Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for solenoid or starter bad
In the competitive landscape of global automotive parts procurement, sourcing reliable solenoids or starters can pose a significant challenge for B2B buyers. These critical components play a vital role in vehicle performance, and their failure can lead to costly downtime and repairs. Understanding the nuances of a “bad starter” or solenoid is essential for making informed purchasing decisions, especially in diverse markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including countries like Vietnam and Brazil.
This comprehensive guide delves into various types of solenoids and starters, their applications across different vehicle models, and the signs indicating potential failures. We will also explore effective strategies for vetting suppliers, ensuring quality and reliability, and examining the cost factors that influence purchasing decisions. By equipping international buyers with actionable insights, this guide empowers them to navigate the complexities of sourcing these essential automotive components confidently.
Whether you are a fleet manager, automotive parts distributor, or a repair shop owner, understanding the intricacies of solenoid and starter procurement will enhance your operational efficiency and reduce risks associated with unreliable parts. With this knowledge, you can secure the best products for your needs, ensuring optimal performance and customer satisfaction.
Table Of Contents
- Top 4 Solenoid Or Starter Bad Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for solenoid or starter bad
- Understanding solenoid or starter bad Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of solenoid or starter bad
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘solenoid or starter bad’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for solenoid or starter bad
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for solenoid or starter bad
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘solenoid or starter bad’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for solenoid or starter bad Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing solenoid or starter bad With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for solenoid or starter bad
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the solenoid or starter bad Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of solenoid or starter bad
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for solenoid or starter bad
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Understanding solenoid or starter bad Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Starter Solenoid Failure | Engine fails to start, single click sound, intermittent operation | Automotive repair, fleet management | Pros: Easy to diagnose; Cons: May require starter replacement. |
| Relay Malfunction | Inconsistent power to starter, buzzing noise, no sound at all | Heavy machinery, automotive service centers | Pros: Often cheaper to replace; Cons: Can lead to broader electrical issues. |
| Stuck Solenoid | Engine starts unexpectedly, solenoid remains engaged | Automotive maintenance, vehicle rental companies | Pros: Clear symptoms; Cons: Can cause damage to starter motor. |
| Corroded Connections | Visible corrosion on terminals, intermittent starting issues | Automotive supply, service workshops | Pros: Simple fixes; Cons: Can be mistaken for solenoid failure. |
| Electrical Short | Sparks, blown fuses, failure to engage starter | Automotive electronics, repair shops | Pros: Identifying shorts can prevent larger issues; Cons: Requires thorough electrical testing. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Starter Solenoid Failure?
Starter solenoid failure is characterized by the engine’s inability to start, often accompanied by a single click sound when the ignition is turned. This type of failure is common in automotive applications where the solenoid is responsible for engaging the starter motor. B2B buyers should consider the solenoid’s compatibility with their specific vehicle models and the ease of replacement, as some solenoids are integrated into the starter assembly.
How Does a Relay Malfunction Impact Performance?
Relay malfunctions can result in inconsistent power delivery to the starter, leading to buzzing noises or complete silence when attempting to start the engine. This issue is prevalent in heavy machinery and automotive service centers. Buyers should focus on the relay’s specifications to ensure proper fit and functionality, as replacing a relay is often more cost-effective than other electrical repairs.
What Are the Implications of a Stuck Solenoid?
A stuck solenoid can lead to dangerous situations where the engine starts without the key being turned. This type of failure is especially critical for automotive maintenance providers and vehicle rental companies. B2B buyers should prioritize high-quality solenoids to prevent such issues, as prolonged engagement can damage the starter motor, leading to higher repair costs.
Why Are Corroded Connections a Common Issue?
Corroded connections are visible indicators of electrical problems and can manifest as intermittent starting issues. This issue is frequently encountered in automotive supply and service workshops. Buyers should consider investing in maintenance solutions that include corrosion-resistant materials, as addressing corroded connections can often resolve solenoid-related issues without the need for complete replacements.
What Are the Risks Associated with Electrical Shorts?
Electrical shorts can cause sparks, blown fuses, and complete failure to engage the starter. This type of failure is critical in automotive electronics and repair shops. B2B buyers should ensure they have the necessary diagnostic tools to identify and address shorts promptly, as neglecting these issues can lead to more extensive damage and costly repairs.
Key Industrial Applications of solenoid or starter bad
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of solenoid or starter bad | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Vehicle ignition systems | Ensures reliable vehicle operation and safety | Quality assurance, compatibility with various models |
| Agriculture | Agricultural machinery starting systems | Enhances efficiency in field operations | Durability in harsh environments, local supplier support |
| Manufacturing | Industrial machinery controls | Minimizes downtime, maximizing production output | Custom solutions, lead time for replacements |
| Construction | Heavy equipment starting mechanisms | Reduces operational delays on job sites | Availability of parts, service and maintenance options |
| Marine | Marine vessel engine ignition | Guarantees vessel readiness and safety | Corrosion resistance, compliance with marine standards |
How is ‘solenoid or starter bad’ utilized in the Automotive Industry?
In the automotive sector, solenoids play a crucial role in vehicle ignition systems, enabling the engine to start efficiently. A faulty solenoid can lead to various issues, such as intermittent starting problems or complete engine failure, which can severely impact vehicle reliability. Buyers in this sector need to ensure that they source high-quality components that are compatible with a range of vehicle models. Additionally, they should consider suppliers who can provide technical support and rapid delivery, especially in regions with varied vehicle types like Africa and South America.
What role does ‘solenoid or starter bad’ play in Agriculture?
In agricultural machinery, solenoids are vital for starting engines in tractors and other equipment. A malfunctioning solenoid can hinder operations, leading to delays during critical planting or harvesting seasons. Businesses benefit from reliable starting systems that ensure their machinery operates efficiently, thereby maximizing productivity. Buyers should focus on sourcing solenoids that are durable and capable of withstanding challenging environmental conditions, as well as suppliers who understand the local agricultural practices and requirements.
How does ‘solenoid or starter bad’ impact Manufacturing?
In manufacturing, solenoids are integral to the operation of industrial machinery, controlling various functions that require high power. A bad solenoid can cause machinery to malfunction, leading to costly downtime. This is particularly critical in industries where production schedules are tight. Buyers should prioritize sourcing components that offer high reliability and quick replacement options, as well as manufacturers who can provide custom solutions tailored to specific machinery needs.
Why is ‘solenoid or starter bad’ significant in Construction?
Heavy equipment in construction often relies on solenoids for starting mechanisms. A faulty solenoid can result in delays and increased costs due to machinery being out of operation. Ensuring these components are reliable is essential for maintaining project timelines. Buyers should consider sourcing from suppliers who can guarantee the availability of parts and offer maintenance services, particularly in regions where construction projects are prevalent, such as in the Middle East and parts of Europe.
How does ‘solenoid or starter bad’ affect the Marine Industry?
In the marine sector, solenoids are crucial for the ignition systems of vessels. A malfunctioning solenoid can prevent a vessel from starting, which poses safety risks and operational inefficiencies. Ensuring that solenoids are corrosion-resistant and compliant with marine standards is vital for buyers. They should seek suppliers with expertise in marine applications and who can provide products that meet the rigorous demands of maritime environments, particularly for operations in regions like South America and Europe.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘solenoid or starter bad’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Delayed Production Due to Equipment Failure
The Problem: In the manufacturing sector, machinery downtime can severely impact production schedules and profitability. A common issue faced by B2B buyers is equipment failure due to a faulty solenoid or starter. When a solenoid fails, it may prevent critical machinery from starting, leading to a halt in operations. This situation is particularly dire in industries where just-in-time production is essential, as even a few hours of downtime can result in missed deadlines and increased operational costs.
The Solution: To mitigate this risk, B2B buyers should implement a proactive maintenance schedule that includes regular checks on solenoids and starters. It is crucial to establish relationships with reliable suppliers who can provide high-quality replacement parts. When sourcing solenoids or starters, buyers should prioritize suppliers that offer comprehensive product specifications, including electrical ratings and compatibility with existing machinery. Additionally, investing in diagnostic tools that can identify early signs of solenoid or starter failure can allow for timely interventions before equipment failure occurs. By integrating these practices into their operations, companies can enhance equipment reliability and reduce the risk of production delays.
Scenario 2: Increased Repair Costs from Improper Diagnosis
The Problem: B2B buyers often face the challenge of escalating repair costs when dealing with solenoid or starter issues. A common scenario is misdiagnosing the problem, which can lead to unnecessary replacements and repairs. For instance, if a buyer assumes that the starter is at fault when the actual issue lies with the solenoid, they may incur additional expenses in labor and parts, as well as potential damage to other components during the troubleshooting process.
The Solution: To avoid misdiagnosis and its associated costs, B2B buyers should invest in training for their maintenance teams on the differences between solenoids and starters, including their functions and common failure signs. Providing access to technical documentation and troubleshooting guides can also empower staff to make informed decisions. Collaborating with experienced technicians or consultants can facilitate accurate diagnosis and repair. Furthermore, buyers should consider establishing a partnership with a trusted supplier who offers diagnostic services or technical support, ensuring that the correct components are identified and sourced efficiently.
Scenario 3: Unpredictable Performance in Fleet Vehicles
The Problem: For businesses relying on a fleet of vehicles—such as logistics companies or delivery services—unpredictable vehicle performance can disrupt operations and customer service. A failing starter or solenoid can lead to intermittent starting issues, resulting in vehicles being unavailable when needed. This unpredictability not only affects scheduling but can also harm the company’s reputation due to delays in service.
The Solution: To enhance the reliability of fleet vehicles, B2B buyers should adopt a rigorous vehicle maintenance program that includes regular inspections of starters and solenoids. This program should emphasize the importance of routine checks and replacements before failures occur. Additionally, buyers should consider implementing a centralized fleet management system that tracks vehicle performance data, enabling early detection of potential issues related to starting mechanisms. Establishing a relationship with a reputable parts supplier that can provide high-quality solenoids and starters, along with fast delivery options, will ensure that any necessary replacements are handled swiftly, minimizing downtime and maintaining service quality.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for solenoid or starter bad
What Are the Key Materials Used for Solenoids and Starters?
When selecting materials for solenoids and starters, it is crucial to consider the specific requirements of the application, including environmental conditions, performance criteria, and compliance with international standards. The following analysis covers four common materials used in solenoids and starter systems, highlighting their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international buyers.
How Does Copper Perform in Solenoid and Starter Applications?
Key Properties: Copper is known for its excellent electrical conductivity, making it a preferred choice for electrical components. It has a high melting point (approximately 1,984°F or 1,085°C) and good corrosion resistance, particularly when coated.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of copper is its superior conductivity, which enhances the efficiency of the solenoid or starter. However, copper can be prone to corrosion in certain environments, which may necessitate protective coatings. Additionally, copper is relatively expensive compared to other conductive materials, which can impact overall production costs.
Impact on Application: Copper is highly compatible with various electrical media and is often used in high-performance applications where efficient power transfer is critical.
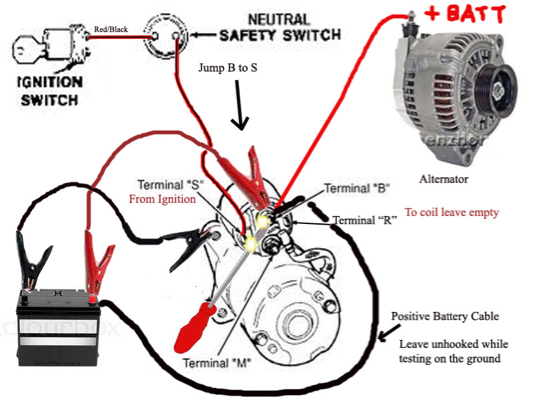
Illustrative image related to solenoid or starter bad
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in regions like Africa and South America should be aware of the fluctuating prices of copper and its availability. Compliance with standards such as ASTM B170 for copper wire may also be relevant.
What Role Does Steel Play in Solenoid and Starter Design?
Key Properties: Steel offers high tensile strength and durability, making it suitable for structural components in solenoids and starters. It has a lower thermal conductivity than copper but can withstand higher pressures and temperatures.
Pros & Cons: The strength of steel makes it ideal for applications requiring robust mechanical support. However, steel is susceptible to rust and corrosion unless properly treated, which can lead to failure in harsh environments. The manufacturing complexity can also increase due to the need for additional coatings or treatments.
Impact on Application: Steel is often used in the housing and structural components of solenoids and starters, where mechanical integrity is crucial.
Considerations for International Buyers: In regions with high humidity or corrosive environments, such as coastal areas in the Middle East, buyers should prioritize corrosion-resistant steel grades (e.g., stainless steel) and ensure compliance with relevant standards like DIN 17440.
Why Is Aluminum a Popular Choice for Solenoids and Starters?
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight, has good corrosion resistance, and excellent thermal conductivity. Its melting point is lower than that of copper and steel, making it easier to work with during manufacturing.
Pros & Cons: The lightweight nature of aluminum can reduce overall system weight, which is beneficial for automotive applications. However, it has lower tensile strength compared to steel, which may limit its use in high-stress applications. Additionally, aluminum is more expensive than steel, which can impact cost-effectiveness.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is often used in applications where weight reduction is essential, such as in automotive starters and solenoids.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider the availability of aluminum alloys that meet specific performance requirements and comply with standards like JIS H 4040 in Japan or ASTM B221 in the U.S.
How Does Plastic Contribute to Solenoid and Starter Functionality?
Key Properties: Engineering plastics, such as polyamide (nylon) or polycarbonate, are often used for insulation and structural components in solenoids and starters. These materials offer good electrical insulation and can withstand moderate temperatures.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of using plastic is its lightweight nature and excellent insulating properties, which reduce the risk of electrical shorts. However, plastics may not withstand high temperatures as well as metals and can be more susceptible to wear and tear over time.
Impact on Application: Plastics are commonly employed in non-load-bearing components, such as housing or insulation, where electrical isolation is necessary.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be mindful of the specific plastic grades used, ensuring they meet the necessary thermal and electrical standards for their applications. Compliance with international standards, such as ISO 1043 for plastic materials, is also essential.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Solenoids and Starters
| Material | Typical Use Case for solenoid or starter bad | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Copper | Electrical connections in solenoids | Excellent electrical conductivity | Prone to corrosion | High |
| Steel | Structural components in starters | High tensile strength | Susceptible to rust | Medium |
| Aluminum | Lightweight components in automotive starters | Lightweight and good corrosion resistance | Lower tensile strength | Medium |
| Plastic | Insulation and housing components | Lightweight and good electrical insulation | Limited high-temperature resistance | Low |
This strategic material selection guide provides a comprehensive overview for international B2B buyers, helping them make informed decisions based on performance, cost, and compliance considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for solenoid or starter bad
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Solenoids and Starters?
The manufacturing process for solenoids and starters involves several key stages that ensure the production of high-quality components. The main stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How Does Material Preparation Impact Quality in Solenoid and Starter Manufacturing?
Material preparation is the foundational step in manufacturing solenoids and starters. This stage involves sourcing high-quality raw materials, such as copper for windings and steel for housing. Suppliers must ensure that materials meet industry specifications and standards, which can be verified through material certificates. Proper handling and storage of these materials are crucial to prevent contamination and degradation, which can lead to performance issues in the final product.
What Techniques Are Used in the Forming Stage of Solenoid and Starter Production?
During the forming stage, manufacturers utilize various techniques to shape the components. Common methods include stamping, machining, and casting.
- Stamping is frequently used for creating metal parts from flat sheets, allowing for high-volume production with minimal waste.
- Machining involves cutting or removing material to achieve precise dimensions and tolerances, essential for components that require exact fitting.
- Casting is employed for producing complex shapes, particularly for solenoid housings, where traditional forming techniques may be inadequate.
Each technique contributes to the overall quality and performance of the solenoid or starter, affecting factors such as durability and operational efficiency.
How Are Solenoids and Starters Assembled?
The assembly stage is critical, as it combines various components into a functional unit. This process often involves the following:
- Winding the Coil: Copper wire is wound around the solenoid core, which is a delicate process requiring precision to ensure optimal electromagnetic performance.
- Component Integration: Other components, such as the plunger and housing, are carefully integrated. This may involve soldering or using fasteners, depending on the design.
- Alignment: Ensuring that all parts are correctly aligned is vital to prevent issues like misfiring or operational failure.
Manufacturers often use automated assembly lines to enhance consistency and efficiency, but manual assembly may still be employed for specialized or low-volume products.
What Finishing Processes Are Essential for Quality Assurance in Solenoids and Starters?
Finishing processes include cleaning, coating, and testing, all aimed at enhancing the product’s durability and performance.
- Cleaning removes any contaminants from the assembly process, which can affect electrical conductivity and performance.
- Coating with protective finishes, such as corrosion-resistant paints or galvanization, extends the lifespan of the components by protecting them from environmental factors.
- Testing at this stage involves functional checks to ensure that solenoids and starters perform as expected under operational conditions.
These finishing processes are crucial for meeting quality standards and ensuring customer satisfaction.
How Is Quality Control Implemented in Solenoid and Starter Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) in solenoid and starter manufacturing is an ongoing process that encompasses multiple checkpoints throughout production. Adhering to international standards like ISO 9001 ensures that manufacturers maintain a consistent quality management system.
What Are the Key QC Checkpoints in the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control checkpoints typically include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial stage checks the quality of incoming materials against specifications. Any materials that do not meet requirements are rejected.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, various inspections are conducted to ensure that production parameters are being met. This can include checks on dimensions, assembly integrity, and functional testing.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): At this stage, completed products undergo thorough testing to verify performance and compliance with standards. This may involve stress testing or lifecycle assessments.
What International Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
For B2B buyers, understanding the relevant international standards is critical. ISO 9001 is a well-recognized quality management standard that ensures a manufacturer’s processes are efficient and consistent. In addition, industry-specific certifications such as CE (Conformité Européenne) for European markets and API (American Petroleum Institute) for products used in oil and gas can indicate compliance with safety and quality requirements.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
B2B buyers can take several proactive steps to verify supplier QC processes:
- Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to assess the manufacturing environment, processes, and adherence to quality standards directly.
- Review of Quality Reports: Requesting and reviewing quality control reports can provide insights into a supplier’s performance history and any previous quality issues.
- Third-party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can offer an unbiased assessment of the manufacturer’s compliance with quality standards.
What Nuances Should International Buyers Consider in Quality Control?
International buyers, particularly those from regions like Africa, South America, and the Middle East, should be aware of several nuances when it comes to quality control:
- Cultural Differences: Different regions may have varying interpretations of quality standards. Understanding local practices can facilitate better communication and expectations.
- Logistics and Supply Chain: International logistics can affect delivery times and the condition of products upon arrival. Buyers should ensure that suppliers have robust logistics practices in place.
- Regulatory Compliance: Different regions may impose specific regulations that affect product quality and safety. Familiarizing oneself with these regulations is essential for ensuring compliance.
By being informed about the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices, B2B buyers can make educated decisions when sourcing solenoids and starters, ultimately leading to more reliable and efficient operations.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘solenoid or starter bad’
To assist B2B buyers in the procurement of solenoids and starters, particularly in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, this practical guide outlines essential steps for sourcing these components effectively. Understanding the intricacies of solenoids and starters can help ensure a successful purchase that meets operational needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before initiating the sourcing process, it is vital to clearly outline the technical specifications required for your solenoid or starter. Consider factors such as voltage ratings, torque requirements, and compatibility with existing systems. This clarity will streamline communication with suppliers and reduce the likelihood of purchasing incompatible components.
Step 2: Research and Identify Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough market research to identify potential suppliers that specialize in solenoids and starters. Utilize industry directories, trade shows, and online platforms to compile a list of manufacturers and distributors. Focus on suppliers with a proven track record in your specific region, as local suppliers may better understand the unique market conditions.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications and Standards
Ensure that potential suppliers meet industry standards and possess relevant certifications. Certifications such as ISO 9001 can indicate a commitment to quality management systems. Verify that the components comply with international safety and performance standards, which is crucial for ensuring reliability and longevity in applications.
Step 4: Request Product Samples for Testing
Before finalizing any orders, request product samples from shortlisted suppliers. Testing these samples can help assess their quality, performance, and compatibility with your systems. Pay attention to the build quality and any specifications that might affect performance, such as response time and durability under operational conditions.
Step 5: Inquire About Warranty and Support Policies
A strong warranty and robust customer support are essential when sourcing solenoids and starters. Inquire about the warranty period, coverage details, and the support structure in place for addressing issues post-purchase. This information can provide peace of mind and protect your investment in the event of product failure.
Step 6: Assess Pricing and Payment Terms
Once you have identified a few reliable suppliers, compare pricing models and payment terms. Ensure that you understand the total cost of ownership, which includes shipping, taxes, and potential customs duties. Negotiating favorable payment terms can improve cash flow and reduce financial strain on your operations.
Step 7: Establish Long-term Relationships
Building long-term relationships with suppliers can provide benefits such as preferential pricing, priority service, and access to new products. Engage in regular communication to keep abreast of any changes in product lines or industry standards. A reliable supplier can become an invaluable partner in your procurement process, supporting your operational needs over time.
By following these steps, B2B buyers can effectively navigate the complexities of sourcing solenoids and starters, ensuring that they procure high-quality products that meet their specific operational requirements.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for solenoid or starter bad Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Solenoids and Starters?
When evaluating the cost structure for solenoids and starters, several key components come into play. These include:
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts costs. High-quality metals and plastics, required for durability and performance, can increase material costs. Suppliers may offer different grades of materials, affecting both price and product longevity.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary widely by region. In areas with higher wage standards, labor costs can be a substantial part of the total expense. Conversely, sourcing from regions with lower labor costs can help achieve better margins, but may compromise quality.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with running a manufacturing facility, such as utilities, rent, and equipment maintenance. Efficient production processes can mitigate these costs, allowing suppliers to offer more competitive pricing.
-
Tooling: The initial setup for manufacturing solenoids and starters involves tooling costs, which can be significant, especially for custom designs. These costs are typically amortized over the production volume, making higher volumes more cost-effective.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that products meet specified standards incurs costs related to testing and inspection. Investing in robust QC processes can lead to long-term savings by reducing returns and warranty claims.
-
Logistics: Transportation and shipping costs vary based on distance, mode of transport, and fuel prices. International shipments may also incur tariffs and customs fees, further complicating the logistics cost structure.
-
Margin: Finally, suppliers will incorporate a profit margin into their pricing. This margin can be influenced by competition, perceived product value, and market demand.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Solenoid and Starter Sourcing?
Several factors influence the final pricing of solenoids and starters:
-
Volume/MOQ: Buyers often benefit from lower prices per unit when ordering in bulk. Understanding the minimum order quantities (MOQ) and negotiating for volume discounts can significantly reduce costs.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom specifications may lead to increased costs due to the need for specialized materials or tooling. Buyers should weigh the benefits of customization against the potential for higher pricing.
-
Materials: The quality and type of materials used can dramatically affect pricing. Buyers should look for suppliers that balance cost with quality, ensuring that the materials used will meet operational demands.
-
Quality and Certifications: Suppliers with recognized quality certifications may charge a premium. However, these certifications often assure buyers of product reliability and performance, justifying the higher price.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reputation, reliability, and service can also influence pricing. Established suppliers may command higher prices but can offer peace of mind regarding product quality and support.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the terms of shipping and delivery (Incoterms) is crucial. These terms dictate who bears the cost and risk during transportation, which can influence the total landed cost of the product.
What Are the Best Negotiation Tips for International Buyers?
For international B2B buyers, particularly in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, successful negotiation can lead to significant cost savings:
-
Understand Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Beyond the initial purchase price, consider maintenance, durability, and potential failure costs. A lower-priced item may not always be the most cost-effective in the long run.
-
Leverage Relationships: Build strong relationships with suppliers. Trust can lead to better pricing, more favorable terms, and increased flexibility in negotiations.
-
Explore Multiple Suppliers: Having options allows for better negotiations. It’s beneficial to compare quotes and capabilities from different suppliers to identify the best deal.
-
Be Informed About Market Trends: Stay updated on market conditions, material costs, and global supply chain dynamics. This knowledge can provide leverage during negotiations.
-
Negotiate Payment Terms: Consider negotiating for more favorable payment terms, such as extended payment periods, which can improve cash flow management.
Conclusion
In summary, sourcing solenoids and starters involves a complex interplay of various cost components and price influencers. For international buyers, understanding these elements and employing effective negotiation strategies can lead to more favorable pricing and enhanced value. Keep in mind that prices can fluctuate based on market conditions, so it’s advisable to regularly assess supplier quotes and market trends.
Disclaimer: The pricing outlined in this analysis is indicative and may vary based on specific supplier agreements, market conditions, and individual buyer circumstances. Always consult with suppliers for the most accurate and current pricing information.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing solenoid or starter bad With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to a Bad Solenoid or Starter
When faced with the challenges of a malfunctioning solenoid or starter, B2B buyers have several alternative solutions to consider. Evaluating these options can lead to more efficient, cost-effective outcomes that align with operational needs. Below, we compare the traditional solenoid or starter system with other viable alternatives, providing insight into their performance, costs, and suitability for different applications.
| Comparison Aspect | Solenoid Or Starter Bad | Alternative 1: Smart Starter Systems | Alternative 2: Integrated Starter-Generator (ISG) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Standard engagement; can fail under load | Enhanced efficiency; quick engagement | Provides dual functionality; smooth start and stop |
| Cost | Low to moderate replacement cost | Higher initial investment; long-term savings | Higher upfront cost; potential fuel savings |
| Ease of Implementation | Simple replacement process | Requires advanced installation | Complex installation; may need modifications |
| Maintenance | Regular checks needed; prone to wear | Lower maintenance; smart diagnostics | Minimal maintenance; integrated design reduces wear |
| Best Use Case | Standard vehicles; cost-sensitive applications | High-performance vehicles; tech-savvy buyers | Hybrid and electric vehicles; fuel-efficient fleets |
What Are the Benefits of Smart Starter Systems?
Smart starter systems incorporate advanced electronics and sensors that optimize the starting process. They offer enhanced performance by reducing the energy required to start the engine, thus minimizing wear on the battery and starter components. While the initial investment is higher than traditional solenoid systems, these systems can lead to long-term savings through improved fuel efficiency and reduced maintenance costs. However, they may require specialized installation, which could be a barrier for some businesses.
How Does an Integrated Starter-Generator (ISG) Work?
The Integrated Starter-Generator (ISG) combines the functions of a starter motor and an alternator into one unit. This technology allows for a smoother start and stop function, making it particularly advantageous for hybrid and electric vehicles. The ISG can regenerate energy during braking and provide additional power during acceleration, leading to improved fuel efficiency. While the upfront costs can be significantly higher than traditional systems, the benefits in terms of fuel savings and reduced emissions make it an appealing option for fleets focused on sustainability.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Needs
Selecting the right solution when dealing with a bad solenoid or starter involves understanding the specific needs of your operation. Consider factors such as performance requirements, budget constraints, and the technological capabilities of your vehicle fleet. For businesses prioritizing cost-effectiveness and simplicity, traditional solenoids or starters may suffice. However, for those looking to invest in advanced technologies that enhance performance and sustainability, smart starter systems or integrated starter-generators could provide substantial long-term benefits. Assessing these alternatives will guide B2B buyers in making informed decisions that align with their operational goals.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for solenoid or starter bad
What Are the Key Technical Properties of a Solenoid or Starter?
Understanding the technical properties of solenoids and starters is crucial for B2B buyers, especially when sourcing components for automotive applications. Here are some essential specifications to consider:
-
Material Grade
The material used in the construction of solenoids and starters significantly impacts durability and performance. Common materials include copper for windings (due to its excellent conductivity) and high-grade steel for housings. High-quality materials ensure longevity and reliability, crucial for automotive applications where failure can lead to costly downtime. -
Voltage Rating
Solenoids and starters are designed to operate at specific voltage levels, typically 12V or 24V in automotive applications. Understanding the voltage rating is essential to ensure compatibility with the vehicle’s electrical system. Using components with incorrect voltage ratings can lead to malfunction or damage, affecting overall vehicle performance. -
Current Rating
The current rating indicates the maximum amount of electrical current the solenoid or starter can handle. For solenoids, this is crucial as they need to switch high currents to engage the starter motor. Selecting components with appropriate current ratings prevents overheating and ensures efficient operation, which is vital for maintaining vehicle reliability. -
Torque Output
Torque output is a critical specification for starters, as it determines the amount of rotational force generated to crank the engine. This is particularly important in larger engines that require higher torque to start. B2B buyers should consider torque output to ensure that the starter will perform adequately under various conditions, such as cold starts. -
Durability Ratings
Durability ratings, often categorized by industry standards, indicate how well a solenoid or starter can withstand environmental factors like temperature fluctuations, moisture, and vibration. Components with high durability ratings are essential for applications in challenging climates or rugged terrains, common in regions like Africa and South America. -
Response Time
The response time of a solenoid refers to how quickly it can engage after receiving an electrical signal. Quick response times are vital for ensuring that starters engage promptly, minimizing wear and tear on the engine. Buyers should prioritize components with low response times to enhance the overall efficiency of the starting system.
What Are Common Trade Terminology Related to Solenoids and Starters?
Familiarity with industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the B2B landscape. Here are key terms relevant to solenoids and starters:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
This term refers to companies that produce parts that are used in the assembly of vehicles. B2B buyers often seek OEM parts for their reliability and compatibility with existing systems. Understanding OEM specifications ensures that sourced components will meet quality standards. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. Buyers must be aware of MOQs to align their purchasing strategies and manage inventory effectively. This term is especially relevant for international buyers looking to minimize costs. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document that buyers send to suppliers to solicit pricing and terms for specific products. Including detailed specifications for solenoids and starters in RFQs can help suppliers provide accurate quotes, ultimately streamlining the purchasing process. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of internationally recognized rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in the shipping process. Understanding Incoterms is essential for B2B transactions, as they clarify shipping costs, risks, and delivery obligations, which can vary significantly between regions. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time between placing an order and receiving the product. In the context of solenoids and starters, understanding lead times is crucial for planning and ensuring timely project completions. Buyers should inquire about lead times to avoid disruptions in their supply chain. -
Aftermarket
The aftermarket encompasses all parts and services sold after the initial sale of a vehicle. B2B buyers may consider aftermarket solenoids and starters as cost-effective alternatives to OEM parts. Understanding the aftermarket landscape can provide insights into competitive pricing and availability.
By grasping these essential technical properties and trade terminologies, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing solenoids and starters, ensuring they meet their operational needs while optimizing costs.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the solenoid or starter bad Sector
What Are the Current Market Trends Impacting the Solenoid and Starter Sector?
The global solenoid and starter market is experiencing dynamic changes driven by technological advancements and increasing demand for reliable automotive components. One significant driver is the ongoing shift towards electric vehicles (EVs) and hybrid models, which has prompted manufacturers to innovate starter systems that cater to these new technologies. Additionally, the automotive industry’s push for enhanced fuel efficiency and performance has led to the development of more robust and efficient solenoids.

Illustrative image related to solenoid or starter bad
Emerging trends in B2B sourcing for solenoids and starters include a greater reliance on digital platforms for procurement, allowing international buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe to streamline their sourcing processes. Buyers are increasingly leveraging data analytics to identify optimal suppliers, assess market conditions, and forecast demand. Moreover, the rise of automation in manufacturing processes is reshaping supply chain dynamics, allowing for faster turnaround times and reduced costs.
International buyers must also navigate varying regional regulations and standards, which can impact sourcing decisions. For instance, compliance with safety and environmental regulations is critical in Europe, while emerging markets may present different challenges related to infrastructure and logistics. As such, understanding the specific market dynamics and trends in each region is crucial for effective sourcing strategies.
How Can B2B Buyers Ensure Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing in the Solenoid and Starter Sector?
Sustainability is becoming a non-negotiable aspect of sourcing strategies in the solenoid and starter market. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes, particularly concerning energy consumption and waste generation, has drawn increased scrutiny from consumers and regulators alike. As a result, B2B buyers are prioritizing suppliers that demonstrate a commitment to sustainable practices, such as reducing emissions and using eco-friendly materials.
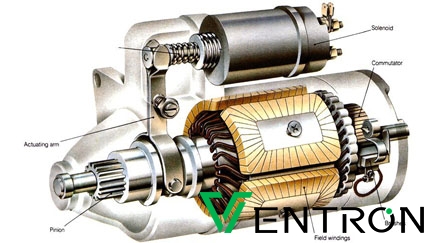
Illustrative image related to solenoid or starter bad
Ethical sourcing is equally important, as buyers seek to ensure that their suppliers adhere to fair labor practices and contribute positively to their communities. This includes verifying that materials used in solenoids and starters are sourced responsibly, avoiding suppliers that engage in exploitative practices. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and Fair Trade can serve as indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability and ethical practices.
Furthermore, the demand for ‘green’ certifications is rising, as international buyers increasingly prefer components that meet environmental standards. This trend not only enhances brand reputation but also aligns with the growing consumer preference for sustainable products. By focusing on ethical sourcing and sustainability, B2B buyers can mitigate risks associated with supply chain disruptions and enhance their overall market competitiveness.
What Is the Historical Context of the Solenoid and Starter Market?
The solenoid and starter market has evolved significantly since the early 20th century, paralleling advancements in automotive technology. Initially, starters were mechanical devices that relied on hand cranks, but the introduction of electric starters in the 1910s revolutionized vehicle ignition systems. This transition not only improved the reliability of starting engines but also paved the way for more complex electrical systems within automobiles.
Over the decades, solenoid technology has advanced, with innovations that have led to more compact, efficient, and durable components. The shift towards electronic control systems in modern vehicles has further enhanced the functionality of starters and solenoids, allowing for features such as remote start and enhanced security systems. As the automotive landscape continues to change, particularly with the rise of electric and hybrid vehicles, the solenoid and starter market is poised for further transformation, emphasizing the need for ongoing innovation and adaptation among suppliers and manufacturers.
In summary, navigating the solenoid and starter market requires an understanding of current trends, a commitment to sustainability and ethical sourcing, and awareness of historical developments that shape today’s automotive technology.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of solenoid or starter bad
-
How do I solve a problem with a bad starter solenoid?
To address issues with a bad starter solenoid, first ensure that the battery is in good condition and fully charged. Next, check for loose or corroded connections, which can impede power flow. If the solenoid is still non-responsive, you may need to replace it. Ensure you have the correct specifications for your vehicle’s make and model. Consult with a qualified technician for diagnosis and replacement to avoid further complications. -
What is the best solenoid for automotive applications?
The best solenoid for automotive applications typically depends on the specific vehicle and its electrical requirements. Look for solenoids that offer high current ratings and robust construction to withstand harsh environments. Brands with a strong reputation for reliability, such as Bosch or Denso, are often preferred. Additionally, ensure compatibility with your vehicle’s ignition system, and consider solenoids with extended warranties for added peace of mind. -
How can I effectively vet suppliers for solenoids?
To vet suppliers for solenoids, start by researching their reputation in the industry. Look for reviews, testimonials, and certifications that indicate quality assurance standards. Request samples of their products to assess quality firsthand. It’s also beneficial to inquire about their production capabilities, lead times, and compliance with international standards, especially if you are sourcing from different regions like Africa or South America. -
What customization options are available for solenoids?
Many manufacturers offer customization options for solenoids, including variations in size, voltage, and current ratings. You can often request specific features like waterproofing or enhanced durability for extreme conditions. When contacting suppliers, clearly communicate your requirements and ask about their capabilities to meet custom specifications. This can help you ensure that the solenoid fits your application perfectly. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for solenoids?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for solenoids can vary widely by supplier and product type. Generally, MOQs can range from as low as 50 units to several hundred. When negotiating with suppliers, inquire about their MOQ policies and whether they can accommodate smaller orders, especially if you are testing new products or entering a new market. Establishing a good relationship with suppliers may also lead to more flexible terms. -
What payment terms are common when sourcing solenoids internationally?
Common payment terms for international transactions include upfront payment, a 30% deposit with the remainder due before shipment, or payment on delivery. It’s important to discuss and agree on payment terms upfront to avoid misunderstandings. Utilizing secure payment methods like letters of credit or escrow services can provide additional protection for both parties. Always verify the supplier’s payment policies and ensure they align with your financial practices. -
What quality assurance measures should I expect from solenoid suppliers?
Expect suppliers to implement rigorous quality assurance measures, including product testing and certifications. Look for suppliers that adhere to international standards such as ISO 9001, which ensures consistent quality management. Inquire about their testing processes, including electrical performance, durability, and safety tests. A reputable supplier should be transparent about their QA procedures and willing to provide documentation as proof of compliance. -
How can I manage logistics when importing solenoids?
Managing logistics when importing solenoids involves coordinating with freight forwarders and understanding customs regulations in your country. Ensure your supplier is familiar with international shipping practices and can provide necessary documentation such as invoices and certificates of origin. It’s also wise to plan for potential delays in transit and customs clearance. Consider using Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) to clarify responsibilities for shipping costs, risks, and insurance during the import process.
Top 4 Solenoid Or Starter Bad Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Reddit – Starter Motor Insights
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: The starter motor is the main component responsible for starting the engine, while the starter solenoid is a part of the starter motor assembly that engages the motor when the ignition key is turned. Most people replace the entire starter motor instead of just the solenoid.
2. Eric’s Car Care – Starter Motor Solutions
Domain: ericscarcare.com
Registered: 2021 (4 years)
Introduction: This company, Eric’s Car Care – Starter Motor Solutions, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
3. Tractor Troubleshooting – Solenoid & Starter Solutions
Domain: forums.yesterdaystractors.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: The discussion revolves around troubleshooting a 1952 tractor’s starting issue, specifically focusing on the solenoid and starter. Key points include: 1. Fresh 6-volt battery; 2. Wiring is correct; 3. Generator is polarized; 4. The solenoid clicks but does not engage the starter; 5. Suggestions for troubleshooting include checking the starter ground, using jumper cables to bypass the solenoid, and…
4. Can-Am – Renegade and Outlander
Domain: facebook.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Can-Am Renegade and Outlander (United States)
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for solenoid or starter bad
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your Business Resilience?
In the competitive landscape of international trade, particularly for solenoid and starter components, strategic sourcing emerges as a critical factor for success. Understanding the signs of a failing starter solenoid not only allows businesses to optimize their supply chain but also minimizes operational disruptions. By prioritizing quality suppliers who offer reliable products, buyers can ensure consistent performance and reduce the risk of unexpected failures.
Moreover, sourcing from diverse regions—such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—can provide access to innovative technologies and cost-effective solutions that enhance overall value. Leveraging partnerships with local manufacturers can also foster sustainable practices and support regional economies.
Looking ahead, it is essential for B2B buyers to stay informed about industry trends and technological advancements in solenoid and starter systems. By actively engaging with suppliers and investing in quality assurance processes, businesses can not only enhance their product offerings but also position themselves as leaders in their markets. Embrace strategic sourcing today to build a resilient future that drives growth and innovation.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.