Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for what is a starter
In today’s competitive landscape, sourcing the right starter for your industrial applications can be a daunting challenge, particularly for international B2B buyers navigating diverse markets. A starter, in its essence, is a device that initiates and regulates the operation of electrical motors, playing a crucial role in various industries. Understanding the different types of starters available, their applications, and how to evaluate suppliers is essential for making informed purchasing decisions.
This comprehensive guide delves into the multifaceted world of starters, exploring various types such as full-voltage and reversing starters, alongside their specific applications across sectors like manufacturing, energy, and transportation. Additionally, we will provide insights into supplier vetting processes, cost considerations, and the latest technological advancements that enhance performance and efficiency.
By equipping B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including key markets like Brazil and Saudi Arabia—with actionable knowledge, this guide empowers you to make informed, strategic decisions. Understanding the complexities of starters not only facilitates better operational outcomes but also strengthens your competitive edge in the global market. Whether you are a seasoned professional or new to the industry, this resource is designed to simplify your sourcing journey and optimize your procurement strategies.
Table Of Contents
- Top 3 What Is A Starter Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for what is a starter
- Understanding what is a starter Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of what is a starter
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘what is a starter’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for what is a starter
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for what is a starter
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘what is a starter’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for what is a starter Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing what is a starter With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for what is a starter
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the what is a starter Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of what is a starter
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for what is a starter
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Understanding what is a starter Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Full Voltage Non-Reversing Starter | Simple design; starts and stops motors; no reversing function | Manufacturing, HVAC, Pumps | Pros: Cost-effective, straightforward installation. Cons: Limited functionality for applications needing direction change. |
| Full Voltage Reversing Starter | Allows for both starting and reversing motor direction | Conveyor systems, cranes, and lifts | Pros: Versatile for dynamic applications. Cons: More complex and higher initial cost. |
| Soft Starter | Gradually increases voltage to reduce inrush current | HVAC systems, compressors | Pros: Minimizes mechanical stress, energy-efficient. Cons: Higher upfront cost, requires more space. |
| Variable Frequency Drive (VFD) | Controls motor speed and torque by varying frequency and voltage | Process control, material handling | Pros: Energy savings, precise control. Cons: Requires technical expertise for setup and maintenance. |
| Definite Purpose Starter | Designed for specific applications with unique requirements | Specialized machinery, food processing | Pros: Tailored for specific tasks, maximizes efficiency. Cons: Limited availability, potentially higher costs. |
What are Full Voltage Non-Reversing Starters and When to Use Them?
Full Voltage Non-Reversing Starters are basic devices that provide power to motors without the capability to reverse direction. They are commonly used in applications such as manufacturing and HVAC systems where motors need to start and stop but do not require directional changes. Buyers should consider their simplicity and cost-effectiveness, making them suitable for straightforward tasks. However, for applications needing more flexibility, these starters may fall short.
How Do Full Voltage Reversing Starters Enhance Operational Flexibility?
Full Voltage Reversing Starters enable motors to start and reverse, making them ideal for applications like conveyor systems and cranes. Their design allows for quick directional changes, which is essential in dynamic environments. While they provide versatility, buyers must weigh their complexity and higher costs against the operational benefits they offer, particularly in industries requiring frequent direction changes.
What Benefits Do Soft Starters Offer for Motor Control?
Soft Starters gradually ramp up the voltage supplied to motors, which minimizes inrush current and mechanical stress during startup. This feature is particularly beneficial in HVAC systems and compressors where sudden starts can cause damage. While they enhance energy efficiency and prolong equipment life, buyers should account for the higher initial investment and the need for additional space in their installations.
Why Choose Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs) for Precision Control?
Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs) are advanced starters that control motor speed and torque by adjusting the frequency and voltage of the electrical supply. They are widely used in process control and material handling, providing significant energy savings and precise operational control. However, VFDs require technical expertise for setup and maintenance, which could be a consideration for buyers in less technologically advanced environments.
What are Definite Purpose Starters and Their Applications?
Definite Purpose Starters are designed for specific applications, such as specialized machinery or food processing equipment. They are tailored to meet unique operational requirements, maximizing efficiency in their intended use. While they can significantly enhance performance, buyers should be aware of their limited availability and potentially higher costs, making them best suited for businesses with particular needs that justify the investment.
Key Industrial Applications of what is a starter
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of what is a starter | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Motor control in assembly lines | Enhances operational efficiency and reduces downtime | Motor specifications, overload protection, and control voltage |
| Agriculture | Starting electric motors for irrigation systems | Increases productivity and optimizes water usage | Environmental conditions, motor type, and maintenance needs |
| Oil & Gas | Starting pumps and compressors in extraction processes | Ensures reliable operation and minimizes failure risks | Voltage ratings, application environment, and safety standards |
| Construction | Powering heavy machinery and cranes | Improves project timelines and equipment reliability | Load capacity, starter type, and compatibility with machinery |
| Transportation | Starting engines in commercial vehicles and fleets | Enhances fleet efficiency and reduces operational costs | Vehicle specifications, type of starter, and warranty terms |
How Are Starters Used in Manufacturing, and What Problems Do They Solve?
In the manufacturing sector, starters are integral to motor control on assembly lines. They initiate, stop, and regulate the speed of electric motors, ensuring that operations run smoothly. By minimizing downtime through reliable starting mechanisms, businesses can enhance productivity. Buyers should consider motor specifications, overload protection features, and control voltage requirements to ensure compatibility with existing systems.
What Role Do Starters Play in Agriculture, Particularly in Irrigation?
Starters in agriculture are crucial for initiating electric motors that power irrigation systems. They help manage water distribution efficiently, which is vital in regions prone to drought. This application not only boosts productivity but also optimizes resource usage. When sourcing starters for agricultural use, buyers must evaluate environmental conditions, the type of motor required, and the maintenance needs to ensure longevity and reliability.
How Are Starters Essential in the Oil & Gas Industry?
In the oil and gas sector, starters are used to power pumps and compressors essential for extraction processes. Their reliability directly affects operational efficiency and safety, as any failure can lead to significant downtime and financial losses. Buyers in this industry should focus on voltage ratings, the application environment, and adherence to safety standards when selecting starters, ensuring they meet the rigorous demands of the field.
Why Are Starters Critical for Heavy Machinery in Construction?
Starters are vital for powering heavy machinery and cranes in construction. They enable the quick and efficient start of engines, which is crucial for maintaining project timelines. A reliable starter reduces the risk of equipment failure, thus enhancing overall project efficiency. Buyers should consider the load capacity, type of starter, and compatibility with their machinery to ensure optimal performance in demanding construction environments.
How Do Starters Enhance Efficiency in Transportation?
In the transportation sector, starters are essential for starting engines in commercial vehicles and fleets. They contribute to fleet efficiency by ensuring reliable engine starts and reducing operational costs associated with maintenance and repairs. When sourcing starters, buyers should pay attention to vehicle specifications, the type of starter required, and warranty terms to ensure they invest in quality products that enhance their fleet’s reliability.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘what is a starter’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Confusion Over Starter Types and Specifications
The Problem: Many B2B buyers encounter confusion when selecting the appropriate type of starter for their applications. With various options available—such as full voltage non-reversing, full voltage reversing, and definite purpose starters—making an informed choice can feel overwhelming. This confusion often leads to procurement delays, increased costs due to wrong purchases, and operational inefficiencies if the wrong starter is implemented in machinery. Additionally, understanding the specific voltage, horsepower, and full-load amps of their motors can be a daunting task, particularly for buyers who lack technical expertise in electrical components.
The Solution: To mitigate these challenges, buyers should start by conducting a comprehensive assessment of their motor specifications, including voltage, horsepower, and full-load amps. Engaging with a knowledgeable supplier or manufacturer can also provide clarity on which starter types are best suited for specific applications. Utilizing online tools and resources, such as calculators for electrical ratings and starter selection guides, can streamline the decision-making process. Furthermore, buyers should consider training sessions or workshops offered by manufacturers to better understand the fundamentals of motor control and starter technology. By being well-informed and proactive, buyers can confidently select the appropriate starter, ensuring optimal performance and reliability in their operations.
Scenario 2: Operational Risks from Inadequate Overload Protection
The Problem: A prevalent issue faced by B2B buyers is the lack of adequate overload protection in starters, which can lead to severe operational risks, such as equipment damage or unplanned downtime. Many buyers may overlook the importance of overload protection mechanisms, assuming that all starters come with built-in safeguards. This oversight can result in motors drawing excessive current, leading to overheating and ultimately causing catastrophic failures. Such incidents not only incur repair costs but can also disrupt production schedules and affect overall business productivity.
The Solution: To address this pain point, buyers must prioritize the inclusion of appropriate overload protection in their starter specifications. They should familiarize themselves with the different types of overload protection available, such as bimetallic thermal overloads and solid-state electronic overloads. When sourcing starters, it is crucial to inquire about the specifications of the overload relays and their trip capabilities. Buyers can also implement a preventive maintenance program that includes regular inspections of overload protection devices to ensure they are functioning correctly. By taking these proactive steps, buyers can significantly reduce the risk of motor damage and enhance the longevity of their equipment.
Scenario 3: High Costs Due to Poor Starter Sizing
The Problem: Poorly sized starters can lead to substantial financial losses for businesses. Buyers often struggle with selecting the right starter that matches their equipment’s requirements, resulting in either underperformance or, conversely, over-specification that incurs unnecessary costs. An incorrectly sized starter can lead to inefficiencies in energy consumption, increased wear on equipment, and even compliance issues with industry standards. This situation is particularly critical for international buyers who may face additional challenges related to varying electrical standards and requirements across different regions.
The Solution: To avoid the pitfalls of poor sizing, buyers should conduct a thorough analysis of their operational requirements and consult with electrical engineers or qualified technical advisors. Buyers must gather detailed motor data, including the motor’s nameplate information, and consider the specific application conditions such as start frequency and load characteristics. When purchasing, it is advisable to choose vendors that offer customizable starter solutions tailored to unique operational needs. Additionally, leveraging software tools for motor control analysis can provide insights into optimal starter sizing, helping to ensure both efficiency and cost-effectiveness. By implementing these strategies, buyers can make informed decisions that enhance operational efficiency and reduce unnecessary expenses.

Illustrative image related to what is a starter
Strategic Material Selection Guide for what is a starter
What are the Common Materials Used for Starters in Electrical Applications?
When selecting materials for starters, particularly in electrical applications, it is crucial to consider their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and compatibility with specific environments. Here, we will analyze four common materials: copper, aluminum, plastic, and steel.
What are the Key Properties of Copper in Starters?
Copper is widely used in electrical components due to its excellent electrical conductivity and thermal properties. It typically operates effectively in a temperature range of -200°C to 200°C and can handle significant electrical loads without overheating. Copper also exhibits good corrosion resistance, especially when coated, making it suitable for various environments.
Pros: Copper’s high conductivity ensures minimal energy loss, enhancing the efficiency of starters. Its durability allows it to withstand mechanical stress and high temperatures, making it a reliable choice for demanding applications.
Cons: The primary drawback of copper is its cost, which is higher than alternatives like aluminum. Additionally, copper components can be heavier, which may not be suitable for all applications.
Impact on Application: Copper is particularly effective in applications requiring high electrical performance, such as in heavy machinery and industrial equipment.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards such as ASTM and IEC is essential. In regions like Brazil and Saudi Arabia, where humidity can be high, selecting copper with appropriate coatings for corrosion resistance is advisable.
How Does Aluminum Compare as a Material for Starters?
Aluminum is another popular choice for electrical starters, known for its lightweight nature and good conductivity. It typically operates within a temperature range of -50°C to 150°C. While it has lower conductivity than copper, it is often used in applications where weight reduction is critical.
Pros: Aluminum is generally more cost-effective than copper, making it an attractive option for budget-conscious projects. Its lightweight nature also simplifies installation and reduces shipping costs.
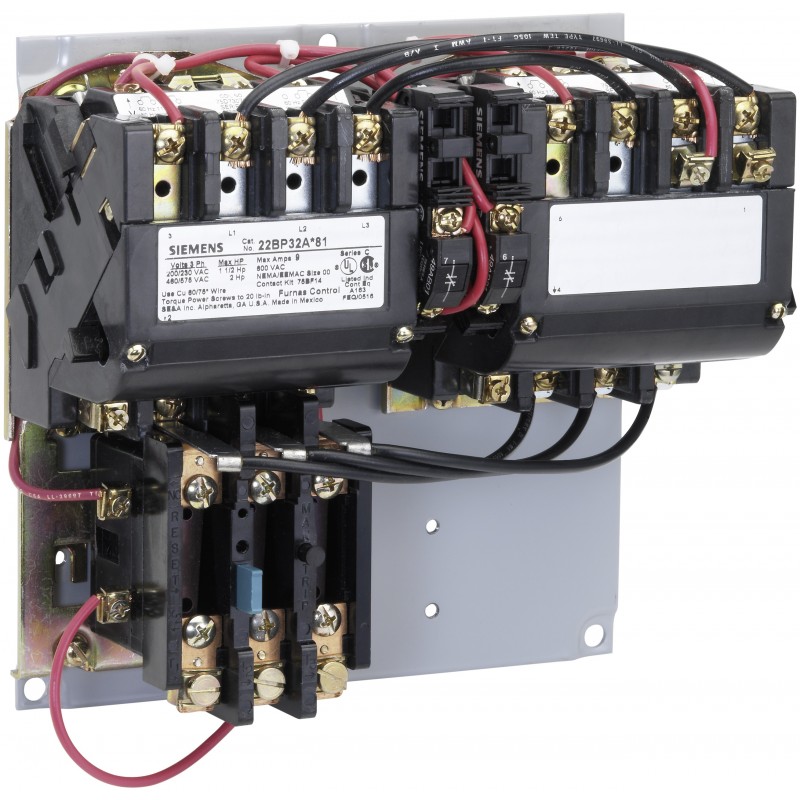

Illustrative image related to what is a starter
Cons: Aluminum is less durable than copper, particularly in high-temperature applications, as it can oxidize and lose conductivity over time. This necessitates careful design considerations to ensure longevity.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is suitable for applications where weight is a significant factor, such as in automotive and aerospace industries.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of local standards regarding aluminum use, particularly in regions with strict electrical safety regulations. In Europe, compliance with EN standards is critical.
Illustrative image related to what is a starter
What Role Does Plastic Play in Starter Construction?
Plastic materials, particularly thermoplastics and thermosetting plastics, are often used in the casing and insulation of starters. They typically withstand temperatures from -40°C to 85°C and offer excellent electrical insulation properties.
Pros: Plastic is lightweight, cost-effective, and resistant to corrosion, making it ideal for protective casings. It also provides good electrical insulation, reducing the risk of short circuits.
Cons: While plastics are durable, they may not withstand extreme temperatures or mechanical stress as well as metals. They can also degrade over time when exposed to UV radiation.
Impact on Application: Plastics are ideal for applications where insulation and protection are paramount, such as in consumer electronics and household appliances.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with safety standards such as UL and CE is crucial. In regions like South America, where UV exposure can be high, selecting UV-resistant plastics is advisable.
How is Steel Utilized in Starters?
Steel, particularly stainless steel, is often used for structural components of starters due to its strength and durability. It typically operates in a temperature range of -20°C to 300°C and offers excellent corrosion resistance when treated.
Pros: Steel’s strength makes it suitable for heavy-duty applications, ensuring that starters can withstand mechanical stress and harsh environments. Stainless steel, in particular, offers superior corrosion resistance.
Cons: The weight of steel can be a disadvantage in applications where weight is a critical factor. Additionally, the cost of high-quality stainless steel can be prohibitive.
Impact on Application: Steel is ideal for industrial applications where durability and strength are essential, such as in manufacturing and heavy machinery.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider local standards for steel quality, especially in regions like the Middle East, where environmental conditions can be harsh. Compliance with ASTM or DIN standards is often required.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Starters
| Material | Typical Use Case for what is a starter | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Copper | Heavy machinery and industrial equipment | High electrical conductivity | Higher cost and weight | High |
| Aluminum | Automotive and aerospace applications | Lightweight and cost-effective | Less durable, oxidizes over time | Medium |
| Plastic | Consumer electronics and appliances | Excellent insulation and corrosion resistance | Limited temperature range | Low |
| Steel | Industrial applications | High strength and durability | Heavier and potentially costly | Medium to High |
This strategic material selection guide provides essential insights for B2B buyers in diverse international markets, ensuring informed decisions for electrical starter applications.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for what is a starter
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Starters?
The manufacturing of electrical starters involves several critical stages that ensure the final product is reliable, efficient, and meets industry standards. The main stages in the manufacturing process include:
Material Preparation
The manufacturing process begins with material preparation, where high-quality raw materials are sourced, such as metals for contactors and plastics for housing. Suppliers often use materials that comply with international standards to ensure durability and performance. In addition, material testing is performed to confirm that the materials meet the required specifications for conductivity, resistance, and mechanical strength.
What Techniques Are Used in Forming Starters?
Once materials are prepared, the next step is forming. This process typically involves several techniques, including:
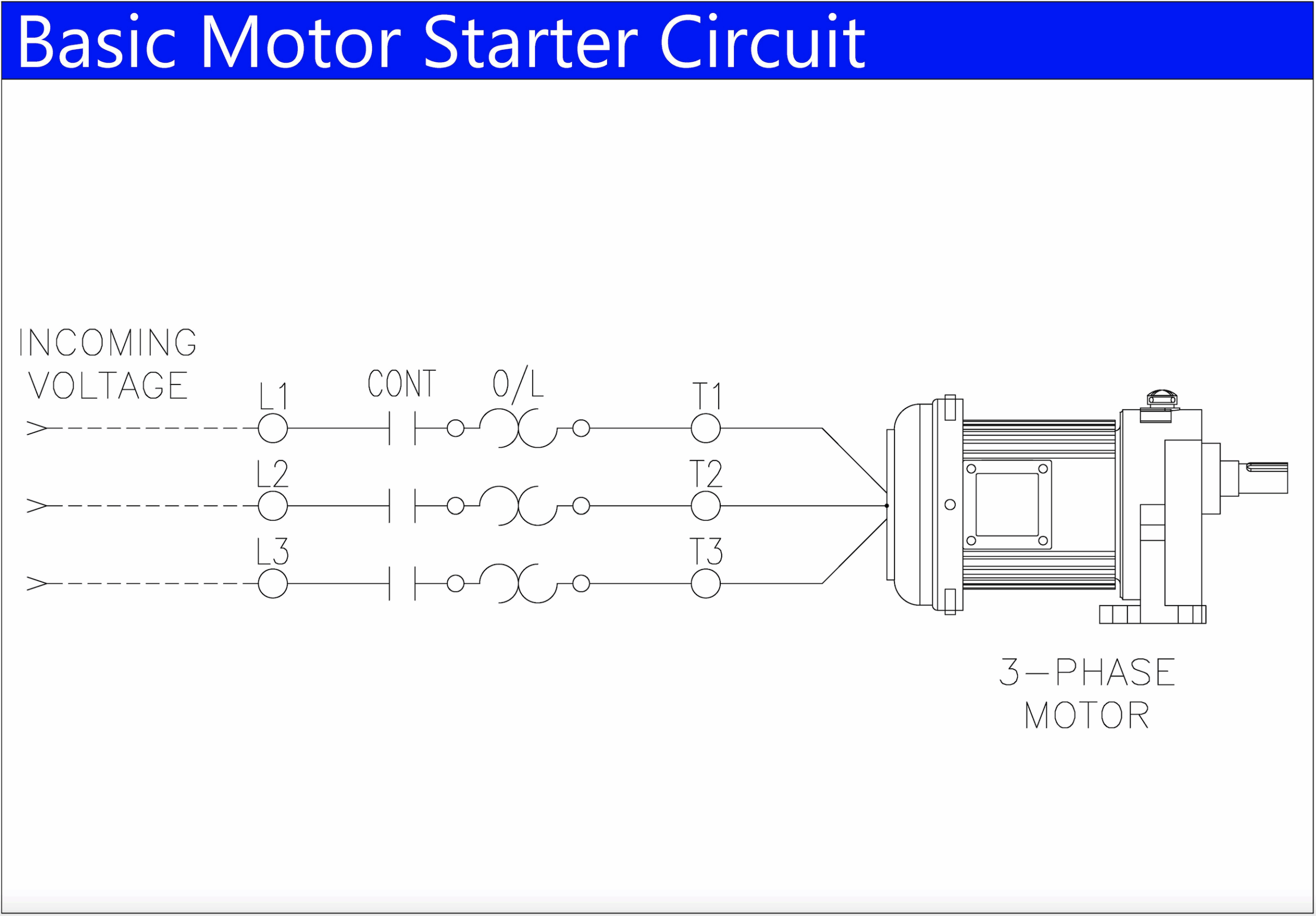
Illustrative image related to what is a starter
- Stamping: Metal sheets are stamped into specific shapes for contactors and overloads. Precision in this stage is crucial as it affects the electrical performance and mechanical fit of the starter components.
- Injection Molding: Plastic components are created using injection molding. This technique allows for high-volume production of complex shapes while maintaining consistency in quality.
- Machining: Some components may require machining to achieve precise dimensions. CNC machines are often used to ensure high accuracy and repeatability.
How Are Starters Assembled?
The assembly stage is where individual components come together to form the final product. This stage typically involves:
- Component Assembly: Workers or automated systems assemble contactors, overloads, and other components according to detailed specifications. Each part is carefully fitted to ensure proper operation.
- Wiring: Electrical connections are made between components, ensuring that circuits are correctly established. This step must be performed with precision to prevent short circuits or failures.
- Quality Control Checkpoints: As each assembly is completed, it undergoes initial quality checks to ensure that all parts are correctly installed and functional.
What Finishing Processes Are Required for Starters?
The finishing stage involves several processes aimed at enhancing the starter’s durability and performance:
- Coating: Components may be coated for corrosion resistance and insulation. Common coatings include powder coating and anodizing, which not only protect the metal but also improve aesthetics.
- Final Assembly: After finishing, the components are assembled into the final product, ensuring that all connections are secure and functional.
- Packaging: The finished starters are then packaged in a manner that protects them during shipping and handling, often including anti-static materials for electronic components.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Implemented in Starter Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is critical in the manufacturing of starters to ensure they meet both international and industry-specific standards. Here are key aspects of the QA process:
Which International Standards Should Buyers Be Aware Of?
Quality assurance in starter manufacturing is often guided by international standards such as ISO 9001, which focuses on quality management systems. Compliance with these standards ensures that manufacturers have robust processes in place for consistent quality. Additionally, certifications like CE (Conformité Européenne) for European markets and API (American Petroleum Institute) for oil and gas applications may be relevant depending on the starter’s intended use.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control (QC) involves several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint assesses the quality of raw materials before production begins. Suppliers are often required to provide certificates of compliance and test results.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing stages, ongoing checks are performed to ensure that each component and assembly meets quality standards. This may include dimensional checks, electrical testing, and visual inspections.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Once manufacturing is complete, the finished starters undergo rigorous testing to confirm their operational reliability. This includes functional tests, stress tests, and performance evaluations.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used for Starters?
Various testing methods are utilized to ensure that starters function correctly:
- Electrical Testing: This includes checking the continuity of circuits, insulation resistance, and voltage ratings. Specialized equipment is used to simulate operational conditions.
- Thermal Testing: Starters are subjected to thermal cycling tests to assess their performance under temperature variations, ensuring they can withstand real-world conditions.
- Durability Testing: Starters may be subjected to mechanical stress tests to evaluate their robustness and longevity.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
B2B buyers should take proactive steps to verify the quality control processes of potential suppliers. Here are effective strategies:
What Audit Processes Should Buyers Consider?
Conducting audits is a crucial step in verifying a supplier’s quality assurance processes. Buyers can request:
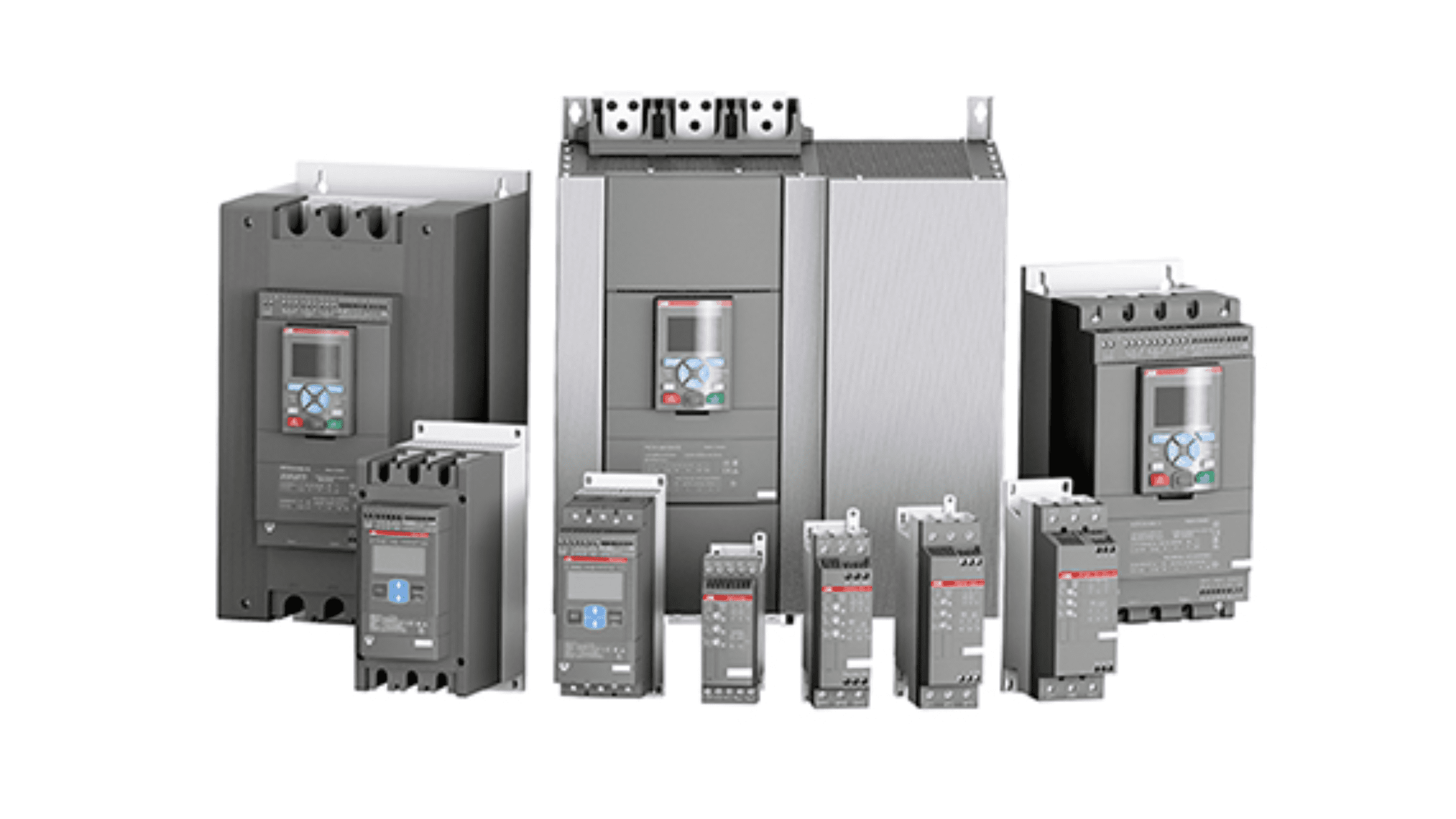

Illustrative image related to what is a starter
- Supplier Audits: On-site audits allow buyers to review manufacturing processes, quality control measures, and compliance with international standards. This provides insight into the supplier’s operational capabilities.
- Document Reviews: Requesting access to quality management documentation, including quality manuals, process flowcharts, and inspection reports, can help buyers assess compliance with standards like ISO 9001.
How Can Buyers Leverage Third-Party Inspections?
Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s quality control processes. Third-party inspectors often specialize in industry-specific standards and can offer detailed reports on compliance and product quality.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International Buyers?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of quality control is essential:
- Regulatory Compliance: Buyers must be aware of local regulations that may affect product certification and compliance. This can vary significantly by country and industry.
- Cultural Considerations: Different regions may have varying expectations regarding quality and service levels. Understanding these cultural nuances can help in building effective partnerships.
- Supply Chain Challenges: Buyers should consider potential challenges in the supply chain that could affect quality, such as transportation issues or delays in sourcing materials.
In conclusion, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for starters is essential for B2B buyers. By focusing on material preparation, forming, assembly, finishing, and rigorous quality control practices, buyers can ensure they procure reliable products that meet their operational needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘what is a starter’
To assist B2B buyers in effectively procuring starters, this guide offers a practical step-by-step checklist. Starters, essential components for motor control and operation, require careful consideration to ensure compatibility, efficiency, and reliability in various applications.

Illustrative image related to what is a starter
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before initiating your search, clearly outline the technical specifications required for your starters. This includes understanding the motor voltage, horsepower (hp), and Full Load Amps (FLA). Knowing these details helps narrow down your options and ensures that the starters you consider will meet your operational needs.
- Key Considerations:
- Is your application single-phase or three-phase?
- What are the specific power requirements and service factors?
Step 2: Identify the Type of Starter Needed
Different applications may require specific types of starters, such as Full Voltage Non-Reversing or Full Voltage Reversing starters. Identifying the type required is crucial to match the starter’s functionality with your operational needs.
- Types to Consider:
- NEMA vs. IEC: Depending on your regional standards, choose between NEMA or IEC starters.
- Definite Purpose Starters: If your application has unique requirements, consider specialized starters designed for those conditions.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Thoroughly vet potential suppliers to ensure they can deliver quality products that meet your specifications. Look for suppliers with a solid reputation and experience in your industry.
- What to Ask For:
- Company profiles and case studies showcasing relevant projects.
- Customer references, particularly from businesses in similar sectors or regions.
Step 4: Verify Certifications and Compliance
Confirm that the starters and suppliers comply with international standards and certifications. This step is essential to ensure that the products are safe, reliable, and suitable for your market.

Illustrative image related to what is a starter
- Key Certifications:
- Look for UL, CE, or ISO certifications, depending on your region.
- Ensure compliance with local electrical codes and regulations.
Step 5: Assess After-Sales Support and Warranty
Evaluate the after-sales support provided by the supplier. A robust support system can significantly reduce downtime and operational disruptions.
- Support Aspects to Check:
- Warranty terms and conditions for the starters.
- Availability of technical support and replacement parts.
Step 6: Request Samples or Demonstrations
Before finalizing your order, request samples or demonstrations of the starters. This will allow you to assess their performance in real-world conditions and ensure they meet your expectations.
- What to Observe:
- Performance under load and during start-up.
- Compatibility with existing systems and ease of installation.
Step 7: Negotiate Terms and Finalize Purchase
Once you have chosen a supplier and assessed the products, engage in negotiations to finalize the terms of your purchase. This includes pricing, delivery timelines, and payment terms.
- Key Negotiation Points:
- Bulk order discounts or payment plans.
- Delivery schedules that align with your project timelines.
Following this checklist will empower B2B buyers to make informed decisions when sourcing starters, ensuring operational efficiency and long-term reliability in their applications.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for what is a starter Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Starters?
When evaluating the cost structure for sourcing starters, it is crucial to break down the various components that contribute to the final price. The primary cost components include:
Illustrative image related to what is a starter
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts cost. Starters are typically made from metals, plastics, and electronic components, which can vary in price based on quality and sourcing region. For instance, high-grade metals may be more expensive but offer better performance and durability.
-
Labor: Labor costs can fluctuate based on the manufacturing location. Regions with lower labor costs, such as some parts of Africa and South America, may offer competitive pricing. However, labor skill levels can also affect the quality of the product.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with factory operations, such as utilities, maintenance, and administrative expenses. Efficient manufacturing processes can help minimize these costs, leading to more competitive pricing.
-
Tooling: Initial setup costs for molds and dies can be significant, especially for customized starters. These costs are often amortized over large production runs, so higher volume orders can lead to lower per-unit costs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing rigorous QC processes ensures product reliability, which can add to the cost. However, investing in quality can reduce long-term costs associated with defects and returns.
-
Logistics: Transportation and handling costs must be factored in, particularly for international shipments. Factors such as distance, shipping method, and Incoterms can significantly affect logistics expenses.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a margin to cover risks and profit. Understanding the market standards for margins can help buyers negotiate better deals.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Starter Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of starters in the B2B marketplace:
-
Volume/MOQ: Manufacturers often have Minimum Order Quantities (MOQs) that can affect pricing. Larger orders generally lead to discounts due to economies of scale.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom specifications can lead to increased costs. While tailored solutions may meet specific needs, they can also require additional design and manufacturing time.
-
Materials: The type and quality of materials used in manufacturing starters can significantly influence costs. Buyers should weigh the benefits of higher-quality materials against their budget constraints.
-
Quality and Certifications: Products that meet international standards and certifications may command higher prices. Buyers should consider whether the added cost is justified by the benefits of enhanced reliability and compliance.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can impact pricing. Established suppliers may charge more but offer better service and quality assurance.
-
Incoterms: The chosen Incoterms dictate the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping costs, insurance, and delivery. Understanding these terms can help buyers avoid unexpected costs.
What Are the Best Negotiation Tips for B2B Buyers Sourcing Starters?
To maximize cost efficiency when sourcing starters, buyers should consider the following strategies:
-
Negotiate Based on Volume: Leverage the purchasing volume to negotiate better pricing. Suppliers are often willing to offer discounts for larger orders.
-
Analyze Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider not only the purchase price but also the long-term costs associated with maintenance, downtime, and energy efficiency. A higher upfront cost for a reliable starter may lead to lower overall costs.
-
Be Informed About Pricing Nuances: Understand the market landscape and typical pricing structures. This knowledge can empower buyers during negotiations.
-
Explore Multiple Suppliers: Don’t settle for the first offer. Comparing quotes from various suppliers can provide leverage in negotiations and help identify the best deal.
-
Consider Local Suppliers: For buyers in regions like Africa and South America, sourcing from local manufacturers may reduce shipping costs and lead times, enhancing overall cost-effectiveness.
Disclaimer on Pricing
Prices for starters can vary widely based on the factors mentioned above. It is essential for buyers to conduct thorough research and obtain multiple quotes to ensure they are getting competitive pricing reflective of their specific needs. Always account for potential fluctuations in material costs and logistics when budgeting for starter purchases.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing what is a starter With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to Starters in Motor Control Solutions
In the realm of motor control solutions, starters play a crucial role in managing electrical power to motors, ensuring their safe and efficient operation. However, buyers may encounter alternative solutions that can also initiate and control motor functions. This analysis will compare traditional starters with two viable alternatives: Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs) and Soft Starters.
| Comparison Aspect | What Is A Starter | Variable Frequency Drive (VFD) | Soft Starter |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Efficiently starts, stops, and protects motors | Provides precise motor control and speed adjustment | Reduces inrush current and mechanical stress |
| Cost | Generally lower initial cost | Higher initial investment | Moderate cost, typically between the two |
| Ease of Implementation | Simple installation | Requires more complex setup | Easier installation than VFDs |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance required | Requires periodic software updates | Low maintenance, but may need periodic checks |
| Best Use Case | Basic applications with on/off control | Applications needing speed control and efficiency | Applications with high inrush current |
What Are the Pros and Cons of Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs)?
Variable Frequency Drives offer enhanced control over motor speed and torque, making them ideal for applications where precise motor control is necessary, such as pumps and conveyor systems. VFDs can significantly improve energy efficiency by adjusting the motor speed to match the load. However, the complexity of installation and higher upfront costs can be a barrier for some businesses, especially those in developing regions where budget constraints are common.
How Do Soft Starters Compare?
Soft Starters are designed to reduce the initial inrush current that occurs when motors are started. By gradually ramping up the voltage, they minimize mechanical stress on the motor and connected machinery, which is particularly beneficial in applications like compressors and fans. While they provide a simpler installation process compared to VFDs, they do not offer the same level of control over motor speed. This makes them less suitable for applications requiring variable speed operation.
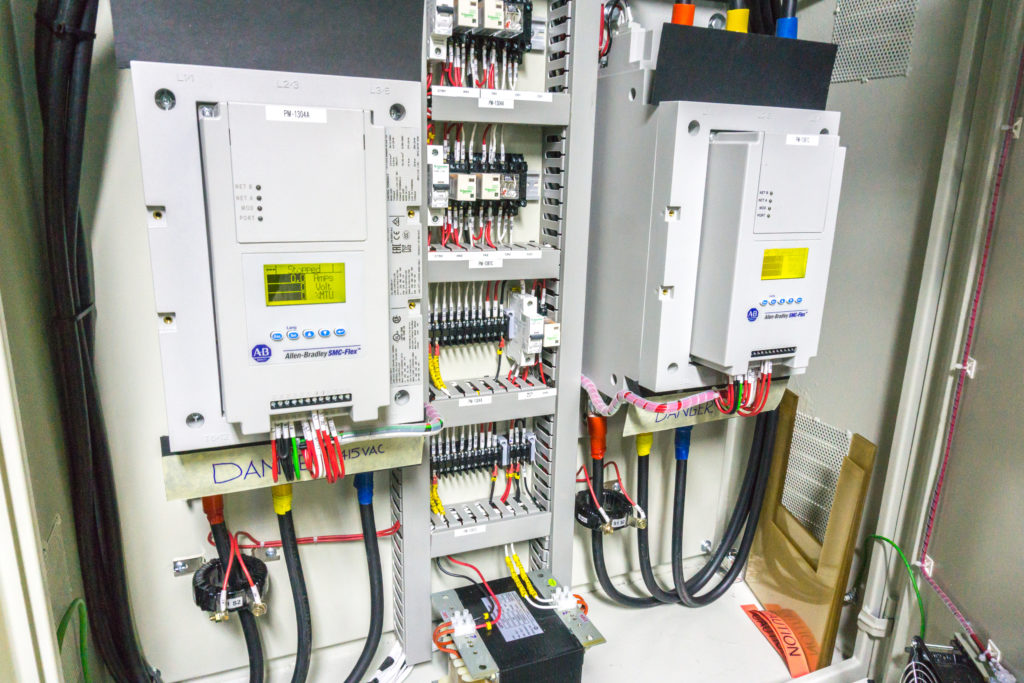

Illustrative image related to what is a starter
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
When selecting the appropriate motor control solution, B2B buyers should carefully assess their specific operational requirements and budget constraints. If the primary goal is to simply start and stop motors with minimal complexity, traditional starters may suffice. For applications needing precise speed control and efficiency, investing in a VFD could yield long-term benefits despite the higher initial costs. Soft starters present a middle ground, ideal for applications with high inrush currents but not requiring variable speed control. Ultimately, the decision should align with both current operational needs and future scalability.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for what is a starter
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Starters in Electrical Applications?
Understanding the essential technical properties of starters is crucial for B2B buyers looking to make informed purchasing decisions. Here are several critical specifications to consider:
1. Voltage Rating
The voltage rating of a starter indicates the maximum voltage it can handle without failure. Common ratings include single-phase (e.g., 120V, 240V) and three-phase (e.g., 400V, 480V). This specification is vital for ensuring compatibility with the motor and electrical systems in use, preventing potential damage or inefficiency.
2. Full Load Amps (FLA)
FLA is the maximum current the motor will draw under normal operating conditions. It is essential for sizing the starter appropriately. Selecting a starter with an FLA rating that matches or exceeds the motor’s requirements ensures proper operation and protects against overheating and equipment failure.
3. Overload Protection Type
Starters incorporate overload protection mechanisms to prevent motors from drawing excessive current. Common types include bimetallic (thermal) and solid-state (electronic) overloads. Understanding the type of overload protection is critical for maintaining motor health and operational reliability in various applications.
4. Control Voltage
The control voltage is the voltage required to operate the starter’s coil. This specification is important for ensuring that the starter can be integrated seamlessly into existing electrical systems. Common control voltages include 24V, 120V, and 230V, depending on the region and application.
5. NEMA vs. IEC Ratings
Starters are categorized by NEMA (National Electrical Manufacturers Association) and IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission) standards, which determine their suitability for various environments and applications. NEMA-rated starters are often used in North America, while IEC ratings are prevalent in Europe and other regions. Understanding these ratings helps buyers select products that comply with local regulations and standards.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Starters?
Familiarity with industry jargon can significantly enhance communication and decision-making in B2B transactions. Here are some common terms:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of starters, knowing whether a product is from an OEM can help buyers assess quality and compatibility with existing systems.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is essential for buyers to plan their procurement strategies and manage inventory effectively, especially in bulk purchasing scenarios.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to request a price quote for specific products or services. This is a critical step in the procurement process, allowing buyers to compare prices and terms from different suppliers.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a series of pre-defined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC). They clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions, including shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Understanding Incoterms helps buyers navigate logistics and cost implications effectively.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time taken from placing an order to the delivery of goods. This is a critical factor in project planning and inventory management, as longer lead times can affect production schedules and operational efficiency.
By grasping these essential technical properties and trade terminology, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing starters for their electrical applications, ensuring compatibility, reliability, and efficiency in their operations.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the what is a starter Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Starter Sector?
In the evolving landscape of the starter sector, international B2B buyers are witnessing several key market dynamics influenced by technological advancements, global demand shifts, and regional trends. One of the most significant drivers is the increasing automation in industries such as manufacturing and agriculture, particularly in emerging markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. These regions are investing heavily in infrastructure, leading to a surge in demand for electrical starters that control machinery and optimize performance.
Additionally, the trend towards digitalization is shaping the starter market. Buyers are now looking for smart starters equipped with IoT capabilities that facilitate remote monitoring and predictive maintenance, minimizing downtime and enhancing operational efficiency. Moreover, as sustainability becomes a priority, there is a growing emphasis on sourcing eco-friendly starters that comply with international standards.
Emerging markets are also experiencing a shift in preferences towards more sophisticated starter solutions, as local industries aim to improve productivity and reduce energy consumption. For instance, Brazil and Saudi Arabia are exploring advanced motor control technologies that not only provide better performance but also align with their sustainability goals. Understanding these trends is crucial for B2B buyers to make informed sourcing decisions that align with both their operational needs and market demands.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact the Starter Sector?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing have become integral to the B2B procurement process in the starter sector. The environmental impact of production processes, particularly in manufacturing electrical components, is under scrutiny. B2B buyers are increasingly required to assess the lifecycle of products and their carbon footprint, seeking suppliers who prioritize sustainable practices.
Incorporating ‘green’ certifications and materials into sourcing strategies is essential. Buyers should consider manufacturers that use recyclable materials and energy-efficient production methods, as these practices not only reduce environmental impact but also appeal to a growing consumer base that values corporate social responsibility. Moreover, ethical supply chains that ensure fair labor practices and transparency are critical for building brand reputation and securing long-term partnerships.
Additionally, as regulatory pressures increase globally, B2B buyers must stay informed about compliance standards related to sustainability. This includes understanding the implications of regulations such as REACH in Europe or the Environmental Protection Agency standards in the U.S. By aligning procurement strategies with sustainable practices, buyers can mitigate risks and enhance their competitive advantage in the market.
What is the Brief History and Evolution of the Starter Sector?
The concept of a “starter” can be traced back to the early 20th century when electric motors began to gain prominence in industrial applications. Initially, starters were rudimentary devices designed to simply switch motors on and off. However, as technology evolved, so did the complexity and functionality of starters. The introduction of contactors and overload relays in the mid-20th century revolutionized the industry, allowing for better control and protection of motors.
The late 20th century saw a shift towards more sophisticated electrical starters, integrating advanced features such as variable frequency drives (VFDs) that enable speed control and energy efficiency. In recent years, the advent of IoT technology has further transformed the starter sector, enabling real-time monitoring and data analytics to optimize performance and maintenance schedules. This evolution reflects the broader trends in industrial automation and sustainability, highlighting the importance of innovation in meeting the demands of modern B2B buyers. As the sector continues to evolve, understanding its historical context provides valuable insights for navigating current and future market dynamics.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of what is a starter
-
How do I choose the right starter for my industrial application?
Choosing the right starter involves understanding the specific requirements of your motor and application. Key factors include the motor’s voltage, horsepower, and full-load amps (FLA). Consider the type of starter needed, such as full voltage non-reversing or full voltage reversing, based on your operational needs. Additionally, assess the necessary overload protection, control voltage, and any additional accessories you may require. Consulting with suppliers who specialize in motor controls can provide tailored recommendations based on your unique operational circumstances. -
What are the main types of starters used in industrial settings?
The primary types of starters include full voltage starters, which provide direct power to the motor, and reduced voltage starters, which limit the initial power to reduce inrush current. Full voltage starters can be further divided into non-reversing and reversing types, based on whether the motor needs to change direction. Additionally, soft starters and variable frequency drives (VFDs) are available for applications requiring gradual acceleration and deceleration. Understanding these options will help you select the most efficient starter for your equipment. -
What is the significance of overload protection in starters?
Overload protection is critical as it prevents motors from drawing excessive current, which can lead to overheating and damage. Starters typically include overload relays that monitor current levels and disconnect the power supply when dangerous thresholds are reached. This protection is vital for ensuring motor longevity and reliability. Different types of overload protection, such as thermal and electronic options, cater to various applications, so it’s important to select one that aligns with your operational needs and environmental conditions. -
How can I ensure the quality of starters when sourcing internationally?
To ensure quality when sourcing starters internationally, it’s essential to vet suppliers thoroughly. Look for manufacturers that comply with international standards such as ISO certification and those that provide detailed product specifications and testing results. Request samples to evaluate performance and durability before making bulk purchases. Additionally, consider suppliers that offer warranties and after-sales support, as this indicates confidence in their product quality and commitment to customer satisfaction. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for starters?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for starters can vary significantly based on the manufacturer and the complexity of the starter type. Commonly, MOQs can range from a few units for standard models to several dozen for customized or specialized starters. When negotiating with suppliers, clarify the MOQ and inquire about the possibility of smaller orders, especially if you are testing a new application or entering a new market. Flexible suppliers may offer lower MOQs for new customers or trial orders. -
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing starters internationally?
Payment terms for international purchases of starters can vary based on the supplier and the nature of the transaction. Common options include advance payment, letters of credit, and payment upon delivery. It’s crucial to negotiate terms that mitigate risk while also accommodating your cash flow needs. Understanding the supplier’s policies and discussing payment schedules upfront can help establish a mutually beneficial agreement. Always ensure that payment terms are documented in the sales contract to avoid misunderstandings. -
What logistics considerations should I be aware of when importing starters?
When importing starters, consider logistics factors such as shipping methods, customs regulations, and delivery timelines. Choose a reliable freight forwarder who is experienced with your target market’s import regulations. Ensure all documentation, such as commercial invoices and packing lists, is accurate to facilitate smooth customs clearance. Additionally, factor in shipping costs and potential duties or tariffs that may apply to your order. Planning ahead can help prevent delays and unexpected expenses during the import process. -
How do I customize starters for specific applications?
Customizing starters for specific applications typically involves working closely with the manufacturer or supplier to define your unique requirements. Discuss the specific operational parameters, such as voltage, current ratings, and environmental conditions. Many manufacturers offer customization options for features like overload settings, control voltages, and auxiliary contacts. Engaging in thorough discussions during the design phase can ensure that the final product meets your operational needs and enhances the efficiency of your equipment.
Top 3 What Is A Starter Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Starter – Definition and Usage
Domain: merriam-webster.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Starter is defined as a noun and an adjective. As a noun, it refers to: 1) a person who initiates or sets something in motion, such as an official who signals the start of a race or a member of a starting lineup in a competition; 2) a device that causes something to begin operating, particularly an electric motor for starting an engine; 3) material containing microorganisms used to induce fermenta…
2. Eaton – Starters
Domain: eaton.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
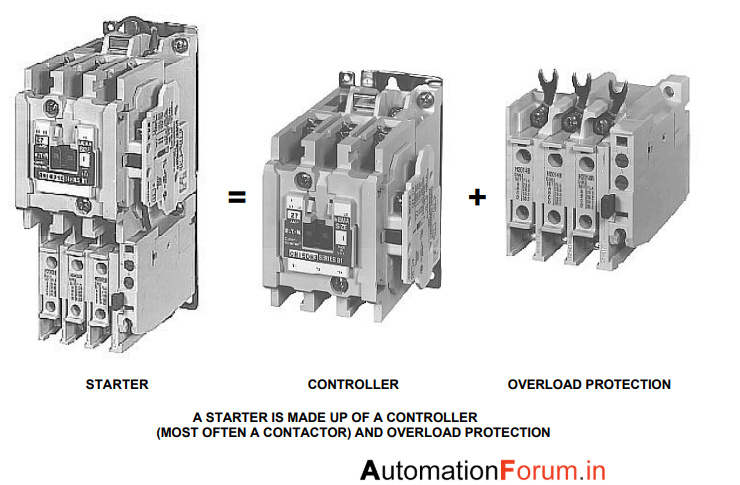
Introduction: Starters are devices that control the use of electrical power to equipment, specifically for starting, stopping, reversing, accelerating, and protecting motors. They consist of two main components: contactors and overloads.
Contactors:
– Control electric current to the motor.
– Establish and interrupt electrical power circuits.
– Operate electromechanically using a small control current.
– U…
3. Haynes – Starter Motors
Domain: us.haynes.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: A starter motor is an essential component of a vehicle’s starting system. It is responsible for turning the engine over to initiate the combustion process. The starter motor receives electrical power from the battery and engages with the engine’s flywheel to crank the engine. This process allows the engine to start running. Starter motors are typically found in cars, trucks, and motorcycles, and t…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for what is a starter
What Are the Key B2B Takeaways for International Buyers?
In the realm of strategic sourcing, understanding what a starter is—whether it’s a device for motor control or an entry-level product—plays a critical role in optimizing procurement strategies. Starters are not just essential components that facilitate operations; they also represent an opportunity for cost-saving and efficiency improvements. By selecting the right starter tailored to specific applications, buyers can enhance equipment performance while safeguarding against potential failures.
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your Procurement Strategy?
The value of strategic sourcing cannot be overstated. It allows businesses to streamline their supply chains, mitigate risks, and foster relationships with suppliers that are both reliable and innovative. For international buyers, especially in emerging markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, leveraging strategic sourcing ensures access to quality products that meet diverse operational needs while adhering to budget constraints.
What’s Next for International B2B Buyers?
As you navigate the procurement landscape, consider engaging with suppliers who offer comprehensive solutions and robust support for starters and other essential components. Embrace the opportunity to drive your business forward by making informed sourcing decisions. The future of your operations hinges on the strategic choices you make today—seize the moment to enhance your supply chain resilience and operational efficiency.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.

Illustrative image related to what is a starter