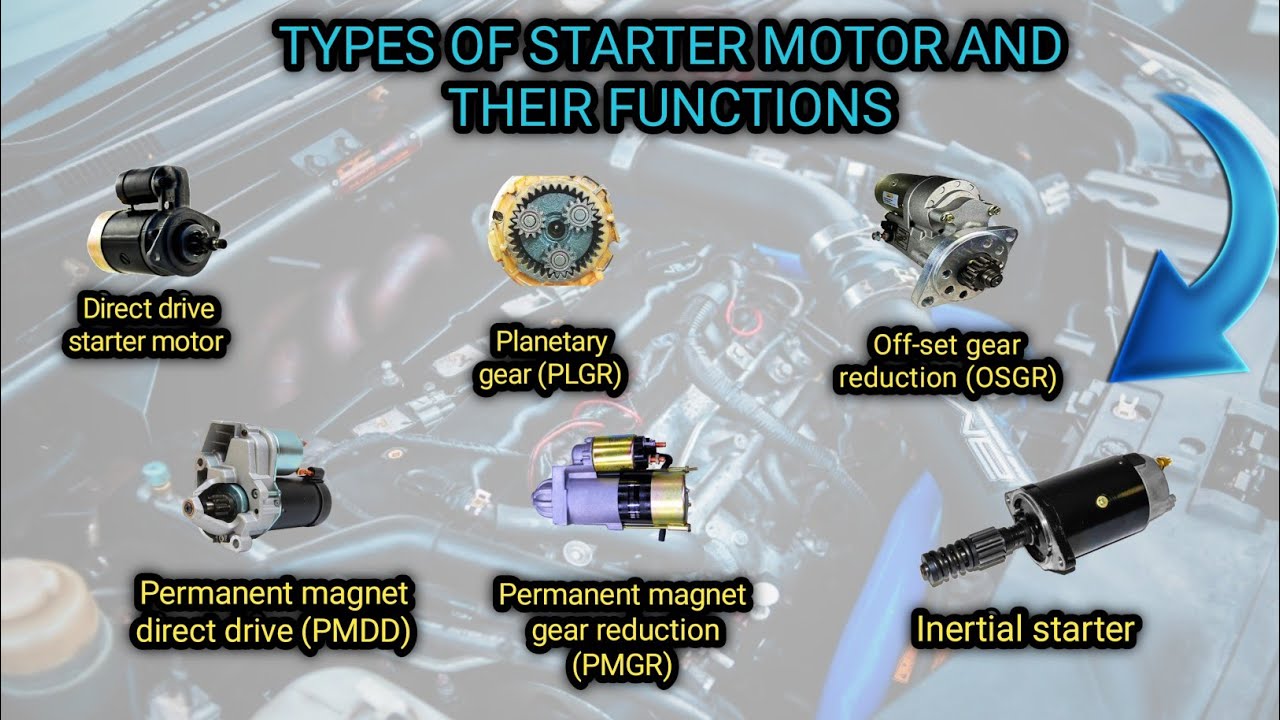
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for types of starter motor
The global market for types of starter motors presents a complex landscape for B2B buyers, particularly when navigating the myriad options available. One of the key challenges companies face is sourcing the right starter motor that not only meets technical specifications but also aligns with operational needs and budget constraints. This guide aims to clarify the various types of starter motors, including their applications, benefits, and performance characteristics, enabling buyers to make informed decisions.
In this comprehensive resource, we delve into the different categories of starter motors—such as Direct On-Line, Soft Starters, and Variable Frequency Drives—providing insights into their functionality and suitability for specific industrial applications. Additionally, we address critical factors for supplier vetting, helping you identify reliable partners across regions, including Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, with a focus on markets like Saudi Arabia and Germany.
By understanding the nuances of each type of starter motor and the associated costs, you will be better equipped to streamline your procurement process. This guide empowers international B2B buyers to navigate the complexities of the starter motor market effectively, ensuring that you select solutions that enhance operational efficiency and safeguard your investments.
Table Of Contents
- Top 2 Types Of Starter Motor Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for types of starter motor
- Understanding types of starter motor Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of types of starter motor
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘types of starter motor’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for types of starter motor
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for types of starter motor
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘types of starter motor’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for types of starter motor Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing types of starter motor With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for types of starter motor
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the types of starter motor Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of types of starter motor
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for types of starter motor
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
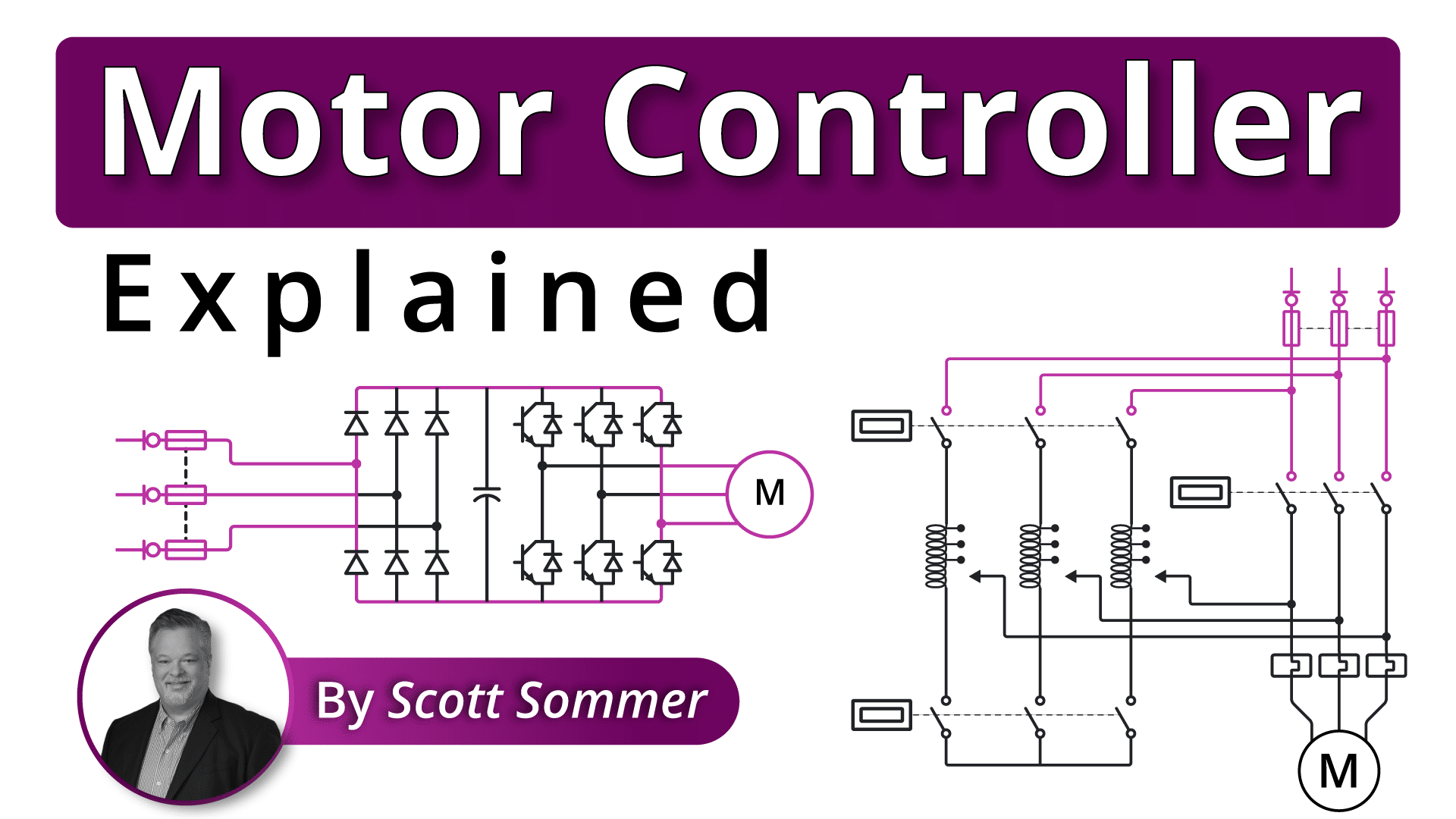
Understanding types of starter motor Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Direct On-Line (DOL) Starter | Connects motor directly to power supply; simple operation. | Small to medium industrial motors. | Pros: Simple, cost-effective. Cons: High inrush current can damage larger motors. |
| Star-Delta Starter | Reduces starting current by switching from star to delta. | Large motors in manufacturing. | Pros: Reduces starting torque and current. Cons: More complex installation. |
| Soft Starter | Gradually increases voltage for smooth acceleration. | HVAC systems, conveyors. | Pros: Extends motor life, reduces mechanical stress. Cons: Higher initial cost. |
| Variable Frequency Drive (VFD) | Controls motor speed by varying frequency of power supply. | Pumps, fans, and compressors. | Pros: Energy-efficient, precise speed control. Cons: Requires advanced setup and programming. |
| Reduced Voltage Starter | Lowers initial voltage to control inrush current. | High-power motors in heavy industries. | Pros: Protects against voltage spikes. Cons: May not be suitable for all applications. |
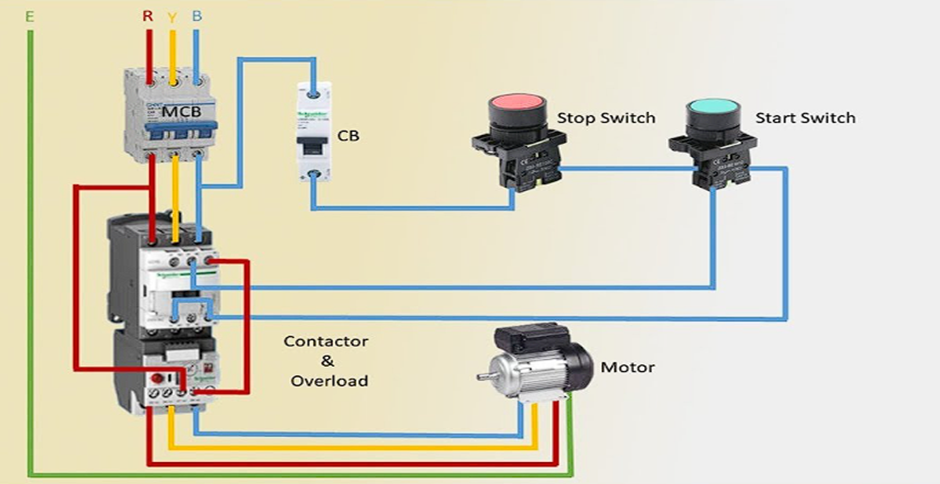
What are the Characteristics and Suitability of Direct On-Line (DOL) Starters for B2B Buyers?
The Direct On-Line (DOL) starter is one of the simplest types of motor starters, connecting the motor directly to the power supply. It is primarily suited for small to medium industrial motors, typically not exceeding five horsepower. DOL starters are favored for their straightforward operation, requiring minimal components, making them a cost-effective choice. However, buyers should consider the risk of high inrush currents, which can be damaging for larger motors or sensitive equipment.
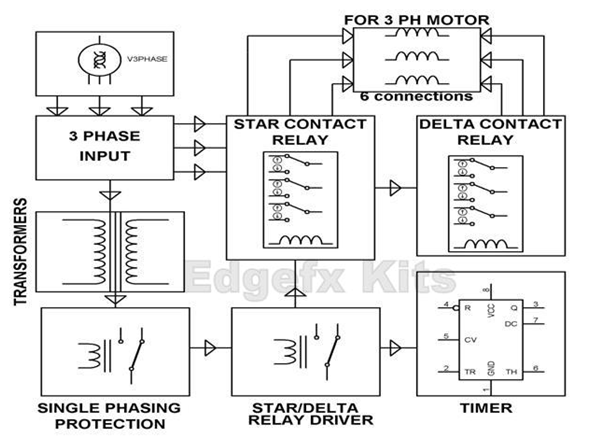
How Does the Star-Delta Starter Benefit Large Motor Applications?
Star-Delta starters are designed to manage large motors by initially connecting in a star configuration, which reduces the starting current. After the motor reaches a certain speed, it switches to a delta configuration for normal operation. This type of starter is ideal for manufacturing applications where large motors are common. While it effectively minimizes starting torque and current, the complexity of installation and maintenance may deter some buyers who prefer simpler systems.
Why Choose a Soft Starter for HVAC Systems and Conveyors?
Soft starters are engineered to provide a gradual increase in voltage, allowing for smooth acceleration of the motor. This feature is particularly beneficial in HVAC systems and conveyor applications, where sudden starts can lead to mechanical stress and premature failure. The extended motor lifespan and reduced energy consumption make soft starters appealing, although the higher initial cost may be a consideration for budget-conscious buyers.
What Advantages Does a Variable Frequency Drive (VFD) Offer for Motor Speed Control?
Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs) are advanced motor starters that adjust the frequency of the power supply to control motor speed and torque precisely. They are commonly used in applications such as pumps, fans, and compressors, where energy efficiency is critical. While VFDs offer significant advantages in terms of energy savings and performance, they do require more complex setup and programming, which may necessitate specialized training or support.
How Do Reduced Voltage Starters Protect High-Power Motors?
Reduced Voltage Starters are designed to lower the initial voltage supplied to a motor, effectively controlling inrush current and protecting against voltage spikes. This makes them particularly suitable for high-power motors used in heavy industries such as mining and manufacturing. While they provide essential protection, buyers should evaluate whether the reduced voltage approach aligns with their specific operational needs, as it may not be suitable for all motor types.
Key Industrial Applications of types of starter motor
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of types of starter motor | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Full Voltage or Across-the-Line Starter for conveyor belts | Ensures reliable operation of heavy machinery, reducing downtime | Compatibility with existing systems and operational voltage |
| Oil & Gas | Soft Starters for pump systems | Reduces mechanical stress and extends equipment lifespan | Environmental ratings and adaptability to harsh conditions |
| Agriculture | Reduced Voltage Starters for irrigation systems | Minimizes energy consumption and protects motors from damage | Efficiency ratings and ease of maintenance |
| Mining | Variable Frequency Drives (VFD) for drills | Provides precise control over motor speed, enhancing productivity | Robustness in extreme conditions and support for multiple motor types |
| Construction | Direct Online (DOL) Starters for cranes | Facilitates immediate motor engagement, crucial for lifting operations | Safety certifications and local regulatory compliance |
How Are Types of Starter Motors Applied in Manufacturing?
In the manufacturing sector, Full Voltage or Across-the-Line Starters are commonly utilized for conveyor belts and heavy machinery. These starters provide a direct connection to the power supply, ensuring reliable operation and minimal downtime. This is particularly critical in environments where continuous operation is necessary for productivity. B2B buyers should consider compatibility with existing systems and the operational voltage to ensure seamless integration.
What Role Do Soft Starters Play in the Oil & Gas Industry?
Soft Starters are essential in the oil and gas sector, particularly for pump systems. They help to gradually ramp up motor voltage, reducing mechanical stress and prolonging the life of the equipment. This is vital in an industry where equipment failure can lead to significant operational disruptions and financial losses. Buyers must focus on sourcing products with appropriate environmental ratings, ensuring they can withstand harsh conditions prevalent in oil and gas operations.
Why Are Reduced Voltage Starters Important for Agriculture?
In agriculture, Reduced Voltage Starters are employed in irrigation systems to minimize energy consumption and protect motors from damaging inrush currents. This is crucial for optimizing operational costs and ensuring the longevity of equipment used in critical farming activities. Buyers should prioritize efficiency ratings and ease of maintenance when sourcing these starters, as they directly impact the operational effectiveness of agricultural machinery.
How Do Variable Frequency Drives Benefit the Mining Sector?
Variable Frequency Drives (VFD) are integral to the mining industry, particularly for drilling operations. They offer precise control over motor speed, which enhances productivity and operational efficiency. The ability to adjust speed according to specific tasks is critical in mining environments where conditions can change rapidly. Buyers need to consider the robustness of these drives, ensuring they can withstand extreme conditions and support multiple motor types.
What Advantages Do Direct Online Starters Provide in Construction?
Direct Online (DOL) Starters are commonly used in construction for cranes and other lifting equipment. They enable immediate motor engagement, which is crucial for operational efficiency in construction projects. The quick start-up time can significantly reduce delays in construction timelines. B2B buyers should ensure that the starters meet safety certifications and comply with local regulatory standards to guarantee safe operation in construction environments.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘types of starter motor’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Overwhelmed by Starter Motor Choices
The Problem: Many B2B buyers find themselves overwhelmed by the vast array of starter motors available on the market. This confusion is particularly acute for those in regions like Africa and South America, where access to technical support may be limited. Buyers often struggle to understand the differences between types, such as Direct-On-Line (DOL), Soft Starters, and Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs). Without a clear understanding of the applications and benefits of each type, they risk selecting a starter motor that is either over-engineered or insufficient for their specific needs, leading to inefficiencies and potential equipment failure.
The Solution: To navigate this complexity, buyers should conduct a thorough needs assessment based on their specific application requirements. This includes evaluating the motor’s power ratings, starting torque, and operational environment. Engaging with reputable suppliers who can provide detailed specifications and case studies relevant to similar industries can also be beneficial. Furthermore, utilizing online tools and calculators that help in determining the appropriate starter type based on motor specifications and application needs can streamline the selection process. Regular training sessions or workshops hosted by manufacturers can also enhance understanding and confidence in the decision-making process.
Scenario 2: Unforeseen Damage from Inrush Current
The Problem: A common issue faced by B2B buyers is the potential for equipment damage caused by inrush current during motor startup. This is particularly concerning in industrial settings where heavy machinery is involved, as the initial surge can lead to overheating and premature equipment failure. Buyers in regions with unstable power supply, such as parts of the Middle East, may experience exacerbated issues if they do not adequately account for inrush current when selecting a starter motor.
The Solution: To mitigate this risk, buyers should opt for motor starters specifically designed to handle inrush current effectively. Reduced Voltage Starters or Soft Starters are excellent options that can limit the initial surge, allowing for a smoother startup process. Additionally, implementing a regular maintenance schedule that includes monitoring the performance of the starter motor can help identify potential issues before they escalate. Collaborating with engineering teams to integrate power management systems can also provide real-time data on current flows, helping to proactively address any anomalies.
Scenario 3: Challenges in Motor Control and Direction Reversal
The Problem: For businesses requiring motors to operate in multiple directions, such as in conveyor systems or cranes, the challenge often lies in selecting a starter motor capable of efficient direction control. Buyers may encounter difficulties with systems that do not support seamless switching between forward and reverse operations, leading to operational delays and increased wear on machinery. This is a critical concern for companies in sectors like logistics and manufacturing in Europe, where precision and reliability are paramount.
The Solution: Buyers should prioritize the acquisition of Full Voltage Reversing Starters or specialized VFDs that provide robust direction control capabilities. It is essential to ensure that the selected starter motor can handle the specific load requirements and provide the necessary torque for both directions. Collaborating with a trusted supplier who offers tailored solutions and ongoing technical support can greatly enhance operational efficiency. Additionally, investing in training for operators on how to effectively use the motor starter can further improve control and reduce the likelihood of errors during operation. Regularly reviewing and updating operational protocols can also help maintain high standards of efficiency and safety in direction-controlled applications.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for types of starter motor
What Are the Key Materials Used in Starter Motors?
When selecting materials for starter motors, it’s essential to consider properties that influence performance, durability, and compatibility with various applications. Below, we analyze four common materials used in the manufacturing of starter motors, focusing on their key properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for international B2B buyers.
How Does Copper Affect Starter Motor Performance?
Copper is widely used in electrical components due to its excellent electrical conductivity and thermal properties. It typically has a high-temperature rating and is resistant to corrosion, making it suitable for various environments.
Pros: Copper’s superior conductivity ensures efficient power transfer, which is crucial for the rapid starting of motors. It also exhibits good thermal conductivity, helping to dissipate heat generated during operation.
Cons: The primary drawback of copper is its cost, which can be relatively high compared to alternatives like aluminum. Additionally, copper is prone to oxidation, which can affect performance if not properly coated or treated.
Impact on Application: Copper is compatible with a wide range of electrical systems and is often used in high-performance applications where reliability is critical.

Illustrative image related to types of starter motor
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM B170 for copper wire is essential. Buyers should also consider local sourcing to mitigate costs, especially in regions like Africa and South America, where import tariffs may apply.
What Role Does Aluminum Play in Starter Motors?
Aluminum is another common material used in starter motors, particularly for components like housings and brackets. It offers a good balance of strength, weight, and cost.
Pros: Aluminum is lightweight, which can reduce the overall weight of the starter motor, enhancing fuel efficiency in automotive applications. It also has good corrosion resistance, especially when anodized.
Cons: While aluminum is cost-effective, it has lower electrical conductivity compared to copper, which can affect performance in high-current applications. Additionally, it may require more complex manufacturing processes to achieve the desired strength.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is suitable for applications where weight savings are crucial, such as in automotive and aerospace sectors.

Illustrative image related to types of starter motor
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with relevant standards like DIN EN 573 for aluminum alloys. In markets like Germany, adherence to local regulations on material specifications is critical.
How Does Steel Contribute to Starter Motor Durability?
Steel, particularly stainless steel, is often used in starter motor components that require high strength and durability, such as shafts and housings.
Pros: Steel offers excellent mechanical strength and wear resistance, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications. Stainless steel, in particular, provides good corrosion resistance, extending the lifespan of components.
Cons: The main disadvantage of steel is its weight, which can be a drawback in applications where minimizing weight is essential. Additionally, steel can be more expensive than aluminum and may require additional treatments to prevent rust.
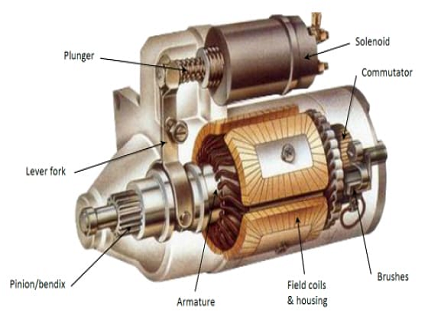
Illustrative image related to types of starter motor
Impact on Application: Steel’s durability makes it suitable for industrial applications where motors are subjected to harsh conditions.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM A240 for stainless steel is important. Buyers in the Middle East and Africa should consider the availability of specific grades to meet local environmental conditions.
What Advantages Does Plastic Offer in Starter Motor Components?
Plastics are increasingly being used in starter motors for non-load-bearing components, such as covers and insulation.
Pros: Plastics are lightweight and can be molded into complex shapes, allowing for design flexibility. They also provide good electrical insulation and can be cost-effective.
Cons: Plastics generally have lower mechanical strength compared to metals and may not withstand high temperatures or mechanical stress. Their long-term durability can also be a concern in harsh environments.
Illustrative image related to types of starter motor
Impact on Application: Plastics are suitable for applications where weight reduction and insulation are priorities, but they may not be appropriate for high-stress components.
Considerations for International Buyers: It’s important to ensure that plastics used comply with international standards such as ISO 1043 for plastic materials. Buyers should also consider the environmental impact and recyclability of plastics in their purchasing decisions.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Starter Motors
| Material | Typical Use Case for types of starter motor | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Copper | Electrical windings and connections | Excellent conductivity and thermal properties | High cost and oxidation susceptibility | High |
| Aluminum | Housings and brackets | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Lower conductivity than copper | Medium |
| Steel | Shafts and heavy-duty components | High strength and wear resistance | Heavier and potentially more expensive | Medium to High |
| Plastic | Covers and insulation | Lightweight and design flexibility | Lower mechanical strength and durability | Low |
In conclusion, selecting the right material for starter motors involves evaluating performance requirements, cost implications, and compliance with international standards. By understanding the properties and suitability of each material, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and market conditions.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for types of starter motor
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Starter Motors?
The manufacturing process of starter motors involves several critical stages, each designed to ensure the final product meets high-performance standards. The main stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
-
Material Preparation:
The first step in manufacturing starter motors involves sourcing and preparing materials. Common materials include steel for the casing, copper for windings, and various plastics for insulation. Quality control begins at this stage, where suppliers must provide certifications for materials, ensuring they meet international standards like ISO 9001. Material testing may include tensile strength, conductivity tests, and dimensional checks to confirm that all components will function as intended. -
Forming:
In the forming stage, the prepared materials are shaped into components. Techniques such as stamping, machining, and die casting are commonly used. For instance, the steel casing may be stamped from sheets, while the rotor and stator windings are typically machined or wound using automated equipment. Precision in this stage is crucial, as any deviations can lead to inefficiencies or failures in the starter motor’s operation. -
Assembly:
After the individual components are formed, they are assembled into the final product. This involves several sub-steps, including the installation of bearings, windings, and electrical connections. Automated assembly lines are frequently utilized to enhance efficiency, but manual assembly may still be necessary for quality-critical components. Quality checks during assembly, known as In-Process Quality Control (IPQC), ensure that each component fits correctly and functions as designed. -
Finishing:
The finishing stage includes surface treatments, painting, and packaging. Surface treatments like galvanizing or powder coating are applied to enhance corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal. Once the finishing touches are complete, the starter motors undergo final inspections to ensure they meet all specifications and standards.
What International Standards and Quality Control Measures Are Critical for Starter Motor Manufacturing?
Quality assurance in starter motor manufacturing is vital for ensuring reliability and safety, particularly for international buyers. Adhering to established standards not only guarantees product quality but also aids in market access.
-
Relevant International Standards:
Compliance with international standards such as ISO 9001 is essential, as it outlines the criteria for a quality management system. Additionally, industry-specific standards like CE marking in Europe, API standards for petroleum applications, and UL certification for electrical safety are crucial. These certifications indicate that the products meet specific safety, health, and environmental protection requirements. -
Quality Control Checkpoints:
Effective quality control involves multiple checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process. Incoming Quality Control (IQC) checks the quality of raw materials upon arrival. IPQC monitors the manufacturing process, ensuring adherence to specifications at various stages. Finally, Final Quality Control (FQC) occurs post-assembly to verify that the finished product meets all performance and safety standards. -
Common Testing Methods:
Various testing methods are employed to ensure the functionality and reliability of starter motors. These include:
– Electrical Testing: Measures resistance, voltage, and current under load conditions.
– Mechanical Testing: Assesses durability through vibration and shock tests.
– Thermal Testing: Evaluates performance under extreme temperature conditions.
– Endurance Testing: Simulates operational wear over extended periods.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
B2B buyers must conduct due diligence when selecting suppliers to ensure that quality control practices align with their expectations. Here are several strategies for verification:
-
Audits:
Conducting regular audits of potential suppliers can provide insight into their manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols. Buyers can assess compliance with international standards and evaluate the effectiveness of quality control measures firsthand. -
Reports and Documentation:
Requesting quality assurance reports, including testing results and compliance certificates, can help buyers gauge a supplier’s commitment to quality. Documentation should include details on the materials used, production processes, and any certifications obtained. -
Third-Party Inspections:
Engaging third-party inspection services can offer an impartial assessment of the supplier’s operations. These services can conduct random inspections and testing to confirm that products meet specified standards before shipment.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International buyers must navigate specific challenges and nuances in quality control when sourcing starter motors from different regions, including Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
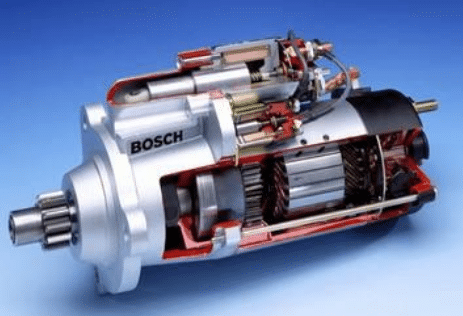
Illustrative image related to types of starter motor
-
Regional Compliance Standards:
Different regions may have varying compliance standards and regulations. For instance, products exported to Europe must meet CE marking requirements, while those entering the Middle East may need to comply with GSO standards. Understanding these nuances is essential for ensuring that products meet local market requirements. -
Cultural and Communication Factors:
Communication barriers can lead to misunderstandings regarding quality expectations. Establishing clear channels for communication and setting explicit quality requirements in contracts can mitigate this risk. Regular follow-ups and visits to the manufacturing site can also enhance mutual understanding. -
Logistical Considerations:
Quality assurance extends to logistics, as improper handling during transportation can compromise product integrity. Buyers should work closely with suppliers to ensure that proper packaging and shipping methods are used to protect starter motors during transit.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures involved in starter motor production, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance operational efficiency and product reliability. This comprehensive approach to quality will ultimately lead to stronger supplier relationships and better overall performance in the marketplace.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘types of starter motor’
In the competitive landscape of B2B procurement, selecting the appropriate starter motor can significantly impact operational efficiency and equipment longevity. This guide aims to streamline your sourcing process by outlining essential steps to ensure you make informed decisions while procuring different types of starter motors.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Begin by clearly outlining the technical requirements for your starter motor. This includes voltage ratings, phase requirements, and specific application needs (e.g., full voltage, soft starters, or variable frequency drives). Knowing these specifications ensures that you avoid compatibility issues and select a motor starter that meets your operational demands.
Step 2: Research Different Types of Starter Motors
Familiarize yourself with the various starter motor types available in the market, such as Direct-On-Line (DOL), Star-Delta, Soft Starters, and Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs). Understanding the advantages and disadvantages of each type will help you determine which motor starter aligns best with your specific applications and energy efficiency goals.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a supplier, conduct thorough due diligence. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from other businesses in similar industries or regions. Check for supplier certifications and compliance with international standards, as these factors can influence product reliability and performance.
- Key questions to ask:
- What is the supplier’s experience in your industry?
- Can they provide testimonials or references from other clients?
Step 4: Assess Quality Assurance Processes
Quality assurance is critical in ensuring the longevity and performance of starter motors. Inquire about the supplier’s manufacturing processes, testing protocols, and warranty offerings. A robust quality assurance program minimizes the risk of defects and operational failures, ultimately saving costs associated with maintenance and replacements.
Step 5: Consider After-Sales Support and Services
Evaluate the level of after-sales support offered by potential suppliers. This includes availability for troubleshooting, technical support, and maintenance services. A supplier that provides comprehensive after-sales assistance can help ensure optimal performance and longevity of your starter motors.
Step 6: Request Quotations and Compare Pricing
Once you have identified suitable suppliers, request detailed quotations that outline pricing, delivery timelines, and payment terms. Comparing these aspects will not only help you find the best value but also provide insights into the supplier’s reliability and responsiveness. Be wary of significantly lower prices that may indicate compromised quality.
Illustrative image related to types of starter motor
Step 7: Finalize the Agreement and Ensure Compliance
Before finalizing your purchase, review the contract thoroughly to ensure it includes all agreed-upon terms, delivery schedules, and compliance with relevant regulations. Proper documentation safeguards against potential disputes and ensures that both parties have a clear understanding of the expectations and responsibilities involved in the transaction.
By following this structured checklist, B2B buyers can confidently navigate the procurement process for starter motors, ensuring that they select the right products that meet their operational requirements while fostering reliable supplier relationships.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for types of starter motor Sourcing
What are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Starter Motors?
When sourcing starter motors, understanding the cost structure is crucial for B2B buyers. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and margin.
Materials typically encompass the raw components such as copper for windings, steel for the casing, and various electronic parts. The quality and source of these materials can significantly affect overall costs. For example, motors using higher-grade materials may have a higher upfront cost but can lead to lower maintenance expenses and longer lifespans.
Labor costs vary depending on the region and the complexity of the manufacturing process. Skilled labor, especially in regions with high labor costs, can increase expenses but also enhance product quality.
Manufacturing overhead includes utilities, rent, and equipment depreciation. Efficient manufacturing processes can help keep these costs down.
Tooling refers to the equipment needed for production. Initial tooling costs can be substantial, particularly for custom starter motors, but these costs are amortized over the production run.
Quality Control (QC) ensures that the motors meet safety and performance standards. Investing in robust QC processes may increase initial costs but ultimately reduces the risk of product failures and recalls.
Logistics involves transportation and warehousing, which can be influenced by the distance from the supplier and the mode of transport. This aspect is particularly important for international buyers who may face additional tariffs and customs fees.
Margin is the profit margin set by the manufacturer, which can vary widely based on brand reputation, market demand, and competition.
What Influences the Pricing of Starter Motors in B2B Transactions?
Several factors influence the pricing of starter motors, making it essential for buyers to understand these nuances.
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ) play a significant role. Higher order volumes often lead to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Suppliers may offer better pricing for larger orders, so negotiating for bulk purchases can be advantageous.
Specifications and Customization can also impact pricing. Custom motors designed for specific applications will typically cost more than standard models. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid unnecessary expenses.
Materials used in manufacturing can vary widely in cost. Premium materials may enhance performance but will also increase the overall price. Buyers should assess whether the benefits justify the additional costs.
Quality and Certifications are crucial considerations. Motors that comply with international standards or have additional certifications (e.g., ISO, CE) may come at a premium but offer greater assurance of reliability and safety.
Supplier Factors such as reputation, reliability, and service levels can affect pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their proven track record, while newer suppliers might offer lower prices to gain market share.
Incoterms dictate the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Understanding these terms can help buyers avoid unexpected costs associated with international shipping.
Illustrative image related to types of starter motor
What Negotiation Tips Can Help Buyers Achieve Cost Efficiency?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, effective negotiation strategies can lead to significant cost savings. Here are some tips:
-
Research and Benchmarking: Understand market prices and compare quotes from multiple suppliers. This knowledge empowers buyers during negotiations.
-
Leverage Volume Discounts: If possible, consolidate orders to meet minimum order quantities that unlock better pricing.
-
Focus on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider not just the purchase price but also maintenance, energy efficiency, and lifespan. A higher initial investment in quality motors may lead to lower overall costs.
-
Be Clear on Specifications: Clearly define your needs to avoid misunderstandings that could lead to increased costs.
-
Explore Flexible Payment Terms: Negotiating favorable payment terms can improve cash flow and reduce immediate financial burdens.
-
Build Long-term Relationships: Establishing a strong relationship with suppliers can lead to better pricing, priority service, and more favorable terms over time.
Are There Any Pricing Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International buyers should be aware of additional pricing nuances that could impact their sourcing decisions. Currency fluctuations can affect pricing, especially in markets with volatile currencies. Additionally, customs duties, tariffs, and import taxes can significantly alter the total cost.
Buyers should also consider the logistical complexities of shipping and potential delays, which can affect project timelines and costs. Understanding the local regulations in the destination country is vital for compliance and to avoid unexpected expenses.
Disclaimer
Prices for starter motors can vary widely based on the factors discussed above. This analysis provides indicative pricing insights, but actual costs will depend on specific circumstances and negotiations with suppliers. Always conduct thorough market research and consult with industry experts when sourcing starter motors.
Illustrative image related to types of starter motor
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing types of starter motor With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Types of Starter Motors
In the realm of electrical systems, the choice of motor starters is critical for ensuring safe and efficient motor operation. However, there are alternative solutions available that can also effectively manage motor performance and operational demands. This analysis compares various types of starter motors with alternative technologies, helping international B2B buyers make informed decisions.
| Comparison Aspect | Types Of Starter Motor | Variable Frequency Drive (VFD) | Soft Starter |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Excellent for managing inrush currents; protects against overload | Provides precise speed control and energy efficiency | Smooth starts reduce mechanical stress, enhancing motor life |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment; ongoing maintenance costs | Higher upfront cost; potential energy savings can offset | Lower initial cost; limited energy savings compared to VFDs |
| Ease of Implementation | Generally straightforward installation; may require some expertise | More complex installation; may need specialized knowledge | Simple installation; user-friendly controls |
| Maintenance | Requires regular checks on components like overload relays | Low maintenance once installed; requires monitoring of settings | Minimal maintenance; routine checks needed for optimal performance |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for applications with fixed-speed requirements | Best for applications needing variable speeds and energy efficiency | Suitable for applications requiring gentle starts and stops |
Understanding Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs)
Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs) are sophisticated devices that control the speed and torque of electric motors by varying the frequency and voltage of the power supply. The primary advantage of VFDs lies in their ability to provide precise speed control, which can lead to significant energy savings, especially in applications with fluctuating load requirements. However, the initial investment for a VFD can be higher than that of traditional starter motors. Additionally, VFDs require a more complex installation process and ongoing monitoring to ensure optimal performance. They are best suited for applications such as pumps and fans where speed variability is essential.
Insights on Soft Starters
Soft starters are designed to gradually increase the voltage supplied to the motor, allowing for a smooth start that minimizes mechanical stress. This feature extends the lifespan of both the motor and connected equipment, making soft starters an attractive option for industries where equipment longevity is critical. They typically come at a lower initial cost compared to VFDs and are easier to install, making them suitable for straightforward applications. However, soft starters do not provide the same level of energy savings as VFDs and are primarily effective in fixed-speed applications where gentle starts are needed.

Illustrative image related to types of starter motor
Conclusion: Making the Right Choice for Your Needs
When selecting between types of starter motors and alternative solutions like VFDs or soft starters, B2B buyers should consider the specific requirements of their applications. Factors such as performance needs, budget constraints, ease of installation, and maintenance capabilities will play a significant role in the decision-making process. By carefully evaluating these aspects, businesses can choose the right solution that not only meets their operational demands but also optimizes efficiency and extends the lifespan of their motor systems.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for types of starter motor
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Starter Motors?
When selecting starter motors for industrial applications, understanding the technical properties is crucial for ensuring compatibility and performance. Here are several essential specifications to consider:
-
Voltage Rating
The voltage rating indicates the maximum voltage the starter motor can handle. Common ratings include 230V, 400V, and 480V for AC motors. For B2B buyers, this specification is vital to ensure the starter motor is compatible with the power supply in their specific region or application, avoiding potential equipment damage or operational failures. -
Current Rating
This specification denotes the maximum current the motor starter can manage safely. It is typically expressed in amperes (A). Knowing the current rating is essential for buyers to ensure that the starter can handle the motor’s starting and running current without tripping or causing damage, thereby enhancing operational reliability. -
Inrush Current
Inrush current refers to the initial surge of current when the motor starts. This value is critical for choosing a starter motor, as it impacts the selection of protective devices and overall system design. Buyers must understand the inrush current characteristics to prevent nuisance tripping and ensure the longevity of both the motor and starter. -
Protection Class
The protection class indicates the starter motor’s resistance to environmental factors such as dust and moisture. Common ratings include IP54 and IP65. This property is particularly important for B2B buyers operating in harsh environments, as it ensures the motor starter can withstand external conditions without failure. -
Control Type
The control type refers to the method used to manage the motor’s operation. Common types include Direct-On-Line (DOL), Star-Delta, and Variable Frequency Drives (VFD). Understanding the control type helps buyers choose a starter motor that aligns with their operational requirements, such as energy efficiency and speed control. -
Operating Temperature Range
This specification indicates the temperature limits within which the starter motor can function effectively. For buyers, it is crucial to ensure that the selected starter can operate reliably under the temperature conditions specific to their application, particularly in extreme environments.
What Are the Common Trade Terms Related to Starter Motors?
Familiarity with trade terminology can significantly enhance communication and negotiation in B2B transactions. Here are several key terms relevant to starter motors:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that manufactures products that are sold under another company’s brand. In the context of starter motors, buyers may work with OEMs to source reliable components that meet specific quality standards. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell at a given time. Understanding MOQ is essential for B2B buyers to assess their purchasing power and inventory needs, ensuring they meet supplier requirements while managing costs effectively. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers asking for a quote on specific products or services. In the starter motor industry, issuing an RFQ allows buyers to compare pricing and terms from different manufacturers, facilitating informed purchasing decisions. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are standardized international trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping goods. Familiarity with Incoterms is crucial for B2B buyers to understand shipping costs, risks, and obligations, ensuring clarity in international transactions. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time taken from placing an order to the delivery of the product. For buyers, understanding lead times is critical for planning operations and ensuring that they have the necessary components available when needed. -
Warranty Period
The warranty period indicates the duration during which the manufacturer stands behind the quality of the starter motor. Buyers should pay attention to warranty terms as they provide insights into the product’s reliability and the manufacturer’s confidence in their offering.
By understanding these key technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they select the most suitable starter motors for their applications while navigating the complexities of international procurement.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the types of starter motor Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics and Trends Affecting the Starter Motor Sector?
The global market for starter motors is influenced by several key drivers, including the increasing demand for energy-efficient solutions and the growth of industrial automation. As industries across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe strive for improved operational efficiency, the adoption of advanced motor starters, such as Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs) and soft starters, has surged. These technologies offer enhanced control over motor speed and torque, leading to significant energy savings and reduced wear on equipment.
Illustrative image related to types of starter motor
Emerging trends also highlight the rise of smart technologies in motor control. The integration of IoT (Internet of Things) with motor starters is enabling predictive maintenance and real-time monitoring, allowing businesses to minimize downtime and optimize performance. As international B2B buyers seek innovative solutions, the demand for advanced motor starters equipped with smart features is expected to grow.
Moreover, the regulatory landscape is evolving, with stricter energy efficiency standards and safety regulations in place, particularly in European markets like Germany. This shift compels manufacturers to focus on developing compliant and high-performance starter motors, making it imperative for buyers to stay informed about the latest technological advancements and regulatory requirements.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact the Starter Motor Sector?
Sustainability is becoming a central theme in the starter motor sector as businesses recognize the importance of minimizing environmental impact. The production and operation of motor starters can contribute to energy consumption and waste generation, prompting the need for eco-friendly practices. Buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to sustainable manufacturing processes, such as using recyclable materials and reducing emissions.
Ethical sourcing is also gaining traction, as businesses aim to establish transparent supply chains that prioritize social responsibility. This includes ensuring fair labor practices and adhering to environmental regulations throughout the supply chain. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management systems and other green credentials are becoming essential considerations for B2B buyers seeking to align with sustainability goals.
Furthermore, the adoption of green technologies in starter motors, such as energy-efficient designs and materials, can significantly enhance a company’s marketability. By investing in sustainable products, companies not only contribute positively to the environment but also appeal to an increasingly eco-conscious customer base, creating a competitive advantage in the marketplace.
How Has the Starter Motor Sector Evolved Over Time?
The evolution of the starter motor sector is marked by significant technological advancements and increasing complexity in motor control systems. Initially, starter motors were simple devices that primarily provided basic on/off functionality. However, as industrial applications grew more sophisticated, the demand for advanced control options became apparent.
In the late 20th century, the introduction of electronic motor starters revolutionized the industry. Features such as overload protection and variable speed control emerged, allowing for more efficient and flexible motor operation. Today, the focus has shifted towards integrating smart technologies and IoT solutions, enhancing operational efficiency and predictive maintenance capabilities.
Illustrative image related to types of starter motor
As international markets continue to evolve, B2B buyers must remain agile and informed about the latest innovations in starter motor technology to leverage competitive advantages and drive operational excellence.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of types of starter motor
-
How do I select the right type of starter motor for my application?
Choosing the right starter motor involves assessing your application’s requirements, including motor size, operational environment, and load characteristics. For example, if you need a simple start-stop function, a Direct-On-Line (DOL) starter may suffice. In contrast, applications requiring variable speeds or direction reversal may benefit from a Variable Frequency Drive (VFD) or a Full Voltage Reversing Starter. Consult with suppliers to ensure compatibility and efficiency, and consider factors like energy consumption, inrush current management, and protection features. -
What is the best starter motor type for high-power applications?
For high-power applications, a Reduced Voltage Starter is often the best choice. This type minimizes inrush current, which can damage motor windings and associated electrical systems. Additionally, consider a Soft Starter for applications where gradual acceleration is crucial, as it reduces mechanical stress and extends motor life. If precise speed control is needed, a Variable Frequency Drive (VFD) would be ideal, allowing for flexible operations while enhancing energy efficiency. -
What customization options are available for starter motors?
Many manufacturers offer customization options for starter motors to meet specific operational needs. Customizations may include different voltage ratings, control methods (manual or automatic), and additional protective features like overload relays or thermal protection. Suppliers can also tailor the size, housing, and mounting configurations based on your installation requirements. Engaging in early discussions with manufacturers about your specific needs ensures that the final product aligns with your operational goals. -
What minimum order quantities (MOQs) should I expect when sourcing starter motors?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for starter motors can vary significantly depending on the supplier and the type of motor. Generally, larger manufacturers may have higher MOQs, while smaller suppliers might accommodate smaller orders. It’s advisable to discuss your specific needs with potential suppliers to negotiate MOQs that work for your business. Additionally, consider ordering in bulk if you anticipate future needs, as this may lead to cost savings. -
What payment terms are typical for purchasing starter motors in international trade?
Payment terms for international purchases of starter motors typically range from advance payment, letters of credit, or net terms (e.g., 30, 60, or 90 days). The choice of payment method often depends on the buyer’s relationship with the supplier, order size, and the level of risk involved. Establishing clear payment terms upfront can help avoid potential disputes. Additionally, consider using secure payment methods and agreements to protect your investment. -
How do I ensure quality assurance when sourcing starter motors?
To ensure quality assurance, select suppliers that adhere to international quality standards such as ISO 9001. Request certifications, product samples, and detailed specifications before finalizing orders. It’s also beneficial to perform factory audits or inspections, especially for large orders. Establishing a robust communication channel with suppliers can help address any quality concerns quickly. Furthermore, consider implementing a testing phase upon receiving products to verify their performance and compliance with your specifications. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing starter motors?
When importing starter motors, consider logistics factors such as shipping methods, lead times, and customs regulations. Determine whether air freight or sea freight is more suitable for your shipment based on urgency and cost. Be aware of any tariffs or duties that may apply to your importation. Collaborating with experienced logistics partners can facilitate smoother transport and clearance processes. Additionally, ensure that the supplier provides necessary documentation to avoid delays at customs. -
How can I vet suppliers for starter motors effectively?
To effectively vet suppliers for starter motors, begin by researching their reputation and track record in the industry. Look for customer reviews, case studies, and references from other B2B buyers. It’s also helpful to assess their production capabilities, quality control processes, and compliance with international standards. Requesting samples and engaging in preliminary discussions can provide insights into their customer service and responsiveness. Finally, consider establishing a trial order to evaluate their product quality and delivery reliability before committing to larger purchases.
Top 2 Types Of Starter Motor Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Campus Component – Motor Starter
Domain: campuscomponent.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: Motor Starter: An electrical device used to safely start, stop, and protect electric motors from damage caused by overcurrent, short circuits, or other faults. It regulates the flow of electrical power to the motor, ensuring smooth operation. Key features include: 1. Starting the motor safely by regulating high inrush current. 2. Stopping the motor reliably through manual or automatic methods. 3. …
2. 1A Auto – Starters
Domain: 1aauto.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Starters are small electric motors that engage with the engine’s flywheel to crank the engine and start the combustion cycle. There are different types of starters: inertia starters, pre-engaged starters, and gear reduction starters. Inertia starters engage the ring gear as the pinion threads out, while pre-engaged starters use a solenoid to push the pinion out before starting the motor. Gear redu…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for types of starter motor
In the evolving landscape of industrial operations, understanding the diverse types of starter motors is paramount for optimizing performance and ensuring safety. Key takeaways include the importance of selecting the appropriate starter type—such as Direct-On-Line, Soft Starters, or Variable Frequency Drives—based on specific application needs. Each type offers unique benefits, including inrush current management, overload protection, and enhanced energy efficiency, which are critical for maintaining operational reliability and extending motor lifespan.
Strategic sourcing of starter motors is essential for international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. By aligning purchasing decisions with quality and performance specifications, businesses can mitigate risks associated with motor failure and operational downtime.
As industries continue to advance, the demand for innovative motor control solutions will grow. Buyers are encouraged to engage with trusted suppliers who can provide insights into the latest technologies and best practices in motor starter selection. Embrace the opportunity to enhance your operations by making informed sourcing decisions today.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.