Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for signs that alternator is bad
In the global marketplace, understanding the signs that an alternator is bad is crucial for B2B buyers in sectors relying on fleet management, automotive repair, and transportation logistics. A malfunctioning alternator can lead to costly downtime and impact operational efficiency, making it imperative to recognize early warning signs. This comprehensive guide delves into various indicators of alternator failure, from electrical malfunctions to unusual sounds, ensuring that buyers are well-equipped to identify potential issues before they escalate.
Navigating the complexities of sourcing reliable alternators involves more than just recognizing symptoms; it requires a thorough understanding of types, applications, and supplier vetting processes. Our guide covers essential topics such as assessing the reliability of suppliers, understanding the cost implications of alternator repairs versus replacements, and evaluating the long-term benefits of quality components. This empowers international B2B buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, to make informed purchasing decisions.
By providing actionable insights and practical advice, this guide aims to enhance your procurement strategies, ensuring that your operations remain uninterrupted and efficient. Whether you’re based in Nigeria, Vietnam, or anywhere else in the world, understanding these signs is key to maintaining a robust and reliable automotive fleet.
Table Of Contents
- Top 3 Signs That Alternator Is Bad Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for signs that alternator is bad
- Understanding signs that alternator is bad Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of signs that alternator is bad
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘signs that alternator is bad’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for signs that alternator is bad
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for signs that alternator is bad
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘signs that alternator is bad’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for signs that alternator is bad Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing signs that alternator is bad With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for signs that alternator is bad
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the signs that alternator is bad Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of signs that alternator is bad
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for signs that alternator is bad
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Understanding signs that alternator is bad Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Starting Problems | Difficulty starting the vehicle; frequent stalling. | Automotive repair shops, fleet management. | Pros: Early detection prevents major breakdowns. Cons: May require immediate service, leading to downtime. |
| Warning Light | Illuminated battery or alternator warning light on dashboard. | Vehicle maintenance services, logistics. | Pros: Quick identification of issues. Cons: May be mistaken for battery issues. |
| Dim or Flickering Lights | Headlights and dashboard lights dimming or flickering. | Vehicle safety inspections, fleet services. | Pros: Indicates electrical system instability. Cons: Can lead to safety hazards if ignored. |
| Strange Noises | Growling or grinding sounds from the alternator. | Auto repair shops, automotive parts suppliers. | Pros: Alerts to potential mechanical failure. Cons: May require extensive diagnostics. |
| Burning Smell | Odor resembling burning rubber or electrical fires. | Fleet management, automotive maintenance. | Pros: Signals overheating components, preventing fire hazards. Cons: Requires immediate attention to avoid damage. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Starting Problems as a Sign of Alternator Failure?
Starting problems are often the first indication of alternator failure. When the alternator is not charging the battery effectively, vehicles may struggle to start or stall unexpectedly during operation. For B2B buyers, especially in automotive repair and fleet management, recognizing these signs early can prevent costly breakdowns. Regular maintenance and diagnostics can help identify these issues before they escalate, ensuring vehicle uptime and reliability.
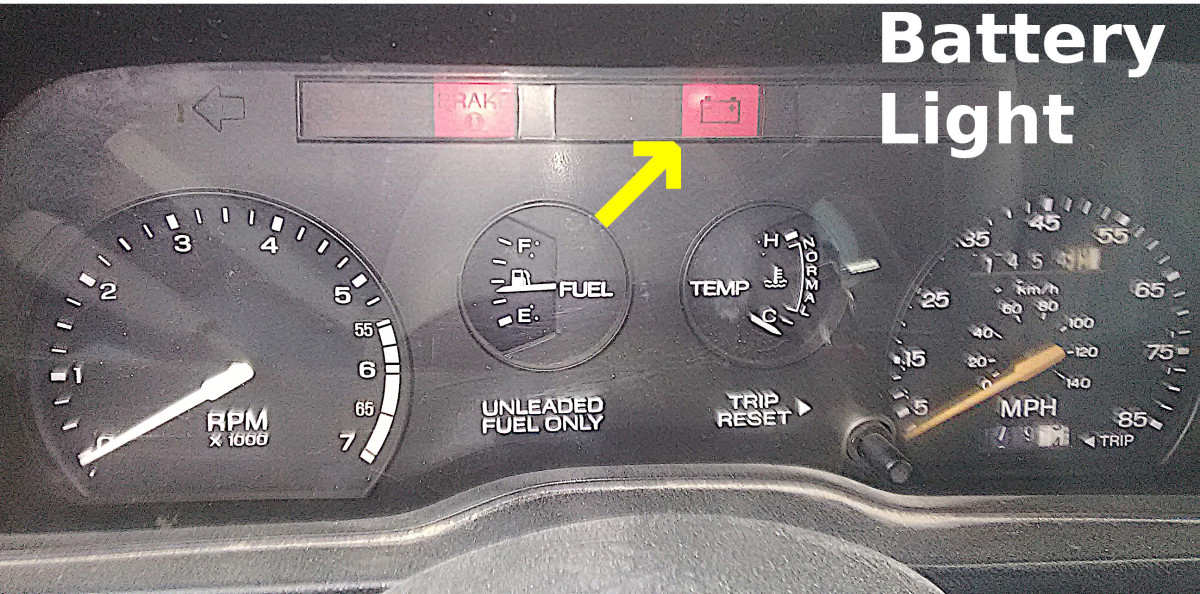
How Can a Warning Light Indicate Alternator Issues?
The warning light on the dashboard serves as a critical alert for potential alternator problems. This light may be misinterpreted as a battery issue, but it often signals that the alternator is not functioning correctly. For businesses involved in vehicle maintenance or logistics, understanding this distinction is vital. Prompt action based on this indicator can save time and resources by addressing the root cause of electrical system failures.
Why Are Dim or Flickering Lights Important for B2B Buyers?
Dim or flickering lights are a clear sign of a failing alternator. This issue can affect not only the headlights but also the dashboard lights and other electrical components. For businesses in the automotive sector, such as safety inspections or fleet services, monitoring these symptoms is essential. Addressing dim lights can enhance vehicle safety and operational efficiency, reducing the risk of accidents due to poor visibility.
What Do Strange Noises from the Alternator Indicate?
Strange noises, such as grinding or growling, often indicate mechanical issues within the alternator. These sounds can signal worn bearings or other internal failures that require immediate attention. For B2B buyers in the automotive repair industry, recognizing these noises can lead to timely repairs and maintenance, preventing more extensive and costly repairs down the line. Regular inspections can help identify these sounds early, ensuring vehicles remain in optimal condition.
How Does a Burning Smell Relate to Alternator Failure?
A burning smell, often associated with overheating electrical components, is a critical warning sign of alternator failure. This odor can indicate that the alternator is working harder than it should, leading to potential fire hazards. For fleet managers and automotive maintenance providers, addressing this issue promptly is crucial to ensure safety and prevent further damage. Regular checks can help identify overheating issues before they escalate, safeguarding both vehicles and personnel.
Key Industrial Applications of signs that alternator is bad
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of signs that alternator is bad | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive Repair | Diagnosing vehicle electrical issues | Reduces downtime through timely repairs, enhancing customer satisfaction | Quality of diagnostic tools and technician training |
| Transportation & Logistics | Fleet management for trucks and buses | Ensures operational efficiency and minimizes breakdowns, reducing costs | Supplier reliability and warranty terms |
| Mining | Heavy machinery maintenance | Prevents unplanned maintenance and costly repairs, ensuring productivity | Access to specialized parts and expertise in machinery repair |
| Agriculture | Farm equipment functionality | Maintains operational efficiency of machinery, ensuring timely harvests | Availability of parts in remote locations |
| Construction | Equipment reliability in construction sites | Minimizes project delays and enhances safety, leading to cost savings | Quality assurance of electrical components |
How Are Signs That the Alternator Is Bad Utilized in Automotive Repair?
In the automotive repair industry, recognizing signs of a failing alternator is crucial for technicians. Common symptoms include dimming headlights, dashboard warning lights, and starting issues. By diagnosing these signs early, repair shops can prevent further electrical system failures, ensuring vehicles remain operational and customers satisfied. For international buyers, sourcing high-quality diagnostic tools and training for technicians is essential to maintain service standards, especially in regions with varying vehicle models and electrical systems.
What Role Do Alternator Signs Play in Transportation & Logistics?
In the transportation and logistics sector, fleet managers must monitor the health of their vehicles to avoid unexpected breakdowns. Signs such as frequent stalling or battery warning lights indicate potential alternator issues, which can lead to costly downtime. By addressing these issues promptly, companies can maintain efficient operations and reduce repair costs. When sourcing parts or services, logistics firms should consider supplier reliability and warranty terms to ensure they receive dependable service and support.
How Is Alternator Maintenance Relevant in Mining Operations?
Mining operations rely heavily on the functionality of heavy machinery, where a failing alternator can lead to significant productivity losses. Signs such as burning smells or odd noises from equipment can indicate alternator problems that need immediate attention. By proactively addressing these issues, mining companies can avoid unplanned maintenance, thereby enhancing productivity. Buyers in this sector should prioritize access to specialized parts and expertise in machinery repair to ensure quick resolution of electrical issues.
Why Are Alternator Signs Important for Agricultural Equipment?
In agriculture, the functionality of farm equipment is vital for timely operations such as planting and harvesting. Signs of alternator failure, like poor battery charging or electronic feature malfunctions, can hinder machinery performance. By recognizing these signs early, farmers can ensure their equipment remains operational, thus avoiding delays in production. Buyers should consider the availability of parts, especially in remote areas, to ensure that repairs can be made swiftly to minimize disruptions.
How Do Signs of a Failing Alternator Affect Construction Projects?
In the construction industry, equipment reliability is paramount to avoid project delays. Signs indicating a failing alternator, such as flickering lights or unusual noises, can signal potential issues that may lead to equipment failure. By addressing these signs early, construction firms can enhance safety and reduce costs associated with downtime. When sourcing electrical components, it is crucial to ensure quality assurance to avoid future complications and maintain project timelines.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘signs that alternator is bad’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty Diagnosing Electrical Issues in Vehicles
The Problem: B2B buyers in the automotive sector, such as fleet managers and auto repair shop owners, often face challenges in diagnosing electrical issues related to alternators. A vehicle that frequently stalls or shows warning lights can lead to significant downtime, lost productivity, and increased repair costs. The complexity of modern vehicle electrical systems complicates the diagnosis, as symptoms can mimic issues related to batteries, wiring, or other components. This ambiguity can lead to misdiagnoses, resulting in unnecessary repairs and expenses.

Illustrative image related to signs that alternator is bad
The Solution: To effectively diagnose alternator issues, B2B buyers should invest in specialized diagnostic tools designed for automotive electrical systems. These tools can read error codes and provide real-time data on voltage levels and battery performance. Additionally, implementing a standardized checklist for diagnosing alternator issues can streamline the process. This checklist should include symptoms like dimming lights, warning lights on the dashboard, and stalling. Training staff on the use of these diagnostic tools and the checklist will enhance their ability to accurately pinpoint alternator problems, ultimately reducing downtime and costs associated with misdiagnoses.
Scenario 2: High Replacement Costs Due to Ignored Warning Signs
The Problem: Many businesses overlook early warning signs of alternator failure, leading to severe damage and higher replacement costs. For instance, a fleet of delivery vehicles may experience sudden alternator failure if minor symptoms—like flickering headlights or a burning smell—are ignored. This not only disrupts operations but can also lead to costly roadside assistance, extended downtime, and potential damage to other electrical components.
The Solution: B2B buyers can mitigate these risks by establishing a proactive maintenance schedule that includes routine checks of the alternator and related components. Educating drivers and maintenance staff to recognize the early warning signs of alternator failure is crucial. Regularly scheduled inspections should focus on the electrical system, including visual checks for signs of wear on belts and connections, testing battery voltage, and monitoring the performance of electrical accessories. By addressing minor issues early on, businesses can prevent unexpected breakdowns and reduce the overall cost of vehicle maintenance.
Scenario 3: Limited Knowledge on Proper Alternator Specifications
The Problem: When sourcing alternators, B2B buyers often struggle with selecting the correct specifications to meet the needs of their vehicles. Mismatched specifications can lead to inadequate power supply, resulting in further electrical issues or premature alternator failure. This is particularly challenging for businesses operating diverse fleets, where variations in vehicle models may require different alternator specifications.
The Solution: To overcome this challenge, B2B buyers should maintain a comprehensive database of the specifications required for each vehicle in their fleet. This database should include details such as amperage ratings, mounting types, and connector configurations. Additionally, buyers should collaborate closely with reputable suppliers who can provide guidance on matching alternators with specific vehicle models. Leveraging technology, such as digital catalog systems that allow for easy cross-referencing of parts, can greatly enhance the accuracy of sourcing the right alternators. This proactive approach not only ensures optimal performance but also extends the lifespan of the vehicles in the fleet.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for signs that alternator is bad
What Materials Are Commonly Used to Identify Signs of a Bad Alternator?
In the automotive industry, particularly in the context of diagnosing alternator issues, various materials are utilized in the components and tools that help identify signs of alternator failure. This analysis focuses on four common materials: copper, aluminum, rubber, and plastic. Each material has distinct properties that influence its performance, durability, and suitability for specific applications.
How Does Copper Impact the Performance of Electrical Diagnostics?
Copper is a highly conductive metal, making it an excellent choice for wiring and electrical components used in alternator diagnostics. Its key properties include a high electrical conductivity rating, which allows for efficient energy transfer, and resistance to corrosion, especially when properly insulated.
Pros: Copper’s excellent conductivity ensures minimal energy loss, which is crucial for accurate diagnostics. It is also relatively durable and can withstand high temperatures, making it suitable for automotive environments.
Cons: However, copper can be more expensive than other materials and is prone to oxidation if not protected, which can affect its performance over time. Additionally, the manufacturing complexity involved in creating copper components can lead to higher costs.
Impact on Application: Copper wiring is essential for connecting diagnostic tools to the vehicle’s electrical system, ensuring accurate readings of voltage and current. International buyers should consider compliance with standards such as ASTM B3 for copper wire.
What Role Does Aluminum Play in Alternator Components?
Aluminum is another common material used in alternator components, particularly in housings and brackets. Its key properties include a lightweight nature and good corrosion resistance, making it ideal for automotive applications.
Pros: The lightweight characteristic of aluminum contributes to overall vehicle efficiency, while its resistance to corrosion extends the lifespan of components. Additionally, aluminum is relatively cost-effective compared to copper.
Illustrative image related to signs that alternator is bad
Cons: On the downside, aluminum is not as strong as steel and can be more prone to deformation under stress. Its thermal conductivity is lower than that of copper, which may affect heat dissipation in high-performance applications.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is often used in the construction of alternator housings, which protect internal components from environmental factors. Buyers in regions like Africa and South America should ensure that aluminum components meet local standards such as ISO 9001 for quality management.
Why Is Rubber Important in Electrical Insulation?
Rubber is primarily used for insulation in wiring and belts associated with alternators. Its key properties include excellent electrical insulation capabilities and flexibility, which allow it to withstand various environmental conditions.
Pros: Rubber’s insulating properties prevent electrical shorts and protect against moisture, which is crucial for automotive applications. Its flexibility also allows for easy installation and maintenance.
Cons: However, rubber can degrade over time due to exposure to heat and UV light, leading to potential failures. Additionally, it may not be suitable for high-temperature applications without specific formulations.
Impact on Application: Rubber insulation is critical for ensuring safe operation of electrical systems in vehicles. International buyers should consider compliance with standards such as ASTM D2000 for rubber materials.
How Does Plastic Contribute to Diagnostic Tools?
Plastic is widely used in the manufacturing of diagnostic tools and components due to its versatility and cost-effectiveness. Key properties include good electrical insulation and resistance to chemicals.
Pros: Plastic is lightweight and can be molded into complex shapes, making it ideal for various diagnostic tools. Its resistance to moisture and chemicals ensures longevity in automotive environments.
Cons: However, plastic may not withstand high temperatures as well as metals, which could limit its application in certain high-heat areas. Additionally, some plastics can become brittle over time.
Impact on Application: Plastic components are often found in diagnostic tools used to assess alternator performance, such as multimeters and connectors. Buyers should ensure that plastic materials comply with relevant standards like ISO 11469 for material identification.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Diagnosing Alternator Issues
| Material | Typical Use Case for signs that alternator is bad | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Copper | Wiring for electrical diagnostics | High conductivity | Prone to oxidation | High |
| Aluminum | Housings and brackets | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Less strong than steel | Medium |
| Rubber | Insulation for wiring and belts | Excellent electrical insulation | Degrades over time | Medium |
| Plastic | Diagnostic tools and connectors | Lightweight and versatile | Limited high-temperature resistance | Low |
This strategic material selection guide provides insight into the materials commonly used in diagnosing alternator issues, helping international B2B buyers make informed decisions based on performance, cost, and compliance with regional standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for signs that alternator is bad
What Are the Key Manufacturing Processes for Identifying Signs of a Bad Alternator?
The manufacturing processes for components related to alternators involve several critical stages, each designed to ensure the functionality and reliability of the final product. Understanding these processes can help B2B buyers make informed decisions when sourcing alternators or related components.
How Are Materials Prepared for Alternator Manufacturing?
The initial stage of manufacturing alternators begins with the preparation of raw materials. Common materials include high-grade steel for the casing, copper for the windings, and various alloys for components like the rotor and stator.
-
Material Selection: Selecting high-quality materials is crucial for ensuring durability and performance. B2B buyers should inquire about the material specifications and certifications to ensure they meet the necessary industry standards.
-
Pre-treatment Processes: Materials often undergo surface treatments such as annealing or galvanizing to enhance corrosion resistance and improve conductivity. This is particularly important for components exposed to harsh environmental conditions.
What Forming Techniques Are Used in Alternator Manufacturing?
After material preparation, the next stage involves forming the various components of the alternator.

Illustrative image related to signs that alternator is bad
-
Stamping and Machining: Components such as the alternator housing and end plates are typically stamped from sheets of metal, while rotors and stators are machined to precise specifications. Precision in these processes is vital for the seamless assembly of the alternator.
-
Winding: The copper wires are then wound around the stator. This process requires meticulous attention to detail to ensure the correct number of turns and the proper tension, which directly affects the alternator’s output.
How Is Assembly Conducted for Alternators?
Once the components are formed, the assembly process begins, which is crucial for the overall performance of the alternator.
-
Component Integration: The assembly involves integrating the rotor, stator, and other components, such as bearings and voltage regulators. Each part must fit perfectly to avoid operational failures.
-
Testing During Assembly: Many manufacturers employ in-process quality control (IPQC) measures during assembly to catch defects early. This may include functional tests to ensure electrical connections are solid and that the components are correctly aligned.
What Finishing Processes Are Critical for Alternators?
The finishing stage includes processes that enhance the durability and performance of the alternator.
-
Coating and Painting: Protective coatings may be applied to prevent corrosion and wear. For B2B buyers, understanding the type of coatings used can be important, especially for applications in humid or corrosive environments.
-
Final Assembly and Inspection: After finishing, the alternator undergoes final assembly, where all components are secured and connected. Final inspections ensure that the alternator meets all specifications before it is shipped.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Essential for Alternator Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is a fundamental aspect of manufacturing alternators, ensuring that they perform reliably and safely. B2B buyers should be aware of the various quality assurance practices that manufacturers employ.
Which International Standards Should B2B Buyers Consider?
Adhering to international standards is vital for ensuring product quality and safety. The most relevant standards for alternator manufacturing include:
-
ISO 9001: This standard outlines criteria for a quality management system, ensuring that manufacturers consistently provide products that meet customer and regulatory requirements.
-
CE Marking: For products sold in Europe, CE marking indicates compliance with safety, health, and environmental protection standards. B2B buyers should verify that suppliers have the appropriate CE certifications.
-
API Standards: In industries such as automotive and heavy machinery, adherence to API standards ensures that the products meet specific performance criteria.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Alternator Manufacturing?
Quality control checkpoints are established throughout the manufacturing process to identify and rectify defects.
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial inspection checks raw materials and components for compliance with specifications before they are used in production.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): As components are assembled, IPQC measures ensure that each stage meets quality standards. This may include functional tests and visual inspections.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Before shipping, a comprehensive FQC is conducted to confirm that the finished alternators meet all performance and safety criteria.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
Verification of a supplier’s quality control practices is crucial for B2B buyers, particularly when sourcing internationally.
-
Audits and Inspections: Regular audits of suppliers can provide insights into their quality control processes. Buyers should request audit reports and certifications to ensure compliance with relevant standards.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection agencies can help verify that products meet specified quality standards. This is especially important for buyers in regions like Africa and South America, where local standards may vary.
-
Documentation: Suppliers should provide comprehensive documentation, including quality assurance reports and test results, to demonstrate compliance with international standards.
What Are the QC and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
When sourcing alternators internationally, B2B buyers should be aware of specific nuances related to quality control and certifications.
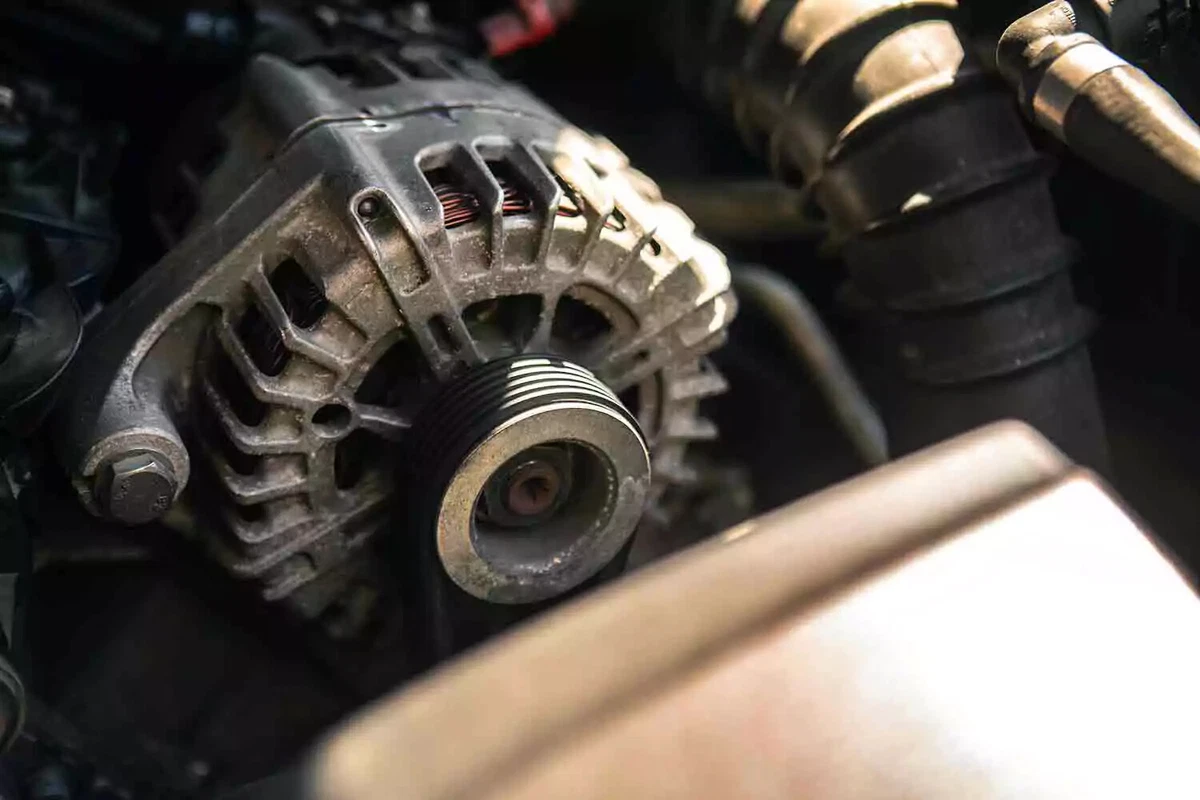
Illustrative image related to signs that alternator is bad
-
Cultural and Regulatory Differences: Different regions may have varying standards and practices. Understanding these differences is essential for ensuring compliance and reliability.
-
Language Barriers: Documentation may be in different languages. Buyers should ensure that they have access to translated materials to understand specifications and compliance requirements fully.
-
Logistics and Supply Chain Considerations: Buyers should consider the logistical challenges associated with international shipping, including customs regulations and potential delays. Clear communication with suppliers can help mitigate these risks.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures associated with alternators, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions when sourcing these critical components. Prioritizing quality and compliance not only ensures operational reliability but also enhances the overall value of their procurement strategies.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘signs that alternator is bad’
In this guide, we aim to equip B2B buyers with a comprehensive checklist for identifying signs of a failing alternator. Understanding these signs is crucial not only for ensuring vehicle performance but also for minimizing downtime and repair costs. This checklist will help you source reliable information and suppliers, ensuring your fleet remains operational.
Step 1: Recognize Common Symptoms of Alternator Failure
Begin by familiarizing yourself with the typical signs of a failing alternator. Key indicators include starting problems, dashboard warning lights, and dimming headlights. Understanding these symptoms allows you to take timely action before they escalate into more significant issues.
Step 2: Document Performance Issues
Keep a detailed record of any performance issues experienced with vehicles in your fleet. Note specific symptoms such as stalling or flickering lights, as these details will be valuable when discussing repairs or replacements with suppliers. Comprehensive documentation helps in negotiating service agreements and understanding the frequency of alternator issues.
Step 3: Evaluate Diagnostic Tools
Invest in diagnostic tools that can help identify alternator problems early. Tools such as multimeters and battery testers can provide insights into the electrical system’s health. Having the right equipment ensures that you can perform regular checks and catch issues before they lead to vehicle breakdowns.
Step 4: Identify Reliable Suppliers
When sourcing alternator replacements or repair services, prioritize suppliers with a proven track record in the automotive industry. Request information about their experience, certifications, and customer reviews. A reliable supplier can significantly reduce your repair time and enhance the overall efficiency of your fleet.
Step 5: Request Detailed Quotations
Always ask for detailed quotations from potential suppliers. This should include labor costs, parts, and any additional fees. Understanding the full scope of expenses will help you budget effectively and avoid unexpected costs down the line.

Illustrative image related to signs that alternator is bad
Step 6: Assess Warranty and Service Options
Inquire about warranty terms and service options for alternators from suppliers. A good warranty can provide peace of mind and protect your investment. Additionally, check if the supplier offers service packages or maintenance plans to ensure long-term support.
Step 7: Conduct Follow-Up Inspections
After repairs or replacements, schedule follow-up inspections to ensure the alternator and electrical system are functioning correctly. Regular maintenance checks can help prevent future issues and extend the lifespan of your vehicles. Establish a routine inspection schedule to stay proactive about vehicle health.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can effectively identify signs of alternator failure, ensure timely procurement of services and parts, and maintain the operational efficiency of their fleet.

Illustrative image related to signs that alternator is bad
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for signs that alternator is bad Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Alternator Signs and Repairs?
When sourcing parts and services related to diagnosing or repairing signs of a faulty alternator, understanding the cost structure is crucial. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margins.
Materials: The cost of materials varies widely based on the quality of the alternator components being used. For instance, premium-grade copper windings and high-grade bearings can significantly increase costs. Selecting cheaper alternatives may lead to lower initial costs but can result in higher maintenance expenses over time.
Labor: Labor costs can fluctuate based on the complexity of the alternator repair or replacement. Skilled technicians are necessary for accurate diagnostics and repairs, and their wages can vary by region. In areas with a higher cost of living, such as parts of Europe, labor costs may be significantly higher.
Illustrative image related to signs that alternator is bad
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes indirect costs associated with the production of alternators, such as factory utilities, depreciation, and administrative expenses. Efficient operations can reduce overhead and thus the overall cost of the alternator.
Tooling: The initial investment in specialized tools required for alternator repairs can also impact pricing. Suppliers who have invested in advanced technology may pass these costs onto buyers.
Quality Control: Rigorous quality assurance processes ensure that the alternators meet safety and performance standards. While this may add to the initial cost, it can prevent costly failures and recalls down the line.
Logistics: Transportation costs can vary widely depending on the distance from the supplier and the chosen shipping method. International shipping may involve additional customs fees and tariffs, which can significantly affect the final price.
Margin: The profit margin included by suppliers will depend on their market strategy, competition, and the perceived value of their products.

Illustrative image related to signs that alternator is bad
How Do Price Influencers Impact the Sourcing of Alternators?
Several factors influence the pricing of alternators and their associated services:
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Bulk purchases can lead to discounts, which is advantageous for larger businesses. Suppliers often provide better pricing for higher volumes, making it essential for buyers to consider their purchasing strategy.
Specifications and Customization: Specific requirements, such as custom alternator designs or additional features, can increase costs. Buyers should weigh the necessity of customization against potential price hikes.
Quality and Certifications: Alternators with certifications (e.g., ISO, CE) typically carry higher prices due to the assurance of quality. Buyers in regions with stringent regulations may need to prioritize certified products, impacting their budget.
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can also influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium for their products, but the assurance of quality and support can justify the additional cost.
Incoterms: Understanding the agreed Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) is vital for international transactions. These terms dictate who bears the costs and risks during shipping and can significantly affect the total landed cost of alternators.
What Are Effective Buyer Tips for Sourcing Alternators?
For international B2B buyers, particularly those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, being strategic in sourcing can lead to significant savings.
Negotiation: Leverage negotiation to achieve better pricing. Understanding the supplier’s cost structure can help buyers identify areas where discounts might be possible.
Cost-Efficiency: Assess the total cost of ownership rather than just the upfront price. Consider factors like durability, maintenance costs, and warranty terms to make a more informed purchasing decision.
Pricing Nuances: Be aware of regional pricing variances due to local market conditions. Prices in emerging markets may differ from those in developed regions, and understanding these nuances can aid in effective budgeting.
Supplier Relationships: Building long-term relationships with suppliers can lead to better terms and pricing. Frequent communication and feedback can foster trust and facilitate smoother transactions.
Disclaimer on Prices: Prices can fluctuate based on market conditions, supply chain disruptions, and currency exchange rates. Buyers should always seek updated quotes to ensure accurate budgeting.
By understanding these components, influencers, and tips, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing alternators and related services, ensuring cost-effectiveness and reliability in their operations.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing signs that alternator is bad With Other Solutions
In the automotive industry, understanding the signs of a failing alternator is crucial for maintaining vehicle performance and preventing costly breakdowns. However, there are alternative methods and technologies that can also help diagnose and address electrical issues in vehicles. This analysis compares the indicators of a bad alternator against other diagnostic solutions, providing valuable insights for B2B buyers who need to make informed decisions for their fleet management or automotive repair services.
| Comparison Aspect | Signs That Alternator Is Bad | Diagnostic Scan Tool | Battery Load Tester |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Identifies electrical issues and potential alternator failures through symptoms | Provides a comprehensive analysis of various electrical components including the alternator | Tests battery capacity under load to determine health and performance |
| Cost | Low to moderate (primarily involves inspection and potential repairs) | Moderate to high (initial purchase cost of the tool) | Low to moderate (affordable for most businesses) |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires manual observation and knowledge of vehicle systems | User-friendly with guided diagnostics for technicians | Simple to use, requiring minimal training for staff |
| Maintenance | Regular visual checks needed; repairs depend on findings | Software updates may be needed for accuracy; hardware should be maintained | Minimal upkeep; replaceable components may be needed over time |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for quick assessments of electrical issues during regular maintenance | Best for comprehensive diagnostics across multiple systems in modern vehicles | Suitable for battery health checks and preventative maintenance |
What Are the Pros and Cons of Using a Diagnostic Scan Tool?
Diagnostic scan tools are valuable for automotive professionals as they provide a comprehensive analysis of the vehicle’s electrical system, including the alternator. The primary advantage of using a scan tool is its ability to deliver detailed error codes and data, allowing technicians to diagnose multiple issues quickly. However, the initial investment can be significant, and technicians need to be trained to interpret the results effectively.
Why Use a Battery Load Tester?
A battery load tester is a cost-effective solution for assessing the health of a vehicle’s battery under load conditions. This tool helps determine if the battery is the root cause of electrical problems, rather than the alternator itself. While it is simple to use and requires minimal training, it does not provide insights into the performance of the alternator or other electrical components, which can be a limitation in diagnosing broader issues.
How Can Buyers Choose the Right Solution?
B2B buyers should consider their specific needs when selecting between these diagnostic options. For businesses focused on preventative maintenance and quick assessments, understanding the signs of a failing alternator might suffice. However, for those managing larger fleets or providing comprehensive automotive services, investing in a diagnostic scan tool could enhance operational efficiency and diagnostic accuracy. Battery load testers serve as an excellent supplementary tool, especially for businesses prioritizing battery health checks. Ultimately, the right choice will depend on the scale of operations, the types of vehicles serviced, and the technical expertise of the team.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for signs that alternator is bad
What Are the Key Technical Properties Related to Bad Alternators?
When evaluating alternators, particularly in the context of identifying signs of failure, several critical technical properties come into play. Understanding these specifications can help B2B buyers make informed decisions regarding procurement and maintenance.
-
Voltage Output
The alternator typically operates within a voltage range of 13.5 to 14.5 volts. This output is crucial for effectively charging the vehicle’s battery and powering electronic components. A voltage output that consistently falls below this range can indicate a failing alternator, leading to battery drainage and electrical system malfunctions. For businesses, monitoring this property ensures optimal performance of fleet vehicles and minimizes downtime. -
Amperage Rating
The amperage rating indicates the maximum current an alternator can provide to the electrical system. Common ratings range from 60 to 200 amps, depending on the vehicle’s requirements. A lower-than-expected amperage output can lead to inadequate charging of the battery and insufficient power for accessories. For B2B buyers managing multiple vehicles, selecting alternators with appropriate amperage ratings is essential to maintain operational efficiency. -
Bearing Quality
The quality of bearings within the alternator affects its longevity and performance. High-grade bearings reduce friction and wear, contributing to quieter operation and less frequent replacements. Businesses should prioritize suppliers who offer alternators with premium bearing materials, as this leads to reduced maintenance costs over time. -
Material Grade
The materials used in the construction of the alternator, such as copper windings and aluminum housings, play a significant role in durability and efficiency. Higher-grade materials can withstand harsher conditions and enhance performance. B2B buyers should consider the material specifications of alternators to ensure they meet industry standards and provide reliable service under varying environmental conditions. -
Thermal Management
Effective thermal management features, such as cooling fins and ventilation designs, are critical for alternator performance. Overheating can lead to premature failure, resulting in costly repairs and downtime. B2B companies should assess thermal management properties when sourcing alternators, particularly for applications in warmer climates or high-demand scenarios.
What Are Common Trade Terms Relevant to Alternator Procurement?
Understanding industry terminology is vital for B2B transactions related to alternators. Here are several key terms that facilitate smoother procurement processes.
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
This term refers to parts made by the original manufacturer of the vehicle. OEM alternators are designed to meet the exact specifications of the original parts. B2B buyers often prefer OEM components for their reliability and compatibility, ensuring that their vehicles operate efficiently. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest amount of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is particularly important for businesses looking to stock alternators or related components. Understanding MOQ helps companies manage inventory costs and avoid overstocking. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document that businesses send to suppliers to request pricing for specific products, including alternators. By issuing an RFQ, companies can compare prices and terms from multiple suppliers, ensuring they secure the best deals for their procurement needs. -
Incoterms
Short for International Commercial Terms, Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding these terms is crucial for B2B buyers sourcing alternators globally, as they outline shipping responsibilities, risk transfers, and cost allocations. -
Warranty Period
The warranty period refers to the duration that a manufacturer guarantees the alternator’s performance. Longer warranty periods often indicate confidence in product quality. B2B buyers should evaluate warranty terms when selecting alternators, as this can impact long-term costs and service reliability.
By familiarizing themselves with these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can enhance their procurement strategies and ensure they are investing in high-quality alternators that meet their operational requirements.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the signs that alternator is bad Sector
What Are the Key Drivers of the Alternator Repair Market?
The global alternator repair market is being shaped by several critical drivers. Increasing vehicle ownership, especially in regions like Africa and South America, is driving demand for automotive parts and services. As emerging economies grow, more consumers are investing in vehicles, leading to a rise in maintenance needs, including alternator repairs. Furthermore, the electrification of vehicles is on the rise, with an increasing number of hybrids and electric vehicles entering the market. This shift necessitates a more nuanced understanding of alternator performance, as these vehicles depend heavily on efficient power management systems.
Current trends also highlight the integration of technology in vehicle diagnostics. Advanced diagnostic tools are now used to identify alternator issues quickly and accurately, reducing the time and cost associated with repairs. This trend is particularly relevant for B2B buyers in the automotive service industry who are seeking to enhance operational efficiency. Additionally, the rise of e-commerce platforms is transforming how businesses source alternators and related components, enabling them to access a wider range of suppliers and competitive pricing.
How Is Sustainability Influencing B2B Sourcing for Alternators?
Sustainability is becoming increasingly important in the sourcing of automotive parts, including alternators. The environmental impact of automotive manufacturing and repair is significant, and businesses are under pressure to adopt more sustainable practices. Ethical sourcing has gained traction, with companies looking for suppliers that adhere to responsible manufacturing processes. This includes sourcing materials that minimize environmental harm and ensuring that labor practices are ethical and fair.
Green certifications and materials are also becoming essential in the alternator sector. Buyers are increasingly favoring suppliers that offer products made from recycled or sustainably sourced materials. This not only appeals to environmentally conscious consumers but also helps businesses comply with evolving regulations regarding environmental sustainability. By aligning with sustainable practices, B2B buyers can enhance their brand reputation and attract a broader customer base.
What Is the Historical Context of Alternator Development in B2B Markets?
The alternator has evolved significantly since its inception in the early 20th century. Originally designed to provide a reliable source of electrical power for vehicles, the alternator has undergone extensive technological advancements. Early models were relatively simple, primarily providing power for lighting and ignition. However, as vehicles became more sophisticated with the introduction of electronic components, the alternator’s role expanded.
Illustrative image related to signs that alternator is bad
In the B2B context, this evolution has led to increased complexity in sourcing and servicing alternators. Modern alternators are equipped with advanced features such as smart charging technology, which optimizes battery performance and extends lifespan. This evolution necessitates that B2B buyers stay informed about the latest advancements and trends in alternator technology to ensure they are sourcing the best products for their needs.
Conclusion
Understanding the market dynamics and sourcing trends related to alternators is crucial for B2B buyers. By keeping abreast of key drivers, sustainability initiatives, and the historical evolution of this vital automotive component, businesses can make informed decisions that not only meet their operational needs but also align with broader market trends. This knowledge ultimately enhances their competitive edge in an increasingly complex automotive landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of signs that alternator is bad
-
How do I identify the signs that an alternator is failing?
To identify a failing alternator, look for several key signs: difficulty starting the vehicle, dimming or flickering headlights, and unusual smells, such as burning rubber or electrical odors. Additionally, if you notice that electronic features like power windows or air conditioning are malfunctioning, it may indicate alternator issues. Regular maintenance checks can help catch these signs early, preventing more extensive repairs or operational downtime. -
What should I do if I suspect my alternator is bad?
If you suspect your alternator is failing, the first step is to perform a visual inspection of the vehicle’s electrical system. Check for warning lights on the dashboard, listen for unusual noises, and assess the condition of the battery. If problems persist, consult a qualified mechanic or automotive expert to conduct a thorough diagnostic. Timely intervention can save costs and ensure the reliability of your vehicle’s performance. -
What is the best alternator replacement for different vehicle types?
The best alternator replacement depends on the specific make and model of the vehicle, as well as its electrical requirements. It’s advisable to source OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) parts for optimal performance, particularly in high-demand vehicles. For international buyers, consider suppliers who offer a range of alternator options tailored to various vehicle types and provide comprehensive product specifications to ensure compatibility. -
How can I vet suppliers for alternator parts effectively?
When vetting suppliers for alternator parts, check their industry reputation, certifications, and customer reviews. Request samples to evaluate product quality and ensure they meet your specifications. Additionally, verify their supply chain reliability, especially for international shipping, and inquire about their quality assurance processes. Building relationships with reputable suppliers can enhance your procurement strategy and ensure consistent product availability. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for alternators?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for alternators can vary significantly among suppliers. Typically, MOQs range from 10 to 100 units, depending on the manufacturer’s production capabilities and the specific part. For international buyers, it is beneficial to negotiate MOQs that align with your inventory needs and storage capabilities, ensuring you maintain a steady supply without overcommitting capital. -
What payment terms are common for international alternator purchases?
Common payment terms for international alternator purchases include options like letters of credit, bank transfers, or payment upon delivery. Many suppliers offer flexible payment plans, especially for bulk orders. It’s essential to discuss and agree on payment terms upfront to avoid any misunderstandings. Additionally, ensure that the terms are documented in the purchase agreement for transparency and security. -
How can I ensure quality assurance for alternator components?
To ensure quality assurance for alternator components, work with suppliers who adhere to international quality standards, such as ISO certification. Request documentation of quality tests performed on the alternators, and consider conducting random inspections upon receipt of goods. Establishing clear quality expectations in your agreements will help mitigate the risk of defective parts entering your supply chain. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing alternators?
When importing alternators, consider factors such as shipping methods, customs regulations, and potential tariffs. Choose reliable logistics partners experienced in handling automotive parts to minimize delays. Ensure that you understand the documentation required for customs clearance, including invoices and packing lists. Planning for potential delays and having contingency measures in place can help maintain your supply chain efficiency.
Top 3 Signs That Alternator Is Bad Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Reddit – Alternator Issues Explained
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: This company, Reddit – Alternator Issues Explained, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
2. Toyota – Alternator
Domain: toyotaofgreenville.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: The alternator is a crucial component in vehicles, responsible for recycling power from the car battery while driving. It supplies power to various systems including climate control, engine management, and entertainment. Signs of a failing alternator include dim lights, dashboard warning lights, weak or dead batteries, strange smells (like burning rubber), odd sounds (grinding or whining), and vis…
3. Alternator Replacement – Cost Overview
Domain: rac.co.uk
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Alternator replacement cost in the UK ranges from £250 to £800, with an average cost of £535.05 for parts and labor. Specific average replacement costs by manufacturer include: Audi £628.59, BMW £603.37, Citroen £629.99, Ford £494.90, Mercedes £614.57, MINI £549.36, Nissan £482.06, Peugeot £663.06, Renault £587.78, Toyota £477.93, Vauxhall £477.93, Volkswagen £507.07, Volvo £539.62.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for signs that alternator is bad
In conclusion, understanding the signs of a failing alternator is crucial for businesses reliant on vehicle performance. Key indicators such as starting difficulties, warning lights, and fluctuating electrical systems can prevent costly breakdowns and unplanned downtimes. For international B2B buyers, especially in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, strategic sourcing of high-quality alternators and related components is essential to ensure operational efficiency and reliability.

Illustrative image related to signs that alternator is bad
Investing in reliable suppliers not only mitigates the risk of alternator failures but also enhances the overall longevity of your fleet. Collaborating with experienced manufacturers and distributors can provide access to advanced technologies and superior products tailored to your specific market needs.
As you consider your sourcing strategies, prioritize partnerships that offer robust warranties and comprehensive support services. This proactive approach will safeguard your investments and ensure your fleet remains operational, ultimately driving your business forward. Embrace this opportunity to enhance your supply chain resilience and maintain a competitive edge in your industry. Take action today to secure the best alternator solutions for your fleet’s needs.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.