Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for what should alternator output be
In today’s competitive landscape, understanding the optimal alternator output is crucial for businesses that rely on efficient power management. With the increasing demands for reliable energy supply across various sectors, sourcing the right alternator can be a complex challenge for B2B buyers, especially in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including key markets such as Saudi Arabia and Brazil. This comprehensive guide aims to demystify the intricacies of alternator output, providing insights into the various types of alternators, their applications, and the critical factors that influence performance.
Navigating the global market for alternators involves understanding specifications, performance standards, and supplier reliability. As businesses seek to optimize their operations, knowing how to evaluate alternator output—typically around 14 volts under operational conditions—is essential for preventing costly downtime and ensuring peak performance. This guide empowers international B2B buyers with actionable strategies for supplier vetting, cost considerations, and performance testing methods. By equipping decision-makers with the knowledge they need, this resource facilitates informed purchasing decisions, ultimately enhancing operational efficiency and reliability in power systems worldwide. Whether you are looking to replace existing equipment or expand your fleet, understanding what alternator output should be is a critical step towards achieving your business goals.
Table Of Contents
- Top 5 What Should Alternator Output Be Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for what should alternator output be
- Understanding what should alternator output be Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of what should alternator output be
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘what should alternator output be’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for what should alternator output be
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for what should alternator output be
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘what should alternator output be’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for what should alternator output be Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing what should alternator output be With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for what should alternator output be
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the what should alternator output be Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of what should alternator output be
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for what should alternator output be
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Understanding what should alternator output be Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Automotive Alternator | Typically outputs 13.8 to 14.5 volts; designed for high RPMs. | Passenger vehicles, light trucks | Pros: Cost-effective, widely available. Cons: Limited output at low RPMs, temperature-sensitive. |
| High Output Alternator | Delivers higher amperage; effective at low RPMs; often temperature-resistant. | Commercial vehicles, marine applications | Pros: Faster battery charging, reliable under heavy loads. Cons: Higher initial cost, may require modifications. |
| Smart Alternator | Automatically adjusts voltage based on battery charge state. | Hybrid vehicles, advanced fleets | Pros: Enhances battery lifespan, optimizes energy use. Cons: More complex, potential compatibility issues. |
| Marine Alternator | Designed for high temperatures and variable RPMs; often ungrounded. | Boats, yachts | Pros: Reliable in harsh conditions, efficient charging. Cons: Higher maintenance, specialized installation. |
| Industrial Alternator | Built for heavy-duty applications; high durability and output. | Mining, construction, agriculture | Pros: Robust and long-lasting, high output. Cons: Expensive, may require specialized knowledge for installation. |
What Are the Characteristics of Standard Automotive Alternators?
Standard automotive alternators are designed primarily for passenger vehicles and light trucks, delivering a voltage output typically between 13.8 and 14.5 volts. They operate effectively at high RPMs, making them suitable for everyday driving conditions. However, their performance can significantly drop in high-temperature environments, which may lead to inadequate battery charging. B2B buyers should consider the reliability and cost-effectiveness of these alternators for standard vehicle fleets but be aware of their limitations in demanding conditions.
How Do High Output Alternators Differ from Standard Types?
High output alternators are engineered to provide greater amperage, particularly useful in commercial vehicles and marine applications where power demands are higher. These alternators can maintain efficiency at lower RPMs and are often designed to withstand higher temperatures, making them ideal for rigorous use. While they offer faster battery charging and better performance under load, B2B buyers must account for their higher initial investment and potential need for modifications to existing systems.
What Are the Benefits of Smart Alternators?
Smart alternators are equipped with technology that allows them to automatically adjust their output based on the state of the battery charge. This feature is particularly beneficial for hybrid vehicles and advanced fleet management, where optimizing energy use can lead to significant cost savings and improved battery life. However, their complexity may pose compatibility challenges, and buyers should ensure their vehicles can accommodate such systems.
Why Are Marine Alternators Specialized for Harsh Conditions?
Marine alternators are specifically designed to operate efficiently in high-temperature and variable RPM environments, making them essential for boats and yachts. Many models are ungrounded, which is critical for aluminum vessels to prevent corrosion. Their reliability in harsh conditions is a significant advantage for B2B buyers in the marine sector, though they may require specialized installation and maintenance.
What Makes Industrial Alternators Suitable for Heavy-Duty Applications?
Industrial alternators are built for heavy-duty applications such as mining, construction, and agriculture, offering high durability and output. These alternators are engineered to withstand extreme conditions and heavy electrical loads, making them ideal for businesses that rely on robust machinery. However, their cost can be a barrier for some, and specialized knowledge may be necessary for installation and maintenance, making them a significant investment for B2B buyers.
Key Industrial Applications of what should alternator output be
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of what should alternator output be | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Fleet Management for Commercial Vehicles | Ensures reliable vehicle operation and minimizes downtime. | High amperage alternators for heavy-duty vehicles; compatibility with existing systems. |
| Marine | Power Supply for Yachts and Commercial Vessels | Maintains onboard electrical systems efficiently, enhancing safety and comfort. | Resistance to high temperatures; ability to operate at low RPMs; proper voltage regulation. |
| Mining | Heavy Machinery and Equipment Operation | Reliable power supply for machinery in remote locations, reducing operational interruptions. | High output capacity; rugged design for harsh environments; availability of spare parts. |
| Renewable Energy | Integration with Solar Power Systems | Efficient battery charging to support off-grid applications, increasing energy independence. | Compatibility with various battery types; voltage output suitable for charging efficiency. |
| Agriculture | Powering Irrigation Systems and Equipment | Ensures consistent operation of vital agricultural equipment, improving crop yield. | Sufficient output for multiple devices; durability under varying weather conditions. |
How is Alternator Output Critical for Fleet Management in the Automotive Sector?
In the automotive sector, particularly for fleet management, the alternator’s output is vital for maintaining the operational reliability of commercial vehicles. A reliable alternator ensures that the electrical systems, including lights, GPS, and climate control, function correctly, preventing costly downtime. Buyers in this sector should consider high-amperage alternators that are compatible with existing vehicle systems to ensure seamless integration and minimal disruption.
What Role Does Alternator Output Play in Marine Applications?
In marine applications, alternator output is crucial for providing a stable power supply to onboard systems in yachts and commercial vessels. The ability to charge batteries efficiently while operating at low RPMs is essential for maintaining safety and comfort on the water. Buyers should prioritize alternators designed to withstand high temperatures and humidity, ensuring reliable performance in challenging marine environments.
Why is Alternator Output Important for Mining Operations?
Mining operations rely heavily on heavy machinery that demands a consistent power supply. Alternators with high output capacity are essential for ensuring that equipment operates smoothly, even in remote locations where power sources may be limited. B2B buyers in this sector should focus on rugged alternators capable of withstanding harsh environmental conditions, along with the availability of spare parts for quick maintenance.
How Does Alternator Output Enhance Renewable Energy Systems?
In renewable energy applications, such as solar power systems, the alternator’s output plays a key role in efficiently charging batteries. Proper voltage levels are necessary to maximize charging efficiency, which is critical for off-grid energy independence. Buyers should seek alternators that are compatible with various battery types and capable of delivering the necessary voltage output to enhance system performance.
What is the Significance of Alternator Output in Agriculture?
In agriculture, reliable alternator output is essential for powering irrigation systems and other vital equipment. Consistent operation of these systems directly impacts crop yield and overall productivity. B2B buyers should look for alternators that can provide sufficient output to support multiple devices while ensuring durability against varying weather conditions to maintain agricultural operations year-round.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘what should alternator output be’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Inconsistent Alternator Output and Equipment Downtime
The Problem:
B2B buyers in industries such as transportation and logistics often face significant challenges when alternators do not deliver consistent output. Inconsistent voltage and amperage can lead to equipment failures, draining batteries faster than expected and causing vehicles to break down. For businesses operating in regions with varying ambient temperatures, such as the Middle East or South America, the problem is exacerbated by the fact that standard alternators can lose efficiency in high heat. This not only leads to costly repairs but also impacts productivity due to unexpected downtime.
The Solution:
To combat these issues, B2B buyers should invest in high-output alternators specifically designed for their operational conditions. For example, consider sourcing alternators that maintain efficiency even at lower RPMs and higher temperatures, such as those offered by manufacturers like Mastervolt. Ensure that the selected alternator’s output specifications align with the power demands of all onboard equipment and battery types. Additionally, implementing a routine testing protocol using a handheld voltmeter and clamp-on ammeter will help monitor output performance consistently. By regularly checking the output at both the alternator and battery, businesses can identify potential issues before they lead to breakdowns, thus minimizing operational disruptions.
Scenario 2: Misunderstanding Alternator Specifications and Battery Compatibility
The Problem:
Many B2B buyers encounter confusion when matching alternator specifications with the requirements of their battery systems. This is particularly common in businesses that utilize various battery types (lead-acid, lithium-ion, etc.) across their fleet. A common scenario involves selecting an alternator with insufficient voltage output, which can lead to batteries being only partially charged and significantly reducing their lifespan. This misunderstanding can result in frequent battery replacements and increased operational costs.
The Solution:
To ensure compatibility, B2B buyers must understand the voltage and amperage requirements of their batteries. Conduct thorough research on the manufacturer’s specifications for both the alternator and batteries. Opt for alternators that provide adjustable voltage outputs or are equipped with smart voltage regulators that can adapt to the battery’s state of charge. For example, if using lithium-ion batteries, ensure the alternator can supply a higher voltage during the charging phase (around 14.25 volts) and then taper off as the battery nears full charge. Additionally, engage with suppliers who can provide detailed specifications and recommendations tailored to your unique battery and operational needs, ensuring optimal performance and longevity.
Scenario 3: Costly Repairs from Neglected Maintenance Practices
The Problem:
Neglecting regular maintenance and testing of alternators can lead to catastrophic failures and expensive repairs. B2B buyers often underestimate the importance of proactive maintenance schedules, particularly in industries with heavy equipment or vehicles that rely on consistent power supply. Without routine checks, businesses may face unanticipated breakdowns, resulting in not only repair costs but also lost revenue due to halted operations.
The Solution:
Implement a comprehensive maintenance strategy that includes regular alternator testing and inspections. Establish a schedule to check voltage output and amperage using appropriate testing tools, ensuring that both the alternator and battery systems are functioning optimally. It’s advisable to train maintenance staff on best practices for alternator testing and to invest in diagnostic tools that can provide real-time feedback on performance. Furthermore, consider building a relationship with a reliable supplier who can assist in sourcing quality alternators and components, ensuring that replacements and repairs are managed efficiently. By prioritizing maintenance, businesses can extend the life of their equipment and reduce the likelihood of unexpected failures, ultimately saving costs in the long run.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for what should alternator output be
What Materials Should Be Considered for Optimizing Alternator Output?
When selecting materials for alternators, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, it’s essential to consider the unique environmental conditions and operational demands. The following analysis focuses on four common materials used in alternator construction: aluminum, copper, steel, and plastic composites. Each material has distinct properties, advantages, and limitations that can significantly impact performance and longevity.
How Does Aluminum Impact Alternator Output?
Aluminum is a lightweight metal with excellent thermal conductivity, making it a popular choice for alternator housings and components. Its temperature rating typically ranges from -50°C to 150°C, allowing it to perform well in various climates. Aluminum is also resistant to corrosion, which is vital for applications in humid or saline environments.
Pros: The lightweight nature of aluminum reduces overall vehicle weight, improving fuel efficiency. It is relatively inexpensive and easy to manufacture, allowing for cost-effective production.
Cons: While aluminum is durable, it can be less robust than other metals under extreme mechanical stress. It may require additional coatings for enhanced corrosion resistance in harsh environments.
Impact on Application: Aluminum’s thermal properties ensure efficient heat dissipation, which is crucial for maintaining optimal alternator output. However, in high-temperature regions, the performance may degrade if not properly managed.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards such as ASTM and DIN is critical. Buyers should ensure that suppliers can provide certifications for aluminum alloys used in alternators to guarantee performance in specific applications.
What Role Does Copper Play in Alternator Performance?
Copper is widely regarded for its exceptional electrical conductivity, making it the ideal choice for windings and connections in alternators. It can handle high currents and has a melting point of approximately 1,085°C, allowing it to perform well under high load conditions.
Pros: Copper’s high conductivity ensures minimal energy loss, leading to better efficiency and performance. It is also highly ductile, making it easy to work with during manufacturing.
Cons: The primary drawback of copper is its cost, which is significantly higher than aluminum. Additionally, copper is prone to corrosion if not properly insulated, which can lead to decreased performance over time.

Illustrative image related to what should alternator output be
Impact on Application: The use of copper enhances the alternator’s ability to maintain output under varying loads, making it suitable for applications requiring reliable power supply.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers must consider the availability of copper and its price fluctuations in different regions. Compliance with electrical standards and regulations is also vital to ensure safety and efficiency.
Why Is Steel Used in Alternator Construction?
Steel is often used for structural components of alternators due to its high strength and durability. It can withstand significant mechanical stress and has a temperature rating of up to 600°C, depending on the alloy.
Pros: Steel’s strength provides excellent structural integrity, ensuring that the alternator can endure vibrations and shocks during operation. It is also relatively cost-effective compared to other metals.
Illustrative image related to what should alternator output be
Cons: Steel is heavier than aluminum and copper, which can negatively impact vehicle weight and fuel efficiency. Additionally, it is susceptible to rust and corrosion if not properly treated.
Impact on Application: Steel components can enhance the longevity of the alternator, but their weight may require careful consideration in vehicle design to avoid compromising performance.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that steel components meet relevant international standards for corrosion resistance, especially in coastal regions where saltwater exposure is a concern.
How Do Plastic Composites Benefit Alternator Design?
Plastic composites are increasingly being used in alternator designs, particularly for non-load-bearing components. They offer excellent insulation properties and can withstand temperatures up to 120°C.
Illustrative image related to what should alternator output be
Pros: The lightweight nature of plastics helps reduce the overall weight of the alternator. They are also resistant to corrosion and can be molded into complex shapes, allowing for innovative designs.
Cons: Plastic composites may not withstand high temperatures or mechanical stresses as well as metals, limiting their application in critical structural components.
Impact on Application: The use of plastic composites can improve insulation and reduce weight, but their limitations in strength may necessitate careful design considerations.

Illustrative image related to what should alternator output be
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should verify compliance with safety and performance standards for plastic materials used in alternators, particularly in high-temperature applications.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Alternator Output
| Material | Typical Use Case for what should alternator output be | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Housings and structural components | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Less robust under extreme stress | Medium |
| Copper | Windings and electrical connections | Excellent electrical conductivity | High cost and corrosion susceptibility | High |
| Steel | Structural components | High strength and durability | Heavier and prone to rust | Medium |
| Plastic Composites | Insulation and non-load-bearing parts | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Limited mechanical strength | Low |
This strategic material selection guide provides B2B buyers with actionable insights into optimizing alternator output based on material properties, advantages, and limitations. By considering these factors, businesses can make informed decisions that enhance performance and reliability in their applications.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for what should alternator output be
The manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for alternators are critical factors for B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Understanding these processes can help buyers make informed decisions when selecting suppliers and ensuring the reliability of alternator outputs. Below is a comprehensive overview of the typical manufacturing stages, quality control standards, and practices that are essential for ensuring optimal alternator performance.
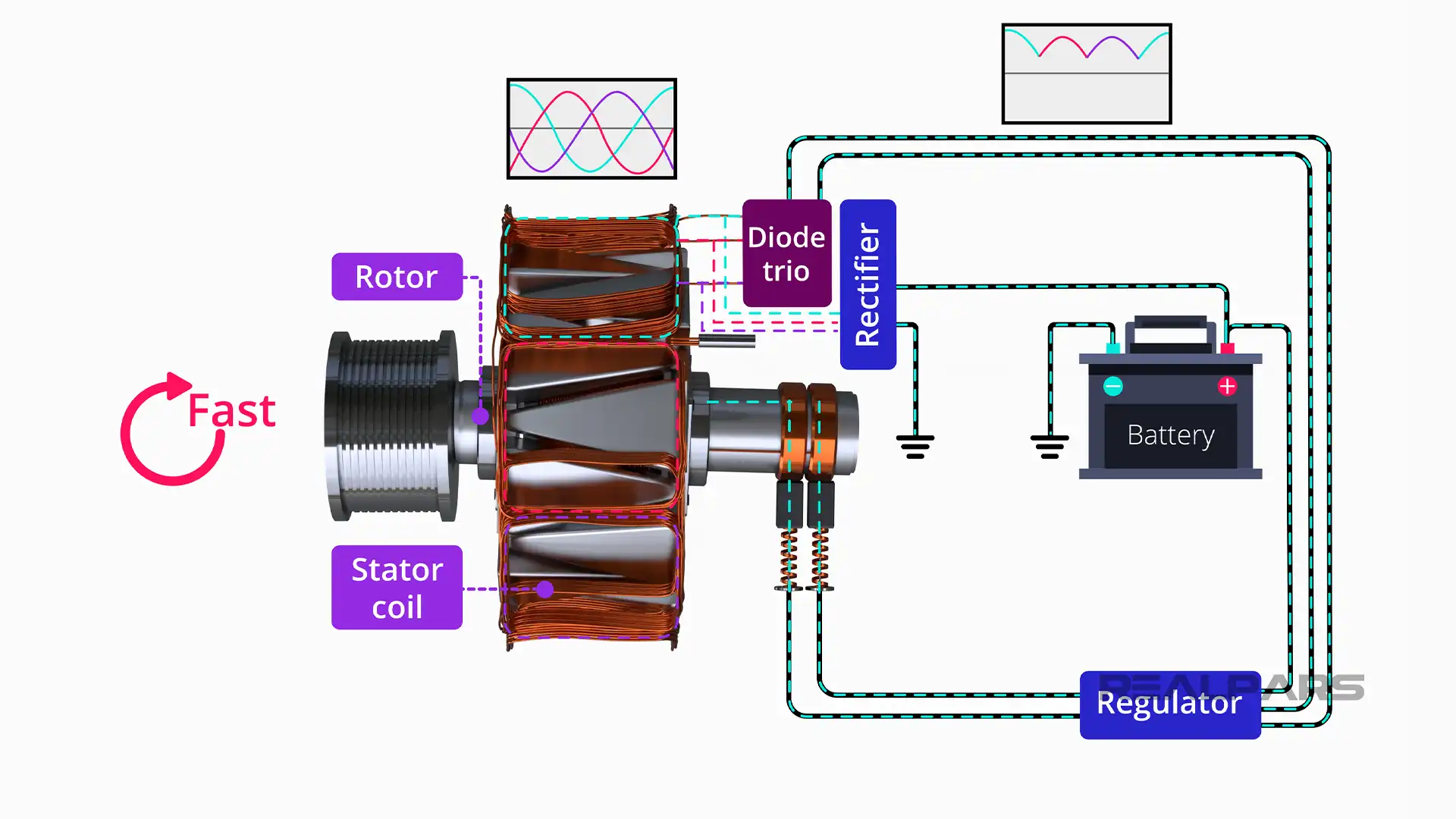
What Are the Main Stages of Alternator Manufacturing?
The manufacturing of alternators involves several key stages, each requiring specific techniques to ensure the final product meets both performance and reliability standards.
1. Material Preparation: What Materials Are Used in Alternator Production?
The first stage in manufacturing alternators is material preparation. Common materials include high-grade steel for the housing, copper for windings, and various alloys for components like rotors and stators. The quality of these materials is essential; hence, suppliers often conduct thorough inspections to ensure compliance with industry standards.
Materials are typically sourced from certified suppliers, and each batch undergoes incoming quality control (IQC) checks to verify their composition and integrity. Certifications like ISO 9001 are often required to ensure that materials meet international quality benchmarks.
2. Forming: How Are Alternator Components Shaped?
The forming stage involves techniques such as stamping, die-casting, and machining to create the individual components of the alternator. For instance, stators are often stamped from sheets of electrical steel, while rotors may be die-cast from aluminum or other lightweight metals to enhance performance.
Advanced CNC (computer numerical control) machines are frequently employed during this stage to ensure precision in component dimensions, which is critical for optimal alternator performance. Consistent calibration and maintenance of these machines are vital to uphold quality standards.
3. Assembly: What Processes Are Involved in Assembling an Alternator?
During the assembly phase, various components are brought together. This includes inserting the rotor into the stator, connecting the windings, and integrating the voltage regulator. Automated assembly lines are common in this phase to enhance speed and accuracy.
Manual assembly may still be employed for certain intricate tasks, where skilled workers ensure that components fit together perfectly. Quality checkpoints are established throughout this stage to catch any defects early, reducing the likelihood of faulty products reaching the market.
4. Finishing: How Is the Alternator Finished for Sale?
The finishing stage includes processes such as painting, coating, and packaging. A protective coating is applied to prevent corrosion, especially for alternators intended for harsh environments.
Final quality control checks are conducted here to assess the overall appearance and functionality of the alternators. This may include visual inspections and electrical testing to ensure each unit meets the specified output voltage and amperage.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Implemented in Alternator Production?
Quality assurance (QA) is a cornerstone of the alternator manufacturing process. It ensures that each unit produced meets the required specifications and performance standards.
Relevant International Standards: Which Standards Should B2B Buyers Look For?
B2B buyers should prioritize suppliers that adhere to international quality standards, such as ISO 9001, which focuses on quality management systems. Additionally, industry-specific certifications, such as CE (Conformité Européenne) for European markets and API (American Petroleum Institute) standards for marine applications, can further assure quality.
These certifications indicate that the manufacturer has implemented effective QA processes that are regularly audited by third parties, ensuring compliance with safety and performance criteria.
Quality Control Checkpoints: What Are the Key QC Phases?
Quality control in alternator manufacturing typically involves several checkpoints:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This phase involves inspecting raw materials and components before they enter the production line.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, various tests are conducted to monitor the quality of the components. This may include dimensional checks and functional tests.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Once the alternator is assembled, it undergoes comprehensive testing to ensure it meets the required output specifications. This includes voltage and amperage testing under various load conditions.
Common Testing Methods: How Are Alternators Tested for Quality?
Testing methods for alternators often include:
- Voltage Output Tests: Verifying that the alternator produces the correct voltage output when the engine is running.
- Amperage Output Tests: Using clamp-on ammeters to measure the current output under load conditions.
- Thermal Testing: Assessing performance under various temperature conditions to ensure reliability in different environments.
These tests are crucial in confirming that the alternator can perform effectively in real-world applications.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers can take several steps to ensure that their suppliers maintain high-quality standards:
Supplier Audits: What Should Buyers Look for in Audits?
Conducting supplier audits is an effective way to verify quality control practices. Buyers should review the supplier’s QA processes, certifications, and compliance with international standards. This can include checking records of past audits and quality reports.
Quality Control Reports: How Important Are They?
Requesting quality control reports can provide insight into a supplier’s consistency in producing high-quality products. These reports should detail testing methodologies, outcomes, and any corrective actions taken in the event of quality failures.
Third-Party Inspections: Why Are They Beneficial?
Engaging third-party inspection services can add an additional layer of assurance. Independent inspectors can verify that the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures are in line with international standards and the buyer’s specific requirements.
What Are the Unique Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, and the Middle East, may face additional challenges related to quality control. It’s essential to understand local regulations and standards, as these can differ significantly from international norms.
Buyers should also consider logistical factors, such as shipping and handling, which can affect product quality. Ensuring that suppliers have robust packaging and handling procedures is crucial to prevent damage during transit.
In conclusion, a comprehensive understanding of manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices is vital for B2B buyers looking to source reliable alternators. By focusing on supplier certifications, conducting thorough audits, and verifying testing methods, buyers can ensure they receive high-quality products that meet their operational needs.
Illustrative image related to what should alternator output be
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘what should alternator output be’
Introduction
This guide provides B2B buyers with a practical checklist for understanding and sourcing alternators based on their output requirements. Proper knowledge of alternator specifications is essential for ensuring reliable performance, reducing downtime, and optimizing energy management in various applications, from automotive to industrial.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Understanding the technical specifications required for your application is the first step in sourcing alternators. Determine the voltage and amperage ratings that will meet your operational needs, considering factors such as the type of batteries used and the electrical load requirements. For instance, standard automotive alternators typically output between 13.8 to 14.5 volts, while higher demands may necessitate specialized high-output models.
Step 2: Assess Environmental Conditions
Evaluate the environmental conditions in which the alternator will operate. High ambient temperatures or unique operational settings, such as marine or industrial environments, can significantly impact alternator performance. Choose alternators designed to withstand these conditions, ensuring they maintain output efficiency without overheating or failing.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a supplier, conduct thorough evaluations. Review company profiles, request case studies, and seek references from existing clients in similar industries or regions. This due diligence will help ensure the supplier has a proven track record of delivering quality products that meet specified output requirements.
Step 4: Verify Product Certifications and Standards
Ensure that the alternators you are considering comply with relevant industry standards and certifications. Look for certifications such as ISO 9001 for quality management systems and compliance with safety standards specific to your region, such as CE marking in Europe or UL certification in the United States. These certifications can indicate a commitment to quality and reliability.
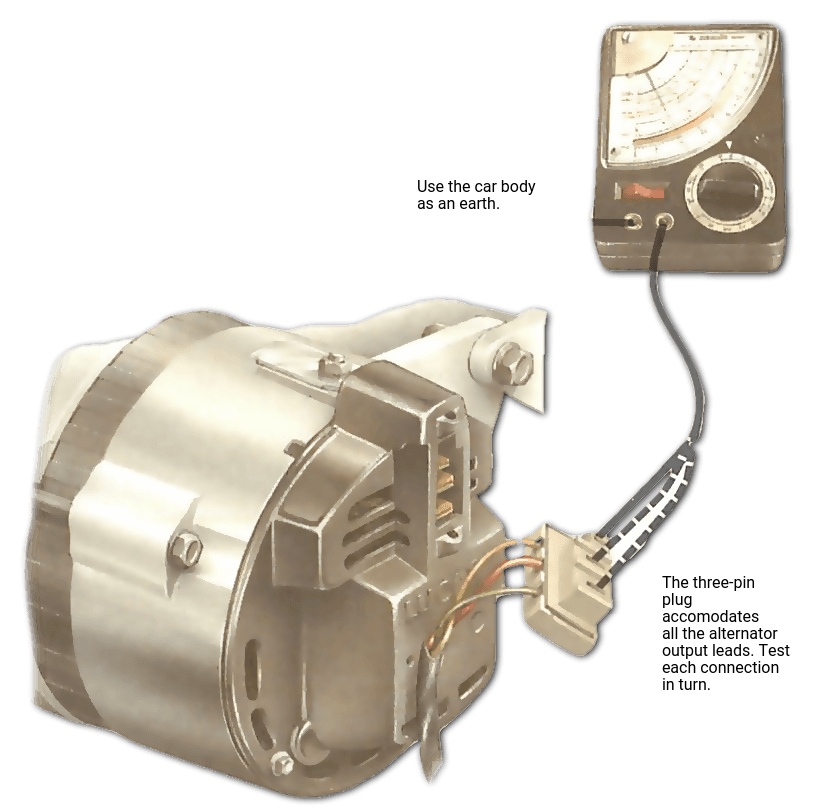
Step 5: Test Output Performance
Implement a testing protocol to verify alternator output before finalizing your purchase. Use a handheld voltmeter to check voltage output, ensuring it falls within the acceptable range (typically around 14 volts with the engine running). Additionally, conduct an amperage output test using a clamp-on ammeter to confirm that the alternator can handle the required load without significant voltage drop.
Step 6: Consider Bulk Purchasing Options
To mitigate the risk of downtime, consider placing bulk orders for alternators, especially if you manage a fleet or multiple applications. This strategy not only ensures availability but may also provide cost savings through volume discounts. Establishing a reliable inventory can prevent operational disruptions caused by unexpected alternator failures.
Step 7: Review Warranty and After-Sales Support
Finally, examine the warranty terms and after-sales support offered by the supplier. A robust warranty can protect your investment and provide peace of mind, while responsive customer support is crucial for addressing any post-purchase issues. Ensure that the supplier offers adequate service options to assist with installation and troubleshooting.
By following these steps, B2B buyers can effectively source alternators that meet their specific output requirements, ensuring optimal performance and reliability for their operations.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for what should alternator output be Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Alternators?
When evaluating the cost structure of sourcing alternators, several components must be considered. Materials are the primary cost driver, accounting for a significant portion of the overall expenses. High-quality copper windings, durable housing materials, and reliable electronic components are essential for ensuring optimal alternator performance. The choice of materials can significantly impact both the price and the longevity of the alternator.
Labor costs also play a critical role, particularly in regions with varying wage standards. Skilled labor is required for assembly, quality control, and testing processes. Manufacturing overhead, including utilities and facility maintenance, contributes to the overall cost, while tooling costs may arise from the need for specialized equipment to produce customized alternators.
Quality Control (QC) is imperative to ensure that the alternators meet industry standards. Rigorous testing of output voltage and amperage is essential, especially for B2B buyers who depend on reliability. Lastly, logistics costs related to shipping, warehousing, and distribution must be factored in, as they can vary widely based on geographic location and transportation methods.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Alternator Sourcing?
Several factors influence the pricing of alternators, particularly for international B2B buyers. Volume or Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ) can significantly affect pricing; larger orders typically lead to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Additionally, specifications and customization can alter the price. Custom alternators designed for specific applications may require additional engineering and testing, thus increasing costs.
The quality of materials used directly impacts the durability and efficiency of the alternator. Certifications and compliance with international standards can also play a role in pricing. Buyers should ensure that suppliers can provide appropriate documentation to avoid costly compliance issues later.
Supplier factors such as reputation, reliability, and lead times can also influence prices. A supplier with a proven track record may command higher prices but could offer better assurance of quality and service. Furthermore, understanding Incoterms is vital for international transactions, as they define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers, impacting total landed costs.
What Are Effective Buyer Tips for Negotiating Alternator Prices?
To achieve cost efficiency when sourcing alternators, buyers should leverage negotiation strategies. Establishing a solid relationship with suppliers can lead to better pricing and terms. Buyers should also consider Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), which includes not just the purchase price but also maintenance, downtime, and replacement costs. This holistic view can lead to more informed purchasing decisions.
Understanding pricing nuances specific to different regions is crucial. For instance, in markets such as Africa and South America, local suppliers may offer competitive pricing due to lower labor costs. However, buyers must weigh this against potential risks, such as quality control and support. In contrast, European suppliers may offer higher-quality products but at a premium price.
Buyers should remain aware of market fluctuations and seasonal trends, as these can impact pricing. Engaging in proactive discussions about future needs can also lead to favorable terms, especially when suppliers can anticipate demand spikes.

Illustrative image related to what should alternator output be
What Should Buyers Remember Regarding Pricing Disclaimers?
While this analysis provides a comprehensive overview of the cost and pricing landscape for sourcing alternators, buyers should remain cautious. Prices can fluctuate based on various factors such as market conditions, material availability, and geopolitical influences. Therefore, it is prudent for buyers to seek multiple quotes and conduct thorough due diligence before finalizing any agreements. Always ensure that the pricing discussed is indicative and may vary based on specific project requirements and market dynamics.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing what should alternator output be With Other Solutions
Introduction: Exploring Alternatives to Standard Alternator Output
Understanding the optimal output of alternators is essential for ensuring the efficient operation of electrical systems in vehicles and equipment. However, several alternative solutions exist that can either complement or replace traditional alternator setups. This analysis compares the standard alternator output with other viable technologies, helping B2B buyers make informed decisions based on performance, cost, and other critical factors.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | What Should Alternator Output Be | High Output Alternators | Solar Power Systems |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | 13.8 – 14.5 volts; 40-120 amps | 14.5 – 16 volts; 100+ amps | Varies; typically 12-14 volts depending on sunlight |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment | Higher initial cost | High initial investment; long-term savings possible |
| Ease of Implementation | Simple installation; requires basic tools | More complex; may require additional pulleys and belts | Requires solar panels, charge controllers, and battery systems |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; periodic checks | Moderate; needs regular checks for output | Low; minimal upkeep but dependent on sunlight |
| Best Use Case | Standard automotive applications | Heavy-duty and marine applications | Remote areas, off-grid applications |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
What Should Alternator Output Be
Standard alternators are designed to provide a reliable output between 13.8 to 14.5 volts and typically range from 40 to 120 amps. They are best suited for automotive applications where maintaining battery charge while operating various electronic systems is crucial. The installation process is straightforward, and ongoing maintenance is minimal, primarily involving voltage checks. However, these units can become less efficient under heavy loads or high temperatures, which may lead to performance issues in demanding environments.
High Output Alternators
High output alternators are engineered to deliver greater power, often exceeding 14.5 volts and capable of providing over 100 amps. They are ideal for heavy-duty vehicles and marine applications where substantial electrical demands are common. While they offer superior performance, the initial cost is considerably higher than standard alternators. Installation can be more complex, requiring additional components such as upgraded pulleys and belts. Maintenance is moderate, as these units need regular checks to ensure optimal function, particularly under high load conditions.
Solar Power Systems
Solar power systems harness energy from sunlight to charge batteries, offering a sustainable alternative to traditional alternators. These systems typically operate within a voltage range of 12-14 volts, depending on the sunlight available. While the initial investment in solar panels and associated equipment can be high, they provide long-term savings on energy costs, especially in remote or off-grid locations. The implementation requires a more extensive setup, including solar panels, charge controllers, and batteries, but once established, they demand minimal maintenance. Their reliance on sunlight can be a limitation, making them less effective in consistently cloudy regions.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Needs
When selecting the appropriate power solution, B2B buyers should consider the specific requirements of their applications. For standard vehicles and light-duty equipment, a traditional alternator output may suffice. However, for heavy-duty operations or marine environments, high output alternators may be necessary to meet increased electrical demands. Conversely, for businesses operating in remote areas, investing in solar power systems can yield significant long-term benefits despite the higher upfront costs. Ultimately, the choice will depend on performance needs, budget constraints, and the operational environment, ensuring that buyers select the most effective solution for their specific circumstances.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for what should alternator output be
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Alternator Output?
When evaluating alternator output, several critical specifications and technical properties play a vital role in ensuring optimal performance, reliability, and compatibility with various applications. Below are essential properties that B2B buyers should consider:
1. Voltage Output
The voltage output of an alternator is crucial for charging batteries effectively. Typically, a well-functioning alternator should produce between 13.8 to 14.5 volts when the engine is running. This range ensures that batteries receive sufficient charge without overloading or damaging the electrical system. Understanding the voltage requirements is vital for applications in various industries, especially in automotive and marine sectors, where battery performance is essential.
2. Amperage Rating
The amperage rating indicates the maximum current an alternator can supply to the electrical system. It is vital for determining whether the alternator can handle the total load of all electrical components. A higher amperage rating ensures that the alternator can charge batteries quickly and power additional devices without strain. For businesses, this means reduced downtime and maintenance costs, especially in commercial fleets or heavy machinery.

Illustrative image related to what should alternator output be
3. Temperature Sensitivity
Alternators are often sensitive to ambient temperature changes, which can significantly affect their output. High temperatures can reduce an alternator’s efficiency, sometimes by as much as 50%. This property is particularly important for equipment used in warmer climates, as it can lead to unexpected failures. B2B buyers must consider temperature ratings when selecting alternators for specific applications to ensure consistent performance.
4. Regulator Type
The type of voltage regulator integrated into an alternator determines how it manages voltage output. Traditional regulators may only provide a fixed voltage, while smart regulators adjust the output based on battery charge levels. Understanding the regulator type is essential for ensuring that the alternator meets the specific charging needs of different battery types and applications, especially for businesses that rely on advanced battery systems.
5. Physical Dimensions and Mounting Configuration
The physical size and mounting configuration of an alternator are critical for compatibility with existing systems. Alternators must fit within specific spatial constraints and align with engine designs. This consideration is particularly relevant for B2B buyers in sectors such as automotive manufacturing or custom vehicle modifications, where precise fitment is necessary to avoid additional costs and delays.
6. Durability and Material Grade
The materials used in constructing an alternator impact its durability and lifespan. For example, components made from high-grade aluminum or reinforced plastics can better withstand harsh conditions. Businesses should prioritize alternators with proven durability, especially in industries where equipment operates in challenging environments, to minimize replacement costs and enhance reliability.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Alternator Output?
Understanding industry jargon can greatly enhance communication and negotiation processes in B2B transactions. Here are some common terms relevant to alternator output:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of alternators, purchasing OEM parts ensures compatibility and reliability, which is crucial for businesses aiming to maintain high-quality standards in their products.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ indicates the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ is essential for B2B buyers to manage inventory effectively and ensure that they meet production needs without overcommitting capital.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document issued by a buyer to solicit price quotes from suppliers. This process helps businesses compare prices and terms before making purchasing decisions, enabling better budget management and supplier negotiation.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping and delivery. Familiarity with these terms helps businesses understand their obligations and liabilities in international transactions, which is crucial for smooth logistics and cost management.
5. Aftermarket Parts
Aftermarket parts are components made by third-party manufacturers, as opposed to OEM parts. While often more cost-effective, B2B buyers should evaluate the quality and compatibility of aftermarket alternators to ensure they meet operational requirements.
6. Load Testing
Load testing measures an alternator’s performance under simulated operational conditions. This process is vital for ensuring that alternators can handle the required electrical loads, thereby preventing potential failures and operational disruptions.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terminology, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing alternators, ensuring they meet their operational needs efficiently and effectively.

Illustrative image related to what should alternator output be
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the what should alternator output be Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics Influencing Alternator Output Needs?
The global alternator market is experiencing significant shifts driven by technological advancements and changing consumer expectations. The demand for higher output alternators is on the rise, especially in sectors such as automotive, marine, and renewable energy. In regions like Africa and South America, where off-grid energy solutions are increasingly sought after, the need for robust alternators that can efficiently charge batteries at lower RPMs is becoming paramount. Moreover, industries are gravitating towards “smart” alternators that can adapt their output based on the battery’s state of charge, thus enhancing efficiency and prolonging battery life.
In the Middle East and Europe, the push for electric vehicles (EVs) is reshaping the alternator landscape. With EVs requiring specialized alternators for their unique power management systems, manufacturers are innovating to meet these needs. The integration of advanced monitoring systems that provide real-time data on alternator performance is also gaining traction among B2B buyers, allowing for proactive maintenance and reduced downtime.
Another emerging trend is the focus on modularity and customization in alternator design. Buyers are increasingly looking for options that allow them to tailor output specifications to their unique applications, which is particularly important in sectors like marine and industrial equipment. As the market evolves, understanding these dynamics will be crucial for international buyers seeking reliable, high-output alternators that meet their operational requirements.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact Alternator Output Procurement?
Sustainability is becoming a critical factor in the procurement of alternators, with increasing scrutiny on the environmental impact of manufacturing processes. International B2B buyers are now prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to ethical sourcing and sustainable practices. This includes the use of recyclable materials, energy-efficient production methods, and adherence to environmental regulations.
Moreover, the importance of ‘green’ certifications is gaining momentum in the alternator sector. Buyers are looking for products that not only meet their technical specifications but also align with their corporate sustainability goals. For instance, alternators that are manufactured with minimal environmental impact or that utilize eco-friendly materials can provide a competitive advantage in the market.
Additionally, as companies strive to reduce their carbon footprints, the demand for alternators that can operate efficiently in a variety of environmental conditions is increasing. This is particularly relevant in regions prone to high temperatures or varied operating conditions, where traditional alternators may underperform. By focusing on sustainable and ethical sourcing, buyers can enhance their brand reputation while also contributing to global sustainability efforts.
What Is the Historical Context Behind Current Alternator Output Standards?
The evolution of alternators has been shaped by technological advancements and changing energy demands over the decades. Initially designed to meet the basic electrical needs of vehicles, alternators have undergone significant transformations to accommodate the increasing power requirements of modern applications.
In the early days, alternators were primarily used in automotive settings, with output levels sufficient to charge batteries and power basic electrical systems. However, as vehicles became more sophisticated with the addition of advanced electronic systems, the demand for higher-output alternators grew. This shift led to the development of “smart” alternators equipped with voltage regulators that adjust output based on battery state, significantly enhancing efficiency.
In marine and industrial applications, the historical reliance on traditional alternators has prompted a reevaluation of output standards. With the need for reliable power sources in off-grid and high-demand scenarios, manufacturers have adapted designs to ensure optimal performance under varying conditions. This evolution reflects a broader trend towards customization and adaptability in alternator technology, which continues to shape market expectations today.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of what should alternator output be
-
1. How do I determine the appropriate alternator output for my application?
To select the right alternator output, assess the total electrical load of your vehicle or equipment, including all accessories and battery charging requirements. Generally, a standard automotive alternator provides around 14 volts and should ideally match or exceed the amperage needs of your system. Consider any additional demands from onboard equipment, especially in commercial applications. Consulting with your equipment supplier can ensure you select an alternator that meets specific performance criteria, especially in high-demand environments like marine or industrial applications. -
2. What is the optimal voltage output for an alternator?
The optimal voltage output for most automotive alternators is typically between 13.8 and 14.5 volts when the engine is running. For specialized applications, such as marine or heavy-duty vehicles, the voltage might need adjustment based on the battery type and load conditions. Regularly testing the output voltage with a voltmeter ensures consistent performance and helps identify potential issues early. If the voltage significantly drops below the optimal range, it may indicate a failing alternator or poor connections that need addressing. -
3. How can I test the amperage output of my alternator?
Testing the amperage output of your alternator involves using a clamp-on ammeter. Start by clamping the ammeter around the positive output wire of the alternator while the engine runs at a steady RPM, ideally around 1,500. This method will provide an accurate reading of the alternator’s performance under load. A well-functioning alternator should produce an amperage close to its rated output. Regular testing is crucial for fleet maintenance, helping to minimize downtime and operational costs. -
4. What factors affect alternator output in different environments?
Environmental conditions, such as temperature and humidity, significantly impact alternator output. In high-temperature settings, common in regions like the Middle East, the efficiency of standard alternators can drop by as much as 50%. Therefore, selecting alternators designed for high-temperature operations or those with enhanced cooling features is vital. Additionally, low RPM operations can affect output; high-output alternators are recommended for applications requiring substantial power at lower engine speeds. -
5. What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for bulk alternator purchases?
MOQs for alternators can vary widely by supplier and region. Typically, manufacturers may set MOQs ranging from 50 to several hundred units, depending on the alternator specifications and customization options required. It’s advisable to negotiate MOQs with suppliers, especially if you have specific needs for your fleet. Establishing a solid relationship with manufacturers can also lead to flexibility in future orders and better pricing structures. -
6. How should I vet suppliers for alternators in international markets?
When sourcing alternators internationally, it’s crucial to conduct thorough due diligence on potential suppliers. Look for certifications that ensure compliance with international quality standards, such as ISO 9001. Request references from other B2B clients in your industry, and consider visiting the supplier’s facilities if feasible. Additionally, reviewing their production capabilities, lead times, and warranty policies will provide insights into their reliability and commitment to quality. -
7. What payment terms are commonly offered for alternator purchases?
Payment terms for alternator purchases can vary by supplier and region, but common options include upfront payment, net 30, or net 60 days. Some suppliers may offer discounts for early payments or larger orders. It’s essential to discuss and agree upon payment terms before finalizing a purchase, ensuring they align with your cash flow requirements. Utilizing secure payment methods and establishing clear contractual terms can protect your interests during international transactions. -
8. How can I ensure quality assurance (QA) in my alternator orders?
To ensure quality assurance in your alternator orders, request detailed specifications and quality control processes from suppliers. Many reputable manufacturers will provide information on their QA protocols, including testing procedures and certifications. Consider implementing a third-party inspection service, especially for large shipments, to verify that products meet your standards before delivery. Establishing clear communication regarding quality expectations upfront can minimize discrepancies and ensure product reliability.
Top 5 What Should Alternator Output Be Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Battery – Brand New
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Brand new battery; Alternator has good voltage but no current.
2. Mastervolt – Alpha Alternators
Domain: mastervolt.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Mastervolt Alpha alternators are designed for ships and professional mobile applications, providing sufficient power at low RPMs with a pulley ratio of 1:3. They are resistant to high temperatures in engine rooms and can charge batteries quickly. Recommended amperage is 30-50% of battery capacity. The Alpha Pro charge regulator maximizes output from Mastervolt alternators, using a 3-step+ charge m…
3. Car Alternator – Output Specifications
Domain: forum.allaboutcircuits.com
Registered: 2003 (22 years)
Introduction: This company, Car Alternator – Output Specifications, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
4. Alternator – Voltage Guidelines
Domain: mechanics.stackexchange.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: Alternator voltage should ideally be between 14.1V and 14.5V. A voltage exceeding 16.5V can indicate a faulty alternator, which may cause damage to the battery and car electronics. Some newer vehicles may have alternators that charge at higher voltages (up to 15.5V) for specific battery types, such as calcium-based batteries. It is important to measure voltage at the battery terminals, as voltage …
5. Counterman – Alternator Testing Guide
Domain: counterman.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: To determine if an alternator is good or bad, it is essential to conduct a bench test on an alternator test stand. A good alternator should produce about 13.5 to 14.5 volts with the engine idling. If the voltage reading is low (12.5 volts or less), it indicates a charging problem, but further diagnosis is required to identify the cause. If the alternator passes the bench test, the issue lies elsew…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for what should alternator output be
In summary, understanding alternator output is critical for international B2B buyers involved in industries reliant on efficient power management, such as automotive and marine applications. Key takeaways include the importance of maintaining optimal voltage levels, which should generally be around 14 volts during operation, and ensuring that amperage output aligns with the specific needs of your equipment. Regular testing and monitoring can prevent costly downtime and extend the lifespan of both alternators and batteries.
Strategic sourcing plays a vital role in securing high-quality alternators that meet your operational requirements. By establishing relationships with reliable suppliers, businesses can ensure consistent access to products that enhance performance and reliability.
Looking ahead, as industries evolve and the demand for sustainable energy solutions grows, investing in high-output alternators will become increasingly important. We encourage international buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe to assess their current sourcing strategies and consider the long-term benefits of integrating advanced alternator technology into their operations. By doing so, you not only enhance operational efficiency but also position your business for success in a competitive marketplace.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.