Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for how much does alternator cost to replace
In the ever-evolving landscape of automotive maintenance, understanding how much it costs to replace an alternator is crucial for international B2B buyers. This component, essential for converting mechanical energy into electrical power, directly affects vehicle performance and reliability. However, the costs associated with alternator replacement can vary significantly based on factors like vehicle make and model, parts availability, and labor complexities. This guide addresses the pressing challenge of sourcing reliable alternator replacement options, providing a detailed breakdown of costs, types of alternators available (OEM, remanufactured, and aftermarket), and insights into the implications of each choice.
For businesses operating in diverse markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, making informed purchasing decisions is paramount. This guide empowers B2B buyers by offering a comprehensive overview of the alternator replacement process, including supplier vetting strategies, potential cost-saving measures, and the importance of professional versus DIY replacement options. By equipping decision-makers with actionable insights, this resource not only simplifies the procurement process but also enhances the operational efficiency of their fleets. Whether you’re managing a logistics company in Nigeria or a transport service in Vietnam, understanding these dynamics will enable you to navigate the global market with confidence and precision.
Table Of Contents
- Top 4 How Much Does Alternator Cost To Replace Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for how much does alternator cost to replace
- Understanding how much does alternator cost to replace Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of how much does alternator cost to replace
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘how much does alternator cost to replace’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for how much does alternator cost to replace
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for how much does alternator cost to replace
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘how much does alternator cost to replace’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for how much does alternator cost to replace Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing how much does alternator cost to replace With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for how much does alternator cost to replace
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the how much does alternator cost to replace Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of how much does alternator cost to replace
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for how much does alternator cost to replace
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Understanding how much does alternator cost to replace Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| OEM Alternators | Manufactured by the vehicle’s original manufacturer | Luxury and high-performance vehicles | Pros: High reliability, perfect fit. Cons: Most expensive option. |
| Aftermarket Alternators | Produced by third-party companies | General automotive repairs | Pros: Cost-effective, varied options. Cons: Quality may vary between brands. |
| Remanufactured Alternators | Refurbished to meet original specifications | Fleet vehicles, budget-conscious repairs | Pros: Cost savings, reliable. Cons: May have limited warranties. |
| Salvage Alternators | Used parts from donor vehicles | DIY mechanics, budget repairs | Pros: Very low cost. Cons: Uncertain reliability, often no warranty. |
| Hybrid Alternators | Combine features of traditional and newer technologies | Innovative vehicle models | Pros: Enhanced efficiency, longer lifespan. Cons: Higher initial investment. |
What are OEM Alternators and Why Are They Preferred?
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) alternators are produced by the vehicle’s manufacturer and are designed to meet the exact specifications of the original part. They are typically preferred for luxury and high-performance vehicles where reliability and performance are critical. B2B buyers should consider the long-term benefits of investing in OEM parts, especially for high-value assets, despite the higher upfront costs. They often come with warranties that can protect against future issues.
How Do Aftermarket Alternators Compare in Cost and Quality?
Aftermarket alternators are produced by independent manufacturers and are available at a lower price point than OEM parts. These alternators can be an attractive option for businesses looking to manage costs, especially in general automotive repairs. However, B2B buyers should carefully evaluate the reputation of the aftermarket brands they consider, as quality can vary significantly. Choosing reputable manufacturers can mitigate risks associated with lower-quality parts.
What Are the Advantages of Remanufactured Alternators?
Remanufactured alternators are previously used units that have been refurbished to meet factory standards. They offer a balance between cost and reliability, making them an excellent choice for fleet vehicles or budget-conscious repairs. B2B buyers should weigh the cost savings against the potential for limited warranties. These alternators are often a preferred choice when looking to maintain operational efficiency without incurring the full cost of new parts.
When Should Businesses Consider Salvage Alternators?
Salvage alternators are used parts sourced from donor vehicles and are the most economical option available. They are suitable for DIY mechanics or businesses operating on tight budgets. However, the uncertainty surrounding the reliability and lack of warranties makes them a risky choice for critical applications. B2B buyers should consider salvage alternators only when they have a thorough understanding of the part’s history and condition.
What Are Hybrid Alternators and Their Benefits?
Hybrid alternators incorporate advanced technology to enhance efficiency and performance. They are suitable for innovative vehicle models that require higher energy outputs. While they may come with a higher initial investment, the potential for improved fuel efficiency and longer lifespan can justify the costs for B2B buyers. Companies focusing on sustainability and long-term operational savings should explore hybrid options as part of their procurement strategy.
Key Industrial Applications of how much does alternator cost to replace
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of how much does alternator cost to replace | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive Repair | Cost analysis for alternator replacement in fleet maintenance | Reduces downtime and improves fleet reliability | Availability of parts, labor rates, and warranty options |
| Transportation & Logistics | Budgeting for vehicle maintenance costs | Enhances financial planning and operational efficiency | Type of alternator (OEM vs. aftermarket), regional pricing |
| Construction Equipment | Evaluating alternator costs for heavy machinery | Ensures machinery uptime and reduces repair costs | Access to specialized parts, local supplier reliability |
| Agricultural Machinery | Assessing replacement costs for farm vehicles | Maintains productivity during harvest seasons | Seasonal demand fluctuations, sourcing from local dealers |
| Energy Sector | Managing costs for service vehicles in remote locations | Optimizes budgeting for maintenance in challenging environments | Supply chain logistics, part compatibility with diverse fleets |
How is ‘how much does alternator cost to replace’ applied in the Automotive Repair Industry?
In the automotive repair sector, understanding alternator replacement costs is crucial for fleet maintenance managers. They must budget effectively to minimize vehicle downtime and ensure reliable operation. By analyzing costs ranging from aftermarket to OEM parts, businesses can make informed decisions that enhance fleet efficiency. Additionally, they should consider sourcing parts from local suppliers to reduce shipping delays, which is particularly important in regions with limited access to automotive components.
What is the significance of alternator replacement costs in Transportation & Logistics?
Transportation and logistics companies benefit from a thorough understanding of alternator replacement costs when budgeting for vehicle maintenance. This insight allows for better financial planning and helps prevent unexpected expenses that could disrupt operations. Companies should compare pricing across various suppliers and parts types to optimize their budget while ensuring that they procure reliable components that meet the specific needs of their vehicle fleet.
How does understanding alternator costs impact Construction Equipment management?
For businesses in the construction industry, evaluating the costs associated with alternator replacements in heavy machinery is essential. Machinery downtime can lead to significant project delays and financial losses. By sourcing reliable alternators and understanding regional pricing variations, construction firms can maintain productivity and minimize repair expenses. It is important to establish relationships with specialized suppliers who can provide the necessary parts quickly to avoid project interruptions.
Why is alternator replacement cost assessment important for Agricultural Machinery?
In agriculture, the timing of maintenance is critical, especially during harvest seasons. Farmers must assess the costs of replacing alternators in their vehicles to ensure they remain operational when it matters most. Understanding local market prices and the availability of parts can significantly impact productivity. Additionally, farmers should consider the reliability of suppliers, especially during peak seasons when demand for parts may surge.
Illustrative image related to how much does alternator cost to replace
How does the Energy Sector benefit from knowing alternator replacement costs?
In the energy sector, service vehicles often operate in remote locations, making maintenance a logistical challenge. Understanding alternator replacement costs helps companies manage their budgets effectively, ensuring that they allocate sufficient resources for vehicle upkeep. By considering factors like part compatibility and supply chain logistics, energy firms can optimize their maintenance strategies and reduce the risk of vehicle failures that could hinder operations in challenging environments.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘how much does alternator cost to replace’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Cost Variability in Alternator Replacement
The Problem: B2B buyers, especially fleet managers or automotive parts resellers, often face the challenge of wide-ranging costs associated with alternator replacement. Depending on the vehicle make, model, and region, the price can vary significantly—from as low as $450 for economy vehicles to over $2,200 for luxury models. This variability creates uncertainty in budgeting for repairs, which can affect overall operational costs and profitability.
The Solution: To manage and anticipate these costs effectively, buyers should conduct thorough market research and establish relationships with multiple suppliers. Comparing quotes from different mechanics and parts vendors can reveal cost-effective options. Additionally, investing in a cost analysis tool that tracks historical pricing data for different vehicle types can provide insights into trends and help forecast future expenses. Consider collaborating with local auto repair shops to negotiate bulk pricing for alternator replacements, thereby ensuring consistency in service quality and cost management across the fleet.
Scenario 2: Understanding Warranty Coverage Limitations
The Problem: Many B2B buyers, particularly those managing new or leased vehicles, may not fully understand the warranty coverage on alternators. This lack of clarity can lead to unexpected expenses if a vehicle’s alternator fails outside the warranty period or if they mistakenly believe repairs will be covered. The complexity of warranties, which can differ by manufacturer and model, adds to the confusion.
The Solution: Buyers should invest time in reviewing the warranty terms for each vehicle in their fleet, paying close attention to the specifics regarding alternator coverage. Creating a detailed summary of warranty details, including expiration dates and coverage limits, will help in making informed decisions. Additionally, working with a knowledgeable automotive consultant can clarify any ambiguous terms and provide guidance on warranty claims. For vehicles approaching the end of their warranty, proactive inspections can prevent costly repairs by identifying potential alternator issues early on.
Scenario 3: Selecting the Right Alternator Type for Cost Efficiency
The Problem: When faced with the need to replace an alternator, B2B buyers often struggle to determine which type of alternator—OEM, remanufactured, or aftermarket—will provide the best balance between cost and reliability. Choosing the wrong type can lead to repeated failures, higher long-term costs, and increased downtime for vehicles, which is particularly detrimental for businesses relying on a fleet.
The Solution: Buyers should conduct a comparative analysis of the three types of alternators based on their specific operational needs and vehicle specifications. Engaging with trusted automotive suppliers to discuss the pros and cons of each option can yield insights into long-term performance and reliability. For many businesses, remanufactured alternators offer a cost-effective solution without sacrificing quality, as they are generally inspected and rebuilt to meet OEM standards. To further ensure reliability, consider establishing a preferred vendor relationship with a supplier who specializes in high-quality alternators and offers warranties on their parts. This approach not only enhances the lifespan of the alternators but also fosters a streamlined procurement process that can save both time and money.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for how much does alternator cost to replace
What Materials are Commonly Used in Alternator Manufacturing and Their Cost Implications?
When considering the cost of replacing an alternator, the choice of materials used in its construction plays a crucial role in determining both performance and price. Here, we analyze four common materials used in alternator manufacturing: aluminum, copper, steel, and plastic. Each material has unique properties that affect durability, cost, and overall suitability for various applications.

Illustrative image related to how much does alternator cost to replace
Aluminum: Lightweight and Corrosion-Resistant
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight, possesses excellent corrosion resistance, and has good thermal conductivity, making it ideal for automotive applications where weight reduction is essential.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of aluminum is its low weight, which contributes to fuel efficiency. However, it can be more expensive than steel and may not withstand high-impact situations as effectively.
Impact on Application: Aluminum’s corrosion resistance makes it suitable for vehicles operating in humid or coastal environments. However, its mechanical properties may limit its use in high-performance applications where strength is critical.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in regions like Africa and South America should ensure that aluminum components comply with local automotive standards, such as ISO or ASTM. The availability of aluminum parts may vary, affecting lead times and costs.
Copper: High Conductivity for Electrical Components
Key Properties: Copper is known for its excellent electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, and ductility, making it a preferred choice for wiring and electrical connections in alternators.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of copper is its superior conductivity, which enhances the alternator’s efficiency. However, copper is more expensive than aluminum and can be prone to corrosion if not properly insulated.
Impact on Application: Copper’s high conductivity ensures efficient power transfer, which is vital for vehicle performance. In regions with high humidity, additional protective coatings may be necessary to prevent corrosion.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with electrical standards (e.g., IEC, JIS) is crucial, especially in regions like the Middle East and Europe. Buyers should also consider the impact of fluctuating copper prices on overall costs.
Steel: Strength and Durability
Key Properties: Steel is known for its high tensile strength and durability, making it suitable for structural components within the alternator.

Illustrative image related to how much does alternator cost to replace
Pros & Cons: The key advantage of steel is its robustness, which ensures long-lasting performance under mechanical stress. However, steel is heavier than aluminum and can be susceptible to rust if not properly treated.
Impact on Application: Steel components are ideal for applications requiring high strength, such as in heavy-duty vehicles. However, the added weight can negatively impact fuel efficiency.
Considerations for International Buyers: In regions like Nigeria and Vietnam, buyers should be aware of local regulations regarding material quality and environmental standards. Steel parts should meet compliance standards such as DIN or ASTM to ensure reliability.
Plastic: Lightweight and Cost-Effective
Key Properties: Plastic is lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and can be molded into complex shapes, making it suitable for non-structural components in alternators.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of plastic is its low cost and versatility in design. However, plastic may not withstand high temperatures or mechanical stress as well as metal alternatives.
Impact on Application: Plastic components are suitable for applications where weight savings are critical, but they may not be appropriate for high-performance or high-temperature environments.
Illustrative image related to how much does alternator cost to replace
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that plastic materials comply with relevant automotive standards, such as ISO or ASTM, particularly in Europe and the Middle East. The availability of high-quality plastics may vary by region, impacting overall costs.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Alternator Replacement Costs
| Material | Typical Use Case for how much does alternator cost to replace | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Housing and structural components in lightweight vehicles | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Higher cost and lower impact resistance | Medium |
| Copper | Wiring and electrical connections | Superior electrical conductivity | Higher cost and corrosion susceptibility | High |
| Steel | Structural components in heavy-duty alternators | High strength and durability | Heavier and prone to rust | Medium |
| Plastic | Non-structural components like covers | Cost-effective and versatile | Limited temperature and stress resistance | Low |
This analysis provides B2B buyers with a comprehensive understanding of the materials used in alternators, helping them make informed decisions based on performance, cost, and regional compliance standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for how much does alternator cost to replace
What Are the Key Manufacturing Processes for Alternators?
Manufacturing alternators involves several critical stages, ensuring that each unit meets the necessary performance standards. The main stages of the manufacturing process include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How Is Material Prepared for Alternator Production?
The first step in the manufacturing process is material preparation. High-quality materials such as copper for windings, steel for the casing, and rare-earth magnets are sourced from reputable suppliers. Suppliers often undergo rigorous vetting to ensure they comply with international standards, such as ISO 9001, which emphasizes quality management systems. This stage may also involve pre-treatment processes, such as degreasing or coating, to enhance material performance.

Illustrative image related to how much does alternator cost to replace
What Forming Techniques Are Used in Alternator Manufacturing?
Forming processes are crucial in shaping the materials into the required components. Techniques such as stamping, forging, and machining are commonly employed to create parts like the rotor, stator, and housing. For instance, the rotor is typically formed through precise machining to ensure optimal fit and function within the alternator. Advanced technologies like CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining are often used to enhance accuracy and reduce waste.
How Is the Assembly Process Conducted for Alternators?
Once the individual components are formed, they move to the assembly stage. This process involves combining the rotor, stator, and other components to create a complete alternator. Automated assembly lines may be utilized to enhance efficiency, but skilled technicians oversee critical assembly points to ensure quality. Quality control measures are integrated into the assembly process, including torque testing and alignment checks, to ensure that each alternator meets specified performance criteria.
What Finishing Techniques Are Applied to Alternators?
The finishing stage of alternator manufacturing often includes painting, coating, or plating to protect against corrosion and wear. This is particularly important for alternators that operate in challenging environments. Additionally, finishing processes may involve electrical testing to verify that the alternator performs within established parameters. This may include load testing, insulation resistance testing, and output voltage testing to ensure reliability.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Implemented in Alternator Manufacturing?
Quality assurance is integral to the manufacturing process of alternators. Various international and industry-specific standards guide these quality assurance measures, ensuring that products are safe, reliable, and efficient.
Which International Standards Apply to Alternator Manufacturing?
ISO 9001 is one of the most recognized international standards for quality management systems. It provides a framework for manufacturers to enhance their processes, improve product quality, and increase customer satisfaction. In addition to ISO 9001, alternator manufacturers may also comply with specific industry standards such as CE marking in Europe, which indicates conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
Illustrative image related to how much does alternator cost to replace
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Alternator Production?
Quality control checkpoints are essential throughout the manufacturing process. These include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This stage involves inspecting raw materials and components upon arrival at the manufacturing facility to ensure they meet specified standards.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, various tests are conducted to monitor quality at each production stage. This may include dimensional checks and functional tests of components.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After assembly, each alternator undergoes comprehensive testing to verify that it meets performance specifications. This may include load testing and durability assessments.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used for Quality Assurance?
Various testing methods are employed to ensure the reliability and safety of alternators. Common techniques include:
-
Electrical Testing: This verifies the output voltage and current to ensure that the alternator operates effectively under load.
-
Thermal Testing: Alternators are subjected to temperature extremes to assess performance under various conditions.
-
Vibration Testing: This evaluates the durability of the alternator by simulating real-world operating conditions.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For B2B buyers, particularly those operating in international markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying supplier quality control is critical to ensure product reliability.
What Steps Can Buyers Take to Audit Suppliers?
Conducting audits of potential suppliers can help buyers gain insights into their manufacturing processes and quality control measures. Buyers should request documentation of quality certifications (e.g., ISO 9001) and inquire about the supplier’s quality management practices. On-site audits can also be beneficial, allowing buyers to assess the facilities and processes firsthand.
How Can Buyers Utilize Quality Reports and Third-Party Inspections?
Buyers should request quality reports from suppliers, detailing their testing methods, results, and compliance with international standards. Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased evaluation of the supplier’s quality control processes. These services often include pre-shipment inspections, which can help identify potential issues before products are delivered.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers should be aware of specific nuances in quality control that may vary by region. For instance, while European manufacturers may adhere strictly to CE marking requirements, suppliers in other regions may have different standards. Understanding these regional differences can help buyers make informed decisions and mitigate risks associated with quality.
In conclusion, navigating the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for alternators requires an understanding of both technical and regulatory frameworks. By being diligent in assessing suppliers and their quality control practices, B2B buyers can ensure they procure reliable alternators that meet their operational needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘how much does alternator cost to replace’
Introduction
This practical sourcing guide is designed to assist B2B buyers in navigating the complex process of determining the costs associated with replacing an alternator. Understanding the financial implications of alternator replacement can enhance decision-making for fleet management, automotive repairs, and inventory procurement, especially in diverse markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Step 1: Assess Your Vehicle Requirements
Before initiating the procurement process, evaluate the specific vehicle models for which you need alternators. Different vehicles, particularly luxury versus economy models, have varying alternator specifications and costs. Ensure you have the make, model, and year of each vehicle on hand to facilitate accurate pricing and part identification.
Step 2: Define Your Budget Parameters
Establish a clear budget for the alternator replacement, including parts and labor. The cost can range significantly, from $450 for basic aftermarket parts to over $2,200 for OEM components on luxury vehicles. Understanding your financial boundaries will help narrow down suppliers and options that fit your budget.
Step 3: Research Supplier Options
Conduct thorough research on potential suppliers, focusing on those that specialize in automotive parts. Look for suppliers with a proven track record and positive reviews from other B2B buyers. This step is crucial to ensure reliability and quality, which directly impacts the longevity and performance of the alternators.
Step 4: Evaluate Part Types and Quality
Determine the type of alternator you need: OEM, remanufactured, or aftermarket. Each type has its benefits and drawbacks:
– OEM: Typically more expensive but offers reliability and compatibility.
– Remanufactured: More cost-effective and generally reliable, as they are rebuilt to factory standards.
– Aftermarket: Often the cheapest option, but quality can vary widely. Ensure that any aftermarket parts meet industry standards.
Step 5: Request Quotes from Multiple Suppliers
Once you have identified potential suppliers, request detailed quotes that include the cost of parts, labor, and any additional fees. This will enable you to compare pricing effectively. Ensure quotes specify whether parts are OEM, remanufactured, or aftermarket, as this can significantly affect the overall cost.
Step 6: Verify Warranty and Return Policies
Before finalizing your purchase, verify the warranty and return policies associated with the alternators. A robust warranty can protect your investment and provide peace of mind, especially in regions where automotive parts may be subject to harsher conditions. Look for suppliers that offer at least a one-year warranty for parts.
Step 7: Consult with a Certified Mechanic
If possible, consult with a certified mechanic to get insights on the best alternator options for your specific vehicles. Mechanics can provide valuable feedback on the reliability of various brands and types, ensuring you make an informed choice that aligns with your operational needs.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can streamline the procurement process for alternator replacements, ensuring they make informed, cost-effective decisions that enhance their automotive operations.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for how much does alternator cost to replace Sourcing
When considering the replacement of an alternator, various cost components and pricing influencers come into play. Understanding these elements can aid international B2B buyers in making informed decisions regarding sourcing and budgeting.
What Are the Key Cost Components in Alternator Replacement?
-
Materials: The cost of the alternator itself can vary significantly based on its type. Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM) parts are generally the most expensive, providing guaranteed compatibility and reliability. Aftermarket and remanufactured alternators typically offer more cost-effective options but may vary in quality and longevity.
-
Labor: Labor costs can fluctuate widely depending on the complexity of the alternator’s installation. For instance, an alternator that is easily accessible may require only one to two hours of labor, while those located deeper within the engine compartment can necessitate several hours of work. Labor rates also differ regionally and between independent shops and dealerships.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with the production of alternators, such as factory operations, equipment maintenance, and utilities. Manufacturers that maintain high-quality standards may have higher overhead, impacting the final price.
-
Tooling and Quality Control (QC): The initial investment in tooling for manufacturing alternators is significant, especially for specialized or high-performance models. Quality control processes ensure that alternators meet safety and performance standards, which can also contribute to the overall cost.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can vary based on the source of the alternator and its destination. International buyers should account for potential tariffs, shipping fees, and handling costs that can affect the total purchase price.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a markup to cover their operational expenses and profit. Understanding the margin applied can help buyers negotiate better pricing.
What Influences Pricing for Alternator Replacement?
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Purchasing in bulk can significantly reduce the unit price of alternators. Suppliers often offer discounts for larger orders, making it advantageous for businesses with high turnover in vehicle maintenance.
-
Specifications and Customization: Buyers requiring specific features or custom-built alternators may face higher costs. Customization often requires additional resources and time, impacting pricing.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Alternators made from higher-grade materials or those that meet specific industry certifications often come at a premium. Buyers should assess whether the added cost translates into improved durability and performance.
-
Supplier Factors: The reliability and reputation of the supplier can also influence pricing. Established suppliers with a track record of quality may charge more, while newer or less reputable suppliers might offer lower prices but with potential risks.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the agreed-upon Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) is crucial for international transactions. These terms dictate the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs, which can impact overall costs.
What Tips Can Help Buyers Optimize Costs for Alternator Replacement?
-
Negotiation: Engage suppliers in discussions about pricing, especially for bulk orders. Many suppliers are open to negotiation, especially if they see potential for long-term partnerships.
-
Focus on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate the long-term costs associated with an alternator, including its lifespan, warranty, and potential for failure. Sometimes, a higher upfront cost can lead to savings in the long run.
-
Understand Regional Pricing Nuances: For international buyers, be aware that prices can vary significantly between regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Factors such as local demand, shipping logistics, and import regulations can influence pricing.
-
Conduct Market Research: Before making a purchase, compare prices from various suppliers. This not only helps in finding competitive rates but also provides insights into market trends.
-
Evaluate Repair vs. Replacement: In some cases, repairing an alternator may be a viable alternative to replacement. Consulting with a trusted mechanic can provide clarity on the best approach based on the specific situation.
Disclaimer
The prices mentioned in this analysis are indicative and can vary based on numerous factors including market conditions, supplier negotiations, and specific vehicle requirements. Always seek multiple quotes and conduct thorough research to ensure the best financial decision for your business needs.

Illustrative image related to how much does alternator cost to replace
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing how much does alternator cost to replace With Other Solutions
When faced with the need to replace an alternator, B2B buyers often seek alternatives that may offer comparable benefits or cost savings. This analysis examines the costs and performance of replacing an alternator against two alternative solutions: installing a high-capacity battery and utilizing a solar power system. Each solution has its unique advantages and disadvantages, which can significantly impact operational efficiency and budgeting decisions.
| Comparison Aspect | How Much Does Alternator Cost To Replace | High-Capacity Battery | Solar Power System |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Essential for vehicle electrical needs; reliable energy source while driving | Improves battery life and performance; may not power all vehicle systems | Provides power for vehicle electronics; requires sunlight |
| Cost | $450 – $2,200 depending on vehicle type and parts used | $300 – $1,000 depending on capacity and brand | $2,000 – $5,000 for installation and equipment |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires professional installation; time-consuming for complex models | Generally easy to install; some DIY potential | Complex installation; may need permits and professional help |
| Maintenance | Minimal post-installation; periodic checks recommended | Requires monitoring and maintenance; lifespan of 3-5 years | Low maintenance; occasional cleaning and monitoring |
| Best Use Case | Traditional vehicles where the alternator is the primary power source | Vehicles with high electrical demands (e.g., sound systems, lighting) | Electric or hybrid vehicles; off-grid applications |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of a High-Capacity Battery?
High-capacity batteries can be a viable alternative to replacing an alternator, particularly in vehicles that require a significant amount of electrical power. These batteries can enhance the performance of the vehicle’s electrical system, providing longer life and better reliability for electronic components. However, while they can support higher loads, they do not replace the functionality of an alternator. This means that if the vehicle’s engine is not running, the battery alone may not provide enough power to start the vehicle or run all systems effectively. Additionally, high-capacity batteries can be expensive, and their lifespan typically ranges from three to five years, necessitating eventual replacement.
How Does a Solar Power System Compare as an Alternative?
Solar power systems present another innovative solution, particularly for electric or hybrid vehicles, by providing a renewable energy source that can power electrical components and recharge batteries. These systems can significantly reduce reliance on traditional power sources and contribute to energy savings over time. However, the initial installation costs can be quite high, ranging from $2,000 to $5,000, and they may require professional installation, which can complicate the implementation process. Additionally, solar systems depend on sunlight availability, which can be a limitation in regions with less consistent weather conditions.
How Can B2B Buyers Make the Right Choice for Their Needs?
Ultimately, the decision on whether to replace an alternator or consider alternatives like high-capacity batteries or solar power systems depends on several factors, including the specific vehicle type, intended use, budget constraints, and operational requirements. B2B buyers should assess their unique needs—such as the electrical demands of their vehicles and potential cost savings over time—before making a decision. Consulting with automotive professionals or industry specialists can also provide valuable insights into the best solution that aligns with their operational goals and financial considerations.
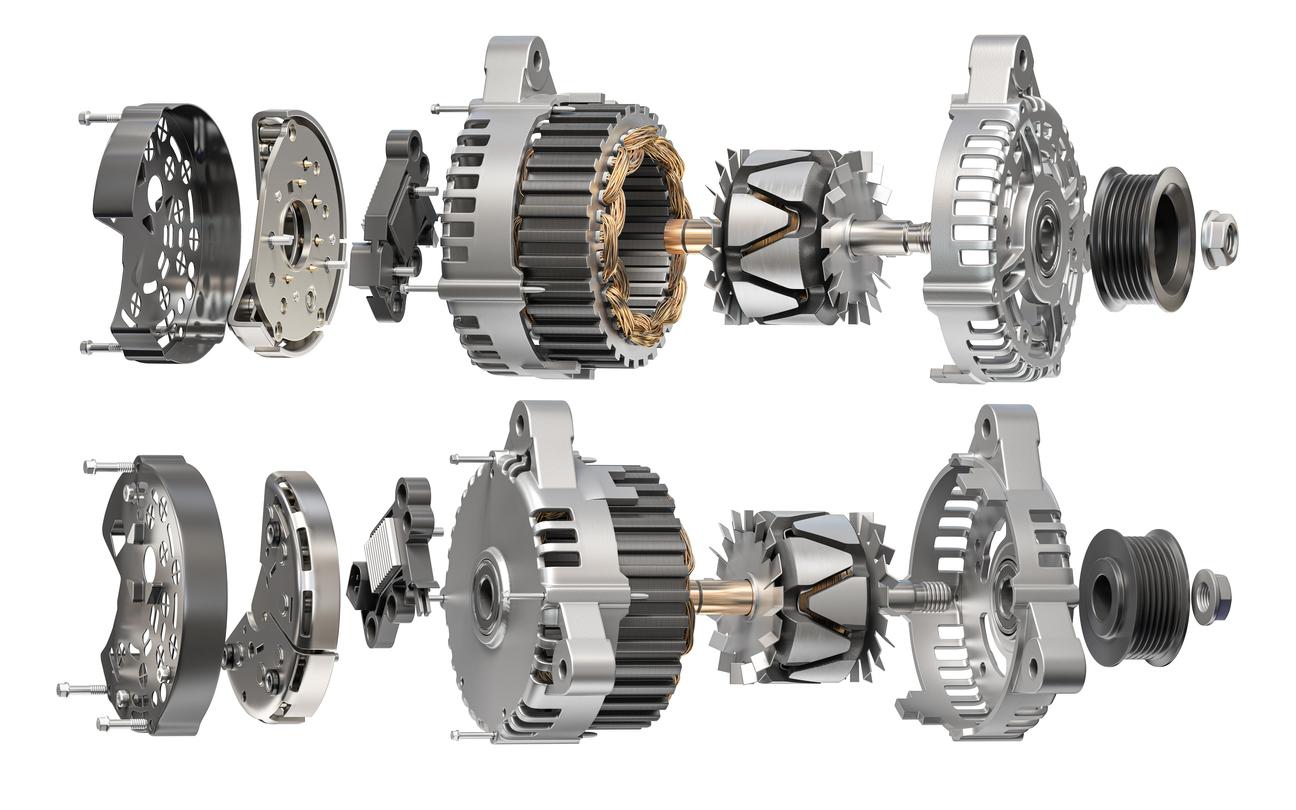

Illustrative image related to how much does alternator cost to replace
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for how much does alternator cost to replace
When considering the cost of replacing an alternator, understanding key technical properties and industry terminology can significantly enhance decision-making for B2B buyers in the automotive sector. Here’s a breakdown of essential specifications and terms that are crucial in this context.
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Alternators?
1. Material Grade
The materials used in alternators, such as copper for windings and high-grade aluminum or steel for housings, affect durability and performance. Higher-grade materials typically provide better conductivity and longevity, which is vital for high-demand applications. Buyers should prioritize quality materials to ensure reliability, especially in regions with extreme weather conditions.
2. Voltage Rating
Alternators are designed to produce a specific voltage output, typically between 12V and 14.5V for most vehicles. Understanding the voltage rating is crucial for compatibility with the vehicle’s electrical system. An alternator with the incorrect voltage output can lead to battery damage or insufficient power supply to electrical components, increasing operational costs.
3. Amperage Output
The amperage rating indicates how much electrical current an alternator can generate. This property is essential for vehicles with high electrical demands, such as those equipped with advanced infotainment systems or multiple electronic accessories. Selecting an alternator with adequate amperage ensures that all components function optimally, avoiding potential failures and costly repairs.
4. Efficiency Rating
The efficiency of an alternator reflects how effectively it converts mechanical energy into electrical energy. Higher efficiency ratings mean less energy waste, leading to improved fuel economy and lower operational costs. B2B buyers should consider this property, particularly in markets where fuel efficiency is a priority.
5. Thermal Tolerance
Alternators operate in environments with varying temperatures, so understanding their thermal tolerance is vital. This specification indicates how well an alternator can withstand heat without failure. Buyers should ensure that the alternator chosen can handle the thermal conditions typical of the vehicle’s operating environment, especially in regions with high ambient temperatures.
What Are Common Trade Terminology and Jargon Related to Alternator Replacement?
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM parts are made by the vehicle’s original manufacturer and are designed to meet specific performance standards. While often more expensive, they provide assurance of quality and compatibility. B2B buyers should weigh the cost against potential long-term benefits and reliability.
2. Aftermarket
Aftermarket alternators are produced by third-party manufacturers. They can offer cost savings compared to OEM parts but may vary in quality. Buyers should conduct thorough research on the aftermarket brands to ensure they meet performance needs and warranty requirements.
3. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is critical for B2B buyers when negotiating with suppliers, as it can impact inventory management and cash flow.
4. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to request pricing for specific quantities of goods, including alternators. B2B buyers should utilize RFQs to gather competitive pricing and terms from multiple suppliers, ensuring they make informed purchasing decisions.
5. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are standardized trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with these terms helps B2B buyers understand shipping costs, risk transfer, and delivery obligations, which are crucial when sourcing alternators from different regions.
Understanding these technical properties and industry terms can empower B2B buyers to make informed decisions when replacing alternators, ultimately enhancing operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness in their automotive operations.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the how much does alternator cost to replace Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics Affecting Alternator Replacement Costs?
The global automotive industry is witnessing significant shifts that impact the cost of alternator replacements, especially for B2B buyers in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Key drivers include increasing vehicle ownership, evolving consumer preferences towards electric vehicles (EVs), and the rising complexity of automotive technology. As a result, the average cost for alternator replacement can range from $450 to over $2,200, depending on vehicle make and model, which adds a layer of complexity for international buyers navigating pricing.

Illustrative image related to how much does alternator cost to replace
Emerging trends in B2B sourcing are also reshaping the landscape. The rise of e-commerce platforms has made it easier for businesses to source automotive parts directly from manufacturers, allowing for competitive pricing and improved supply chain efficiency. Additionally, the shift towards remanufactured and aftermarket parts is gaining traction due to cost-saving benefits and better availability. This trend is particularly relevant for markets in Africa and South America, where budget constraints often dictate sourcing decisions.
Furthermore, the integration of digital tools and platforms enables buyers to compare prices, assess supplier reliability, and streamline procurement processes. By leveraging these technologies, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and budget constraints while ensuring they maintain quality standards.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact Alternator Replacement Costs?
In the context of alternator replacement, sustainability and ethical sourcing are becoming increasingly significant for B2B buyers. The automotive sector is under pressure to minimize its environmental impact, and this extends to the sourcing of components like alternators. Buyers are now more inclined to seek suppliers who adhere to sustainable practices, which can influence both cost and availability.
The use of ‘green’ certifications and materials is gaining momentum. Suppliers that demonstrate compliance with environmental standards often command a premium, but they also provide long-term value through enhanced brand reputation and customer loyalty. For instance, sourcing remanufactured alternators not only reduces waste but can also lower costs, as these components typically range 25% cheaper than brand-new alternatives.
Moreover, ethical supply chains that ensure fair labor practices and responsible sourcing of raw materials can enhance a company’s corporate social responsibility (CSR) profile. This is particularly important in markets across Africa and the Middle East, where consumers and businesses alike are increasingly prioritizing ethical considerations in their purchasing decisions. Therefore, while sustainability may initially raise costs, it can lead to significant savings and a competitive edge in the long run.
Illustrative image related to how much does alternator cost to replace
What Is the Historical Evolution of Alternator Technology and Its Relevance to B2B Buyers?
The alternator has evolved significantly since its inception in the early 20th century, transitioning from simple mechanical devices to complex electronic components essential for modern vehicles. Initially, vehicles relied on generators, which were less efficient and required more maintenance. The introduction of the alternator in the 1960s revolutionized automotive electrical systems, providing more reliable power and requiring less upkeep.
This evolution is crucial for B2B buyers, as understanding the technological advancements in alternators can inform sourcing decisions. Modern alternators are designed for greater efficiency and durability, which can influence replacement costs. For instance, luxury vehicles might require specialized OEM parts, driving up costs significantly compared to aftermarket options available for standard models. As the automotive landscape continues to shift towards electric and hybrid vehicles, B2B buyers must stay informed about these changes to adapt their sourcing strategies effectively.
In summary, navigating the complexities of alternator replacement costs requires a multifaceted approach that considers market dynamics, sustainability, and the historical context of automotive technology. By leveraging this knowledge, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that optimize their procurement processes and align with their strategic objectives.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of how much does alternator cost to replace
-
How much does it typically cost to replace an alternator?
The cost to replace an alternator varies significantly based on vehicle make and model. Generally, prices range from $450 for aftermarket parts on economy vehicles to over $2,200 for OEM parts on luxury models. Labor costs can add an additional $200 to $1,000, depending on accessibility and regional labor rates. It’s essential to consider both parts and labor when budgeting for this repair. -
What factors influence the cost of alternator replacement?
Several factors affect the cost of alternator replacement, including the vehicle’s make and model, the type of alternator (OEM, remanufactured, or aftermarket), and the complexity of the labor involved. Additionally, regional pricing differences and the specific mechanic or shop chosen can lead to variations in overall costs. Understanding these elements can help you make informed sourcing decisions. -
How can I source alternators cost-effectively for my business?
To source alternators cost-effectively, consider building relationships with multiple suppliers to compare prices and quality. Evaluate options between OEM, remanufactured, and aftermarket parts, and communicate your needs clearly to suppliers. Leverage bulk purchasing agreements to negotiate lower prices, and inquire about discounts for larger orders to maximize savings. -
What should I consider when vetting alternator suppliers?
When vetting alternator suppliers, assess their reputation, production quality, and compliance with international standards. Request samples and review warranty terms to ensure product reliability. It’s also important to evaluate their logistical capabilities, including shipping options and delivery timelines, to ensure they can meet your demand efficiently. -
Are there minimum order quantities (MOQs) when purchasing alternators?
Many suppliers impose minimum order quantities (MOQs) for alternators, which can range from a few units to several hundred, depending on the supplier and part type. Discuss MOQs upfront with potential suppliers to avoid unexpected costs and ensure that your order aligns with your inventory needs. Flexibility in your order quantity can also help in negotiations. -
What payment terms are typically offered for bulk alternator purchases?
Payment terms for bulk alternator purchases can vary by supplier but commonly include options such as net 30, net 60, or even cash in advance. Some suppliers may offer discounts for early payments or bulk orders. It’s crucial to negotiate terms that align with your cash flow and operational needs to maintain financial stability. -
How can I ensure quality assurance for alternators I source?
To ensure quality assurance for sourced alternators, request certifications and compliance documentation from suppliers. Implement a quality control process that includes inspection upon receipt, and consider conducting random sampling of the products. Establishing clear return and warranty policies can also help mitigate risks associated with defective parts. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing alternators?
When sourcing alternators, consider logistics factors such as shipping costs, delivery times, and customs regulations. Evaluate whether suppliers can accommodate your preferred shipping methods and provide tracking information. Additionally, understanding the import/export regulations specific to your region can prevent delays and additional costs.
Top 4 How Much Does Alternator Cost To Replace Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Toyota – RAV4 Alternator Replacement
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: 2006 Toyota RAV4 alternator replacement; cost: $450 (includes labor); parts cost approximately $350.
2. J.D. Power – Alternator Replacement Costs
Domain: jdpower.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Alternator replacement costs range from $350 to $900, with average parts costing $100 to $350, and luxury models costing $500 to $700. Labor costs can add $350 to $500, and replacing the serpentine belt may add $20 to $50. Rebuilt alternators are available and should match or exceed the original amp rating. DIY installation is possible for skilled individuals, potentially saving on labor costs.
3. Facebook – Car Repair Quotes
Domain: facebook.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: This company, Facebook – Car Repair Quotes, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
4. CarTalk – Alternator Replacement Guide
Domain: cartalk.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: The cost to replace an alternator ranges from $600 to $1,500. An alternator is a critical component that maintains the charge of the battery and powers various electrical systems in the vehicle. It converts mechanical energy into electrical energy and is driven by an accessory belt in the engine. Signs of a failing alternator include a check engine light, dimming headlights, and the need for jump-…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for how much does alternator cost to replace
In summary, understanding the costs associated with alternator replacement is crucial for B2B buyers in the automotive sector. The price for alternator replacement typically ranges from $450 to over $2,200, influenced by factors such as vehicle make and model, the type of alternator selected, and regional labor costs. Strategic sourcing plays a vital role in mitigating these expenses. By evaluating options such as OEM, remanufactured, and aftermarket parts, businesses can optimize their procurement processes while ensuring quality and reliability.
International buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should leverage local suppliers and mechanics to gain insights into the most cost-effective solutions tailored to their specific markets. Additionally, maintaining strong relationships with parts manufacturers can facilitate better pricing and availability.

Illustrative image related to how much does alternator cost to replace
As the automotive industry continues to evolve, staying informed about market trends and cost-saving strategies will empower businesses to make informed decisions. Engage with trusted suppliers, explore diverse sourcing options, and position your company for success in a competitive landscape. The future of your automotive operations depends on strategic sourcing and the ability to adapt to changing market conditions.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.