Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for what is the alternator
In the dynamic landscape of global commerce, sourcing reliable alternators poses a significant challenge for B2B buyers across diverse markets, including Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. As a critical component in automotive and industrial machinery, the alternator plays a pivotal role in converting mechanical energy into electrical energy, thus ensuring the seamless operation of vehicles and equipment. Understanding the intricacies of alternators—from their types and applications to supplier vetting and cost considerations—is essential for making informed purchasing decisions.
This comprehensive guide serves as an invaluable resource for international B2B buyers seeking to navigate the complexities of the alternator market. By delving into various alternator types, their specific applications across industries, and the nuances of sourcing from reputable suppliers, this guide empowers businesses to optimize their procurement strategies. Additionally, it offers insights into cost factors, enabling buyers to align their budgets with market realities while ensuring quality and reliability.
With a focus on actionable insights and expert recommendations, this guide aims to equip decision-makers with the knowledge needed to mitigate risks and enhance operational efficiency. Whether you are in Saudi Arabia looking to source automotive parts or in Germany evaluating industrial machinery components, understanding what an alternator is and how to select the right one can significantly impact your business’s success.
Table Of Contents
- Top 3 What Is The Alternator Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for what is the alternator
- Understanding what is the alternator Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of what is the alternator
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘what is the alternator’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for what is the alternator
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for what is the alternator
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘what is the alternator’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for what is the alternator Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing what is the alternator With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for what is the alternator
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the what is the alternator Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of what is the alternator
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for what is the alternator
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Understanding what is the alternator Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Alternator | Converts mechanical energy to electrical energy via a rotor and stator; typically used in combustion engine vehicles. | Automotive manufacturing and repair | Pros: Reliable, widely available. Cons: Limited to traditional vehicles. |
| High-Output Alternator | Designed to produce more electrical power; ideal for vehicles with high electrical demands like sound systems or off-road lights. | Custom automotive, racing, and off-road vehicles | Pros: Supports additional accessories. Cons: Higher cost, may require modifications. |
| Smart Alternator | Features advanced technology to optimize power output and efficiency; often includes a built-in voltage regulator. | Modern vehicles, electric and hybrid applications | Pros: Improved fuel efficiency, reduces battery wear. Cons: More complex, potentially higher repair costs. |
| Marine Alternator | Built for durability and corrosion resistance; designed to withstand harsh marine environments. | Marine applications and boating industries | Pros: Enhanced durability, reliable in harsh conditions. Cons: Heavier and may be more expensive than standard alternators. |
| Diesel Alternator | Specifically engineered for diesel engines, providing higher output and efficiency to meet the demands of larger vehicles. | Heavy-duty trucks, construction equipment | Pros: High reliability, designed for tough conditions. Cons: Bulkier, may have compatibility issues with non-diesel engines. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Standard Alternators?
Standard alternators are the most common type found in vehicles, converting mechanical energy from the engine into electrical energy to power the vehicle’s electrical systems and recharge the battery. They are typically compact and efficient, making them suitable for a wide range of automotive applications. B2B buyers should consider their reliability and availability, as these alternators are crucial for standard automotive manufacturing and repair. However, they may not meet the demands of vehicles with extensive electrical accessories.
How Do High-Output Alternators Meet Specific Needs?
High-output alternators are designed for vehicles that require more electrical power, such as those with aftermarket audio systems or additional lighting. These alternators generate significantly more current than standard models, ensuring that all electrical components function optimally. Businesses in the custom automotive or racing sectors should consider these alternators to support enhanced electrical needs. However, buyers should be aware of potential compatibility issues and the higher costs associated with installation.
What Advantages Do Smart Alternators Offer?
Smart alternators incorporate advanced technology that optimizes power output based on real-time demands. They often include features like intelligent voltage regulation to enhance fuel efficiency and prolong battery life. This makes them particularly suitable for modern vehicles, including electric and hybrid models. For B2B buyers, investing in smart alternators can lead to long-term savings, but they may come with increased complexity and repair costs.
Why Are Marine Alternators Essential for Boating Industries?
Marine alternators are specifically engineered to withstand the harsh conditions of marine environments, including exposure to saltwater and humidity. They are built with corrosion-resistant materials and robust designs to ensure reliability. Businesses in the marine industry should prioritize these alternators for their boats and vessels, as they provide peace of mind in challenging conditions. However, their specialized nature may come with a higher price point and weight considerations.
How Do Diesel Alternators Cater to Heavy-Duty Applications?
Diesel alternators are tailored for heavy-duty applications, providing high output and efficiency to meet the demands of larger vehicles such as trucks and construction equipment. They are robust and designed to handle the rigors of demanding environments. B2B buyers in sectors like transportation and construction should consider diesel alternators for their reliability and performance. However, their bulkiness and potential compatibility issues with non-diesel engines should be taken into account during purchasing decisions.
Key Industrial Applications of what is the alternator
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of what is the alternator | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive Manufacturing | Powering vehicle electrical systems | Ensures reliable operation of vehicles, enhancing safety and performance | Quality certifications, compatibility with various vehicle models |
| Renewable Energy | Wind turbines and solar energy systems | Converts mechanical energy to electrical energy, optimizing energy output | Durability in harsh environments, efficiency ratings |
| Agriculture | Agricultural machinery (tractors, harvesters) | Powers essential electronic components for operation, improving productivity | Resistance to vibrations, moisture, and dust |
| Marine Industry | Power generation in boats and ships | Provides reliable electricity for navigation and onboard systems | Marine-grade materials, corrosion resistance |
| Construction | Heavy machinery (excavators, cranes) | Supports electronic controls and safety systems, enhancing operational efficiency | Robustness and reliability under heavy loads |
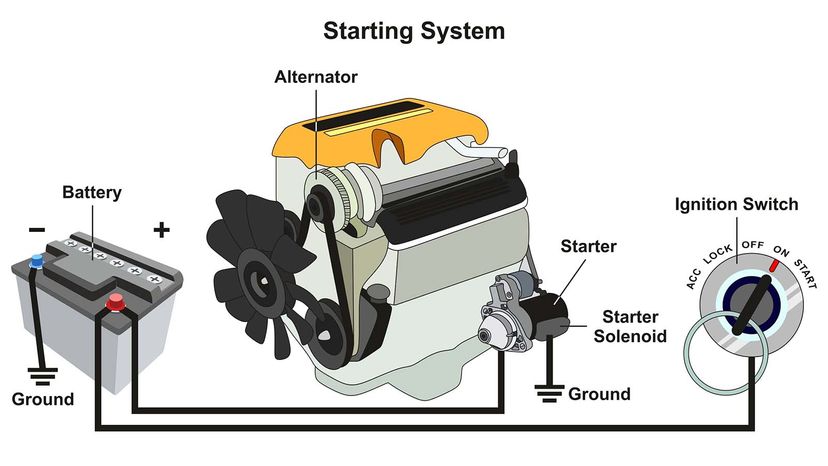
How is the alternator used in automotive manufacturing to ensure vehicle reliability?
In the automotive manufacturing sector, alternators play a pivotal role by supplying power to various electrical components such as headlights, infotainment systems, and safety features. A well-functioning alternator ensures that vehicles operate reliably, significantly enhancing both safety and performance for end-users. For international buyers, especially in Africa and South America, sourcing high-quality alternators that meet specific vehicle compatibility and quality certifications is crucial to maintain production standards.
What role does the alternator play in renewable energy systems?
In renewable energy applications, particularly in wind turbines and solar energy systems, alternators convert mechanical energy into electrical energy, optimizing the energy output from these sources. This conversion is vital for maximizing efficiency and ensuring a stable power supply. Buyers from the Middle East and Europe should prioritize sourcing alternators that are durable and efficient, especially in harsh environmental conditions, to ensure long-term performance and reliability.
How does the alternator enhance productivity in agriculture?
In agriculture, alternators are essential for powering agricultural machinery such as tractors and harvesters. These machines rely on electrical systems for navigation, controls, and other functionalities that enhance productivity. Farmers and agricultural equipment manufacturers in regions like Africa must consider sourcing alternators that can withstand vibrations, moisture, and dust, ensuring uninterrupted operation during critical farming seasons.
Why is the alternator critical in the marine industry?
In the marine industry, alternators are vital for generating electricity on boats and ships, powering navigation systems and essential onboard electronics. A reliable alternator ensures that vessels operate safely and efficiently, which is crucial for both commercial and recreational boating. Buyers in this sector should focus on sourcing marine-grade alternators that offer corrosion resistance and durability to withstand harsh marine environments.
How does the alternator support heavy machinery in construction?
Heavy machinery in the construction sector, such as excavators and cranes, relies on alternators to power electronic controls and safety systems. This functionality enhances operational efficiency and safety on job sites. Construction companies and equipment suppliers in Europe and the Middle East should prioritize sourcing robust and reliable alternators capable of performing under heavy loads, ensuring consistent and safe machinery operation.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘what is the alternator’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Understanding Alternator Functionality for Fleet Management
The Problem: For businesses operating a fleet of vehicles, understanding the functionality of the alternator is crucial. Fleet managers often face challenges when vehicles experience electrical failures, leading to unexpected downtime and increased maintenance costs. A lack of knowledge about how alternators work can result in misdiagnosing issues as battery problems, thereby prolonging vehicle downtime. This not only affects operational efficiency but can also lead to unscheduled repairs that strain budgets.
The Solution: To mitigate these challenges, fleet managers should invest in training programs that educate their teams on the role of the alternator within the vehicle’s electrical system. By understanding that the alternator converts mechanical energy into electrical energy, fleet personnel can better identify symptoms of alternator failure, such as dimming lights or difficulty starting the engine. Additionally, implementing a regular maintenance schedule that includes checks on the alternator’s performance can prevent unexpected failures. Investing in diagnostic tools that monitor the health of the alternator and associated components can also empower fleet managers to address issues proactively, minimizing downtime and maximizing operational efficiency.
Scenario 2: Sourcing Quality Alternators for International Purchases
The Problem: International B2B buyers often encounter difficulties sourcing quality alternators that meet their specific regional standards and vehicle requirements. Discrepancies in specifications, compatibility issues, and varying quality among suppliers can lead to poor purchasing decisions, resulting in additional costs and logistical challenges. This is especially true in regions like Africa and South America, where access to reliable suppliers may be limited, and counterfeit products are prevalent.
The Solution: To ensure quality procurement, buyers should establish relationships with reputable suppliers who specialize in alternators and have a proven track record of servicing the automotive industry. Conducting thorough due diligence, including reviewing certifications and customer testimonials, can help identify trustworthy partners. Furthermore, leveraging technology such as online platforms that aggregate supplier ratings and product specifications can streamline the sourcing process. Buyers should also consider engaging in direct negotiations with manufacturers to customize alternator specifications that suit their local vehicles, ensuring compatibility and performance. Finally, implementing a quality assurance process upon receipt of products can safeguard against potential defects.
Scenario 3: Mitigating Risks of Alternator Failure in Heavy Equipment
The Problem: Companies operating heavy machinery face significant risks associated with alternator failure, which can lead to equipment breakdowns and costly project delays. Understanding the signs of alternator wear is often overlooked, leading to reactive rather than proactive maintenance strategies. This lack of awareness can result in severe operational disruptions, particularly in industries like construction and mining, where equipment reliability is paramount.
The Solution: To address these risks, organizations should develop a comprehensive maintenance program that prioritizes the health of the alternator in heavy equipment. This includes regular inspections, testing the output voltage, and monitoring for unusual sounds or performance issues. Providing training for operators on the importance of alternator functionality can foster a culture of preventative maintenance. Additionally, implementing a predictive maintenance strategy that utilizes IoT sensors to monitor alternator performance in real-time can enable companies to anticipate failures before they occur. By integrating these practices, organizations can enhance equipment reliability, reduce downtime, and ultimately improve project timelines and profitability.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for what is the alternator
When selecting materials for alternators, it is crucial to consider the properties that directly affect performance, durability, and cost. Here, we analyze four common materials used in the construction of alternators: aluminum, copper, steel, and plastic composites. Each material has unique characteristics that can influence the efficiency and longevity of alternators, particularly in varying international markets.
What Are the Key Properties of Aluminum in Alternators?
Aluminum is widely used in alternator housings and components due to its lightweight and excellent thermal conductivity. It typically withstands temperatures up to 150°C and is resistant to corrosion, making it suitable for diverse environments, including humid and coastal regions.
Pros: Aluminum’s lightweight nature reduces the overall weight of the alternator, enhancing fuel efficiency in vehicles. It also allows for easier manufacturing and machining.
Illustrative image related to what is the alternator
Cons: While aluminum is durable, it may not withstand extreme mechanical stresses as well as some metals. Its cost can be moderate, but the price may vary based on alloy specifications.
Impact on Application: Aluminum’s corrosion resistance makes it ideal for applications in regions with high humidity, such as parts of Africa and South America.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards such as ASTM and DIN is essential. Buyers should ensure that the aluminum used meets local regulations regarding recyclability and environmental impact.
How Does Copper Contribute to Alternator Performance?
Copper is primarily used in the windings of alternators due to its exceptional electrical conductivity. It can handle high temperatures (up to 200°C) and has excellent fatigue resistance.
Pros: Copper’s high conductivity ensures efficient energy transfer, which is critical for the alternator’s performance. Its durability contributes to the longevity of electrical components.

Illustrative image related to what is the alternator
Cons: Copper is relatively expensive compared to other conductive materials, and its weight can add to the overall mass of the alternator.
Impact on Application: The high conductivity of copper allows for quick charging of batteries and efficient power supply to electrical systems, making it suitable for high-demand applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of copper’s market fluctuations and consider sourcing from regions with stable supply chains. Compliance with electrical safety standards is also vital.
What Role Does Steel Play in Alternators?
Steel is often used for structural components of alternators, including the rotor and stator cores. It provides strength and stability, with temperature ratings typically around 300°C.
Illustrative image related to what is the alternator
Pros: Steel’s strength ensures that the alternator can withstand mechanical stresses and vibrations, which is particularly important in heavy-duty applications.
Cons: Steel is heavier than aluminum and may lead to increased overall weight, potentially affecting fuel efficiency. It is also prone to corrosion unless treated.
Impact on Application: Steel is suitable for applications requiring high durability, such as commercial vehicles and machinery used in rugged environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider the corrosion resistance treatments available for steel, especially in regions with high humidity or salt exposure, such as coastal areas in the Middle East.
How Do Plastic Composites Enhance Alternator Design?
Plastic composites are increasingly being used in alternator components, particularly for insulation and housing parts. These materials can withstand temperatures up to 120°C and are resistant to chemical degradation.
Pros: Plastic composites are lightweight and can be molded into complex shapes, allowing for innovative designs. They also offer good electrical insulation properties.
Illustrative image related to what is the alternator
Cons: While they are resistant to corrosion, plastic composites may not withstand high mechanical stresses as effectively as metals, leading to potential durability concerns.
Impact on Application: The use of plastic composites can reduce the weight of alternators, making them suitable for electric and hybrid vehicles that prioritize efficiency.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with environmental regulations regarding plastic use is essential. Buyers should also assess the long-term performance of plastic composites in specific climates.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Alternators
| Material | Typical Use Case for what is the alternator | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Housing and structural components | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Less durable under extreme mechanical stress | Medium |
| Copper | Windings and electrical connections | Excellent conductivity for efficient energy transfer | Higher cost and added weight | High |
| Steel | Rotor and stator cores | High strength and stability | Heavier and prone to corrosion without treatment | Medium |
| Plastic Composites | Insulation and housing parts | Lightweight and moldable for innovative designs | May lack durability under mechanical stress | Low |
This analysis provides a comprehensive overview of material options for alternators, helping international B2B buyers make informed decisions based on performance requirements and regional considerations.
Illustrative image related to what is the alternator
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for what is the alternator
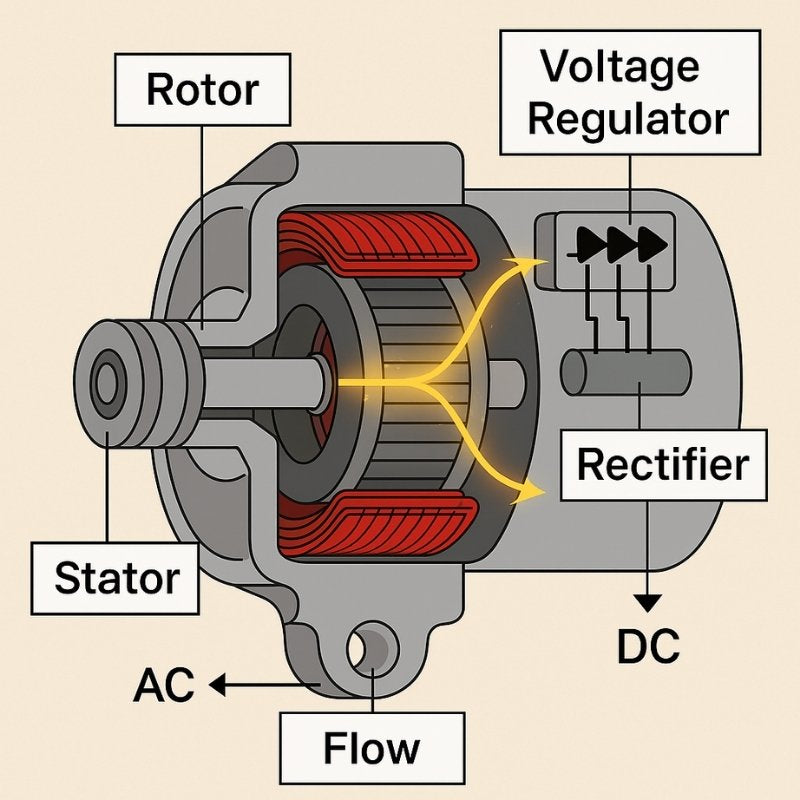
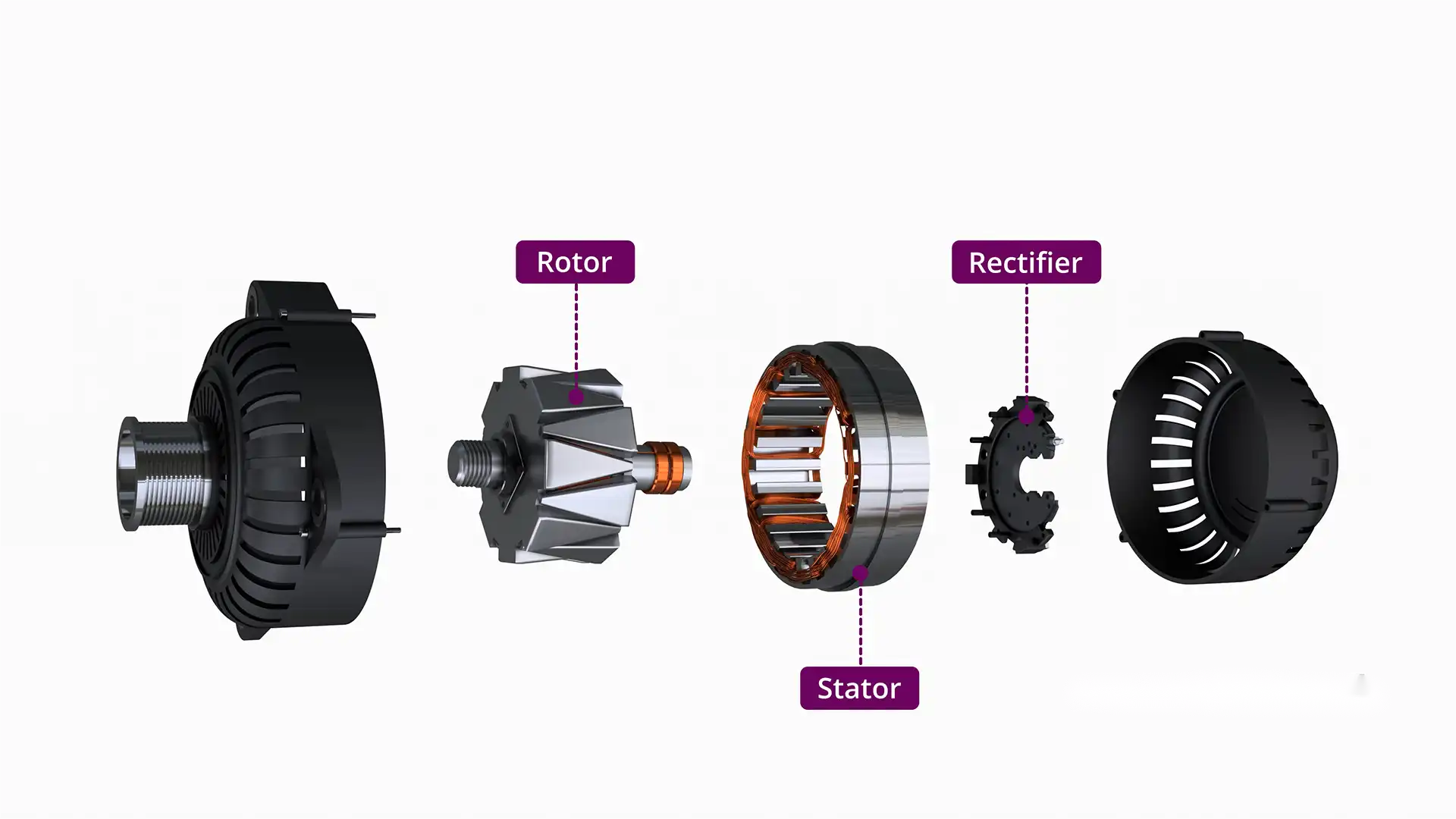
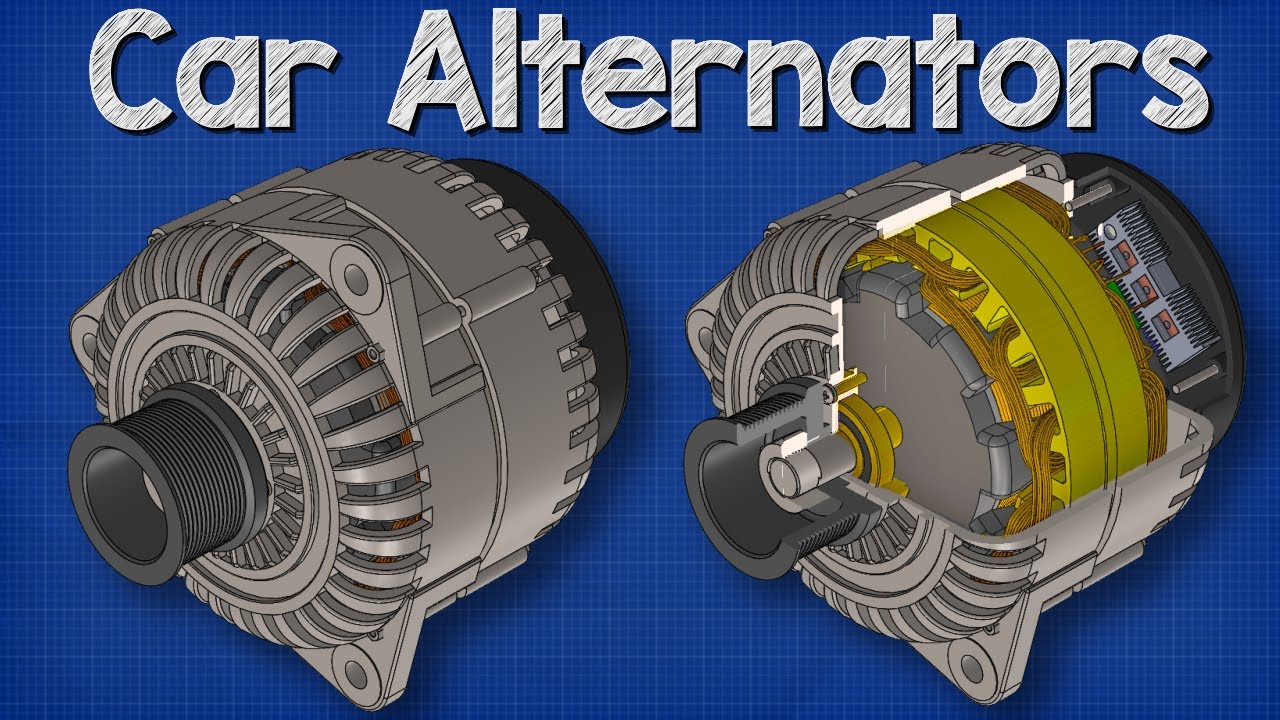
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of an Alternator?
Manufacturing an alternator involves several key stages that ensure its functionality and reliability. These stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
Material Preparation
The first step in alternator manufacturing is sourcing high-quality raw materials. Key components such as copper wire, steel for the rotor and stator, and various electronic parts are carefully selected. Suppliers must adhere to strict specifications to ensure optimal performance. Material checks are conducted to confirm compliance with industry standards, which may vary by region, such as ASTM standards in the U.S. or ISO standards internationally.
Forming
In this phase, the raw materials undergo various forming processes. The rotor and stator are typically machined from steel, using techniques such as stamping or forging to achieve the desired shapes and dimensions. The copper wire is wound into coils, which are critical for generating electricity. This phase requires precision, as any deviation can lead to inefficiencies or failures in the alternator’s performance.
Assembly
Once the components are formed, they proceed to the assembly stage. This is where the rotor and stator are combined, along with other essential parts such as the voltage regulator and diode rectifier. Automated assembly lines may be employed to enhance efficiency and consistency. Skilled technicians also perform manual assembly for more complex components, ensuring that every piece is correctly positioned and secured.
Finishing
The final stage involves quality checks and finishing touches. This includes applying protective coatings to prevent corrosion, as well as electrical testing to ensure that the alternator functions correctly. Each alternator is subjected to rigorous testing protocols to confirm that it meets performance specifications. Common tests include voltage output tests and load tests, which simulate real-world conditions.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Alternator Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is crucial in the manufacturing of alternators to ensure their reliability and safety. Various international standards and industry-specific certifications guide these processes.
What International Standards Apply to Alternator Manufacturing?
ISO 9001 is the most recognized quality management standard applicable to the manufacturing sector. It emphasizes a process-oriented approach, focusing on customer satisfaction and continuous improvement. Additionally, certifications such as CE (Conformité Européenne) for products sold in Europe and API (American Petroleum Institute) standards for certain industrial applications are critical for compliance. B2B buyers should ensure that suppliers hold these certifications to guarantee product quality.
Illustrative image related to what is the alternator
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are integral to the manufacturing process. These typically include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Raw materials are inspected upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Regular checks during the manufacturing process help identify any deviations from quality standards. This can include monitoring machine settings and verifying component dimensions.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Once assembly is complete, the finished alternator undergoes comprehensive testing to ensure it meets performance requirements.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used in Quality Assurance for Alternators?
Various testing methods are employed to assess the quality and performance of alternators, ensuring they meet both safety and performance standards.
Electrical Testing
This is one of the most critical tests, where the alternator is connected to a test bench to measure voltage output and current draw. This helps verify that the alternator can produce the necessary electrical power.
Illustrative image related to what is the alternator
Load Testing
Load tests simulate real-world operating conditions by applying a controlled load to the alternator. This testing ensures that the alternator can maintain performance under various operational scenarios.
Thermal Testing
Thermal testing assesses how well the alternator can dissipate heat generated during operation. Excessive heat can lead to failure, so it’s essential to ensure that the design and materials used can withstand high temperatures.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
For international B2B buyers, particularly in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is crucial to ensuring product reliability.
What Are the Best Practices for Supplier Audits?
Conducting supplier audits is one of the most effective ways to assess quality control practices. This involves evaluating the supplier’s manufacturing processes, quality management systems, and compliance with international standards. Buyers should look for suppliers that are open to audits and willing to provide evidence of their quality management practices.

Illustrative image related to what is the alternator
How Can Buyers Use Reports and Third-Party Inspections?
Requesting reports from suppliers that detail their quality control measures and testing results can provide valuable insights. Additionally, engaging third-party inspection services can offer an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s manufacturing capabilities and adherence to quality standards.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
Navigating quality control in international markets can be complex, especially when dealing with suppliers from different regions. Buyers should be aware of the following nuances:
Cultural and Regulatory Differences
Quality expectations and regulatory requirements can vary significantly across regions. For example, European standards may be more stringent than those in other markets. B2B buyers should familiarize themselves with local regulations and standards to ensure compliance.
Logistics and Supply Chain Considerations
Quality assurance does not end at the manufacturing facility. Logistics play a vital role in maintaining quality during transportation. Buyers should ensure that suppliers have robust packaging and shipping protocols to prevent damage during transit.
Building Relationships with Suppliers
Establishing strong relationships with suppliers can facilitate better communication regarding quality concerns. This partnership can lead to continuous improvement in quality assurance processes and ultimately enhance the reliability of the alternators supplied.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures in alternator production, B2B buyers can make informed decisions and ensure they source high-quality products that meet their operational needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘what is the alternator’
In the competitive landscape of automotive parts procurement, understanding the intricacies of components like the alternator is vital. This guide serves as a practical checklist for B2B buyers seeking to source alternators effectively, ensuring that they make informed decisions that align with their operational needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before initiating the procurement process, clearly define the technical specifications required for the alternator. Consider factors such as power output, size, and compatibility with existing vehicle models. This step is crucial to ensure that the alternator meets the specific demands of your fleet or inventory.
- Power Output: Determine the wattage and amperage needed based on vehicle requirements.
- Compatibility: Ensure the alternator fits the engine types you work with to avoid compatibility issues.
Step 2: Research Market Trends
Understanding market trends in alternator technology can help you identify potential suppliers who offer innovative solutions. Research current advancements, such as increased efficiency and reduced weight, to make informed decisions.
Illustrative image related to what is the alternator
- Efficiency Standards: Look for suppliers offering high-efficiency models that comply with international standards.
- Material Innovations: Explore options that utilize lightweight materials for better performance.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a supplier, conduct thorough evaluations. Request company profiles, performance histories, and references from other clients in your region. This step is essential to ensure reliability and quality.
- Supplier Reputation: Investigate their standing in the industry through reviews and testimonials.
- Product Range: Assess whether they offer a diverse selection of alternators that can cater to various applications.
Step 4: Check Compliance and Certifications
Verify that potential suppliers comply with relevant industry standards and possess necessary certifications. This step protects your business from liability issues and ensures product quality.
- ISO Certifications: Confirm that the supplier is ISO-certified, indicating adherence to quality management standards.
- Local Compliance: Ensure compliance with local regulations, especially if you are sourcing from international markets.
Step 5: Request Samples and Perform Quality Testing
Before finalizing an order, request samples of the alternators for quality testing. This step allows you to evaluate the performance and durability of the product under real conditions.
- Performance Testing: Conduct tests to measure efficiency, output, and compatibility with your vehicles.
- Durability Assessment: Evaluate materials used and overall build quality to anticipate long-term performance.
Step 6: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Once you have selected a supplier, engage in negotiations regarding pricing, delivery schedules, and payment terms. Clear communication at this stage is vital to avoid misunderstandings later.
- Bulk Purchase Discounts: Inquire about discounts for larger orders.
- Delivery Guarantees: Ensure that the supplier can meet your delivery timelines to avoid operational disruptions.
Step 7: Establish a Long-term Partnership
After successful procurement, consider establishing a long-term relationship with your supplier. This can lead to better pricing, priority service, and collaboration on future projects.
Illustrative image related to what is the alternator
- Regular Communication: Maintain open lines of communication to discuss any issues or future needs.
- Feedback Mechanism: Provide feedback on product performance to help suppliers improve their offerings.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can effectively navigate the sourcing process for alternators, ensuring they procure high-quality products that meet their operational requirements.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for what is the alternator Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Alternator Sourcing?
When sourcing alternators, understanding the cost structure is crucial for B2B buyers. The primary components of cost include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margins.
-
Materials: The core materials for alternators typically include copper for windings, steel for the rotor and stator, and various plastics for housing components. Fluctuations in raw material prices can significantly affect the overall cost. Buyers should keep an eye on commodity markets to anticipate price changes.
-
Labor: Labor costs are influenced by the location of manufacturing. Regions with lower labor costs can offer more competitive pricing, but this may come at the expense of quality. Skilled labor is essential for the assembly of complex components, which can drive up costs in more developed countries.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses expenses related to factory operations, including utilities, equipment maintenance, and indirect labor. Efficient manufacturing processes can help reduce overhead costs, which is essential for maintaining competitive pricing.
-
Tooling: Tooling costs involve the initial setup of production lines and molds necessary for alternator manufacturing. These costs can be amortized over large production runs, making it beneficial for buyers to consider minimum order quantities (MOQs) to spread these costs effectively.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that alternators meet specific quality standards involves rigorous testing and inspection processes. Higher QC standards can increase costs but are vital for ensuring reliability, especially in demanding environments.
-
Logistics: Shipping and transportation costs can vary widely based on the distance from the manufacturer to the buyer. Understanding Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) is essential for determining who bears the cost and risk during transportation.
-
Margin: The profit margin for manufacturers and suppliers can vary based on market competition, brand reputation, and perceived value. Buyers should compare multiple suppliers to understand the typical margins in the market.
What Influences Pricing for Alternators?
Several factors can influence the pricing of alternators, particularly for international B2B buyers:
-
Volume/MOQ: Larger orders typically result in lower per-unit costs. Buyers should negotiate MOQs that align with their inventory needs while optimizing pricing.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom-built alternators to meet specific requirements can lead to higher costs. Buyers should assess whether standard models can suffice or if customization is necessary.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: The choice of materials and any certifications (such as ISO or SAE) can impact pricing. Higher quality and certified products often carry a premium but can lead to better performance and reliability.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can affect pricing. Established suppliers may charge more for their products but often provide better support and warranty services.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is crucial in international sourcing. They define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers concerning shipping, insurance, and tariffs, influencing the total landed cost.
How Can Buyers Negotiate Effectively for Alternators?
-
Research and Benchmarking: Buyers should conduct thorough research to understand market prices and benchmarks for alternators. This information can empower negotiations.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider not just the purchase price but the total cost of ownership, which includes maintenance, warranty, and operational costs over the product’s lifespan. A higher initial investment may yield lower TCO if the product is more reliable.
-
Volume Commitments: Offering to commit to larger volumes can provide leverage in negotiations for better pricing. Suppliers may be willing to offer discounts for guaranteed business.
-
Understanding Local Markets: Buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should be aware of local market dynamics, as these can influence both pricing and availability.
Disclaimer
The prices and cost components mentioned in this analysis are indicative and may vary based on specific circumstances, supplier agreements, and market conditions. Always consult multiple sources and suppliers to obtain accurate pricing tailored to your needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing what is the alternator With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to the Alternator: Exploring Viable Solutions
When evaluating power generation systems for vehicles, understanding the role of the alternator is crucial. However, alternative technologies and methods also exist that can fulfill similar needs, particularly in powering electrical systems and recharging batteries. This analysis will compare the traditional alternator with two notable alternatives: the DC Generator and Battery Management Systems (BMS). Each option has unique characteristics that can influence a buyer’s decision based on performance, cost, and application.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | What Is The Alternator | DC Generator | Battery Management System (BMS) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Converts mechanical energy to electrical energy; reliable for continuous use. | Generates DC power but generally less efficient than alternators for high loads. | Manages battery charging and discharging, optimizing battery life and performance. |
| Cost | Moderate initial cost; long-term value due to durability. | Generally lower initial cost but may require more frequent replacements. | Can be expensive initially; cost-effective over time through improved battery life. |
| Ease of Implementation | Easy to install in most vehicles; standard component. | Requires compatibility checks with vehicle systems; may need additional components. | Installation can be complex; requires integration with existing battery systems. |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; lasts 7-10 years under normal conditions. | Higher maintenance needs; may require regular servicing. | Minimal maintenance, but software updates may be necessary. |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for standard combustion engine vehicles with consistent electrical needs. | Suitable for smaller applications or older vehicles needing basic power generation. | Best for electric vehicles or hybrid systems where battery optimization is critical. |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
What Is The Alternator
The alternator is a vital component in combustion engine vehicles, converting mechanical energy from the engine into electrical energy. This process powers various electrical systems, such as lights and infotainment, while also recharging the vehicle’s battery. Its long lifespan and low maintenance requirements make it a dependable choice for many automotive applications.
Alternative 1: DC Generator
DC generators serve as a simpler alternative to alternators, generating direct current for smaller applications. While they are generally less efficient, they can be cost-effective for vehicles with lower power demands or older models that do not require high electrical output. However, their performance may suffer under heavy loads, leading to potential power shortages for essential systems.
Alternative 2: Battery Management Systems (BMS)
BMS technology is increasingly popular, particularly in electric and hybrid vehicles. These systems optimize battery usage, ensuring that the battery is charged efficiently and prolonging its lifespan. While the initial investment for a BMS can be higher than traditional alternators or generators, the long-term savings from improved battery health and performance can outweigh the upfront costs. However, the complexity of installation and integration may pose challenges for some users.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
When selecting between an alternator, DC generator, or Battery Management System, B2B buyers must consider their specific applications, budget constraints, and performance requirements. The alternator remains a reliable choice for conventional vehicles, while DC generators may cater to simpler or older models. For businesses focused on electric vehicles, investing in a sophisticated BMS could yield significant long-term benefits. Understanding the nuances of each option enables informed decision-making, ensuring that buyers choose the most suitable solution for their operational needs.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for what is the alternator
What Are the Key Technical Properties of an Alternator?
Understanding the essential technical properties of alternators is crucial for B2B buyers, especially those involved in automotive manufacturing, repair, and maintenance. Here are some critical specifications to consider:
1. Voltage Rating
The voltage rating of an alternator typically ranges from 12V to 24V for automotive applications. This rating indicates the electrical potential the alternator can produce. In a B2B context, selecting the correct voltage rating is vital for ensuring compatibility with vehicle electrical systems and avoiding potential damage to components.
2. Amperage Output
Amperage output refers to the current the alternator can supply, usually ranging from 40A to 200A for most vehicles. Higher amperage outputs are essential for vehicles with multiple electronic accessories. For B2B buyers, understanding amperage requirements helps in sourcing alternators that meet specific vehicle demands, ensuring operational efficiency.
3. Cooling Mechanism
Alternators are equipped with cooling fans or heat sinks to dissipate heat generated during operation. Effective cooling mechanisms are essential for maintaining performance and longevity. In B2B transactions, discussing cooling designs can help buyers ensure that the alternators can withstand the operational environment, particularly in regions with high ambient temperatures.
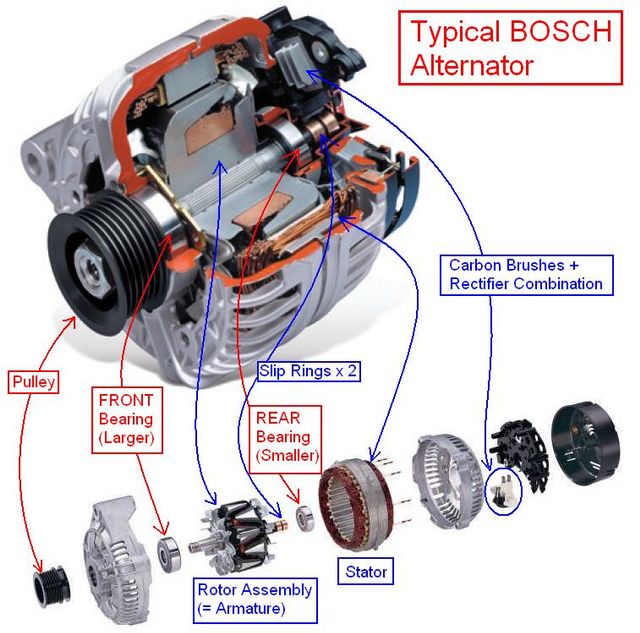
Illustrative image related to what is the alternator
4. Material Composition
Common materials used in alternator construction include aluminum for the housing and copper for the windings. The choice of materials affects durability, weight, and efficiency. For B2B purchasers, understanding material properties can influence decisions regarding cost, performance, and suitability for specific applications.
5. Regulator Type
Alternators may utilize either internal or external voltage regulators. Internal regulators are more common in modern vehicles due to their compact design and efficiency. Knowledge of regulator types helps B2B buyers determine replacement needs and compatibility with existing systems.
6. Lifespan and Warranty
Typically, alternators have a lifespan of 60,000 to 100,000 miles or approximately 7 to 10 years. Warranties often range from 1 to 3 years. B2B buyers should pay attention to warranty terms, as a longer warranty can indicate manufacturer confidence in product durability, aiding in long-term cost savings.
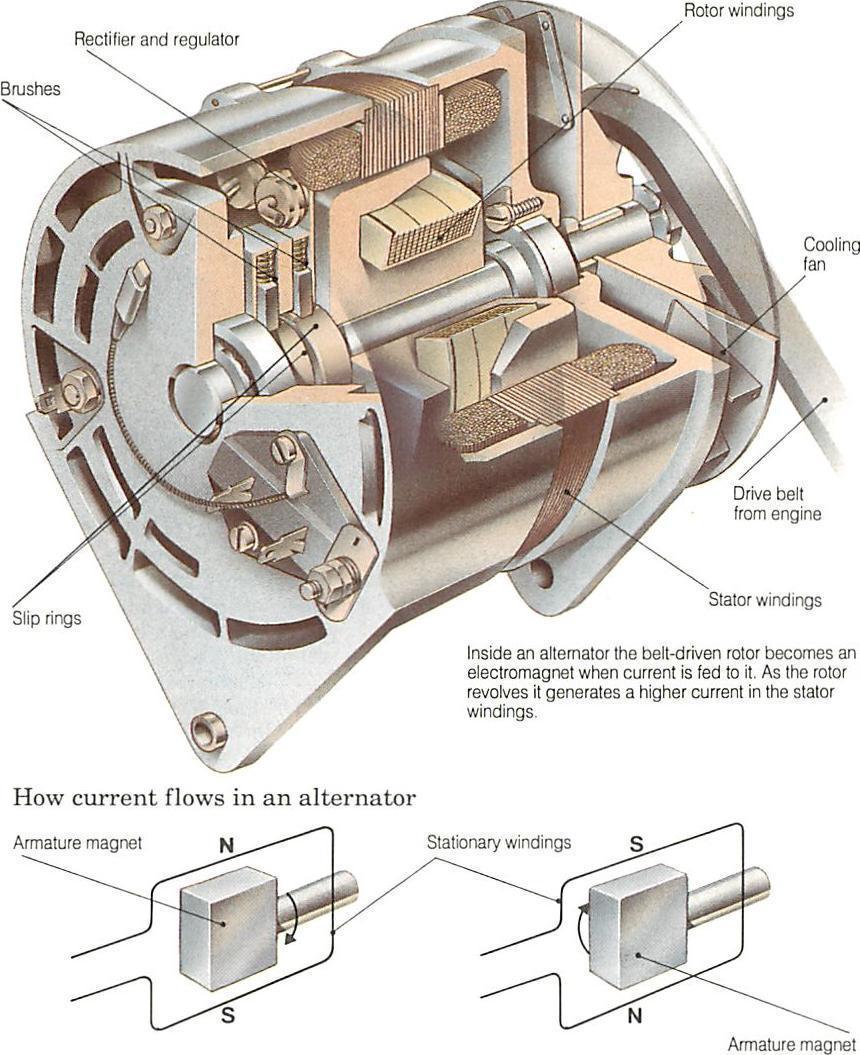
Illustrative image related to what is the alternator
What Are Common Trade Terms Associated with Alternators?
Familiarity with industry jargon is critical for effective communication and negotiation in B2B transactions. Here are several common terms related to alternators:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to components made by the original manufacturer of the vehicle. In the context of alternators, sourcing OEM parts ensures compatibility and quality. B2B buyers often prefer OEM parts for reliability and warranty purposes.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ indicates the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is crucial for B2B buyers to manage inventory levels and ensure cost-effectiveness when ordering alternators, especially for large-scale operations.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document that buyers use to solicit price quotes from suppliers. For alternators, an RFQ may include specifications such as voltage, amperage, and quantity. This process helps B2B buyers compare offers and make informed purchasing decisions.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of international rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in global trade. They cover aspects like shipping, insurance, and risk transfer. Understanding Incoterms is essential for B2B buyers engaged in international transactions involving alternators, as they dictate costs and obligations.
5. Aftermarket
The aftermarket refers to the market for parts and accessories sold after the original sale of the vehicle. For alternators, aftermarket options may provide cost-effective alternatives to OEM parts. B2B buyers should evaluate aftermarket products for quality and compatibility.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions regarding alternators, enhancing operational efficiency and reducing downtime in their businesses.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the what is the alternator Sector
What Are the Key Drivers Shaping the Global Alternator Market?
The global alternator market is witnessing significant growth, driven by the increasing demand for vehicles, particularly in emerging economies across Africa, South America, and the Middle East. As urbanization accelerates in these regions, the need for reliable transportation solutions is paramount. Additionally, the shift towards electric and hybrid vehicles is reshaping the traditional alternator market. Manufacturers are investing in advanced technologies to produce alternators that are more efficient and compatible with electric drivetrains, ensuring they meet the rising expectations of eco-conscious consumers.
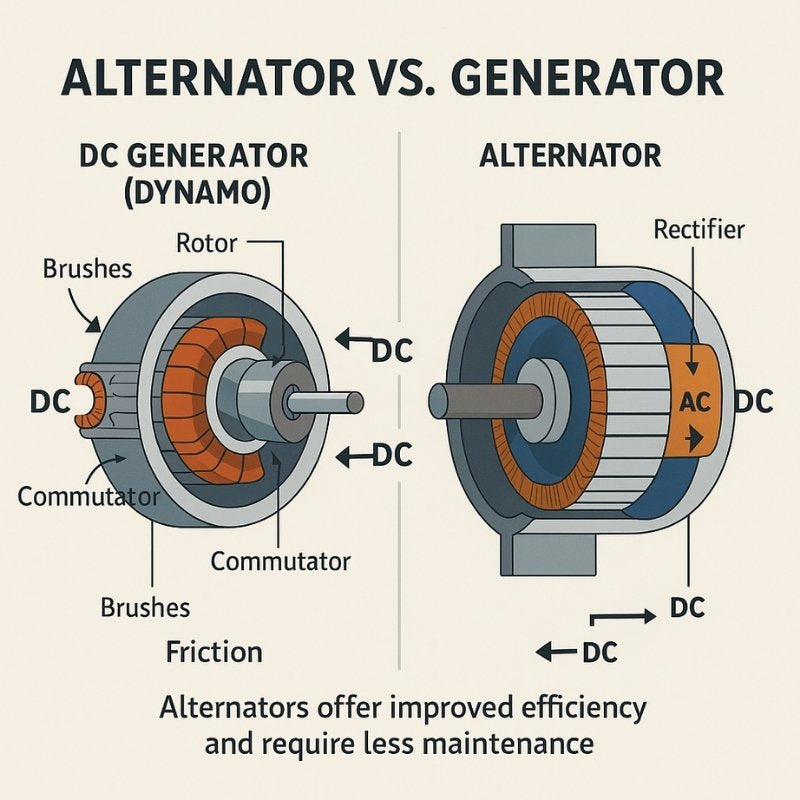
Illustrative image related to what is the alternator
In Europe, particularly in Germany, there is a strong emphasis on innovation and high-quality engineering, which drives the demand for advanced alternators. The trend towards automation and Industry 4.0 is also influencing sourcing strategies, as companies increasingly leverage IoT and AI technologies to enhance production processes and supply chain management. International B2B buyers must stay informed about these technological advancements to remain competitive.
Moreover, the rise of e-commerce platforms is transforming how businesses source alternators. Buyers can now access a wider range of suppliers globally, facilitating better price comparisons and quality assessments. This trend emphasizes the importance of robust supply chain networks and relationships with manufacturers to ensure timely delivery and reliability.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact the Alternator Supply Chain?
Sustainability is becoming a core consideration in the alternator sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes and materials used in alternators is under scrutiny. B2B buyers must prioritize suppliers that adopt sustainable practices, such as reducing carbon footprints and minimizing waste. This includes sourcing materials that are recyclable or derived from sustainable sources, thereby contributing to a circular economy.
Ethical sourcing is equally important. As consumers demand more transparency in product origins, companies that can demonstrate responsible supply chains will gain a competitive edge. Certifications like ISO 14001, which focuses on effective environmental management systems, can enhance credibility and appeal to eco-conscious clients. Additionally, incorporating ‘green’ materials, such as low-impact metals or biodegradable components, can further align product offerings with global sustainability goals.
For international buyers, particularly in regions like Saudi Arabia and Europe, understanding local regulations regarding environmental compliance is crucial. This knowledge will not only ensure adherence to legal standards but also resonate with customers who are increasingly valuing sustainability in their purchasing decisions.
What Is the Historical Evolution of the Alternator?
The alternator has evolved significantly since its inception in the early 20th century. Originally developed as a means to generate electrical power for automobiles, it has undergone numerous technological advancements. Early models were relatively simple, providing minimal power and efficiency. However, as automotive technology progressed, so did the alternator’s design and functionality.
By the 1960s, the introduction of more sophisticated electronic components allowed for improved performance and reliability. This evolution was further accelerated by the rise of electronic systems in vehicles, which increased the demand for efficient power generation. Today’s alternators are compact yet powerful, capable of meeting the diverse energy needs of modern vehicles, including advanced infotainment systems and hybrid technologies.
As B2B buyers navigate the current market, understanding this historical context can provide insights into future trends and innovations, helping them to make informed sourcing decisions that align with their business objectives.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of what is the alternator
-
How do I determine if an alternator needs replacement?
To assess if an alternator requires replacement, monitor your vehicle for common signs of failure. These include dimming dashboard lights, difficulty starting the engine, or electrical accessories that operate slowly. Additionally, if you frequently need to jump-start your battery, it may indicate that the alternator isn’t charging it effectively. Regular inspections can help identify potential issues early, and if problems persist, consult a qualified technician for a thorough evaluation. -
What is the best alternator for commercial vehicles?
The ideal alternator for commercial vehicles depends on the specific power requirements of the electrical systems in use. Look for high-output alternators that can handle increased loads from additional accessories and equipment. Brands with proven reliability, such as Bosch or Denso, are often preferred in the industry. Ensure that the alternator meets the OEM specifications for your vehicle to maintain performance and longevity. -
How can I vet suppliers for alternators in international trade?
When vetting suppliers for alternators, start by checking their certifications and compliance with international quality standards like ISO 9001. Assess their production capabilities, lead times, and history of fulfilling orders. Request references or testimonials from other B2B clients, and conduct background checks to verify their legitimacy. Engaging in direct communication can also help gauge their responsiveness and willingness to address your specific needs. -
What customization options are available for alternators?
Many manufacturers offer customization options for alternators to suit specific applications. These can include variations in output voltage, physical size, and additional features like built-in voltage regulators or cooling systems. When sourcing alternators, discuss your requirements with suppliers to explore available modifications that align with your operational needs and ensure compatibility with your vehicles. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for alternators?
Minimum order quantities for alternators can vary significantly based on the supplier and the type of alternator required. Some manufacturers may have MOQs as low as 10 units, while others, especially for specialized or high-output models, might require orders of 50 or more. Always inquire about MOQs during the initial discussions to ensure they align with your purchasing capabilities and inventory needs. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing alternators internationally?
Payment terms for international purchases of alternators can differ widely among suppliers. Common arrangements include upfront payments, letters of credit, or payment upon delivery. It’s crucial to negotiate terms that protect your interests, such as escrow services or partial payments linked to milestones in production or shipping. Clear communication about payment expectations can help build trust and streamline transactions. -
How do I ensure quality assurance (QA) for alternators?
To ensure quality assurance for alternators, request documentation of the supplier’s QA processes and inspection methods. Many reputable manufacturers will provide certificates of compliance and testing results for their products. Establish a clear QA agreement outlining acceptable standards and procedures for defect resolution. Consider conducting third-party inspections or audits, especially for large orders, to verify product quality before shipment. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing alternators?
When importing alternators, consider factors such as shipping methods, customs clearance, and local regulations. Choose a reliable freight forwarder who understands the complexities of international shipping. Be aware of potential tariffs and taxes that may apply to your shipment. Additionally, plan for adequate lead times and track your shipment closely to address any issues that may arise during transit, ensuring timely delivery to your operations.
Top 3 What Is The Alternator Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Lakeside Tire – Alternators
Domain: lakesidetire.com
Registered: 2011 (14 years)
Introduction: Alternators are a part of the vehicle’s charging system, which includes the battery, voltage regulator, and alternator itself. They generate electrical currents to power all electrical components in the car, such as headlights and dashboard lights. Located at the front of the engine, alternators are powered by the engine’s serpentine belt, using power from the crankshaft to create electrical curre…
2. Kia – Alternator Essentials
Domain: kia.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: An alternator is an integral part of every combustion engine vehicle, responsible for converting chemical energy to electrical energy to charge and replenish the battery and other electrical components in a car. It works as part of the vehicle’s charging system, which includes the car battery, voltage regulator, and alternator. The alternator converts mechanical energy to electrical energy with al…
3. Nationwide – Alternator Overview
Domain: blog.nationwide.com
Registered: 1994 (31 years)
Introduction: The alternator is a generator that produces electricity for the vehicle and recharges the battery. It is about the size of a coconut and is mounted to the front of the engine, connected via a belt. Key components include: 1. Rotor and Stator: The rotor spins inside the stator, creating electricity through the movement of magnets over copper wiring. 2. Voltage Regulator: Monitors and manages the ou…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for what is the alternator
The alternator is a critical component in modern vehicles, acting as the backbone of the electrical system by converting mechanical energy into electrical energy to charge the battery and power various systems. For B2B buyers in diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the intricacies of alternators is essential for making informed purchasing decisions.
Strategic sourcing of high-quality alternators can significantly impact operational efficiency, vehicle reliability, and overall maintenance costs. By forging partnerships with reputable suppliers and manufacturers, businesses can ensure they receive durable products that meet rigorous standards, ultimately enhancing their service offerings.
As global automotive markets continue to evolve, the demand for reliable and efficient alternators will grow. International buyers are encouraged to stay ahead of market trends and technological advancements. Investing in robust sourcing strategies not only secures quality components but also positions businesses to capitalize on emerging opportunities.
Take proactive steps today to evaluate your supply chain, and consider how strategic sourcing can bolster your operations and strengthen your market presence in the automotive industry.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.