Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for cost to fix an alternator
In the ever-evolving landscape of the automotive industry, understanding the cost to fix an alternator is crucial for international B2B buyers. Whether you’re sourcing parts for a fleet in Nigeria or managing repairs in Saudi Arabia, the challenge lies not just in identifying quality suppliers but also in navigating the complexities of pricing, quality assurance, and logistics. This guide delves into the multifaceted aspects of alternator repairs, including an overview of types, applications, and the critical process of supplier vetting.
By breaking down the cost components associated with alternator replacement and repair, we aim to equip businesses with the knowledge needed to make informed purchasing decisions. We will explore factors influencing costs, such as labor rates and part quality, and provide insights on how to evaluate potential suppliers effectively. Furthermore, we will highlight regional variations in pricing and availability, ensuring that buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe can strategize their procurement processes efficiently.
Our goal is to empower B2B buyers with actionable insights, helping them to mitigate risks and enhance their operational efficiency when it comes to alternator repairs. By understanding the nuances of sourcing and cost structures, businesses can optimize their budgets and ensure reliable vehicle performance, ultimately driving their success in a competitive global market.
Table Of Contents
- Top 2 Cost To Fix An Alternator Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for cost to fix an alternator
- Understanding cost to fix an alternator Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of cost to fix an alternator
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘cost to fix an alternator’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for cost to fix an alternator
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for cost to fix an alternator
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘cost to fix an alternator’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for cost to fix an alternator Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing cost to fix an alternator With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for cost to fix an alternator
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the cost to fix an alternator Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of cost to fix an alternator
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for cost to fix an alternator
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Understanding cost to fix an alternator Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Full Alternator Replacement | Complete replacement of the alternator with a new or remanufactured unit. | Fleet maintenance, automotive repair shops. | Pros: Reliable performance, warranty options. Cons: Higher initial cost. |
| Alternator Repair | Minor repairs or part replacements within the existing alternator. | Small garages, independent mechanics. | Pros: Lower cost, quicker turnaround. Cons: Potential for recurring issues. |
| Used Alternator | Purchasing a second-hand alternator, often at a reduced price. | Budget-conscious repair shops, DIY enthusiasts. | Pros: Cost-effective. Cons: Uncertain reliability and lack of warranty. |
| OEM Replacement | Using original equipment manufacturer parts for replacements. | Dealerships, high-end repair services. | Pros: Guaranteed compatibility and quality. Cons: Premium pricing. |
| Aftermarket Alternator | Non-OEM parts that may offer varying levels of quality and price. | Cost-sensitive businesses, aftermarket specialists. | Pros: Competitive pricing, wide availability. Cons: Risk of lower quality, potential compatibility issues. |
What Are the Characteristics of Full Alternator Replacement?
A full alternator replacement involves removing the old alternator and installing a new or remanufactured unit. This option is suitable for businesses that prioritize reliability, especially those operating fleets where vehicle downtime can be costly. While it typically incurs a higher initial cost, the long-term reliability and warranty options often justify the investment. B2B buyers should consider the total cost of ownership, including potential downtime and maintenance needs.
When Is Alternator Repair a Viable Option?
Alternator repair focuses on addressing specific issues, such as replacing worn-out components or cleaning electrical connections. This approach is beneficial for small garages or independent mechanics looking to minimize costs and expedite repairs. However, it’s essential for B2B buyers to evaluate the long-term viability of repairs versus replacements, as frequent repairs can lead to higher cumulative costs and reliability concerns.
What Are the Risks of Purchasing a Used Alternator?
Buying a used alternator can be an attractive option for budget-conscious businesses or DIY enthusiasts. However, the significant downside is the uncertainty regarding the part’s reliability and lifespan. B2B buyers should be cautious, as used parts often lack warranties and can lead to unexpected failures, which may result in additional costs down the line. It’s advisable to verify the source and condition of the part before proceeding.
Why Choose OEM Replacement for Your Alternator Needs?
OEM replacements are manufactured by the original equipment manufacturer, ensuring compatibility and quality. This option is often preferred by dealerships and high-end repair services that prioritize customer satisfaction and vehicle performance. While the cost is typically higher, B2B buyers can benefit from peace of mind knowing they are using parts that meet the vehicle’s specifications.
How Do Aftermarket Alternators Compare to OEM Options?
Aftermarket alternators provide a cost-effective alternative to OEM parts, often available at lower prices. They are widely used by cost-sensitive businesses and specialists in the aftermarket sector. However, the quality can vary significantly, which may pose compatibility issues. B2B buyers should conduct thorough research on the manufacturer and product reviews to ensure they are making a sound investment that won’t compromise vehicle performance.
Key Industrial Applications of cost to fix an alternator
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of cost to fix an alternator | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive Repair | Cost analysis for vehicle fleet maintenance | Reduces downtime and maintenance costs for fleet operations | Availability of OEM vs aftermarket parts, warranty terms |
| Transportation | Budgeting for logistics and delivery vehicles | Ensures reliable vehicle operation, enhancing delivery efficiency | Geographic availability of parts, labor costs in local markets |
| Mining and Construction | Heavy machinery maintenance budgeting | Minimizes operational disruptions and enhances productivity | Quality of parts, local service capabilities, repair time |
| Public Transportation | Cost management for bus and taxi fleets | Improves service reliability and customer satisfaction | Procurement of quality alternators, service contracts |
| Agricultural Equipment | Maintenance budgeting for farming machinery | Ensures continuous operation of essential equipment | Sourcing durable parts, understanding local environmental factors |
How Can Automotive Repair Shops Leverage Cost Insights on Alternator Repairs?
Automotive repair shops can utilize cost insights on alternator repairs to create competitive pricing models for their services. By understanding the average costs associated with both OEM and aftermarket parts, these businesses can offer tailored solutions to their clients. This knowledge helps repair shops to reduce customer downtime and enhance service efficiency, which is particularly crucial in regions with limited access to replacement parts. Additionally, they can establish partnerships with reliable parts suppliers to ensure quality and availability.
What Role Does Cost Analysis Play in Transportation Sector Budgeting?
In the transportation sector, particularly for logistics and delivery services, understanding the cost implications of alternator repairs is vital for effective budgeting. By accurately forecasting repair costs, businesses can allocate resources more efficiently, thereby minimizing unexpected expenses. This proactive approach ensures that vehicles remain operational, directly impacting service delivery and customer satisfaction. International buyers, especially in developing regions, should consider local labor costs and parts availability when planning maintenance budgets.
How Can Mining and Construction Companies Optimize Maintenance Costs?
For mining and construction companies, the cost to fix an alternator is a critical factor in maintenance budgeting for heavy machinery. These industries rely heavily on equipment uptime; thus, having a clear understanding of repair costs can prevent operational disruptions. Companies must evaluate the quality of parts used and the expertise of local service providers to ensure that repairs are performed efficiently and effectively. This is especially important in remote areas where access to quality parts may be limited.
Why is Cost Management Important for Public Transportation Fleets?
Public transportation operators must prioritize cost management, particularly regarding the maintenance of bus and taxi fleets. Understanding the costs associated with alternator repairs allows these operators to maintain reliable service, which is essential for user satisfaction. By sourcing quality parts and establishing service contracts with reputable suppliers, public transportation entities can reduce long-term operational costs. This approach is particularly relevant in regions where public transport is a primary means of mobility.
How Do Agricultural Businesses Benefit from Understanding Alternator Repair Costs?
In agriculture, the cost to fix an alternator is vital for maintaining the functionality of essential farming machinery. Given the seasonal nature of agricultural work, any downtime can significantly impact productivity and profit. Farmers and agricultural businesses can benefit from understanding repair costs, allowing them to budget effectively and ensure that their equipment is always operational. It is crucial for international buyers to consider the reliability of local parts suppliers and the service capabilities available in their regions.

Illustrative image related to cost to fix an alternator
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘cost to fix an alternator’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Unexpected High Repair Costs
The Problem: B2B buyers managing vehicle fleets often face the challenge of unexpected repair costs when replacing an alternator. For instance, a company operating in a region with limited access to quality auto parts may find that local mechanics charge exorbitant rates for both parts and labor. This can lead to unplanned expenses that disrupt budgets and affect overall operational efficiency. Moreover, the confusion over whether to choose OEM parts versus aftermarket options can complicate decision-making, often resulting in higher costs due to poor initial choices.
The Solution: To mitigate unexpected costs, it’s essential to establish relationships with reliable suppliers who can provide high-quality alternators at competitive prices. Consider creating a list of vetted local and international suppliers who specialize in automotive parts, particularly those with a track record of quality and affordability. Additionally, maintaining a fleet maintenance schedule can help identify potential issues before they escalate, allowing for proactive repairs rather than emergency fixes. When sourcing parts, favor remanufactured over rebuilt alternators, as they often offer better quality assurance without significantly increasing costs. This proactive approach not only aids in budget management but also enhances vehicle longevity and reliability.
Scenario 2: Limited Availability of Quality Parts
The Problem: In regions such as parts of Africa and South America, sourcing quality alternators can be a significant pain point for B2B buyers. The challenge often lies in the limited availability of reliable parts, which can lead to long downtimes and impact operational capabilities. Fleet managers might find themselves torn between purchasing cheaper, lower-quality parts that could fail quickly or facing prolonged vehicle unavailability while waiting for quality parts to be shipped from abroad.
The Solution: To address this issue, B2B buyers should consider establishing partnerships with reputable suppliers who specialize in sourcing and distributing high-quality automotive parts within their regions. Collaborating with local businesses that import quality components can streamline the procurement process, ensuring that reliable parts are available when needed. Additionally, investing in a local inventory of commonly needed parts, including alternators, can reduce downtime. Fleet managers should also encourage their maintenance teams to provide regular feedback on part performance to inform future purchasing decisions, ultimately leading to better quality assurance.
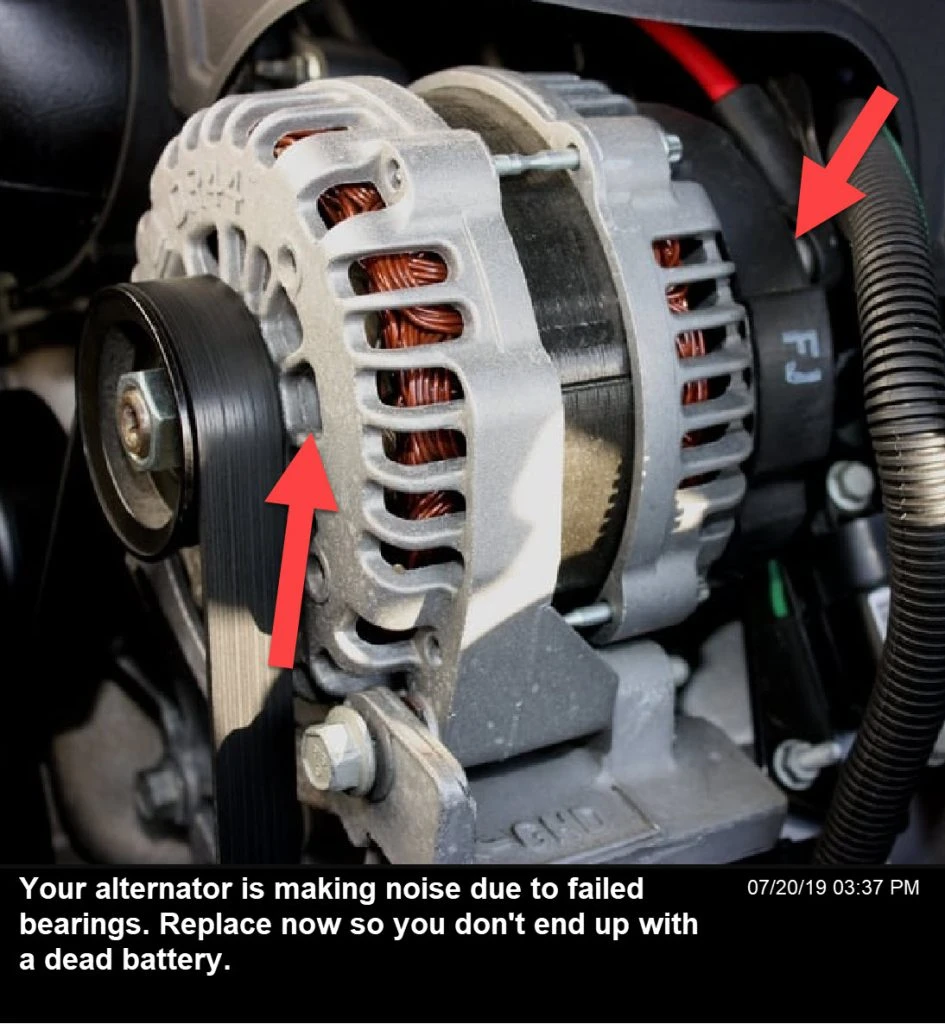
Illustrative image related to cost to fix an alternator
Scenario 3: Lack of Skilled Labor for Installation
The Problem: A common challenge faced by B2B buyers is the lack of skilled labor for the installation of alternators, especially in remote areas. This shortage can lead to delays in repairs, increased labor costs, and a higher likelihood of errors during installation. Companies may struggle to find technicians who are experienced with the specific make and model of their vehicles, which can be particularly frustrating when time is of the essence.
The Solution: To overcome the challenge of skilled labor shortages, B2B buyers should invest in training programs for their existing staff. Partnering with vocational schools or technical institutes can provide employees with the necessary skills to perform alternator replacements and other critical repairs. Additionally, consider implementing a mentorship program where experienced technicians can train new hires. This not only helps build a more skilled workforce but also fosters a culture of continuous learning within the organization. Furthermore, utilizing online resources, such as instructional videos and manuals specific to the vehicles in the fleet, can empower less experienced staff to perform installations correctly, reducing reliance on external labor and associated costs.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for cost to fix an alternator
What Materials Are Commonly Used for Fixing Alternators?
When considering the cost to fix an alternator, the selection of materials plays a crucial role in determining the overall performance, durability, and cost-effectiveness of the repair. Here are four common materials used in alternator repairs and replacements, analyzed from a B2B perspective.

Illustrative image related to cost to fix an alternator
1. Aluminum
Key Properties:
Aluminum is lightweight and possesses excellent corrosion resistance. Its thermal conductivity allows for efficient heat dissipation, which is essential for the alternator’s performance under varying operating conditions.
Pros & Cons:
Aluminum is durable and relatively inexpensive compared to other metals. However, it can be prone to deformation under high stress, which may affect its longevity in demanding environments. Manufacturing complexity is moderate, as aluminum can be easily machined and formed.
Impact on Application:
Aluminum is suitable for applications where weight savings are critical, such as in automotive components. However, it may not be ideal for high-temperature applications without proper thermal management.
Considerations for International Buyers:
In regions like Africa and South America, aluminum’s lightweight nature can be advantageous for transportation costs. Buyers should ensure compliance with local standards and consider the availability of aluminum parts in their markets.
2. Copper
Key Properties:
Copper is known for its excellent electrical conductivity and resistance to corrosion, making it a preferred choice for electrical connections within alternators.
Pros & Cons:
While copper offers superior conductivity and durability, it is more expensive than aluminum. The manufacturing process can also be complex, especially for high-purity copper needed in electrical applications.
Impact on Application:
Copper’s high conductivity makes it ideal for wiring and electrical components in alternators. However, its weight can be a disadvantage in applications where reducing weight is a priority.

Illustrative image related to cost to fix an alternator
Considerations for International Buyers:
In regions like the Middle East, where high temperatures can affect electrical systems, using copper can enhance reliability. Buyers should be aware of the fluctuating copper prices and consider sourcing from reputable suppliers to ensure quality.
3. Steel
Key Properties:
Steel is known for its high strength and durability. It can withstand high temperatures and pressures, making it suitable for structural components in alternators.
Pros & Cons:
Steel is generally more affordable and widely available. However, it is heavier than aluminum and can be susceptible to corrosion if not properly treated. Manufacturing processes can vary, but steel components are typically easier to produce.
Impact on Application:
Steel is often used for brackets and housing in alternators, providing structural integrity. However, its weight may impact overall vehicle performance.

Illustrative image related to cost to fix an alternator
Considerations for International Buyers:
In Europe, compliance with environmental regulations regarding steel production and recycling is crucial. Buyers should ensure that their steel components meet local standards to avoid compliance issues.
4. Plastic Composites
Key Properties:
Plastic composites are lightweight and can be engineered for specific performance characteristics, such as resistance to heat and chemicals.
Pros & Cons:
These materials are cost-effective and can reduce the overall weight of the alternator. However, they may not offer the same level of durability as metals and can be susceptible to wear over time.
Impact on Application:
Plastic composites are often used for non-structural components in alternators, such as covers and insulators. Their performance can vary based on the specific formulation used.
Considerations for International Buyers:
In regions with strict regulations on materials, such as parts of Europe, ensuring that plastic composites meet safety and environmental standards is essential. Buyers should also consider the availability of these materials in their local markets.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Alternator Repair
| Material | Typical Use Case for cost to fix an alternator | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Alternator housings and brackets | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Prone to deformation under stress | Medium |
| Copper | Electrical wiring and connectors | Excellent electrical conductivity | Higher cost and manufacturing complexity | High |
| Steel | Structural components and brackets | High strength and durability | Heavier and susceptible to corrosion | Low |
| Plastic Composites | Covers and insulators | Cost-effective and lightweight | Less durable than metals | Low |
This strategic material selection guide provides B2B buyers with essential insights into the various materials used in alternator repairs, highlighting their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international markets. Understanding these factors can aid in making informed purchasing decisions that align with operational needs and budget constraints.

Illustrative image related to cost to fix an alternator
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for cost to fix an alternator
What Are the Main Stages in Manufacturing Alternators?
The manufacturing process of alternators involves several critical stages designed to ensure optimal performance and reliability. Understanding these stages can help B2B buyers make informed decisions regarding supplier selection and product quality.
Material Preparation: What Materials Are Used in Alternator Manufacturing?
The first stage of alternator manufacturing involves sourcing and preparing high-quality raw materials. Key materials typically include:
- Copper Wire: Used for the windings, copper is chosen for its excellent electrical conductivity.
- Steel or Aluminum Casings: These materials provide structural integrity and protection for internal components.
- Magnetic Materials: Usually ferrite or neodymium, these are essential for creating the magnetic field necessary for electricity generation.
- Insulation Materials: High-temperature resistant polymers are used to insulate windings and prevent short circuits.
Before manufacturing, these materials undergo rigorous testing to ensure they meet industry standards and specifications.
Forming: How Are Alternator Components Shaped?
The forming stage employs various techniques to shape the materials into components. Common methods include:

Illustrative image related to cost to fix an alternator
- Stamping: Used for creating metal casings and brackets from sheets of steel or aluminum. This process ensures precision and consistency in the dimensions of the components.
- Winding: Copper wire is wound into coils, which are then assembled into the rotor and stator. This step is crucial, as the number of turns and the arrangement of the wire affect the alternator’s efficiency.
- Casting: Some parts, such as the rotor and housing, may be cast to achieve complex shapes that would be difficult to produce through other methods.
Each of these techniques is closely monitored to ensure that the specifications are met, and any deviations can lead to performance issues.
Assembly: What Does the Assembly Process Involve?
During the assembly stage, the various components come together to form a complete alternator. Key steps include:
- Component Integration: The rotor and stator are fitted together, ensuring proper alignment and spacing.
- Connection: Electrical connections are made, linking the windings to the diodes and voltage regulator.
- Quality Checks: As components are assembled, immediate quality checks are performed to identify any defects or misalignments.
Effective assembly is critical for the performance of the alternator, and many manufacturers employ automated systems to enhance precision and efficiency.
Finishing: What Are the Final Steps in Alternator Manufacturing?
The finishing stage involves several processes designed to enhance the durability and performance of the alternator:
- Coating: Applying protective coatings to prevent corrosion and enhance aesthetic appeal.
- Final Testing: This includes functionality tests where the alternator is subjected to various loads to ensure it operates within specified parameters.
- Packaging: Proper packaging is essential to protect the alternators during transportation and storage.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are in Place for Alternator Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is integral to the manufacturing process, ensuring that alternators meet both industry and customer standards. B2B buyers should be aware of the following key aspects of QA in alternator production.
What Are the Relevant International Standards for Alternator Quality?
Manufacturers typically adhere to international standards such as ISO 9001, which outlines the requirements for a quality management system. Compliance with these standards indicates that the manufacturer has established processes to maintain product quality consistently.
Additionally, industry-specific certifications such as CE (Conformité Européenne) and API (American Petroleum Institute) may be relevant, particularly for alternators used in specific applications like automotive or heavy machinery.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints During Production?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are strategically placed throughout the manufacturing process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Inspection of raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during the manufacturing stages, including forming and assembly, to catch defects early.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): A thorough evaluation of the finished alternator, including performance testing and visual inspections.
These checkpoints help minimize the risk of defective products reaching the market.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
B2B buyers can take several steps to verify the quality control processes of their suppliers:
- Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits can provide firsthand insights into the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures in place.
- Quality Reports: Requesting detailed reports on quality metrics, defect rates, and compliance with international standards can help assess a supplier’s reliability.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection agencies can provide an unbiased evaluation of the manufacturing and QC processes.
Buyers should prioritize suppliers who are transparent about their QC processes and willing to share documentation and certifications.
What Are the Quality Control and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers, especially those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of specific nuances in quality control and certification:
- Regional Standards: Different regions may have unique quality standards and certifications. Familiarity with these can help buyers ensure compliance.
- Import Regulations: Understanding the import regulations and standards required in the buyer’s home country can prevent costly delays and rejections at customs.
- Cultural Considerations: Building strong relationships with suppliers and understanding cultural nuances can enhance communication and lead to better quality outcomes.
By considering these factors, international buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing high-quality alternators effectively.

Illustrative image related to cost to fix an alternator
Conclusion: Ensuring Quality and Cost-Effectiveness in Alternator Procurement
In conclusion, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures associated with alternators is vital for B2B buyers. By focusing on material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing, alongside rigorous quality control measures, buyers can ensure they select reliable and cost-effective alternators that meet their operational needs. Building strong relationships with manufacturers and leveraging international standards will further enhance procurement success.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘cost to fix an alternator’
To effectively navigate the complexities of sourcing the cost to fix an alternator, this guide provides a structured approach to ensure you make informed decisions. Whether you are an auto parts distributor, repair shop owner, or fleet manager, understanding the intricacies of alternator replacement can significantly impact your bottom line. Follow this checklist to streamline your procurement process.
Step 1: Assess Your Needs for Alternator Replacement
Begin by determining the specific requirements for the alternators you need. Consider factors such as vehicle make and model, the average lifespan of alternators in your fleet, and typical failure rates. This step is crucial as it helps you avoid over-purchasing or acquiring parts that don’t meet your operational needs.
Step 2: Conduct Market Research for Pricing
Investigate the current market prices for alternators and associated labor costs in your region. Compare prices from various suppliers, including local auto parts stores and online retailers. Understanding the price range will help you negotiate better and make cost-effective decisions.
- Tip: Take note of regional pricing differences, especially if you operate across multiple countries or continents.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a supplier, conduct a thorough evaluation. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in a similar industry or region. This due diligence is essential to verify the supplier’s reliability, product quality, and customer service.
- What to Look For:
- Customer reviews and testimonials
- Supplier certifications and warranties
Step 4: Verify Product Quality and Specifications
Ensure that the alternators you are considering meet the necessary quality standards and specifications. Look for original equipment manufacturer (OEM) parts or high-quality aftermarket options. This is vital as subpar components can lead to increased failures and higher long-term costs.
- Key Questions:
- Do the parts come with a warranty?
- Are they compatible with your vehicle’s electrical system?
Step 5: Consider the Total Cost of Ownership
When evaluating the cost to fix an alternator, consider not just the upfront costs but the total cost of ownership. This includes installation costs, potential future repairs, and any downtime your vehicles might experience. A cheaper part may not always be the best choice if it leads to more frequent replacements.
Step 6: Establish a Relationship with Your Supplier
Building a strong relationship with your chosen supplier can lead to better pricing, priority service, and access to exclusive deals. Regular communication about your needs and feedback on products can create a mutually beneficial partnership.

Illustrative image related to cost to fix an alternator
- Action Item: Schedule regular check-ins or reviews to discuss performance and needs.
Step 7: Plan for Future Needs
Finally, consider your long-term requirements for alternator replacements. Monitor trends in vehicle maintenance and repair costs, and adjust your procurement strategy accordingly. Staying proactive can help you anticipate changes in demand and pricing fluctuations.
By following these steps, B2B buyers can streamline their procurement process for alternator repairs, ensuring they make informed and strategic purchasing decisions that align with their operational needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for cost to fix an alternator Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Fixing an Alternator?
When assessing the cost to fix an alternator, several components come into play, including materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control, logistics, and profit margins.
-
Materials: The primary material cost involves the alternator itself, which can range from $100 to $350 depending on the make and model. Additional parts, such as serpentine belts or wiring harnesses, may incur extra costs, generally adding $20 to $50. For international buyers, sourcing quality parts from reliable suppliers is crucial to avoid additional costs due to failures or reworks.
-
Labor: Labor charges typically range from $120 to $200 for a job that requires two to three hours of work. In regions with higher labor costs, such as Europe, this may be on the upper end, while costs could be lower in Africa or South America.
-
Manufacturing Overhead and Tooling: These costs are often factored into the pricing by suppliers, particularly those providing OEM parts. Overhead can include the costs of factory operations, machinery depreciation, and utilities, while tooling costs relate to the equipment used to produce alternators.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that alternators meet specific standards may add to the cost. Certifications from recognized automotive standards can enhance pricing but also ensure reliability, which is crucial for B2B buyers.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can vary significantly based on the geographic location of the supplier and the buyer. Incoterms play a vital role in defining the responsibilities for these costs, influencing the total landed cost of the alternator.
-
Margin: Supplier margins can vary based on competition, demand, and the exclusivity of the part. Understanding the market dynamics in different regions can help buyers negotiate better prices.
How Do Price Influencers Affect the Cost of Alternator Repairs?
Several factors can influence the final price of alternator repairs, particularly for international B2B buyers.
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Purchasing in bulk can lead to significant discounts. Suppliers often have tiered pricing structures, where larger orders reduce the per-unit cost.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom specifications, such as enhanced durability for extreme climates, can increase costs. Buyers must balance the need for customization with budget constraints.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: The source of the alternator—whether OEM or aftermarket—affects pricing. OEM parts tend to be more expensive but often come with guarantees of quality. For businesses operating in regions with diverse automotive standards, understanding the implications of material quality is essential.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can also influence pricing. Well-established suppliers may charge a premium, but they often provide better warranties and customer service.
What Are the Best Negotiation Tips for B2B Buyers in Different Regions?
Understanding the nuances of pricing can help international buyers negotiate effectively.
-
Research Market Prices: Familiarize yourself with average costs in your region and for your specific vehicle model. This knowledge will empower you during negotiations.
-
Consider Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Factor in not just the initial purchase price but also the long-term costs associated with quality, reliability, and maintenance. A slightly higher upfront cost for a quality part may lead to lower maintenance costs down the line.
-
Leverage Local Relationships: Building relationships with local suppliers in regions like Africa or South America can lead to better pricing and terms, as familiarity can foster trust and flexibility.
-
Negotiate Shipping Terms: Understanding Incoterms can help negotiate shipping costs, which can significantly impact total expenses. Opt for terms that minimize your liability while ensuring timely delivery.
Conclusion: What Should Buyers Keep in Mind?
When sourcing alternator repairs, it’s vital to consider the comprehensive cost structure and the various price influencers. While indicative prices for alternator replacements typically range from $350 to $900, the final cost can vary widely based on the factors discussed. Always approach negotiations with a clear understanding of your needs and market conditions to achieve the best possible outcomes.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing cost to fix an alternator With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Fixing an Alternator
When faced with a failing alternator, businesses often seek the most cost-effective and efficient solutions. While replacing an alternator is a common practice, alternative methods can provide significant savings or enhanced performance. This analysis will compare the cost to fix an alternator against two viable alternatives: using a high-quality aftermarket alternator and opting for a remanufactured alternator.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Cost To Fix An Alternator | Aftermarket Alternator | Remanufactured Alternator |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High (OEM parts) | Variable (may vary by brand) | Comparable to new OEM |
| Cost | $350 – $900 | $100 – $350 | $150 – $400 |
| Ease of Implementation | Moderate (requires labor) | Moderate (requires labor) | Moderate (requires labor) |
| Maintenance | Low (new part) | Medium (varies by quality) | Low (warranty typically included) |
| Best Use Case | Long-term vehicle use | Cost-sensitive replacements | Budget-friendly, reliable option |
What Are the Benefits and Drawbacks of Aftermarket Alternators?
Aftermarket alternators offer a cost-effective solution for businesses looking to replace a faulty unit without breaking the bank. Typically priced between $100 and $350, aftermarket options can save significant costs compared to OEM replacements. However, the performance and reliability can vary widely depending on the manufacturer. While some aftermarket parts can be of high quality and perform well, others may compromise on durability, leading to potential failures down the line. Businesses should conduct thorough research on brands and possibly seek recommendations to ensure they choose a reputable aftermarket alternator.
Why Consider Remanufactured Alternators?
Remanufactured alternators present a balanced approach for companies seeking an economical yet reliable solution. Priced between $150 and $400, these units undergo a rigorous process where all internal components are replaced, offering performance comparable to new units. Moreover, remanufactured alternators often come with warranties, providing peace of mind regarding their reliability. However, they may still carry some risk compared to brand-new parts, particularly if the remanufacturing process is not well-regarded. Businesses must verify the reputation of the remanufacturer to avoid subpar quality.
Conclusion: How Should B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution?
When selecting the best solution for a failing alternator, B2B buyers should weigh the total cost, reliability, and intended use of the vehicle. If long-term performance and reliability are paramount, investing in a new OEM alternator may be justified despite the higher cost. Conversely, if immediate budget constraints are critical, exploring high-quality aftermarket or remanufactured options may provide a satisfactory balance of cost and performance. Ultimately, aligning the choice with the operational needs and maintenance strategy of the vehicle fleet will lead to the most effective and economical decision.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for cost to fix an alternator
What Are the Key Technical Properties to Consider When Fixing an Alternator?
When evaluating the cost to fix an alternator, several critical technical properties come into play. Understanding these specifications can help B2B buyers make informed decisions regarding quality, longevity, and overall value.

Illustrative image related to cost to fix an alternator
1. Material Grade
The alternator’s construction material significantly impacts its durability and performance. Common materials include aluminum for the housing and copper for the windings. Higher-grade materials typically offer better thermal and electrical conductivity, leading to improved efficiency and longevity. For international buyers, sourcing parts made from high-quality materials can reduce long-term operational costs and minimize the risk of premature failure.
2. Electrical Output
The electrical output, measured in amperes (A), indicates the alternator’s ability to supply power to the vehicle’s electrical systems. This specification is crucial because different vehicles require varying amounts of power based on their electrical load. Ensuring that the alternator meets or exceeds the vehicle’s specifications can prevent issues related to underperformance, such as dimming lights or malfunctioning electronics.
3. Compatibility
Compatibility refers to how well an alternator fits with a specific vehicle make and model. This includes physical dimensions and electrical connectors. For B2B buyers, ensuring compatibility is vital to avoid costly returns and delays. Using an alternator designed for a particular vehicle model can also enhance reliability and performance.
4. Heat Resistance
Alternators operate under high temperatures, making heat resistance a critical property. Components that can withstand higher temperatures generally have a longer lifespan. Buyers should consider alternators with enhanced heat-resistant features, particularly in regions with extreme climates, as this can lead to reduced maintenance costs over time.
5. Warranty Period
The warranty period for an alternator reflects the manufacturer’s confidence in the product’s durability. A longer warranty often indicates higher quality and reliability. For B2B buyers, this can be a crucial factor in assessing the overall value and potential long-term costs associated with replacement parts.
What Are Some Common Trade Terms Related to Alternator Repair Costs?
Navigating the terminology in the automotive parts industry can be daunting. Here are several common jargon and trade terms essential for understanding the cost to fix an alternator.
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM parts are components made by the vehicle’s original manufacturer. These parts typically guarantee a perfect fit and performance, which can justify their higher price compared to aftermarket alternatives. For B2B buyers, understanding the difference between OEM and aftermarket parts is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is vital for B2B buyers who may need to purchase multiple alternators or components at once. Knowing the MOQ can help buyers manage inventory and budget effectively.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to request pricing information for specific products or services. B2B buyers should utilize RFQs to compare prices and terms from various suppliers, ensuring they get the best deal for alternator repairs or replacements.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a series of pre-defined commercial terms used in international trade. They define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Familiarity with these terms can help B2B buyers navigate logistics and avoid unexpected costs when importing alternator parts from abroad.

Illustrative image related to cost to fix an alternator
5. Aftermarket Parts
Aftermarket parts are components manufactured by companies other than the original vehicle manufacturer. These can often be less expensive than OEM parts. However, quality can vary significantly, so B2B buyers should evaluate the reputation of aftermarket suppliers before purchasing.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance their operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness when dealing with alternator repairs or replacements.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the cost to fix an alternator Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends Influencing the Cost to Fix an Alternator?
The global market for vehicle maintenance, including alternator repairs and replacements, is experiencing notable shifts due to several factors. One of the primary drivers is the increasing age of vehicles on the road, which contributes to a higher demand for alternator replacements. Many vehicles now exceed 100,000 miles, leading to a greater likelihood of alternator failure. Additionally, the rise in electric and hybrid vehicles is changing the landscape, as these vehicles have different power management systems, which may affect traditional alternator sourcing.
Emerging technologies such as advanced diagnostics and predictive maintenance tools are reshaping how businesses approach alternator repairs. B2B buyers are increasingly turning to suppliers that offer smart diagnostic tools, enabling them to better assess alternator health and lifecycle. The integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in inventory management is also streamlining the sourcing process, ensuring that businesses have the right alternators in stock without excessive overhead.
For international B2B buyers, understanding regional market dynamics is crucial. In Africa, for instance, the automotive repair market is expanding due to rising vehicle ownership. In South America and the Middle East, fluctuating currency rates can impact the cost of imported alternators, making local sourcing more appealing. European buyers are focusing on quality and reliability, often preferring OEM parts despite the higher costs, driven by stringent regulations on vehicle safety and emissions.

Illustrative image related to cost to fix an alternator
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact the Cost to Fix an Alternator?
The sustainability of supply chains is increasingly important in the automotive sector, particularly concerning alternators. The extraction and manufacturing of electrical components can have significant environmental impacts, from resource depletion to pollution. As a result, B2B buyers are prioritizing suppliers who adhere to sustainable practices, which often include reducing carbon footprints and utilizing renewable energy sources in manufacturing processes.
Ethical sourcing has become a vital consideration for international buyers. This includes ensuring that raw materials are sourced responsibly, which can mitigate risks related to labor exploitation and environmental degradation. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and ISO 50001 (Energy Management) are becoming essential criteria in the sourcing process. Additionally, buyers are increasingly interested in “green” alternatives, such as remanufactured alternators, which can offer cost savings while minimizing environmental impact.
As sustainability becomes a key differentiator in supplier selection, B2B buyers must evaluate their potential partners not just on cost but also on their commitment to ethical practices and environmental stewardship. This shift can influence long-term supplier relationships and impact overall costs associated with alternator repairs and replacements.
What Is the Historical Context of Alternator Sourcing and Its Evolution?
Historically, the alternator has been a critical component in vehicle electrical systems, evolving significantly since its inception in the early 20th century. Initially, alternators were primarily mechanical devices, but advancements in technology have led to the development of more efficient, electronic systems. In the past, sourcing alternators was often limited to local auto parts suppliers or dealerships, which could lead to high costs and limited options for buyers.
As globalization took hold, the supply chain for alternators expanded, providing buyers access to a broader range of products from various manufacturers worldwide. This evolution has led to the emergence of aftermarket suppliers who offer competitive pricing and alternative options, such as remanufactured or refurbished units. However, this has also introduced challenges related to quality control and the reliability of parts.
Today, the sourcing landscape for alternators is shaped by technological advancements, regional market dynamics, and a growing emphasis on sustainability and ethical practices. B2B buyers must navigate this complex environment to ensure they procure high-quality alternators that meet their operational needs while also aligning with their corporate values.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of cost to fix an alternator
-
How do I determine the cost to fix an alternator for my fleet of vehicles?
To estimate the cost of fixing an alternator for a fleet, consider both parts and labor. Labor rates vary by region, typically ranging from $120 to $200 per hour. The cost of an alternator can range from $100 to $350 depending on the vehicle model. For bulk purchases, negotiate with suppliers for discounts. Conduct a thorough analysis of the total cost per vehicle to budget effectively, factoring in potential additional repairs like serpentine belts. -
What factors influence the price of alternator repairs in different regions?
The cost of alternator repairs can vary significantly based on geographical location, local labor rates, and the availability of parts. Regions with a higher cost of living may have elevated labor costs. Additionally, consider the supply chain dynamics in areas like Africa or South America, where logistics may affect part availability and pricing. Understanding these regional differences is crucial for effective budgeting and supplier selection. -
What is the best type of alternator for international shipping?
When sourcing alternators for international shipping, opt for remanufactured units instead of used or rebuilt ones. Remanufactured alternators typically offer a warranty and meet higher quality standards. Ensure that the supplier can provide documentation confirming compliance with international quality standards. This choice reduces the risk of future failures and ensures reliability for your fleet. -
How can I verify the quality of alternators from international suppliers?
To ensure quality, request certifications and warranties from suppliers. Conduct background checks and read reviews from other B2B buyers. If possible, ask for samples to evaluate performance. Engaging with suppliers who have established reputations and track records in your region can further mitigate risks associated with quality control. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for alternators from suppliers?
MOQs for alternators can vary widely based on the supplier and the type of alternator. Some manufacturers may have MOQs of as low as 10 units, while others may require orders of 50 or more. It’s advisable to negotiate MOQs based on your fleet size and specific needs. Establishing a good relationship with suppliers may also allow for more flexible ordering options. -
What payment terms should I consider when sourcing alternators internationally?
When sourcing alternators internationally, consider payment terms that protect your investment. Common options include letters of credit, advance payments, or payment upon delivery. Negotiate terms that allow for partial payments based on milestones, such as order confirmation and shipping. This approach minimizes risk and ensures supplier accountability throughout the transaction. -
How do I handle logistics for shipping alternators internationally?
Logistics for international shipping of alternators involves selecting reliable freight forwarders and understanding customs regulations in both the exporting and importing countries. Ensure that your logistics partner can handle the complexities of international shipping, including tariffs and duties. Tracking shipments and maintaining communication with suppliers will help mitigate delays and ensure timely delivery. -
What quality assurance measures should I implement when sourcing alternators?
Implement a comprehensive quality assurance strategy by establishing clear specifications for the alternators you require. Conduct pre-shipment inspections and request quality control reports from suppliers. Consider using third-party inspection services to verify compliance with your standards. Continuous communication with suppliers and feedback loops will also enhance quality assurance throughout the sourcing process.
Top 2 Cost To Fix An Alternator Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Toyota – RAV4 Alternator Replacement
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: 2006 Toyota RAV4 alternator replacement, $450 total cost including labor.
2. Facebook – Cost Estimate
Domain: facebook.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: This company, Facebook – Cost Estimate, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for cost to fix an alternator
In conclusion, understanding the costs associated with alternator repair and replacement is crucial for international B2B buyers. The average cost for a complete alternator replacement can range from $350 to $900, influenced by factors such as vehicle make, model, and location. Strategic sourcing plays a pivotal role in managing these expenses effectively. By prioritizing quality over price—opting for OEM or reliable aftermarket parts—businesses can ensure long-term performance and reliability of their vehicles, ultimately reducing downtime and maintenance costs.

Illustrative image related to cost to fix an alternator
Furthermore, recognizing the signs of a failing alternator can facilitate timely interventions, preventing more significant issues down the line. For buyers in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, leveraging local suppliers while maintaining quality standards can yield significant cost savings and efficiency.
As the automotive landscape continues to evolve, staying informed and proactive in your sourcing strategies will be essential. Engage with trusted suppliers, explore remanufactured options, and keep abreast of market trends to ensure your fleet remains operational and cost-effective. Take the next step in optimizing your sourcing practices today.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.