Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for weak starter symptoms
Navigating the complexities of weak starter symptoms is a pivotal challenge for B2B buyers in the automotive sector, especially when sourcing reliable components for vehicle maintenance. Weak starter symptoms can lead to significant operational disruptions and costly downtime if not identified and addressed promptly. This guide offers an in-depth exploration of the various types of starter issues, their applications, and the implications for vehicle performance.
Throughout this comprehensive resource, we will cover essential topics such as identifying key symptoms, understanding the root causes of starter failures, and evaluating the most effective troubleshooting techniques. Additionally, we will provide insights on supplier vetting processes, cost considerations, and best practices for procurement, tailored specifically for international buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including markets such as Saudi Arabia and Germany.
By equipping buyers with the knowledge to discern and respond to weak starter symptoms, this guide empowers informed purchasing decisions that enhance operational efficiency and reduce maintenance costs. Our aim is to foster a proactive approach to vehicle management, ensuring that businesses can maintain their fleet’s reliability and performance, ultimately leading to improved productivity and customer satisfaction.
Table Of Contents
- Top 2 Weak Starter Symptoms Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for weak starter symptoms
- Understanding weak starter symptoms Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of weak starter symptoms
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘weak starter symptoms’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for weak starter symptoms
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for weak starter symptoms
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘weak starter symptoms’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for weak starter symptoms Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing weak starter symptoms With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for weak starter symptoms
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the weak starter symptoms Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of weak starter symptoms
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for weak starter symptoms
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Understanding weak starter symptoms Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Intermittent Starting | Engine starts occasionally, often requiring multiple attempts | Fleet management, logistics companies | Pros: Cost-effective; Cons: Unreliable performance |
| Clicking Noise | Single or repeated clicking sounds without engine cranking | Automotive repair shops, vehicle maintenance | Pros: Easy to diagnose; Cons: May indicate deeper issues |
| Dim Lights | Headlights and dashboard lights dim when attempting to start | Transportation services, delivery companies | Pros: Indicates electrical issues; Cons: Can disrupt operations |
| No Response | Dashboard lights up, but engine fails to turn over | Car rental services, taxi companies | Pros: Clear symptom; Cons: May require professional assessment |
| Smoke Emission | Visible smoke or burning smell during attempts to start | Heavy machinery operators, construction firms | Pros: Indicates serious issue; Cons: Risk of further damage |
What are the characteristics of Intermittent Starting symptoms and their suitability for B2B buyers?
Intermittent starting symptoms manifest when a vehicle occasionally starts, requiring multiple attempts to ignite the engine. This can be particularly frustrating for fleet management and logistics companies, where downtime can lead to significant operational losses. Buyers should consider the reliability of the starter system, as prolonged issues can escalate repair costs and affect service delivery. Investing in high-quality starter components can mitigate these risks.
How can Clicking Noise symptoms impact B2B operations?
A clicking noise when attempting to start the engine is a common indicator of starter issues. This symptom is easily identifiable and can be diagnosed quickly by automotive repair shops. For businesses reliant on vehicle maintenance, understanding this symptom can lead to timely interventions, preventing further complications. However, buyers should be cautious, as clicking noises may also indicate underlying problems that require more comprehensive repairs.
Why are Dim Lights a critical indicator for transportation services?
Dim lights during starting attempts are a clear sign of electrical issues, often linked to battery or alternator problems. For transportation services and delivery companies, this symptom can disrupt operations and lead to delays. Buyers should prioritize vehicles with robust electrical systems and consider regular maintenance checks. Addressing dim light symptoms early can prevent more severe failures, ensuring smooth business operations.
What does No Response mean for car rental and taxi companies?
When the dashboard lights illuminate but the engine does not turn over, it signifies a serious starter or electrical issue. For car rental and taxi companies, this symptom can lead to customer dissatisfaction and loss of revenue. Buyers must ensure their fleet vehicles are equipped with reliable starters and consider investing in extended warranties for added protection. Professional assessments are often necessary to diagnose the underlying problem effectively.
How should Smoke Emission symptoms be handled in heavy machinery operations?
Smoke emission during starting attempts indicates a critical failure, often linked to overheating or electrical shorts. Heavy machinery operators and construction firms must act swiftly to address this symptom, as it poses risks of further damage and operational downtime. Buyers should prioritize equipment with high safety standards and consider investing in comprehensive service agreements. Regular inspections can help catch issues before they escalate, safeguarding investments and ensuring operational continuity.
Key Industrial Applications of weak starter symptoms
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of weak starter symptoms | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive Repair | Diagnosing vehicle starting issues | Reduces downtime and repair costs | Quality of diagnostic tools and technician training |
| Transportation & Logistics | Fleet management and maintenance | Enhances fleet reliability and operational efficiency | Availability of parts and service support |
| Construction Equipment | Maintenance of heavy machinery | Increases equipment uptime and productivity | Durability of components and local service availability |
| Agriculture | Start-up diagnostics for farm machinery | Maximizes operational efficiency during peak seasons | Compatibility with various machinery brands |
| Mining | Ensuring operational readiness of mining vehicles | Minimizes delays in extraction processes | Robustness of parts and adaptability to harsh conditions |
How are ‘weak starter symptoms’ utilized in the automotive repair industry?
In the automotive repair sector, identifying weak starter symptoms is crucial for diagnosing vehicle starting issues. Mechanics rely on clear indicators such as clicking sounds or unresponsive engines to pinpoint starter failures. By addressing these symptoms promptly, repair shops can minimize vehicle downtime and reduce repair costs. International buyers must consider sourcing high-quality diagnostic tools and ensuring that technicians are well-trained in recognizing these symptoms to enhance service efficiency.
What role do weak starter symptoms play in transportation and logistics?
In transportation and logistics, fleet management heavily depends on the reliability of vehicles. Weak starter symptoms can lead to unexpected breakdowns, impacting delivery schedules. By implementing regular diagnostics and maintenance routines focused on starter performance, companies can enhance fleet reliability and operational efficiency. Buyers in this sector should prioritize suppliers who offer comprehensive parts availability and robust service support to ensure minimal disruption.
How do weak starter symptoms affect construction equipment maintenance?
Weak starter symptoms are critical in the construction industry, where heavy machinery must be operational at all times. Symptoms such as grinding sounds or failure to crank can indicate underlying issues that, if not addressed, can lead to significant downtime. Regular inspections and diagnostics can help identify these symptoms early, thereby increasing equipment uptime and overall productivity. Buyers should focus on sourcing durable components and ensuring local service availability to facilitate timely repairs.
Why are weak starter symptoms important for agricultural machinery?
In agriculture, the ability to start machinery efficiently is vital during peak planting and harvesting seasons. Weak starter symptoms may hinder operations, leading to costly delays. Farmers and agricultural businesses can benefit from proactive diagnostics to ensure their machinery is always ready for use. Buyers should consider compatibility with various machinery brands and the availability of parts to ensure seamless operations during critical periods.
How do weak starter symptoms impact mining operations?
In mining, operational readiness of vehicles is paramount to avoid delays in extraction processes. Weak starter symptoms can signal potential issues that could halt operations, leading to financial losses. By regularly monitoring and addressing these symptoms, mining companies can maintain a steady workflow. Buyers in this sector should look for robust parts that can withstand harsh conditions and ensure adaptability for various vehicle types used in mining operations.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘weak starter symptoms’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Identifying the Root Cause of Starting Issues
The Problem:
B2B buyers, especially those managing fleets or automotive repair businesses, often encounter vehicles that exhibit weak starter symptoms. This can manifest as slow engine cranking or intermittent starting failures. The challenge lies in accurately diagnosing whether the issue stems from the starter itself, the battery, or the alternator. Misdiagnosis can lead to unnecessary repairs and increased downtime, which is particularly detrimental for businesses reliant on vehicle performance.
The Solution:
To effectively diagnose starting issues, implement a systematic troubleshooting approach. Begin with the battery, as it is often the most overlooked component. Use a multimeter to check the battery voltage; a reading below 12.4 volts typically indicates a weak battery. Next, inspect the battery terminals for corrosion or loose connections, as these can impede electrical flow. If the battery checks out, proceed to the starter by performing a jump-start test. If the vehicle starts but dies once the jumper cables are removed, the alternator may be the culprit. Document these tests and findings to establish a pattern, which can be invaluable for future reference and for training your staff on troubleshooting techniques.
Scenario 2: Unpredictable Vehicle Performance and Downtime
The Problem:
For B2B buyers managing delivery or transportation services, unpredictable vehicle performance due to weak starter symptoms can lead to significant operational challenges. Vehicles that frequently fail to start or exhibit unusual noises can delay shipments and create customer dissatisfaction. The inability to pinpoint the issue compounds the frustration, as it can lead to extended periods of vehicle downtime and increased repair costs.

Illustrative image related to weak starter symptoms
The Solution:
Establish a preventive maintenance schedule that includes regular inspections of the starter system, battery, and alternator. Utilize diagnostic tools to read error codes from the vehicle’s onboard computer, which can provide insights into potential starter-related issues. Encourage your team to adopt a checklist approach for vehicle assessments, focusing on auditory signs (like clicking or grinding) and visual inspections (for oil leaks or corrosion). Additionally, train staff to recognize the early signs of starter problems—such as slow cranking or dashboard lights flickering—allowing for proactive measures before a vehicle becomes inoperable. By integrating these practices into your operations, you can enhance vehicle reliability and reduce unexpected downtimes.
Scenario 3: Managing Cost-Effective Repairs
The Problem:
In an increasingly competitive market, B2B buyers are often tasked with managing tight budgets while ensuring their vehicle fleets are operational. When faced with weak starter symptoms, the uncertainty about whether to repair or replace components can lead to significant financial strain. Companies may either overspend on unnecessary replacements or risk vehicle failure due to inadequate repairs.
The Solution:
Adopt a cost-effective strategy by prioritizing comprehensive diagnostics before making repair decisions. Invest in training for your mechanics on the nuances of starter systems and their interaction with the battery and alternator. This training should include how to perform quick tests, such as the jump-start test, and how to interpret the results accurately. Encourage the use of high-quality replacement parts that come with warranties, as they can save money in the long run by reducing the frequency of repairs. Additionally, consider developing relationships with trusted suppliers who can provide bulk pricing on starter components, ensuring you have access to quality parts without breaking your budget. By taking a strategic approach to repairs and replacements, you can maintain fleet functionality while managing costs effectively.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for weak starter symptoms
What Are the Key Materials for Addressing Weak Starter Symptoms?
In the context of diagnosing and addressing weak starter symptoms, selecting the right materials for components such as starters, batteries, and electrical connections is crucial. Below, we analyze four common materials used in automotive applications, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international B2B buyers.
How Do Copper Components Enhance Starter Performance?
Key Properties: Copper is known for its excellent electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, and corrosion resistance. It can withstand high temperatures, making it ideal for applications where heat dissipation is critical.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of copper is its superior conductivity, which ensures efficient power transfer from the battery to the starter. However, copper is relatively expensive compared to alternatives like aluminum, and its manufacturing process can be complex. Additionally, copper components may require protective coatings to prevent corrosion in harsh environments.
Impact on Application: Copper’s high conductivity makes it suitable for electrical connections and starter windings, ensuring reliable operation. However, in regions with high humidity or exposure to corrosive elements, additional protective measures may be necessary.
Specific Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM B170 for copper wire is essential. Buyers from regions like Europe (Germany) or the Middle East (Saudi Arabia) should also consider local regulations regarding the use of copper in automotive applications.
Illustrative image related to weak starter symptoms
Why Is Aluminum a Popular Choice for Starter Components?
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight, has good corrosion resistance, and offers decent electrical conductivity, although not as high as copper.
Pros & Cons: The advantages of aluminum include its lower cost and lighter weight, which can enhance fuel efficiency in vehicles. However, its conductivity is inferior to copper, which may affect performance in high-demand applications. Additionally, aluminum components can be more susceptible to mechanical wear over time.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is often used in starter housings and brackets due to its lightweight nature. While it provides adequate performance, it may not be suitable for high-performance applications where maximum conductivity is required.
Specific Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that aluminum components meet standards such as ASTM B221. In markets like Africa and South America, where cost may be a significant factor, aluminum’s affordability can be a strong selling point.
How Do Steel and Stainless Steel Parts Contribute to Starter Durability?
Key Properties: Steel and stainless steel offer high strength and durability, with stainless steel providing excellent corrosion resistance.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of using steel is its strength, making it ideal for structural components. Stainless steel, while more expensive, offers superior corrosion resistance, which is essential in harsh environments. However, both materials are heavier than aluminum and copper, which could impact vehicle performance.
Impact on Application: Steel is commonly used for starter casings and mounting brackets, providing robust support. Stainless steel may be preferred in environments with high exposure to moisture or corrosive substances.
Specific Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM A240 for stainless steel is important. Buyers in Europe may have specific preferences for stainless steel due to stringent corrosion resistance requirements.

Illustrative image related to weak starter symptoms
What Role Do Plastics Play in Electrical Connections?
Key Properties: Plastics are lightweight, non-conductive, and can be engineered for high-temperature resistance.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of plastics is their insulation properties, which prevent electrical shorts. They are also cost-effective and can be molded into complex shapes. However, plastics may not withstand high temperatures as effectively as metals, and their mechanical strength is generally lower.
Impact on Application: Plastics are often used for connectors and housings in starter systems, providing insulation and protection from environmental factors. However, they may require careful selection to ensure they can handle the specific thermal and mechanical demands of the application.
Specific Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider the thermal and chemical resistance properties of plastics, ensuring compliance with standards like DIN EN ISO 1043 for material properties. In regions with extreme temperatures, selecting high-performance plastics is crucial.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Weak Starter Symptoms
| Material | Typical Use Case for weak starter symptoms | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Copper | Electrical connections and windings | Excellent electrical conductivity | High cost, complex manufacturing | High |
| Aluminum | Starter housings and brackets | Lightweight, cost-effective | Lower conductivity than copper | Medium |
| Steel | Structural components for starters | High strength and durability | Heavier than aluminum | Medium |
| Plastics | Connectors and housings | Insulation and cost-effective | Lower mechanical strength | Low |
This analysis provides actionable insights for B2B buyers looking to address weak starter symptoms effectively through strategic material selection. Understanding the properties, advantages, and limitations of these materials will facilitate informed purchasing decisions tailored to specific regional requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for weak starter symptoms
What Are the Key Stages in Manufacturing Starters for Vehicles?
The manufacturing process for automotive starters involves several critical stages, each designed to ensure the final product meets high performance and reliability standards. Understanding these stages helps B2B buyers evaluate potential suppliers.
1. Material Preparation: Selecting Quality Components
The manufacturing journey begins with material selection. High-grade metals, such as steel and aluminum, are chosen for their durability and strength. Copper is often used for electrical connections due to its excellent conductivity. Quality assurance starts here, as suppliers must provide material certifications to ensure compliance with international standards.

Illustrative image related to weak starter symptoms
2. Forming: Shaping the Components
Once materials are procured, they undergo various forming processes, including stamping, casting, and machining. For example, the housing of the starter is typically stamped from sheet metal, while the armature is cast to shape. Advanced techniques like CNC machining ensure precision in creating components that fit together seamlessly.
3. Assembly: Bringing Components Together
In the assembly phase, individual components are put together using both manual labor and automated systems. This stage often involves soldering electrical connections, installing brushes, and integrating the starter relay. Quality control checks at this stage are crucial, as any misalignment can lead to starter failure.
4. Finishing: Ensuring Durability and Functionality
The finishing stage includes surface treatments to prevent corrosion, such as electroplating or powder coating. Additionally, components may undergo testing for thermal and electrical properties to ensure they meet specifications. This stage is vital for enhancing the longevity and reliability of the starter, particularly in harsh environments.
How is Quality Assurance Implemented in Starter Manufacturing?
Quality assurance is an integral part of the manufacturing process, ensuring that every starter produced meets established performance and safety standards. B2B buyers should pay close attention to the quality control measures in place.

Illustrative image related to weak starter symptoms
Relevant International Standards: What Should Buyers Look For?
Manufacturers must comply with international standards such as ISO 9001, which outlines requirements for quality management systems. This certification indicates that the manufacturer has established processes to enhance customer satisfaction and ensure consistent quality.
For specific components, other certifications may be relevant, such as CE marking in Europe, which indicates compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards. In the oil and gas sector, API certifications are crucial for components used in starters for heavy machinery.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control checkpoints are established throughout the manufacturing process to identify defects early. Common checkpoints include:

Illustrative image related to weak starter symptoms
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Materials and components are inspected upon arrival to ensure they meet specifications.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Random checks during the manufacturing process help catch defects as they occur. This may involve measuring tolerances or testing electrical connections.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Before shipment, each starter undergoes rigorous testing, including operational tests and performance assessments.
Which Testing Methods Are Commonly Used in Starter Manufacturing?
Testing methods vary depending on the component and its intended use. Some common methods include:
- Electrical Testing: Ensures that the starter meets electrical performance specifications, such as voltage and current draw.
- Load Testing: Simulates real-world conditions to verify that the starter can handle the required loads without failure.
- Durability Testing: Components are subjected to extreme conditions, such as temperature fluctuations and moisture exposure, to assess their resilience.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
B2B buyers should conduct thorough due diligence when selecting suppliers. Here are some actionable steps:
Conducting Audits: What to Look For
Audits are essential for verifying a supplier’s adherence to quality control processes. Buyers should look for:
- Documentation of Quality Management Systems: Ensure the supplier has a documented process that aligns with ISO 9001 or other relevant standards.
- Records of Quality Control Checks: Review reports that detail IQC, IPQC, and FQC outcomes to assess the effectiveness of their quality assurance measures.
Requesting Reports and Certifications: What Is Essential?
Buyers should request copies of relevant certifications and test reports. Key documents include:
- Material Certifications: Confirm that raw materials meet industry standards.
- Testing Certifications: Ensure that the finished products have undergone necessary testing and meet performance specifications.
Engaging Third-Party Inspectors: When Is It Necessary?
In some cases, engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s quality control processes. These services can conduct audits, verify compliance with standards, and perform random inspections on production batches.
What Are the QC and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
B2B buyers from diverse regions, including Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of specific nuances regarding quality control and certification:
- Understanding Regional Standards: Different regions may have unique quality standards and certifications. Familiarizing oneself with these can help in selecting the right suppliers.
- Navigating Import Regulations: Compliance with local regulations regarding imported automotive components is crucial. Buyers should ensure that suppliers can provide necessary documentation to facilitate smooth customs processes.
- Language and Communication Barriers: Effective communication is vital for understanding quality control processes. Buyers should seek suppliers that provide clear documentation in languages they are comfortable with, reducing the risk of miscommunication.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures in starter production, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when selecting suppliers, ensuring they procure reliable and high-quality products for their operations.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘weak starter symptoms’
Introduction
This practical sourcing guide aims to assist B2B buyers in identifying and addressing weak starter symptoms in vehicles, ensuring efficient procurement of components or services that can effectively resolve these issues. Understanding the nuances of starter problems is crucial for maintaining vehicle performance, particularly in regions with varying climatic conditions and operational demands.
Step 1: Identify Symptoms of Weak Starter Performance
Recognizing the signs of a failing starter is the first step toward effective procurement. Common indicators include unusual sounds such as clicking or grinding, dashboard lights illuminating without the engine starting, or a complete lack of response when turning the key. Documenting these symptoms can help you communicate effectively with potential suppliers and technicians.
Step 2: Assess the Overall Electrical System
Before sourcing starter components, evaluate the vehicle’s electrical system as a whole. The starter, battery, and alternator work in unison; a failure in one can affect the others. Check for battery health, wiring integrity, and any signs of corrosion, as these factors can lead to misdiagnosis and unnecessary expenditures.

Illustrative image related to weak starter symptoms
Step 3: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outlining the technical requirements for the starter components is crucial for procurement. Consider factors like the vehicle make and model, compatibility with existing systems, and performance specifications. This ensures that the components you source will effectively address the identified symptoms without causing further complications.
Step 4: Research and Verify Suppliers
Finding reliable suppliers is essential to ensure quality and reliability. Look for suppliers with a proven track record in the automotive sector, particularly those specializing in starter systems. Request case studies, customer testimonials, and certifications to evaluate their credibility and expertise in handling similar issues.
Step 5: Evaluate Warranty and Support Options
When sourcing starter components, consider the warranty and post-purchase support offered by suppliers. A robust warranty can provide peace of mind against potential defects, while responsive customer support can be invaluable in addressing any issues that arise post-installation. Ensure that the supplier offers sufficient support, especially if your operations rely heavily on vehicle uptime.
Step 6: Request Quotes and Compare Pricing
Once you have a shortlist of potential suppliers, request detailed quotes that include pricing, delivery timelines, and any additional services offered, such as installation or after-sales support. Comparing these quotes will help you make an informed decision based on budget constraints and service quality.
Illustrative image related to weak starter symptoms
Step 7: Conduct a Trial Order
Before committing to a large order, consider placing a smaller trial order with your selected supplier. This allows you to assess the quality of the components and the reliability of the supplier without a significant financial commitment. Monitor the performance of the starter components during this period to ensure they meet your operational needs.
By following this comprehensive checklist, B2B buyers can effectively navigate the complexities of sourcing solutions for weak starter symptoms, ensuring that they procure the right components and services for their vehicles.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for weak starter symptoms Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing for Weak Starter Symptoms?
When sourcing components related to weak starter symptoms, understanding the cost structure is essential. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and margins.
-
Materials: The cost of materials varies significantly based on the quality and type of components. For instance, high-performance starters may utilize advanced materials like copper windings and durable plastics, which can increase costs but enhance reliability.
-
Labor: Labor costs are influenced by the region of production. Countries with lower labor costs might offer competitive pricing, but this can sometimes come at the expense of quality.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes the costs associated with the production environment, such as utilities and equipment maintenance. Efficient manufacturing processes can help reduce these overheads.
-
Tooling: Initial tooling costs for custom components can be substantial. However, these costs are typically amortized over larger production runs, making it crucial to consider order volumes.
-
Quality Control: Ensuring that components meet specified standards can involve additional QC costs. Certifications (e.g., ISO) can also influence pricing due to the need for compliance and regular audits.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can vary widely based on the origin of the components, the distance to the buyer, and chosen shipping methods.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a margin to cover their costs and profit. This margin can vary based on market conditions and the competitive landscape.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Sourcing Decisions?
Several factors can influence pricing when sourcing components for weak starter symptoms. These include volume, specifications, material choices, quality certifications, supplier factors, and Incoterms.
-
Volume/MOQ: Larger order quantities (MOQ) usually lead to lower per-unit costs. Buyers should assess their needs carefully to determine the most cost-effective order size.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom specifications can significantly impact costs. While tailored components may offer better performance, they often come with higher prices due to the complexity involved.
-
Materials and Quality: Higher-quality materials typically incur greater costs but can lead to improved durability and reliability, reducing long-term maintenance expenses.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation, reliability, and location of suppliers can affect both pricing and lead times. Establishing strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing and priority service.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is critical for international transactions. They dictate the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping costs, insurance, and risk. Misunderstanding these terms can lead to unexpected costs.
What Are Effective Buyer Tips for Negotiating Prices?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, effective negotiation strategies can lead to significant savings.
-
Leverage Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Buyers should evaluate the total cost of ownership rather than just the purchase price. This includes considering installation, maintenance, and potential downtime costs associated with inferior products.
-
Negotiate Terms: Engage suppliers in discussions about payment terms, lead times, and shipping arrangements. Flexibility in these areas can lead to cost savings.
-
Conduct Market Research: Understanding market rates and competitor pricing can empower buyers during negotiations. This knowledge can help in securing better deals.
-
Explore Regional Partnerships: Forming alliances with local suppliers can reduce logistics costs and improve responsiveness. This is particularly beneficial in regions with high import duties or logistical challenges.
-
Evaluate Certifications and Quality: Ensure that suppliers meet necessary quality standards. While these may come at a premium, they can save costs in the long run by minimizing failures and replacements.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for components related to weak starter symptoms are subject to fluctuations based on market conditions, supplier pricing strategies, and geopolitical factors. Buyers are encouraged to conduct thorough market research and consult with multiple suppliers to obtain accurate and current pricing information tailored to their specific needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing weak starter symptoms With Other Solutions
Introduction to Alternative Solutions for Diagnosing Automotive Issues
In the automotive industry, diagnosing issues such as weak starter symptoms is crucial for maintaining vehicle performance and reliability. However, alternative methods and technologies can also be employed to identify and resolve these issues. This analysis will compare the traditional approach of diagnosing weak starter symptoms with two viable alternatives: advanced diagnostic tools and mobile diagnostic services. Each option presents unique advantages and challenges, making it essential for B2B buyers to understand their distinctions.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Weak Starter Symptoms | Advanced Diagnostic Tools | Mobile Diagnostic Services |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Relies on auditory and visual cues | Offers precise data and diagnostics | Provides on-site diagnostics and convenience |
| Cost | Minimal, often just user knowledge | Moderate to high, depending on technology | Variable, usually includes a service fee |
| Ease of Implementation | Simple, requires minimal training | Requires technical knowledge to operate | Very user-friendly, requires no tools |
| Maintenance | No maintenance needed | Regular updates and calibration needed | No maintenance; relies on the service provider |
| Best Use Case | Initial troubleshooting | Comprehensive diagnostics for multiple systems | Quick assessments in remote locations |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Advanced Diagnostic Tools
Advanced diagnostic tools, such as OBD-II scanners, utilize sophisticated software to provide detailed insights into vehicle performance. These tools can diagnose a wide range of issues beyond just starter problems, including engine codes, fuel efficiency, and emissions data. The primary advantage is their accuracy; however, they can be expensive and require trained personnel to operate effectively. For businesses with a fleet of vehicles, investing in such tools can enhance maintenance efficiency, but they may be overkill for smaller operations.

Illustrative image related to weak starter symptoms
Mobile Diagnostic Services
Mobile diagnostic services bring the mechanic to the vehicle, offering convenience and speed. Technicians equipped with portable diagnostic equipment can assess and resolve issues on-site, making this option particularly valuable for businesses with vehicles in remote locations or limited access to repair shops. The primary benefit is the immediacy of service, reducing downtime. However, the cost may vary based on distance and service complexity, and the availability of skilled technicians can be a limiting factor in some regions.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
When selecting a method for diagnosing weak starter symptoms, B2B buyers must consider their specific operational needs and resources. For businesses that prioritize speed and convenience, mobile diagnostic services may offer the best solution, especially in remote areas. Conversely, companies aiming for comprehensive vehicle management may benefit more from investing in advanced diagnostic tools, despite the higher initial costs. Ultimately, understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each alternative will empower buyers to make informed decisions that enhance their fleet’s performance and reliability.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for weak starter symptoms
What Are the Key Technical Properties for Identifying Weak Starter Symptoms?
When dealing with weak starter symptoms, understanding specific technical properties can significantly impact decision-making for procurement and maintenance. Here are several critical specifications that B2B buyers should consider:
-
Material Grade of Starter Components
– The material grade refers to the quality and type of materials used in manufacturing the starter motor, including metals like copper and aluminum. High-grade materials enhance conductivity and durability, which are crucial for reliable performance. For B2B buyers, investing in starters made from superior materials means fewer replacements and reduced downtime. -
Voltage Rating
– The voltage rating of a starter is typically 12V for most vehicles. This specification is essential as it determines the starter’s compatibility with the vehicle’s electrical system. Understanding voltage ratings can help buyers avoid mismatches that could lead to equipment failure or inefficiency. -
Current Draw (Amperage)
– Current draw indicates the amount of electrical current the starter requires to function. A typical starter draws between 150 to 300 amps during cranking. For B2B buyers, knowing the current draw is vital to ensure that the vehicle’s battery and alternator can support the starter’s demands, preventing potential electrical issues. -
Torque Output
– Torque output measures the rotational force produced by the starter motor to crank the engine. This specification is critical for ensuring that the starter can effectively initiate engine combustion. Buyers should look for starters that meet or exceed the OEM specifications for torque output to ensure optimal performance. -
Temperature Tolerance
– The temperature tolerance of starter components indicates their ability to operate under extreme conditions. Starters may be exposed to high heat from the engine compartment or low temperatures during winter. For B2B buyers, selecting starters with high temperature tolerance ensures longevity and reliability, particularly in regions with extreme weather. -
Duty Cycle
– The duty cycle refers to the time a starter can operate before needing a cooldown period. A high duty cycle means the starter can handle repeated starts without overheating. For businesses relying on fleet vehicles, understanding duty cycles can help in selecting starters that minimize service interruptions.
What Common Trade Terms Should B2B Buyers Know in Relation to Starter Systems?
Navigating the procurement landscape involves familiarizing oneself with specific trade terminology. Here are some essential terms relevant to weak starter symptoms:
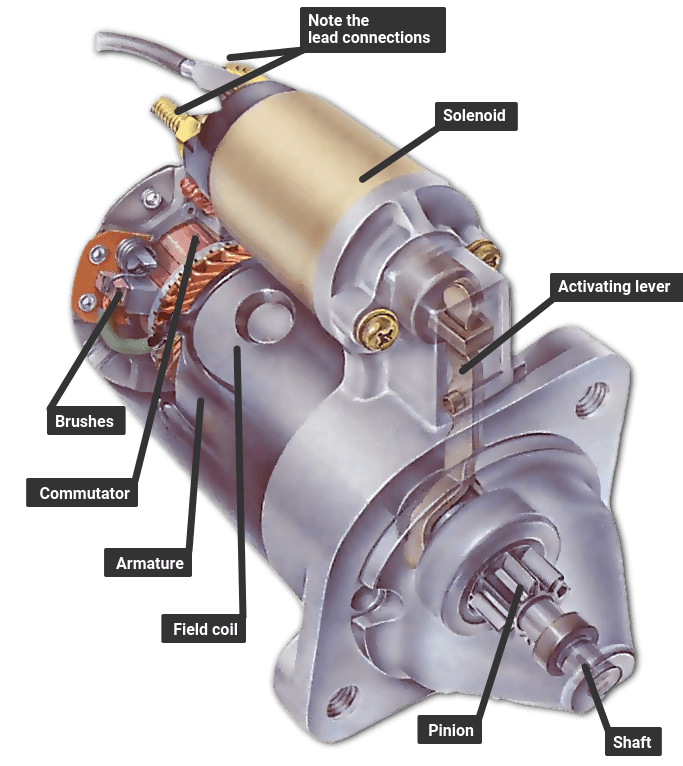
Illustrative image related to weak starter symptoms
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– OEM refers to parts made by the vehicle’s original manufacturer. These components are designed to meet the exact specifications of the vehicle, ensuring compatibility and performance. B2B buyers often prefer OEM parts for their reliability and warranty support. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is crucial for B2B buyers as it affects inventory management and cost efficiency. Buyers should negotiate MOQs that align with their operational needs to avoid excess inventory. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for specific products. B2B buyers use RFQs to compare prices and terms from different suppliers, facilitating informed decision-making. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Incoterms are internationally recognized rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping goods. Familiarity with Incoterms helps B2B buyers understand shipping costs, risks, and responsibilities associated with their orders, particularly in international transactions. -
Lead Time
– Lead time refers to the time between placing an order and receiving the goods. Understanding lead times is essential for B2B buyers to manage their supply chain effectively, ensuring they have the necessary components on hand when needed. -
Warranty Period
– The warranty period is the time frame during which a manufacturer guarantees the performance of a product. For B2B buyers, considering the warranty period can provide peace of mind and reduce the risk of unexpected costs associated with faulty components.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terminologies, B2B buyers can enhance their decision-making processes regarding starter systems, ultimately leading to improved vehicle reliability and operational efficiency.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the weak starter symptoms Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics Impacting the Weak Starter Symptoms Sector?
The weak starter symptoms sector is experiencing notable shifts driven by several global factors. The increasing reliance on automotive technologies and the rising demand for efficient vehicle performance are primary drivers. With the automotive industry transitioning towards electric vehicles (EVs) and hybrid models, there is a growing need for reliable starter systems that can handle the unique demands of these vehicles. International B2B buyers, especially in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, are increasingly seeking suppliers who can provide advanced starter technologies that are compatible with both traditional and emerging vehicle types.
Emerging B2B tech trends, such as the integration of IoT in automotive diagnostics, are revolutionizing the way weak starter symptoms are identified and addressed. Digital platforms that offer remote diagnostics and predictive maintenance tools enable businesses to proactively manage starter issues, reducing downtime and operational costs. Moreover, the trend towards e-commerce in the automotive parts sector has made sourcing more accessible, allowing buyers to compare suppliers and technologies more efficiently.
Sourcing strategies are evolving as buyers emphasize partnerships with suppliers that offer comprehensive support and technical expertise. The preference for suppliers who can provide not just products but also value-added services, such as installation guidance and after-sales support, is becoming more pronounced. This trend is particularly significant in regions where technical expertise may be limited, making it essential for suppliers to offer robust training programs alongside their products.
How Is Sustainability Influencing Sourcing Decisions in the Weak Starter Symptoms Sector?
Sustainability is becoming a critical consideration for B2B buyers in the weak starter symptoms sector. The environmental impact of automotive components, including starters, is under increasing scrutiny. Buyers are prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to reducing their carbon footprint through sustainable manufacturing practices. This includes using recycled materials, minimizing waste during production, and adopting energy-efficient processes.
Ethical sourcing is also gaining traction, with buyers looking for transparency in supply chains. They want assurance that the components they procure are produced under fair labor conditions and that suppliers adhere to ethical standards. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and ISO 9001 for quality management can serve as indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability and ethical practices.
In addition, the demand for ‘green’ materials is influencing sourcing decisions. Suppliers who can offer starter systems made from environmentally friendly materials or those that utilize innovative technologies to reduce emissions are likely to gain a competitive edge. As B2B buyers increasingly align their procurement strategies with sustainability goals, the pressure on suppliers to innovate and adapt to these demands will continue to grow.
What Is the Historical Context Behind Weak Starter Symptoms in the Automotive Sector?
The history of weak starter symptoms can be traced back to the evolution of automotive technology. Early vehicles relied on simple mechanical systems to start engines, which often faced challenges related to reliability and efficiency. As automotive technology advanced, the introduction of electric starters in the early 20th century revolutionized vehicle ignition, significantly improving performance and reliability.
Over the decades, the complexity of starter systems has increased in tandem with advancements in automotive technology. The integration of electronic components and the development of high-performance batteries have made starters more efficient but have also introduced new failure modes. Today, understanding weak starter symptoms requires a comprehensive knowledge of the interplay between the battery, alternator, and starter motor, as these components must work seamlessly together to ensure optimal vehicle performance.
This historical context is crucial for B2B buyers as it highlights the importance of staying informed about technological advancements and sourcing components that align with the latest industry standards. As the automotive landscape continues to evolve, so too will the challenges and solutions related to weak starter symptoms, making it essential for buyers to partner with knowledgeable suppliers who can navigate these changes effectively.

Illustrative image related to weak starter symptoms
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of weak starter symptoms
-
How do I solve issues with a weak starter in my vehicle?
To address a weak starter, first, check the battery and connections for corrosion or looseness. A jump-start can help determine if the issue lies with the starter or battery. If the battery is functioning but the starter remains unresponsive, inspect the starter for loose wiring or damaged components. In some cases, gently tapping the starter can temporarily restore functionality. However, if problems persist, consulting a professional technician for a thorough inspection and potential replacement is advisable. -
What is the best way to identify weak starter symptoms?
Common symptoms of a weak starter include clicking sounds when attempting to start the vehicle, dim dashboard lights, and the engine failing to crank. Additionally, if the starter emits whirring or grinding noises, it may indicate internal damage. Observing these signs early can help prevent more severe issues down the line. Regular maintenance and inspections can also aid in identifying problems before they escalate. -
How do I vet suppliers for starter components in international trade?
When vetting suppliers for starter components, prioritize those with a proven track record and positive customer reviews. Check for certifications such as ISO or relevant industry standards, which indicate quality assurance. Request samples to evaluate product quality and compatibility. Additionally, inquire about the supplier’s experience with international shipping, including handling customs regulations and logistics, to ensure smooth transactions. -
What customization options are available for starters?
Customization options for starters may include variations in voltage, size, and mounting configurations to fit specific vehicle models. Some suppliers may offer tailored solutions for high-performance applications or unique environmental conditions. When discussing customization, provide detailed specifications and requirements to ensure the supplier can meet your needs effectively. Always request prototypes or samples to validate the customization before bulk orders. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for starter components?
Minimum order quantities for starter components can vary widely among suppliers, often ranging from 100 to 1,000 units depending on the manufacturer’s capabilities and the product type. It’s essential to communicate your expected demand and negotiate MOQs that align with your business needs. Some suppliers may offer flexibility in MOQs for new customers or for custom orders, so it’s worth discussing your specific situation. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing starters internationally?
Payment terms for international orders typically include options such as advance payment, letter of credit, or payment upon delivery. It’s common to negotiate terms based on your relationship with the supplier, the order size, and shipping logistics. Be mindful of currency exchange rates and transaction fees, and consider using secure payment methods to protect your financial interests during the transaction. -
How can I ensure quality assurance (QA) for starter components?
To ensure quality assurance for starter components, establish clear specifications and standards with your supplier. Request documentation such as certificates of conformity and inspection reports. Implement a quality control process that includes pre-shipment inspections and testing of samples. Building a strong relationship with your supplier can also facilitate better communication regarding quality expectations and improvements. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind for importing starters?
When importing starters, consider logistics factors such as shipping methods, lead times, and customs clearance procedures. Collaborate with reliable freight forwarders who understand the intricacies of international shipping and can navigate customs regulations efficiently. Additionally, be aware of potential tariffs and taxes that may affect overall costs. Planning for these logistics in advance can help avoid delays and ensure timely delivery of your components.
Top 2 Weak Starter Symptoms Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Can-Am – Renegade & Outlander
2. Northrich Automotive – Starter System Diagnostics & Repairs
Domain: northrichauto.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: Northrich Automotive offers automotive repair services including starter system diagnostics and repairs. Key signs of a failing starter include slow cranking, refusal to start, intermittent starting issues, dimming interior lights, grinding noises, whirring sounds without cranking, continuous running after starting, burning smells or smoke, and oil leaks onto the starter system. If these issues ar…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for weak starter symptoms
As businesses in diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe navigate the complexities of vehicle maintenance, understanding weak starter symptoms becomes essential. Key takeaways from this guide highlight the intricate interplay between the battery, alternator, and starter system. Recognizing signs of potential failures—such as unusual noises, dashboard alerts, and unresponsive engines—can prevent costly downtime and ensure optimal vehicle performance.
Strategic sourcing of high-quality components and services is vital. By establishing relationships with trusted suppliers who understand the unique needs of your market, you can secure reliable parts that enhance vehicle longevity and reduce repair costs. Additionally, leveraging local expertise can expedite troubleshooting and maintenance, minimizing operational disruptions.
Looking ahead, international B2B buyers are encouraged to prioritize proactive maintenance strategies and invest in quality components. By doing so, you can enhance your fleet’s reliability and performance. Don’t hesitate to engage with your suppliers and service providers to discuss tailored solutions that meet your business’s specific requirements. Empower your operations today by taking informed steps towards effective vehicle management.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.