Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for the car alternator
In an increasingly competitive automotive landscape, effectively sourcing car alternators can pose significant challenges for international B2B buyers, particularly those operating in diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including Germany and Nigeria. The alternator is a critical component of every vehicle, responsible for converting mechanical energy into electrical energy to power essential systems. Understanding the nuances of sourcing high-quality alternators—ranging from types and applications to supplier vetting and cost considerations—can directly impact the efficiency and reliability of automotive operations.
This comprehensive guide aims to empower B2B buyers by providing a detailed exploration of the car alternator market. It covers various types of alternators, their applications across different vehicle models, and essential factors to consider when evaluating suppliers. Additionally, we delve into cost structures and potential savings strategies, ensuring that buyers can make informed purchasing decisions that align with their operational needs.
By leveraging the insights contained in this guide, international buyers can navigate the complexities of the global car alternator market with confidence. Whether you are seeking to enhance your supply chain or improve the reliability of your automotive offerings, this resource will equip you with the knowledge necessary to optimize your procurement strategy and drive sustainable growth in your business.
Table Of Contents
- Top 3 The Car Alternator Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for the car alternator
- Understanding the car alternator Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of the car alternator
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘the car alternator’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for the car alternator
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for the car alternator
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘the car alternator’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for the car alternator Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing the car alternator With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for the car alternator
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the the car alternator Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of the car alternator
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for the car alternator
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Understanding the car alternator Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Conventional Alternator | Uses a belt-driven design; generates AC power | Standard vehicles, fleet services | Pros: Cost-effective; Cons: Less efficient at low RPMs |
| High-Output Alternator | Designed for higher electrical demands; larger capacity | Performance vehicles, aftermarket upgrades | Pros: Supports additional accessories; Cons: Higher cost |
| Smart Alternator | Features advanced voltage regulation and diagnostics | Luxury vehicles, advanced automotive systems | Pros: Improved efficiency; Cons: Complex installation |
| Brushless Alternator | No brushes or commutators; uses electronic controls | Electric vehicles, hybrid models | Pros: Longer lifespan; Cons: More expensive upfront |
| Regenerative Alternator | Captures energy during braking to recharge the battery | Electric vehicles, hybrid applications | Pros: Enhances energy efficiency; Cons: Requires compatible systems |
What Are the Characteristics of Conventional Alternators?
Conventional alternators are the most widely used type in standard vehicles. They operate using a belt-driven mechanism that converts mechanical energy from the engine into electrical energy. This type is well-suited for everyday applications and is commonly found in fleet vehicles and standard passenger cars. When purchasing, B2B buyers should consider factors such as durability and compatibility with existing vehicle systems, as well as the total cost of ownership, which includes maintenance and potential replacement frequency.
How Do High-Output Alternators Meet Increased Power Needs?
High-output alternators cater to vehicles with higher electrical demands, such as those equipped with aftermarket sound systems or additional lighting. These alternators feature a larger capacity and are designed to handle increased loads effectively. They are ideal for performance vehicles and those used in commercial settings where electrical accessories are prevalent. B2B buyers should evaluate the specific power requirements of their applications and consider the trade-off between initial investment and long-term benefits, such as improved performance and reliability.
What Advantages Do Smart Alternators Offer for Modern Vehicles?
Smart alternators represent the cutting-edge of automotive technology, incorporating advanced voltage regulation and diagnostic capabilities. They are typically found in luxury vehicles and sophisticated automotive systems, where efficiency and performance are paramount. These alternators can adjust their output based on real-time electrical demands, enhancing overall vehicle efficiency. For B2B buyers, it is essential to assess compatibility with existing vehicle electronics and the potential for reduced fuel consumption, despite higher upfront costs.
Why Are Brushless Alternators Gaining Popularity?
Brushless alternators eliminate the need for brushes and commutators, using electronic controls instead. This design results in reduced wear and tear, leading to a longer lifespan and lower maintenance costs. They are particularly suited for electric and hybrid vehicles, where efficiency is critical. When purchasing brushless alternators, B2B buyers should be aware of the higher initial costs and ensure that their vehicles are compatible with this advanced technology.
How Do Regenerative Alternators Enhance Energy Efficiency?
Regenerative alternators are specifically designed to capture energy during braking, converting it into electrical energy to recharge the vehicle’s battery. This technology is commonly utilized in electric and hybrid vehicles, where maximizing energy efficiency is essential. B2B buyers should consider the overall system compatibility and the potential for energy savings, alongside the initial investment. This type of alternator can lead to significant operational cost reductions over time, making it an attractive option for businesses focused on sustainability.
Key Industrial Applications of the car alternator
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of the car alternator | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive Manufacturing | Power supply for vehicle electrical systems | Ensures reliable operation of vehicles, enhancing safety and performance | Quality assurance of components, OEM standards, local regulations |
| Transportation | Fleet management vehicles | Reduces downtime and maintenance costs, improving operational efficiency | Durability under various conditions, compatibility with fleet models |
| Renewable Energy | Hybrid and electric vehicle systems | Supports energy management and efficiency, reducing reliance on traditional energy sources | Integration with battery systems, regulatory compliance, scalability |
| Heavy Machinery | Construction and agricultural vehicles | Powers essential equipment, ensuring uninterrupted operations in demanding environments | Robustness against harsh conditions, service support, part availability |
| Emergency Services | Ambulances and rescue vehicles | Provides consistent power supply for medical and communication equipment | Reliability, quick delivery times, adherence to safety standards |
How is the car alternator utilized in the automotive manufacturing sector?
In the automotive manufacturing sector, the car alternator serves as a critical component that powers the vehicle’s electrical systems, including lighting, infotainment, and safety features. Its reliable operation ensures that vehicles can perform optimally while meeting safety regulations. For B2B buyers, sourcing high-quality alternators that comply with OEM standards is crucial, as it directly impacts vehicle performance and customer satisfaction. Additionally, understanding local regulations regarding automotive parts in different regions, such as Africa or Europe, is vital to ensure compliance and market access.
What role does the car alternator play in the transportation industry?
In the transportation industry, particularly for fleet management, the alternator is essential for maintaining the electrical systems of commercial vehicles. It ensures that all electronic components function correctly, which minimizes the risk of breakdowns and enhances operational efficiency. For international buyers, factors such as the durability of the alternator under various driving conditions and its compatibility with different vehicle models are critical. This helps reduce maintenance costs and downtime, ultimately leading to improved profitability.
How is the car alternator applied in renewable energy vehicles?
In the renewable energy sector, particularly in hybrid and electric vehicles, the car alternator plays a significant role in energy management. It helps convert mechanical energy into electrical energy, which is essential for recharging batteries and powering electric motors. For B2B buyers, sourcing alternators that can seamlessly integrate with advanced battery systems and comply with environmental regulations is paramount. This not only boosts the efficiency of electric vehicles but also aligns with global sustainability goals, making it an attractive investment.
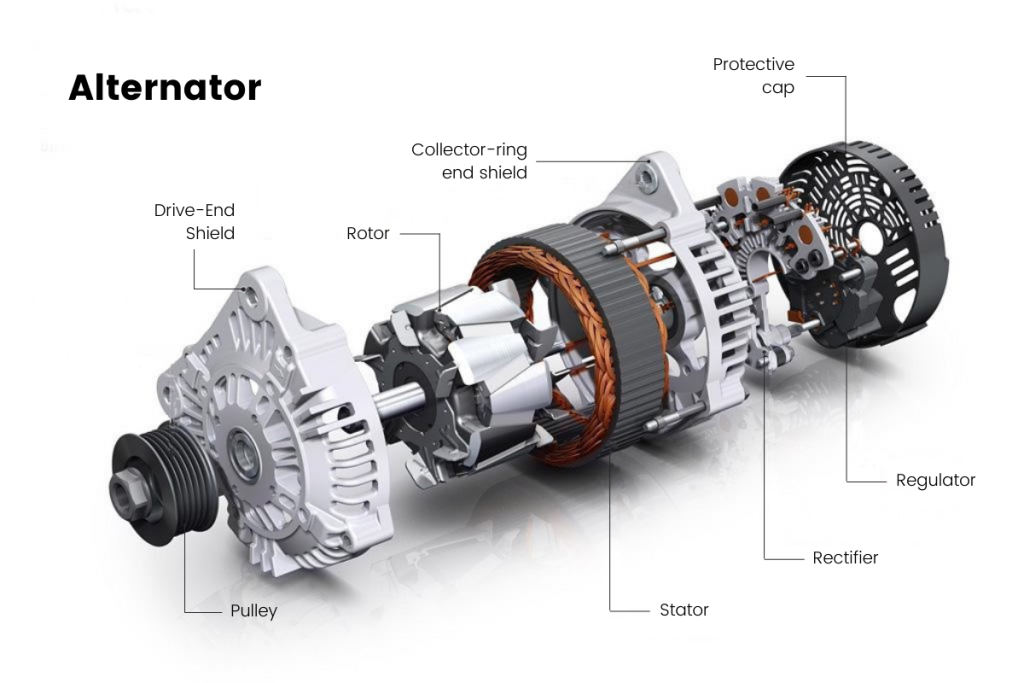
Illustrative image related to the car alternator
Why is the car alternator important in heavy machinery?
The use of car alternators in heavy machinery, such as construction and agricultural vehicles, ensures that essential equipment remains powered during operation. These alternators are designed to withstand harsh conditions, providing reliable power to critical systems. For buyers in this sector, sourcing robust and durable alternators is essential to prevent operational interruptions. Additionally, having access to service support and readily available parts can significantly influence purchasing decisions, as it impacts the total cost of ownership and operational efficiency.
How does the car alternator benefit emergency services?
In emergency services, such as ambulances and rescue vehicles, the car alternator is vital for ensuring that medical and communication equipment remains operational during critical situations. A reliable power supply can be the difference between life and death, making the quality of the alternator non-negotiable. For B2B buyers in this sector, considerations include the reliability of the alternator, quick delivery times, and adherence to safety standards. These factors help ensure that emergency vehicles are always ready to respond when needed, enhancing public safety and service effectiveness.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘the car alternator’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: The Unforeseen Breakdown of Fleet Vehicles
The Problem: For B2B buyers managing a fleet of vehicles, the sudden failure of a car alternator can lead to significant operational disruptions. Such breakdowns not only affect the reliability of service delivery but also result in unexpected repair costs and downtime. For example, a logistics company in Nigeria may find that a single vehicle’s alternator failure delays deliveries, impacting customer satisfaction and potentially leading to lost business. The cost of repairs, coupled with the impact on productivity, creates a compounded financial burden.
The Solution: To mitigate the risk of alternator failures, fleet managers should implement a proactive maintenance schedule that includes regular inspections of electrical components. This involves training technicians to recognize early warning signs, such as dimming lights or unusual noises, that may indicate alternator issues. Additionally, sourcing high-quality, OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) alternators from reputable suppliers ensures that replacements are durable and reliable. For fleet operations, investing in a diagnostic tool can also be advantageous, allowing for real-time monitoring of vehicle electrical systems, which can identify potential alternator failures before they occur.
Scenario 2: Difficulty in Distinguishing Between Battery and Alternator Issues
The Problem: Many B2B buyers face challenges in accurately diagnosing whether a vehicle’s electrical problems stem from a failing battery or a malfunctioning alternator. This confusion can lead to unnecessary costs and time spent on repairs. For instance, an automotive repair shop in South America may receive numerous vehicles with starting issues, only to find that misdiagnosing the problem leads to replacing batteries that were actually fine, while the alternator remained defective.
The Solution: To enhance diagnostic accuracy, buyers should consider investing in advanced diagnostic equipment that can differentiate between battery and alternator issues. This equipment can perform voltage tests and analyze the electrical system’s performance under load. Furthermore, creating a standardized checklist for technicians to follow can streamline the diagnostic process. This checklist should include symptoms such as dashboard warning lights and performance tests, helping to ensure that the correct component is addressed. Training staff on the nuances between battery and alternator functions will also improve service efficiency and customer trust.
Scenario 3: High Replacement Costs Due to Poor Quality Parts
The Problem: B2B buyers often struggle with high costs associated with frequently replacing alternators that fail prematurely. This is particularly concerning for businesses that depend on vehicles for daily operations. For example, a construction company in Germany may experience frequent alternator failures due to sourcing low-quality aftermarket parts, leading to increased operational costs and project delays.
The Solution: To combat the issue of high replacement costs, it is crucial for buyers to establish relationships with trusted suppliers who provide high-quality, OEM alternators. Conducting thorough research and reviews on suppliers can help ensure that the parts meet industry standards for durability and performance. Additionally, implementing a quality assurance program that includes inspecting parts upon arrival can prevent the installation of subpar components. By prioritizing quality over cost, businesses can reduce the frequency of replacements and enhance the overall reliability of their fleet, ultimately leading to significant long-term savings.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for the car alternator
What Materials Are Commonly Used in Car Alternators?
When selecting materials for car alternators, several options are prevalent in the industry, each with unique properties that influence performance, durability, and cost. Below is an analysis of four common materials used in alternator construction, focusing on their key properties, advantages and disadvantages, and considerations for international B2B buyers.
1. Aluminum: Lightweight and Corrosion-Resistant
Key Properties:
Aluminum is known for its lightweight nature, excellent corrosion resistance, and good thermal conductivity. It typically withstands temperatures up to 150°C (302°F) and is effective in dissipating heat generated during alternator operation.
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage of aluminum is its weight, which can enhance fuel efficiency in vehicles. It is also relatively inexpensive and easy to manufacture. However, aluminum may not provide the same level of strength as other metals, making it less suitable for high-stress applications.
Impact on Application:
Aluminum is compatible with various media and environments, making it a versatile choice for alternators. However, it may require protective coatings in harsh environments, especially in regions with high humidity or salt exposure.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers from regions like Europe and the Middle East should ensure compliance with EU regulations regarding material safety and environmental impact. Standards such as DIN 1725 for aluminum alloys may also be relevant.
2. Copper: Superior Electrical Conductivity
Key Properties:
Copper is renowned for its exceptional electrical conductivity, with a conductivity rating of 97% IACS (International Annealed Copper Standard). It can handle high temperatures up to 200°C (392°F) and is resistant to corrosion when properly treated.
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage of copper is its efficiency in electrical applications, leading to better performance of the alternator. However, copper is heavier and more expensive than aluminum, which can increase the overall cost of the alternator.
Impact on Application:
Copper’s superior conductivity makes it ideal for wiring and components within the alternator. However, its weight may affect vehicle performance, especially in smaller cars.
Considerations for International Buyers:
In regions like South America and Africa, buyers should consider the availability of copper and any tariffs or import duties that may apply. Compliance with local standards, such as ASTM B170 for copper wire, is also crucial.
3. Steel: Strength and Durability
Key Properties:
Steel offers high tensile strength and durability, making it suitable for components subject to mechanical stress. It can withstand high temperatures and pressures, typically up to 250°C (482°F) depending on the alloy.
Pros & Cons:
The main advantage of steel is its strength, which allows for the construction of robust alternator housings and components. However, it is heavier and can be prone to corrosion without proper treatment, leading to increased maintenance costs.
Impact on Application:
Steel is particularly effective in applications requiring high structural integrity, such as in heavy-duty vehicles. However, its weight may negatively impact fuel efficiency.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Steel buyers should be aware of compliance with international standards such as JIS G3101 for structural steel, especially in regions like Germany, where stringent regulations apply.
4. Plastic Composites: Lightweight and Cost-Effective
Key Properties:
Plastic composites are lightweight and can be engineered for specific thermal and electrical properties. They typically have a temperature rating of around 80°C (176°F) and are resistant to corrosion.
Pros & Cons:
The key advantage of plastic composites is their low cost and lightweight nature, which can enhance overall vehicle efficiency. However, they may not provide the same mechanical strength as metals, limiting their use in high-stress applications.
Impact on Application:
Plastic composites are suitable for non-structural components within the alternator, such as housings or covers. However, they may not perform well in high-temperature environments.

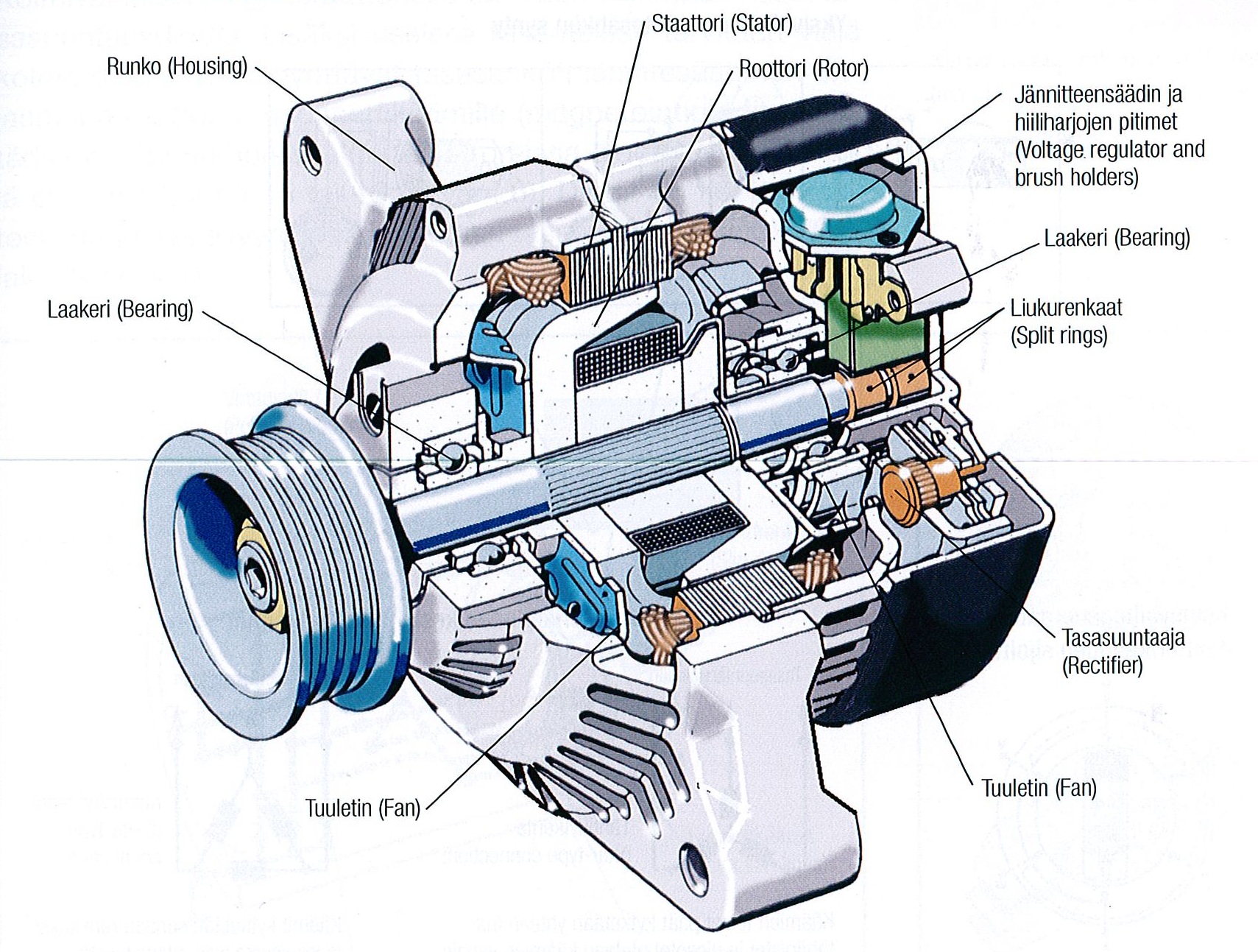
Illustrative image related to the car alternator
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should ensure that plastic composites meet relevant safety and environmental regulations, such as REACH in Europe, and consider local manufacturing capabilities for composite materials.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for the car alternator | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Housing and structural components | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Lower strength compared to metals | Medium |
| Copper | Wiring and electrical components | Superior electrical conductivity | Higher cost and weight | High |
| Steel | Structural components | High strength and durability | Heavier and prone to corrosion | Medium |
| Plastic Composites | Non-structural components | Lightweight and cost-effective | Limited mechanical strength | Low |
This comprehensive analysis of materials used in car alternators provides B2B buyers with actionable insights to make informed decisions based on performance requirements, cost considerations, and regional compliance standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for the car alternator
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Car Alternators?
The manufacturing process of car alternators involves several critical stages, each designed to ensure efficiency and quality. Understanding these stages can help B2B buyers assess the capabilities and reliability of potential suppliers.
Illustrative image related to the car alternator
1. Material Preparation: What Raw Materials Are Used?
The primary materials used in alternator manufacturing include aluminum, copper, and various plastics. Aluminum is typically used for the housing due to its lightweight and corrosion-resistant properties, while copper is essential for electrical components due to its excellent conductivity. Quality control starts at this stage, with suppliers required to provide material certifications and test reports confirming compliance with industry standards.
2. Forming: How Are Components Shaped?
The forming process involves several techniques, including die casting, machining, and stamping. Die casting is commonly used for creating the alternator housing, allowing for precise shapes and reduced waste. Machining is employed to achieve the necessary tolerances for components such as the rotor and stator. Stamping is utilized for producing electrical contacts and other smaller parts. Each of these processes requires strict adherence to specifications, and buyers should inquire about the equipment used and the capabilities of the manufacturing facility.
3. Assembly: What Does the Assembly Process Entail?
Once the components are formed, the assembly process begins. This involves the precise alignment of the rotor, stator, and diode rectifier within the alternator housing. Automated assembly lines often enhance efficiency and accuracy, but manual inspection remains crucial to ensure that every component is correctly installed. During assembly, it’s vital to monitor torque settings and ensure that electrical connections are secure. B2B buyers should consider suppliers that utilize both automated and manual processes to maintain high quality.
4. Finishing: How Is the Alternator Prepared for Market?
The finishing stage includes surface treatment, painting, and packaging. Surface treatments, such as anodizing or powder coating, enhance corrosion resistance and durability. Packaging must also be robust enough to protect the alternator during shipping, particularly for international buyers. Suppliers should provide details on their finishing processes and the types of coatings used, as these can significantly impact the product’s lifespan and performance.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Implemented in Alternator Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is a critical component of alternator manufacturing, ensuring that products meet both internal and international standards.
Illustrative image related to the car alternator
1. What Are the Relevant International Standards for Alternator Quality?
Manufacturers of car alternators often adhere to ISO 9001, which outlines requirements for a quality management system. Compliance with CE marking standards is also essential for products sold within the European market. For specific automotive applications, adherence to API standards may be necessary. B2B buyers should seek suppliers who can demonstrate compliance with these standards through certificates and audit reports.
2. What Are the Key QC Checkpoints During Production?
Quality control checkpoints are strategically placed throughout the manufacturing process:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint assesses the quality of raw materials and components before they enter the production line. Buyers should request reports detailing IQC results to ensure materials meet specifications.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During assembly and forming, IPQC monitors processes to catch defects early. It may involve regular inspections and measurements to verify that components are produced within tolerances.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Before packaging, FQC ensures that the finished alternator meets all functional and aesthetic requirements. This may include electrical testing, performance validation, and visual inspections.
3. What Common Testing Methods Are Used to Ensure Quality?
Testing methods for alternators typically include:
- Electrical Testing: To verify the output voltage and current capabilities of the alternator.
- Load Testing: To assess performance under various electrical loads.
- Environmental Testing: To simulate conditions such as temperature variations and humidity to ensure durability.
- Vibration Testing: To identify potential mechanical failures under operational conditions.
B2B buyers should inquire about the specific tests conducted and request documentation of test results to verify quality.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
Establishing trust with suppliers involves verifying their quality control practices. Here are actionable steps for buyers:
1. What Should Buyers Look for in Supplier Audits and Reports?
Request copies of audit reports from recognized third-party organizations. These reports should detail compliance with international standards and any corrective actions taken for non-conformities. Regular audits not only reflect the supplier’s commitment to quality but also their willingness to maintain transparency.
2. How Can Buyers Utilize Third-Party Inspections?
Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s manufacturing processes and quality control systems. This can be especially valuable for international buyers who may face language barriers or cultural differences. Choose inspection services that have experience in automotive components to ensure thorough evaluations.
Illustrative image related to the car alternator
3. What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International Buyers?
International buyers should be aware of regional regulations and standards that may affect product quality. For example, while CE marking is crucial for Europe, other regions may have different certification requirements. Understanding these nuances can help buyers avoid compliance issues and ensure that products meet local market expectations.
Conclusion: Why Is Understanding Manufacturing and Quality Assurance Crucial for B2B Buyers?
A comprehensive understanding of the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for car alternators equips B2B buyers to make informed decisions. By assessing suppliers based on their manufacturing capabilities, adherence to international standards, and proven quality control practices, buyers can secure reliable products that meet their operational needs. This diligence not only enhances supply chain reliability but also contributes to long-term business success in the automotive sector.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘the car alternator’
This guide provides a systematic approach for B2B buyers looking to procure car alternators. Understanding the importance of this component and the nuances involved in sourcing it can save businesses time and resources while ensuring quality and reliability.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications for the alternators you need is critical. This includes voltage output, current rating, and compatibility with specific vehicle models. Understanding these requirements ensures that you procure alternators that meet your operational needs and avoid costly returns or replacements.
Step 2: Research Supplier Credentials
Before engaging with suppliers, it’s essential to verify their credentials. Look for certifications such as ISO 9001 or industry-specific standards that demonstrate their commitment to quality. Suppliers with these certifications are more likely to provide reliable products and maintain consistent manufacturing practices.
Illustrative image related to the car alternator
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Experience and Reputation
Investigate the experience and reputation of potential suppliers in the automotive industry. A supplier with a proven track record is more likely to understand your needs and provide quality products. Check customer testimonials, case studies, and industry reviews to gauge their reliability and service level.
Step 4: Request Product Samples
Before finalizing your order, request samples of the alternators. This step allows you to assess the quality and performance of the product firsthand. Testing samples can help you identify any potential issues early on, ensuring that the final products meet your specifications.
Step 5: Discuss Warranty and Return Policies
Understanding warranty terms and return policies is crucial when sourcing alternators. A robust warranty can indicate the supplier’s confidence in their product quality. Ensure that the return policy is favorable, allowing you to return faulty products without incurring significant costs.
Step 6: Negotiate Pricing and Payment Terms
Once you have shortlisted suppliers, engage in negotiations regarding pricing and payment terms. Consider bulk order discounts and payment schedules that align with your cash flow needs. A favorable financial arrangement can significantly impact your overall procurement costs.
Step 7: Plan for Logistics and Delivery
Finally, coordinate logistics and delivery timelines with your chosen supplier. Ensure that they can meet your scheduling needs and discuss shipping options. Proper planning will help you avoid delays in production or service due to late deliveries, keeping your operations running smoothly.

Illustrative image related to the car alternator
By following these steps, B2B buyers can effectively navigate the procurement process for car alternators, ensuring quality, reliability, and cost-effectiveness in their sourcing strategy.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for the car alternator Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Sourcing Car Alternators?
When sourcing car alternators, understanding the cost structure is essential for informed decision-making. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and margin.
Materials: The materials used in car alternators, such as copper for windings and high-quality steel for components, significantly impact costs. Prices for these raw materials can fluctuate based on global demand and supply chain dynamics.
Labor: Labor costs vary based on the region and the skill level required for assembly. In countries with lower labor costs, such as those in parts of Africa and South America, sourcing may be more economical compared to regions with higher labor rates, such as Western Europe.

Illustrative image related to the car alternator
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to facility maintenance, utilities, and indirect labor. Efficient manufacturing processes can help reduce these costs, making the sourcing more competitive.
Tooling: Tooling costs are associated with the equipment and molds necessary for production. Investing in high-quality tooling can lead to better product consistency and reduced scrap rates, ultimately lowering costs.
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that alternators meet safety and performance standards can add to the cost. However, rigorous QC can prevent costly recalls or warranty claims, which is crucial for maintaining brand reputation.
Logistics: Transportation costs can vary significantly based on the sourcing location. Factors such as distance, shipping methods, and Incoterms impact the overall logistics expenses. Efficient logistics planning can help minimize these costs.
Margin: The supplier’s profit margin is an important aspect of the overall price. Understanding the market dynamics and competitive landscape can help buyers negotiate better terms.
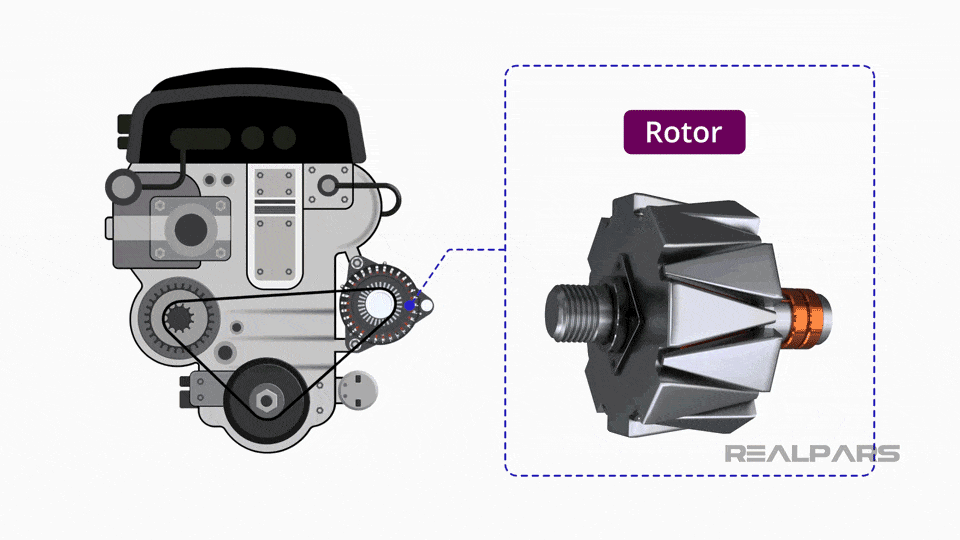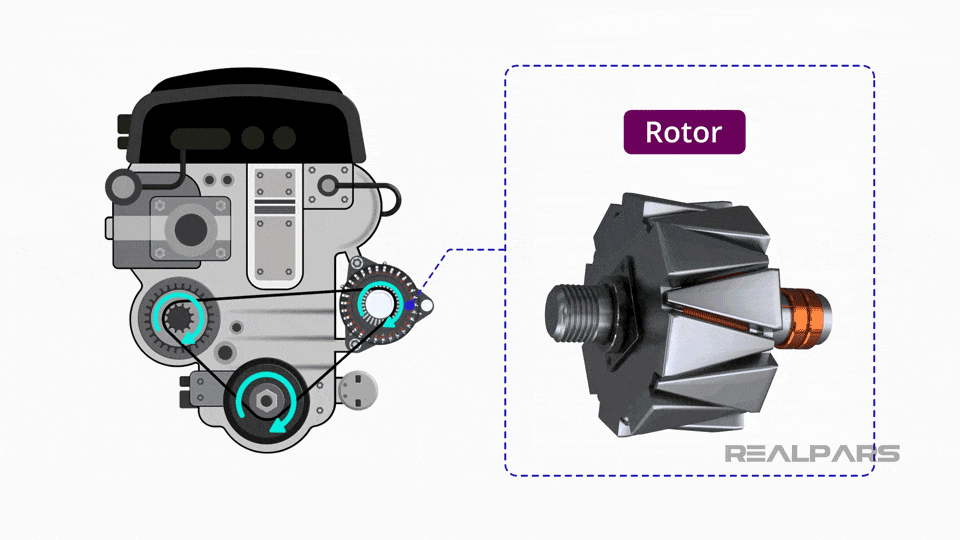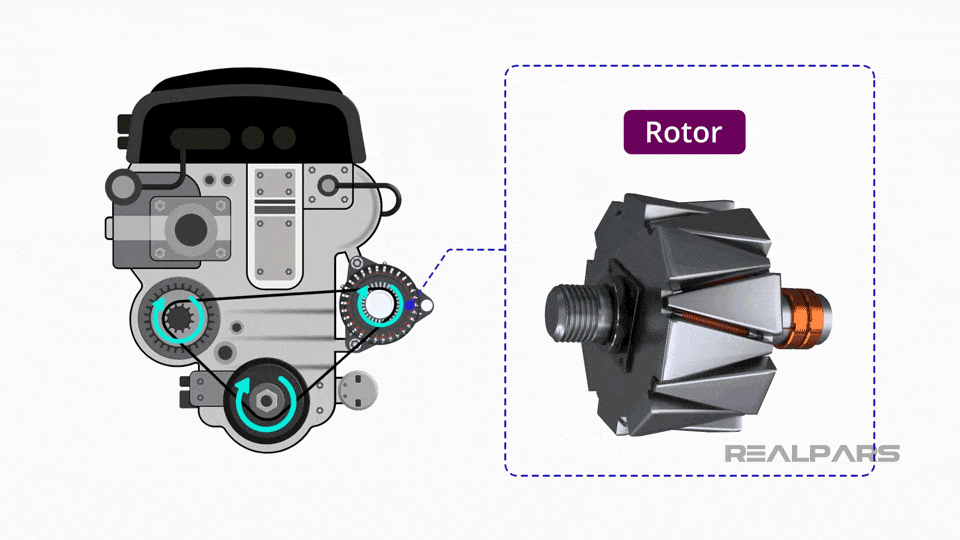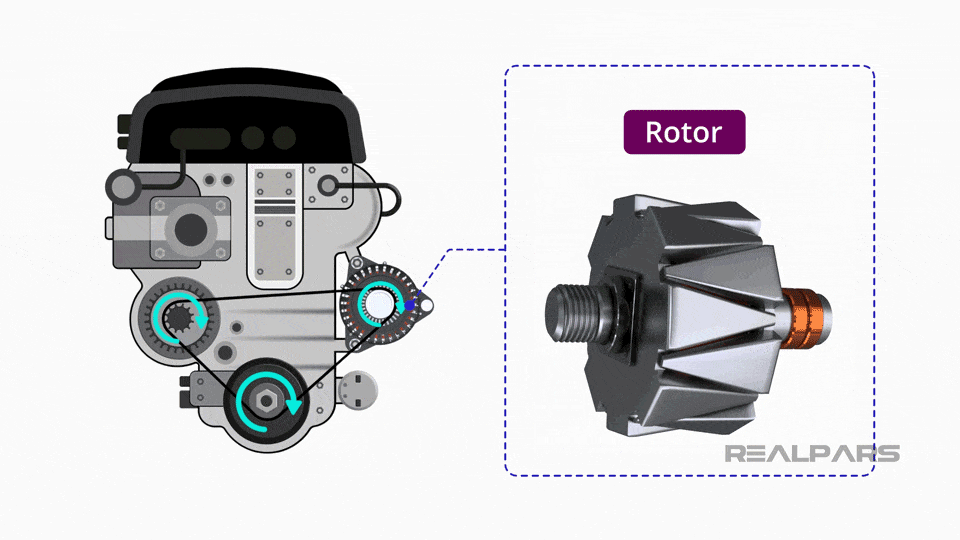
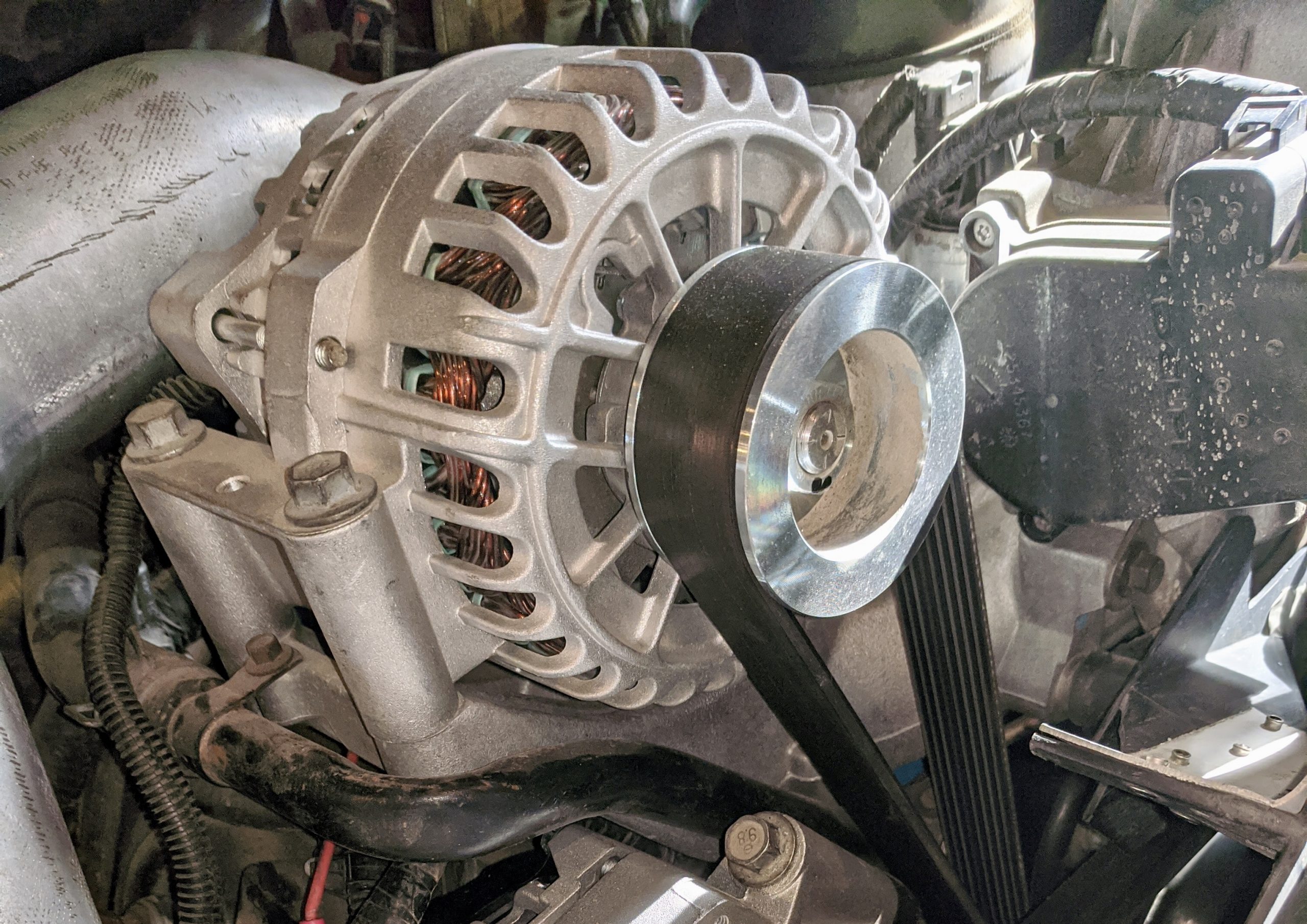
Illustrative image related to the car alternator
What Influences the Pricing of Car Alternators?
Several factors influence the pricing of car alternators, impacting how buyers approach sourcing decisions.
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Higher purchase volumes often lead to lower per-unit costs. Negotiating favorable terms based on anticipated order quantities can significantly impact overall costs.
Specifications and Customization: Custom alternators designed for specific vehicle models or performance standards may incur additional costs. It’s important for buyers to clearly communicate specifications to avoid unexpected expenses.
Materials and Quality Certifications: The choice of materials and the presence of quality certifications (e.g., ISO, TS16949) can affect pricing. Alternators made with premium materials or certified processes may command higher prices, but they often offer better performance and longevity.
Illustrative image related to the car alternator
Supplier Factors: The reputation, reliability, and financial stability of suppliers can influence pricing. Established suppliers may have higher prices but offer better support and warranty services.
Incoterms: Understanding the Incoterms used in the transaction is crucial, as they define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Selecting the right Incoterm can lead to cost savings and reduced risks.
What Are Some Tips for Negotiating and Achieving Cost Efficiency in Alternator Sourcing?
For international B2B buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, effective negotiation and cost-efficiency strategies can lead to significant savings.
Negotiation: Engage suppliers in discussions about pricing structures, volume discounts, and payment terms. Building a strong relationship can also provide leverage for better deals.
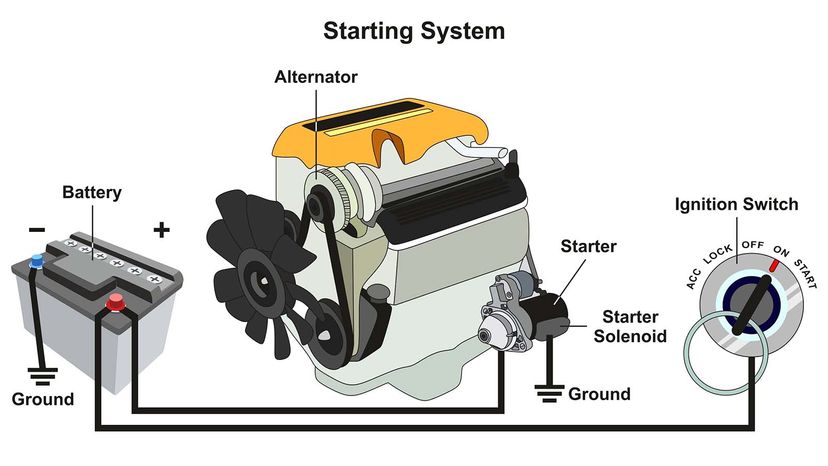
Illustrative image related to the car alternator
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider the TCO rather than just the upfront cost. This includes factors such as warranty, expected lifespan, and maintenance costs. A higher initial investment may lead to lower overall expenses if the alternator has a longer lifespan and better performance.
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Be aware of exchange rates, tariffs, and duties that can affect the final cost. It’s advisable to work with local experts who understand the market dynamics in your region.
Quality Over Price: While cost is a critical factor, prioritizing quality can prevent future expenses related to failures or replacements. Ensure that the alternators sourced meet necessary performance and safety standards.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for car alternators can vary widely based on the aforementioned factors. It is crucial for buyers to conduct thorough market research and obtain multiple quotes to ensure competitive pricing and value for their specific needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing the car alternator With Other Solutions
Introduction: Exploring Alternatives to the Car Alternator
When considering automotive electrical solutions, the traditional car alternator is often the first choice due to its reliability and efficiency. However, various alternative technologies and methods exist that can serve similar functions or offer unique advantages. This analysis aims to provide B2B buyers with a comprehensive understanding of these alternatives, facilitating informed decisions based on performance, cost, and maintenance considerations.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | The Car Alternator | Lithium-Ion Battery Systems | Solar-Powered Generators |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High efficiency in converting mechanical energy to electrical energy; supports all vehicle electrical needs. | Provides high energy density and longer life but limited by charging cycles; requires additional systems for effective usage in vehicles. | Can generate energy independently but performance heavily depends on sunlight availability; may require battery storage for nighttime use. |
| Cost | Generally affordable; prices range from $100 to $300 depending on the brand and model. | Higher initial investment (upwards of $500) but can save costs over time with reduced fuel consumption. | Varies significantly based on installation; initial costs can be high, but long-term operational costs are low. |
| Ease of Implementation | Straightforward installation in most vehicles; widely available with established service networks. | Installation may require specialized knowledge; integration with existing systems can be complex. | Installation can be complicated and requires space for solar panels; not feasible for all vehicle types. |
| Maintenance | Minimal maintenance required; periodic inspections recommended. | Requires monitoring and potential replacement every 5-10 years; sensitive to temperature changes. | Low maintenance; however, solar panels may need cleaning and inspection for optimal performance. |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for standard vehicles relying on internal combustion engines; proven technology for reliable electrical supply. | Best for electric or hybrid vehicles aiming for sustainability; excellent for long-term energy savings. | Suitable for off-grid applications or specialized vehicles designed for renewable energy use. |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Lithium-Ion Battery Systems:
Lithium-ion battery systems have gained traction, particularly in electric and hybrid vehicles. They offer a higher energy density compared to traditional lead-acid batteries, which translates to longer driving ranges and less frequent recharging. However, their higher upfront cost and the need for complex integration with vehicle electronics can be drawbacks. Additionally, while they are efficient, their performance can degrade with extreme temperatures, which may be a concern in regions with fluctuating climates.
Solar-Powered Generators:
Solar-powered generators present an innovative alternative, harnessing renewable energy to power vehicle electrical systems. They can significantly reduce reliance on fossil fuels and lower operational costs over time. However, their effectiveness is largely dependent on sunlight availability, making them less reliable in regions with limited sun exposure. Installation can also be a hurdle, as it may require significant modifications to the vehicle and sufficient space for solar panels.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
Selecting the most suitable electrical solution for vehicles involves weighing various factors, including performance, cost, and maintenance. The traditional car alternator remains a robust choice for many vehicles, especially those relying on internal combustion engines. However, alternatives like lithium-ion battery systems and solar-powered generators can offer significant benefits in specific contexts, particularly for those prioritizing sustainability or operating in diverse environments. B2B buyers should consider their operational needs, budget constraints, and long-term goals when evaluating these options to ensure they choose the best solution for their unique circumstances.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for the car alternator
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Car Alternators?
Understanding the technical specifications of car alternators is crucial for B2B buyers, as it influences both performance and compatibility with various vehicle models. Here are some essential properties to consider:
1. Output Voltage
The output voltage of an alternator typically ranges from 12V to 14.5V. This voltage range is critical as it must be compatible with the vehicle’s electrical system. For international buyers, knowing the correct output voltage ensures that the alternator can efficiently power electrical components and recharge the battery without causing damage.
2. Amperage Rating
The amperage rating indicates the maximum electrical current the alternator can produce, usually measured in amps (A). A higher amperage rating is essential for vehicles with numerous electronic features, such as power windows and advanced audio systems. Buyers should assess the amperage needs based on the vehicle’s specifications to avoid underperformance or battery drain.
3. Size and Weight
Typically, alternators weigh between 10 to 20 pounds and are compact, roughly the size of a coconut. The size and weight are significant for compatibility with engine compartments. Buyers must ensure that the alternator fits within the designated space while maintaining the vehicle’s performance standards.
4. Material Composition
Most alternators are constructed from materials like aluminum and copper. Aluminum is lightweight and resistant to corrosion, while copper is essential for efficient electrical conductivity. Understanding the materials used can help buyers choose products that offer durability and reliability, especially in harsh environments.
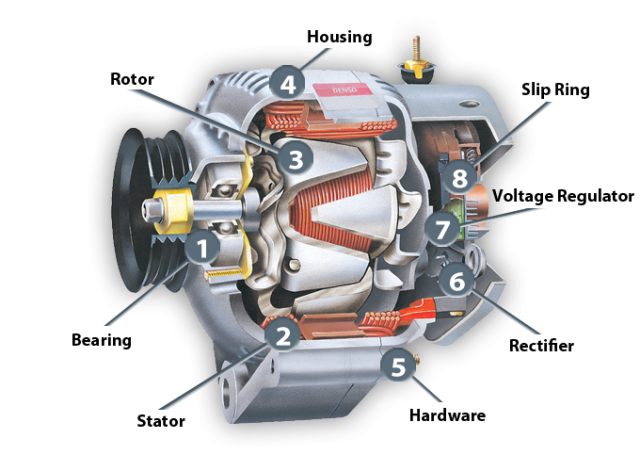
Illustrative image related to the car alternator
5. Cooling Mechanism
Alternators may include built-in cooling fans or venting systems to dissipate heat generated during operation. Effective cooling is crucial for maintaining performance and prolonging lifespan. Buyers should consider the cooling design when selecting alternators for vehicles that operate in hot climates or under heavy loads.
What Are Common Trade Terms Associated with Car Alternators?
Familiarity with industry terminology is essential for effective communication and negotiation in B2B transactions. Here are some common terms related to car alternators:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to parts made by the manufacturer of the original vehicle components. These parts often come with guarantees of quality and compatibility, making them a preferred choice for many buyers. Understanding OEM specifications is vital for ensuring that the alternators meet original performance standards.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell in a single order. For B2B buyers, knowing the MOQ helps in budgeting and inventory management. It’s essential to negotiate this term to align with business needs, especially in regions where demand may fluctuate.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to solicit pricing and terms for specific products. For alternators, including detailed specifications in an RFQ ensures that suppliers provide accurate quotes. This process is crucial for maintaining cost-effectiveness and ensuring the right product fit.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international trade, including shipping, risk, and costs. Understanding these terms is essential for B2B transactions involving alternators, as they dictate who bears the costs and risks during transportation, which is particularly important for international buyers from Africa, South America, and the Middle East.
5. Warranty Period
The warranty period refers to the time frame during which the manufacturer guarantees the alternator’s performance. This period can range from one year to several years, depending on the manufacturer. Buyers should assess warranty offerings to ensure they receive adequate protection against defects and failures.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing car alternators, ultimately enhancing operational efficiency and product reliability.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the the car alternator Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Car Alternator Sector?
The global car alternator market is experiencing significant growth driven by several factors, including the rising demand for electric vehicles (EVs), advancements in automotive technology, and an increasing focus on vehicle electrification. As countries move towards stricter emissions regulations, manufacturers are investing in efficient alternator designs that support hybrid and fully electric systems. This trend is particularly pronounced in Europe, where countries like Germany are leading the charge with innovative automotive solutions.
Emerging technologies, such as smart alternators and integrated power management systems, are reshaping how alternators function, offering benefits like improved fuel efficiency and better energy recovery. For international B2B buyers, particularly from Africa and South America, understanding these advancements is crucial for sourcing products that align with the future of automotive technology. The integration of digital solutions in the supply chain, such as IoT for performance monitoring, is also becoming prevalent, allowing companies to optimize their operations and reduce downtime.
Furthermore, the demand for aftermarket services and parts is on the rise as vehicle owners become more proactive about maintenance. This trend opens up opportunities for international suppliers to provide high-quality replacement parts and services, catering to markets that prioritize longevity and performance. Buyers should focus on suppliers that not only offer products but also support services to enhance vehicle performance and reliability.
How Are Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Shaping the Car Alternator Industry?
Sustainability is becoming increasingly important in the automotive sector, and the car alternator industry is no exception. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes and the sourcing of raw materials are under scrutiny, leading to a demand for ethical supply chains. B2B buyers are now more inclined to partner with manufacturers who prioritize sustainability, utilizing recycled materials and reducing waste in their production processes.
Ethical sourcing is also critical, as consumers and businesses alike are now more aware of the social and environmental implications of their purchases. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and adherence to the Responsible Business Alliance (RBA) standards are becoming essential indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability. B2B buyers should seek out suppliers who can demonstrate transparency in their supply chains, ensuring that the components used in alternators are sourced responsibly.
Moreover, the shift towards ‘green’ materials, such as biodegradable lubricants and recyclable components, is gaining traction. This not only helps in reducing the carbon footprint but also appeals to environmentally conscious consumers. Buyers looking to enhance their sustainability profile should prioritize partnerships with manufacturers that align with these eco-friendly initiatives.
What Is the Brief Evolution and History of Car Alternators Relevant to B2B Buyers?
The car alternator has evolved significantly since its inception in the early 20th century, transitioning from simple generators to sophisticated electrical components essential for modern vehicles. Initially, vehicles relied on DC generators that were less efficient and required frequent maintenance. The introduction of the alternator in the 1960s revolutionized automotive electrical systems by providing higher output at lower RPMs, thus enhancing reliability and performance.
As automotive technology advanced, so did the alternator, incorporating features like voltage regulation and improved cooling systems. This evolution has been driven by increasing electrical demands from modern vehicles, which now require power for a multitude of systems, including infotainment, safety features, and electric drivetrains. For B2B buyers, understanding this evolution is crucial, as it highlights the importance of sourcing high-quality, advanced alternators that meet contemporary performance standards while also considering future trends in electric and hybrid vehicles.
Overall, keeping abreast of these historical developments and current trends enables buyers to make informed decisions about sourcing and partnerships in the car alternator sector.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of the car alternator
-
How do I determine if an alternator is compatible with my vehicle?
To ensure compatibility, first consult your vehicle’s manual or specifications for the exact alternator model required. Look for the part number, voltage rating, and amperage output. You can also reach out to suppliers with these details; they often have databases to cross-reference parts. If sourcing internationally, confirm that the alternator meets your region’s electrical standards, such as voltage and frequency, to avoid operational issues. -
What are the key features to look for when sourcing car alternators?
When sourcing car alternators, prioritize features such as durability, output capacity, and warranty. Look for alternators made with high-quality materials that can withstand harsh driving conditions. Consider those with built-in voltage regulators for better performance and reliability. Additionally, inquire about customization options, such as color or branding, to meet your specific market needs. -
What is the typical lead time for ordering car alternators from international suppliers?
Lead times can vary significantly based on supplier location, production capacity, and shipping methods. Generally, you can expect anywhere from 4 to 12 weeks for delivery. It’s essential to discuss timelines upfront and factor in potential customs delays. Establishing a reliable relationship with suppliers can also lead to faster processing and delivery times, especially for repeat orders. -
How can I vet suppliers when sourcing car alternators?
To effectively vet suppliers, begin by checking their business credentials, including registration and certifications. Look for reviews or testimonials from other B2B buyers to gauge reliability. Request samples of the alternators to assess quality firsthand. Additionally, consider suppliers who can provide detailed product specifications and compliance certifications, especially for international standards, to ensure you are making a sound investment. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for car alternators?
Minimum order quantities can vary widely among suppliers, with some requiring as few as 10 units while others may set MOQs in the hundreds. Always clarify this upfront to avoid unexpected costs. If you are a new buyer or testing a market, inquire about flexible MOQ options or trial orders. Some suppliers may accommodate smaller orders with higher pricing or offer discounts on bulk purchases. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing car alternators internationally?
Payment terms can differ greatly depending on the supplier’s policies and your relationship with them. Common arrangements include upfront payments, deposits with balance upon shipment, or net payment terms (e.g., net 30 or net 60 days). It’s advisable to negotiate favorable terms, especially for larger orders. Always confirm the currency of payment and factor in any additional banking fees associated with international transactions. -
What quality assurance measures should I look for in car alternators?
Quality assurance is crucial when sourcing car alternators. Look for suppliers that adhere to international quality standards, such as ISO certification. Inquire about their testing processes, including electrical performance and durability tests. Request documentation of quality checks performed on the alternators prior to shipment. A good supplier should also offer warranties or guarantees to protect your investment against defects. -
How can I ensure timely logistics and shipping for my alternator orders?
To ensure timely logistics, communicate clearly with your supplier about your delivery requirements. Choose suppliers with established logistics partnerships for efficient shipping. Discuss shipping methods and timelines upfront, considering factors like air vs. sea freight and customs clearance. Additionally, work with freight forwarders familiar with international shipping to navigate any potential challenges, ensuring your alternators arrive on schedule.
Top 3 The Car Alternator Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Robert Basil – Alternators
Domain: robertbasilcars.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: The alternator sends power to the car’s electrical system when the vehicle is running. It works like a generator using the gas engine as an energy source. Common signs of a failing alternator include: battery warning light on the dashboard, dim headlights or interior lights, burning rubber smell, devices not charging, whining or screeching sounds, and inability to start the vehicle. The average li…
2. Paulding Chrysler Dodge Jeep Ram – Alternator Maintenance
Domain: pauldingchryslerdodgejeepram.net
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: This company, Paulding Chrysler Dodge Jeep Ram – Alternator Maintenance, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
3. Matthews Tire – Electrical System Check
Domain: matthewstire.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: Matthews Tire offers a complete electrical system check for just $39.95. They provide services related to battery and alternator health, including wiring a battery tender to keep vehicles charged. The average life of a battery is 4-5 years, and they emphasize the importance of regular vehicle use to maintain battery health.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for the car alternator
In navigating the complexities of the automotive supply chain, strategic sourcing of car alternators presents a significant opportunity for international B2B buyers. Understanding the critical role that alternators play in vehicle performance and the factors influencing their longevity is essential for making informed procurement decisions. As alternators typically have a lifespan of 60,000 to 150,000 miles, sourcing high-quality components can minimize operational disruptions and enhance customer satisfaction.
Investing in reputable manufacturers and suppliers ensures that businesses can rely on durable, efficient alternators that meet their specific needs. Furthermore, maintaining awareness of emerging technologies and trends, such as advancements in alternator design and electric vehicle integration, will empower buyers to stay ahead in a competitive market.
Looking ahead, the demand for reliable alternators is poised to grow, driven by increasing vehicle ownership and the shift towards sustainable energy solutions. As you consider your sourcing strategies, prioritize partnerships that align with your business objectives and regional market dynamics. Engage with suppliers who can provide not only quality products but also insights into the evolving automotive landscape, ensuring your business remains resilient and innovative in the years to come.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.