Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for is it the alternator or the battery
In the complex world of automotive maintenance, determining whether an issue lies with the alternator or the battery can be a significant challenge for international B2B buyers. This guide, “Is it the Alternator or the Battery?”, is designed to provide clarity and actionable insights into these crucial components of your vehicle’s electrical system. Understanding the differences in function, common failure signs, and maintenance needs is essential for preventing unexpected breakdowns and costly repairs, particularly in diverse markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including regions like Saudi Arabia and Nigeria.
Throughout this comprehensive guide, we will explore the types of batteries and alternators available, their applications in various vehicle models, and the importance of supplier vetting to ensure quality. We will also delve into cost considerations, helping you make informed decisions that align with your business needs. By equipping yourself with knowledge about these vital components, you can improve your procurement strategies and reduce downtime associated with vehicle malfunctions.
This guide empowers B2B buyers to navigate the global market confidently, ensuring that you source the right products tailored to your operational requirements while enhancing overall vehicle reliability. Prepare to engage with this vital information and make purchasing decisions that will keep your fleet running smoothly.
Table Of Contents
- Top 2 Is It The Alternator Or The Battery Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for is it the alternator or the battery
- Understanding is it the alternator or the battery Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of is it the alternator or the battery
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘is it the alternator or the battery’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for is it the alternator or the battery
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for is it the alternator or the battery
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘is it the alternator or the battery’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for is it the alternator or the battery Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing is it the alternator or the battery With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for is it the alternator or the battery
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the is it the alternator or the battery Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of is it the alternator or the battery
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for is it the alternator or the battery
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Understanding is it the alternator or the battery Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lead-Acid Battery | Traditional battery type; relies on lead plates and sulfuric acid. | Automotive, heavy machinery, and backup power systems. | Pros: Cost-effective, widely available. Cons: Limited lifespan (3-5 years), sensitive to temperature. |
| Lithium-Ion Battery | Lightweight, longer lifespan, and faster charging capabilities. | Electric vehicles, renewable energy storage, and portable electronics. | Pros: High energy density, low self-discharge. Cons: Higher upfront cost, requires specialized charging systems. |
| Alternator (Standard) | Converts mechanical energy to electrical energy; typically 12V output. | Automotive applications, industrial machinery, and power generation. | Pros: Reliable power source for vehicle accessories, minimal maintenance. Cons: May fail due to wear or overloading. |
| Smart Alternator | Features advanced electronics for better energy management. | Modern vehicles and hybrid systems. | Pros: Improved fuel efficiency, optimized battery charging. Cons: More complex and expensive to replace. |
| Heavy-Duty Alternator | Designed for high-demand applications; higher output capacity. | Commercial vehicles, construction equipment, and emergency services. | Pros: Provides ample power for additional accessories. Cons: Higher cost and weight, potential compatibility issues. |
What Are the Characteristics of Lead-Acid Batteries for B2B Buyers?
Lead-acid batteries are the most common type used in automotive applications, particularly in regions with established infrastructure. They are cost-effective and widely available, making them suitable for various industries, including automotive and heavy machinery. However, their limited lifespan of 3-5 years and sensitivity to extreme temperatures necessitate regular monitoring and replacement, which can impact operational costs.
How Do Lithium-Ion Batteries Compare in Suitability for Modern Applications?
Lithium-ion batteries are gaining traction in B2B sectors due to their lightweight design and longer lifespan, often exceeding ten years. They are ideal for electric vehicles and renewable energy storage systems. While their initial investment is higher, the long-term savings from reduced maintenance and replacement costs can be significant. B2B buyers should consider the need for specialized charging systems when opting for this technology.
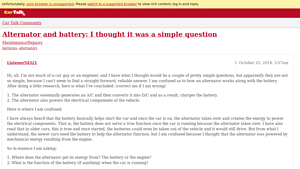
What Should B2B Buyers Know About Standard Alternators?
Standard alternators are critical in automotive and industrial applications, converting mechanical energy to electrical energy to power vehicle accessories. Their reliability and minimal maintenance requirements make them a preferred choice for many businesses. However, wear and tear can lead to failure, especially if the alternator is overloaded. Regular checks and understanding the electrical load requirements are essential for optimal performance.
Why Are Smart Alternators Beneficial for Modern Vehicles?
Smart alternators incorporate advanced electronics to enhance energy management, making them increasingly popular in modern vehicles, especially hybrids. They offer improved fuel efficiency and optimized battery charging, which can lead to lower operational costs. However, their complexity and higher replacement costs may deter some buyers. Understanding the vehicle’s electrical system and compatibility is crucial when considering this option.
What Are the Advantages of Heavy-Duty Alternators in Commercial Applications?
Heavy-duty alternators are designed to meet the high power demands of commercial vehicles and equipment. Their robust output capacity is essential for applications requiring multiple electrical accessories, such as emergency services and construction machinery. While they provide significant advantages in power supply, their higher cost and weight can be drawbacks. Buyers must assess their specific power needs against the potential for increased operational costs.
Key Industrial Applications of is it the alternator or the battery
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of is it the alternator or the battery | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive Manufacturing | Quality control in vehicle assembly lines | Ensures reliable vehicle performance and safety | Sourcing high-quality batteries and alternators from reputable manufacturers to meet safety standards |
| Transportation & Logistics | Fleet vehicle maintenance and management | Reduces downtime and maintenance costs | Establishing partnerships with local suppliers for timely parts replacement and service availability |
| Renewable Energy | Off-grid solar power systems | Provides reliable energy storage and usage | Selecting batteries that are compatible with solar inverters and ensuring availability of service for remote areas |
| Mining and Construction | Heavy machinery power systems | Enhances operational efficiency and reduces failures | Sourcing rugged alternators and batteries designed for harsh environments to ensure durability |
| Telecommunications | Backup power systems for communication networks | Ensures continuous service and reduces outages | Ensuring batteries have a long life cycle and sourcing from vendors with robust support networks |
How is ‘is it the alternator or the battery’ Used in Automotive Manufacturing?
In automotive manufacturing, the alternator and battery play a crucial role in vehicle assembly lines. Quality control processes often involve testing these components to ensure they meet performance and safety standards. A reliable battery provides the initial power needed for testing and assembly, while the alternator is vital for maintaining electrical flow during operation. Businesses benefit from sourcing high-quality components from reputable manufacturers, as this ensures the final product’s reliability and safety, ultimately leading to customer satisfaction and brand loyalty.
What Role Does it Play in Transportation & Logistics?
In the transportation and logistics sector, maintaining fleet vehicles is essential for operational efficiency. Regular checks on the battery and alternator can prevent unexpected breakdowns, which can lead to costly downtime. Companies benefit from a proactive maintenance strategy that includes timely replacement of these components, thus minimizing disruptions to service. Establishing partnerships with local suppliers ensures that parts are readily available, allowing for quick repairs and enhanced fleet reliability, especially in regions where access to services may be limited.
How is it Applied in Renewable Energy Systems?
Off-grid solar power systems rely heavily on a combination of batteries and alternators to store and manage energy. The battery stores solar energy for use during non-sunny periods, while the alternator can be used in conjunction with generators to ensure a constant power supply. Businesses in this sector must focus on sourcing batteries that are compatible with their solar inverters and capable of withstanding various environmental conditions. This ensures reliable energy storage, which is crucial for operations in remote areas, particularly in Africa and South America.
Why is it Important for Mining and Construction?
In the mining and construction industries, heavy machinery is often exposed to harsh conditions, making the reliability of alternators and batteries paramount. These components are critical for starting and operating equipment effectively. Businesses benefit from sourcing rugged, durable batteries and alternators designed specifically for tough environments, which reduces the frequency of failures and maintenance needs. This not only enhances operational efficiency but also ensures worker safety, as machinery that fails can pose serious risks on-site.
What is the Importance in Telecommunications?
In telecommunications, backup power systems are essential for maintaining continuous service. Batteries and alternators are integral to these systems, ensuring that communication networks remain operational during power outages. Businesses in this sector must prioritize sourcing high-quality batteries with a long life cycle and robust support networks to minimize service interruptions. This reliability is particularly crucial in regions with unstable power supplies, such as parts of the Middle East and Africa, where communication infrastructure is vital for economic activities and emergency services.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘is it the alternator or the battery’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: The Frustration of Inconsistent Vehicle Performance
The Problem: B2B buyers managing fleets often face the challenge of inconsistent vehicle performance, which can lead to downtime and increased operational costs. A vehicle that frequently fails to start or exhibits flickering lights can disrupt schedules and affect productivity. In regions with extreme weather conditions, the strain on both the battery and alternator can exacerbate these issues, making it hard to pinpoint the root cause. This uncertainty can lead to unnecessary repairs or replacements, straining budgets and resources.
The Solution: To address this pain point, implement a systematic maintenance schedule that includes regular checks on both batteries and alternators. Invest in diagnostic tools that can accurately assess the health of these components, allowing for early detection of potential failures. Training staff on the signs of battery and alternator issues, such as slow engine cranking or dimming lights, can empower them to take proactive measures. Additionally, sourcing high-quality batteries and alternators from reputable suppliers ensures reliability and performance, reducing the likelihood of breakdowns. Regular maintenance and swift diagnostics can significantly enhance vehicle uptime and overall fleet performance.
Scenario 2: The Challenge of Unclear Warranty and Service Options
The Problem: B2B buyers often navigate complex warranty and service agreements when it comes to vehicle components like batteries and alternators. Misunderstandings regarding warranty coverage can lead to unexpected costs if components fail prematurely. This is particularly critical for businesses operating in diverse markets, such as Africa and South America, where service infrastructure may be less accessible. The lack of clarity can result in frustration and financial strain when trying to resolve these issues.
The Solution: Establish clear communication with suppliers regarding warranty terms for batteries and alternators. Before making a purchase, inquire about the specifics of what is covered and the conditions that may void the warranty. Additionally, create a comprehensive service plan that includes regular inspections and documentation of any work done. This not only helps in keeping track of component health but also provides leverage when discussing warranty claims. Partnering with local service providers who understand the regional market can also streamline the maintenance process, ensuring that issues are addressed promptly and effectively.
Scenario 3: The Burden of High Replacement Costs
The Problem: High replacement costs for batteries and alternators can be a significant concern for B2B buyers managing vehicle fleets. Businesses may struggle with the financial implications of having to replace these components frequently, especially in harsh environments where wear and tear occur faster. This challenge is compounded by the need for reliable performance, as any vehicle downtime can lead to lost revenue and customer dissatisfaction.
The Solution: To mitigate replacement costs, adopt a preventive maintenance strategy that emphasizes regular inspections and timely replacements based on usage patterns rather than waiting for failure. Keep detailed records of battery and alternator performance, and analyze this data to identify trends that may indicate when replacements are necessary. Explore bulk purchasing agreements with suppliers to reduce costs and ensure a steady supply of high-quality components. Furthermore, consider investing in training for maintenance personnel to recognize early signs of failure, allowing for timely interventions that can extend the life of both batteries and alternators, ultimately leading to cost savings over time.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for is it the alternator or the battery
What Materials Are Commonly Used in Alternators and Batteries?
When selecting materials for alternators and batteries, it is crucial to understand the properties and performance characteristics that influence their functionality and longevity. Below, we analyze four common materials used in these components, focusing on their key properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international B2B buyers.
1. Lead-Acid (for Batteries)
Key Properties: Lead-acid batteries are composed of lead dioxide (positive plate), sponge lead (negative plate), and sulfuric acid (electrolyte). They operate effectively within a temperature range of -20°C to 50°C and can withstand high currents.
Pros & Cons: Lead-acid batteries are durable and cost-effective, making them a popular choice for automotive applications. However, they are heavy and have a limited cycle life (typically 3-5 years). Manufacturing complexity is moderate, as the production process requires stringent safety measures due to the toxic nature of lead.

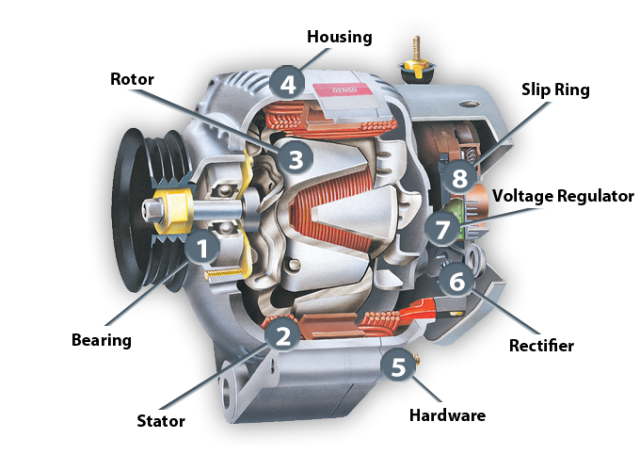
Illustrative image related to is it the alternator or the battery
Impact on Application: Lead-acid batteries are well-suited for starting engines and powering accessories. However, they are less efficient in high-temperature environments, which may lead to reduced performance in hotter regions like parts of Africa and the Middle East.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with environmental regulations regarding lead disposal is essential. Buyers should also consider local standards such as ASTM and IEC for quality assurance.
2. Lithium-Ion (for Batteries)
Key Properties: Lithium-ion batteries are lighter and have a higher energy density compared to lead-acid batteries. They operate efficiently within a temperature range of -20°C to 60°C and have a longer life cycle (up to 10 years).
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of lithium-ion batteries is their lightweight and compact design, which enhances vehicle efficiency. However, they are more expensive and require sophisticated battery management systems to ensure safety and longevity.
Impact on Application: Lithium-ion batteries are increasingly used in electric vehicles and hybrid systems due to their efficiency. Their performance can be compromised in extreme temperatures, necessitating thermal management solutions.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with international shipping regulations, as lithium-ion batteries are classified as hazardous materials. Familiarity with standards like UL and IEC is also crucial.
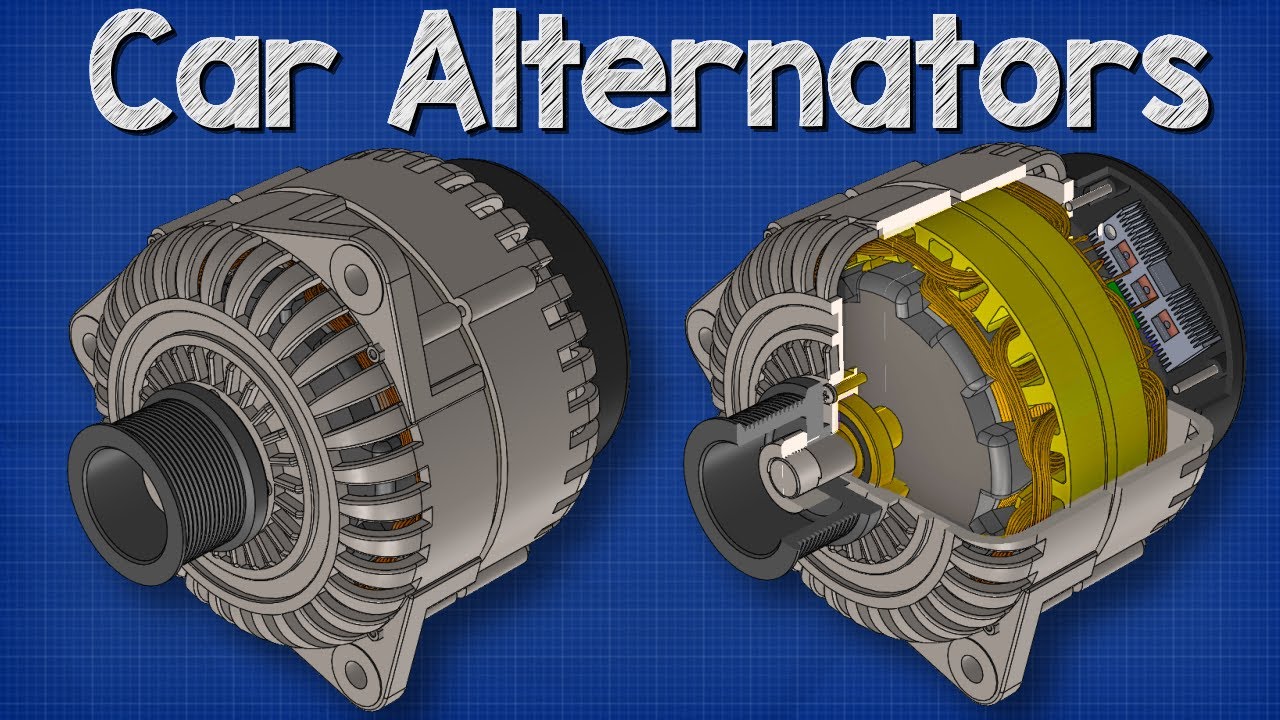
3. Aluminum (for Alternators)
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and has good thermal conductivity. It can operate effectively in a wide temperature range, making it suitable for various automotive applications.
Pros & Cons: The use of aluminum in alternators reduces weight, which can enhance fuel efficiency. However, it may not be as durable as other metals like copper or steel, leading to potential wear over time.
Illustrative image related to is it the alternator or the battery
Impact on Application: Aluminum alternators are particularly beneficial in applications where weight reduction is critical, such as in performance vehicles. However, they may not withstand high-stress conditions as effectively as heavier metals.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider the availability of aluminum and its recycling potential, especially in regions with strong environmental regulations. Compliance with standards like ISO 9001 can also be a factor in supplier selection.
4. Copper (for Alternators)
Key Properties: Copper is known for its excellent electrical conductivity and thermal properties. It operates effectively in high-temperature environments and has good corrosion resistance when treated.
Pros & Cons: Copper is a reliable choice for electrical components due to its conductivity, which enhances alternator efficiency. However, it is heavier and more expensive than aluminum, which may affect overall vehicle weight and cost.
Impact on Application: Copper is ideal for high-performance applications where electrical efficiency is paramount. Its weight may be a consideration in vehicle design, particularly for manufacturers focused on fuel economy.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the fluctuating copper prices and potential supply chain issues. Compliance with international standards such as ASTM for quality assurance is also essential.
Illustrative image related to is it the alternator or the battery
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for is it the alternator or the battery | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lead-Acid | Automotive batteries for starting and powering systems | Cost-effective and durable | Heavy and limited cycle life | Low |
| Lithium-Ion | Electric and hybrid vehicle batteries | Lightweight with high energy density | Expensive and requires management systems | High |
| Aluminum | Alternator housings and components | Reduces weight, corrosion-resistant | Less durable than other metals | Medium |
| Copper | Electrical wiring and components in alternators | Excellent conductivity | Heavier and more expensive | High |
This guide serves as a strategic resource for B2B buyers seeking to understand the material implications for alternators and batteries, enabling informed decisions that align with their operational needs and compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for is it the alternator or the battery
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Alternators and Batteries?
The manufacturing processes for alternators and batteries are intricate and involve multiple stages to ensure optimal performance and reliability. Understanding these stages can help B2B buyers make informed decisions when sourcing these critical components.
Material Preparation
The first stage in manufacturing alternators and batteries involves selecting and preparing high-quality raw materials. For batteries, this typically includes lead, sulfuric acid, and various plastics, while alternators require materials such as copper for windings, aluminum for housings, and steel for components.
- Sourcing: Suppliers must be vetted to ensure materials meet industry standards and are sourced sustainably.
- Testing: Incoming materials undergo rigorous quality checks to ensure they meet specifications. This could involve chemical analysis for batteries and dimensional checks for alternator parts.
Forming and Component Fabrication
Once materials are prepared, they undergo various forming processes to create the individual components of alternators and batteries.
- Battery Manufacturing: The lead plates are cast, and separators are fabricated. The plates are then immersed in sulfuric acid to form lead sulfate, which is crucial for battery performance.
- Alternator Manufacturing: The fabrication process involves stamping metal sheets to create the rotor and stator. Precision machining is also employed to ensure proper fit and function of components.
Assembly
Assembly is a critical stage where various components come together to form the final product.
- Battery Assembly: Involves stacking the lead plates and inserting separators before filling the cells with electrolyte. This stage often requires automated machinery to ensure consistency and quality.
- Alternator Assembly: Components such as the rotor, stator, diodes, and voltage regulators are assembled, often in a clean room environment to prevent contamination.
Finishing
The finishing stage includes testing, sealing, and packaging.
- Sealing: Batteries are sealed to prevent leakage, while alternators are often coated for corrosion resistance.
- Final Testing: This is where products undergo electrical testing to ensure they meet specifications. For batteries, this might involve checking voltage and capacity, while alternators are tested for output voltage and frequency.
What Are the Quality Control (QC) Measures for Alternators and Batteries?
Quality control is paramount in ensuring that both alternators and batteries meet international standards and customer expectations.
International Standards and Industry-Specific Certifications
Adhering to international standards is critical for manufacturers looking to establish credibility in the global market.
- ISO 9001: This quality management standard outlines the requirements for an effective quality management system, ensuring that products consistently meet customer and regulatory requirements.
- CE Marking: For products sold in Europe, CE marking indicates conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: For automotive batteries, adherence to standards set by the American Petroleum Institute (API) can be a significant differentiator in quality.
Key QC Checkpoints in the Manufacturing Process
Quality control checkpoints are strategically placed throughout the manufacturing process to catch defects early.
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specifications.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Ongoing checks during manufacturing help to monitor the production process and identify any deviations from standards.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Before products leave the facility, they undergo comprehensive testing to ensure performance metrics are met.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used for Quality Assurance?
Testing methods vary based on the component being manufactured but generally include both destructive and non-destructive tests.
- Electrical Testing: For both batteries and alternators, electrical tests are conducted to verify performance under load conditions.
- Thermal Testing: Batteries are tested for temperature stability to ensure they can function in extreme conditions.
- Mechanical Testing: This includes vibration and shock tests, especially for alternators, to ensure durability and reliability under various driving conditions.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers, particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should take proactive steps to verify the quality control processes of potential suppliers.
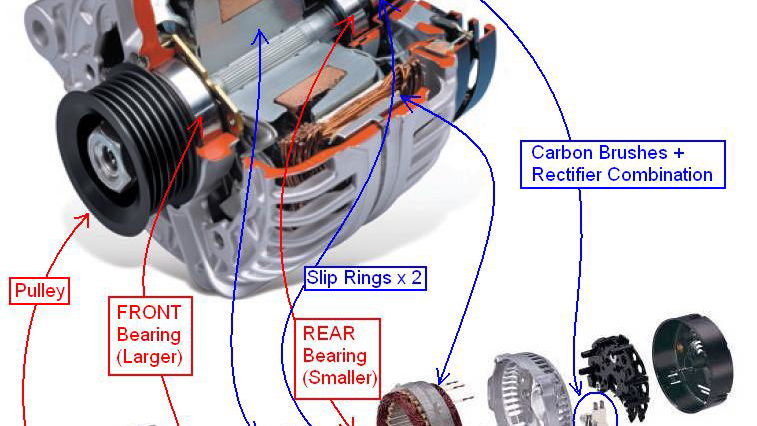
Illustrative image related to is it the alternator or the battery
Conducting Audits
Regular audits can provide insights into a supplier’s manufacturing practices and quality assurance protocols.
- On-Site Audits: Visiting the manufacturing facility allows buyers to assess production processes, quality control measures, and compliance with international standards.
- Third-Party Audits: Engaging independent auditors can provide an unbiased review of a supplier’s practices and certifications.
Requesting Quality Reports
Buyers should request detailed quality reports from suppliers, which should include:
- Test Results: Documentation of test results for batches of products to ensure they meet specifications.
- Certification Copies: Proof of certifications, such as ISO 9001 or CE marking, should be readily available for review.
What Are the Nuances of Quality Control for International B2B Buyers?
When sourcing alternators and batteries from international suppliers, there are specific nuances to consider.
Compliance with Local Regulations
Different regions may have specific regulations regarding automotive components. It’s essential for buyers to ensure that products meet these local requirements to avoid compliance issues.
Understanding Cultural and Economic Factors
Cultural attitudes towards quality and manufacturing practices can vary significantly between regions. Buyers should be aware of these differences and adapt their quality assurance processes accordingly.
Illustrative image related to is it the alternator or the battery
Building Relationships with Suppliers
Establishing strong relationships with suppliers can facilitate better communication regarding quality control measures and lead to more favorable terms. Regular engagement can also help in addressing any quality issues proactively.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for alternators and batteries, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that not only meet their operational needs but also align with international standards and best practices. This insight is crucial in navigating the complexities of global sourcing, especially in diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘is it the alternator or the battery’
Introduction
When faced with vehicle issues, particularly concerning whether the problem lies with the alternator or the battery, a systematic approach to sourcing the right components is essential. This guide outlines a practical checklist for B2B buyers, enabling you to make informed decisions when procuring these critical automotive parts. Understanding the differences between the two components and knowing how to identify reliable suppliers can significantly reduce downtime and maintenance costs.
Step 1: Identify Your Vehicle Specifications
Understanding the specific requirements of your vehicles is the first step in the procurement process. Different models and makes have unique battery and alternator specifications, including size, voltage, and amperage ratings. Ensure you gather the necessary information from vehicle manuals or manufacturer databases to avoid mismatches that could lead to performance issues.
Step 2: Assess Your Needs Based on Usage
Consider how the vehicles are used within your operations. For instance, vehicles frequently engaged in short trips may require batteries with higher cold cranking amps, while those operating in extreme temperatures may need specialized alternators. By aligning your procurement strategy with operational needs, you can enhance performance and longevity.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a supplier, it’s crucial to conduct thorough evaluations. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in a similar industry or region. Look for suppliers that demonstrate a solid track record in delivering quality alternators and batteries, as this can significantly impact your operational reliability.
Step 4: Verify Certifications and Compliance
Ensure that the suppliers you are considering have the necessary certifications and comply with local and international automotive standards. Certifications such as ISO and adherence to specific safety regulations are indicators of quality. This step is vital to ensure that the parts you procure will meet performance expectations and regulatory requirements.
Step 5: Request Product Samples
Before finalizing your order, request samples of the batteries and alternators. This allows you to assess the quality and compatibility of the components firsthand. Testing samples in your operational environment can prevent costly errors and ensure that the products meet your performance standards.
Step 6: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Once you have identified potential suppliers, it’s time to negotiate terms and conditions, including pricing, warranty, and delivery schedules. A clear understanding of these aspects can prevent disputes later and ensure a smooth procurement process. Focus on establishing a mutually beneficial relationship that can lead to long-term partnerships.
Step 7: Establish a Maintenance Plan
After procurement, implement a maintenance plan for the batteries and alternators. Regular inspections can help identify early signs of wear and tear, allowing for timely replacements and repairs. By staying proactive, you can minimize unexpected breakdowns and maximize the lifespan of your components.
Illustrative image related to is it the alternator or the battery
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing alternators and batteries effectively, ensuring operational efficiency and vehicle reliability.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for is it the alternator or the battery Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Alternators and Batteries?
When evaluating the cost structure for sourcing alternators and batteries, several key components come into play. The primary cost elements include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and margins.
-
Materials: The choice of materials directly impacts the cost of both batteries and alternators. For batteries, lead-acid, lithium-ion, and other advanced materials vary significantly in price. Alternators typically require high-grade metals and electronic components, which can be affected by global market fluctuations.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region. In countries with higher wage standards, such as those in Europe, labor will constitute a larger portion of the overall cost. Conversely, labor-intensive manufacturing in regions like South America or Africa may reduce costs but could introduce variability in quality.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with the production process, such as utilities, equipment depreciation, and facility maintenance. Efficient manufacturing processes can help mitigate overhead costs.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in tooling for battery and alternator production can be significant. Custom tooling for unique specifications or high-volume orders can further increase costs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring compliance with international quality standards is crucial, especially for B2B suppliers. The costs associated with QC processes must be factored into the pricing structure.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can vary dramatically based on the shipping method, distance, and geopolitical factors. International buyers must consider customs duties and taxes as part of their logistics costs.
-
Margin: The supplier’s profit margin will vary based on market conditions and competition. Typically, margins for automotive components range from 10% to 30%.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Sourcing Decisions?
Several factors influence pricing when sourcing alternators and batteries:
-
Volume/MOQ: Minimum order quantities (MOQs) can significantly affect pricing. Bulk purchases often lead to discounted rates, making it essential for buyers to negotiate favorable terms based on their projected needs.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom specifications can lead to increased costs due to the need for specialized materials or manufacturing processes. Buyers must weigh the benefits of customization against the potential for higher expenses.
-
Materials: The choice of materials not only affects the initial cost but also the long-term performance and durability of the product. Investing in higher-quality materials may reduce the total cost of ownership by extending the lifespan of the component.
-
Quality Certifications: Products that meet international quality certifications may command higher prices, but they also offer assurance of reliability and performance, which can be critical in automotive applications.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium for their products due to perceived reliability, while new entrants may offer lower prices to gain market share.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is crucial for international buyers. These terms dictate the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs, which can significantly affect the overall cost.
What Are Some Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficiency in Sourcing?
For B2B buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, several strategies can enhance cost-efficiency in sourcing alternators and batteries:
-
Negotiation: Buyers should leverage their purchasing power to negotiate better terms, especially for large orders. Establishing long-term relationships with suppliers can also yield favorable pricing.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Buyers should evaluate not only the initial purchase price but also the TCO, which includes maintenance, operational efficiency, and potential downtime costs. A slightly higher upfront cost may be justified by lower long-term expenses.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Currency fluctuations, import/export duties, and local market conditions can affect pricing. Buyers should stay informed about these factors to make timely purchasing decisions.
-
Market Research: Conducting thorough market research can provide insights into the best suppliers and pricing strategies. Engaging with industry networks and attending trade shows can also uncover valuable opportunities.
Disclaimer on Pricing
Prices for alternators and batteries can fluctuate due to various market conditions, including supply chain disruptions, material costs, and geopolitical factors. Buyers are advised to conduct their own market analysis and consult with multiple suppliers to obtain the most accurate and competitive pricing.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing is it the alternator or the battery With Other Solutions
Introduction: Exploring Alternatives to Diagnosing Electrical Issues
When faced with vehicle performance issues, particularly starting problems, determining whether the culprit is the alternator or the battery is crucial. However, there are alternative solutions and methods that can assist in diagnosing and resolving these electrical system challenges. This analysis will compare the traditional approach of diagnosing electrical issues—identifying whether it is the alternator or the battery—against other viable methods and technologies.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Is It The Alternator Or The Battery | Battery Load Tester | Multimeter Testing |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Provides clear identification of the faulty component | Effective in assessing battery health | Accurate for diagnosing both battery and alternator issues |
| Cost | Moderate cost for diagnostics, possibly higher if replacement is needed | Low-cost tool, typically under $50 | Moderate cost, generally $20-$100 |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires basic knowledge of vehicle systems | Simple to use, requires minimal training | Requires some technical knowledge to operate accurately |
| Maintenance | Regular checks recommended to prevent failure | Low maintenance; occasional calibration needed | Requires careful handling and storage |
| Best Use Case | Best for straightforward battery or alternator issues | Ideal for testing battery capacity and charge | Best for comprehensive electrical diagnostics in complex scenarios |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Battery Load Tester
A battery load tester is a straightforward device used to assess the health of a battery under load conditions. Its primary advantage is its affordability and ease of use, making it accessible for many businesses. However, while it effectively determines whether a battery can hold a charge, it does not provide insights into alternator functionality. Thus, while it’s a valuable tool for battery assessments, it lacks the comprehensive diagnostic capability needed for complete electrical system evaluations.
Multimeter Testing
Using a multimeter offers a versatile approach to diagnosing both battery and alternator issues. This device measures voltage, current, and resistance, allowing for a thorough analysis of the vehicle’s electrical system. The primary advantage of a multimeter is its ability to diagnose a wider range of electrical problems beyond just battery or alternator issues. However, it requires a certain level of technical knowledge to interpret the results accurately, which may be a barrier for some users. Additionally, while multimeters are generally affordable, the investment can be higher than simpler testing tools.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
For B2B buyers, selecting the appropriate diagnostic method hinges on their specific requirements and operational context. If the goal is to quickly identify battery issues, a battery load tester is a cost-effective and easy-to-use solution. Conversely, for those needing a comprehensive analysis of both the battery and alternator, investing in a multimeter may provide the best long-term value. Ultimately, understanding the unique demands of your fleet or service operations will guide you in choosing the right diagnostic approach, ensuring efficient and effective vehicle maintenance.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for is it the alternator or the battery
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Car Batteries and Alternators?
When evaluating whether the issue with a vehicle lies with the alternator or the battery, it is essential to understand specific technical properties that influence performance, longevity, and reliability. Here are critical specifications to consider:
-
Voltage Rating
The standard voltage rating for automotive batteries is 12 volts, while alternators typically produce between 13.5 to 14.5 volts while the engine runs. Understanding these voltage parameters is crucial for B2B buyers to ensure compatibility with vehicle specifications and to avoid potential electrical failures. An alternator must provide sufficient voltage to recharge the battery while powering the vehicle’s electrical systems. -
Cold Cranking Amps (CCA)
This specification measures a battery’s ability to start an engine in cold temperatures. A higher CCA rating indicates better performance in low temperatures, which is vital for regions with extreme weather conditions. B2B buyers should consider CCA ratings when sourcing batteries for different climates, ensuring that the products meet the demands of their local markets. -
Reserve Capacity (RC)
Reserve capacity indicates how long a battery can power the vehicle’s electrical systems without the alternator. Measured in minutes, this specification is essential for evaluating battery performance during emergencies or when the alternator fails. Understanding RC helps businesses choose batteries that provide reliability and safety for their customers. -
Durability and Cycle Life
The cycle life of a battery refers to the number of complete charge and discharge cycles it can undergo before its capacity significantly degrades. For alternators, durability is often indicated by their ability to handle electrical loads without overheating. These properties are particularly important for B2B buyers focused on long-term performance and lower replacement costs. -
Material Composition
The materials used in battery construction, such as lead-acid or lithium-ion, impact performance, weight, and environmental considerations. Alternators often use copper windings and durable casings to ensure effective power generation. Buyers need to be aware of the material properties to comply with local regulations and sustainability standards.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Alternators and Batteries?
Familiarity with industry jargon is crucial for B2B transactions, ensuring clear communication between suppliers and buyers. Here are some common terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
This term refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. For alternators and batteries, OEM parts are preferred by many businesses because they guarantee compatibility and performance standards set by vehicle manufacturers. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is vital for B2B buyers to manage inventory effectively and to negotiate better terms with suppliers, especially for bulk purchases of batteries and alternators. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and details for specific products. For businesses sourcing alternators or batteries, an RFQ can help streamline the procurement process, ensuring competitive pricing and timely delivery. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
These are international rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers for the delivery of goods. Understanding Incoterms is essential for B2B buyers engaged in international trade, as they clarify shipping responsibilities, risk management, and cost allocation. -
Aftermarket Parts
This term refers to parts made by companies other than the original manufacturer. While often less expensive, aftermarket alternators and batteries can vary significantly in quality and performance. B2B buyers must evaluate the reliability of aftermarket options to ensure customer satisfaction.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, businesses can make informed decisions when sourcing batteries and alternators, ultimately enhancing their operational efficiency and customer satisfaction.
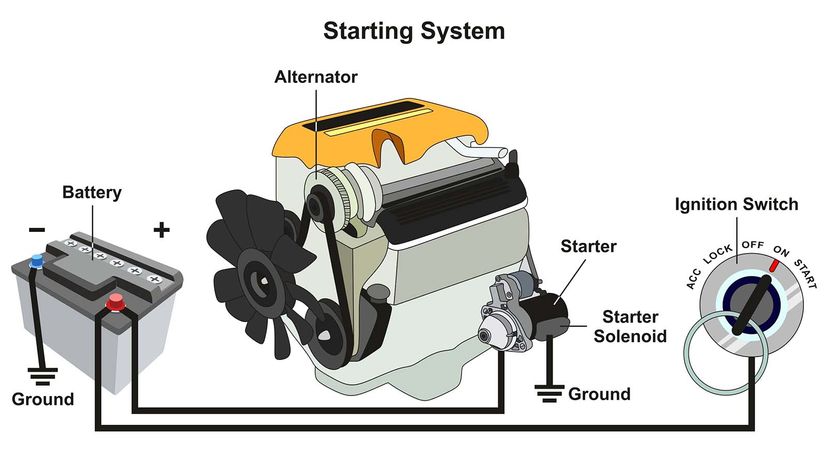
Illustrative image related to is it the alternator or the battery
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the is it the alternator or the battery Sector
What Are the Key Market Drivers Influencing the Battery and Alternator Sector?
The battery and alternator sector is witnessing significant transformation driven by the increasing demand for electric vehicles (EVs) and hybrid models. As countries across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe push for cleaner energy solutions, the reliance on advanced battery technologies has escalated. The global shift towards sustainable transportation and energy storage solutions is a primary driver, encouraging manufacturers to innovate and improve battery performance and longevity. Furthermore, technological advancements, such as smart batteries and integrated energy systems, are reshaping the landscape, offering enhanced capabilities for both consumers and businesses.
Emerging sourcing trends are heavily influenced by the increasing adoption of e-commerce and digital platforms for procurement. B2B buyers are now leveraging online marketplaces to source batteries and alternators efficiently, ensuring competitive pricing and availability. Additionally, the rise of automation in manufacturing processes is enhancing production efficiency, leading to reduced lead times and improved quality control. International buyers should also be aware of the geopolitical factors affecting supply chains, such as trade tariffs and regulations, which can impact sourcing strategies and costs.
How Is Sustainability Shaping Sourcing Decisions in the Battery and Alternator Industry?
Sustainability has become a cornerstone of sourcing strategies in the battery and alternator industry. The environmental impact of battery production, particularly concerning lithium extraction and chemical waste, has prompted companies to seek more sustainable practices. Ethical sourcing of materials, such as lithium, cobalt, and nickel, is increasingly important as businesses strive to minimize their carbon footprint and ensure responsible supply chains.
International B2B buyers are now prioritizing suppliers that demonstrate commitment to sustainability through certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and adherence to the Responsible Minerals Initiative. The demand for recycled materials and eco-friendly manufacturing processes is also on the rise, with companies seeking to reduce reliance on virgin materials. By aligning with suppliers that focus on green practices, businesses can not only fulfill regulatory requirements but also enhance their brand reputation and appeal to environmentally conscious consumers.
How Has the Battery and Alternator Sector Evolved Over Time?
The evolution of the battery and alternator sector has been marked by significant technological advancements and changing consumer needs. Initially dominated by lead-acid batteries, the market has shifted towards lithium-ion technologies, which offer higher energy density and longer life spans. The introduction of smart batteries, equipped with monitoring systems to track performance and health, has further transformed the industry, providing users with real-time data for better maintenance.
Similarly, alternator designs have evolved to become more efficient, with advancements in materials and engineering that enhance durability and performance. This evolution has been driven by the increasing complexity of vehicle electrical systems and the need for reliable power sources to support a growing array of electronic features in modern vehicles. As the sector continues to innovate, international B2B buyers must stay informed of these trends to effectively navigate the market and make strategic sourcing decisions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of is it the alternator or the battery
-
How do I determine if my vehicle issue is related to the battery or the alternator?
To accurately diagnose whether the problem lies with the battery or the alternator, start by observing the symptoms. A weak battery often results in slow engine cranking, dim lights, or the need for frequent jump starts. In contrast, a failing alternator may cause flickering lights, malfunctioning electrical accessories, or stalling. Conduct a voltage test on the battery; if it shows low voltage even after a recharge, the battery may be at fault. Conversely, if the battery is charged and issues persist, the alternator is likely the culprit. -
What are the common signs of a failing alternator?
Common signs of a failing alternator include flickering headlights, dim dashboard lights, and malfunctioning electrical components such as the radio or power windows. Additionally, if the battery warning light on the dashboard illuminates, it signals potential alternator issues. Unusual noises like grinding or whining, as well as burning smells, can indicate internal damage. Monitoring these signs can help prevent unexpected vehicle failures and costly repairs. -
What are the best practices for sourcing batteries and alternators for international trade?
When sourcing batteries and alternators for international trade, prioritize suppliers with a proven track record of quality and reliability. Request samples and certifications to ensure products meet international standards. Establish clear communication regarding specifications, warranties, and after-sales support. Additionally, consider suppliers who offer competitive pricing without compromising quality and are experienced in exporting to your target market, ensuring compliance with local regulations. -
How can I vet suppliers for batteries and alternators effectively?
To vet suppliers, start by researching their reputation and customer reviews. Look for industry certifications, such as ISO, which indicate adherence to quality standards. Request references from previous clients and verify their experience with international shipping. Conduct on-site visits if feasible, or utilize third-party inspection services to evaluate product quality. Lastly, assess their responsiveness and willingness to customize products to meet your specific requirements. -
What customization options should I consider when sourcing batteries and alternators?
Customization options can vary widely among suppliers, but you should consider specifications such as voltage, capacity, size, and terminal configuration. Additionally, inquire about branding opportunities, including labeling and packaging that align with your business identity. Discuss your specific application needs, such as temperature resistance or enhanced durability for extreme conditions. Working closely with suppliers on customization can lead to products that better suit your target market. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for batteries and alternators?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for batteries and alternators can vary significantly based on the supplier and product type. Generally, MOQs may range from 50 to several hundred units. It’s essential to discuss your needs with potential suppliers, as some may be flexible with MOQs, especially for new clients or bulk orders. Understanding the MOQ can help you manage inventory and cash flow effectively while ensuring you meet market demand. -
What payment terms are common when purchasing batteries and alternators internationally?
Common payment terms for international purchases of batteries and alternators include options like advance payment, letter of credit, and net 30 or 60 days after shipment. The choice of payment method often depends on the buyer’s relationship with the supplier and the perceived risk level. Establishing favorable payment terms can enhance cash flow management and minimize financial risks. Always ensure that payment terms are clearly outlined in the purchase agreement to avoid misunderstandings. -
How can I ensure quality assurance (QA) when sourcing batteries and alternators?
To ensure quality assurance (QA) when sourcing batteries and alternators, establish a comprehensive quality control plan that includes product testing and inspection protocols. Request detailed specifications and quality certifications from suppliers. Implement regular audits of the manufacturing process and consider third-party inspections to verify product quality before shipment. By prioritizing QA, you can reduce the risk of defects and ensure that the products meet the required standards for performance and safety.
Top 2 Is It The Alternator Or The Battery Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Nissan Altima – Power Diagnosis Guide
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: The discussion revolves around diagnosing issues related to a 2009 Nissan Altima that has no power. Key components mentioned are the battery, alternator, and starter. The battery provides power to the vehicle’s electronics and the starter, while the alternator charges the battery when the engine is running. A dead battery is suspected, possibly due to a bad alternator not charging it properly. Sig…
2. CarTalk – Alternator & Battery Essentials
Domain: community.cartalk.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: This company, CarTalk – Alternator & Battery Essentials, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for is it the alternator or the battery
In navigating the complexities of vehicle maintenance, understanding whether the issue lies with the battery or the alternator is crucial for optimizing operational efficiency and minimizing downtime. Both components play vital roles in the vehicle’s electrical system, and recognizing the signs of failure can prevent costly repairs and unexpected breakdowns. Strategic sourcing of quality parts and reliable service providers is essential for international B2B buyers, especially in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where supply chain dynamics may vary.
Investing in regular maintenance and quality components not only ensures vehicle reliability but also enhances overall productivity. Buyers should prioritize suppliers who offer comprehensive diagnostics and maintenance solutions tailored to their specific needs. This proactive approach will lead to smoother operations and a more sustainable business model.
As we look to the future, it’s imperative for B2B buyers to stay informed about the latest advancements in automotive technology and sourcing strategies. By partnering with trusted suppliers and maintaining a focus on quality, businesses can navigate challenges effectively and drive long-term success. Engage with your suppliers today to ensure your fleet is equipped for tomorrow’s demands.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.