Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for starter relay vs solenoid
In the complex world of automotive components, understanding the differences between a starter relay and a solenoid is crucial for B2B buyers navigating the global market. Both devices play pivotal roles in the engine start-up process, yet they are often misunderstood, leading to challenges in sourcing the right parts for specific applications. This guide delves into the intricacies of starter relays and solenoids, exploring their types, applications, and the nuances that distinguish them.
With a focus on supplier vetting and cost considerations, we provide actionable insights that empower international buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including emerging markets like Vietnam and Brazil. By understanding the operational mechanics and market dynamics, buyers can make informed decisions that enhance their procurement strategies.
This comprehensive resource equips B2B buyers with the knowledge needed to differentiate between these essential components, ensuring they select the appropriate device for their automotive needs. Whether you are looking to streamline your supply chain or optimize operational efficiency, this guide serves as a valuable tool in your sourcing journey, ultimately driving business success in a competitive landscape.
Table Of Contents
- Top 3 Starter Relay Vs Solenoid Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for starter relay vs solenoid
- Understanding starter relay vs solenoid Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of starter relay vs solenoid
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘starter relay vs solenoid’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for starter relay vs solenoid
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for starter relay vs solenoid
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘starter relay vs solenoid’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for starter relay vs solenoid Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing starter relay vs solenoid With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for starter relay vs solenoid
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the starter relay vs solenoid Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of starter relay vs solenoid
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for starter relay vs solenoid
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Understanding starter relay vs solenoid Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electromechanical Relay | Uses electromagnetic coils to mechanically open/close circuits. | Automotive, industrial machinery | Pros: Reliable, cost-effective; Cons: Limited current capacity compared to solenoids. |
| Starter Solenoid | Directly attached to the starter motor; high current capacity. | Automotive, heavy machinery | Pros: High power output, compact design; Cons: More prone to wear under heavy use. |
| Solid State Relay | No moving parts; uses semiconductor technology for switching. | HVAC systems, lighting control | Pros: Long lifespan, faster switching; Cons: Higher initial cost, sensitive to heat. |
| Latching Relay | Maintains its position after being activated until reset. | Security systems, automation | Pros: Energy-efficient, reduces power consumption; Cons: More complex circuitry. |
| Miniature Relay | Smaller size for compact applications; low power requirement. | Consumer electronics, automotive | Pros: Space-saving, versatile; Cons: Limited current handling capability. |
What Are the Characteristics of Electromechanical Relays?
Electromechanical relays are widely used in automotive and industrial applications due to their ability to control high-power circuits with low-power signals. They operate using electromagnetic coils that mechanically switch contacts. For B2B buyers, reliability and cost-effectiveness are major advantages; however, their limited current capacity may restrict their use in high-demand applications. When purchasing, consider the specific current ratings and operational environment to ensure they meet your requirements.
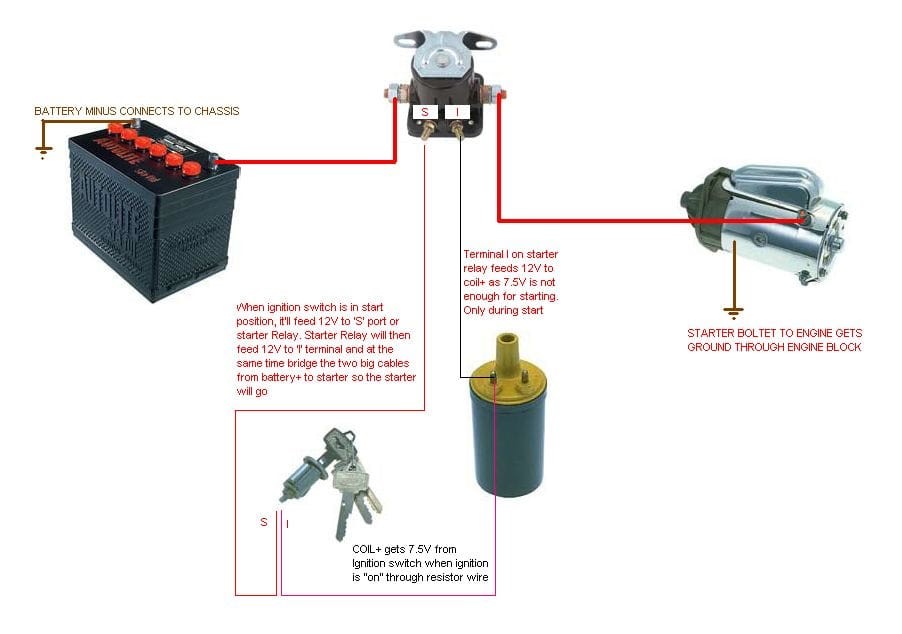
How Does a Starter Solenoid Differ from Other Types?
Starter solenoids are designed for automotive use, directly attached to the starter motor. They can handle high currents necessary for starting engines, making them essential in vehicles and heavy machinery. Buyers should note that while they offer high power output and a compact design, they are also more susceptible to wear under continuous use. When sourcing, assess the solenoid’s compatibility with the intended vehicle model and operational conditions.
What Advantages Do Solid State Relays Offer?
Solid state relays utilize semiconductor technology to control circuits without moving parts, providing faster switching and a longer lifespan than traditional relays. They are commonly found in HVAC systems and lighting controls. B2B buyers appreciate their durability and efficiency, but the higher initial costs and sensitivity to heat can be drawbacks. When considering solid state relays, evaluate the thermal management and ensure they fit within your budget constraints.
In What Scenarios Are Latching Relays Most Effective?
Latching relays are ideal for applications requiring a maintained state after activation, such as security systems and automation. They are energy-efficient, as they consume power only during the switching process. However, their complex circuitry may pose challenges in some installations. Buyers should consider the specific requirements of their applications, including reset mechanisms and compatibility with existing systems, when selecting latching relays.
Why Choose Miniature Relays for Compact Applications?
Miniature relays are designed for applications with limited space, such as consumer electronics and automotive systems. They are versatile and can handle low power requirements efficiently. While their space-saving design is advantageous, they do have limitations in current handling capability. B2B buyers should assess the specific power needs of their applications and ensure that miniature relays can meet these requirements without compromising performance.
Key Industrial Applications of starter relay vs solenoid
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of starter relay vs solenoid | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Engine starting systems in vehicles | Ensures reliable engine start, reducing downtime | Compatibility with vehicle models, quality standards |
| Agricultural Machinery | Starting systems for tractors and heavy equipment | Enhances operational efficiency in the field | Durability under harsh conditions, power handling |
| Industrial Equipment | Powering heavy machinery and production equipment | Increases productivity and minimizes maintenance costs | Voltage ratings, size constraints, and load capacity |
| Marine Applications | Starting systems in boats and marine vehicles | Guarantees reliable operation in challenging environments | Corrosion resistance, marine-grade specifications |
| Renewable Energy Systems | Control systems for wind turbines and solar inverters | Optimizes energy production and system reliability | Environmental ratings, lifecycle considerations |
How Are Starter Relays and Solenoids Used in the Automotive Industry?
In the automotive sector, starter relays and solenoids play a crucial role in engine starting systems. When the ignition key is turned, a low-power signal activates the relay or solenoid, allowing high-power current to flow to the starter motor. This mechanism ensures a reliable engine start, essential for minimizing downtime and enhancing vehicle reliability. International buyers, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, should focus on sourcing components that meet specific vehicle compatibility and quality standards to ensure optimal performance.
What Role Do Starter Relays and Solenoids Play in Agricultural Machinery?
In agricultural machinery, such as tractors and harvesters, starter relays and solenoids are vital for initiating engine operations. These components enable the transition from low-power signals to high-power demands required for starting heavy equipment. Their reliability directly impacts operational efficiency in the field, where downtime can lead to significant financial losses. Buyers from regions with intensive agricultural practices, like Brazil, should prioritize sourcing durable solenoids and relays that can withstand harsh conditions and high power loads.
How Are Starter Relays and Solenoids Utilized in Industrial Equipment?
In the industrial sector, starter relays and solenoids are essential for powering heavy machinery and production equipment. They facilitate the control of high-voltage circuits, enabling machinery to operate efficiently. This application is critical for increasing productivity and reducing maintenance costs. B2B buyers in Europe and the Middle East must consider voltage ratings, size constraints, and load capacity when sourcing these components to ensure they meet the demands of their specific equipment.
Why Are Starter Relays and Solenoids Important in Marine Applications?
In marine applications, starter relays and solenoids are key to the reliable operation of boats and marine vehicles. They ensure that engines start efficiently, even in adverse conditions, which is crucial for safety and operational dependability. Buyers should seek components with corrosion-resistant properties and marine-grade specifications to withstand the harsh marine environment, ensuring longevity and performance.
How Do Starter Relays and Solenoids Contribute to Renewable Energy Systems?
In renewable energy systems, such as wind turbines and solar inverters, starter relays and solenoids are used to control power flow and system activation. They optimize energy production and enhance system reliability, which is vital for maximizing output in energy generation. Buyers should focus on sourcing components with robust environmental ratings and lifecycle considerations, especially in regions heavily investing in renewable energy infrastructure.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘starter relay vs solenoid’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Confusion Over Relay and Solenoid Specifications
The Problem: Many B2B buyers face confusion when trying to differentiate between starter relays and solenoids, especially when sourcing parts for diverse vehicle models. This confusion can lead to incorrect purchases, resulting in costly downtime and repair delays. For companies involved in automotive repairs or parts distribution, understanding the specifications and applications of these components is critical. The challenge lies in the technical language used by suppliers and the varied configurations across vehicle manufacturers, creating a barrier to effective sourcing.
The Solution: To overcome this confusion, it’s essential for buyers to invest time in understanding the technical specifications of both starter relays and solenoids. Begin by consulting detailed product catalogs or technical datasheets from reputable manufacturers. Look for clear diagrams and descriptions that illustrate the differences in construction and function. Establish a relationship with knowledgeable suppliers who can provide tailored advice based on your specific vehicle models. Additionally, consider training staff on the key characteristics and applications of each component to minimize miscommunication during the procurement process.
Scenario 2: Difficulty Diagnosing Electrical Issues
The Problem: Another common pain point is the difficulty in diagnosing electrical issues related to starter systems, particularly when the vehicle exhibits symptoms like intermittent starting or failure to start. B2B buyers, especially those in the automotive repair sector, may struggle to pinpoint whether the issue lies with the starter relay, solenoid, or another component entirely. This uncertainty can lead to unnecessary part replacements and increased labor costs, ultimately affecting customer satisfaction and profitability.
The Solution: Implement a systematic diagnostic approach when troubleshooting starter-related issues. Encourage technicians to follow a flowchart that outlines specific tests for the starter relay and solenoid, such as voltage checks and continuity tests. Invest in diagnostic tools that can help identify electrical faults more accurately. Additionally, consider creating a standardized checklist for technicians to use during inspections, which includes common symptoms and potential causes associated with both components. This practice not only streamlines the diagnosis process but also enhances the overall efficiency of your operations.
Scenario 3: Sourcing Quality Components for Diverse Markets
The Problem: Sourcing high-quality starter relays and solenoids can be particularly challenging for B2B buyers operating in international markets, such as those in Africa, South America, or the Middle East. Variability in local suppliers, differences in product quality, and a lack of standardized parts across regions can complicate procurement efforts. Buyers may find themselves overwhelmed by subpar components that fail to meet the required performance standards, leading to increased returns and customer dissatisfaction.
The Solution: To address these sourcing challenges, establish strong partnerships with reliable manufacturers who have a track record of producing high-quality starter components. Conduct thorough research to identify suppliers with certifications, such as ISO, that ensure product quality. Utilize online platforms and industry trade shows to connect with reputable suppliers and seek testimonials from other businesses that have successfully sourced components from them. Consider implementing a quality assurance process for incoming parts, including testing and inspection protocols, to verify that all components meet the necessary performance standards before they are installed or sold. This proactive approach will help mitigate risks and ensure that your business is equipped with dependable starter relays and solenoids.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for starter relay vs solenoid
What Are the Key Materials Used in Starter Relays and Solenoids?
When selecting materials for starter relays and solenoids, understanding the properties, advantages, and limitations of each material is crucial for B2B buyers. This section analyzes several common materials used in these components, focusing on their performance characteristics, application impacts, and considerations for international markets.
How Does Copper Perform in Starter Relays and Solenoids?
Key Properties: Copper is known for its excellent electrical conductivity and thermal properties. It can withstand high temperatures, making it suitable for applications where heat dissipation is critical.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of copper is its superior conductivity, which ensures efficient power transfer. However, copper is prone to corrosion, especially in humid or saline environments, which can affect its longevity. Additionally, copper components can be more expensive than alternatives like aluminum.
Impact on Application: Copper is highly compatible with various electrical systems, but its susceptibility to corrosion may limit its use in harsh environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in regions with high humidity or saline conditions, such as coastal areas in Africa and South America, should consider protective coatings for copper components to enhance durability. Compliance with international standards such as ASTM B187 for copper products is essential.
What Role Does Aluminum Play in Starter Relays and Solenoids?
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight and has good corrosion resistance, especially when anodized. It also has decent electrical conductivity, although not as high as copper.
Illustrative image related to starter relay vs solenoid
Pros & Cons: The lightweight nature of aluminum makes it an attractive option for automotive applications, reducing overall vehicle weight. However, its lower conductivity can lead to higher energy losses, which may be a concern in high-performance applications.
Impact on Application: Aluminum’s corrosion resistance makes it suitable for use in various environments, although it may not perform as well as copper in high-current applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the specific grades of aluminum used, as some may not meet the necessary strength or conductivity requirements. Compliance with standards like ASTM B221 for aluminum extrusions is important for ensuring quality.
How Does Plastic Contribute to Starter Relay and Solenoid Designs?
Key Properties: Plastics, particularly engineering-grade thermoplastics, offer excellent insulation properties and are lightweight. They can withstand moderate temperatures and provide good chemical resistance.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of plastic is its insulating properties, which prevent electrical shorts. However, plastics can be less durable than metals and may degrade under prolonged exposure to high temperatures or UV light.

Illustrative image related to starter relay vs solenoid
Impact on Application: Plastics are often used in non-load-bearing components of relays and solenoids, where electrical insulation is crucial.
Considerations for International Buyers: Different regions may have varying regulations regarding plastic materials, particularly concerning fire safety and environmental impact. Buyers should ensure compliance with standards such as ISO 9001 for quality management systems.
What Advantages Does Steel Offer for Starter Relays and Solenoids?
Key Properties: Steel is known for its strength and durability, making it suitable for components that require structural integrity. It can withstand high pressures and temperatures, depending on the alloy used.
Pros & Cons: The key advantage of steel is its robustness, which allows it to endure harsh operating conditions. However, steel is heavier than other materials and is susceptible to corrosion unless properly treated.
Impact on Application: Steel is commonly used in the housing or casing of relays and solenoids, providing protection for internal components.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider the type of steel and any protective coatings, especially in regions with high humidity or corrosive environments. Compliance with standards such as ASTM A36 for structural steel is crucial for ensuring performance.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Starter Relays and Solenoids
| Material | Typical Use Case for starter relay vs solenoid | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Copper | Electrical connections in relays and solenoids | Excellent electrical conductivity | Prone to corrosion | High |
| Aluminum | Structural components and casings | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Lower conductivity than copper | Medium |
| Plastic | Insulating components and housings | Good electrical insulation | Less durable under extreme conditions | Low |
| Steel | Structural housing for relays and solenoids | High strength and durability | Heavier and susceptible to corrosion | Medium |
This analysis provides a comprehensive overview of materials used in starter relays and solenoids, equipping international B2B buyers with the insights needed to make informed decisions based on performance, cost, and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for starter relay vs solenoid
The manufacturing processes and quality assurance mechanisms for starter relays and solenoids are essential factors for B2B buyers looking for reliable automotive components. Understanding the complexities involved in the production and validation of these critical components can help buyers make informed purchasing decisions. Here, we delve into the typical manufacturing stages, quality control standards, and verification methods relevant to international buyers.
What are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Starter Relays and Solenoids?
The manufacturing processes for starter relays and solenoids can be broken down into several key stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Each stage is crucial for ensuring that the final product meets industry standards and customer expectations.

Illustrative image related to starter relay vs solenoid
How is Material Prepared for Starter Relays and Solenoids?
The first step involves sourcing high-quality raw materials, such as copper for electrical conductors, plastic for housing, and steel for internal components. Suppliers are typically evaluated based on their ability to provide materials that comply with international standards, such as ISO 9001. This ensures that the materials used are free from defects and suitable for high-performance applications.
What Techniques are Employed in the Forming Stage?
In the forming stage, various techniques are used to shape the materials into the required components. For starter solenoids, processes like stamping and machining are common for producing the metal parts. Injection molding is typically used for creating the plastic housings of both relays and solenoids. These techniques are selected based on factors like precision, cost-effectiveness, and scalability.
How are Starter Relays and Solenoids Assembled?
The assembly stage is where individual components come together to form the final product. This often involves manual labor as well as automated assembly lines. Key processes include soldering electrical connections, installing internal components, and fitting the housing. Each assembly line may be equipped with specialized tools to ensure that components are fitted securely and correctly.
What Finishing Techniques are Used?
Finishing processes enhance the durability and appearance of the starter relays and solenoids. Common techniques include surface treatment to prevent corrosion, painting or coating for aesthetics, and final inspections to ensure compliance with specifications. Each finishing step plays a role in the longevity and reliability of the product.
What Quality Control Measures are Implemented During Manufacturing?
Quality assurance is critical in the manufacturing of starter relays and solenoids. Various international standards and industry-specific certifications guide the quality control processes.
Which International Standards are Relevant for Quality Assurance?
ISO 9001 is a widely recognized standard that outlines the criteria for quality management systems. Compliance with this standard indicates that a manufacturer has established a robust quality management framework. Additionally, certifications such as CE (Conformité Européenne) and API (American Petroleum Institute) may be required depending on the target market and application of the product.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control checkpoints are essential for identifying defects early in the manufacturing process. Common checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specifications.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during production helps identify issues in real-time.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): A comprehensive inspection is conducted before products are shipped to ensure they meet all quality standards.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used?
Testing methods can vary but often include electrical testing to verify performance, mechanical testing for durability, and environmental testing for resilience against conditions like temperature and humidity. Manufacturers may also conduct lifecycle testing to assess how products perform over extended periods.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers must ensure that their suppliers adhere to strict quality control practices. Here are several effective methods for verification:
What Steps Can Buyers Take to Audit Suppliers?
Conducting audits is one of the most effective ways to assess a supplier’s quality control processes. Buyers can schedule on-site visits to evaluate manufacturing practices, inspect facilities, and review quality assurance documentation. This hands-on approach can provide insights into the supplier’s commitment to quality.
How Can Buyers Request Quality Assurance Reports?
Buyers should request comprehensive quality assurance reports that detail testing methods, results, and compliance with international standards. These reports can provide valuable information about the reliability and safety of the components.
What Role Do Third-Party Inspections Play?
Engaging third-party inspection services can offer an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s quality control practices. These inspections can be scheduled at various stages of production, providing additional reassurance that the products meet specified standards.
What Are the QC/Cert Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers must navigate various nuances related to quality control and certification. Each region may have different requirements regarding product safety, environmental impact, and performance standards. For example, products exported to Europe must comply with CE marking requirements, while those going to the Middle East may need to adhere to GCC standards.
How Can Buyers Ensure Compliance with Regional Standards?
Buyers should familiarize themselves with the specific regulatory requirements for their target markets. This may involve consulting with local experts or legal advisors who understand the nuances of automotive component regulations. Ensuring that suppliers are certified to meet these standards can mitigate the risk of non-compliance.
Conclusion
The manufacturing processes and quality assurance mechanisms for starter relays and solenoids are intricate and critical for ensuring product reliability. By understanding the main stages of manufacturing, quality control measures, and how to verify supplier practices, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs. This not only enhances the quality of the components they procure but also contributes to the overall efficiency and safety of their operations.

Illustrative image related to starter relay vs solenoid
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘starter relay vs solenoid’
In today’s competitive automotive market, sourcing the right components for vehicle ignition systems, such as starter relays and solenoids, is crucial for ensuring reliability and performance. This guide offers B2B buyers a practical checklist to facilitate informed procurement decisions when selecting these components.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before initiating any procurement process, it’s essential to outline the technical requirements for starter relays and solenoids. Consider factors such as voltage ratings, current capacity, and physical dimensions. Clearly defined specifications will help streamline the sourcing process and ensure compatibility with existing systems.
Step 2: Research Market Trends and Suppliers
Stay informed about the latest market trends and technologies related to starter relays and solenoids. Understanding current innovations and shifts can provide insight into the best products available. Investigate suppliers who specialize in automotive components, particularly those with a strong reputation in your target markets, such as Africa, South America, and Europe.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Verify that potential suppliers possess relevant industry certifications and quality assurance standards. Certifications such as ISO 9001 demonstrate a commitment to quality management practices. This step is vital for ensuring that the components you procure meet safety and performance benchmarks, reducing the risk of operational failures.
Step 4: Request Product Samples
Before finalizing any orders, request samples of the starter relays and solenoids you are considering. Testing samples allows you to evaluate the quality and functionality of the products firsthand. Ensure the samples meet your specifications and perform reliably under various conditions, as this will influence your decision-making.
Step 5: Assess Warranty and Support Policies
Investigate the warranty and customer support policies offered by suppliers. A comprehensive warranty can protect your investment and provide peace of mind should issues arise with the components. Additionally, reliable customer support ensures that you can obtain assistance or replacements quickly, minimizing downtime.
Step 6: Analyze Pricing and Payment Terms
Compare pricing structures among different suppliers while keeping quality in mind. Look for competitive pricing that aligns with your budget without compromising on quality. Additionally, evaluate payment terms to ensure they are favorable and fit within your financial planning.
Step 7: Check Customer Reviews and References
Before making a final decision, review customer feedback and seek references from other businesses that have sourced similar components. Insights from previous buyers can provide valuable information about supplier reliability, product quality, and overall satisfaction. This step can help mitigate risks associated with procurement.

Illustrative image related to starter relay vs solenoid
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can confidently navigate the procurement process for starter relays and solenoids, ensuring they select the right components for their automotive needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for starter relay vs solenoid Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Starter Relays and Solenoids?
When sourcing starter relays and solenoids, understanding the cost structure is crucial. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margins.
-
Materials: The cost of raw materials like copper, plastics, and metals significantly affects the overall price. High-quality materials often increase durability and performance, impacting long-term value.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region. For instance, sourcing from countries with lower labor costs may lead to savings, but this can affect quality and consistency. Skilled labor is necessary for the assembly and quality assurance of these components.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses the indirect costs associated with production, such as utilities and maintenance. Efficient manufacturing processes can reduce these costs, which is essential for competitive pricing.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in tooling is significant, especially for custom designs. Tooling costs are amortized over the production volume, so larger orders generally result in lower per-unit costs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that each component meets specific standards is essential, particularly for automotive applications. Higher QC standards can increase costs but are necessary to prevent failures that may lead to safety issues.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can vary based on the geographical location of suppliers and buyers. Understanding Incoterms is vital to determining who bears these costs, impacting the total expense.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically apply a markup on their costs to ensure profitability. The margin can vary based on market competition, demand, and the supplier’s pricing strategy.
How Do Price Influencers Impact the Cost of Starter Relays and Solenoids?
Several factors influence pricing in the B2B marketplace for starter relays and solenoids:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Bulk purchases often lead to lower per-unit costs. Negotiating favorable MOQs can optimize pricing, especially for international buyers looking to stock inventory.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom designs or specific performance requirements can significantly affect costs. Buyers should clearly define their specifications to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Components made with premium materials or those that meet international quality certifications (e.g., ISO, TS16949) typically command higher prices. Buyers should assess the balance between cost and quality.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their proven track record, while newer suppliers might offer lower prices to attract business.
-
Incoterms: Understanding shipping terms and responsibilities can impact overall costs. For instance, FOB (Free on Board) pricing may differ significantly from DDP (Delivered Duty Paid), affecting the total landed cost.
What Buyer Tips Can Enhance Cost-Efficiency When Sourcing?
International buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should consider the following strategies for effective sourcing:
-
Negotiate Smartly: Leverage your purchasing power by negotiating terms that benefit both parties. Discussing long-term partnerships can also lead to better pricing and service.
-
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Beyond the initial purchase price, consider maintenance, durability, and potential failures. A cheaper component may lead to higher long-term costs if it requires frequent replacements.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances: Be aware of currency fluctuations, tariffs, and trade regulations that can impact costs. Establishing relationships with local suppliers may mitigate some of these risks.
-
Conduct Market Research: Understanding regional market trends and competitor pricing can provide leverage in negotiations. This knowledge can also help identify the best suppliers who offer the right balance of quality and cost.
-
Seek Volume Discounts: If possible, consolidate orders to achieve better pricing. Suppliers are often more willing to negotiate on larger volumes.
Disclaimer on Pricing
Prices for starter relays and solenoids can vary widely based on the factors discussed above. It is essential for buyers to conduct thorough research and obtain multiple quotes to ensure competitive pricing.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing starter relay vs solenoid With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternative Solutions to Starter Relays and Solenoids
In the automotive and machinery sectors, effective starting mechanisms are critical for operational efficiency. While starter relays and solenoids are commonly employed for this purpose, alternative solutions can offer varying benefits. Understanding these alternatives allows B2B buyers to make informed decisions that align with their specific operational needs.
| Comparison Aspect | Starter Relay Vs Solenoid | Alternative 1 Name | Alternative 2 Name |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High power handling; good for triggering starters | Smart Starter Systems | Capacitor-Based Starters |
| Cost | Generally low cost | Moderate initial investment | Higher initial cost but lower long-term costs |
| Ease of Implementation | Straightforward installation | Requires integration with existing systems | More complex installation |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance required | Moderate maintenance; software updates needed | Low maintenance but may require periodic checks |
| Best Use Case | Standard vehicles and machinery | Advanced vehicles with integrated systems | High-performance applications requiring quick starts |
What Are Smart Starter Systems and How Do They Compare?
Smart starter systems are an advanced alternative that utilizes microcontroller technology to manage the starting process. They provide diagnostic capabilities and can optimize performance based on real-time data. The main advantage of smart systems is their ability to integrate with vehicle electronics, offering enhanced performance and reliability. However, they typically come with a moderate initial investment and require regular software updates, which may complicate maintenance.
How Do Capacitor-Based Starters Function as an Alternative?
Capacitor-based starters use stored electrical energy to deliver a high burst of power for starting engines. This technology is particularly effective in high-performance applications, as it can provide rapid starts and reduce wear on the starter motor. While they tend to have a higher initial cost, they can lower long-term expenses by decreasing the frequency of starter replacements. Their installation is more complex than traditional systems, requiring professional setup and periodic checks to ensure optimal performance.
How Can B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution for Their Needs?
When selecting between starter relays, solenoids, or alternative solutions, B2B buyers should assess their specific operational requirements. Factors such as performance needs, budget constraints, and existing system compatibility play crucial roles in decision-making. For standard applications, traditional starter relays and solenoids may suffice. In contrast, for advanced machinery or high-performance vehicles, smart starter systems or capacitor-based starters may provide the necessary reliability and efficiency. Ultimately, understanding the unique demands of your operation will guide you toward the most suitable choice.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for starter relay vs solenoid
What Are the Essential Technical Properties of Starter Relays and Solenoids?
When evaluating starter relays and solenoids, understanding their technical specifications is critical for B2B buyers, especially in industries such as automotive, machinery, and construction. Here are some key properties to consider:
-
Material Grade
– Definition: The materials used in the construction of relays and solenoids, typically metals like copper for electrical components and high-grade plastics for casings.
– Importance: High-quality materials enhance durability and performance, reducing the likelihood of failure in harsh environments. Buyers should look for components that can withstand temperature fluctuations and corrosion. -
Electrical Current Rating
– Definition: This specification indicates the maximum current the relay or solenoid can handle, often measured in Amperes (A).
– Importance: Selecting a component with an appropriate current rating is essential to ensure reliable operation. Underestimating this can lead to overheating and failure, resulting in costly downtime. -
Coil Resistance
– Definition: The resistance of the coil in a solenoid or relay, usually measured in Ohms (Ω).
– Importance: Coil resistance affects the power consumption and efficiency of the component. Understanding this helps buyers choose products that balance performance with energy efficiency, which is particularly crucial for industries focused on sustainability. -
Operating Voltage
– Definition: The voltage required for the relay or solenoid to operate, typically ranging from 12V to 24V for automotive applications.
– Importance: Matching the operating voltage to the vehicle or equipment specifications is vital. Mismatched voltages can lead to malfunction or damage, underscoring the importance of proper specification. -
Tolerance and Specifications
– Definition: This includes the acceptable variations in dimensions, weight, and performance parameters.
– Importance: High precision in manufacturing tolerances ensures that components fit correctly and function as intended. In industries where reliability is paramount, such as automotive manufacturing, precise tolerances are non-negotiable.
What Are Common Trade Terminology and Jargon in the Starter Relay and Solenoid Market?
Understanding industry-specific terminology is essential for effective communication and negotiation in B2B transactions. Here are some common terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Definition: A company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer.
– Importance: OEM parts are often seen as more reliable than aftermarket alternatives, making them a preferred choice for many buyers looking for quality assurance. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– Definition: The smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell.
– Importance: Knowing the MOQ helps buyers plan their inventory and budgeting, particularly important for businesses with limited cash flow or storage capacity. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– Definition: A document sent to suppliers to solicit price quotes for specific products or services.
– Importance: RFQs enable buyers to compare prices and terms from multiple suppliers, fostering competitive pricing and informed purchasing decisions. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Definition: A series of predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) relating to international commercial law.
– Importance: Understanding Incoterms is crucial for international trade as they define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs, thereby minimizing misunderstandings. -
Lead Time
– Definition: The amount of time it takes from placing an order to receiving the product.
– Importance: Knowing the lead time helps businesses manage their supply chain effectively, ensuring that they maintain operational continuity without delays. -
Compatibility
– Definition: Refers to whether a relay or solenoid can work with specific vehicle models or systems.
– Importance: Ensuring compatibility reduces the risk of purchasing incorrect parts, which can lead to increased costs and project delays.
By understanding these essential technical properties and trade terminologies, B2B buyers can make informed purchasing decisions, leading to improved operational efficiency and reduced costs.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the starter relay vs solenoid Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Starter Relay vs Solenoid Sector?
The starter relay and solenoid market is witnessing significant growth driven by the increasing demand for efficient automotive components across various regions, particularly in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Key factors propelling this market include the rise in vehicle production and the growing preference for electric and hybrid vehicles, which necessitate advanced starting systems. Furthermore, as automotive technologies evolve, manufacturers are incorporating smart technologies and electronic controls, which enhance the functionality of relays and solenoids.
Emerging trends in B2B sourcing include a shift towards automation and digitalization, which streamline procurement processes and enhance supply chain visibility. International buyers are increasingly leveraging e-commerce platforms and digital marketplaces to source components, allowing for more competitive pricing and improved access to diverse suppliers. Additionally, the focus on localization of supply chains is gaining traction as companies seek to mitigate risks associated with global disruptions, such as those seen during the COVID-19 pandemic. This trend is particularly relevant for regions like Africa and South America, where local manufacturing capabilities are expanding.
Moreover, manufacturers are increasingly adopting just-in-time (JIT) inventory systems to reduce holding costs and improve efficiency. This approach necessitates reliable partnerships with suppliers who can ensure timely delivery of quality components, emphasizing the importance of strong supplier relationships in navigating the complexities of the market.
How Does Sustainability Impact the Sourcing of Starter Relays and Solenoids?
Sustainability is becoming a critical consideration in the sourcing of starter relays and solenoids. The automotive industry is under increasing pressure to reduce its environmental footprint, prompting manufacturers to adopt sustainable practices throughout their supply chains. This includes sourcing materials that have a lower environmental impact and ensuring that production processes are energy-efficient and minimize waste.
Ethical sourcing is equally important, as international buyers are increasingly favoring suppliers who adhere to social responsibility standards and demonstrate transparency in their operations. Companies are now seeking partners who can provide documentation of their environmental certifications and ethical practices, such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and ISO 45001 for occupational health and safety.
Additionally, the adoption of “green” materials in the manufacturing of starter relays and solenoids is on the rise. This includes the use of recyclable materials and components that are free from harmful substances. Buyers should look for suppliers who can provide eco-friendly alternatives and demonstrate a commitment to sustainability through certifications like REACH and RoHS compliance.
What Is the Brief Evolution of Starter Relays and Solenoids in the Automotive Sector?
The evolution of starter relays and solenoids has been closely tied to advancements in automotive technology. Initially, starter systems relied on simple mechanical switches, which were prone to failure and inefficiency. The introduction of electromagnetic relays and solenoids in the mid-20th century revolutionized the starting process, allowing for more reliable and efficient operation.

Illustrative image related to starter relay vs solenoid
As vehicle technology advanced, so did the complexity of starter systems. The integration of electronic controls in modern vehicles has led to the development of advanced relays and solenoids capable of handling higher currents and providing enhanced functionality. Today, these components are essential for the operation of not only traditional internal combustion engines but also electric and hybrid vehicles, reflecting the ongoing transformation of the automotive landscape.
This historical context highlights the importance of sourcing high-quality components that meet the evolving demands of the automotive industry. Buyers should prioritize suppliers who are innovating and adapting to these technological changes to ensure they are getting the best products for their needs.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of starter relay vs solenoid
-
How do I determine whether to source a starter relay or a solenoid for my vehicles?
To decide between a starter relay and a solenoid, consider the specific requirements of your vehicle and its electrical system. A relay is generally suited for controlling lower power signals, while a solenoid is designed to manage higher current loads. Analyze your vehicles’ specifications and consult with your suppliers about which component would be the most efficient and reliable based on the starting system design. Always consider the manufacturer’s recommendations and the typical failure rates of each component in your region. -
What are the signs of a failing starter relay or solenoid?
Common signs of a failing starter relay include a single click sound when the ignition is turned or intermittent engine starting issues. For solenoids, look for symptoms such as the engine not starting at all, repeated clicking sounds, or the starter engaging without the key being turned. Understanding these signs can help you quickly diagnose issues, allowing for timely replacements and minimizing downtime in your operations. -
What factors should I consider when selecting a supplier for starter relays and solenoids?
When selecting a supplier, evaluate their experience in the automotive parts industry, particularly with starter relays and solenoids. Consider their manufacturing capabilities, quality assurance processes, and compliance with international standards. Look for reviews or testimonials from other B2B clients, and ensure they offer competitive pricing, reasonable minimum order quantities (MOQs), and reliable logistics solutions to meet your delivery needs. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for starter relays and solenoids?
MOQs for starter relays and solenoids can vary widely depending on the supplier and the specific product. Generally, MOQs can range from 50 to several hundred units. It’s essential to discuss your purchasing needs with potential suppliers to understand their terms. Some suppliers may offer flexibility for first-time buyers or bulk orders, allowing you to negotiate based on your business requirements. -
How can I ensure the quality of starter relays and solenoids from international suppliers?
To ensure quality, request samples before placing a bulk order and conduct thorough inspections upon receipt. Ask suppliers for their certifications, such as ISO or TS16949, which indicate adherence to quality management standards. Additionally, consider establishing a clear quality assurance agreement that outlines your expectations regarding product specifications, testing, and warranties. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing starter relays and solenoids internationally?
Payment terms can vary by supplier and region, but common practices include a percentage upfront (typically 30%) and the balance upon delivery or before shipment. Some suppliers may offer net payment terms (e.g., net 30 or net 60 days) based on your relationship and order history. Always clarify payment terms in advance and consider using secure payment methods to protect your financial interests. -
How can I manage logistics effectively when importing starter relays and solenoids?
Effective logistics management involves selecting reliable freight forwarders who understand the nuances of international shipping, including customs regulations and duties. Plan your shipments well in advance and maintain clear communication with your suppliers about lead times and delivery schedules. Additionally, consider using Incoterms to specify the responsibilities of each party regarding transportation, insurance, and risk management. -
What customization options are available for starter relays and solenoids?
Many suppliers offer customization options, including specific voltage ratings, connector types, and dimensions tailored to your vehicle models. Discuss your requirements early in the procurement process to determine feasibility and associated costs. Customization can enhance compatibility with your applications and improve overall performance, but be prepared for longer lead times and potential increases in MOQs.
Top 3 Starter Relay Vs Solenoid Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Ford Trucks – Starter Relay and Solenoid
Domain: ford-trucks.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Starter Relay and Starter Solenoid are often confused terms in automotive contexts. A starter relay is used to connect the high current required by the starter and is typically mounted on the firewall or inner fender. In contrast, a starter solenoid is an electrically controlled device that activates the starter motor and is mounted directly on the starter. The relay controls a high current supply…
2. Dotheton – Relays and Solenoids
Domain: dotheton.com
Registered: 2007 (18 years)
Introduction: Relays and solenoids are both electro-mechanical devices used for switching electricity. A relay is an electrically controlled switch, while a solenoid is an electrically controlled plunger. Solenoids typically handle higher current loads than relays, with relays usually rated between 10A to 50A and solenoids capable of handling up to 600A in automotive applications. Starter solenoids and starter …
3. Overland Bound – High Current Solutions
Domain: overlandbound.com
Registered: 2011 (14 years)
Introduction: Relay: 120 amp capacity, used for low current applications like fog lights and horns. Solenoid: Generally used for higher current applications (40a and above), such as winches. High current solenoids can be rated up to 500 amps for dual battery setups. Smart solenoids are recommended for better management of battery connections, preventing dead batteries from drawing from the main battery during i…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for starter relay vs solenoid
In the realm of automotive electrical components, understanding the distinctions and applications of starter relays and solenoids is crucial for effective sourcing. Both components serve as electromagnetic switches that facilitate the transition from low-power signals to high-power demands essential for engine ignition. However, their construction and placement in the vehicle can vary significantly, leading to potential sourcing challenges.
For B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, strategic sourcing entails not only identifying quality suppliers but also understanding the unique requirements of your market. Assessing the reliability and performance of starter relays versus solenoids can lead to reduced operational downtime and increased customer satisfaction.
As the automotive landscape evolves, driven by technological advancements and shifting consumer preferences, it is imperative to stay informed about these components. Engaging with reputable suppliers who can provide insights on the latest innovations and performance metrics will enhance your competitive edge.
Now is the time to reevaluate your sourcing strategies and partner with manufacturers that prioritize quality and reliability. By doing so, you can position your business for sustained growth in an ever-changing market.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.