Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for alternator cost car
Navigating the complexities of the global market for alternator costs can be daunting for B2B buyers, especially when sourcing reliable components that meet specific vehicle requirements. The alternator is a crucial part of a vehicle’s electrical system, responsible for powering everything from headlights to onboard computers. Understanding the variations in alternator types, applications, and the factors influencing their costs is essential for making informed purchasing decisions.
This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of alternator pricing, offering insights into the types of alternators available, their specific applications across different vehicle models, and strategies for vetting suppliers. Additionally, we will explore the cost implications, including labor and part quality, to help buyers navigate the often-overwhelming landscape of automotive components.
For international B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including key markets like Brazil and Saudi Arabia—this guide serves as an invaluable resource. It empowers you to make strategic purchasing decisions, ensuring you acquire quality alternators that not only fit your operational needs but also align with your budgetary constraints. By equipping yourself with this knowledge, you can mitigate risks associated with sourcing and enhance the efficiency of your supply chain.
Table Of Contents
- Top 3 Alternator Cost Car Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for alternator cost car
- Understanding alternator cost car Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of alternator cost car
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘alternator cost car’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for alternator cost car
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for alternator cost car
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘alternator cost car’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for alternator cost car Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing alternator cost car With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for alternator cost car
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the alternator cost car Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of alternator cost car
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for alternator cost car
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Understanding alternator cost car Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| OEM Alternators | Manufactured by the original vehicle manufacturer | Auto dealerships, fleet management companies | Pros: Guaranteed fit and quality; often backed by warranty. Cons: Higher cost compared to aftermarket options. |
| Aftermarket Alternators | Produced by third-party manufacturers, often less expensive | Independent repair shops, auto parts retailers | Pros: Cost-effective; broader availability. Cons: Quality can vary; may not fit all vehicle models perfectly. |
| Remanufactured Alternators | Rebuilt from used alternators, tested for quality | Auto repair shops, budget-conscious consumers | Pros: Eco-friendly; lower cost than new. Cons: May have shorter lifespan; warranty terms can vary. |
| High-Output Alternators | Designed to produce more amperage for high-demand vehicles | Performance vehicles, custom builds | Pros: Supports additional electrical accessories; enhances vehicle performance. Cons: Higher price; may require modifications for installation. |
| One-Wire Alternators | Simplified installation with a single connection | Older vehicle restorations, classic car markets | Pros: Easy installation; cost-effective. Cons: Limited amperage output; may not meet modern electrical demands. |
What Are OEM Alternators and When Should B2B Buyers Choose Them?
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) alternators are designed specifically for each vehicle model, ensuring compatibility and optimal performance. These are the preferred choice for auto dealerships and fleet management companies where reliability and warranty coverage are paramount. B2B buyers should consider OEM options when maintaining high-value fleets or servicing newer vehicles to minimize the risk of compatibility issues and ensure adherence to manufacturer specifications.
How Do Aftermarket Alternators Differ and What Are Their Applications?
Aftermarket alternators are produced by various manufacturers and can often be found at a lower price point than OEM alternatives. They cater to independent repair shops and auto parts retailers looking to provide cost-effective solutions to their customers. While they offer broader availability and competitive pricing, buyers must assess the quality of the manufacturer to avoid compatibility issues or subpar performance.
What Makes Remanufactured Alternators a Viable Option for B2B Buyers?
Remanufactured alternators are refurbished units that have been tested and restored to meet original specifications. They are an eco-friendly choice for auto repair shops and budget-conscious consumers, providing a lower-cost alternative to new parts. However, B2B buyers should evaluate warranty terms and expected lifespan, as these can vary widely among different suppliers.
Why Consider High-Output Alternators for Performance Needs?
High-output alternators are specifically designed to provide increased amperage, making them suitable for performance vehicles and custom builds that require additional electrical support. Businesses engaged in the performance automotive market should consider these alternators to enhance vehicle capabilities, especially when integrating advanced electrical systems. However, buyers should be aware of the potential for higher costs and installation modifications.
What Are the Benefits of One-Wire Alternators in Classic Car Markets?
One-wire alternators simplify installation with a single connection, making them ideal for older vehicle restorations and classic car markets. They are typically more affordable and easier to install, appealing to DIY enthusiasts and smaller shops. However, B2B buyers should note that these alternators may not provide the necessary amperage for modern electrical demands, limiting their suitability for vehicles with extensive electrical systems.
Key Industrial Applications of alternator cost car
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of alternator cost car | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive Manufacturing | Replacement parts for assembly lines | Ensures operational efficiency and reduces downtime | Specifications matching OEM standards; warranty options |
| Fleet Management | Regular maintenance of vehicle fleets | Enhances reliability and extends vehicle lifespan | Bulk purchasing agreements; quality assurance from suppliers |
| Transportation and Logistics | Maintenance for commercial delivery vehicles | Minimizes disruptions in service and delivery timelines | Availability of parts for various vehicle models; logistics support |
| Automotive Repair Services | Providing alternator replacement services | Attracts customers seeking reliable repairs | Access to a variety of alternators; competitive pricing |
| Export and Import Businesses | Trading in used or remanufactured alternators | Cost-effective solutions for vehicle maintenance | Compliance with international standards; sourcing reputable suppliers |
How is ‘alternator cost car’ utilized in automotive manufacturing?
In the automotive manufacturing sector, the cost of alternators is crucial for assembling vehicles. Manufacturers must ensure that the alternators they source meet stringent quality and performance specifications to maintain production efficiency. A reliable supply chain minimizes downtime on assembly lines, which is vital for meeting production targets. Buyers in this sector should prioritize suppliers that offer OEM-standard components and robust warranty options to mitigate risks associated with defects.
What role does alternator cost car play in fleet management?
For fleet management companies, understanding alternator costs is essential for the regular maintenance of their vehicle fleets. A well-functioning alternator ensures that vehicles operate reliably, reducing the frequency of breakdowns and extending the lifespan of fleet assets. By establishing bulk purchasing agreements with reputable suppliers, fleet managers can secure cost-effective pricing while ensuring the availability of high-quality alternators tailored to various vehicle models. This proactive approach to maintenance can significantly enhance operational efficiency.
How do transportation and logistics industries benefit from alternator cost car?
In the transportation and logistics sector, the performance of commercial delivery vehicles heavily relies on the alternator’s functionality. A malfunctioning alternator can lead to service disruptions, impacting delivery schedules and customer satisfaction. By investing in high-quality alternators and maintaining an efficient supply chain, businesses can minimize the risk of operational delays. Key considerations for international buyers include ensuring parts compatibility and having logistics support to facilitate timely repairs and replacements.
Why is alternator cost car significant for automotive repair services?
Automotive repair services rely on the availability and cost-effectiveness of alternators to attract customers seeking reliable repairs. By providing a range of alternators, including both new and remanufactured options, repair shops can cater to various customer needs while maintaining competitive pricing. Sourcing from suppliers who guarantee quality and offer diverse options can enhance service offerings and improve customer satisfaction, making it a vital aspect of their business strategy.
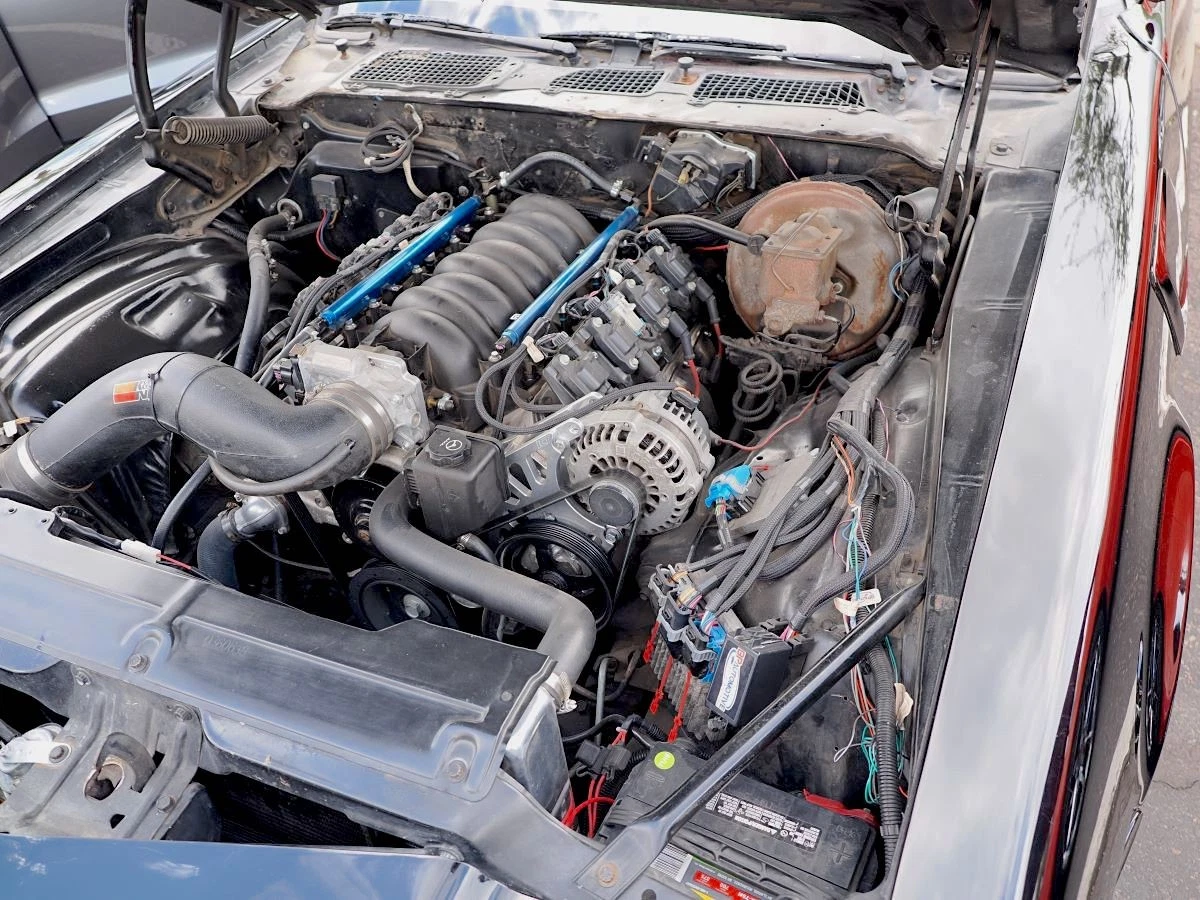

Illustrative image related to alternator cost car
How does the export and import business utilize alternator cost car?
Export and import businesses can capitalize on the alternator market by trading in used or remanufactured components. This approach offers cost-effective solutions for vehicle maintenance, particularly in regions where new parts may be prohibitively expensive. Compliance with international standards is crucial for these businesses, as it ensures the quality and reliability of the alternators being traded. Establishing relationships with reputable suppliers can enhance credibility and streamline the sourcing process.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘alternator cost car’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Understanding the Variability in Alternator Costs
The Problem:
B2B buyers often face significant challenges when trying to determine the right budget for alternators due to the vast variability in costs. Factors such as the vehicle’s make, model, and year can drastically influence pricing. Additionally, the differences between new and remanufactured alternators, as well as variations in warranty terms, can leave buyers confused and potentially overspending. This unpredictability can hinder effective budgeting and financial planning, especially for businesses managing fleets or repair shops.
The Solution:
To navigate the fluctuating costs of alternators, B2B buyers should adopt a systematic approach to sourcing. Start by gathering detailed specifications for the alternators needed, including the vehicle’s make, model, engine size, and electrical requirements. Utilize online databases and supplier catalogs to compare prices across multiple vendors, paying close attention to warranty options and the reputation of aftermarket parts. Establishing relationships with trusted suppliers who offer consistent pricing and quality assurance can also provide leverage in negotiations, helping to secure bulk purchase discounts. Keeping a spreadsheet to track pricing trends over time can further enhance budgeting accuracy.
Scenario 2: Managing Inventory and Supply Chain Issues for Alternators
The Problem:
For businesses that rely on alternator replacements, managing inventory can be a daunting task. Fluctuations in demand due to seasonality or market changes can lead to either stock shortages or excess inventory. Additionally, sourcing alternators from multiple suppliers can complicate logistics, increasing the risk of delays or receiving substandard products that could affect service quality.
The Solution:
Implementing a just-in-time (JIT) inventory system can help B2B buyers efficiently manage alternator stock. This approach involves closely monitoring sales data to predict demand accurately, allowing for timely orders that reduce excess inventory costs. Partnering with reliable suppliers who can offer rapid delivery options is essential. Furthermore, utilizing inventory management software can streamline tracking and reporting, enabling businesses to quickly identify which alternators are in high demand and which ones are not moving. Regular communication with suppliers about anticipated demand changes can also mitigate supply chain disruptions.
Scenario 3: Ensuring Quality and Reliability in Alternator Sourcing
The Problem:
Quality assurance is a significant concern for B2B buyers when sourcing alternators, particularly when considering the performance and longevity of the parts. Purchasing low-cost options may seem tempting, but inferior quality can lead to frequent failures, resulting in higher replacement costs and potential downtime for vehicles. This can be particularly damaging for businesses that depend on reliability, such as transportation or logistics companies.
The Solution:
To ensure quality and reliability in alternator sourcing, B2B buyers should prioritize OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) parts or reputable aftermarket alternatives known for their durability. When selecting suppliers, it’s crucial to verify their quality control processes and certifications. Request samples and conduct performance tests to gauge the reliability of the alternators before committing to larger orders. Additionally, establishing a robust feedback mechanism with technicians can help identify any recurring issues with specific brands or models. Regularly reviewing supplier performance and remaining open to switching vendors based on quality metrics can significantly enhance the overall reliability of the alternators used in operations.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for alternator cost car
When selecting materials for alternators in vehicles, particularly for B2B buyers in diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, it is essential to consider the properties, advantages, limitations, and regulatory requirements of each material. Below, we analyze four common materials used in alternators: copper, aluminum, steel, and plastic.
What Are the Key Properties of Copper in Alternators?
Copper is a widely used material in alternators due to its excellent electrical conductivity and thermal properties. It can withstand high temperatures and is resistant to corrosion, making it suitable for automotive applications. The typical operating temperature range for copper in alternators is between -40°C to 150°C, ensuring reliable performance in various climates.
Pros and Cons of Copper:
The primary advantage of copper is its superior conductivity, which enhances the efficiency of the alternator. However, copper is relatively expensive compared to other materials, which can increase the overall cost of the alternator. Additionally, the manufacturing process can be complex, requiring specialized techniques to ensure the integrity of the electrical connections.

Illustrative image related to alternator cost car
Impact on Application:
Copper’s compatibility with high electrical loads makes it ideal for alternators that power numerous electrical components in modern vehicles. However, its weight can be a consideration for performance-oriented applications.
Considerations for International B2B Buyers:
Buyers should ensure that the copper used complies with international standards such as ASTM B170 or JIS H3100. Markets in Brazil and Saudi Arabia may have specific regulations regarding the sourcing and quality of copper.
How Does Aluminum Compare as a Material for Alternators?
Aluminum is another common material used in the construction of alternators, particularly for housings and brackets. Its lightweight nature helps reduce the overall weight of the vehicle, which can improve fuel efficiency.
Pros and Cons of Aluminum:
Aluminum has good corrosion resistance and is easier to machine than copper, which can simplify the manufacturing process. However, its electrical conductivity is lower than that of copper, which may impact the efficiency of the alternator if used in the windings.
Impact on Application:
Aluminum is suitable for applications where weight reduction is critical, but it may not be the best choice for high-performance alternators that require maximum electrical output.
Illustrative image related to alternator cost car
Considerations for International B2B Buyers:
Buyers should verify that aluminum components meet standards such as ASTM B221 or EN 573. In regions like Europe, compliance with RoHS regulations regarding hazardous substances is also essential.
What Role Does Steel Play in Alternator Manufacturing?
Steel is often used in the production of alternator frames and brackets due to its strength and durability. It can withstand significant mechanical stress, which is crucial for components that experience vibration during operation.
Pros and Cons of Steel:
The main advantage of steel is its robustness, which contributes to the longevity of the alternator. However, steel is heavier than aluminum, which can negate some of the weight-saving benefits. Additionally, it is susceptible to rust if not properly coated or treated.
Impact on Application:
Steel is ideal for heavy-duty applications where durability is paramount. However, its weight may be a disadvantage in performance-focused vehicles.
Considerations for International B2B Buyers:
Steel components should comply with standards such as ASTM A36 or JIS G3101. Buyers in South America and the Middle East should be aware of local regulations regarding the use of recycled materials in steel production.
How Is Plastic Used in Alternator Design?
Plastic is commonly used for non-structural components in alternators, such as covers and insulators. It is lightweight and can be molded into complex shapes, which allows for design flexibility.
Pros and Cons of Plastic:
The primary advantage of plastic is its weight and resistance to corrosion. However, it may not withstand high temperatures as effectively as metals, which can limit its application in high-heat areas of the alternator.
Impact on Application:
Plastic is suitable for components that do not bear significant loads but require protection from environmental factors. Its use can enhance the overall efficiency of the alternator by reducing weight.
Considerations for International B2B Buyers:
Buyers should ensure that the plastics used are compliant with standards such as ASTM D638 or ISO 527. In regions like Europe, compliance with REACH regulations is critical for the safe use of chemical substances.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Alternators
| Material | Typical Use Case for alternator cost car | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Copper | Windings and electrical connections | Superior electrical conductivity | High cost and complex mfg | High |
| Aluminum | Housings and brackets | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Lower conductivity than copper | Medium |
| Steel | Frames and structural components | High strength and durability | Heavier than aluminum | Medium |
| Plastic | Covers and insulators | Lightweight and design flexibility | Limited high-temperature resistance | Low |
This guide provides actionable insights for B2B buyers in the automotive sector, emphasizing the importance of material selection in the cost and performance of alternators. Understanding the properties and implications of each material can lead to more informed purchasing decisions, ensuring compliance with regional standards and optimizing product performance.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for alternator cost car
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Alternators?
The manufacturing process of alternators involves several critical stages that ensure the final product meets the necessary performance and quality standards. Understanding these stages can help B2B buyers make informed decisions when selecting suppliers.
Material Preparation: How Are Raw Materials Sourced and Processed?
The manufacturing of alternators begins with the careful selection of raw materials. Key components include copper for the windings, steel for the casing, and various types of plastics for insulation. The quality of these materials directly impacts the alternator’s efficiency and lifespan.
Once sourced, materials undergo preprocessing. Copper is typically drawn into wires, while steel sheets are cut and shaped for the casing. Buyers should inquire about the suppliers’ sourcing practices to ensure compliance with international standards and sustainability practices, particularly if they are sourcing from regions with varying regulations.
Illustrative image related to alternator cost car
Forming: What Techniques Are Used to Create Alternator Components?
The forming stage involves several techniques to shape the raw materials into functional components. Common methods include:
-
Stamping: This technique is used to create the steel casing and other metal parts. High-precision stamping ensures that each part fits together correctly, which is crucial for the alternator’s performance.
-
Winding: The copper wire is wound into coils, which are essential for generating electricity. Automated winding machines are often employed to enhance precision and efficiency.
-
Casting: Some components may be produced through casting, particularly those requiring complex shapes that cannot be easily stamped or machined.
During this stage, it’s essential for manufacturers to adhere to precise specifications to ensure that each component meets the design requirements. B2B buyers should request detailed information about the forming techniques used by potential suppliers, including any proprietary methods that may enhance quality.
Assembly: How Are Alternators Put Together?
Once all components are formed, the assembly process begins. This stage includes:
-
Component Integration: The stator, rotor, and other parts are assembled in a clean environment to prevent contamination.
-
Electrical Connections: Proper electrical connections are made to ensure efficient power generation. This is often done using automated systems to reduce human error.
-
Mechanical Assembly: The entire assembly is then enclosed in the casing, with attention paid to tolerances and alignments that affect the alternator’s operational efficiency.
As assembly is a critical stage where defects can arise, B2B buyers should inquire about the assembly process and whether it is automated or manual. Automation typically results in higher consistency and lower defect rates.
Finishing: What Quality Controls Are Implemented Post-Assembly?
The finishing stage includes surface treatments, painting, and quality checks. Coatings may be applied to prevent corrosion and enhance durability.

Illustrative image related to alternator cost car
This stage is also crucial for ensuring that the alternators meet specific performance benchmarks before they are shipped. Buyers should look for suppliers that conduct extensive final inspections and testing before dispatching products.
How Is Quality Assurance Integrated into the Manufacturing Process?
Quality assurance (QA) is essential throughout the alternator manufacturing process. Suppliers must comply with both international and industry-specific quality standards to ensure their products are reliable and safe.
What International Standards Should B2B Buyers Consider?
B2B buyers should prioritize suppliers that adhere to internationally recognized quality standards such as:
-
ISO 9001: This standard focuses on quality management systems and ensures that manufacturers consistently meet customer and regulatory requirements.
-
ISO/TS 16949: This specific standard for automotive suppliers incorporates the principles of ISO 9001 with additional quality requirements tailored for the automotive industry.
In addition to these, compliance with regional standards such as CE marking in Europe or API standards in oil and gas applications can further validate a manufacturer’s commitment to quality.

Illustrative image related to alternator cost car
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are critical for maintaining high standards in alternator production. Key checkpoints include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards before production begins.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, continuous monitoring and testing are conducted to catch defects early. This includes checking dimensions, electrical properties, and assembly integrity.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once the alternators are assembled, they undergo comprehensive testing, including functional tests to measure voltage output and load capacity.
B2B buyers should request documentation of these QC processes, including inspection reports and testing results, to verify the quality of the products they are considering.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
When sourcing alternators, B2B buyers should implement thorough verification processes to ensure supplier quality.
What Audit Processes Should Be in Place?
Buyers should conduct supplier audits to assess their manufacturing capabilities and quality assurance practices. This includes:
-
Facility Inspections: Visiting the manufacturing site can provide insight into production capabilities, cleanliness, and adherence to safety standards.
-
Document Review: Requesting quality management documentation, including certifications, test reports, and process flowcharts, can help confirm compliance with international standards.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging a third-party inspection service can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control processes and product reliability.
What Are the QC/CERT Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International buyers must also consider the nuances of quality control certifications that may vary by region. For instance, suppliers in Africa and South America may have different regulatory requirements compared to those in Europe or the Middle East.
Understanding these differences is crucial for ensuring compliance with local regulations, and buyers should leverage local expertise or consultants to navigate these complexities.
Conclusion: Why Is a Robust Manufacturing and Quality Assurance Process Essential for Alternator Cost?
Investing time in understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices of alternator suppliers is essential for B2B buyers. By focusing on material preparation, forming techniques, assembly practices, and rigorous quality control measures, buyers can ensure they select reliable partners that provide high-quality alternators at competitive costs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘alternator cost car’
To effectively navigate the complexities of sourcing alternators for vehicles, this guide offers a step-by-step checklist tailored for B2B buyers. Understanding the various aspects of alternator procurement can help you make informed decisions that ensure reliability and cost-effectiveness in your supply chain.

Illustrative image related to alternator cost car
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is essential to ensure the alternators you procure meet the operational requirements of your vehicles. Consider factors such as the year, make, model, and engine size of the vehicles in question. Additionally, evaluate the amperage needs and any specific mounting styles required to ensure compatibility.
Step 2: Research Market Prices
Understanding the price range for alternators is vital for budgeting and negotiation. Prices can vary significantly based on factors like brand, quality, and whether the alternator is new or remanufactured. Conduct a market analysis to gather information on average costs, which typically range from $100 to $1,000, depending on the specifications.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before making a purchase, it’s crucial to vet suppliers thoroughly. Look for company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in similar industries or regions. Ensure that the suppliers have a track record of reliability and quality, as the alternator’s performance is directly linked to the supplier’s reputation.

Illustrative image related to alternator cost car
- Supplier Certifications: Check for ISO or other relevant certifications that indicate a commitment to quality standards.
- Warranty Options: Assess the warranty terms offered, as a longer warranty often reflects confidence in product quality.
Step 4: Assess Quality and Compliance Standards
Quality assurance is critical in automotive parts procurement. Verify that the alternators meet international standards and regulations, particularly in your target markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Compliance with local regulations can prevent future legal issues and enhance customer satisfaction.
Step 5: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Once you have selected potential suppliers, engage in negotiations to secure favorable terms. This includes price, payment terms, delivery schedules, and return policies. Aim for a balance between cost savings and ensuring that the quality of the alternators is not compromised.
- Volume Discounts: Inquire about discounts for bulk purchases to optimize your procurement costs.
- Delivery Schedules: Establish clear timelines for delivery to avoid disruptions in your operations.
Step 6: Plan for After-Sales Support and Service
After securing your supply of alternators, consider the importance of after-sales support. A reliable supplier should offer technical assistance, troubleshooting guidance, and a robust return policy. This support can be crucial in addressing any issues that may arise post-purchase.
Step 7: Monitor Performance and Supplier Relations
After the procurement process, continuously monitor the performance of the alternators and maintain a good relationship with your suppliers. Regular feedback and communication can lead to improvements in product quality and service, ultimately benefiting your operations in the long run.
By following this structured approach, B2B buyers can effectively source alternators that meet their needs while ensuring cost efficiency and reliability in their supply chains.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for alternator cost car Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Alternator Sourcing?
When considering the cost structure for sourcing alternators, various components contribute to the final price. The primary cost elements include:
-
Materials: The quality and type of materials, particularly copper for windings and high-grade plastics for casings, significantly affect the cost. Higher amperage alternators typically require more copper and other materials, leading to increased costs.
-
Labor: Manufacturing labor costs vary by region and can impact overall pricing. In regions with higher labor costs, such as parts of Europe, the total production cost will be higher.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to facility operations, equipment maintenance, and utility costs. Efficient manufacturing processes can help reduce overhead.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in tooling for production can be substantial, especially for custom or specialized alternators. This cost is often amortized over the production volume.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing rigorous QC measures ensures that alternators meet performance and safety standards, which can add to the production costs but is essential for maintaining brand reputation.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs can vary widely depending on the supplier’s location and the buyer’s destination. This includes shipping fees, customs duties, and handling charges.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a margin to cover their operational costs and profit. Understanding the expected margin can aid in negotiations.
How Do Pricing Influencers Impact Alternator Costs?
Several factors influence the pricing of alternators in the B2B market:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders often qualify for discounts, making it essential for buyers to evaluate their needs against supplier MOQ requirements.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom alternators tailored to specific vehicle models or electrical requirements can significantly increase costs. Buyers should clearly define their specifications to avoid unnecessary expenses.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Alternators made from higher-quality materials or those that meet specific certifications (like ISO standards) may carry a premium price. Buyers should weigh the long-term benefits of investing in quality against initial costs.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their proven track record and quality assurance processes.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the agreed Incoterms is crucial for calculating total costs, as they dictate who bears responsibility for shipping costs, insurance, and customs duties.
What Buyer Tips Can Help Optimize Alternator Sourcing Costs?
For B2B buyers, particularly in international markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, several strategies can enhance cost efficiency:
-
Negotiate Pricing: Leverage volume purchases or long-term contracts to negotiate better pricing. Building a relationship with suppliers can also lead to favorable terms.
-
Consider Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Beyond the initial purchase price, evaluate factors such as durability, warranty, and potential repair costs. Investing in a higher-quality alternator can reduce long-term expenses.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances for International Transactions: Be aware of currency fluctuations, import tariffs, and local regulations that may impact costs. Collaborating with local partners can help navigate these complexities.
-
Utilize Local Suppliers When Possible: Sourcing from local manufacturers can reduce logistics costs and lead times, making it a practical choice for many buyers.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
It is important to note that the prices for alternators can vary significantly based on the factors mentioned above. The information provided is indicative and should be used as a guideline for budgeting and planning. Buyers are encouraged to conduct thorough market research and consult multiple suppliers to obtain accurate pricing tailored to their specific needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing alternator cost car With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Alternator Cost for Automotive Solutions
In the automotive industry, understanding the cost and function of an alternator is essential for B2B buyers. However, there are alternative solutions that may serve the same purpose or enhance vehicle performance. This section compares the traditional alternator cost against two viable alternatives: battery management systems and hybrid vehicle technologies.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Alternator Cost Car | Battery Management System | Hybrid Vehicle Technology |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Provides steady power for electrical systems while charging the battery. | Optimizes battery usage and lifespan, ensuring efficient power management. | Combines internal combustion engine with electric propulsion, offering superior fuel efficiency. |
| Cost | $100 – $1,000 (varies by model and specifications). | $200 – $600 (system and installation costs). | $20,000 – $40,000 (initial vehicle cost; includes battery and engine technology). |
| Ease of Implementation | Generally straightforward; requires matching specifications. | Moderate complexity; requires integration with existing systems. | High complexity; involves vehicle redesign and advanced technology. |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; typically lasts 7-10 years. | Moderate maintenance; periodic checks and potential software updates needed. | Higher maintenance; battery replacement and system checks are required. |
| Best Use Case | Standard vehicles requiring reliable power supply. | Electric vehicles or systems focused on battery longevity. | Eco-conscious consumers or businesses looking for fuel efficiency. |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Battery Management System (BMS)
A battery management system optimizes the performance and longevity of batteries used in electric or hybrid vehicles. It monitors the state of charge, health, and temperature of the battery, ensuring that it operates within safe limits. The advantages of a BMS include improved efficiency and extended battery life, making it an excellent choice for businesses that rely on electric vehicles. However, installation can be moderately complex, and ongoing maintenance is required to ensure software updates and system integrity.
Hybrid Vehicle Technology
Hybrid vehicles utilize both an internal combustion engine and an electric motor, providing an innovative solution to reduce fuel consumption and emissions. This technology offers significant performance benefits, particularly in urban environments where stop-and-go traffic is common. The initial investment in hybrid technology is considerably higher than traditional alternators, ranging from $20,000 to $40,000. Furthermore, the complexity of these vehicles means that maintenance can be more demanding, especially regarding battery health and system checks. Nevertheless, for businesses focused on sustainability and fuel efficiency, hybrids present a compelling option.
Conclusion: Making an Informed Decision on Automotive Solutions
When selecting the right solution for automotive power needs, B2B buyers should assess their specific requirements, including performance, budget constraints, and maintenance capabilities. While traditional alternators provide a reliable and cost-effective power source, alternatives such as battery management systems and hybrid technologies may offer enhanced efficiency and sustainability. It is crucial to align the choice of technology with the operational goals and long-term strategy of the business to ensure optimal performance and cost-effectiveness.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for alternator cost car
What Are the Essential Technical Properties of Alternators for Cost Consideration?
When evaluating the cost of alternators for vehicles, understanding their technical properties is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. Here are several key specifications that impact both performance and pricing:
1. Amperage Output
The amperage rating indicates the electrical current the alternator can produce, which is essential for powering various vehicle systems. Typically, alternators range from 40 to 200 amps. For B2B buyers, selecting the right amperage is vital; underpowered alternators can lead to system failures, while over-specification can unnecessarily inflate costs.
Illustrative image related to alternator cost car
2. Material Composition
Alternators are primarily composed of materials such as copper and aluminum, which affect durability and efficiency. For example, higher copper content in the windings typically translates to better conductivity and performance. Buyers should assess the material grades used in alternators, as this directly influences longevity and operational efficiency, impacting total cost of ownership.
3. Mounting Style
The mounting style of an alternator determines its compatibility with specific vehicle models. Common types include pad mount and side mount configurations. For B2B buyers, ensuring the correct mounting style is critical; incorrect fitment can lead to additional costs for modifications or replacements, thereby affecting overall project budgets.
4. Electrical Connections
Alternators can feature different types of electrical connections, such as 1-wire and 3-wire systems. The complexity of the electrical connection affects installation ease and compatibility with vehicle systems. Understanding these variations helps buyers select the right alternator while avoiding unexpected labor costs during installation.
5. Warranty Period
Warranty offerings can vary significantly among alternators, with options ranging from 1 year to a lifetime guarantee. A longer warranty period often indicates higher quality and reliability. B2B buyers should consider warranty terms as part of their total cost analysis, as investing in a more durable product can minimize future replacement costs.
6. Core Availability for Remanufacturing
The availability of cores for remanufacturing impacts both cost and sustainability. Certain vehicles may have limited core availability, leading to higher prices for remanufactured units. Buyers need to assess market availability to ensure they can procure alternators without incurring excessive costs or delays.

Illustrative image related to alternator cost car
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Alternator Costs?
Navigating the terminology associated with alternator purchases is just as important as understanding the technical properties. Here are several key trade terms that B2B buyers should be familiar with:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to parts made by the same manufacturer that produced the original components for the vehicle. OEM alternators are typically more expensive but offer guaranteed compatibility and performance. B2B buyers should weigh the benefits of OEM against aftermarket options, considering reliability and potential long-term savings.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ indicates the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is essential for B2B buyers, as it directly affects inventory costs and order planning. Buyers should negotiate MOQs that align with their operational needs to optimize purchasing efficiency.

Illustrative image related to alternator cost car
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal process used by buyers to solicit price quotes from suppliers. This document outlines specifications and quantities, allowing vendors to provide competitive pricing. For B2B buyers, issuing RFQs can ensure they receive the best market rates for alternators, facilitating budget management.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions, including shipping, insurance, and customs clearance. Familiarity with Incoterms is crucial for B2B buyers engaging in cross-border purchases of alternators, as they dictate cost liabilities and delivery expectations.
5. Aftermarket
The aftermarket refers to parts and components that are not sourced from the OEM but are manufactured by third parties. While aftermarket alternators can be more affordable, buyers should ensure they meet quality standards to avoid costly failures. This term is critical for evaluating potential cost savings against reliability.
Understanding these technical properties and trade terminology empowers B2B buyers to make informed decisions regarding alternator costs, enhancing their procurement strategies and operational efficiency.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the alternator cost car Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics Influencing Alternator Costs in the Automotive Sector?
The global alternator market is evolving rapidly, driven by several key factors. Increasing vehicle electrification, particularly in emerging markets like Brazil and Saudi Arabia, is creating a surge in demand for high-performance alternators. As more vehicles integrate advanced electrical systems, the need for reliable and efficient alternators becomes paramount. Additionally, the growth of electric vehicles (EVs) is altering traditional supply chains, with a greater emphasis on sourcing components that can handle higher electrical loads. This shift is particularly relevant for international B2B buyers looking to invest in durable and efficient products.
Another significant trend is the rise of digital technologies in sourcing. B2B buyers are increasingly leveraging e-commerce platforms and digital marketplaces to streamline procurement processes. This trend is particularly pronounced in regions like Africa and South America, where traditional supply chains may be less developed. Advanced analytics tools are also being employed to assess market trends, enabling buyers to make informed decisions based on real-time data.
Furthermore, international trade dynamics, including tariffs and regulatory frameworks, are influencing sourcing strategies. Buyers must stay attuned to geopolitical changes that could affect the cost and availability of alternators. Understanding these market dynamics is crucial for B2B buyers, as they navigate an increasingly complex landscape to ensure they are sourcing the right products at competitive prices.
How Does Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact Alternator Procurement in the Automotive Sector?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing are becoming integral to the automotive supply chain, particularly for alternators. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes and the materials used in alternator production are under scrutiny. B2B buyers are now prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to reducing their carbon footprint and employing sustainable practices. This includes sourcing raw materials responsibly and ensuring that manufacturing processes minimize waste and emissions.

Illustrative image related to alternator cost car
Additionally, the demand for ‘green’ certifications is growing. Buyers are increasingly seeking suppliers who can provide documentation that verifies the sustainability of their products. This includes certifications for recycled materials used in alternators, such as copper and aluminum, which are critical components. By prioritizing suppliers who adhere to these standards, B2B buyers not only contribute to environmental conservation but also align their purchasing decisions with consumer expectations for sustainability.
Ethical supply chains are also a focus area, particularly in regions where labor practices may be less regulated. Buyers must ensure that their suppliers comply with ethical labor standards, contributing to fair working conditions and community development. This commitment to ethical sourcing not only enhances brand reputation but also mitigates risks associated with supply chain disruptions.
What Historical Developments Have Shaped the Alternator Market?
The evolution of the alternator market can be traced back to the early 20th century when automobiles primarily relied on direct current (DC) generators. The introduction of the alternator in the 1960s marked a significant advancement, as it allowed for greater efficiency and power generation. Over the decades, technological innovations have led to the development of compact, high-output alternators that meet the growing electrical demands of modern vehicles.
The rise of electronic systems in cars has further transformed the alternator’s role, necessitating more sophisticated designs that can support complex electrical architectures. Today, the alternator serves as a critical component, not only powering essential vehicle functions but also supporting advanced safety and entertainment systems. This historical context underscores the importance of sourcing quality alternators that can meet the demands of contemporary automotive technology, providing B2B buyers with insights into the longevity and reliability of the products they procure.
Conclusion
Understanding the current market dynamics, sustainability imperatives, and historical context surrounding alternators is vital for international B2B buyers. By aligning sourcing strategies with these insights, businesses can ensure they are not only meeting immediate needs but also positioning themselves for long-term success in a rapidly evolving automotive landscape.

Illustrative image related to alternator cost car
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of alternator cost car
-
How do I determine the right alternator for my vehicle model?
To ensure you source the correct alternator, start by identifying the year, make, model, and engine size of the vehicle. Alternators must match the specific electrical requirements and mounting styles of your vehicle. It’s advisable to consult the vehicle’s manual or a reliable database to verify specifications. Additionally, consider the amperage needs based on the electrical accessories in the vehicle, as this will affect the alternator’s performance and longevity. -
What factors influence the cost of an alternator?
The cost of an alternator can vary significantly based on several factors, including the vehicle’s make and model, the type of alternator (new vs. remanufactured), and the amperage rating. Additionally, warranty duration can impact price; parts with longer warranties typically cost more. Geographic location and supplier pricing strategies also play a role, particularly in international markets where shipping and tariffs may apply. -
What should I consider when sourcing alternators from international suppliers?
When sourcing alternators internationally, assess the supplier’s reliability and reputation. Check for certifications, customer reviews, and quality assurance processes. It’s essential to understand the terms of trade, including payment methods, delivery times, and return policies. Additionally, ensure that the supplier can provide documentation for warranty and compliance with local regulations, particularly in regions like Africa and the Middle East, where standards may vary. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for alternators?
Minimum order quantities for alternators can vary widely among suppliers. Typically, larger manufacturers may have higher MOQs due to production costs, while smaller suppliers might offer more flexibility. It’s essential to negotiate these terms based on your purchasing capacity and market demand. Consider discussing the potential for bulk discounts or trial orders to establish a relationship without committing to large quantities upfront. -
How can I ensure quality assurance when purchasing alternators?
To ensure quality assurance when purchasing alternators, request detailed product specifications and certifications from the supplier. Engage in pre-shipment inspections or third-party quality checks to validate the products before they leave the supplier’s facility. Establish a clear return policy and warranty terms that protect your investment. Additionally, maintaining open communication with the supplier can help address any quality concerns promptly. -
What payment terms are common for international alternator purchases?
Common payment terms for international purchases include letters of credit, wire transfers, and payment on delivery. Many suppliers prefer a partial upfront payment, followed by the balance upon shipment or delivery. It’s crucial to discuss and agree upon payment terms before finalizing the order to avoid misunderstandings. Additionally, consider using secure payment methods that offer buyer protection, especially when dealing with new suppliers. -
How do logistics and shipping affect alternator costs?
Logistics and shipping significantly impact the overall cost of sourcing alternators, particularly for international transactions. Factors such as shipping distance, weight, and urgency can influence freight costs. Additionally, customs duties and taxes may apply, depending on the destination country. It’s advisable to work with experienced logistics partners who can provide accurate shipping estimates and handle customs clearance efficiently to minimize delays and unexpected expenses. -
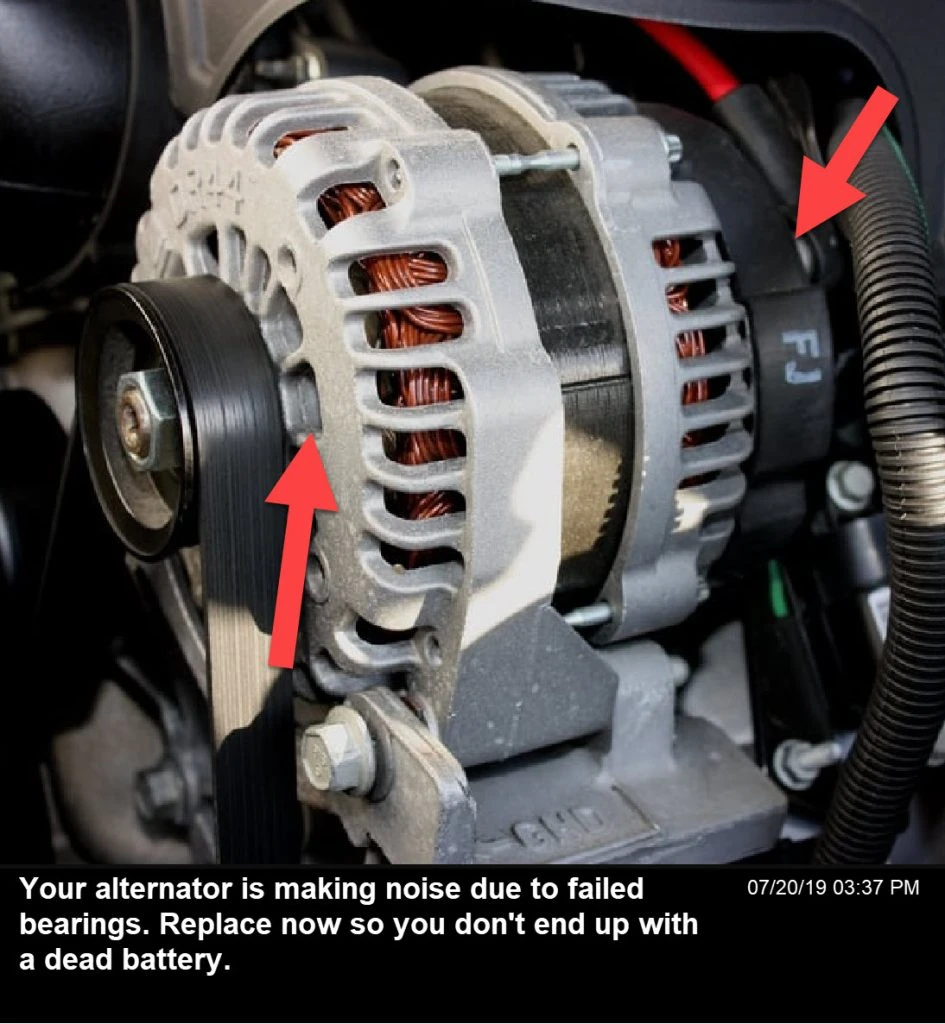
What are the signs of a failing alternator that I should communicate to clients?
Educating clients on the signs of a failing alternator is essential for customer satisfaction and repeat business. Key indicators include dimming headlights, unusual noises from the engine, and dashboard warning lights. Other signs may include electrical malfunctions in components like windows and radios. Encourage clients to address these issues promptly to avoid more extensive vehicle damage and higher repair costs.
Top 3 Alternator Cost Car Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Toyota – RAV4 Alternator Replacement
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: 2006 Toyota RAV4 alternator replacement; cost: $450 (includes labor); previous alternator cost: over $350.
2. CARFAX – Gebrauchtwagenhistorien
Domain: carfax.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: CARFAX bietet Zugang zur weltweit größten Datenbank für Gebrauchtwagenhistorien, die Informationen zu Schäden, Unfällen, Wartungen, Tachomanipulationen, Importinformationen, Diebstählen, Eigentumswechsel, Taxi- oder Mietwagennutzung und offenen Rückrufen des Herstellers enthält. Das Unternehmen verfolgt das Ziel, den Gebrauchtwagenmarkt transparenter zu gestalten und die Sicherheit auf den Straßen…
3. CarTalk – Alternator Replacement Costs
Domain: cartalk.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: The cost to replace an alternator ranges from $600 to $1,500. An alternator is a critical component that converts mechanical force into electrical energy, powering the engine, lights, and charging the battery. Symptoms of a failing alternator include a check engine light, dimming headlights, and the need for jump starts. Alternators can fail due to mechanical wear or electrical component failure. …
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for alternator cost car
In navigating the complexities of alternator costs, international B2B buyers must prioritize strategic sourcing to maximize value while minimizing risks. Understanding the factors that influence alternator pricing—such as vehicle specifications, amperage requirements, and warranty options—can lead to more informed purchasing decisions. By considering both new and remanufactured alternatives, businesses can strike a balance between cost-efficiency and quality assurance.
Moreover, recognizing the signs of a failing alternator is crucial for timely interventions that prevent cascading failures and expensive repairs. As vehicles age, the likelihood of alternator replacement increases, making it imperative for buyers to establish reliable supply chains that can deliver high-quality parts promptly.
Looking ahead, the global automotive market is poised for growth, with demand for reliable alternators expected to rise. Buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should leverage this opportunity to build partnerships with trusted suppliers. By doing so, they can ensure access to competitively priced, high-quality alternators that meet their operational needs. Engage with local distributors and manufacturers to enhance your sourcing strategy and secure your place in this evolving marketplace.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.

Illustrative image related to alternator cost car
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.