and the labor involved. Generally, a DIY rebuild kit can range from $25 to $60, which includes components like bearings, voltage regulators, and brushes. If you opt for professional services, the total cost may escalate to between $100 and $300, depending on labor rates and the complexity of the alternator design. Always consider both parts and labor costs when budgeting for a rebuild. -
What factors influence the cost of rebuilding an alternator?
Several factors can affect the overall cost of rebuilding an alternator. These include the specific make and model of the vehicle, the availability of parts, and the extent of damage to the alternator. Additionally, the geographical location and the labor rates of the repair shop can also play a significant role. For B2B buyers, understanding these variables can help in negotiating prices with suppliers and service providers. -
Is it more cost-effective to rebuild or replace an alternator?
In many cases, rebuilding an alternator is more cost-effective than replacing it with a new unit. Rebuilding allows for reusing the main components, which can significantly reduce costs. However, if the alternator has extensive damage or if replacement parts are expensive or hard to source, purchasing a remanufactured or new alternator might be a better option. B2B buyers should evaluate the specific circumstances of each case before making a decision. -
What should I look for when sourcing alternator rebuild kits?
When sourcing alternator rebuild kits, prioritize quality and compatibility with your vehicle’s specifications. Look for kits that include all necessary components and are made from durable materials. Supplier reputation is crucial; check reviews and testimonials to gauge reliability. Additionally, consider the availability of technical support from the supplier, especially if you plan to handle the rebuild process in-house. -
How can I vet suppliers for alternator parts and rebuild kits?
To vet suppliers effectively, begin by researching their business history and reputation in the industry. Request references from previous clients and check for certifications or quality assurance processes they may have. Additionally, consider visiting their facilities if possible or requesting samples of their products. Establishing a clear line of communication regarding terms of service, delivery timelines, and warranties will also help build a trustworthy partnership. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for alternator rebuild kits?
Minimum order quantities for alternator rebuild kits can vary significantly between suppliers. Some may offer flexible options with no MOQ, while others might require bulk purchases to reduce costs. When negotiating with suppliers, clarify their MOQ policies and assess how they align with your purchasing needs. This is particularly important for B2B buyers who may require consistent replenishment for maintenance services. -
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing alternator rebuild kits?
Payment terms can vary based on the supplier’s policies and your business relationship. Common terms include upfront payments, net 30, or net 60 days. For international transactions, consider additional factors like currency exchange rates and transaction fees. Establishing clear payment terms upfront can help avoid misunderstandings and ensure smooth transactions. -
What logistics considerations should I be aware of when importing alternator rebuild kits?
When importing alternator rebuild kits, be mindful of shipping costs, delivery times, and customs regulations specific to your country. Verify that the supplier can provide necessary documentation for customs clearance. Additionally, consider partnering with logistics providers who specialize in international shipping to streamline the process. Efficient logistics planning can minimize delays and enhance your supply chain efficiency.
Top 4 How Much Does It Cost To Rebuild An Alternator Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Reddit – Reman Alternators
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Alternator rebuilding, reman alternators, lifetime warranty on reman starters/alternators, quality concerns with reman products, experience with rebuilding alternators, tools needed for rebuilding (ohm meter), potential issues with alternator performance (overloading, higher amperage needs, shorts).
2. CarTalk – Alternator Replacement Cost
Domain: cartalk.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: The cost to replace an alternator ranges from $600 to $1,500. An alternator is a critical component that maintains the charge of the battery and powers various electrical systems in the vehicle. Symptoms of a failing alternator include a check engine light, dimming headlights, and the need for jump-starts. Alternators can fail due to mechanical wear or electrical component failure. New car warrant…
3. LS1 Tech – Alternator Rebuild Services
Domain: ls1tech.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: Rebuilding an alternator for a 2000 LS1 F-body typically costs between $38 to $90. It is possible to increase the amp output during the rebuild, but this may depend on the specific components used and the shop’s capabilities. Customers should inquire about the possibility of upgrading the alternator’s amp output when discussing the rebuild with the shop.
4. Alternators – Rebuild Estimates and Options
Domain: mgexp.com
Registered: 2011 (14 years)
Introduction: Alternator rebuild estimates range from $100 to $145. A rebuilt alternator from O’Reilly costs $60 and comes with a lifetime warranty. A Bosch alternator for a 1980 Ford Fiesta can be ordered online for around $70, with a recommendation to ensure it is a Bosch and not an Autolite. One user mentioned purchasing a Bosch unit from Autozone for $66 with a lifetime warranty. There are discussions about…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for how much does it cost to rebuild an alternator
In conclusion, understanding the costs associated with rebuilding an alternator is crucial for international B2B buyers, particularly those operating in diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. The average cost for a rebuild can range from $25 to $60 for a DIY kit, while professional services may see prices escalate based on the complexity of the alternator and the necessary parts. By strategically sourcing quality components and reliable service providers, businesses can achieve significant cost savings and maintain operational efficiency.
Investing in a rebuilt alternator not only extends the life of existing equipment but also promotes sustainability by reducing waste. As global markets continue to evolve, it is essential for B2B buyers to stay informed about the best practices in sourcing and rebuilding automotive components. Embracing these practices will not only enhance profitability but also ensure a competitive edge in the marketplace.
As you navigate your sourcing strategies, consider the long-term benefits of establishing relationships with reputable suppliers who can provide high-quality parts and services. Now is the time to act—optimize your procurement processes and make informed decisions that will secure your business’s future in the automotive industry.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.

Illustrative image related to how much does it cost to rebuild an alternator