Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for all the parts of a car
In today’s competitive landscape, sourcing reliable and high-quality parts for vehicles can pose significant challenges for international B2B buyers. The complexities of the automotive supply chain, coupled with varying regional standards and regulations, make it essential for businesses to have a comprehensive understanding of the various components that constitute a car. This guide serves as an essential resource for sourcing all the parts of a car, from engines and transmissions to braking systems and electrical components.
By delving into the types, applications, and functionalities of each part, this guide empowers buyers to make informed purchasing decisions. It will also explore critical aspects such as supplier vetting, cost analysis, and potential challenges in logistics and compliance, tailored specifically for businesses operating in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including markets like Germany and Vietnam.
Arming yourself with the right knowledge about automotive components not only enhances your procurement strategies but also ensures that your business remains competitive and efficient. With this guide, navigate the global market with confidence, ensuring that you select the best parts for your operational needs and maintain optimal vehicle performance in any region.
Table Of Contents
- Top 3 All The Parts Of A Car Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for all the parts of a car
- Understanding all the parts of a car Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of all the parts of a car
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘all the parts of a car’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for all the parts of a car
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for all the parts of a car
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘all the parts of a car’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for all the parts of a car Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing all the parts of a car With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for all the parts of a car
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the all the parts of a car Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of all the parts of a car
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for all the parts of a car
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Understanding all the parts of a car Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Internal Combustion Engine | Comprises pistons, crankshaft, camshaft, and fuel injection systems | Automotive manufacturing, parts distribution | Pros: Well-established technology, high performance; Cons: Higher emissions, requires regular maintenance. |
| Transmission Systems | Includes manual, automatic, and CVT gearboxes | Automotive repair shops, vehicle assembly | Pros: Various options for performance; Cons: Complexity can lead to higher repair costs. |
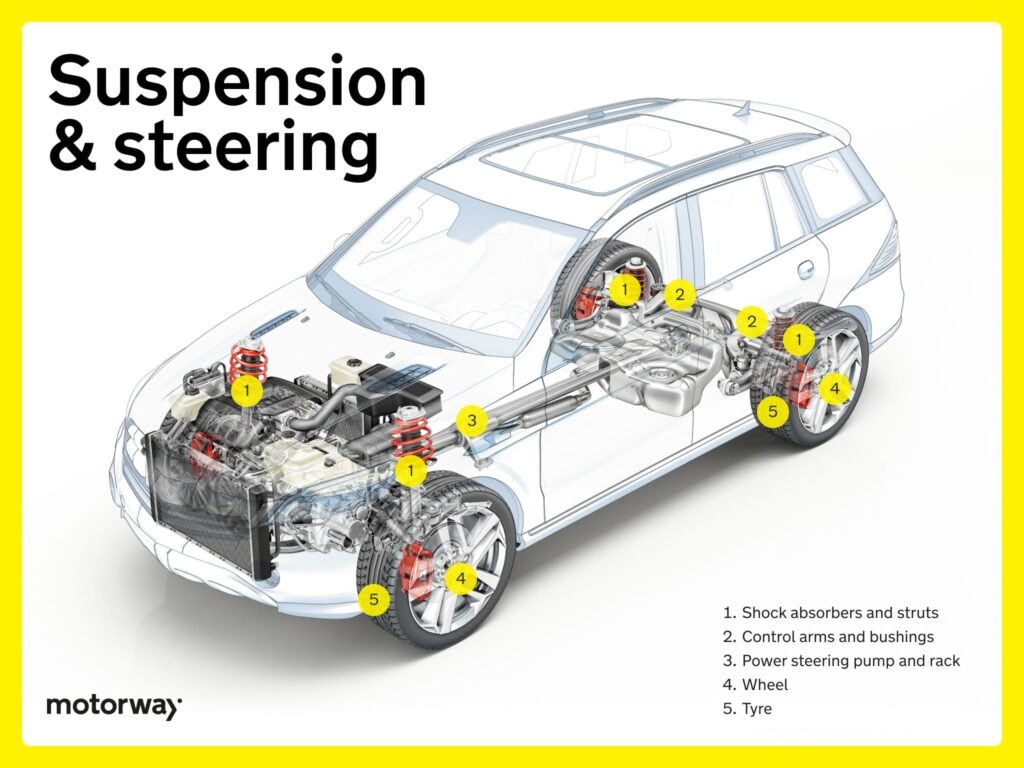
| Suspension Systems | Features components like shocks, struts, and control arms | Vehicle safety assessments, aftermarket upgrades | Pros: Enhances ride quality; Cons: Can be costly to replace. |
| Electrical Systems | Encompasses batteries, alternators, and wiring harnesses | Electrical part suppliers, vehicle assembly | Pros: Vital for modern vehicle functionality; Cons: Failure can lead to complete vehicle shutdown. |
| Exhaust Systems | Comprises catalytic converters, mufflers, and tailpipes | Emission control solutions, aftermarket sales | Pros: Reduces harmful emissions; Cons: Can be expensive to repair or replace. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Internal Combustion Engines?
Internal combustion engines (ICE) are the backbone of most vehicles, utilizing components like pistons and crankshafts to convert fuel into mechanical energy. These engines are widely used in various automotive applications, making them a primary focus for B2B buyers in manufacturing and parts distribution. When purchasing ICE components, buyers should consider factors such as compatibility with existing vehicle models, performance specifications, and emissions regulations. While these engines offer high performance and a proven track record, they also require regular maintenance and contribute to environmental concerns due to emissions.
How Do Transmission Systems Vary and What Are Their Applications?
Transmission systems are essential for controlling the power generated by the engine and come in several types: manual, automatic, and continuously variable transmissions (CVT). Each type has its unique features and applications, ranging from enhanced driver control in manual systems to the seamless operation of CVTs. B2B buyers in automotive repair and vehicle assembly must weigh the performance needs against potential repair costs, as more complex systems may require specialized knowledge and tools. While these systems can enhance driving experience, their complexity might lead to increased maintenance expenses.
What Are the Benefits of Advanced Suspension Systems?
Suspension systems play a critical role in vehicle safety and comfort, incorporating components like shocks and control arms. These systems are crucial for maintaining vehicle stability and handling, making them a focal point for automotive safety assessments and aftermarket upgrades. B2B buyers should consider the cost-effectiveness of replacing or upgrading suspension components, as they can significantly impact ride quality and vehicle longevity. While high-quality suspension parts enhance driving comfort and safety, they can also be costly to replace, necessitating careful budgeting.
Why Are Electrical Systems Vital for Modern Vehicles?
The electrical system in a vehicle is vital for its operation, encompassing batteries, alternators, and wiring harnesses. This system powers essential functions, from ignition to entertainment systems, making it indispensable for automotive manufacturers and electrical part suppliers. B2B buyers must consider the quality and reliability of electrical components, as failures can lead to significant operational downtime. While these systems are crucial for modern vehicle functionality, their complexity can lead to complete vehicle shutdowns if not properly maintained or replaced.
How Do Exhaust Systems Contribute to Vehicle Performance?
Exhaust systems, including catalytic converters and mufflers, play a crucial role in managing vehicle emissions and noise. They are vital for compliance with environmental regulations and are commonly sourced by emission control solutions providers and aftermarket sales. B2B buyers should prioritize high-quality exhaust components that meet regulatory standards while also considering the total cost of ownership, including installation and potential repair expenses. Although these systems help in reducing harmful emissions, they can be expensive to repair or replace, which is an important consideration in purchasing decisions.
Key Industrial Applications of all the parts of a car
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of all the parts of a car | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive Manufacturing | Production of vehicles, including assembly and quality control | Streamlined operations, reduced production costs | Quality certifications, supplier reliability, cost-effectiveness |
| Aftermarket Parts | Supply of replacement parts for maintenance and upgrades | Increased customer satisfaction, extended vehicle lifespan | Compatibility with various vehicle models, warranty terms |
| Fleet Management | Maintenance and repair of commercial vehicle fleets | Improved fleet reliability, reduced downtime | Bulk purchasing options, logistics support, service agreements |
| Automotive Repair Shops | Provision of parts for repair and service work | Enhanced service quality, customer retention | Diverse inventory, rapid delivery, competitive pricing |
| Electric Vehicle (EV) | Integration of electric components and systems | Access to growing EV market, sustainability alignment | Innovation in technology, compliance with environmental standards |
How Are Automotive Parts Used in Manufacturing Industries?
In the automotive manufacturing sector, all parts of a car play a crucial role in the production and assembly processes. Manufacturers rely on high-quality components, such as engines, transmissions, and suspension systems, to ensure vehicles meet safety and performance standards. By sourcing reliable parts, manufacturers can streamline operations and reduce production costs, ultimately leading to better profit margins. For international buyers, considerations like quality certifications and supplier reliability are paramount to maintain production efficiency.
What Role Do Aftermarket Parts Play in Vehicle Maintenance?
Aftermarket parts are essential for maintaining and upgrading vehicles, providing businesses with the opportunity to enhance customer satisfaction and extend the lifespan of their products. Suppliers of these parts must ensure compatibility with various vehicle models, as well as offer competitive pricing and warranty terms. This sector is particularly relevant for international B2B buyers seeking to tap into local markets with diverse vehicle populations, especially in regions like Africa and South America where vehicle longevity is critical.
Illustrative image related to all the parts of a car
How Do Fleet Management Companies Benefit from Automotive Parts?
Fleet management companies heavily rely on the maintenance and repair of their vehicles to ensure reliability and minimize downtime. By sourcing high-quality automotive parts, these companies can improve operational efficiency and reduce costs associated with vehicle breakdowns. Key considerations for fleet managers include bulk purchasing options, logistics support for timely deliveries, and service agreements that guarantee part availability. This is especially significant in regions with varied road conditions and vehicle usage patterns, such as the Middle East and Africa.
Why Are Automotive Repair Shops Dependent on Quality Parts?
Automotive repair shops depend on a steady supply of quality parts to provide effective repair and service solutions to their customers. By offering a diverse inventory of components, repair shops can enhance service quality and foster customer loyalty. Rapid delivery and competitive pricing are critical factors for these businesses, particularly for international buyers who may face logistical challenges. Ensuring parts compatibility with a wide range of vehicles is also crucial to meet the diverse needs of their clientele.
What Innovations Are Driving Electric Vehicle Parts Sourcing?
As the automotive industry shifts towards electric vehicles (EVs), the integration of innovative electric components becomes increasingly important. Businesses involved in the EV sector can benefit from sourcing advanced parts that align with sustainability goals and technological advancements. International B2B buyers must focus on compliance with environmental standards and the latest innovations to stay competitive in this growing market. This shift not only addresses consumer demand for greener alternatives but also positions companies favorably in a rapidly evolving industry landscape.
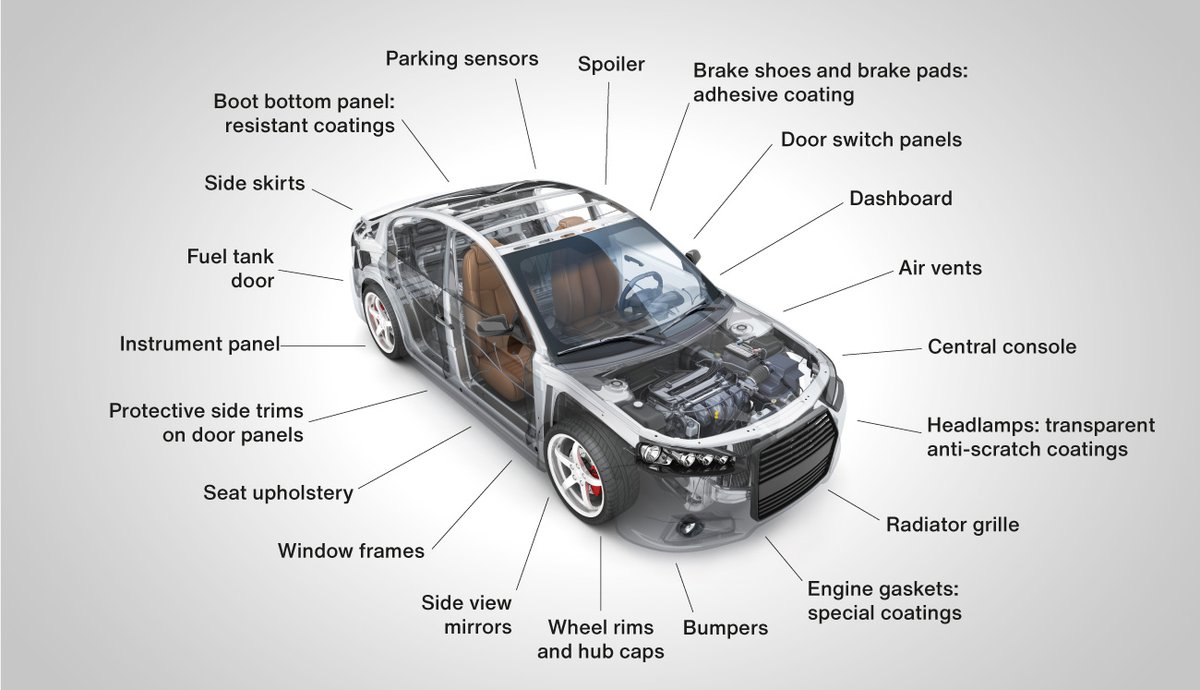
Illustrative image related to all the parts of a car
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘all the parts of a car’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Complex Supply Chains for Automotive Parts
The Problem: B2B buyers often face challenges in managing complex supply chains when sourcing automotive parts. The automotive industry is characterized by a diverse range of components, each sourced from different suppliers around the globe. For international buyers, particularly from regions like Africa or South America, delays in shipping, fluctuating costs, and inconsistent quality can severely impact their operations. Furthermore, the lack of reliable information on parts specifications can lead to purchasing errors, resulting in increased downtime and repair costs.
The Solution: To overcome these challenges, B2B buyers should establish strong relationships with multiple suppliers to create a diversified supply chain. This not only mitigates risks associated with dependency on a single source but also allows for competitive pricing. Additionally, leveraging technology such as inventory management software can streamline the procurement process, providing real-time data on stock levels and shipment statuses. Buyers should also invest time in understanding the specifications of the parts they require, perhaps by consulting with technical experts or using detailed product catalogs, to ensure they are ordering the right components for their vehicles. Regular audits of suppliers and their capabilities can further enhance quality assurance.
Scenario 2: Ensuring Compatibility of Parts Across Different Vehicle Models
The Problem: Another significant pain point for B2B buyers is ensuring the compatibility of parts across various vehicle models. With the automotive market continually evolving, new models and variations can make it difficult to determine which parts are interchangeable. This is particularly relevant for buyers in emerging markets where a mix of older and newer vehicle models is common. Incompatible parts can lead to costly returns and wasted resources, as well as delays in repairs and maintenance.
The Solution: To address this issue, B2B buyers should utilize comprehensive databases or software that provide detailed compatibility information for automotive parts. Investing in platforms that offer VIN (Vehicle Identification Number) lookup can help buyers quickly identify the correct parts for specific vehicle models. Furthermore, collaborating with manufacturers or parts distributors who specialize in the regions’ vehicles can provide insights into common compatibility issues. Establishing a systematic approach to inventory management—where parts are categorized by vehicle compatibility—can streamline operations and reduce errors in ordering.
Scenario 3: Managing Rising Costs and Budget Constraints for Automotive Parts
The Problem: As global supply chains become more strained, B2B buyers are increasingly faced with rising costs for automotive parts. Price hikes can result from a variety of factors, including raw material shortages, increased shipping fees, and geopolitical tensions. For businesses operating under tight budgets, such fluctuations can complicate financial planning and lead to reduced profit margins. Buyers must balance cost-saving measures without compromising the quality and reliability of parts.

Illustrative image related to all the parts of a car
The Solution: To manage rising costs effectively, B2B buyers should consider bulk purchasing agreements or long-term contracts with suppliers. These arrangements often provide more favorable pricing and can shield buyers from sudden price increases. Additionally, exploring alternative sourcing options, such as local suppliers or refurbished parts, can help reduce costs without sacrificing quality. Conducting a thorough market analysis to understand pricing trends and potential cost-saving opportunities is also crucial. Regularly reviewing supplier performance and pricing can help buyers negotiate better terms and maintain a competitive edge in a challenging market.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for all the parts of a car
What Are the Key Materials Used in Car Parts?
In the automotive industry, material selection is crucial for optimizing performance, safety, and cost-effectiveness. Understanding the properties, advantages, and limitations of various materials can help international B2B buyers make informed decisions. Below, we analyze four common materials used in car manufacturing: steel, aluminum, plastics, and composites.
How Does Steel Contribute to Automotive Parts Performance?
Steel is one of the most widely used materials in car manufacturing due to its strength and durability. It typically boasts high tensile strength, making it suitable for structural components such as the chassis and body panels. Steel can withstand high temperatures and pressures, which is essential for components like the engine block and transmission cases.
Pros: Steel is highly durable and cost-effective, making it a popular choice for mass production. Its recyclability also aligns with sustainability goals, appealing to environmentally conscious buyers.
Cons: However, steel is prone to corrosion if not properly treated, which can lead to increased maintenance costs. Additionally, its weight can negatively impact fuel efficiency.
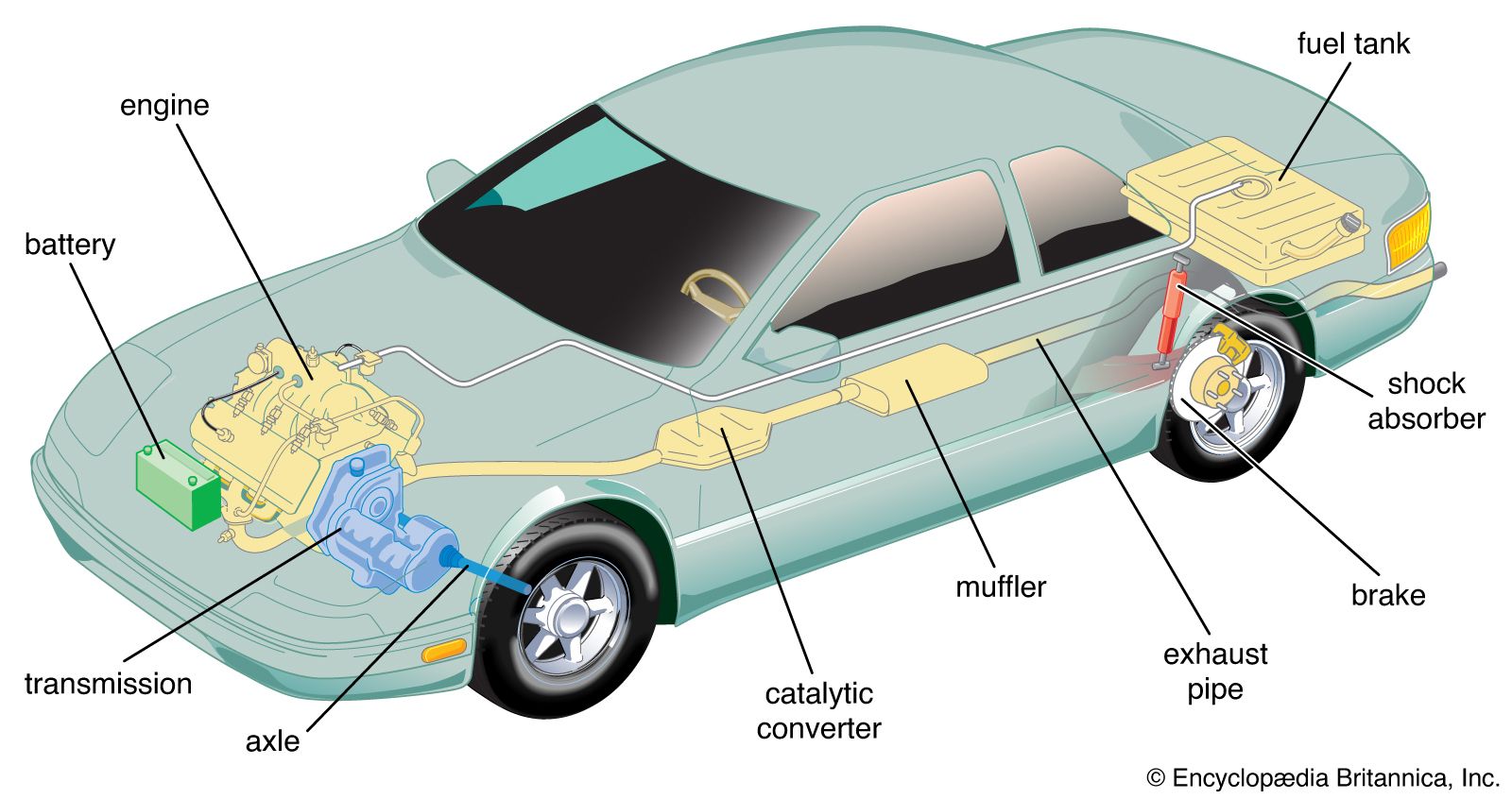
Illustrative image related to all the parts of a car
Impact on Application: Steel’s compatibility with welding processes makes it ideal for structural integrity, but buyers must consider corrosion-resistant coatings for longevity.
International Considerations: Buyers in regions like Europe and the Middle East should be aware of compliance with standards such as ASTM and DIN for quality assurance.
What Role Does Aluminum Play in Vehicle Manufacturing?
Aluminum is increasingly favored in the automotive sector for its lightweight properties, which contribute to improved fuel efficiency. It has excellent corrosion resistance and can withstand high temperatures, making it suitable for engine components and body panels.
Pros: The primary advantage of aluminum is its lightweight nature, which enhances vehicle performance and efficiency. Its resistance to corrosion reduces maintenance needs over time.
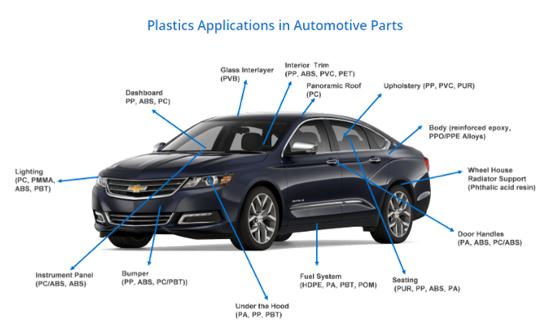
Illustrative image related to all the parts of a car
Cons: On the downside, aluminum can be more expensive than steel and may require specialized manufacturing techniques, such as welding or riveting, which can complicate production.
Impact on Application: Aluminum’s compatibility with various finishing processes allows for aesthetic customization, but its higher cost may deter budget-conscious buyers.
International Considerations: Buyers should ensure compliance with international standards like JIS for aluminum specifications, particularly in markets like Japan and Germany.
How Do Plastics Enhance Automotive Design and Functionality?
Plastics are commonly used in non-structural components such as dashboards, panels, and interior fittings. They offer excellent flexibility and can be molded into complex shapes, allowing for innovative designs.
Pros: The main advantage of plastics is their lightweight nature and resistance to corrosion, which can significantly reduce vehicle weight and improve fuel efficiency.
Cons: However, plastics may not withstand high temperatures as well as metals, and their durability can be lower in high-stress applications.
Impact on Application: Plastics are ideal for aesthetic components but may require careful selection to ensure they meet performance standards in critical areas.
International Considerations: Buyers should be aware of material safety standards and regulations in their respective regions, such as REACH in Europe, which governs chemical substances.
What Advantages Do Composites Offer in Automotive Applications?
Composite materials, often made from a combination of fibers and resins, are gaining traction for their high strength-to-weight ratio. They are particularly used in high-performance vehicles and specific components like body panels and structural reinforcements.
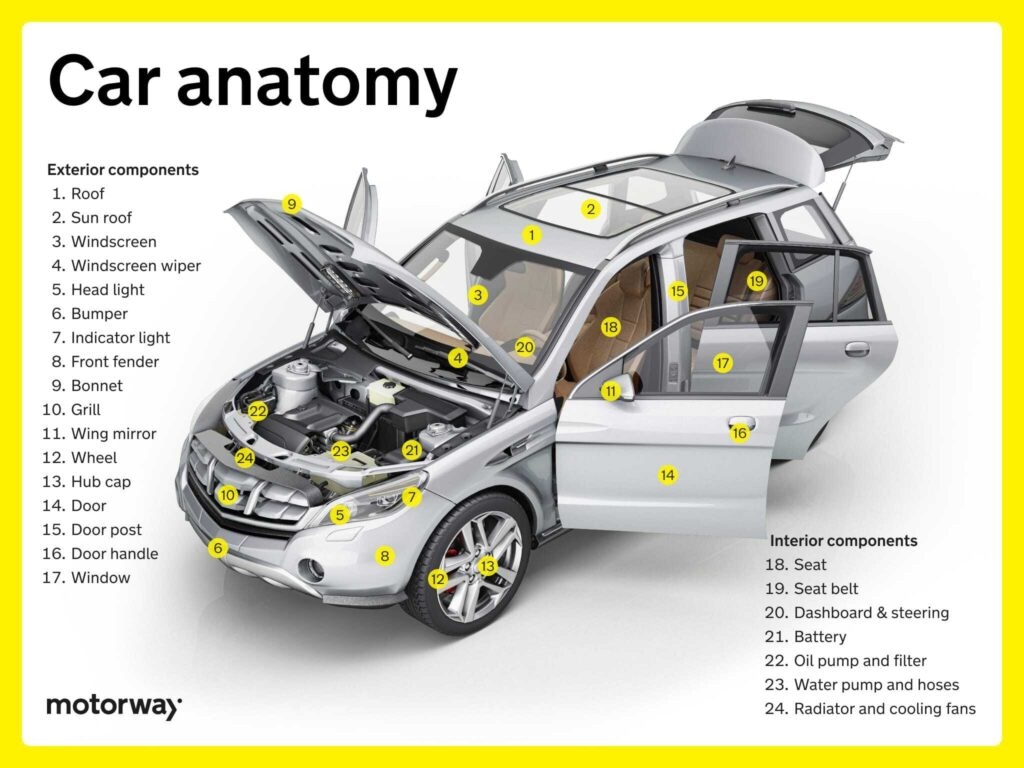
Illustrative image related to all the parts of a car
Pros: Composites offer exceptional strength while being lightweight, which is crucial for enhancing performance and efficiency. They also have excellent corrosion resistance.
Cons: The primary limitation of composites is their higher manufacturing cost and complexity, which can deter widespread adoption in budget vehicles.
Impact on Application: Composites can be tailored for specific performance characteristics, but their use may require specialized knowledge in manufacturing processes.
International Considerations: Buyers should consider compliance with ASTM standards for composite materials, particularly in markets focused on high-performance vehicles.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Automotive Parts
| Material | Typical Use Case for all the parts of a car | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Chassis, engine block, structural components | High strength and durability | Prone to corrosion | Low |
| Aluminum | Body panels, engine components | Lightweight, corrosion-resistant | Higher cost, complex manufacturing | Medium |
| Plastics | Interior fittings, dashboards | Lightweight, flexible design | Lower durability at high temperatures | Low |
| Composites | Body panels, structural reinforcements | High strength-to-weight ratio | High manufacturing cost | High |
This analysis provides a comprehensive overview of material options for automotive parts, enabling international B2B buyers to make informed decisions based on performance requirements, cost considerations, and compliance with local standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for all the parts of a car
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Car Parts?
The manufacturing process of car parts involves several critical stages, each designed to ensure the highest quality and performance. These stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Understanding each step can help B2B buyers assess supplier capabilities and the quality of components being sourced.
How is Material Prepared for Car Part Manufacturing?
Material preparation is the first step in the manufacturing process. It involves selecting the right materials based on the specific requirements of the car part. Common materials include steel, aluminum, plastic, and composites.
Illustrative image related to all the parts of a car
- Material Selection: Suppliers must consider factors such as strength, weight, corrosion resistance, and cost.
- Material Processing: This may involve cutting, bending, or surface treatment to ensure that the materials meet specifications before moving to forming.
B2B buyers should verify the sourcing and quality of materials used by suppliers, as they significantly affect the durability and performance of the final product.
What Forming Techniques Are Commonly Used in Car Part Manufacturing?
Forming is a critical stage where raw materials are shaped into desired forms. Several techniques are employed in the automotive industry, including:
- Stamping: Commonly used for metal parts, stamping involves pressing sheets of metal into shapes using dies.
- Injection Molding: This technique is predominantly used for plastic components, where heated plastic is injected into molds to create intricate shapes.
- Casting: Involves pouring molten metal into molds, allowing it to cool and solidify into the desired shape.
- Machining: Precision machining is used for parts that require tight tolerances, involving processes like turning, milling, and drilling.
Understanding these techniques enables B2B buyers to assess the capabilities of potential suppliers and the complexity of parts they can manufacture.

Illustrative image related to all the parts of a car
How Are Car Parts Assembled?
Assembly is where individual components come together to form a complete part. This stage can vary significantly depending on the complexity of the part being produced.
- Sub-Assembly: Components are often assembled into sub-units before being integrated into the final product. For example, an engine may be assembled in sections, such as the cylinder head and block.
- Automation vs. Manual Assembly: Many manufacturers employ robotic systems for precision assembly, while others may rely on manual labor for complex parts that require a human touch.
- Quality Control During Assembly: It’s crucial to have checkpoints during assembly to ensure that each part meets specifications before moving to the next stage.
B2B buyers should inquire about a supplier’s assembly techniques and the level of automation used, as this impacts efficiency and quality.
What Finishing Processes Are Applied to Car Parts?
The finishing stage enhances the appearance and performance of car parts. Common finishing processes include:
- Surface Treatment: Techniques such as anodizing, painting, or plating improve corrosion resistance and aesthetics.
- Quality Checks: Final inspections are performed to ensure that parts meet all specifications and standards before packaging and shipping.
- Packaging: Proper packaging is essential to prevent damage during transportation.
Buyers should ensure that suppliers follow best practices in finishing to maintain the integrity and performance of the parts.
What Quality Assurance Standards Are Relevant for Car Parts?
Quality assurance (QA) is crucial in the automotive industry, where safety and performance are paramount. Various international and industry-specific standards guide the QA process.

Illustrative image related to all the parts of a car
- ISO 9001: This international standard outlines the criteria for a quality management system, ensuring consistent quality in products and services.
- CE Marking: Particularly relevant in Europe, CE marking indicates conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: The American Petroleum Institute sets standards for automotive lubricants and components, ensuring reliability and performance.
B2B buyers should verify that their suppliers are compliant with these standards, as this provides assurance of quality and reliability.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Car Part Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) involves several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process to catch defects early and ensure product reliability.
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This checkpoint involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specifications.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, periodic checks are made to ensure that processes are within tolerances and that parts are being produced correctly.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): This final inspection checks the finished product against specifications before it is shipped.
Understanding these QC checkpoints can help B2B buyers gauge the thoroughness of a supplier’s quality assurance processes.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
B2B buyers must take proactive steps to verify the quality control practices of potential suppliers. Here are some effective methods:
Illustrative image related to all the parts of a car
- Supplier Audits: Conducting regular audits can provide insights into the supplier’s manufacturing processes, quality controls, and compliance with standards.
- Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports, including defect rates, inspection results, and corrective actions taken, can offer transparency.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased evaluation of the supplier’s quality practices.
What Are the Nuances of Quality Control for International B2B Buyers?
For B2B buyers in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of quality control is critical.
- Cultural and Regulatory Differences: Different regions may have varying standards and practices that affect quality control. Buyers should familiarize themselves with local regulations and expectations.
- Supply Chain Management: The complexity of international supply chains can introduce risks. Establishing clear communication channels and expectations with suppliers is essential for maintaining quality.
- Logistics and Transportation: Ensuring that parts are handled correctly during transportation can mitigate risks associated with damage or deterioration before reaching the end user.
By understanding these nuances, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions and establish strong partnerships with their suppliers.
In conclusion, a thorough understanding of the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for car parts is essential for B2B buyers. By assessing suppliers based on their manufacturing capabilities and adherence to quality standards, buyers can ensure they source reliable and high-quality automotive components.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘all the parts of a car’
Introduction
Navigating the procurement of automotive parts can be complex, especially for B2B buyers operating in diverse international markets. This step-by-step checklist is designed to streamline the sourcing process for all car parts, ensuring that you make informed decisions that align with your operational needs and quality standards.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before initiating the procurement process, clearly outline the technical specifications for the car parts you need. This includes dimensions, material requirements, and performance standards. Having precise specifications is essential to ensure compatibility with existing systems and to avoid costly errors later in the process.
Illustrative image related to all the parts of a car
- Focus on industry standards: Ensure that your specifications align with relevant industry standards to facilitate compliance and quality assurance.
Step 2: Conduct Market Research
Gather information on the current market landscape for automotive parts. Research potential suppliers, pricing trends, and available technologies to understand your options better. This will help you identify reliable suppliers who can meet your needs efficiently.
- Utilize industry reports: Leverage resources like market analysis reports and trade publications to gain insights into supplier performance and market dynamics.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a supplier, conduct a thorough evaluation. Request detailed company profiles, including their history, certifications, and case studies relevant to your industry. This ensures that you are partnering with a reputable supplier capable of delivering quality parts.
- Seek references: Ask for references from previous clients, particularly those in similar markets or industries, to gauge supplier reliability and service quality.
Step 4: Verify Supplier Certifications
Ensure that your chosen suppliers hold necessary certifications that validate their compliance with industry standards. This can include ISO certifications, quality management certifications, or specific automotive industry standards.
- Confirm international standards: Check if the certifications are recognized in your region, especially if you are sourcing from international suppliers.
Step 5: Request Samples and Conduct Testing
Before finalizing any orders, request samples of the parts to evaluate their quality and compatibility with your requirements. Conduct thorough testing to ensure they meet your performance standards and operational expectations.
- Establish testing protocols: Define clear testing protocols to assess functionality, durability, and safety, which can prevent future operational issues.
Step 6: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Once you have selected a supplier, engage in negotiations to finalize terms and conditions. This includes pricing, delivery schedules, payment terms, and warranties. Clear agreements can prevent misunderstandings and protect your investment.
- Consider long-term relationships: Look for opportunities to establish long-term partnerships, which can lead to better pricing and service over time.
Step 7: Monitor Supplier Performance
After procurement, continuously monitor supplier performance against the agreed terms. Regular assessments can help identify areas for improvement and ensure that the supplier consistently meets your quality and delivery standards.
- Implement feedback loops: Create a system for providing feedback to suppliers, fostering a collaborative relationship aimed at continuous improvement.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can effectively navigate the complexities of sourcing automotive parts, ensuring quality, compliance, and operational efficiency in their procurement processes.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for all the parts of a car Sourcing
Understanding the cost structure and pricing dynamics of automotive parts is essential for international B2B buyers, especially those operating in diverse markets like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This analysis will delve into the various cost components and price influencers that can impact sourcing decisions.
What Are the Key Cost Components for Sourcing Automotive Parts?
-
Materials: The cost of raw materials significantly affects the pricing of automotive parts. Common materials include steel, aluminum, plastics, and rubber. Fluctuations in material costs due to market conditions can lead to varying prices for parts. Buyers should monitor global commodity prices and consider long-term contracts with suppliers to hedge against volatility.
-
Labor: Labor costs can vary widely based on geographic location and the complexity of the manufacturing process. Regions with lower labor costs may offer more competitive pricing, but this can come at the expense of quality or longer lead times. Assessing labor costs in conjunction with quality standards is crucial for making informed sourcing decisions.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses the indirect costs associated with production, such as utilities, rent, and equipment depreciation. These costs are often allocated across all products manufactured, so understanding the overhead structure of potential suppliers can provide insights into pricing.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling for specialized parts can represent a significant upfront investment. Buyers should factor in these costs when assessing the total price, particularly for custom or high-specification components. It’s advisable to discuss tooling costs upfront with suppliers to avoid unexpected charges later.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that parts meet required specifications involves QC processes that can add to the overall cost. Suppliers with stringent quality assurance practices may charge more, but this can ultimately save costs related to returns or failures in the field.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs, including shipping and handling, are vital components of the total cost structure. Factors like distance, mode of transport, and Incoterms used in the transaction can significantly influence logistics costs. Buyers should evaluate the logistics capabilities of suppliers to ensure timely delivery and cost-efficiency.
-
Margin: Supplier profit margins will vary based on competition, market demand, and their operational costs. Understanding the market landscape can help buyers gauge whether the margins are reasonable and negotiate better pricing.
What Influences the Price of Automotive Parts?
-
Volume/MOQ: The minimum order quantity (MOQ) can dramatically influence unit prices. Larger orders typically reduce per-unit costs due to economies of scale. International buyers should assess their purchasing patterns and negotiate favorable terms based on projected volumes.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom parts or those made to specific specifications generally incur higher costs due to the additional complexity in manufacturing. It’s essential to balance the need for customization with budget constraints.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Higher-quality materials or certifications (like ISO or TS standards) can increase prices. Buyers should evaluate whether the added costs align with their operational needs and customer expectations.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of a supplier can impact pricing. Established suppliers with a track record of quality may charge premium prices, but the associated risk of defects or delays may be lower.
-
Incoterms: The choice of Incoterms can significantly impact total costs. Understanding the implications of different terms (e.g., FOB, CIF) is critical for managing logistics and cost responsibilities between buyers and suppliers.
What Are the Best Practices for Negotiating Automotive Parts Pricing?
- Conduct Comprehensive Market Research: Understanding market trends, competitor pricing, and regional dynamics is essential for effective negotiation.
- Leverage Long-Term Relationships: Building strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing and terms over time.
- Consider Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Focus on long-term value rather than just initial costs. Analyze factors such as durability, warranty, and after-sales support.
- Explore Multiple Suppliers: Diversifying your supplier base can create competitive pressure, leading to more favorable pricing.
Conclusion
Navigating the complexities of automotive parts pricing requires a comprehensive understanding of cost components and price influencers. By implementing strategic sourcing practices and maintaining open communication with suppliers, B2B buyers can optimize their procurement processes, ultimately enhancing their competitive edge in the market. Always remember that prices can fluctuate, and it’s prudent to seek multiple quotes and conduct thorough due diligence before finalizing any sourcing decisions.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing all the parts of a car With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to Traditional Car Parts
In the automotive industry, the traditional assembly of car parts serves as the foundation for vehicle performance and functionality. However, emerging technologies and alternative solutions are redefining how vehicles can operate. For B2B buyers, understanding these alternatives is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions that align with their operational needs and budget constraints.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | All The Parts Of A Car | Electric Vehicle Components | Public Transportation Systems |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High, dependent on part quality | Excellent, especially in urban areas | Variable, often high during peak times |
| Cost | High initial investment | Moderate, but lower long-term costs | Lower operational costs per passenger |
| Ease of Implementation | Complex assembly and integration | Requires specialized knowledge | Established systems, less flexible |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance required | Lower maintenance needs | Maintenance managed by transit authorities |
| Best Use Case | Personal and commercial vehicles | Urban commuting and eco-friendly options | Mass transit in urban areas |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Electric Vehicle Components
Electric vehicles (EVs) utilize components such as batteries, electric motors, and regenerative braking systems. The performance of EVs is often superior in urban settings, where they can leverage their instant torque for quick acceleration. While the initial investment can be moderate, buyers benefit from lower operating costs due to fewer moving parts and less frequent maintenance needs compared to traditional combustion engines. However, implementing EV technology requires specialized knowledge and infrastructure, which may not be readily available in all regions.
Public Transportation Systems
Public transportation systems offer an alternative to individual car ownership, particularly in densely populated urban areas. These systems can include buses, trams, and subways, providing a variable performance based on demand and infrastructure quality. The cost per passenger is generally lower than the total cost of ownership of a car, making it an economically viable option for cities. However, public transport systems can be less flexible, often requiring fixed routes and schedules that may not meet all user needs. Maintenance is managed by public authorities, which can be both a benefit and a drawback depending on the efficiency of local governance.

Illustrative image related to all the parts of a car
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
For B2B buyers, the choice between traditional car parts, electric vehicle components, and public transportation systems depends on several factors, including operational requirements, cost constraints, and market demands. Evaluating the performance, cost, ease of implementation, and maintenance needs of each alternative can help buyers align their choices with their strategic goals. Whether opting for the reliability of traditional parts or exploring innovative alternatives like EVs and public transport, understanding the nuances of each option is essential for maximizing value and efficiency.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for all the parts of a car
What Are the Essential Technical Properties for Car Parts?
Understanding the technical specifications of car parts is crucial for B2B buyers, particularly those in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Here are some key properties that influence procurement decisions:
1. Material Grade
The material grade refers to the quality and composition of the materials used in manufacturing car parts. Common materials include steel, aluminum, and composites. The grade affects durability, weight, and corrosion resistance, which are vital for performance and longevity. Buyers should prioritize high-grade materials to ensure safety and reliability, particularly in harsh operating conditions.
2. Tolerance Levels
Tolerance levels define the permissible limits of variation in a part’s dimensions. These specifications are critical for ensuring that parts fit together correctly and function as intended. For instance, tighter tolerances are essential for components like engine parts and transmission systems, where precision is crucial. Understanding tolerance requirements helps buyers avoid costly reworks or failures in assembly.
3. Load Capacity
Load capacity indicates the maximum weight or force that a part can withstand without failing. This property is particularly important for structural components like axles, suspensions, and chassis. Buyers must consider the intended use of the vehicle and ensure that parts meet or exceed these specifications to prevent accidents and enhance vehicle performance.
4. Thermal Resistance
Thermal resistance measures a part’s ability to withstand high temperatures without degrading. This property is vital for components like the engine, brakes, and exhaust systems, which operate under extreme conditions. Selecting parts with appropriate thermal resistance can significantly impact the vehicle’s reliability and efficiency, especially in markets with diverse climates.
5. Surface Finish
Surface finish refers to the texture and smoothness of a part’s surface. It affects not only the aesthetic appeal but also the performance characteristics, such as friction, wear, and corrosion resistance. A high-quality surface finish can enhance the lifespan of components and reduce maintenance costs, making it an important consideration for B2B buyers.
What Are Common Trade Terminology and Jargon Used in the Automotive Industry?
Familiarity with industry-specific terminology is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the automotive parts market. Here are some common terms:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce parts that are used in the assembly of vehicles. These parts are designed to meet the original specifications set by the vehicle manufacturer. B2B buyers often prefer OEM parts for their reliability and compatibility, making them a critical consideration in procurement strategies.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest number of units that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is vital for buyers to understand as it impacts inventory management and cash flow. Suppliers may set MOQs based on production costs, so it’s essential for buyers to negotiate terms that align with their purchasing needs.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document that buyers send to suppliers to request pricing and terms for specific parts. This process allows buyers to compare offers and make informed decisions. Including detailed specifications in an RFQ can streamline negotiations and ensure that suppliers provide accurate quotes.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of predefined commercial terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding these terms is crucial for B2B buyers engaged in cross-border trade, as they clarify shipping costs, risk transfer, and delivery obligations.
5. Aftermarket
The aftermarket refers to the secondary market for automotive parts, which includes replacement parts, accessories, and enhancements. Understanding this sector can provide insights into consumer trends and opportunities for B2B buyers looking to diversify their offerings.
By grasping these essential technical properties and trade terminologies, B2B buyers can enhance their decision-making processes, ensuring they procure high-quality parts that meet their operational needs.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the all the parts of a car Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics and Trends Influencing the Global Automotive Parts Sector?
The global automotive parts sector is experiencing significant shifts driven by technological advancements, changing consumer preferences, and regulatory pressures. One of the most notable trends is the increasing integration of digital technologies in manufacturing and supply chain management. B2B buyers are now leveraging advanced analytics, artificial intelligence, and IoT to streamline operations, enhance inventory management, and improve forecasting accuracy. For international buyers, particularly in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these technologies is essential for making informed sourcing decisions.
Additionally, electric vehicle (EV) adoption is rapidly reshaping the market dynamics. As more manufacturers pivot towards EV production, there is a growing demand for specialized components such as batteries, electric motors, and advanced electronic systems. This shift presents both opportunities and challenges for B2B buyers, who must adapt to a new landscape where traditional parts may be phased out in favor of innovative solutions.
Moreover, geopolitical factors and supply chain disruptions due to events like the COVID-19 pandemic have underscored the importance of diversifying sourcing strategies. Buyers are increasingly looking beyond traditional markets, exploring suppliers in emerging economies that offer competitive pricing and quality. This trend is particularly relevant for regions such as Africa and South America, where local manufacturing capabilities are being developed.
Illustrative image related to all the parts of a car
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Shaping the Automotive Parts Industry?
Sustainability has become a critical focus for B2B buyers in the automotive parts sector. The environmental impact of automotive manufacturing is significant, with traditional processes contributing to pollution and resource depletion. As a result, companies are prioritizing ethical sourcing practices and seeking suppliers who adhere to environmental standards.
Buyers are increasingly looking for ‘green’ certifications and materials that minimize ecological footprints. This includes sourcing parts made from recycled materials, adopting eco-friendly manufacturing processes, and ensuring that suppliers comply with international environmental regulations. For instance, parts such as catalytic converters and batteries are now being produced with an emphasis on sustainability, reducing harmful emissions and promoting recycling initiatives.
Furthermore, ethical supply chains are gaining traction as consumers demand transparency and responsibility from manufacturers. B2B buyers must ensure that their suppliers not only meet quality and cost expectations but also adhere to ethical labor practices and sustainability standards. This commitment to responsible sourcing not only enhances brand reputation but also aligns with the growing regulatory requirements across various regions.
What Is the Historical Context of Automotive Parts Manufacturing for B2B Buyers?
The evolution of the automotive parts industry can be traced back to the early 20th century when mass production techniques revolutionized manufacturing. The introduction of the assembly line by Henry Ford enabled the efficient production of vehicles, which in turn created a demand for standardized parts. This marked the beginning of a complex supply chain that has continued to evolve.
Over the decades, the industry has witnessed several transformative phases, including the shift towards globalization in the late 20th century. As manufacturers sought cost efficiencies, they began sourcing parts from different regions, leading to the establishment of intricate international supply networks. The rise of technology in the 21st century has further accelerated this evolution, with digital tools facilitating more efficient sourcing and inventory management.
Today, B2B buyers face a landscape characterized by rapid technological advancements, regulatory changes, and a heightened focus on sustainability. Understanding this historical context is crucial for navigating the current market dynamics and making strategic sourcing decisions that align with future trends.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of all the parts of a car
-
How do I ensure the quality of car parts when sourcing internationally?
To ensure quality when sourcing car parts internationally, start by vetting suppliers thoroughly. Look for certifications such as ISO 9001, which indicate adherence to quality management standards. Request samples before committing to large orders to assess product quality. Additionally, consider visiting the supplier’s facility if possible, or utilize third-party inspection services to verify compliance with your specifications. Establishing clear quality assurance protocols and maintaining open communication with your suppliers can also help mitigate risks. -
What are the best practices for negotiating payment terms with international suppliers?
When negotiating payment terms with international suppliers, clarity and mutual understanding are key. Aim for terms that balance your cash flow needs with the supplier’s financial security. Common practices include requiring a deposit upfront, followed by the balance upon delivery or after inspection. Consider using letters of credit for higher-value transactions to minimize risk. Always document the agreed terms in a contract, and be prepared for potential currency fluctuations, which can affect final costs. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) I should expect from car parts suppliers?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) vary significantly among suppliers based on factors like the type of part, manufacturing processes, and market demand. Some manufacturers may set MOQs as low as 100 units, while others, especially those offering customized parts, might require larger orders. It’s advisable to communicate your needs upfront and negotiate MOQs that align with your business model. In some cases, suppliers may be willing to accommodate lower MOQs for first orders to establish a working relationship. -
How can I customize car parts to meet specific requirements?
To customize car parts, first, clearly define your specifications and desired modifications. Engage directly with your supplier’s engineering or design team to discuss feasibility, lead times, and costs associated with customization. Providing detailed drawings or prototypes can facilitate better communication. Keep in mind that customization may affect MOQs and pricing. It’s also important to establish a timeline for revisions and approvals to avoid delays in production. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing car parts?
When importing car parts, consider factors such as shipping methods, lead times, and customs regulations. Choose a reliable freight forwarder who understands the automotive industry and can navigate international shipping complexities. Be aware of the Incoterms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers. Additionally, factor in potential delays at customs and ensure that all necessary documentation, including invoices and certificates of origin, is prepared in advance to avoid unnecessary costs. -
How do I identify reliable suppliers for car parts in international markets?
Identifying reliable suppliers involves thorough research and due diligence. Start by leveraging industry networks, attending trade shows, and utilizing online B2B platforms to find potential suppliers. Check reviews and ratings from previous customers, and request references to validate their reputation. Engage in direct communication to assess responsiveness and professionalism. Additionally, consider suppliers who are members of industry associations, as this often indicates a commitment to quality standards. -
What are the key components of an effective quality assurance (QA) process for car parts?
An effective QA process for car parts should include several key components: defining quality standards based on industry benchmarks, implementing regular inspections at various stages of production, and conducting final product testing before shipment. Establishing a feedback loop with suppliers to address quality issues promptly is essential. Documentation of all QA processes, including inspection reports and corrective actions, is crucial for maintaining accountability and ensuring continuous improvement. -
How can I navigate different regulations and standards for car parts in various countries?
Navigating regulations and standards for car parts requires thorough research on each target market’s legal requirements. Start by consulting local automotive industry associations or regulatory bodies for information on compliance standards. Be aware of specific certifications required for different regions, such as CE marking in Europe or EPA standards in the U.S. Collaborating with local experts or legal advisors can help ensure adherence to regulations while avoiding costly penalties or product recalls.
Top 3 All The Parts Of A Car Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Moog – Steering and Suspension Parts
Domain: moogparts.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: The text provides an overview of various parts of a car, including: 1. Steering System: Center Drag Links, Idler Arms, Pitman Arms, Steering Stabilizers, Complete Pre-Assembled Steering Linkage, Tie Rods. 2. Suspension: Solid Sway Bar Kits, Alignment Parts, Bushings, Coil Springs, Control Arms, Sway Bar Links, Ball Joints. 3. Driveline: PTO/AG, Universal Joints, Couplers, Constant Velocity Axles. …
2. Pinterest – Car Parts Gallery
3. Reddit – Automotive Maintenance
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: This company, Reddit – Automotive Maintenance, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for all the parts of a car
In today’s global automotive market, strategic sourcing of car parts is essential for optimizing supply chains and enhancing competitiveness. By understanding the intricate anatomy of a vehicle—ranging from the engine to the braking system—international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that lead to cost savings and improved performance. Prioritizing quality parts from reliable suppliers not only ensures vehicle reliability but also bolsters brand reputation in emerging markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
As the automotive industry faces rapid technological advancements and shifting consumer preferences, fostering partnerships with manufacturers who emphasize innovation and sustainability will be crucial. Buyers should actively engage with suppliers who are committed to maintaining high standards in production and environmental responsibility.
Looking ahead, the focus should shift toward building resilient supply chains that can adapt to market fluctuations and regulatory changes. By leveraging strategic sourcing practices, companies can position themselves to capitalize on growth opportunities and meet the evolving demands of the automotive sector. Now is the time to strengthen your sourcing strategies and connect with trusted suppliers to secure a competitive edge in this dynamic landscape.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.