Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for parts of a car alternator
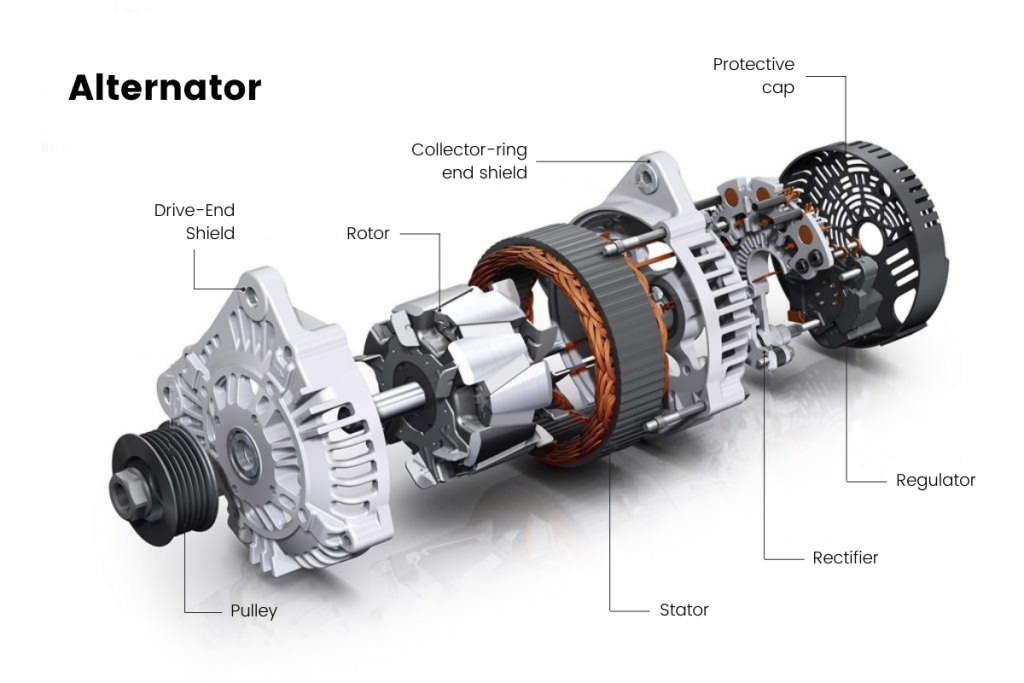
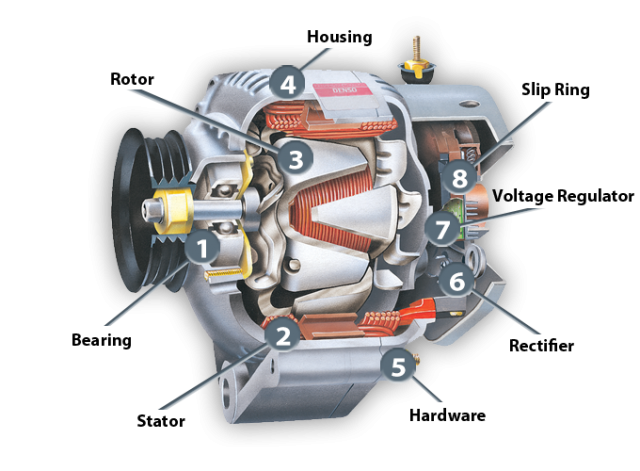
In the competitive landscape of automotive parts, sourcing reliable components, particularly for car alternators, poses a significant challenge for international B2B buyers. The alternator, a crucial device that converts mechanical energy into electrical power, consists of various intricate parts such as rotors, stators, rectifiers, and voltage regulators. Understanding these components and their functionalities is essential for ensuring optimal performance in vehicles, making it imperative for buyers to be well-informed.
This comprehensive guide delves into the myriad parts of a car alternator, exploring their types, applications, and the critical role they play in automotive systems. It also offers insights into effective supplier vetting processes, cost considerations, and potential sourcing strategies tailored to different global markets, including Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. By equipping B2B buyers with actionable knowledge and practical tips, this guide empowers them to make informed purchasing decisions that align with their operational needs and budget constraints.
Whether you are a distributor in Nigeria navigating supplier relationships or a manufacturer in Germany seeking cost-effective alternatives, this resource serves as a valuable tool in your procurement strategy. With a focus on enhancing efficiency and reliability in automotive operations, understanding the global market for alternator parts can significantly impact your bottom line and overall success.
Table Of Contents
- Top 2 Parts Of A Car Alternator Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for parts of a car alternator
- Understanding parts of a car alternator Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of parts of a car alternator
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘parts of a car alternator’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for parts of a car alternator
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for parts of a car alternator
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘parts of a car alternator’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for parts of a car alternator Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing parts of a car alternator With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for parts of a car alternator
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the parts of a car alternator Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of parts of a car alternator
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for parts of a car alternator
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
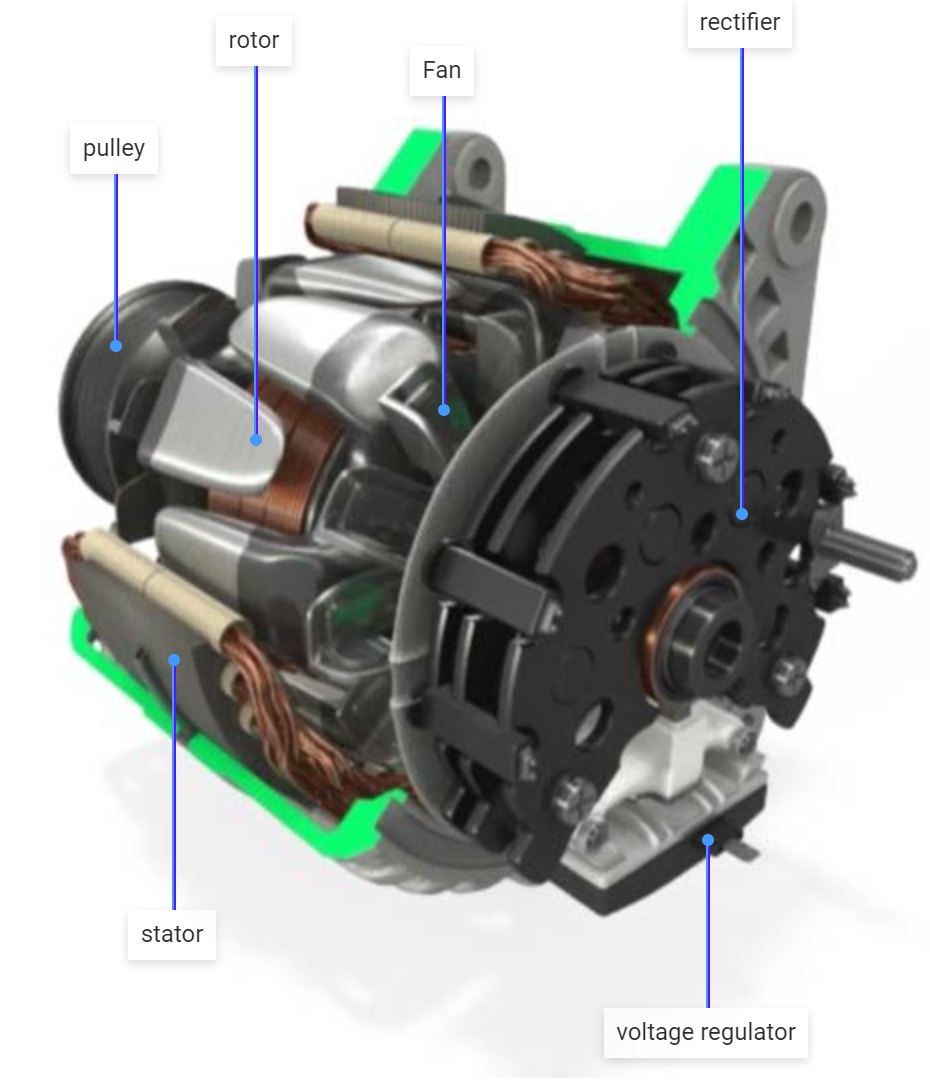
Understanding parts of a car alternator Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rotor | Rotates to create a magnetic field; contains finger poles | Automotive manufacturing, aftermarket parts | Pros: Essential for power generation; Cons: Requires precise fit to ensure optimal performance. |
| Stator | Static component with insulated windings; converts AC to DC | Automotive, marine, and industrial applications | Pros: Durable and reliable; Cons: Can be costly to replace if damaged. |
| Rectifier | Converts AC to DC; consists of diodes | Electrical systems in vehicles, generators | Pros: Essential for battery charging; Cons: May require frequent maintenance in high-load applications. |
| Voltage Regulator | Balances voltage output; prevents overcharging | Automotive, heavy machinery, and power supplies | Pros: Protects electrical systems; Cons: Failure can lead to system overload. |
| Clutch Pulley | Engages and disengages drive belt; improves efficiency | Automotive, especially in hybrid vehicles | Pros: Enhances fuel efficiency; Cons: Complex installation can increase labor costs. |
What Are the Characteristics of a Rotor in an Alternator?
The rotor is a critical part of the alternator, responsible for creating the electromagnetic field necessary for power generation. It typically features finger poles that rotate around the stator, inducing voltage. In B2B applications, understanding the rotor’s specifications—such as size, weight, and material—is crucial for ensuring compatibility with various vehicle models. Buyers should consider the rotor’s efficiency and durability, as these factors directly impact the overall performance of the alternator.
How Does the Stator Function in an Alternator?
The stator serves as the stationary counterpart to the rotor, containing insulated windings that convert the alternating current (AC) produced by the rotor into direct current (DC). This conversion is vital for the electrical systems in vehicles. In B2B purchasing, companies should focus on the stator’s build quality and insulation properties, as these will affect the longevity and reliability of the alternator. A robust stator can withstand high temperatures and electrical stresses, making it a worthwhile investment.
Why is a Rectifier Important in an Alternator?
The rectifier is essential for converting the AC generated by the rotor and stator into DC, which is necessary for charging the vehicle’s battery and powering its electrical systems. It typically comprises diodes that can handle varying current loads. B2B buyers should evaluate the rectifier’s capacity and efficiency, as a high-quality rectifier minimizes energy loss and ensures consistent power delivery. Regular maintenance and timely replacement are crucial to avoid system failures.
What Role Does a Voltage Regulator Play in an Alternator?
The voltage regulator is responsible for maintaining a consistent voltage level, preventing overcharging and damage to the vehicle’s electrical systems. It adjusts the output based on the vehicle’s power demands. For B2B buyers, understanding the regulator’s specifications, such as voltage range and response time, is vital for selecting the right part. A reliable voltage regulator can enhance the lifespan of electrical components, making it a critical investment for fleet operators and automotive manufacturers.
How Does a Clutch Pulley Enhance Alternator Efficiency?
The clutch pulley is designed to engage and disengage the drive belt, optimizing the alternator’s performance based on the engine’s operational needs. This component is especially important in hybrid vehicles, where efficiency is paramount. B2B buyers should consider the clutch pulley’s design and compatibility with existing systems. While it can improve fuel efficiency and reduce wear, the complexity of installation may lead to higher labor costs, which should be factored into purchasing decisions.
Key Industrial Applications of parts of a car alternator
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of parts of a car alternator | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive Manufacturing | Integration of alternators in electric and hybrid vehicles | Enhances vehicle performance and energy efficiency | Quality control, compliance with international standards |
| Heavy Equipment | Use of alternators in construction machinery | Provides reliable power supply for heavy machinery | Durability under harsh conditions, sourcing local suppliers |
| Renewable Energy | Alternators in wind turbine systems | Converts mechanical energy into electrical energy | Efficiency ratings, compatibility with existing systems |
| Marine Industry | Alternators for powering onboard electrical systems | Ensures reliability and efficiency in marine applications | Resistance to corrosion, compliance with maritime regulations |
| Automotive Repair and Aftermarket | Replacement parts for vehicle alternators in repair shops | Ensures customer satisfaction and vehicle reliability | Availability of parts, warranty and service support |
How Are Parts of a Car Alternator Used in Automotive Manufacturing?
In the automotive manufacturing sector, parts of a car alternator are crucial for integrating efficient power generation in electric and hybrid vehicles. The alternator converts mechanical energy from the engine into electrical energy, ensuring that batteries are charged and that electrical systems function optimally. This not only enhances vehicle performance but also contributes to energy efficiency, aligning with global sustainability trends. For international buyers, especially in regions like Europe and South America, sourcing high-quality alternators that meet stringent regulatory standards is essential for maintaining competitiveness.
What Role Do Alternator Parts Play in Heavy Equipment?
In the heavy equipment industry, alternators are integral to construction machinery, providing a reliable power supply essential for operations. These components ensure that machinery, such as excavators and bulldozers, can function effectively in demanding environments. The durability of alternator parts is critical, as they must withstand harsh conditions. Buyers in Africa and the Middle East should focus on sourcing alternators that are robust and capable of performing under extreme temperatures and dust, ensuring longevity and reduced maintenance costs.
How Are Alternators Utilized in Renewable Energy Applications?
In renewable energy sectors, particularly wind energy, alternators convert mechanical energy generated by wind turbines into electrical energy. This conversion is vital for integrating renewable sources into the electrical grid, promoting sustainability. Businesses involved in this sector must prioritize efficiency ratings of alternators, ensuring they can operate effectively at varying wind speeds. International buyers should also consider the compatibility of these alternators with existing energy systems to maximize investment returns.
Why Are Alternators Important in the Marine Industry?
The marine industry relies on alternators to power onboard electrical systems, which are critical for navigation, communication, and safety. The reliability of these systems is paramount in ensuring safe operations at sea. Marine alternators must be resistant to corrosion due to the harsh saltwater environment. Buyers in this sector need to ensure that the alternators they source comply with maritime regulations and are designed to withstand extreme conditions, thus ensuring operational reliability.
What Is the Importance of Alternator Parts in Automotive Repair and Aftermarket Services?
In the automotive repair and aftermarket sector, the availability of high-quality replacement parts for alternators is essential for maintaining vehicle reliability and customer satisfaction. Repair shops depend on dependable alternators to ensure that vehicles are restored to optimal performance levels. For B2B buyers, factors such as the availability of parts, warranty provisions, and service support are critical when sourcing alternators, particularly in competitive markets like Germany and Nigeria, where customer expectations are high.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘parts of a car alternator’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Sourcing Quality Alternator Parts
The Problem: B2B buyers often face challenges in sourcing high-quality alternator parts that meet industry standards. This difficulty can arise from a lack of reliable suppliers, especially in regions where automotive parts distribution networks are underdeveloped. Buyers may receive subpar components that do not fit specifications or that fail prematurely, leading to increased operational costs and downtime.
The Solution: To overcome this issue, B2B buyers should establish relationships with reputable manufacturers and suppliers known for their quality control and certification standards. Conduct thorough research on potential suppliers by reviewing their track records, seeking client testimonials, and verifying their compliance with international automotive standards such as ISO/TS 16949. Furthermore, buyers should consider implementing a robust supplier evaluation process that includes quality audits and performance metrics to ensure they consistently receive high-quality alternator parts. Leveraging technology, such as supplier management software, can also streamline this process and enhance communication with suppliers.
Scenario 2: Compatibility Issues with Alternator Components
The Problem: Another common pain point is compatibility issues between different parts of the alternator, especially when dealing with multiple car models. B2B buyers often find themselves in situations where they purchase components that do not fit or work well together, leading to inefficiencies and additional costs for returns and replacements.
The Solution: To avoid compatibility issues, buyers must invest time in understanding the specifications and compatibility of the alternator components they are sourcing. This includes detailed knowledge of vehicle makes and models as well as the specific alternator parts needed (e.g., rotor, stator, voltage regulator). Buyers should utilize detailed product catalogs and technical datasheets from manufacturers, which provide critical information about compatibility. Engaging with knowledgeable technical support teams from suppliers can also provide insights into which parts are interchangeable or specific to certain models. Additionally, using software tools for inventory management that track part specifications and compatibility can help streamline the ordering process and reduce errors.
Scenario 3: Inefficient Voltage Regulation Leading to System Failures
The Problem: Voltage regulation is a crucial aspect of alternator functionality, and many B2B buyers encounter issues with voltage regulators that do not maintain consistent power output. This can lead to electrical failures in vehicles, negatively impacting customer satisfaction and increasing warranty claims. In markets where electrical systems are sensitive, the inability to maintain stable voltage can be particularly problematic.
The Solution: To address voltage regulation issues, buyers should prioritize sourcing high-quality voltage regulators from reputable manufacturers that offer robust testing and validation processes. It is vital to educate the purchasing team on the importance of voltage regulator specifications, such as the voltage output range and response time. Implementing a proactive maintenance strategy can also help identify voltage regulation issues early. Regular inspections and testing of the alternator systems, particularly the voltage regulators, can detect problems before they escalate. Additionally, collaborating with automotive engineers during the sourcing process can provide insights into the latest technologies and innovations in voltage regulation, ensuring that buyers invest in the most effective solutions for their needs.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for parts of a car alternator
What Materials Are Commonly Used in Car Alternator Components?
In the manufacturing of car alternators, material selection is critical to ensure performance, durability, and compliance with international standards. Below, we analyze four common materials used in various parts of a car alternator: aluminum, copper, steel, and plastic.
How Does Aluminum Benefit Alternator Housing and Components?
Aluminum is widely used for the outer housing of alternators due to its lightweight and non-magnetic properties. It effectively dissipates heat generated during operation, which is crucial for maintaining efficiency. The temperature rating of aluminum can handle high operational temperatures, making it suitable for automotive applications.
Pros: Aluminum is durable, resistant to corrosion, and offers excellent thermal conductivity, which helps in heat management. It is relatively inexpensive and easy to manufacture, allowing for cost-effective production.
Cons: While aluminum is strong, it is less robust compared to steel and can be prone to deformation under extreme conditions. Its manufacturing process may involve additional steps to enhance strength, which can increase complexity.
Impact on Application: Aluminum’s compatibility with various automotive fluids and its lightweight nature contribute to improved fuel efficiency. However, international buyers should ensure compliance with standards such as ASTM B221 for aluminum extrusions.
Why is Copper Essential for Electrical Conductivity in Alternators?
Copper is the preferred material for electrical windings, including the rotor and stator coils, due to its excellent electrical conductivity. It can handle high current loads, essential for the alternator’s functionality in charging the battery and powering electrical systems.
Pros: Copper’s high conductivity results in lower energy losses, enhancing the overall efficiency of the alternator. It is also highly ductile, allowing for intricate winding designs.
Cons: The primary drawback of copper is its susceptibility to corrosion, particularly in environments with high moisture or salt exposure. Additionally, copper is more expensive than aluminum, which may affect overall production costs.
Impact on Application: Copper’s performance is critical in high-demand applications, such as in regions with extreme climates. Buyers in humid or coastal areas should consider corrosion-resistant coatings or alloys to prolong the lifespan of copper components.
How Does Steel Contribute to the Durability of Alternator Components?
Steel is often used in components that require high strength and durability, such as the rotor shaft and bearings. Its ability to withstand mechanical stress makes it indispensable in ensuring the alternator operates efficiently under various load conditions.
Illustrative image related to parts of a car alternator
Pros: Steel is robust and can handle high operational pressures and temperatures. It is also relatively cost-effective compared to other metals, making it a popular choice for manufacturers.
Cons: Steel is heavier than aluminum and can be prone to rust if not properly treated. The manufacturing process for steel components can be more complex, requiring additional steps for surface treatment.
Impact on Application: Steel’s strength is essential for components subjected to mechanical stress, particularly in rugged terrains. Buyers should ensure compliance with standards such as DIN EN 10025 for structural steel to guarantee quality.
What Role Does Plastic Play in Alternator Design?
Plastic is commonly used for non-load-bearing components, such as housings for electrical connectors and insulation for wiring. Its lightweight nature and versatility make it an attractive option for reducing overall weight.
Illustrative image related to parts of a car alternator
Pros: Plastic is resistant to corrosion and can be molded into complex shapes, allowing for design flexibility. It is also cost-effective, contributing to lower manufacturing costs.
Cons: Plastic may not withstand high temperatures as effectively as metals, which can lead to deformation over time. Its mechanical strength is also lower compared to metals, limiting its use to specific applications.
Impact on Application: The use of plastic can help in reducing the overall weight of the alternator, improving fuel efficiency. International buyers should consider compliance with standards like ISO 9001 for quality management systems.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Car Alternators
| Material | Typical Use Case for parts of a car alternator | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Outer housing, cooling fans | Lightweight and excellent heat dissipation | Less robust than steel | Medium |
| Copper | Rotor and stator windings | High electrical conductivity | Susceptible to corrosion | High |
| Steel | Rotor shaft, bearings | High strength and durability | Heavier and prone to rust | Medium |
| Plastic | Electrical connectors, insulation | Corrosion-resistant and cost-effective | Lower temperature tolerance | Low |
This strategic material selection guide provides insights that can help international B2B buyers make informed decisions when sourcing components for car alternators, ensuring compliance with regional standards and optimizing performance.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for parts of a car alternator
What Are the Key Manufacturing Processes for Car Alternator Parts?
The manufacturing of car alternator parts is a meticulous process that involves several stages, each critical to ensuring the efficiency and reliability of the final product. Here’s an overview of the main stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How is Material Prepared for Alternator Components?
Material preparation is the foundational step in manufacturing alternator parts. Typically, high-grade aluminum and copper are chosen for their lightweight and conductive properties.
-
Material Selection: Choosing the right materials is crucial. Aluminum is favored for the housing due to its heat dissipation and non-magnetizing properties, while copper is used for windings due to its excellent conductivity.
-
Material Treatment: The selected materials undergo treatments such as anodizing or coating to enhance their corrosion resistance and durability. This step is vital for components exposed to high temperatures and varying environmental conditions.
-
Quality Control: Before proceeding, materials are subjected to incoming quality control (IQC) checks to ensure they meet specified standards, including dimensional accuracy and material integrity.
What Forming Techniques Are Used in Manufacturing Alternator Parts?
Once materials are prepared, they undergo various forming techniques to shape them into the necessary components.
-
Casting and Machining: The aluminum housing is typically cast using sand or die-casting techniques. This is followed by precision machining to achieve the required tolerances and surface finishes.
-
Stator and Rotor Formation: The rotor is formed by winding copper wire around a laminated core, which is crucial for generating the electromagnetic field. Techniques such as automatic winding machines are often employed to ensure uniformity and efficiency.
-
Assembly of Electromechanical Components: Components such as slip rings, brushes, and rectifiers are assembled with precision. Automated assembly lines may be used to enhance efficiency and reduce human error.
How Are Alternator Parts Assembled?
The assembly stage integrates all the manufactured components into a complete alternator.
-
Component Integration: The rotor is fitted within the stator, and the assembly is secured with precise alignments to ensure optimal performance.
-
Installation of Electrical Components: The voltage regulator, rectifier, and other electrical components are installed during this stage. Each component must be correctly positioned to ensure the alternator functions as intended.
-
Final Assembly Checks: Quality checks are performed at various points during the assembly process to catch defects early. This includes verifying the alignment of components and ensuring that all electrical connections are secure.
What Finishing Processes Are Applied to Alternator Parts?
Finishing processes enhance the durability and aesthetic appeal of alternator parts.
-
Surface Treatments: Final treatments such as painting or powder coating are applied to the exterior of the alternator to prevent corrosion and enhance visual appeal.
-
Quality Assurance Testing: After finishing, components undergo rigorous testing. This includes electrical testing to ensure proper functionality and durability tests to simulate operational conditions.
-
Packaging and Labeling: Proper packaging is essential to prevent damage during transportation. Components are labeled according to international standards for easy identification and compliance.
How is Quality Assurance Implemented in Alternator Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is integral to the manufacturing process, ensuring that each alternator meets international standards and customer expectations.
What International Standards Should B2B Buyers Consider?
B2B buyers should be aware of various international quality standards that govern manufacturing processes:
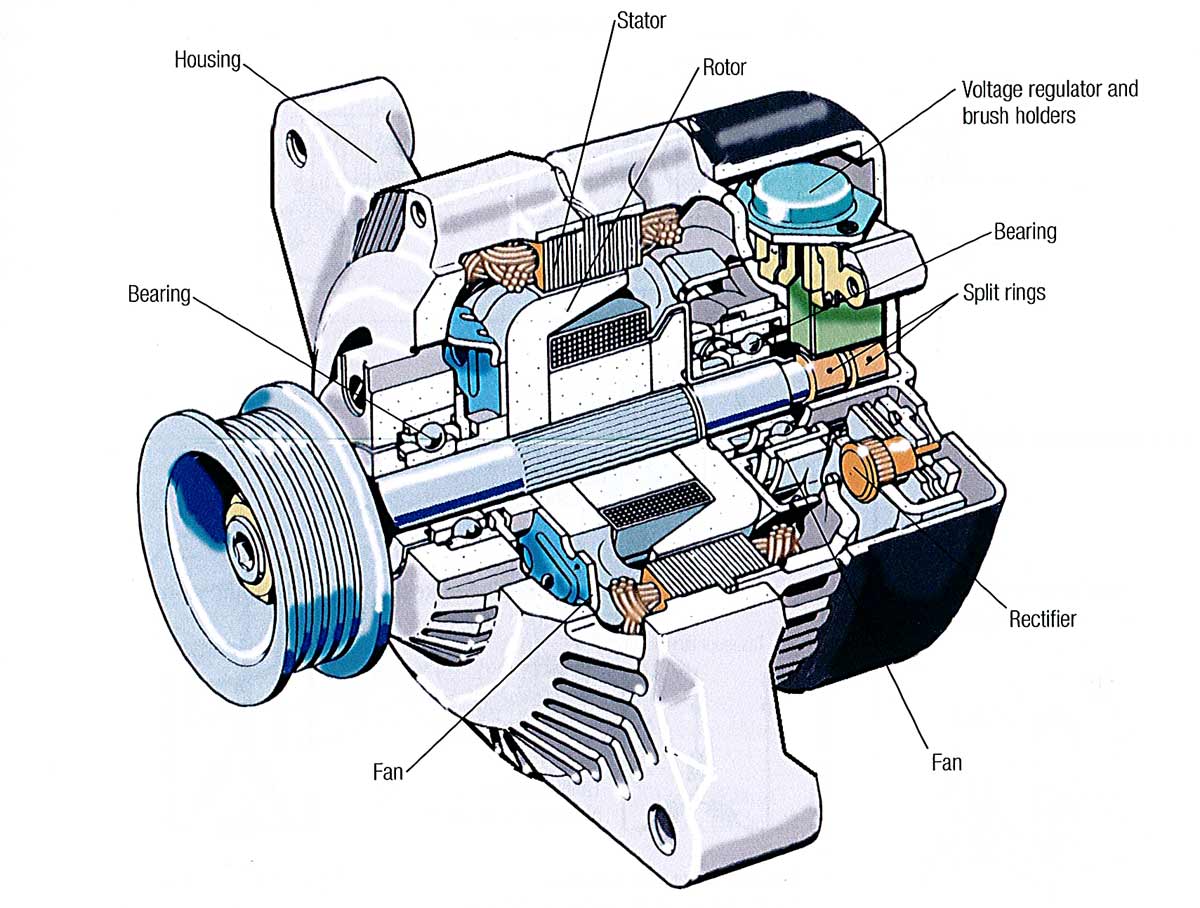
Illustrative image related to parts of a car alternator
-
ISO 9001: This widely recognized standard outlines the requirements for a quality management system (QMS). Manufacturers must demonstrate their ability to consistently provide products that meet customer and regulatory requirements.
-
CE Marking: For products sold in Europe, CE marking indicates compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards. B2B buyers should verify that suppliers have the necessary certifications.
-
API Standards: For buyers in specific markets, such as the oil and gas sector, compliance with American Petroleum Institute (API) standards may be relevant.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control checkpoints are crucial throughout the manufacturing process:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint assesses raw materials for compliance with specifications before they enter production.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, IPQC ensures that each stage meets quality standards. This may involve monitoring machine calibration, alignment, and material integrity.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After assembly, FQC tests the complete alternator for performance, electrical output, and durability. This stage is essential to guarantee the product’s reliability before it reaches the market.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used for Quality Assurance?
Several testing methods are employed to verify the quality of alternator parts:
-
Electrical Testing: This includes testing the output voltage, current, and efficiency of the alternator. Any discrepancies can indicate issues with assembly or component integrity.
-
Thermal Testing: Alternators are subjected to thermal cycling tests to ensure they can withstand the heat generated during operation without failure.
-
Vibration and Noise Testing: These tests simulate real-world operating conditions, helping to identify potential mechanical failures.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international buyers, especially from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying supplier quality control is essential.
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting regular audits of suppliers can provide insights into their manufacturing processes and quality control measures. Audits should assess compliance with international standards and internal quality protocols.
-
Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports, including IQC, IPQC, and FQC results, can help buyers understand the supplier’s commitment to quality.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control processes and product reliability.
What Quality Control Nuances Should International Buyers Be Aware Of?
International buyers must navigate various nuances in quality control that can affect procurement:
-
Cultural Differences: Understanding cultural attitudes toward quality and compliance can influence supplier relationships. Open communication about quality expectations is essential.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Different regions may have varying regulatory requirements. Buyers should ensure that suppliers can meet specific local and international regulations.
-
Logistics Considerations: Shipping and handling can affect product integrity. Buyers should discuss packaging and transportation protocols with suppliers to mitigate risks during transit.
By understanding these manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices, B2B buyers can make informed decisions and establish reliable partnerships with alternator part manufacturers, ensuring they receive high-quality products that meet their operational needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘parts of a car alternator’
In the competitive landscape of automotive parts sourcing, particularly for car alternators, having a systematic approach is essential. This guide offers a detailed checklist for B2B buyers to streamline the procurement process, ensuring that you acquire high-quality alternator components that meet your operational needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is crucial to ensure compatibility and performance of the alternator parts. Consider factors such as the vehicle make and model, electrical requirements, and specific part attributes (e.g., size, material, and voltage ratings). This step minimizes the risk of sourcing incompatible components, which can lead to costly delays and repairs.
Step 2: Research Market Trends and Standards
Stay informed about the latest trends and standards in alternator technology. Understanding advancements such as improved efficiency, lightweight materials, and eco-friendly components can help you make informed decisions. Look for certifications like ISO or SAE that indicate compliance with international quality standards.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a supplier, thorough vetting is essential. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from other clients in your industry or region. Assess their reputation, reliability, and customer service quality. Be wary of suppliers who cannot provide evidence of their credibility or past performance.
- Tip: Utilize platforms such as LinkedIn or industry-specific forums to gather insights about potential suppliers.
Step 4: Request Samples for Quality Assessment
Obtaining samples of the alternator parts you intend to procure is a vital step in evaluating quality. Inspect the samples for craftsmanship, material durability, and compliance with your technical specifications. This hands-on assessment allows you to gauge whether the parts meet your expectations before making a bulk purchase.
Step 5: Negotiate Pricing and Terms
Once you have identified suitable suppliers and evaluated samples, engage in price negotiations. Aim for a balance between cost-effectiveness and quality assurance. Discuss payment terms, delivery schedules, and warranty options to ensure a comprehensive agreement that safeguards your interests.
- Tip: Consider the total cost of ownership, including shipping and potential tariffs, especially when sourcing from international suppliers.
Step 6: Verify After-Sales Support and Warranty Options
Before finalizing your order, confirm the supplier’s after-sales support and warranty terms. A reliable supplier should provide assistance with installation, troubleshooting, and potential returns. Understanding warranty coverage will also help protect your investment against defects or performance issues.
Step 7: Establish a Long-Term Relationship
Building a long-term partnership with your chosen supplier can lead to more favorable terms and faster service in the future. Maintain open lines of communication and provide feedback on product performance. A strong relationship can facilitate better pricing, priority support, and access to new products as they emerge in the market.
By following these steps, B2B buyers can effectively navigate the complexities of sourcing parts for car alternators, ensuring they secure high-quality components that meet their operational demands.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for parts of a car alternator Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Alternator Parts?
When sourcing parts for car alternators, understanding the cost structure is crucial for effective budgeting and pricing strategy. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margins.
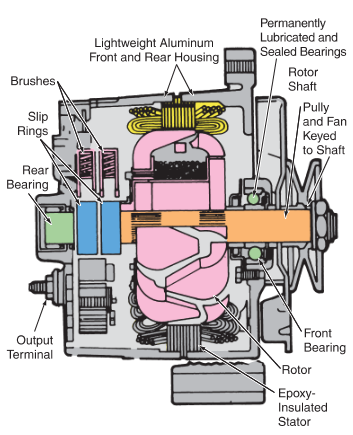
Illustrative image related to parts of a car alternator
Materials make up a significant portion of the total cost, with aluminum being a common choice for housing due to its lightweight and heat-dissipating properties. Additionally, components like the rotor, stator, diode rectifier, and voltage regulator utilize various metals and electrical materials, which can fluctuate in price based on market demand and availability.
Labor costs vary widely depending on the region of sourcing. In regions like Africa and South America, labor may be less expensive, but this can be offset by other costs like logistics.
Manufacturing overhead encompasses the indirect costs associated with production, such as utilities and maintenance of machinery. These can be higher in regions with less developed infrastructure.
Tooling costs relate to the initial investment in molds and machinery specific to the production of alternator parts. This is a one-time cost but can be significant, especially for customized components.
Quality control is essential in ensuring that parts meet industry standards and regulations. The cost of QC can vary based on the complexity of the components and the certifications required, which are increasingly important for international buyers.
Logistics costs include transportation and warehousing, which can be considerable, especially for international shipments. Factors like Incoterms influence these costs, determining who is responsible for shipping and insurance.
Profit margins for suppliers can vary significantly based on the competitive landscape and the supplier’s value proposition, including quality and service levels.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Alternator Parts Sourcing?
Several factors influence the pricing of alternator parts, which are crucial for B2B buyers to consider. Volume or Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ) plays a significant role; larger orders often yield lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale.
Specifications and customization requirements can also impact pricing. Custom parts may necessitate additional tooling and longer lead times, leading to higher costs.
Material quality and certifications are paramount, especially for international buyers. Parts that meet stringent quality standards may cost more but can reduce warranty claims and enhance customer satisfaction.
Supplier factors such as reputation, reliability, and service level can also influence pricing. Established suppliers with a proven track record may command higher prices, but they often provide better support and reliability.
What Buyer Tips Can Help Negotiate Better Prices for Alternator Parts?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, effective negotiation and strategic purchasing can lead to significant savings.
Negotiation tactics should focus on building long-term relationships with suppliers, which can lead to better pricing and terms over time. Understanding the supplier’s cost structure can also provide leverage during negotiations.
Cost-efficiency should be evaluated beyond the initial price. Consider the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), which includes maintenance, potential downtime, and warranty claims. Investing in higher-quality parts may result in lower TCO over time.
Pricing nuances for international transactions can involve currency fluctuations and additional costs like tariffs and duties. Being aware of these factors can help in making informed purchasing decisions.
Lastly, always request indicative pricing and quotes from multiple suppliers to compare costs effectively. This will provide leverage in negotiations and help ensure that you are receiving a competitive price for the parts needed.
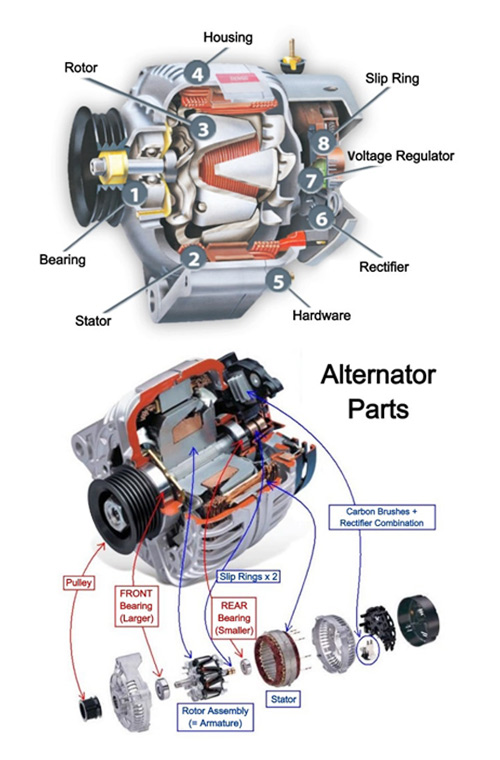
Illustrative image related to parts of a car alternator
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing parts of a car alternator With Other Solutions
Alternatives in automotive electrical solutions can significantly impact vehicle performance, reliability, and operational costs. Understanding how the parts of a car alternator stack up against alternative technologies is crucial for international B2B buyers. This analysis will focus on comparing the traditional alternator components with two viable alternatives: the DC generator and the battery management system (BMS).
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Parts of a Car Alternator | DC Generator | Battery Management System (BMS) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High efficiency in power generation, maintains battery charge effectively | Moderate, less efficient than alternators | High, optimizes battery life and efficiency |
| Cost | Moderate upfront costs, but long-term savings on maintenance | Generally lower initial cost, but higher maintenance | Higher initial investment, cost-effective in long run |
| Ease of Implementation | Standard installation in most vehicles | Requires adaptation for modern vehicles | Complex integration with existing systems |
| Maintenance | Regular checks required, generally low maintenance | Higher maintenance needs due to mechanical components | Minimal maintenance, software updates required |
| Best Use Case | Conventional vehicles needing reliable electrical supply | Older vehicles or industrial applications | Electric vehicles and modern battery systems |
In-Depth Analysis of Alternatives
DC Generator
DC generators have been a traditional source of electrical power, especially in older vehicles. Their initial costs are generally lower than those of alternators, making them attractive for budget-conscious buyers. However, they are less efficient in power generation compared to modern alternators. Maintenance is a significant drawback; mechanical parts require frequent attention to ensure optimal performance. While DC generators may serve well in specific applications, they are often unsuitable for newer vehicles that demand higher efficiency and reliability.
Battery Management System (BMS)
A Battery Management System is increasingly popular, especially in electric vehicles and hybrids. BMS technology optimizes battery performance, ensuring longer life and better efficiency. Although the initial investment is higher than that of traditional alternators, the long-term savings on battery replacement and energy efficiency can justify the cost. The complexity of integrating a BMS into existing systems can pose challenges during installation, but its minimal maintenance requirements and advanced features make it a worthwhile consideration for businesses focused on sustainability and operational efficiency.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Needs
When selecting the right electrical power solution for your vehicles, consider the specific requirements of your operation. If your fleet consists of conventional vehicles and you prioritize reliability and low maintenance, parts of a car alternator remain the optimal choice. However, for businesses looking towards the future with electric or hybrid vehicles, investing in a Battery Management System may provide long-term benefits in efficiency and cost-effectiveness. Understanding your operational needs and budget will guide your decision in choosing the most suitable technology for your fleet, ensuring you remain competitive in the evolving automotive landscape.
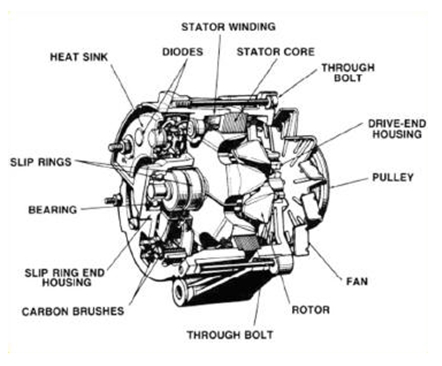
Illustrative image related to parts of a car alternator
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for parts of a car alternator
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Car Alternator Parts?
When sourcing parts for car alternators, understanding specific technical properties is essential for ensuring compatibility, performance, and durability. Here are some critical specifications that international B2B buyers should consider:
-
Material Grade:
The outer housing of most alternators is typically made from aluminum due to its lightweight and non-magnetic properties. This material facilitates efficient heat dissipation, essential for maintaining performance under high loads. Buyers should verify the aluminum grade used, as it impacts the alternator’s resistance to corrosion and mechanical stress. -
Electrical Resistance:
Components such as the rotor, stator, and rectifier must have specific electrical resistance values to ensure efficient power generation and conversion. High-quality materials should be selected to minimize losses and maintain optimal conductivity. Understanding resistance specifications can help buyers select parts that enhance performance and reduce energy waste. -
Tolerance Levels:
Tolerance refers to the allowable variation in dimensions of component parts. For alternators, tight tolerances between the rotor and stator are critical for preventing mechanical failure and ensuring effective electromagnetic induction. Buyers should seek manufacturers that can guarantee precise tolerances to enhance reliability and longevity. -
Temperature Ratings:
Alternators operate in varying temperature conditions, and the materials used must withstand these fluctuations. Components like the voltage regulator and diode rectifier should have specified temperature ratings to ensure they function correctly without degradation. Buyers should ensure that parts can handle the thermal stress typical in automotive applications. -
Voltage and Current Ratings:
Each alternator part must have defined voltage and current ratings to ensure compatibility with the vehicle’s electrical system. This specification is crucial for safety and performance. B2B buyers should confirm that the alternator parts meet or exceed the required specifications to prevent electrical failures.
What Are Common Trade Terminology and Jargon in the Alternator Parts Industry?
Familiarity with industry-specific terms can streamline the purchasing process and improve communication between buyers and suppliers. Here are some common terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer):
OEM parts are components made by the original manufacturer of the vehicle. They guarantee compatibility and quality, making them a preferred choice for many buyers. Understanding the difference between OEM and aftermarket parts is crucial for ensuring reliability. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity):
MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is significant for B2B buyers, as understanding MOQ can impact inventory management and cash flow. Buyers should negotiate MOQs that align with their operational needs. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation):
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to request pricing and terms for specific products. Utilizing RFQs helps buyers compare costs and terms from multiple suppliers, ensuring they get the best deal. -
Incoterms:
International Commercial Terms (Incoterms) are a set of rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with these terms can help buyers understand shipping costs, risk management, and delivery obligations. -
Lead Time:
Lead time is the duration from the placement of an order to its delivery. Understanding lead times is essential for inventory planning and meeting production schedules, especially in international supply chains. -
Warranty Period:
This term refers to the time frame during which the manufacturer guarantees the performance and quality of the part. Knowing the warranty period helps buyers assess risk and make informed purchasing decisions.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terminologies, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing car alternator parts, ultimately leading to better performance and satisfaction in their operations.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the parts of a car alternator Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Parts of a Car Alternator Sector?
The global market for car alternator parts is experiencing significant growth, driven by the increasing demand for vehicles, especially in emerging economies across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Factors such as urbanization, rising disposable incomes, and a growing middle class are propelling vehicle ownership in these regions. Additionally, advancements in automotive technology, such as the shift towards electric and hybrid vehicles, are creating new opportunities for alternator manufacturers.
B2B tech trends are reshaping the sourcing landscape, with digital platforms facilitating real-time procurement processes and enhancing transparency in supply chains. International buyers are increasingly leveraging data analytics to assess supplier reliability and product quality, ensuring they source components that meet stringent performance criteria. Additionally, automation in manufacturing is streamlining production, reducing costs, and improving turnaround times, making it essential for buyers to stay informed about supplier capabilities and technological advancements.
Moreover, the rise of e-commerce has simplified the sourcing of alternator parts, enabling buyers to access a wider range of suppliers and compare prices with ease. This trend is particularly beneficial for international buyers from regions like Nigeria and Germany, where sourcing high-quality components at competitive prices is crucial for maintaining profitability.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impacting the Alternator Parts Market?
The automotive industry’s environmental impact is prompting a shift towards sustainable practices in the production of alternator parts. B2B buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers that adopt eco-friendly manufacturing processes and materials. This includes sourcing components made from recycled or sustainably sourced materials, which not only minimizes waste but also reduces the carbon footprint associated with production.
Ethical supply chains are becoming a focal point for international buyers. Transparency in sourcing practices helps companies align with global sustainability goals and meet the expectations of environmentally conscious consumers. Certifications such as ISO 14001 and adherence to initiatives like the UN’s Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) are becoming essential for suppliers looking to establish credibility in the marketplace.
Illustrative image related to parts of a car alternator
Furthermore, the demand for ‘green’ certifications is increasing, with buyers seeking out parts that comply with environmental regulations. This trend not only enhances brand reputation but also opens up new markets, particularly in Europe, where regulatory standards are stringent. For B2B buyers, partnering with suppliers committed to sustainable practices can lead to long-term cost savings and improved product quality.
What Is the Brief Evolution of the Alternator Parts Market?
The alternator has evolved significantly since its inception in the early 20th century. Initially, vehicles relied on generators for electrical power, but the introduction of the alternator in the 1960s revolutionized automotive electrical systems. The alternator’s ability to produce more electricity at lower engine speeds made it a more efficient choice for powering modern vehicles.
Over the decades, the design and functionality of alternators have improved with technological advancements. The shift towards electronic components, such as smart voltage regulators and high-efficiency diodes, has enhanced performance and reliability. As the automotive industry moves towards electrification, the alternator’s role is being redefined, highlighting the need for continuous innovation in its parts and components to meet the evolving demands of the market.
In summary, international B2B buyers must navigate a dynamic landscape characterized by technological advancements, sustainability challenges, and a growing emphasis on ethical sourcing to successfully procure parts of car alternators. Understanding these trends will enable them to make informed decisions that align with both market demands and corporate social responsibility objectives.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of parts of a car alternator
-
1. How do I identify high-quality alternator parts for my business?
To identify high-quality alternator parts, start by sourcing from reputable manufacturers with certifications such as ISO 9001. Look for detailed product specifications, including material composition and performance standards. Request samples to evaluate the quality and durability of the components. Additionally, consider suppliers who offer comprehensive warranties, as this indicates confidence in their product’s reliability. Engaging in industry forums and seeking recommendations from other businesses can also help identify trustworthy suppliers. -
2. What are the best practices for vetting alternator parts suppliers?
Vetting suppliers involves multiple steps. First, check their business credentials, including registration and compliance with local regulations. Conduct a background check to assess their reputation in the market, including customer reviews and testimonials. Request references from other B2B clients and inquire about their experiences. Additionally, visiting the supplier’s facility, if possible, can provide insights into their production processes and quality control measures, ensuring they meet your standards. -
3. What customization options should I consider when sourcing alternator parts?
Customization options may include specific material choices, dimensions, and performance specifications tailored to your market needs. Discuss your requirements with potential suppliers to determine their ability to accommodate custom orders. Some suppliers may offer design services, allowing you to create parts that fit unique applications. Ensure that any customizations do not compromise the quality or functionality of the alternator components. -
4. What is the typical minimum order quantity (MOQ) for alternator parts?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) can vary widely based on the supplier and the specific part. Generally, MOQs range from 50 to 500 units for standard parts, while custom components may have higher MOQs. When negotiating with suppliers, express your needs clearly and inquire if they can accommodate smaller orders, especially for new businesses or initial test runs. Some suppliers might offer flexible terms for first-time buyers. -
5. What payment terms are commonly offered by alternator parts suppliers?
Payment terms can significantly impact cash flow, so it’s essential to clarify these before finalizing orders. Common terms include upfront payment, 30/60/90 days net, or payment upon delivery. Some suppliers may offer discounts for early payments or flexible financing options for larger orders. Always ensure that the payment terms align with your financial capabilities and negotiate terms that minimize risk. -
6. How can I ensure quality assurance (QA) in the alternator parts I purchase?
To ensure quality assurance, request a detailed QA plan from your suppliers, including testing methods and standards they adhere to. Look for suppliers who conduct routine inspections and provide documentation of their quality control processes. Additionally, consider implementing your QA checks upon receipt of goods, including functional testing and dimensional inspections, to verify that components meet your specifications before distribution. -
7. What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing alternator parts?
Logistics considerations include understanding shipping methods, transit times, and customs regulations in your country. Work with suppliers who have experience in international shipping and can provide Incoterms to clarify responsibilities for shipping costs and risks. Assess the reliability of shipping partners and consider insurance options to protect your investment during transit. Plan for potential delays and ensure that you have adequate warehousing solutions upon arrival. -
8. How do I handle returns or warranty claims for defective alternator parts?
Establish a clear return and warranty policy with your suppliers before placing orders. This policy should outline the process for returning defective parts, including timeframes and documentation required. Communicate any issues promptly and maintain thorough records of all transactions. Suppliers with good reputations typically offer support in resolving warranty claims efficiently, ensuring that you can maintain customer satisfaction and trust in your supply chain.
Top 2 Parts Of A Car Alternator Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. HowStuffWorks – Alternators
Domain: auto.howstuffworks.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Alternators are small and lightweight, roughly the size of a coconut, constructed with an aluminum outer housing for heat dissipation and non-magnetization. Key components include:
– Drive pulley attached to the rotor shaft, converting mechanical energy to electrical power.
– Terminals: S terminal (senses battery voltage), IG terminal (ignition switch for voltage regulator), L terminal (closes c…
2. Electude – Alternator
Domain: electude.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: An alternator is a crucial automotive component that converts mechanical energy into electrical energy, generating power for the vehicle’s electrical consumer units and battery. Key components include:
– Pulley: Transfers mechanical energy from the engine to the alternator.
– Rotor: Creates the magnetic field for generating alternating current.
– Stator: The static part where voltage is generat…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for parts of a car alternator
As we conclude our exploration of the essential components of car alternators, it is vital for international B2B buyers to recognize the strategic importance of sourcing high-quality parts. The efficiency and reliability of alternators hinge on components like rotors, stators, rectifiers, and voltage regulators. Understanding the functionality and interdependence of these parts not only enhances product quality but also drives operational efficiency.
Strategic sourcing allows businesses to mitigate risks, reduce costs, and ensure consistent supply chains. For buyers in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, building strong relationships with manufacturers can yield significant competitive advantages. Consider prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to innovation, quality assurance, and sustainable practices.
Looking ahead, the automotive industry is poised for rapid technological advancements, including electric and hybrid vehicles. This shift underscores the need for sourcing partners who are adaptable and forward-thinking. Engage proactively with your suppliers and invest in long-term partnerships that align with your strategic goals. By doing so, you not only secure your supply chain but also position your business for success in an evolving market landscape.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.