Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for why electric cars are better than gas
As global markets evolve, international B2B buyers face the critical challenge of sourcing sustainable transportation solutions. The shift toward electric cars presents an opportunity not just for environmental stewardship, but also for significant cost savings and operational efficiency. This guide delves into the myriad reasons why electric vehicles (EVs) are better than gas-powered cars, offering insights into the types of EVs available, their applications across various industries, and the supplier vetting processes crucial for informed decision-making.
The comprehensive scope of this guide addresses key considerations such as the comparative costs of ownership, the long-term benefits of reduced maintenance requirements, and the potential for tax incentives in different regions. Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including countries like Germany and Saudi Arabia, will find valuable information tailored to their unique market dynamics.
By equipping decision-makers with actionable insights and strategic recommendations, this guide empowers businesses to transition smoothly to electric vehicle fleets, aligning their operations with global sustainability goals while enhancing their bottom line. The journey toward electrification is not just a trend; it is a pivotal movement toward a more sustainable and economically viable future.
Table Of Contents
- Top 3 Why Electric Cars Are Better Than Gas Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for why electric cars are better than gas
- Understanding why electric cars are better than gas Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of why electric cars are better than gas
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘why electric cars are better than gas’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for why electric cars are better than gas
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for why electric cars are better than gas
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘why electric cars are better than gas’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for why electric cars are better than gas Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing why electric cars are better than gas With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for why electric cars are better than gas
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the why electric cars are better than gas Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of why electric cars are better than gas
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for why electric cars are better than gas
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Understanding why electric cars are better than gas Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cost Efficiency | Lower fuel and maintenance costs compared to gas vehicles | Fleet management, logistics companies | Pros: Significant savings over time. Cons: Higher upfront cost. |
| Environmental Impact | Zero tailpipe emissions and reduced carbon footprint | Corporate sustainability initiatives | Pros: Enhances corporate image. Cons: Limited charging infrastructure in some regions. |
| Technological Advancements | Integration of advanced tech like regenerative braking and smart features | Tech-driven industries, R&D sectors | Pros: Access to cutting-edge technology. Cons: Potential for higher repair costs. |
| Government Incentives | Availability of tax credits and grants for electric vehicle purchases | Companies seeking financial incentives | Pros: Reduces overall purchase cost. Cons: Incentives may vary by region and change frequently. |
| Operational Longevity | Longer lifespan of electric vehicles compared to gas counterparts | Long-term fleet operations | Pros: Reduced frequency of vehicle replacement. Cons: Battery replacement can be costly. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Cost Efficiency in Electric Vehicles?
Cost efficiency is a primary reason businesses consider electric vehicles (EVs). With lower fuel costs—electricity is generally cheaper than gasoline—and reduced maintenance expenses due to fewer moving parts, companies can significantly lower their operational costs. For B2B buyers, this translates into more predictable budgeting and potential savings in fleet management. However, the initial investment in electric vehicles can be higher, which necessitates careful financial planning.
How Does the Environmental Impact of Electric Vehicles Influence B2B Decisions?
The environmental benefits of electric vehicles are compelling for businesses aiming to enhance their sustainability credentials. By adopting EVs, companies can reduce their carbon emissions and contribute to global efforts against climate change. This is particularly relevant for businesses in sectors where corporate social responsibility is increasingly scrutinized. Nevertheless, the availability of charging stations and the overall infrastructure can be a challenge in certain regions, which should be considered when making purchasing decisions.
Illustrative image related to why electric cars are better than gas
Why Are Technological Advancements Important for Businesses Considering Electric Vehicles?
Electric vehicles often come equipped with advanced technologies, including regenerative braking and smart connectivity features. For businesses in tech-driven industries, these innovations can lead to improved efficiency and operational effectiveness. However, while the technology can offer significant advantages, buyers must also weigh the potential for higher repair costs, particularly if specialized knowledge is required for maintenance.
What Government Incentives Should B2B Buyers Consider When Purchasing Electric Vehicles?
Government incentives play a crucial role in making electric vehicles more financially viable for businesses. Tax credits, grants, and subsidies can significantly offset the initial purchase price, making EVs an attractive option for many organizations. However, these incentives can vary widely by region and may change over time, so businesses should stay informed about local regulations and opportunities to maximize their investment.
How Does the Operational Longevity of Electric Vehicles Benefit B2B Buyers?
Electric vehicles are known for their longevity, often outlasting traditional gas vehicles. This durability can lead to lower total cost of ownership over time, especially for companies that rely on long-term fleet operations. However, the potential high cost of battery replacement can be a concern, requiring businesses to factor in long-term maintenance strategies when considering their fleet composition.
Key Industrial Applications of why electric cars are better than gas
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of why electric cars are better than gas | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Logistics & Transportation | Transitioning delivery fleets to electric vehicles | Reduced fuel costs and lower maintenance expenses | Availability of charging infrastructure and fleet size |
| Public Transportation | Electrification of public transit systems | Lower operational costs and enhanced environmental image | Government incentives and local energy costs |
| Tourism & Hospitality | Electric vehicle rentals for eco-conscious travelers | Attracting environmentally aware customers | Partnerships with EV manufacturers and charging stations |
| Construction & Heavy Industry | Using electric trucks for site transport | Decreased emissions and compliance with regulations | Battery capacity and range suited for heavy loads |
| Agriculture | Electric vehicles for farm operations | Lower fuel and maintenance costs, improved sustainability | Compatibility with existing farm equipment and charging options |
In the logistics and transportation sector, companies are increasingly transitioning their delivery fleets to electric vehicles (EVs). This shift not only reduces fuel costs but also significantly lowers maintenance expenses, as electric motors require less upkeep than traditional combustion engines. For international buyers, sourcing EVs may require assessing the availability of charging infrastructure in their regions, particularly in remote areas of Africa or South America, where such facilities might still be developing.
Public transportation systems are also embracing electrification as a means to enhance operational efficiency. Electric buses and trams can significantly lower operational costs while improving the environmental footprint of urban transit. For B2B buyers in Europe, especially in countries like Germany, navigating government incentives for electric public transit vehicles will be essential to maximizing financial benefits and ensuring compliance with local regulations.
In the tourism and hospitality industry, electric vehicle rentals are becoming increasingly popular among eco-conscious travelers. By offering EVs, businesses can attract a customer base that prioritizes sustainability. International B2B buyers should consider forming partnerships with EV manufacturers and ensuring access to charging stations to meet this rising demand effectively.
The construction and heavy industry sectors can benefit from using electric trucks for transporting materials on-site. These vehicles help companies decrease emissions and comply with increasingly stringent environmental regulations. When sourcing electric trucks, businesses need to consider battery capacity and range to ensure they meet the demands of heavy loads and long working hours.
Finally, in agriculture, electric vehicles can play a vital role in operations, from transporting goods to fieldwork. The reduced fuel and maintenance costs associated with electric vehicles can significantly enhance profitability. Buyers in this sector should evaluate the compatibility of electric vehicles with existing farm equipment and available charging options to ensure seamless integration into their operations.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘why electric cars are better than gas’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Understanding the Total Cost of Ownership for Electric vs. Gas Vehicles
The Problem: Many B2B buyers are often focused solely on the initial purchase price of electric vehicles (EVs) compared to gas vehicles, neglecting the long-term financial implications. This narrow perspective can lead to a misinformed decision that overlooks the significantly lower total cost of ownership associated with EVs. Buyers may be concerned about higher upfront costs, without recognizing the substantial savings on fuel and maintenance over the vehicle’s lifespan. This challenge is particularly pronounced in regions where fuel prices are volatile, making budgeting difficult.
Illustrative image related to why electric cars are better than gas
The Solution: To overcome this pain point, B2B buyers should conduct a comprehensive total cost of ownership (TCO) analysis before making any purchase decisions. This analysis should include not only the purchase price but also the costs of insurance, maintenance, fuel (or charging), and potential tax incentives. Tools and calculators are available online to help estimate these costs accurately. Additionally, buyers can seek advice from financial experts familiar with the automotive sector to help model various scenarios based on their specific usage patterns and regional electricity costs. By understanding the full financial picture, businesses can make informed decisions that highlight the cost-effectiveness of switching to electric vehicles.
Scenario 2: Overcoming Range Anxiety in Electric Vehicle Adoption
The Problem: Despite the growing popularity of electric vehicles, many B2B buyers express concerns about range anxiety—fear that the vehicle will run out of battery before reaching a charging station. This is especially relevant for businesses operating in regions with limited charging infrastructure or those needing to cover long distances regularly. Such worries can hinder the transition to electric vehicles, as buyers may perceive them as less reliable than traditional gas vehicles.
The Solution: To alleviate range anxiety, B2B buyers should invest in thorough planning and the adoption of advanced telematics systems. These systems can provide real-time data on vehicle performance, including battery status and the locations of nearby charging stations. Buyers can also consider implementing a mixed fleet strategy where electric vehicles are complemented by gas vehicles for longer trips. Additionally, engaging with local governments or electric utility companies to advocate for more charging infrastructure can enhance confidence in electric vehicle adoption. Businesses should also educate their staff about efficient driving practices that maximize the range of electric vehicles, ensuring that they feel comfortable and secure when making the switch.
Scenario 3: Navigating Incentives and Regulations for Electric Vehicles
The Problem: B2B buyers often face confusion regarding the various incentives, rebates, and regulations associated with electric vehicle purchases. This confusion can lead to missed opportunities for cost savings or compliance issues, particularly in regions where laws and incentives differ significantly. Inconsistent information can cause businesses to hesitate in making the switch to electric vehicles, fearing financial penalties or lost incentives.
The Solution: To effectively navigate this complex landscape, B2B buyers should prioritize establishing relationships with local dealerships, electric vehicle advocacy groups, and government agencies. These connections can provide up-to-date information on available incentives, such as tax credits, rebates for charging infrastructure, and grants for fleet upgrades. Buyers should also consider attending informational workshops or webinars that focus on electric vehicle policies and incentives in their respective regions. Furthermore, leveraging expert consultancy services that specialize in sustainable transportation can help streamline the process, ensuring compliance with regulations while maximizing available financial benefits. By proactively engaging with the regulatory environment, businesses can not only minimize risks but also capitalize on opportunities for significant savings.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for why electric cars are better than gas
What Materials Contribute to the Superiority of Electric Cars Over Gas Vehicles?
In the context of electric vehicles (EVs) versus gasoline-powered vehicles, the materials used in their construction and components play a crucial role in performance, sustainability, and overall cost-effectiveness. Here, we analyze several key materials commonly utilized in electric cars, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for international B2B buyers.

Illustrative image related to why electric cars are better than gas
Lithium-Ion Batteries: The Heart of Electric Vehicles
Key Properties: Lithium-ion batteries are known for their high energy density, lightweight nature, and ability to withstand numerous charge-discharge cycles. They typically operate effectively within a temperature range of -20°C to 60°C and have a voltage rating of 3.7 volts per cell.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of lithium-ion batteries is their efficiency in energy storage, allowing electric vehicles to travel longer distances on a single charge. However, they can be expensive to manufacture and may require complex battery management systems to ensure safety and longevity. Additionally, the mining of lithium can have environmental impacts.
Impact on Application: Lithium-ion batteries are essential for powering electric motors, making them a critical component in EV performance. Their compatibility with various charging infrastructures enhances their usability across different regions.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should be aware of the varying regulations regarding battery disposal and recycling. Compliance with local environmental standards, such as the European Union’s Battery Directive, is essential.
Aluminum: Lightweight and Corrosion-Resistant
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight, with a density of about 2.7 g/cm³, and exhibits excellent corrosion resistance, particularly when anodized. It can withstand temperatures up to 600°C.
Pros & Cons: The lightweight nature of aluminum improves vehicle efficiency by reducing overall weight, which can enhance range and performance. However, aluminum can be more expensive than traditional steel, and its manufacturing process is energy-intensive.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is commonly used in the body and frame of electric vehicles, contributing to overall vehicle efficiency and performance. Its corrosion resistance is particularly beneficial in regions with high humidity or salt exposure.
Considerations for International Buyers: B2B buyers should consider the availability of aluminum in their regions and the associated costs. Compliance with international standards such as ASTM and DIN for material quality is crucial for ensuring product reliability.

Illustrative image related to why electric cars are better than gas
Carbon Fiber: Strength and Lightweight Properties
Key Properties: Carbon fiber composites have a high strength-to-weight ratio, with tensile strengths exceeding 500 MPa and a density of around 1.6 g/cm³. They can operate effectively in a wide range of temperatures.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of carbon fiber is its exceptional strength combined with low weight, which can significantly enhance vehicle performance and efficiency. However, the high cost of production and complex manufacturing processes can be prohibitive for widespread use.
Impact on Application: Carbon fiber is often used in high-performance electric vehicles, especially in structural components and body panels, to maximize efficiency and minimize weight.

Illustrative image related to why electric cars are better than gas
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the limited availability of carbon fiber and the need for specialized manufacturing capabilities. Compliance with international standards for composite materials is also important.
Steel: A Traditional Yet Effective Material
Key Properties: Steel is known for its high tensile strength and durability, with a density of approximately 7.85 g/cm³. It can withstand high temperatures and is recyclable.
Pros & Cons: Steel is cost-effective and widely available, making it a popular choice for many automotive applications. However, its weight can negatively impact the efficiency of electric vehicles compared to lighter materials like aluminum and carbon fiber.
Impact on Application: Steel is commonly used in the chassis and structural components of electric vehicles, providing strength and safety.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with local and international standards for steel quality and safety is essential. Buyers should also consider the impact of tariffs and trade regulations on steel imports.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for why electric cars are better than gas | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lithium-Ion Batteries | Powering electric motors and energy storage | High energy density and efficiency | High manufacturing cost and environmental concerns | High |
| Aluminum | Body and frame construction | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Higher cost and energy-intensive production | Med |
| Carbon Fiber | Structural components and body panels | Exceptional strength-to-weight ratio | High production cost and complexity | High |
| Steel | Chassis and structural components | Cost-effective and widely available | Heavier, impacting vehicle efficiency | Low |
This analysis highlights the diverse materials that contribute to the advantages of electric vehicles over gasoline-powered counterparts. Understanding these materials is vital for B2B buyers as they navigate the complexities of sourcing, compliance, and cost in different international markets.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for why electric cars are better than gas
What Are the Main Stages of Electric Car Manufacturing?
The manufacturing process for electric vehicles (EVs) is complex and involves several key stages that differ significantly from traditional gasoline vehicles. Understanding these processes is crucial for B2B buyers looking to invest in electric car technology.
Material Preparation: What Materials Are Used in Electric Cars?
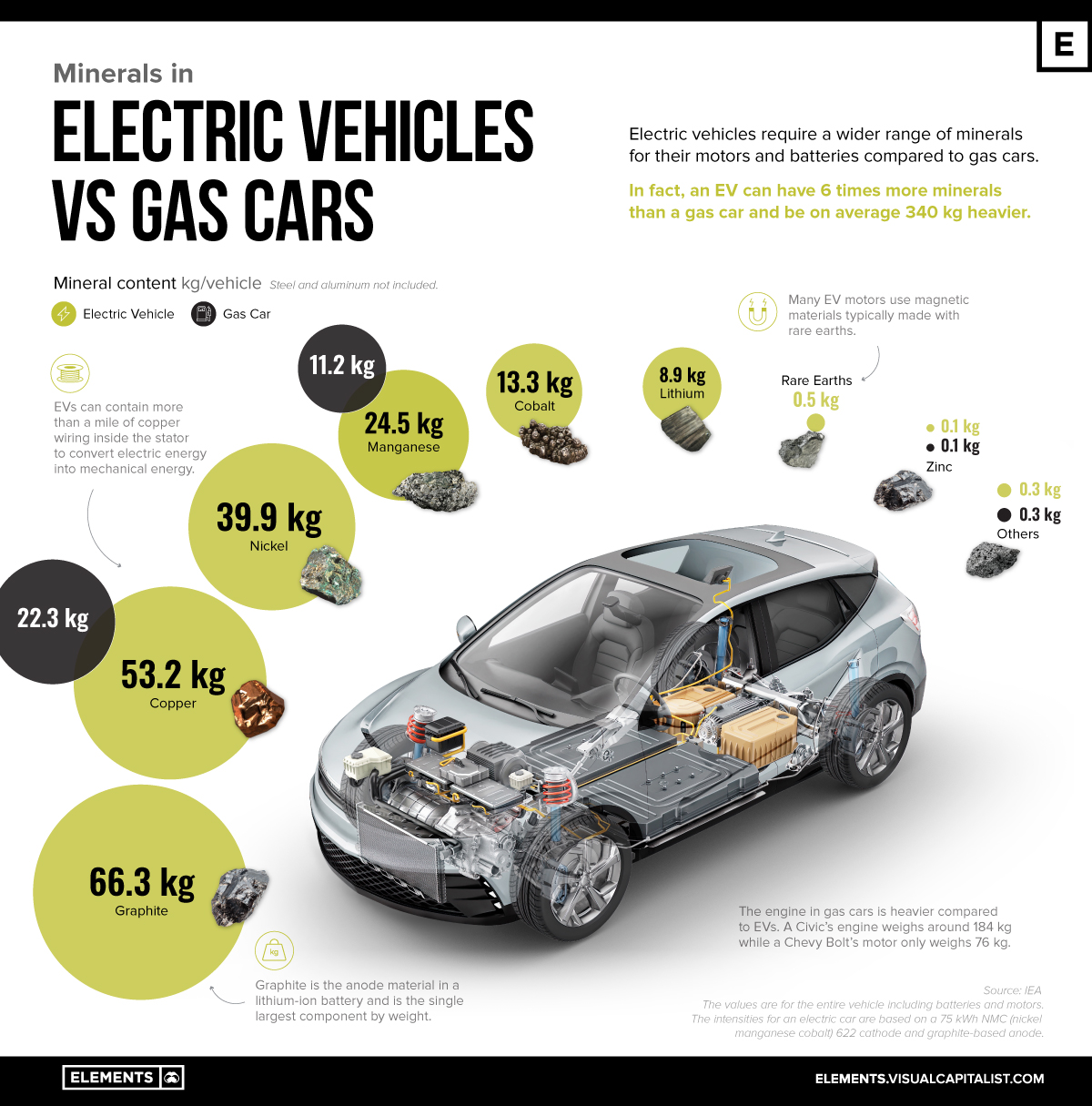
The first stage in manufacturing electric cars focuses on sourcing and preparing the necessary materials. Electric vehicles primarily utilize lightweight materials such as aluminum and high-strength steel, which are essential for improving efficiency and range. Additionally, lithium, cobalt, and nickel are crucial for the production of lithium-ion batteries.
The sourcing of these materials is critical, especially for international buyers who may face supply chain challenges. It is advisable to verify the ethical sourcing of materials through certifications or supplier audits to ensure compliance with environmental and social standards.
How Are Electric Cars Formed and Assembled?
Once the materials are prepared, the next stage involves forming and assembling various components. Advanced techniques such as stamping and extrusion are employed to create the vehicle’s body panels, while precision machining is used for battery housings and electric motors.
In the assembly phase, components such as the battery pack, electric drive train, and electronic control systems are integrated into the vehicle. Robotics and automation play a significant role here, enhancing precision and reducing the likelihood of human error.
B2B buyers should consider suppliers that utilize state-of-the-art technologies in their manufacturing processes, as this can lead to higher quality products and improved production efficiency.
What Finishing Techniques Are Used in Electric Vehicle Manufacturing?
The finishing stage involves painting and coating the vehicle to enhance aesthetics and protect against environmental factors. High-quality paint systems and corrosion-resistant coatings are critical in ensuring long-term durability. This step is particularly important for international buyers operating in diverse climates, from humid tropical regions to arid deserts.
Moreover, the finishing process often includes rigorous inspections to ensure that all surfaces meet quality standards. Buyers should inquire about the specific finishing techniques used by suppliers and whether they employ environmentally friendly practices, such as water-based paints.
What Quality Control Measures Are Implemented in Electric Vehicle Manufacturing?
Quality assurance is paramount in the manufacturing of electric vehicles, given the stringent safety and performance standards they must meet. The quality control process typically adheres to international standards such as ISO 9001, which provides a framework for consistent quality management systems.

Illustrative image related to why electric cars are better than gas
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Electric Vehicle Production?
Quality control checkpoints are integrated throughout the manufacturing process. Common checkpoints include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial stage involves inspecting raw materials and components before they enter the production line. Ensuring that materials meet predefined specifications is crucial for maintaining overall vehicle quality.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the assembly phase, ongoing inspections are conducted to verify that each component is correctly integrated. This may involve monitoring the torque of fasteners, the alignment of components, and the functionality of electronic systems.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): At the end of the production line, a comprehensive inspection is performed to ensure that the vehicle meets all safety and performance standards. This may include road testing, battery performance evaluations, and emission testing (for hybrid models).
B2B buyers should ask potential suppliers about their quality control processes and how they ensure compliance with international standards.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used in Electric Vehicle Quality Assurance?
Testing methods for electric vehicles encompass a wide range of evaluations, including:
-
Battery Testing: This includes cycle testing, thermal testing, and performance testing to ensure the battery operates efficiently under various conditions. Battery performance is critical for the vehicle’s range and longevity.
-
Safety Testing: Electric vehicles undergo crash tests to evaluate passenger safety. Additionally, electrical safety tests are conducted to ensure that all components are insulated and protected against short circuits.
-
Durability Testing: This involves simulating real-world driving conditions to assess how the vehicle performs over time. Factors like corrosion resistance and component wear are evaluated during this phase.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international B2B buyers, verifying a supplier’s quality control practices is essential to ensure product reliability and compliance with industry standards. Here are some strategies to consider:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits can provide insights into a supplier’s manufacturing processes and quality control measures. It allows buyers to verify compliance with international standards and assess the overall capabilities of the supplier.
-
Quality Assurance Reports: Requesting detailed quality assurance reports can help buyers understand the supplier’s testing methodologies and results. These reports should outline how the supplier ensures product quality throughout the manufacturing process.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspectors to evaluate a supplier’s manufacturing facilities can provide an unbiased assessment of quality control measures. This is especially useful for buyers operating in regions with varying regulatory standards.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers must navigate various quality control nuances, especially when sourcing from different regions. These can include:
-
Regulatory Compliance: Different countries have distinct regulatory requirements for vehicle safety and emissions. Buyers must ensure that their suppliers comply with both local and international regulations.
-
Cultural Considerations: Understanding the cultural context of the supplier’s location can impact quality assurance practices. For example, differing attitudes toward quality can influence the rigor of quality control measures.
-
Logistics and Supply Chain Management: International buyers should be aware of potential logistical challenges, such as delays in shipping or customs inspections, which can impact the timely delivery of quality products.
In conclusion, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures in electric vehicle production is essential for B2B buyers seeking to invest in this rapidly evolving sector. By focusing on these aspects, businesses can make informed decisions that align with their sustainability goals and operational needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘why electric cars are better than gas’
Introduction
In today’s evolving automotive landscape, electric vehicles (EVs) present compelling advantages over traditional gasoline-powered cars. This guide serves as a practical checklist for B2B buyers considering the transition to electric vehicles, detailing essential steps to understand why electric cars are a superior choice for both cost and environmental impact.
Step 1: Assess Total Cost of Ownership
Understanding the total cost of ownership (TCO) is crucial when comparing electric and gas vehicles. TCO encompasses not only the initial purchase price but also fuel costs, maintenance, and depreciation. Electric vehicles typically offer lower fuel and maintenance costs, which can significantly enhance overall savings.
- Fuel Costs: Calculate the cost of charging an EV compared to fueling a gas vehicle. Look at local electricity rates and average gas prices.
- Maintenance Savings: Factor in reduced maintenance needs for EVs, such as the absence of oil changes and fewer moving parts.
Step 2: Evaluate Environmental Impact
For companies focused on sustainability, assessing the environmental benefits of electric vehicles is essential. Electric cars produce zero tailpipe emissions, contributing to cleaner air and a reduced carbon footprint.
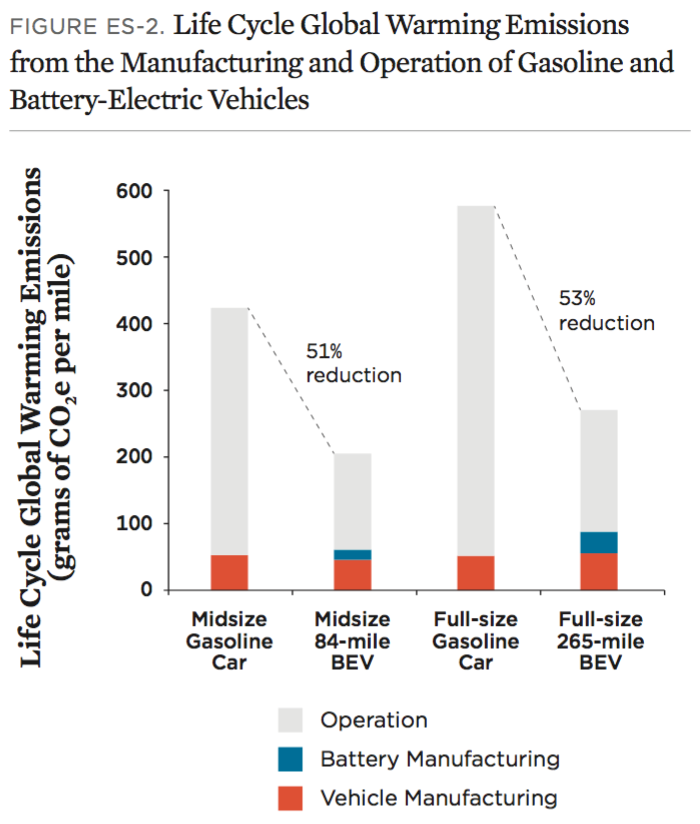
- Lifecycle Emissions: Investigate the full lifecycle emissions of both vehicle types, including manufacturing and disposal.
- Renewable Energy Sources: Consider charging options that utilize renewable energy, enhancing the environmental benefits of EVs.
Step 3: Identify Available Incentives and Rebates
Various governments worldwide offer incentives for adopting electric vehicles. Understanding these financial benefits can influence your procurement decision.
- Tax Credits: Research local and national tax credits for electric vehicle purchases and infrastructure investments.
- Grants and Subsidies: Look for available grants for businesses transitioning to electric fleets or installing charging stations.
Step 4: Explore Charging Infrastructure Options
A robust charging infrastructure is critical for the successful integration of electric vehicles into your operations. Assess the availability of charging stations and the feasibility of installing in-house charging solutions.
- Public Charging Availability: Investigate the proximity and accessibility of public charging stations in your operational area.
- In-House Charging Solutions: Analyze options for installing charging stations at your facilities to facilitate easy access for your fleet.
Step 5: Research Vehicle Models and Specifications
Different electric vehicle models offer varied specifications and features. Thorough research ensures you choose the right vehicles to meet your operational needs.

Illustrative image related to why electric cars are better than gas
- Range and Performance: Evaluate the range of different EV models, particularly for long-distance travel.
- Payload Capacity: For commercial applications, assess the payload capacity to ensure vehicles can meet business demands.
Step 6: Consult Industry Case Studies
Learning from other businesses that have transitioned to electric vehicles can provide valuable insights. Case studies reveal real-world experiences, challenges, and benefits.
- Peer Comparisons: Look for case studies in your industry to understand the impact of EV adoption on operational efficiency and costs.
- Networking: Engage with industry groups or forums discussing EV transitions to gather firsthand experiences and recommendations.
Step 7: Verify Supplier Credentials
Before making a procurement decision, ensure your potential suppliers are reputable and trustworthy. This step safeguards your investment in electric vehicles.
- Supplier Audits: Request audits or certifications that demonstrate compliance with industry standards.
- Customer Testimonials: Seek feedback from previous clients to gauge the reliability and service quality of the suppliers.
By following this structured checklist, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with both financial objectives and sustainability goals when considering electric vehicles over gasoline-powered options.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for why electric cars are better than gas Sourcing
What are the Key Cost Components in Electric Vehicle Sourcing Compared to Gas Vehicles?
When evaluating the cost structure for electric vehicles (EVs) versus gas-powered vehicles, several components must be considered. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and margin.
Materials: The materials used in EVs, particularly lithium-ion batteries, represent a significant portion of the cost. The volatility in the prices of raw materials such as lithium, cobalt, and nickel can impact the overall cost structure. Comparatively, gas vehicles rely on traditional metals and components, which may have more stable pricing.
Labor and Manufacturing Overhead: Labor costs in EV manufacturing can vary based on location and the level of automation in the production process. While EV assembly may require specialized skills, advancements in automation can help mitigate these costs. Manufacturing overhead also differs; EV plants may necessitate unique tooling and equipment, influencing the overall budget.
Tooling and Quality Control: Specialized tooling for battery assembly and electric drivetrains can increase initial setup costs. Quality control processes are crucial in EV manufacturing to ensure battery safety and performance, often leading to higher QC costs compared to traditional vehicles.
Logistics and Margin: The logistics of sourcing materials and distributing finished EVs can be complex, especially given the geographical distribution of battery materials. Margins in the EV sector can be tighter due to the competitive landscape and the need for continuous innovation.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Electric Vehicle Sourcing Decisions?
Several factors influence pricing in the EV market, impacting international B2B buyers.
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Buyers can often negotiate better pricing based on volume. Higher order quantities typically reduce per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Understanding the MOQ requirements from suppliers is essential for effective budgeting.
Specifications and Customization: The specifications of the electric vehicle, such as battery capacity, range, and additional features, can significantly influence pricing. Customization requests may lead to increased costs; therefore, aligning specifications with budget constraints is crucial.
Illustrative image related to why electric cars are better than gas
Materials and Quality Certifications: The quality of materials used in EVs and any certifications (e.g., safety, environmental) can affect pricing. Buyers should assess the quality of components to ensure they meet their operational standards while also considering potential long-term savings from higher-quality materials.
Supplier Factors and Incoterms: The choice of supplier can influence pricing based on their location, reputation, and reliability. Additionally, understanding Incoterms is vital for determining who bears the costs and risks during transportation, which can affect total pricing.
What Buyer Tips Can Help Navigate the Electric Vehicle Market?
For international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, several strategies can enhance cost efficiency.
Negotiation Strategies: Strong negotiation skills can lead to better pricing and terms. Establishing long-term relationships with suppliers may also provide leverage for future negotiations.
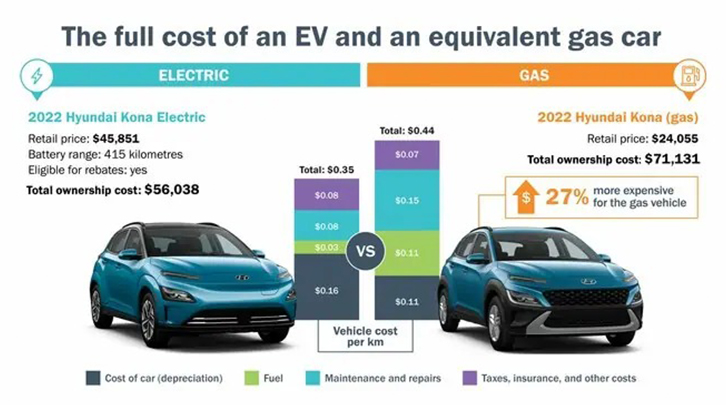
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Buyers should assess the TCO, which includes not only the purchase price but also operational costs such as fuel (electricity vs. gas), maintenance, and potential incentives. EVs typically offer lower operational costs, which can lead to substantial savings over time.
Pricing Nuances for International Markets: Different regions may have varying tax incentives, regulatory environments, and fuel costs, impacting the overall pricing strategy. Buyers should conduct thorough market research to identify the best options available in their specific regions.
Conclusion: Understanding the Cost Dynamics in Electric Vehicle Sourcing
In conclusion, the transition from gas to electric vehicles presents a complex landscape of costs and pricing structures. By understanding the key cost components and price influencers, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their financial goals and sustainability objectives. It is essential to approach this transition with a comprehensive understanding of the total cost implications, ensuring that investments in electric vehicles yield long-term benefits.
Disclaimer: Pricing information is indicative and subject to change based on market conditions, supplier agreements, and regional factors. Always consult with suppliers for the most accurate and current pricing information.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing why electric cars are better than gas With Other Solutions
Introduction: Understanding Alternatives in Automotive Solutions
As the automotive industry evolves, businesses must evaluate various transportation solutions that align with their operational goals, sustainability targets, and cost-efficiency strategies. While electric vehicles (EVs) are gaining momentum for their environmental and economic benefits, it is crucial to explore other alternatives that may also serve similar objectives. This section compares electric cars to hybrid vehicles and hydrogen fuel cell vehicles, providing insights into their respective advantages and limitations.

Illustrative image related to why electric cars are better than gas
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Why Electric Cars Are Better Than Gas | Hybrid Vehicles | Hydrogen Fuel Cell Vehicles |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Instant torque, smooth acceleration | Good fuel efficiency, but less power than EVs | High range and quick refueling |
| Cost | Lower fuel and maintenance costs | Moderate fuel savings, but still reliant on gas | High initial investment, lower running costs |
| Ease of Implementation | Growing charging infrastructure | Established fuel stations | Limited refueling stations |
| Maintenance | Minimal routine care required | Regular maintenance needed | Requires specific maintenance |
| Best Use Case | Urban commuting and fleet operations | Mixed driving conditions | Long-distance travel |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Hybrid Vehicles: A Compromise Between Gas and Electric
Hybrid vehicles combine a gasoline engine with an electric motor, offering a middle ground between traditional gas vehicles and full EVs. They excel in fuel efficiency, reducing gasoline consumption and CO2 emissions compared to conventional cars. However, hybrids still rely on fossil fuels, which limits their sustainability benefits. Maintenance is also more frequent than with EVs, as they require oil changes and other routine services associated with gas engines. Businesses operating in diverse environments may find hybrids suitable for varied driving conditions but may not fully align with eco-friendly initiatives.
Hydrogen Fuel Cell Vehicles: The Future of Clean Energy?
Hydrogen fuel cell vehicles operate on electricity generated from hydrogen, producing only water vapor as a byproduct. They boast high range capabilities and can be refueled in minutes, making them ideal for long-distance travel and heavy-duty applications. However, the infrastructure for hydrogen refueling is still limited, especially in regions outside of developed countries. Additionally, the initial cost of hydrogen vehicles can be significantly higher than electric and gas counterparts, which may deter businesses with budget constraints. While promising, hydrogen technology may not yet be the most practical choice for all operational needs.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Business Needs
When considering the transition to electric vehicles or other alternatives, B2B buyers should assess their unique requirements, including operational scope, budget constraints, and sustainability goals. Electric vehicles offer substantial savings on fuel and maintenance, making them an attractive option for urban fleets. However, hybrid and hydrogen fuel cell vehicles also present viable solutions depending on specific use cases. By thoroughly analyzing each alternative, businesses can make informed decisions that align with their strategic objectives and contribute to a more sustainable future.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for why electric cars are better than gas
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Electric Cars That Make Them Superior to Gas Vehicles?
Electric vehicles (EVs) come with specific technical properties that differentiate them from gasoline-powered cars. Understanding these properties is crucial for B2B buyers, especially when considering the long-term benefits and operational efficiencies of EVs.
-
Energy Efficiency
EVs typically convert over 60% of the electrical energy from the grid to power at the wheels, compared to gasoline vehicles, which convert only about 20% of the energy stored in gasoline. This high energy efficiency leads to reduced operational costs and lower emissions, making EVs a more sustainable choice. -
Battery Capacity (kWh)
The capacity of an electric vehicle’s battery, measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh), determines its range and performance. A higher kWh rating allows for longer driving distances between charges. For B2B buyers, understanding battery capacity is essential for fleet operations, as it impacts logistics, charging infrastructure, and overall vehicle utilization. -
Regenerative Braking
This technology allows electric vehicles to recover energy during braking and convert it back into electrical energy to recharge the battery. This feature not only enhances energy efficiency but also reduces wear on brake components, leading to lower maintenance costs. For businesses with fleets, this can translate to significant savings over time. -
Charging Time
Charging time varies based on the type of charger used—Level 1 (standard outlet), Level 2 (home or public charging stations), or DC Fast Charging. Understanding charging times is vital for businesses to plan operations and minimize downtime. For example, DC Fast Charging can charge a vehicle to 80% in about 30 minutes, making it suitable for high-utilization fleets. -
Powertrain Components
Electric vehicles have fewer moving parts compared to internal combustion engine vehicles. This simplicity reduces maintenance requirements and associated costs. Key components include the electric motor, inverter, and onboard charger. B2B buyers should evaluate these components to understand the reliability and longevity of the vehicles being considered.
What Are Common Trade Terminology and Jargon Related to Electric Vehicles?
Familiarity with industry-specific terms can help B2B buyers navigate discussions and negotiations regarding electric vehicles.
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
This term refers to companies that manufacture parts or vehicles that are sold under another brand name. In the context of EVs, understanding which OEMs produce the vehicles can help buyers assess quality and reliability. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ denotes the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. For businesses looking to purchase electric vehicle fleets, knowing the MOQ can affect budgeting and inventory planning. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a business process where a company solicits price bids from suppliers for specific products or services. B2B buyers should prepare RFQs to ensure competitive pricing when sourcing electric vehicles or related components. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
These are standardized terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding Incoterms is crucial for B2B buyers to avoid miscommunication and ensure smooth logistics when importing electric vehicles. -
TCO (Total Cost of Ownership)
TCO encompasses all costs associated with acquiring and operating a vehicle over its lifetime, including purchase price, maintenance, fuel (or charging), and depreciation. This metric is critical for B2B buyers to evaluate the financial viability of electric vehicles compared to gas vehicles. -
EVSE (Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment)
This term refers to the charging infrastructure necessary for electric vehicles. For businesses, investing in EVSE is essential for supporting fleet operations and ensuring vehicles are charged efficiently.
Understanding these technical properties and trade terminologies can empower B2B buyers to make informed decisions about transitioning to electric vehicles, aligning with sustainability goals and cost-saving initiatives.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the why electric cars are better than gas Sector
Understanding the Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends for Electric Vehicles
What are the Global Drivers and Key Trends Influencing Electric Vehicles in B2B Markets?
The electric vehicle (EV) sector is experiencing significant growth driven by a combination of environmental awareness, technological advancements, and regulatory policies. In international markets, particularly in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the shift towards electric cars is being accelerated by governmental incentives aimed at reducing carbon emissions and promoting sustainable transportation solutions. Countries like Germany and Saudi Arabia are investing heavily in EV infrastructure, such as charging stations, which is crucial for increasing consumer confidence in electric mobility.
Emerging technologies, including battery innovations and renewable energy integration, are reshaping the sourcing landscape. B2B buyers are increasingly focused on sourcing vehicles that utilize sustainable materials and incorporate advanced technologies such as smart charging solutions. Additionally, the growing trend of fleet electrification is gaining traction among businesses looking to reduce operating costs and enhance their corporate social responsibility profiles. The total cost of ownership (TCO) analysis now often favors electric vehicles, making them an attractive option for fleet managers and organizations seeking long-term savings.
How Does Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact the Electric Vehicle Sector?
Sustainability is at the forefront of the electric vehicle market. The environmental impact of EVs is significantly lower compared to gasoline vehicles, primarily due to the absence of tailpipe emissions and the potential for utilizing renewable energy sources for charging. For B2B buyers, the importance of ethical sourcing cannot be overstated. Companies are increasingly held accountable for their supply chains, which includes ensuring that the materials used in EV production, such as lithium for batteries, are sourced responsibly.
Green certifications and sustainable materials are becoming essential criteria for procurement decisions. Certifications like ISO 14001 for environmental management or LEED for sustainable building practices can enhance a company’s reputation and appeal to eco-conscious consumers. Furthermore, ethical sourcing practices can mitigate risks associated with supply chain disruptions and compliance with international regulations, making them a critical consideration for international buyers.
What is the Historical Context of Electric Vehicles in the B2B Space?
The evolution of electric vehicles dates back to the early 19th century, but significant advancements in technology and a growing awareness of environmental issues have propelled EVs into the mainstream over the past two decades. Initially, electric cars were viewed as niche products, limited by battery technology and range anxiety. However, the rise of lithium-ion batteries and improvements in charging infrastructure have transformed the landscape.
As governments worldwide implement stricter emissions regulations and consumers become more environmentally conscious, electric vehicles are no longer just an alternative; they are becoming essential to automotive strategies. For B2B buyers, understanding this evolution is crucial for making informed sourcing decisions that align with both current trends and future market expectations. By embracing electric vehicles, businesses can position themselves as leaders in sustainability, ultimately driving growth and innovation within their sectors.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of why electric cars are better than gas
-
How do I evaluate the cost benefits of electric vehicles over gas vehicles for my business?
To evaluate the cost benefits, consider the total cost of ownership, which includes purchase price, fuel costs, and maintenance expenses. Electric vehicles typically have lower fuel costs, as electricity is often cheaper than gasoline. Additionally, maintenance costs are reduced due to fewer moving parts and no need for oil changes. Conduct a detailed analysis by comparing the initial investment, available tax credits, and potential savings on fuel and maintenance over time to determine the financial impact on your business. -
What incentives are available for businesses purchasing electric vehicles internationally?
Incentives vary by region but can include tax credits, rebates, and grants for purchasing electric vehicles. Some governments offer reduced registration fees or exemptions from tolls. In addition, businesses may qualify for incentives related to installing EV charging infrastructure. Research specific local and national programs in your target markets, such as Germany or Saudi Arabia, to maximize financial benefits when investing in electric vehicles. -
How can I ensure the quality of electric vehicles I source from international suppliers?
To ensure quality, conduct thorough vetting of potential suppliers by checking certifications, production capabilities, and customer reviews. Request documentation regarding compliance with international safety and environmental standards. Consider visiting manufacturing facilities if possible, and ask for samples or test units to evaluate performance. Building relationships with trusted suppliers and utilizing third-party quality assurance services can further mitigate risks associated with sourcing electric vehicles. -
What customization options should I consider when sourcing electric vehicles for my fleet?
Customization options can include vehicle size, battery capacity, and technology features such as telematics and charging capabilities. Determine your specific operational needs, such as range and payload requirements, to guide your customization choices. Discuss options with suppliers to explore how modifications can enhance efficiency and align with your business goals. Additionally, consider the aesthetics and branding opportunities that customization can provide for your fleet. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for electric vehicles from international suppliers?
Minimum order quantities can vary significantly based on the supplier and the type of electric vehicle. Some manufacturers may require bulk orders to ensure profitability, while others might accommodate smaller quantities for businesses just starting to transition to electric. Clarify MOQs during negotiations and explore options for phased purchases, which can help you manage cash flow while gradually expanding your electric vehicle fleet. -
How do I manage logistics for importing electric vehicles into my region?
Managing logistics requires careful planning, including understanding import regulations, tariffs, and taxes specific to your region. Work with a logistics partner experienced in automotive imports to streamline the shipping process. Consider factors such as transportation modes, lead times, and storage facilities. Ensuring compliance with local safety and environmental standards is crucial to avoid delays and additional costs upon arrival. -
What payment terms should I negotiate when sourcing electric vehicles?
When negotiating payment terms, aim for favorable conditions that protect your cash flow while ensuring supplier reliability. Common terms include advance payments, net 30/60/90 days, or installment payments based on delivery milestones. Discuss options for financing or leasing, which can provide flexibility and reduce upfront costs. Ensure clarity on all terms, including penalties for late payments and conditions for potential refunds or returns. -
How can I assess the environmental impact of electric vehicles for my business?
To assess the environmental impact, evaluate the lifecycle emissions of electric vehicles compared to gas vehicles, including production, usage, and end-of-life disposal. Consider the source of the electricity used to charge the vehicles—renewable energy sources significantly reduce overall emissions. Additionally, analyze how transitioning to electric vehicles aligns with your corporate sustainability goals and can enhance your brand’s reputation in increasingly eco-conscious markets.
Top 3 Why Electric Cars Are Better Than Gas Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Toyota – Electric Vehicles
Domain: toyotamarin.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: 1. Lower Carbon Footprint: Electric vehicles (EVs) reduce carbon emissions and do not produce tailpipe emissions, positively impacting the environment. 2. No Gas Costs: EVs operate on electric motor systems, eliminating gasoline expenses and potentially saving drivers 60% on fuel costs compared to gas vehicles. 3. Fewer Maintenance Costs: EVs have fewer maintenance needs as they do not require oil…
2. Constellation – Electric vs. Gas Cars Comparison
Domain: constellation.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Electric cars vs. gas cars comparison focuses on cost, convenience, and environmental impact. Key details include: 1. Cost considerations: Look beyond sticker price to include power and maintenance costs. 2. Tax credits: Eligible for 30% tax credit on EV charger installation, up to $1,000. 3. Fuel costs: Calculate charging costs based on local electricity rates and driving habits; EVs generally co…
3. Facebook – Electric Cars
Domain: facebook.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: This company, Facebook – Electric Cars, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for why electric cars are better than gas
In evaluating the transition to electric vehicles (EVs) over traditional gas-powered cars, B2B buyers across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe can glean significant strategic advantages. Key takeaways include lower operational costs driven by reduced fuel and maintenance expenses, along with potential tax incentives that can further enhance financial viability. The environmental benefits of EVs not only contribute to corporate sustainability goals but also align with global trends towards greener business practices.
Strategic sourcing of electric vehicles can lead to long-term savings and operational efficiencies, positioning businesses as forward-thinking leaders in their respective markets. As the global automotive landscape shifts towards electrification, companies that invest in EVs will likely benefit from enhanced brand reputation and customer loyalty, especially in regions where eco-consciousness is rising.

Illustrative image related to why electric cars are better than gas
Looking ahead, international buyers should seize the opportunity to integrate electric vehicles into their fleets, ensuring they remain competitive and compliant with evolving regulations. As the adoption of EV technology accelerates, now is the time to engage with suppliers and manufacturers to secure favorable terms and capitalize on this transformative shift in the automotive industry.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.

Illustrative image related to why electric cars are better than gas