Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for how to test starter motor solenoid
In the competitive landscape of automotive repair and maintenance, effectively testing a starter motor solenoid is crucial for ensuring reliable vehicle performance. Many businesses face challenges in diagnosing electrical issues, which can lead to costly repairs and downtime. This guide on how to test starter motor solenoids provides a comprehensive overview tailored for international B2B buyers, especially those operating in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including markets like Saudi Arabia and Germany.
Our in-depth resource covers various testing methods, including visual inspections, electrical assessments, and practical troubleshooting techniques. We delve into the types of starter motor solenoids available, their applications across different vehicle models, and the importance of proper supplier vetting to ensure high-quality components. Moreover, we address cost considerations, helping you navigate pricing structures and potential sourcing strategies.
By empowering businesses with actionable insights, this guide enables informed purchasing decisions that can enhance operational efficiency and minimize repair costs. Whether you are a fleet manager, automotive service provider, or parts distributor, understanding how to effectively test starter motor solenoids is essential for maintaining your vehicles and ensuring customer satisfaction. With this knowledge, you can confidently approach suppliers and optimize your procurement process in a global market.
Table Of Contents
- Top 4 How To Test Starter Motor Solenoid Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for how to test starter motor solenoid
- Understanding how to test starter motor solenoid Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of how to test starter motor solenoid
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘how to test starter motor solenoid’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for how to test starter motor solenoid
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for how to test starter motor solenoid
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘how to test starter motor solenoid’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for how to test starter motor solenoid Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing how to test starter motor solenoid With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for how to test starter motor solenoid
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the how to test starter motor solenoid Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of how to test starter motor solenoid
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for how to test starter motor solenoid
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Understanding how to test starter motor solenoid Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Visual Inspection | Basic check for physical damage and proper connections | Automotive repair shops, fleet maintenance | Pros: Quick and cost-effective. Cons: May overlook internal faults. |
| Multimeter Testing | Measures voltage and resistance to assess functionality | Diagnostic services, automotive parts suppliers | Pros: Provides precise measurements. Cons: Requires technical knowledge. |
| Test Light Method | Uses a test light to check power flow through the solenoid | Auto service centers, DIY workshops | Pros: Simple setup, effective for basic checks. Cons: Limited diagnostic depth. |
| Bench Testing | Involves removing the solenoid and testing it outside the vehicle | Specialized repair shops | Pros: Comprehensive analysis of solenoid performance. Cons: Time-consuming and requires tools. |
| Load Testing | Assesses solenoid performance under load conditions | Heavy machinery, commercial vehicle services | Pros: Accurate representation of real-world performance. Cons: More complex setup required. |
What Are the Characteristics of Visual Inspection for Starter Motor Solenoid Testing?
Visual inspection is the most straightforward method for assessing the starter motor solenoid. It involves checking for obvious signs of wear, damage, or loose connections. This method is particularly suitable for automotive repair shops and fleet maintenance operations where quick assessments are needed. While it is cost-effective and requires minimal tools, it may not detect internal faults, making it less reliable for comprehensive diagnostics.
How Does Multimeter Testing Provide Insight into Solenoid Functionality?
Multimeter testing is a precise method that measures voltage and resistance levels within the solenoid. This technique is essential for diagnostic services and automotive parts suppliers, allowing technicians to pinpoint electrical issues accurately. While it provides detailed insights into solenoid functionality, it requires a certain level of technical expertise, which can be a barrier for some buyers.
Why Use the Test Light Method for Quick Diagnostics?
The test light method is a practical approach that employs a simple test light to check for power flow through the solenoid. This method is ideal for auto service centers and DIY workshops, offering a quick and effective way to determine whether the solenoid is receiving power. However, its limitations include a lack of depth in diagnostics, as it does not measure voltage levels or resistance.
What Are the Benefits of Bench Testing for Starter Motor Solenoids?
Bench testing involves removing the solenoid from the vehicle and testing it in a controlled environment. This method is favored by specialized repair shops that need to conduct thorough evaluations of solenoid performance. While it offers the most comprehensive analysis, the process is time-consuming and requires specific tools, which may not be feasible for all buyers.
How Does Load Testing Ensure Reliable Performance of Solenoids?
Load testing assesses the solenoid’s performance under actual operating conditions, making it crucial for heavy machinery and commercial vehicle services. This method provides an accurate representation of how the solenoid will perform in real-world scenarios. However, it requires a more complex setup and can be resource-intensive, which may limit its use among smaller operations or those with budget constraints.
Key Industrial Applications of how to test starter motor solenoid
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of how to test starter motor solenoid | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive Repair | Diagnostic testing of starter systems in vehicles | Improved service efficiency and customer satisfaction | Availability of quality testing equipment and components |
| Construction Equipment | Maintenance checks on heavy machinery starters | Reduced downtime and increased productivity | Access to specialized tools for various machine types |
| Transportation & Logistics | Ensuring reliability of fleet vehicles | Enhanced fleet reliability and reduced operational costs | Compatibility with diverse vehicle models |
| Agriculture Machinery | Testing solenoids in tractors and harvesters | Increased uptime during critical harvest periods | Knowledge of agricultural machinery specifications |
| Marine & Aerospace | Troubleshooting starter systems in boats and aircraft | Safety and operational integrity assurance | Availability of marine and aerospace-specific parts |
How is ‘how to test starter motor solenoid’ applied in the automotive repair sector?
In the automotive repair industry, testing the starter motor solenoid is a crucial diagnostic step when vehicles fail to start. Technicians utilize specialized tools to check the solenoid’s functionality, ensuring that the electrical current flows correctly from the battery to the starter. This process helps identify whether the problem lies within the solenoid, the starter, or the battery itself, thus minimizing unnecessary repairs and enhancing customer satisfaction. For international buyers, sourcing reliable diagnostic tools and solenoids that meet local vehicle specifications is essential.
What role does testing starter motor solenoids play in construction equipment maintenance?
In construction, heavy machinery often relies on robust starting systems to ensure operational efficiency. Regular testing of starter motor solenoids prevents unexpected machinery failures that can lead to costly downtime. By implementing a proactive maintenance schedule that includes solenoid testing, construction companies can enhance productivity and reduce repair costs. Buyers in this sector should consider sourcing durable testing equipment capable of withstanding harsh working environments and compatible with various machinery types.
How does testing solenoids contribute to fleet vehicle reliability in transportation and logistics?
For transportation and logistics companies, fleet reliability is paramount. Regular testing of starter motor solenoids ensures that vehicles start smoothly, which is critical for timely deliveries. By diagnosing and addressing solenoid issues early, companies can avoid breakdowns that disrupt operations and lead to financial losses. Sourcing high-quality solenoids and testing equipment that cater to a diverse range of vehicle models is crucial for maintaining fleet integrity across different regions, including Africa and South America.
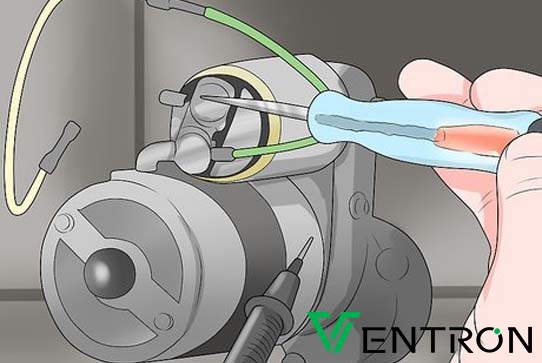
Illustrative image related to how to test starter motor solenoid
Why is testing starter motor solenoids vital for agricultural machinery?
In the agriculture sector, the performance of equipment such as tractors and harvesters can significantly affect productivity, especially during peak seasons. Testing starter motor solenoids ensures that these machines are ready for operation when needed. By identifying potential failures early, farmers can avoid delays that could impact crop yields. International buyers should focus on sourcing solenoids and testing tools that align with the specific requirements of their agricultural machinery, ensuring compatibility and reliability.
How is starter motor solenoid testing applied in marine and aerospace industries?
In the marine and aerospace industries, where safety is critical, testing starter motor solenoids is essential for operational integrity. These sectors require stringent checks to ensure that starting systems function correctly, preventing potential failures during critical operations. By utilizing specialized testing equipment, companies can maintain high safety standards and reliability. Buyers in these industries should prioritize sourcing parts and tools that meet stringent regulatory requirements and are designed for high-performance environments.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘how to test starter motor solenoid’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Identifying the Root Cause of Starting Issues
The Problem: B2B buyers often encounter a situation where vehicles fail to start, but the source of the problem is unclear. It could be the starter motor, solenoid, or even the battery. This ambiguity can lead to unnecessary parts replacements and extended downtime, which is particularly costly for businesses that rely on their vehicles for operations. The inability to quickly diagnose the issue can frustrate technicians and lead to a loss of productivity.
The Solution: To effectively identify the problem, start by performing a systematic approach to testing the starter motor solenoid. Begin with a simple battery check using a voltmeter to ensure it has sufficient charge (around 12 volts). If the battery is fine, proceed to test the solenoid directly. Listen for a clicking sound when turning the ignition; this indicates whether the solenoid is attempting to engage. If there’s no sound, check the connections and ground, as loose or corroded wires can impede functionality. By following these steps, technicians can accurately diagnose whether the issue lies with the solenoid, starter motor, or battery, ensuring efficient repairs and reduced downtime.
Scenario 2: Complicated Testing Procedures for Non-Technical Staff
The Problem: Many B2B companies employ staff who may not have extensive technical training but are responsible for vehicle maintenance. These employees often struggle with the technical aspects of testing components like the starter motor solenoid, leading to confusion and potential errors during the testing process. This knowledge gap can result in misdiagnosis, wasted resources, and delays in getting vehicles back into service.
The Solution: To empower non-technical staff, create a step-by-step testing guide that breaks down the process into clear, easy-to-follow instructions. This guide should include visual aids, such as diagrams or photos of the starter solenoid’s location and connections. Additionally, providing hands-on training sessions can help demystify the process. For instance, during a training session, illustrate how to use a test light or voltmeter to check for current flow. By simplifying the testing procedures and offering practical training, companies can enable their staff to conduct basic diagnostics confidently and accurately, improving overall operational efficiency.
Scenario 3: Sourcing Quality Replacement Parts Efficiently
The Problem: When a starter motor solenoid fails, sourcing the correct replacement parts can be a significant challenge for B2B buyers. With numerous suppliers and varying quality levels, businesses risk purchasing subpar components that can lead to further mechanical issues or shortened lifespans. This not only affects vehicle reliability but also increases maintenance costs, creating a cycle of inefficiency and frustration.
The Solution: To streamline the sourcing process, establish partnerships with reputable suppliers who provide high-quality starter motor solenoids. Create a checklist of specifications for the parts needed, including compatibility with specific vehicle makes and models, warranty information, and certifications. Leverage online platforms that offer reviews and ratings for different suppliers to make informed decisions. Additionally, consider bulk purchasing options to reduce costs and ensure a readily available inventory for quick replacements. Implementing a systematic approach to sourcing will not only enhance the reliability of vehicle operations but also contribute to long-term cost savings and operational efficiency.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for how to test starter motor solenoid
What Materials are Commonly Used for Testing Starter Motor Solenoids?
When testing starter motor solenoids, the choice of materials for the testing equipment is crucial. Different materials offer unique properties that can affect the performance and reliability of the testing process. Below, we analyze four common materials used in the context of testing starter motor solenoids, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international B2B buyers.
1. Copper
Key Properties:
Copper is known for its excellent electrical conductivity, which is critical for effective testing of electrical components like solenoids. It also has good thermal conductivity, allowing for efficient heat dissipation during testing.
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage of copper is its high conductivity, which ensures accurate readings and efficient power transfer. However, copper is prone to corrosion, especially in humid environments, which can affect its longevity and reliability.
Impact on Application:
Copper’s compatibility with various electrical media makes it suitable for testing solenoids, but its susceptibility to oxidation may necessitate regular maintenance or protective coatings.
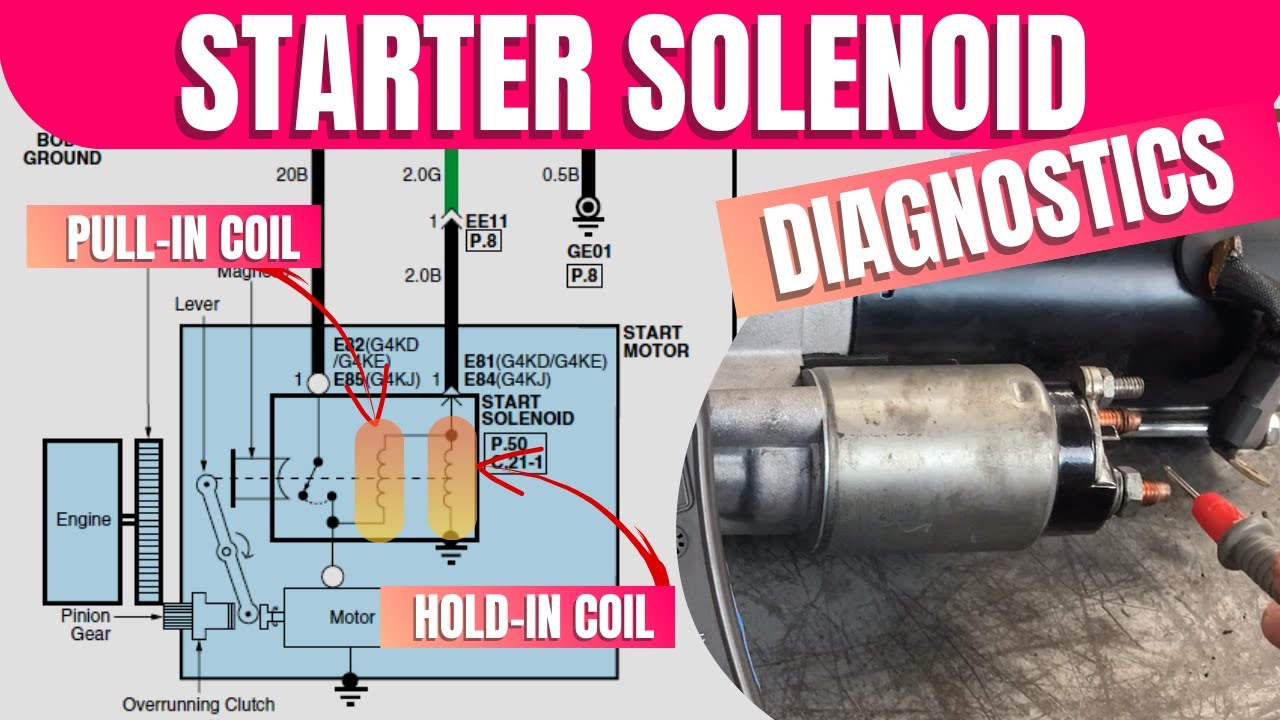
Illustrative image related to how to test starter motor solenoid
International Considerations:
In regions like Europe and the Middle East, compliance with standards such as DIN and ASTM is essential. Buyers should ensure that the copper used meets these standards, particularly regarding electrical conductivity and corrosion resistance.
2. Aluminum
Key Properties:
Aluminum is lightweight and offers good conductivity, though not as high as copper. It has excellent corrosion resistance, making it suitable for various environments.
Pros & Cons:
The lightweight nature of aluminum makes it easy to handle during testing. Its corrosion resistance is a significant advantage in humid or coastal regions. However, its lower conductivity compared to copper may lead to less accurate readings.
Impact on Application:
Aluminum is compatible with many testing applications, but users must be aware of its limitations in high-current scenarios where copper would be more effective.
International Considerations:
Aluminum’s widespread use means it generally meets international standards. However, buyers should verify that the aluminum components used in testing equipment comply with local regulations, particularly in South America and Africa.
3. Steel
Key Properties:
Steel is known for its strength and durability, making it a common choice for structural components in testing equipment. It has moderate electrical conductivity and is often coated to enhance corrosion resistance.
Pros & Cons:
The durability of steel is a significant advantage, especially in rugged testing environments. However, its lower conductivity compared to copper and aluminum can lead to inefficiencies in testing.
Impact on Application:
Steel is typically used for housing or structural elements of testing devices rather than the conductive components. Its compatibility with various media is generally acceptable, but it may require additional coatings for corrosion protection.
International Considerations:
Steel components must comply with various international standards, including JIS and ASTM. Buyers should ensure that the steel used is of appropriate grade and treated to withstand environmental conditions in their specific regions.
4. Plastic Composites
Key Properties:
Plastic composites are lightweight, resistant to corrosion, and can be engineered for specific electrical properties, including insulation.
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage of plastic composites is their corrosion resistance and versatility in design. However, they may not withstand high temperatures or mechanical stresses as well as metals.
Impact on Application:
Plastic composites are often used for insulating components in testing equipment, making them suitable for applications where electrical isolation is critical. However, their use in high-stress environments may be limited.
International Considerations:
Plastic composites must meet specific safety and performance standards, especially in regions like Europe, where regulations are stringent. Buyers should ensure compliance with relevant standards to guarantee product reliability.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Testing Starter Motor Solenoids
| Material | Typical Use Case for how to test starter motor solenoid | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Copper | Conductive wiring and test leads | High electrical conductivity | Prone to corrosion | Medium |
| Aluminum | Lightweight test equipment components | Excellent corrosion resistance | Lower conductivity than copper | Medium |
| Steel | Structural components and housings | High strength and durability | Moderate electrical conductivity | Low |
| Plastic Composites | Insulating components in testing devices | Corrosion resistant and versatile | Limited high-temperature performance | Low |
This strategic material selection guide provides international B2B buyers with critical insights into the materials used for testing starter motor solenoids, enabling informed decisions that align with specific operational needs and regional compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for how to test starter motor solenoid
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Starter Motor Solenoids?
Manufacturing starter motor solenoids involves several critical stages that ensure the final product meets both performance and quality standards. Understanding these stages is essential for B2B buyers looking to partner with reliable suppliers.
How Is Material Prepared for Starter Motor Solenoid Manufacturing?
The manufacturing process begins with material preparation, where high-quality raw materials, such as copper for wiring and durable plastics or metals for the casing, are sourced. Suppliers often use materials that meet specific international standards to ensure longevity and performance. For solenoids, materials must be resistant to corrosion and capable of withstanding high temperatures.
Before production, materials undergo inspection to verify their compliance with industry specifications. This step is crucial in preventing defects that could lead to operational failures in starter systems.
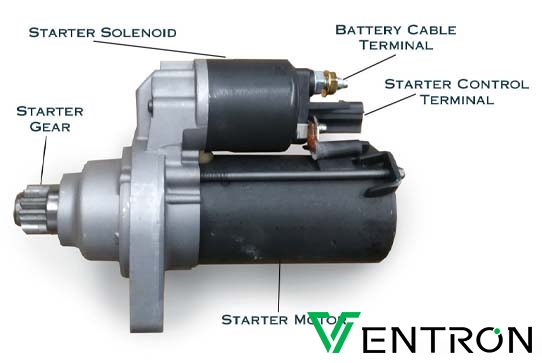
Illustrative image related to how to test starter motor solenoid
What Techniques Are Used in the Forming Stage?
In the forming stage, manufacturers employ techniques such as stamping, machining, and molding to create the various components of the starter motor solenoid.
-
Stamping: This technique is often used for creating metal parts, such as the solenoid casing, from flat sheets of metal. Precision stamping ensures that each component is uniform in size and shape, reducing variability in the assembly process.
-
Machining: For components that require tight tolerances, machining processes like CNC milling and turning are utilized. This allows for precise fitting of parts, which is crucial for the solenoid’s performance.
-
Molding: Plastic parts, including the housing and insulation components, are typically produced through injection molding. This method offers flexibility in design and ensures consistent quality across batches.
How Are Components Assembled in Starter Motor Solenoid Production?
The assembly phase is where the individual components come together to form a complete starter motor solenoid. This process is often semi-automated to enhance efficiency while maintaining quality control.
During assembly, technicians or machines install the solenoid’s coil, plunger, and casing, ensuring that all components fit perfectly. The assembly line is designed to facilitate quick assembly while allowing for real-time quality checks.
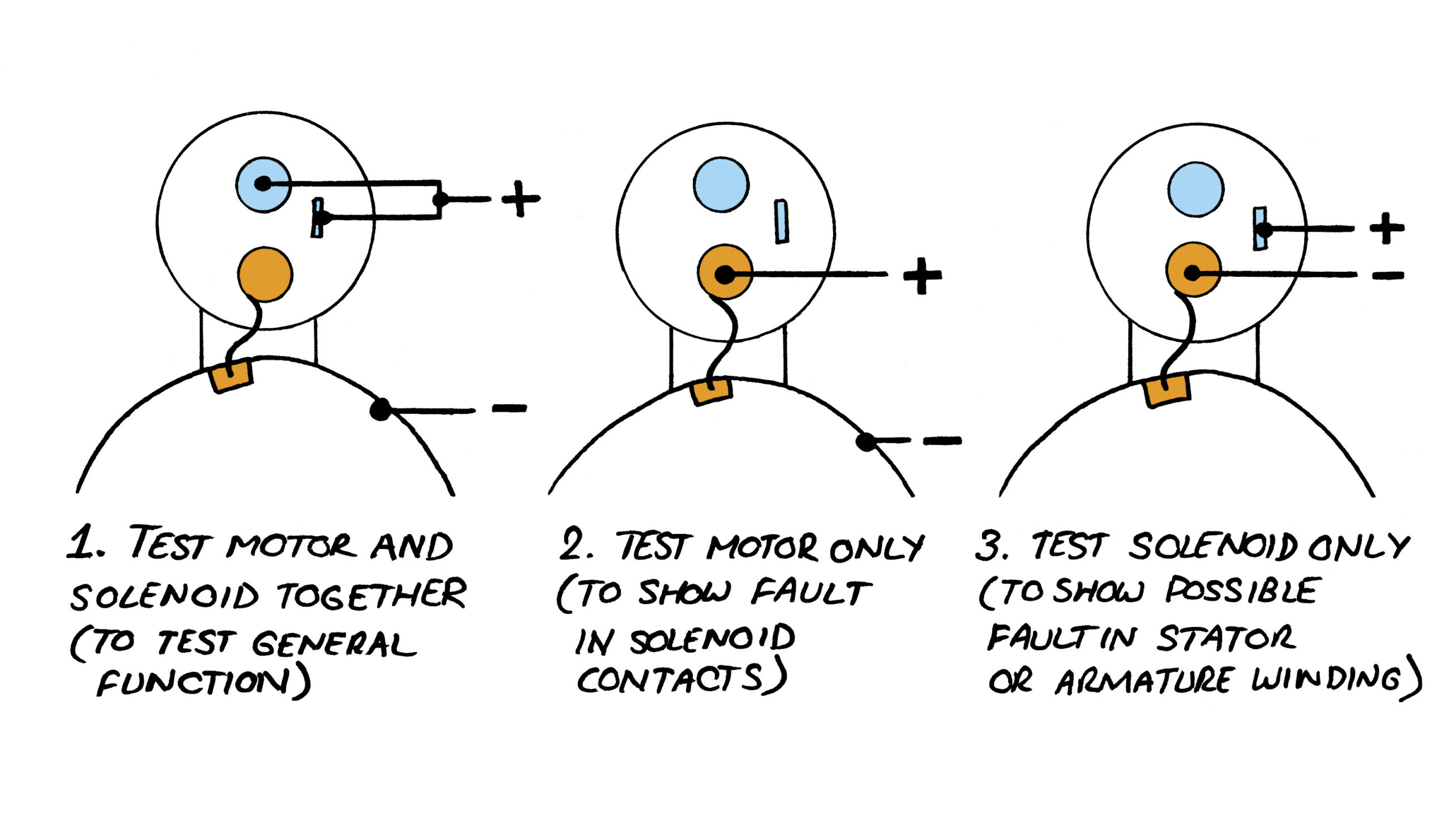
Illustrative image related to how to test starter motor solenoid
What Finishing Processes Are Common in Solenoid Manufacturing?
Finishing processes are essential for enhancing the durability and performance of the starter motor solenoid. Common finishing techniques include:
- Coating: Applying protective coatings to metal components to prevent corrosion and enhance electrical conductivity.
- Cleaning: Post-assembly cleaning ensures that no debris or contaminants remain, which could affect performance.
- Testing: Each solenoid undergoes rigorous testing to ensure it meets operational specifications before packaging.
What Quality Assurance Standards Are Relevant for Starter Motor Solenoids?
Quality assurance is a vital aspect of manufacturing starter motor solenoids. B2B buyers should be aware of the international and industry-specific standards that suppliers must adhere to.
Which International Standards Should Buyers Look For?
ISO 9001 is a globally recognized standard that outlines the criteria for a quality management system. Manufacturers certified under this standard demonstrate their commitment to quality and continuous improvement.
In addition to ISO 9001, industry-specific certifications such as CE (Conformité Européenne) for products sold in Europe and API (American Petroleum Institute) standards for automotive components may also apply. These certifications ensure that products comply with safety, health, and environmental regulations.

Illustrative image related to how to test starter motor solenoid
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Solenoid Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are crucial for maintaining the integrity of the manufacturing process. Common QC checkpoints include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials and components upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Throughout the manufacturing process, real-time checks are performed to identify and rectify defects early. This may include dimensional checks, visual inspections, and functional tests.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Before products are packaged and shipped, final inspections are conducted to ensure that each solenoid meets the required specifications and performance criteria.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
For international buyers, especially those from diverse regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control practices is essential.
What Audits and Reports Should Be Considered?
Buyers should request access to the supplier’s quality management system documentation, including audit reports and quality manuals. Regular internal and external audits conducted by third-party organizations can provide insights into the supplier’s adherence to quality standards.
Additionally, buyers should consider implementing their own audits to assess compliance with quality assurance protocols. This proactive approach ensures that the supplier aligns with the buyer’s quality expectations.
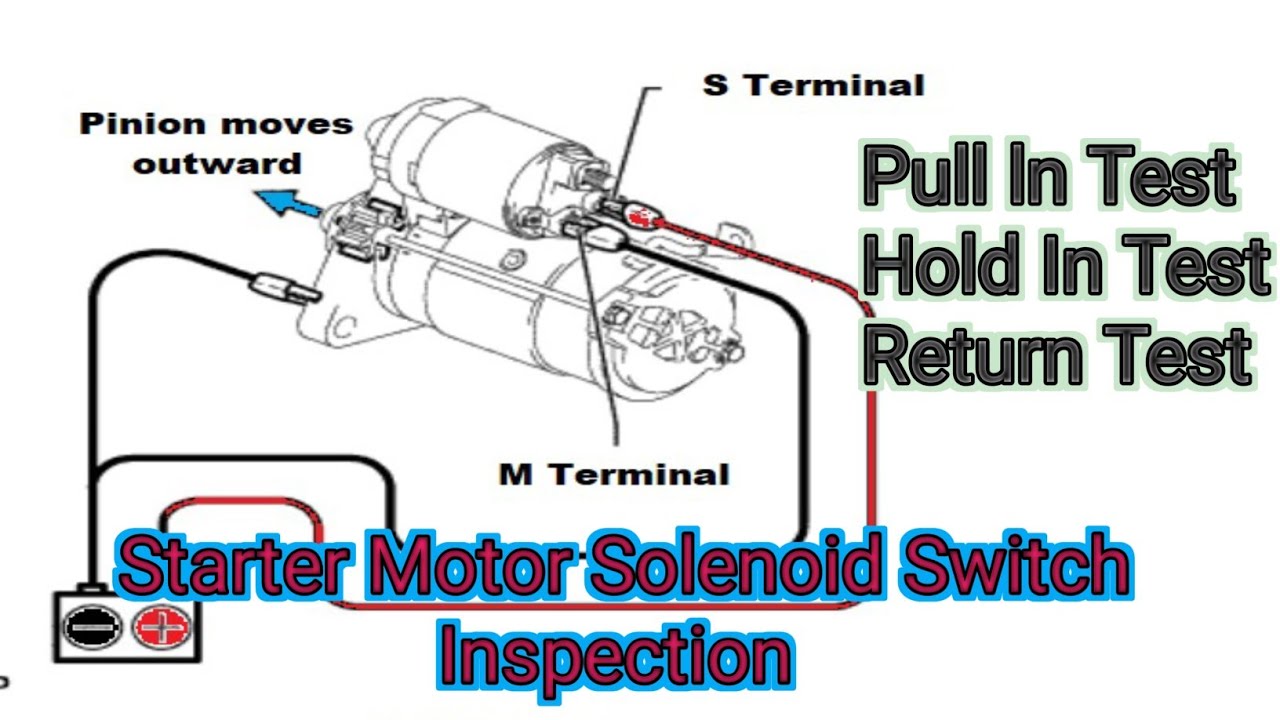
Illustrative image related to how to test starter motor solenoid
How Do Third-Party Inspections Work?
Third-party inspections offer an unbiased evaluation of the manufacturing process and product quality. By engaging independent inspection agencies, buyers can gain confidence in the reliability of the supplier’s products. These inspections typically include checks on raw materials, manufacturing processes, and final product evaluations.
What Quality Control Nuances Should International Buyers Be Aware Of?
Understanding the nuances of quality control in different regions is crucial for international B2B buyers.
-
Cultural Differences: Different countries may have varying standards and practices related to quality assurance. Buyers should familiarize themselves with local regulations and expectations to ensure compliance.
-
Logistics and Supply Chain Factors: International logistics can impact product quality. Ensuring that suppliers have robust logistics and supply chain management practices in place is essential to maintain product integrity from the factory to the end-user.
-
Communication and Transparency: Establishing clear communication channels with suppliers enhances transparency in quality control processes. Regular updates and open dialogue can help address potential quality issues before they escalate.
By focusing on these manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when selecting suppliers for starter motor solenoids, ensuring they receive reliable, high-quality products that meet their operational needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘how to test starter motor solenoid’
Introduction
This practical sourcing guide aims to provide B2B buyers with a systematic approach to acquiring the necessary tools and knowledge for testing starter motor solenoids. Understanding how to accurately test these components is vital for ensuring automotive reliability, reducing downtime, and optimizing maintenance costs. By following this checklist, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is the cornerstone of any successful procurement process. Identify the specific requirements for the starter motor solenoid testing tools, including voltage ranges, compatibility with different vehicle models, and whether you need manual or digital testing equipment. This clarity will help streamline your sourcing process.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify reputable suppliers who specialize in automotive testing equipment. Look for suppliers with a strong track record in the industry, positive customer feedback, and comprehensive product offerings. Investigate their presence in your target markets, such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, as local support can be a significant advantage.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Before making a commitment, verify that potential suppliers hold relevant certifications and comply with industry standards. Certifications like ISO 9001 for quality management systems or CE marking for safety can provide assurance of product reliability and adherence to international standards. This step is crucial for minimizing risk and ensuring that your investment meets quality expectations.
Step 4: Request Product Samples
Where possible, request samples of the testing equipment before finalizing your order. Testing samples allows you to assess the quality, usability, and effectiveness of the tools in real-world conditions. Pay attention to the ease of use and whether the equipment meets your technical specifications, as this can impact your team’s efficiency.
Step 5: Compare Pricing and Terms
Gather quotes from multiple suppliers to compare pricing and payment terms. Ensure you understand the total cost of ownership, which includes not only the purchase price but also shipping, taxes, and potential customs fees. Look for suppliers who offer favorable payment terms, as this can impact your cash flow positively.
Step 6: Assess After-Sales Support and Warranty
Investigate the after-sales support offered by potential suppliers, as this can be a critical factor in your decision-making process. Ensure they provide adequate training, troubleshooting assistance, and a clear warranty policy. A strong support system can enhance your operational efficiency and provide peace of mind in the long run.
Step 7: Finalize Your Purchase Decision
After evaluating all factors—technical specifications, supplier reliability, pricing, and support—make an informed purchase decision. Ensure that all agreements are documented, including warranties and service agreements. A well-documented purchase helps protect your interests and ensures clarity in future interactions with the supplier.
By following these steps, B2B buyers can effectively navigate the sourcing process for testing starter motor solenoids, ensuring they invest in reliable tools that meet their operational needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for how to test starter motor solenoid Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Testing Starter Motor Solenoids?
Understanding the cost structure associated with testing starter motor solenoids is crucial for international B2B buyers. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margins.
-
Materials: The materials used in starter motor solenoid testing typically include electrical components (such as solenoids and wiring), tools (like voltmeters and test lights), and safety equipment. Sourcing quality materials is essential to ensure reliability and accuracy during testing.
-
Labor: Labor costs can vary significantly based on geographical location, expertise, and training levels of technicians. In regions with higher labor costs, such as Western Europe, buyers may experience increased service fees. Conversely, in emerging markets like Africa and South America, labor may be more cost-effective, but buyers should ensure that technicians are adequately trained.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses expenses related to facilities, equipment maintenance, utilities, and administrative costs. Buyers should consider suppliers with optimized manufacturing processes that can reduce overhead costs.
-
Tooling: Specialized tools for testing starter motor solenoids can require significant investment. Buyers should evaluate the necessity of owning versus renting tools based on their testing volume and frequency.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing rigorous QC processes is vital to ensure the reliability of testing procedures. Costs associated with QC can include equipment calibration, staff training, and compliance with industry standards.
-
Logistics: Transportation and handling costs can impact the overall pricing structure. International buyers must factor in import duties, shipping fees, and potential delays that can arise from customs processes.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically include a profit margin in their pricing. Understanding the expected margin can help buyers negotiate better deals and identify suppliers who offer competitive pricing without compromising quality.
How Do Price Influencers Affect the Cost of Testing Starter Motor Solenoids?
Several factors influence the pricing of starter motor solenoid testing services:
-
Volume/MOQ: Suppliers often offer discounts for bulk purchases or larger minimum order quantities (MOQs). Buyers should assess their testing needs to capitalize on volume pricing.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom solutions may incur higher costs due to additional engineering and manufacturing efforts. Buyers should define their requirements clearly to avoid unnecessary expenses.
-
Materials: The quality of materials used can significantly affect pricing. High-grade materials may cost more upfront but can reduce long-term maintenance and replacement costs.
-
Quality/Certifications: Products with industry certifications or higher quality standards often command higher prices. Buyers should weigh the benefits of these certifications against their budget constraints.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation, location, and reliability of suppliers can influence pricing. Establishing relationships with reputable suppliers can lead to better pricing and service.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is essential for international transactions. They define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping costs, insurance, and risk, which can impact the total cost of ownership.
What Tips Can Help Buyers Optimize Costs When Sourcing Solenoid Testing Services?
To maximize value when sourcing starter motor solenoid testing services, buyers should consider the following strategies:
-
Negotiation: Engage in negotiations with suppliers to secure better pricing, especially for bulk orders. Highlighting long-term partnership potential can incentivize suppliers to offer discounts.
-
Cost Efficiency: Look for suppliers that provide comprehensive services, including testing, maintenance, and repair, to reduce the total cost of ownership. Bundling services can lead to significant savings.
-
Total Cost of Ownership: Assess not just the initial purchase price but also ongoing costs such as maintenance, repairs, and potential downtime. A higher upfront cost may be justified by lower long-term expenses.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Be aware of currency fluctuations, tariffs, and local market conditions that may affect pricing. Establishing contracts in stable currencies can mitigate risks.
-
Disclaimer for Indicative Prices: Pricing can vary widely based on the aforementioned factors. Buyers should seek quotes from multiple suppliers to ensure competitive pricing and make informed decisions.
By carefully evaluating these cost components and price influencers, international B2B buyers can make strategic sourcing decisions that align with their operational needs and budget constraints.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing how to test starter motor solenoid With Other Solutions
Introduction to Alternatives for Testing Starter Motor Solenoids
When it comes to diagnosing issues with starter motor solenoids, various methods can be employed. While traditional testing techniques have proven effective, alternative solutions may offer advantages in specific contexts, such as speed, accuracy, or cost-effectiveness. This section will compare the conventional method of testing a starter motor solenoid with two viable alternatives: using a multimeter and employing an advanced diagnostic tool. Understanding these alternatives can help B2B buyers make informed decisions based on their unique operational needs.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | How To Test Starter Motor Solenoid | Multimeter Testing | Advanced Diagnostic Tool |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Reliable for basic diagnostics | High accuracy in voltage measurement | Comprehensive diagnostics |
| Cost | Low cost (basic tools needed) | Moderate cost (multimeter required) | Higher cost (tool purchase or lease) |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires basic technical skills | Requires familiarity with multimeters | User-friendly, often automated |
| Maintenance | Minimal (occasional tool upkeep) | Low (regular battery checks needed) | Regular software updates required |
| Best Use Case | DIY repairs, basic troubleshooting | Accurate voltage diagnostics in workshops | Professional auto repair shops, fleet maintenance |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
How to Test Starter Motor Solenoid
This method involves simple steps such as locating the starter solenoid, checking for current, and testing resistance using basic tools like a test light or voltmeter. It is cost-effective and requires minimal investment, making it accessible for DIY enthusiasts and smaller workshops. However, it can be time-consuming and may not always provide a comprehensive diagnosis, especially if the issue lies deeper in the electrical system.

Illustrative image related to how to test starter motor solenoid
Multimeter Testing
Using a multimeter allows for precise measurement of voltage and current flowing through the starter solenoid. This method offers high accuracy, making it suitable for workshops aiming to provide detailed diagnostics. While the initial cost of a quality multimeter can be moderate, the investment pays off in terms of reliability and reduced labor time. However, it requires familiarity with electrical measurements, which may necessitate additional training for staff.
Advanced Diagnostic Tool
Advanced diagnostic tools provide a comprehensive analysis of the vehicle’s electrical system, including the starter motor solenoid. These tools often feature automated processes that can quickly identify faults, making them ideal for professional auto repair shops or fleet maintenance operations. Although they come with a higher price tag, the efficiency and accuracy they offer can significantly reduce diagnostic time and improve service quality. The downside is the need for regular software updates and potential training for optimal use.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Testing Solution for Your Needs
Selecting the appropriate method to test a starter motor solenoid depends on various factors, including the operational scale, budget, and required accuracy. For smaller businesses or DIY enthusiasts, the traditional testing method remains a viable choice due to its low cost and simplicity. Conversely, workshops aiming for precision and efficiency may benefit more from investing in a multimeter or an advanced diagnostic tool. Ultimately, understanding these alternatives will empower B2B buyers to make informed decisions that align with their operational requirements and budget constraints.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for how to test starter motor solenoid
What Are the Key Technical Properties to Consider When Testing a Starter Motor Solenoid?
When assessing a starter motor solenoid, understanding its technical properties is essential for B2B buyers involved in automotive parts procurement. Here are several critical specifications to consider:
-
Voltage Rating
The voltage rating of a starter solenoid typically ranges between 12V to 24V, depending on the vehicle’s electrical system. This rating is crucial as it determines whether the solenoid can operate effectively within a specific vehicle’s electrical architecture. Selecting a solenoid with an incompatible voltage rating can lead to malfunction or damage. -
Current Capacity
Measured in amperes (A), the current capacity indicates how much electrical current the solenoid can handle without overheating. For automotive applications, solenoids often handle currents between 50A to 300A. Understanding this specification helps ensure that the solenoid will perform reliably under load, which is essential for preventing vehicle starting failures. -
Material Composition
The materials used in the construction of the solenoid—such as copper for the winding and durable plastics or metals for the casing—impact its longevity and performance. High-quality materials can withstand harsh environments, improving the solenoid’s durability and reliability over time, which is particularly important for B2B buyers in regions with extreme weather conditions. -
Resistance Measurement
Resistance, measured in ohms (Ω), is a critical property that affects the solenoid’s efficiency. A solenoid with too high or too low resistance may not activate correctly, leading to vehicle starting issues. Regular testing of resistance can help identify potential failures before they occur, allowing for proactive maintenance. -
Mounting Configuration
The mounting configuration specifies how the solenoid is attached to the starter motor and vehicle chassis. It is essential to ensure compatibility with the vehicle’s design to facilitate easy installation and maintenance. Mismatched configurations can lead to installation challenges and increased labor costs. -
Operating Temperature Range
The operating temperature range indicates the environmental conditions within which the solenoid can function efficiently. Solenoids designed for extreme temperatures are essential for vehicles operating in harsh climates. Understanding this property helps buyers select suitable products for their specific market needs.
What Are the Common Trade Terms Related to Testing Starter Motor Solenoids?
In the context of testing starter motor solenoids, several industry terms are commonly used that are important for B2B buyers to understand:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to components made by the original manufacturer of the vehicle. These parts are typically of higher quality and reliability than aftermarket alternatives. B2B buyers often prefer OEM solenoids to ensure compatibility and performance. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ indicates the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is crucial for buyers, especially when entering new markets or working with budget constraints. It helps in negotiating bulk purchases and managing inventory effectively. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal process where buyers request pricing and terms from suppliers. For buyers looking to purchase starter motor solenoids, issuing an RFQ can lead to competitive pricing and better procurement strategies, allowing for cost-effective sourcing. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international trade. Familiarity with these terms helps buyers understand shipping costs, risk management, and delivery responsibilities, which are crucial when importing starter motor solenoids from different regions. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the amount of time it takes from placing an order until it is delivered. For businesses that rely on rapid vehicle repairs or production schedules, understanding lead times can help in planning and ensuring timely availability of necessary parts. -
Warranty Period
The warranty period is the duration during which a manufacturer guarantees the performance of a product. For starter motor solenoids, a longer warranty period can indicate confidence in the product’s reliability and quality, making it a significant consideration for B2B buyers.
Understanding these technical properties and trade terms enables B2B buyers to make informed purchasing decisions, ensuring they procure the right starter motor solenoids for their specific needs.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the how to test starter motor solenoid Sector
What Are the Key Trends Affecting the Starter Motor Solenoid Testing Market?
The market for testing starter motor solenoids is influenced by several global drivers, including the rapid growth of the automotive sector, technological advancements, and an increasing demand for efficient vehicle maintenance solutions. In regions like Africa, South America, and the Middle East, the rise in vehicle ownership is prompting a greater need for reliable testing methods to ensure optimal performance and longevity of automotive components. In Europe, particularly in Germany, stringent regulations regarding vehicle emissions and efficiency are pushing manufacturers and service providers to adopt advanced diagnostic tools for early detection of starter motor issues.
Emerging trends in B2B tech include the integration of IoT devices that provide real-time monitoring and diagnostics, enabling technicians to identify issues before they escalate. Additionally, mobile applications that facilitate remote testing and diagnostics are gaining traction, allowing businesses to streamline operations and enhance customer service. Suppliers and buyers are increasingly focusing on partnerships that promote innovation, with a shift towards sourcing components that incorporate smart technologies.

Illustrative image related to how to test starter motor solenoid
International B2B buyers should also be aware of the market dynamics shaped by fluctuating raw material costs and supply chain disruptions, particularly in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic. Establishing strong relationships with reliable suppliers who can offer timely and consistent product availability is crucial for navigating these challenges effectively.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impacting the Starter Motor Solenoid Sector?
Sustainability has become a pivotal concern in the automotive industry, with increasing scrutiny on the environmental impact of manufacturing processes and supply chains. In the context of starter motor solenoids, businesses are encouraged to adopt practices that minimize waste and reduce carbon footprints. This includes sourcing materials from suppliers who prioritize eco-friendly production methods and utilize recyclable components.
The importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated, especially for international buyers. Ensuring that suppliers adhere to ethical labor practices and environmental standards not only enhances brand reputation but also aligns with the growing consumer demand for responsible sourcing. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and the use of ‘green’ materials can serve as indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability.

Illustrative image related to how to test starter motor solenoid
Moreover, businesses that implement sustainable practices can benefit from cost savings in the long run. For instance, investing in energy-efficient production processes can lead to reduced operational costs and improved margins. As the global market moves towards greener alternatives, international B2B buyers must prioritize partnerships with suppliers that demonstrate a commitment to sustainability and ethical sourcing.
What Is the Historical Context Behind Starter Motor Solenoid Testing Methods?
The evolution of starter motor solenoid testing methods has been significantly shaped by advancements in automotive technology and the increasing complexity of vehicle electrical systems. Initially, testing methods were rudimentary, relying on simple visual inspections and basic electrical tests. However, as vehicles became more sophisticated, the need for more accurate and reliable testing methods emerged.
In the late 20th century, the introduction of electronic diagnostic tools revolutionized the way technicians approached starter motor issues. These tools allowed for more precise measurements of electrical current and resistance, leading to quicker and more accurate diagnoses. As technology continues to evolve, modern testing methods now incorporate digital solutions, including mobile applications and IoT devices, which facilitate real-time diagnostics and remote troubleshooting.
This historical progression highlights the importance of staying abreast of technological advancements in the automotive sector, particularly for B2B buyers looking to maintain competitive advantages in an increasingly tech-driven marketplace. Understanding the evolution of testing methods can inform better sourcing decisions and improve operational efficiencies.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of how to test starter motor solenoid
-
How do I determine if my starter motor solenoid is faulty?
To assess the functionality of a starter motor solenoid, start by listening for a clicking sound when the ignition key is turned. If there’s no click, the solenoid may not be engaging, possibly due to a dead battery or faulty wiring. Use a multimeter to check for voltage at the solenoid terminals. If power is present but the solenoid does not activate, it is likely defective and needs replacement. This diagnostic approach can save costs and time in sourcing parts. -
What are the signs of a failing starter solenoid?
Common indicators of a failing starter solenoid include intermittent starting issues, a clicking noise when attempting to start the engine, or complete silence with no response when the ignition is turned. Additionally, if the engine cranks slowly or not at all, it may suggest a problem with the solenoid. Recognizing these signs early can facilitate prompt action, preventing further complications or damage to the vehicle’s electrical system. -
What tools do I need to test a starter motor solenoid?
Essential tools for testing a starter motor solenoid include a multimeter or voltmeter, a test light, and basic hand tools like wrenches and screwdrivers for accessing the solenoid. A pair of insulated gloves is also recommended for safety. Having these tools on hand will enable effective diagnostics, ensuring accurate assessments and efficient repairs, which are crucial for maintaining operational vehicles in a fleet. -
How can I ensure the quality of the starter motor solenoid I purchase?
To ensure high-quality starter motor solenoids, source from reputable manufacturers or suppliers with a proven track record. Verify certifications and compliance with international quality standards, such as ISO 9001. Request samples or detailed product specifications before placing bulk orders. Additionally, review feedback from other customers and check for warranties, which can indicate the supplier’s confidence in their products and commitment to quality. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for starter motor solenoids?
The MOQ for starter motor solenoids varies by supplier and can depend on factors such as production capabilities and existing inventory. Generally, it can range from a few pieces to several hundred units. It’s advisable to discuss your specific needs with potential suppliers to negotiate favorable terms that align with your business requirements. Understanding MOQs is crucial for inventory management and cost control in B2B purchasing. -
What payment terms are commonly offered for international purchases of starter motor solenoids?
Payment terms for international transactions typically include options such as advance payment, letters of credit, or payment upon delivery. Common practices involve a 30% deposit with the balance due before shipment or upon receipt of goods. It’s essential to clarify payment methods with suppliers and ensure they align with your cash flow management and risk tolerance. Understanding these terms can help avoid financial disputes and ensure smooth transactions. -
How can I vet suppliers for starter motor solenoids effectively?
To vet suppliers, start by researching their reputation and history in the industry. Look for reviews, ratings, and testimonials from other B2B buyers. Request references and assess their responsiveness to inquiries. Additionally, evaluate their compliance with international quality standards and their ability to meet your specific requirements, such as customization options. Conducting a site visit, if feasible, can also provide valuable insights into their operations and reliability. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing starter motor solenoids?
When sourcing starter motor solenoids, consider logistics factors such as shipping methods, lead times, and customs regulations in your region. Evaluate the supplier’s ability to manage logistics efficiently, including packaging and handling to prevent damage during transit. Understand potential tariffs and import duties that may affect your overall costs. Collaborating with a logistics provider can streamline the process and ensure timely delivery, which is crucial for maintaining your business operations.
Top 4 How To Test Starter Motor Solenoid Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. WikiHow – Starter Solenoid Testing Guide
Domain: wikihow.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: The starter solenoid is a simple mechanism that transmits electrical current from the battery to the starter. It engages when the key is turned, using the starter’s electrical motor to start the engine. If the solenoid fails, the vehicle may not start. Key steps to test the solenoid include locating it near the starter, listening for a clicking sound when attempting to start the vehicle, checking …
2. Reddit – Solenoid Jump Start Cable
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: solenoid jump start cable, multimeter, battery, starter solenoid
3. LinkedIn – Starter Solenoid
Domain: linkedin.com
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
Introduction: Starter solenoid is an electromagnetic switch that engages the starter motor when the ignition key is turned to the ‘start’ position. It controls the high current needed to operate the starter motor safely, ensuring clean engagement and disengagement to reduce wear and tear. Symptoms of a bad starter solenoid include clicking noises, failure to crank, difficulty starting the engine, decreased acce…
4. Dotheton – Starter Solenoid for 1976 CB550k
Domain: dotheton.com
Registered: 2007 (18 years)
Introduction: Starter solenoid for 1976 CB550k motorcycle, non-OEM unit, issues with wiring and functionality, testing methods discussed include using an ohm meter and applying 12VDC to terminals.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for how to test starter motor solenoid
To effectively test a starter motor solenoid, international B2B buyers must understand the critical steps involved in diagnosing and addressing potential issues. Key takeaways include the importance of systematically locating the solenoid, verifying electrical current, and testing current resistance. This process not only helps in identifying whether the solenoid or another component is at fault but also ensures efficient resource allocation when sourcing replacement parts.
Strategic sourcing plays a pivotal role in enhancing operational efficiency, especially when procuring quality starter solenoids and related components. By building relationships with reliable suppliers, businesses can ensure they have access to high-quality parts that meet their specific requirements, ultimately reducing downtime and repair costs.
Looking ahead, as the automotive market continues to evolve, it is essential for buyers in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe to stay informed about best practices in sourcing and testing automotive components. Embrace the opportunity to optimize your supply chain by partnering with trusted suppliers, ensuring your operations remain competitive and resilient. Take the next step in enhancing your automotive services by prioritizing strategic sourcing today.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.

Illustrative image related to how to test starter motor solenoid
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.