Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for how a starter relay works
Before delving into the intricacies of how a starter relay works, it’s vital to understand the challenges faced by international B2B buyers in sourcing reliable automotive components. The starter relay is a crucial component that ensures vehicles start efficiently, but the complexities surrounding its functionality, types, and applications can be daunting. This guide aims to illuminate the operational mechanics of starter relays, providing a thorough overview that encompasses various types, their specific applications in different vehicles, and essential supplier vetting strategies.
Understanding how a starter relay operates not only enhances product knowledge but also aids in making informed purchasing decisions, especially for businesses in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including countries such as Brazil and Nigeria. By exploring the nuances of starter relays, buyers can better assess product quality and compatibility with their specific needs.
Moreover, this comprehensive guide will address cost considerations and potential pitfalls in the sourcing process, empowering B2B buyers to navigate the global market confidently. With actionable insights and expert advice, you will be equipped to make decisions that enhance operational efficiency and reliability in your automotive endeavors. Whether you are a distributor, a manufacturer, or a fleet manager, understanding the dynamics of starter relays will be pivotal in optimizing your procurement strategies and ensuring the longevity of your vehicle systems.
Table Of Contents
- Top 4 How A Starter Relay Works Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for how a starter relay works
- Understanding how a starter relay works Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of how a starter relay works
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘how a starter relay works’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for how a starter relay works
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for how a starter relay works
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘how a starter relay works’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for how a starter relay works Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing how a starter relay works With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for how a starter relay works
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the how a starter relay works Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of how a starter relay works
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for how a starter relay works
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Understanding how a starter relay works Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electromechanical Relay | Utilizes electromagnetic coils to operate contacts | Automotive, Agriculture, Industrial | Pros: Reliable, simple design. Cons: Limited lifespan due to mechanical wear. |
| Solid State Relay | Uses semiconductor devices for switching | Robotics, HVAC, Industrial Controls | Pros: Longer lifespan, faster switching. Cons: Higher initial cost. |
| Four-Post Relay | Features multiple terminals for various connections | Diesel engines, Heavy machinery | Pros: Versatile, allows for complex systems. Cons: More complex installation. |
| Two-Post Relay | Basic design with two terminals | Simple automotive applications | Pros: Cost-effective, easy to install. Cons: Limited functionality. |
| Latching Relay | Maintains its state after being activated | Security systems, Automation | Pros: Energy-efficient, reduces power consumption. Cons: More complex circuitry. |
What are the characteristics of Electromechanical Relays in starter systems?
Electromechanical relays are traditional devices that utilize coils and mechanical contacts to complete or break electrical circuits. They are widely used in automotive and agricultural machinery due to their reliability and straightforward design. B2B buyers should consider their operational environment, as these relays can wear out over time, necessitating regular maintenance or replacement. While they are cost-effective, the potential for mechanical failure can affect operational efficiency.
How do Solid State Relays differ from traditional relays?
Solid State Relays (SSRs) employ semiconductor technology instead of mechanical components, which allows for faster switching and longer operational life. They are ideal for applications in robotics, HVAC systems, and industrial controls where reliability and speed are crucial. B2B buyers should weigh the higher upfront costs against the long-term savings on maintenance and downtime, as SSRs can operate in more extreme conditions without degradation.
What makes Four-Post Relays suitable for diesel engines?
Four-Post Relays are designed to handle the specific requirements of diesel engines, which often involve complex electrical systems. These relays feature multiple terminals that facilitate various connections, making them ideal for heavy machinery and commercial vehicles. When purchasing, B2B buyers should consider the relay’s compatibility with existing systems and the potential need for specialized installation, as their complexity can lead to higher labor costs.
Why choose a Two-Post Relay for simple applications?
Two-Post Relays are the simplest form of starter relays, featuring only two terminals for straightforward on/off control. They are cost-effective and easy to install, making them suitable for basic automotive applications. However, buyers should be aware of their limitations, as these relays may not support more complex electrical systems and can lead to inefficiencies in more demanding environments.
What are the benefits of Latching Relays in automated systems?
Latching Relays are unique in that they maintain their last state after being activated, making them energy-efficient for applications like security systems and automation. These relays reduce power consumption, which can be particularly beneficial for B2B operations looking to minimize energy costs. However, the complexity of their circuitry may require specialized knowledge for installation and maintenance, making it essential for buyers to consider their technical capabilities when purchasing.
Key Industrial Applications of how a starter relay works
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of how a starter relay works | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive Manufacturing | Automotive starter systems in vehicles | Ensures reliable engine starting, reducing downtime | Quality assurance, compatibility with various vehicle models |
| Agriculture | Tractors and heavy machinery ignition systems | Enhances operational efficiency in farming equipment | Durability under harsh conditions, easy installation |
| Construction | Starter relays in construction machinery | Minimizes equipment failure, ensuring project timelines | Robust design, availability of spare parts |
| Marine | Starter relays in marine engines | Ensures reliable operation in challenging marine environments | Resistance to corrosion, compliance with marine standards |
| Industrial Equipment | Starter relays in generators and industrial motors | Improves energy efficiency and reduces operational costs | Energy rating, adaptability to different power loads |
How Does a Starter Relay Work in Automotive Manufacturing?
In the automotive manufacturing sector, starter relays are crucial for the ignition systems of vehicles. They act as a bridge between the battery and the starter motor, ensuring that a large current is safely transmitted when the ignition is turned on. This functionality is essential for maintaining reliable engine performance and reducing vehicle downtime. For international buyers, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, sourcing high-quality starter relays that are compatible with various vehicle models is vital. They should consider suppliers that offer warranties and have a proven track record in quality assurance.
What Role Do Starter Relays Play in Agriculture?
In agriculture, starter relays are integral to the ignition systems of tractors and heavy machinery. They facilitate the efficient starting of these powerful machines, which are essential for modern farming operations. A reliable starter relay can significantly enhance operational efficiency by minimizing equipment failure, which can lead to costly delays. Buyers in this sector must prioritize sourcing durable relays that can withstand the harsh conditions often found in agricultural environments, ensuring long-term reliability and performance.
How Are Starter Relays Utilized in Construction Machinery?
Starter relays are also vital in construction machinery, where they ensure that equipment such as excavators and bulldozers starts reliably. This reliability is crucial for keeping projects on schedule and avoiding costly downtime. For businesses in the construction sector, selecting starter relays that are robust and designed for heavy-duty use is important. Additionally, buyers should look for suppliers who provide easy access to spare parts to maintain the longevity of their machinery.
Why Are Starter Relays Important in Marine Applications?
In the marine industry, starter relays are used in the ignition systems of various types of boats and marine engines. They ensure that engines start reliably, even in challenging maritime conditions. The importance of sourcing starter relays that are resistant to corrosion and comply with marine standards cannot be overstated, as these factors directly affect the longevity and reliability of marine engines. International buyers should focus on suppliers who specialize in marine-grade components to ensure optimal performance.
What Benefits Do Starter Relays Offer in Industrial Equipment?
Starter relays are essential in industrial equipment, particularly in generators and heavy motors. They improve energy efficiency and help reduce operational costs by managing the electrical load during startup. For businesses in this sector, it is crucial to source relays with appropriate energy ratings and adaptability to various power loads. Buyers should consider suppliers that provide comprehensive technical support and can offer solutions tailored to specific industrial applications, ensuring seamless integration into existing systems.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘how a starter relay works’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty Understanding Relay Functionality in Complex Systems
The Problem:
B2B buyers, particularly in the automotive and machinery sectors, often grapple with the complexities of how starter relays function within multi-component systems. This challenge is exacerbated when dealing with equipment that incorporates multiple starter relays or different types of relays across various models. Misunderstanding the role of the starter relay can lead to incorrect installations, wasted resources, and increased downtime. For instance, a buyer may mistakenly source the wrong type of relay for a particular application, resulting in operational failures and potential safety hazards.
The Solution:
To mitigate these issues, it is essential to invest in comprehensive training and documentation for your team. Providing detailed manuals and diagrams that illustrate the starter relay’s role in the overall electrical system will enhance understanding. Additionally, consider collaborating with suppliers who offer technical support and resources. For example, hosting workshops or webinars on starter relay functionality can empower your staff to make informed decisions. Lastly, ensure that you specify the correct relay type based on the system’s requirements, including voltage ratings and compatibility, to prevent misapplication.
Scenario 2: Overcoming Starter Relay Failure in Harsh Environments
The Problem:
In regions with extreme climates—such as the heat of Africa or the humidity in parts of South America—starter relays can fail prematurely due to environmental stresses. Buyers often find themselves facing frequent equipment malfunctions, leading to costly repairs and operational delays. The challenge lies in identifying the right starter relays that can withstand such conditions without compromising performance.
The Solution:
To address this pain point, buyers should focus on sourcing starter relays specifically designed for high-temperature or high-humidity environments. Look for products that feature robust housing materials and enhanced sealing against moisture and dust. Additionally, consider implementing regular maintenance schedules that include inspecting and testing the relay functionality to catch issues before they lead to failure. Partnering with manufacturers that offer guarantees or warranties on their products can also provide peace of mind, ensuring that your investment is protected against the rigors of harsh environments.
Scenario 3: Managing Supply Chain Challenges for Starter Relays
The Problem:
International B2B buyers frequently encounter supply chain disruptions that can delay the delivery of critical components, including starter relays. Inconsistent availability can hinder production schedules and lead to financial losses. Furthermore, buyers may struggle to find reliable suppliers who can provide both the quality and quantity needed for their operations.
The Solution:
To effectively navigate these supply chain challenges, it is prudent to establish strong relationships with multiple suppliers across different regions. This diversification can help mitigate risks associated with single-source dependency. Additionally, consider implementing inventory management systems that allow for real-time tracking of starter relay stock levels, ensuring that you can anticipate shortages before they become critical. Engaging in strategic partnerships with suppliers who prioritize transparency in their supply chain processes can also enhance reliability. By fostering these relationships, you can secure better pricing and more favorable terms, ultimately leading to a more resilient procurement strategy.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for how a starter relay works
When selecting materials for starter relays, it is essential to consider their properties, performance, and suitability for specific applications. Various materials can influence the relay’s functionality, durability, and overall effectiveness in different environments. Below, we analyze four common materials used in starter relays, focusing on their key properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for international buyers.
What are the Key Properties of Copper in Starter Relays?
Copper is widely used in starter relays due to its excellent electrical conductivity and thermal properties. It typically operates effectively in temperature ranges from -40°C to 200°C, making it suitable for various automotive applications. Additionally, copper exhibits good corrosion resistance when properly coated, which is vital for maintaining performance in humid or saline environments.
Pros: Copper’s high conductivity ensures minimal energy loss, enhancing the relay’s efficiency. It is also relatively easy to manufacture and shape, allowing for intricate designs.
Cons: The primary drawback of copper is its susceptibility to corrosion if not adequately protected, which can lead to electrical failures. Moreover, copper can be more expensive than some alternative materials, impacting overall production costs.
Impact on Application: Copper’s compatibility with high current loads makes it ideal for starter relays, where significant power is required to engage the starter motor.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards such as ASTM B170 for copper wire is crucial. Buyers in regions like Africa and South America should consider local environmental conditions that may affect copper’s longevity.
How Does Aluminum Compare as a Material for Starter Relays?
Aluminum is another common material used in starter relays, known for its lightweight and good conductivity, albeit lower than copper. It typically operates effectively in similar temperature ranges as copper but has a lower melting point, which may limit its use in high-temperature applications.
Pros: Aluminum is less expensive than copper, making it a cost-effective option for manufacturers. Its lightweight nature can also contribute to overall vehicle weight reduction.
Cons: While aluminum is resistant to corrosion, it can suffer from oxidation, which may affect its conductivity over time. Additionally, it is not as durable as copper, especially under mechanical stress.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is suitable for starter relays in applications where weight savings are prioritized, but its lower conductivity may necessitate larger cross-sectional areas to achieve the same performance as copper.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with standards such as ASTM B221 for aluminum extrusions. In regions like the Middle East, where high temperatures are common, the thermal properties of aluminum must be carefully evaluated.
What Role Does Plastic Play in Starter Relay Housing?
Plastic materials, particularly thermoplastics and thermosetting plastics, are often used for the housing of starter relays. These materials provide insulation and protection against environmental factors, with temperature ratings typically ranging from -20°C to 120°C.
Pros: Plastics are lightweight, cost-effective, and can be molded into complex shapes, allowing for versatile designs. They also provide excellent insulation properties, reducing the risk of electrical shorts.
Cons: Plastics can be less durable than metals, particularly in high-temperature or high-stress environments. They may also degrade over time when exposed to UV light or certain chemicals.
Impact on Application: The use of plastic housings is critical in preventing short circuits and protecting internal components from moisture and dust.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as UL 94 for flammability is essential. Buyers in Europe may also need to consider REACH compliance for plastic materials.
How Does Steel Contribute to the Durability of Starter Relays?
Steel, particularly stainless steel, is used in certain components of starter relays, such as mounting brackets and contacts. Its high strength and resistance to wear make it suitable for applications requiring durability.
Pros: Steel provides excellent mechanical strength and can withstand high pressures and temperatures, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications.
Cons: Steel is heavier than other materials and can corrode if not properly treated or coated, which may affect its longevity in harsh environments.
Impact on Application: The use of steel components can enhance the overall durability of starter relays, particularly in commercial vehicles operating in demanding conditions.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with standards such as ASTM A240 for stainless steel. In regions with high humidity, such as parts of Africa, corrosion resistance is a critical factor.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Starter Relays
| Material | Typical Use Case for how a starter relay works | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Copper | Electrical contacts in starter relays | High conductivity and efficiency | Susceptible to corrosion | High |
| Aluminum | Lightweight relay components | Cost-effective and lightweight | Lower conductivity than copper | Medium |
| Plastic | Relay housing and insulation | Excellent insulation properties | Less durable in extreme conditions | Low |
| Steel | Mounting brackets and structural components | High strength and durability | Heavier and potential for corrosion | Medium |
By understanding the properties and implications of these materials, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and regional conditions.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for how a starter relay works
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing a Starter Relay?
The manufacturing process of a starter relay involves several key stages, each critical for ensuring the final product meets operational and quality standards. These stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How Is Material Prepared for Starter Relay Production?
Material preparation begins with sourcing high-quality materials that can withstand electrical and mechanical stresses. Common materials include copper for electrical connections, plastic or resin for the housing, and steel for the relay’s internal components. Suppliers must ensure that these materials comply with international standards, such as ISO 9001, to guarantee their quality and reliability.
During this phase, materials undergo rigorous inspection and testing to verify their properties. This includes checking for conductivity in copper, thermal resistance in plastics, and tensile strength in steel. Proper documentation of these material specifications is vital for traceability and quality assurance.
What Techniques Are Used in the Forming Stage?
The forming stage utilizes various techniques to shape the materials into the required components. This often includes stamping, molding, and machining processes.
-
Stamping is commonly used for producing the relay contacts and other metallic components. High-precision dies ensure that each piece meets exact specifications, which is crucial for the relay’s functionality.
-
Injection molding is often employed for the plastic housing. This technique allows for the efficient production of complex shapes while maintaining consistent quality.
-
Machining may be used for parts that require tight tolerances or specific surface finishes, ensuring a snug fit during assembly.
Throughout the forming stage, strict adherence to quality control measures is essential. Any deviations can lead to failures in the relay’s performance, impacting customer satisfaction.
How Is Assembly Conducted for Starter Relays?
Once the components are formed, the assembly process begins. This involves the careful integration of all parts, including the coil, contacts, and housing. Assembly is typically conducted in a clean environment to prevent contamination, which can lead to malfunctions.
Automated assembly lines are often used to enhance efficiency and accuracy. Each relay undergoes a series of assembly checkpoints to ensure that all components are correctly installed. Human operators may conduct final checks to confirm that the assembly meets operational standards.
During this stage, it is crucial to document the assembly process meticulously. This documentation serves as evidence of compliance with quality standards and can be beneficial for B2B buyers seeking assurance of product integrity.
What Finishing Processes Are Involved in Starter Relay Production?
The finishing stage enhances the aesthetic and functional qualities of the starter relay. This may include surface treatments such as electroplating or painting to improve corrosion resistance and durability.
Additionally, electrical testing is conducted at this stage to ensure that each relay operates within specified parameters. This includes checking for continuity, insulation resistance, and operational current draw. The performance of each unit is critical for reliability, especially in demanding environments typical of automotive and industrial applications.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Essential for Starter Relay Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is integral to the manufacturing of starter relays. Adherence to international standards, such as ISO 9001, ensures that companies implement effective QA systems that enhance product quality and customer satisfaction.
Which International Standards Should B2B Buyers Consider?
For B2B buyers, understanding relevant international standards is crucial. ISO 9001 focuses on quality management systems, ensuring that manufacturers consistently produce products that meet customer and regulatory requirements. Other industry-specific certifications, such as CE marking for European markets and API for petroleum applications, may also be relevant depending on the relay’s intended use.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control (QC) involves several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): At this stage, raw materials are inspected upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): This involves monitoring the manufacturing process itself, including inspections during forming, assembly, and finishing stages.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Before shipping, each starter relay undergoes comprehensive testing to verify functionality and compliance with performance standards.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier QC Practices?
B2B buyers should actively verify the QC practices of potential suppliers. Conducting audits of manufacturing facilities can provide insights into their adherence to quality standards and processes. Additionally, requesting quality reports, certificates of conformity, and third-party inspection documents can help buyers assess reliability.
Furthermore, engaging with suppliers who have a transparent QC process and are open to regular audits can foster long-term partnerships. Buyers from diverse regions, including Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should pay attention to any nuances in certification requirements that may affect their procurement process.
What Are the Common Testing Methods for Starter Relays?
Testing methods are critical in ensuring the reliability of starter relays. Common tests include:
-
Functional Testing: Verifying that the relay operates correctly under various conditions, simulating actual usage scenarios.
-
Environmental Testing: Assessing the relay’s performance under extreme temperatures and humidity levels to ensure durability.
-
Electrical Testing: Measuring parameters such as resistance, inductance, and current draw to confirm that the relay meets design specifications.
-
Mechanical Testing: Evaluating the physical integrity of the relay components under stress to prevent mechanical failures.
By understanding these manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing starter relays, ensuring they invest in products that meet their operational requirements and quality expectations.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘how a starter relay works’
Introduction
In the realm of automotive and machinery components, understanding how a starter relay operates is essential for B2B buyers in sourcing the right parts for their needs. This guide provides a step-by-step checklist to help you navigate the procurement process, ensuring you acquire quality starter relays that meet your technical requirements and operational standards.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before beginning your search for a starter relay, clearly outline your technical specifications. Identify the voltage, current ratings, and compatibility with the systems where the relay will be integrated.
– Voltage and Current Ratings: Ensure that the relay can handle the required electrical load to prevent failure.
– Compatibility: Check that the relay matches the specific vehicle or machinery model to avoid installation issues.
Step 2: Research Reliable Manufacturers
Investigating potential manufacturers is crucial to ensure quality and reliability. Look for manufacturers with a strong reputation in the automotive or machinery sectors.
– Industry Experience: Prioritize manufacturers with extensive experience in producing starter relays.
– Customer Reviews: Read reviews and testimonials to gauge the reliability of their products and customer service.

Illustrative image related to how a starter relay works
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a supplier, conduct thorough evaluations. Request detailed company profiles, product catalogs, and case studies that illustrate their expertise in starter relays.
– References: Ask for references from buyers in similar industries to validate the supplier’s reliability and product performance.
– Certifications: Ensure suppliers possess necessary quality certifications (e.g., ISO) that demonstrate adherence to international standards.
Step 4: Assess Product Quality and Testing Procedures
Quality assurance is paramount when procuring starter relays. Inquire about the testing procedures that the manufacturer employs to ensure product reliability.
– Quality Control: Understand the quality control measures in place during production.
– Testing Standards: Verify that the relays undergo rigorous testing to meet industry standards before shipping.
Step 5: Request Samples for Evaluation
Once you have shortlisted potential suppliers, request samples of the starter relays for testing. This step is vital to ascertain that the product meets your specifications and performance expectations.
– Functional Testing: Conduct tests to confirm that the relay operates correctly within your system.
– Durability Assessment: Evaluate the relay’s build quality and longevity under normal operating conditions.
Step 6: Negotiate Pricing and Terms
With a clear understanding of your needs and the products available, it’s time to negotiate pricing and terms. Aim for a mutually beneficial agreement that considers both quality and cost.
– Bulk Purchase Discounts: Inquire about discounts for larger orders, which can significantly reduce overall costs.
– Payment Terms: Establish clear payment terms and conditions, including warranties and return policies.
Step 7: Finalize the Order and Monitor Delivery
After reaching an agreement, finalize your order and ensure that delivery timelines are clearly communicated. Monitor the delivery process to prevent delays.
– Order Confirmation: Confirm all details regarding specifications, quantities, and delivery dates.
– Follow-Up: Maintain communication with the supplier during shipping to address any potential issues proactively.
By following this checklist, you can streamline the procurement process for starter relays, ensuring that you source high-quality components that meet your operational needs effectively.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for how a starter relay works Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Starter Relays?
When considering the sourcing of starter relays, understanding the cost structure is paramount for international B2B buyers. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and margins.
-
Materials: The cost of materials for starter relays can vary significantly based on the quality and specifications required. Common materials include copper for wiring, plastic for housing, and various metals for internal components. Buyers should assess material quality to ensure durability and performance, which can impact long-term costs.
-
Labor: Labor costs depend on the region of production and the complexity of the relay design. Regions with lower labor costs may offer competitive pricing, but it’s essential to consider the skill level and expertise of the workforce to ensure high-quality production.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses the indirect costs associated with production, such as utilities, rent, and administrative expenses. Efficient manufacturing processes can help reduce overhead costs, which can be passed on to buyers.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling for specific relay designs can represent a significant upfront investment. Buyers should consider whether they can share tooling costs across multiple orders or product lines to improve cost efficiency.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing strict quality control measures is crucial to avoid defects and ensure product reliability. While higher QC standards may increase upfront costs, they can reduce the risk of failures and recalls, thereby lowering the total cost of ownership.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can vary based on the distance from the manufacturer to the buyer, the mode of transport, and the volume of the order. Understanding Incoterms can help buyers negotiate better logistics terms and manage shipping risks.
-
Margin: Suppliers will typically add a margin to cover their costs and desired profit. This margin can fluctuate based on market demand, competition, and the supplier’s negotiation power.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Starter Relay Costs?
Several factors influence the pricing of starter relays, which B2B buyers should consider during negotiations:
-
Volume/MOQ: Suppliers often provide discounts for larger orders due to economies of scale. Buyers should assess their needs carefully and consider bulk purchasing to reduce unit costs.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom specifications can lead to higher costs due to the need for specialized materials or tooling. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Materials: The choice of materials directly affects pricing. Higher-quality materials may incur higher costs but can lead to enhanced performance and longevity, impacting the total cost of ownership positively.
-
Quality/Certifications: Products that meet specific quality standards or certifications (like ISO) may be priced higher, but they often provide better reliability and performance, making them a worthwhile investment.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, location, and relationship with the buyer can significantly impact pricing. Established suppliers may command higher prices due to trust and reliability, while new suppliers may offer lower rates to build their client base.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is vital for managing logistics costs. These terms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping arrangements and can affect the overall price.
What Negotiation Tips Can Help Reduce Costs for International Buyers?
B2B buyers, especially in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, can leverage several strategies to negotiate better prices on starter relays:
-
Highlight Long-Term Partnerships: Emphasizing the potential for ongoing business can encourage suppliers to offer better terms.
-
Request Multiple Quotes: Obtaining quotes from various suppliers provides leverage during negotiations and can help identify the best pricing available.
-
Consider Total Cost of Ownership: Evaluate not just the purchase price but the long-term costs associated with maintenance, reliability, and performance. Investing in higher-quality relays may yield savings over time.
-
Be Cautious with Pricing Nuances: International buyers should be aware of currency fluctuations, import duties, and taxes that may affect the final cost. Including these factors in negotiations can prevent unexpected expenses.
In conclusion, understanding the comprehensive cost structure and the various price influencers will equip international B2B buyers with the knowledge needed to make informed purchasing decisions regarding starter relays. Careful consideration of negotiation strategies can further enhance cost-effectiveness in sourcing.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing how a starter relay works With Other Solutions
Introduction: Exploring Alternatives to Starter Relays
In the automotive and machinery sectors, starter relays are essential components that facilitate the ignition process by managing the electrical flow between the battery and the starter motor. However, several alternative solutions exist that can achieve similar outcomes. Understanding these alternatives allows B2B buyers to make informed decisions based on performance, cost, and application suitability.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | How A Starter Relay Works | Alternative 1: Solid-State Relay | Alternative 2: Push-Button Start System |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Reliable under high load; handles significant current | Faster switching, minimal voltage drop | Convenient for modern vehicles, enhances user experience |
| Cost | Generally low-cost and widely available | Higher initial cost, but long-term savings | Moderate cost, potential for additional features |
| Ease of Implementation | Simple integration into existing systems | Requires knowledge of electronic circuits | Easy to install; replaces traditional ignition systems |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance, but susceptible to wear | Very low maintenance, long lifespan | Minimal maintenance; depends on other systems |
| Best Use Case | Traditional vehicles, heavy machinery | High-performance applications, electric vehicles | Modern vehicles, custom builds |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Solid-State Relay (SSR)
Solid-state relays utilize semiconductor devices to switch electrical circuits, providing a more efficient and durable alternative to traditional mechanical relays. Their major advantage lies in their ability to handle high frequencies and rapid switching without wear and tear. This results in a longer lifespan and reduced maintenance costs. However, SSRs can be more expensive initially and require a solid understanding of electronic systems for proper integration. They are best suited for high-performance applications and electric vehicles where efficiency is crucial.
Push-Button Start System
The push-button start system is an innovative alternative that enhances user convenience and modernizes vehicle operation. This system replaces traditional key ignitions with a simple button press, streamlining the start process. While installation is generally straightforward, it may require modifications to the vehicle’s wiring and electrical systems. The cost is moderate, but the added convenience and potential for integrating other features (like keyless entry) can justify the investment. This solution is ideal for modern vehicles and custom builds, providing a contemporary user experience.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
When selecting the appropriate starting mechanism for vehicles or machinery, B2B buyers should consider their specific operational needs, budget constraints, and technical capabilities. Traditional starter relays remain a reliable choice for many applications, particularly in conventional vehicles and machinery. However, for buyers focused on efficiency and modern user experiences, exploring solid-state relays or push-button start systems could yield significant benefits. Ultimately, the right choice will depend on balancing performance requirements with cost-effectiveness and ease of implementation.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for how a starter relay works
What Are the Critical Technical Properties of a Starter Relay?
Understanding the essential technical properties of a starter relay can significantly influence purchasing decisions in the B2B sector. Here are some key specifications to consider:
-
Material Grade
The materials used in the construction of a starter relay, such as copper for electrical contacts and durable plastics for the housing, are critical. High-grade materials ensure better conductivity and resistance to heat and corrosion, which is essential for reliability in various environments, especially in regions with extreme weather conditions. -
Coil Resistance
This refers to the resistance of the coil winding within the relay. Typically measured in ohms, the coil resistance affects the current draw from the ignition circuit. A lower resistance value often indicates a more efficient relay, which is crucial for energy conservation and optimal performance, especially in high-demand situations. -
Current Rating
The current rating indicates the maximum current the relay can handle safely, usually expressed in amperes (A). Understanding the current rating is vital for ensuring that the relay can manage the load without overheating or failing, which is especially important for heavy machinery or vehicles in industrial applications. -
Switching Voltage
This property defines the voltage level at which the relay operates effectively. It is crucial for compatibility with the vehicle’s electrical system. Most automotive starter relays operate at 12V or 24V, and ensuring the correct voltage can prevent electrical failures and enhance overall system stability. -
Temperature Range
The operational temperature range indicates the environmental conditions in which the starter relay can function effectively. A wider temperature range is particularly important for B2B buyers in regions with extreme climates, as it ensures that the relay will perform reliably under varying conditions. -
Life Cycle Rating
This rating reflects the expected operational lifespan of the relay, often measured in on-off cycles. A higher life cycle rating indicates durability, which is a crucial consideration for businesses looking to minimize maintenance costs and downtime in their operations.
What Are Common Trade Terms Associated with Starter Relays?
Familiarity with specific trade terminology can facilitate smoother communication and transactions in the B2B marketplace. Here are several important terms related to starter relays:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
This term refers to companies that produce parts that are sold to other manufacturers for incorporation into their products. Understanding OEM specifications is crucial for buyers who require components that meet original manufacturing standards for quality and compatibility. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ represents the minimum number of units that a supplier is willing to sell in a single order. This is an important consideration for B2B buyers as it affects inventory management and cost efficiency, especially when sourcing components for large-scale operations. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document issued by a buyer to solicit price quotes from suppliers for specific products or services. In the context of starter relays, issuing an RFQ can help businesses compare prices and ensure they are getting the best deal for their required components. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
These are a series of predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding Incoterms is vital for B2B buyers to avoid misunderstandings regarding shipping, insurance, and delivery responsibilities. -
Lead Time
This term refers to the amount of time it takes from placing an order until it is delivered. For B2B buyers, understanding lead times is crucial for project planning and ensuring that necessary components, like starter relays, are available when needed. -
Aftermarket
This term refers to parts and accessories that are not sourced from the original manufacturer but are designed to fit or enhance the original product. Understanding the aftermarket can provide B2B buyers with alternative options that might be more cost-effective while still meeting performance standards.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing starter relays, ensuring optimal performance and reliability for their applications.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the how a starter relay works Sector
What Are the Key Market Trends Influencing the Starter Relay Sector?
The global starter relay market is experiencing transformative shifts driven by technological advancements and changing consumer demands. The automotive sector, particularly in emerging markets like Brazil and Nigeria, is increasingly adopting advanced relay systems that enhance vehicle efficiency and reliability. This trend is bolstered by the growing need for electric and hybrid vehicles, which require more sophisticated starter relay designs to manage higher electrical loads. Additionally, the rise of smart vehicles equipped with advanced electronics necessitates starter relays that can interface seamlessly with complex automotive systems.
Moreover, the integration of Industry 4.0 technologies is reshaping the sourcing landscape. B2B buyers are leveraging data analytics and IoT solutions to optimize procurement processes, enabling them to make informed decisions about sourcing starter relays. This trend is particularly relevant for international buyers in Africa and the Middle East, who seek to streamline their supply chains and improve operational efficiency.
As manufacturers increasingly focus on customization, buyers are encouraged to engage in collaborative partnerships that allow for tailored solutions to meet specific operational needs. This shift towards customer-centric sourcing is reshaping market dynamics, emphasizing the importance of innovation in product development and supplier relationships.
How Are Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impacting the Starter Relay Market?
In the contemporary B2B landscape, sustainability and ethical sourcing have become critical considerations for companies involved in the starter relay market. The environmental impact of production processes, particularly in the automotive sector, has prompted manufacturers to adopt greener practices. This includes the use of recyclable materials and energy-efficient manufacturing methods that reduce waste and carbon footprints.
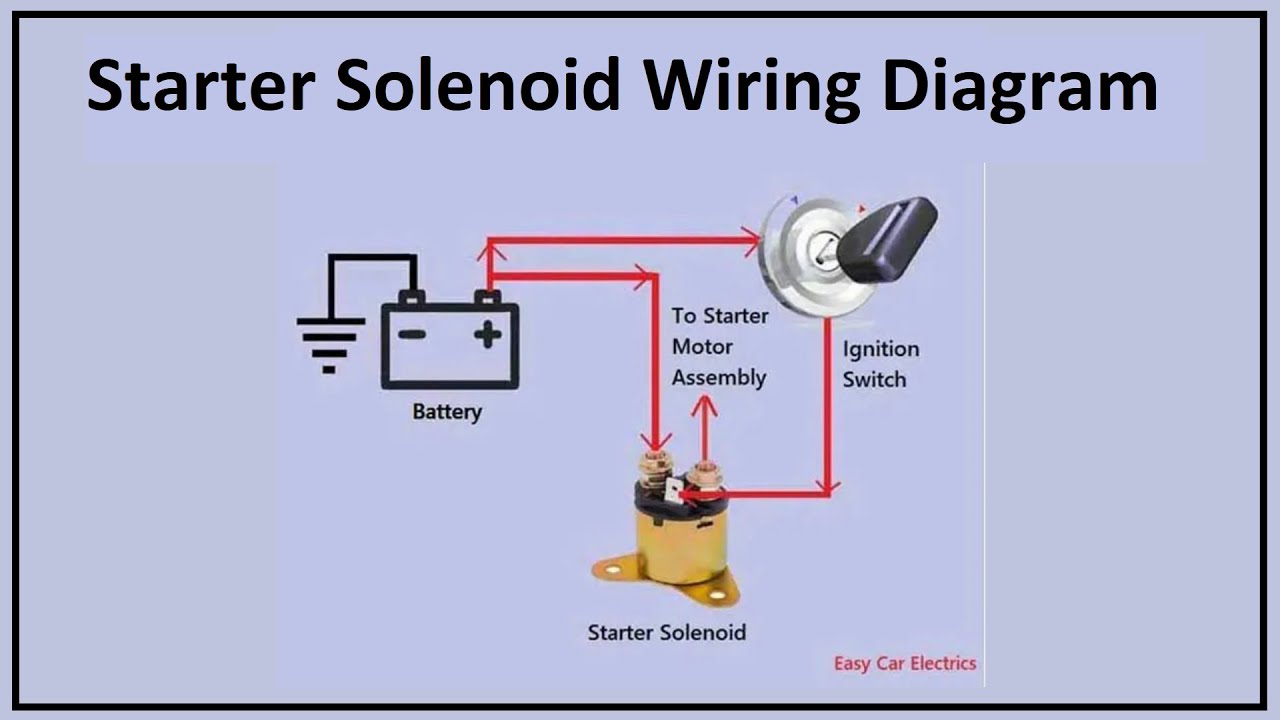
Illustrative image related to how a starter relay works
Furthermore, ethical supply chains are gaining traction as buyers increasingly prioritize suppliers who adhere to responsible sourcing practices. This trend is particularly significant in regions like Africa and South America, where social responsibility and community engagement are paramount. B2B buyers are encouraged to seek partners who possess certifications such as ISO 14001, which demonstrates a commitment to environmental management, and those who utilize eco-friendly materials in their products.
Investing in sustainability not only enhances brand reputation but also aligns with the growing consumer demand for environmentally responsible products. As such, international buyers are strategically positioning themselves to leverage these trends, ensuring that their sourcing strategies reflect a commitment to sustainability while also meeting regulatory requirements.
What Is the Historical Context Behind Starter Relays in B2B Transactions?
The evolution of starter relays dates back to the early days of automotive engineering, where basic relay systems were employed to manage electrical currents for ignition systems. Initially, these relays were simple mechanical devices that provided a connection between the battery and starter motor. However, as automotive technology advanced, so did the complexity of starter relays.
In the 1960s and 1970s, the introduction of electronic ignition systems necessitated the development of more sophisticated relays capable of handling higher electrical loads and providing better reliability. This evolution laid the groundwork for the modern starter relay, which now incorporates advanced materials and design innovations to enhance performance.
Today, the starter relay market reflects a rich history of innovation, with ongoing advancements driven by the demand for efficiency and sustainability. As B2B buyers navigate this landscape, understanding the historical context provides valuable insights into current trends and future developments in the sector.
Conclusion
Navigating the market dynamics and sourcing trends in the starter relay sector requires an understanding of the interplay between technological advancements, sustainability, and historical context. By staying attuned to these factors, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs while also contributing to a more sustainable future.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of how a starter relay works
-
How do I solve issues related to starter relay failure?
To address starter relay failures, start by diagnosing the issue. Common symptoms include clicking sounds when turning the key or no response at all. Check the battery voltage and connections first, as low power can cause relay malfunction. If the relay is confirmed faulty, replace it with a compatible model. Ensure that the new relay matches the specifications of your vehicle or equipment. Regular maintenance, including cleaning connections and inspecting wiring, can also prevent future failures. -
What is the best starter relay for heavy machinery?
When sourcing a starter relay for heavy machinery, prioritize relays designed for high current applications and durability. Look for relays with robust construction, high-temperature resistance, and weatherproof features. Brands with a strong reputation for reliability in industrial settings, such as Bosch or Omron, are often recommended. Additionally, consider relays that offer customization options to fit specific machinery requirements, ensuring compatibility and optimal performance. -
How can I vet suppliers of starter relays internationally?
To vet suppliers of starter relays, start by researching their reputation through online reviews, industry forums, and trade associations. Request references from previous clients and verify their production capabilities and quality assurance processes. Additionally, assess their certifications, such as ISO standards, to ensure compliance with international quality standards. A factory visit can provide insights into their manufacturing practices and reliability. Establish clear communication to gauge responsiveness and professionalism. -
What are common minimum order quantities (MOQs) for starter relays?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for starter relays can vary significantly depending on the supplier and the type of relay. Typically, MOQs can range from 100 to 1,000 units for standard models. However, specialized or customized relays may have higher MOQs. When negotiating with suppliers, express your needs clearly and inquire about flexibility in MOQs, especially if you are a smaller buyer. Some suppliers might offer lower MOQs for first-time orders or trial runs. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing starter relays?
Payment terms when sourcing starter relays typically range from upfront payments to net 30 or net 60 days. Many suppliers may request a deposit (usually 30-50%) before production, with the balance due upon shipment or delivery. International buyers should also consider currency exchange rates and transaction fees. Establishing clear payment terms in the contract can help avoid misunderstandings. Discuss options for letters of credit or escrow services for larger transactions to enhance security. -
How do I ensure quality assurance for starter relays?
To ensure quality assurance for starter relays, request detailed product specifications and quality control processes from your supplier. It’s beneficial to ask for samples before placing a large order. Implementing third-party inspections during production and before shipment can help catch defects early. Additionally, establish a return policy in case of defects and ensure the supplier provides warranty coverage for their products, which can safeguard your investment. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind for importing starter relays?
When importing starter relays, consider logistics factors such as shipping methods, lead times, and customs regulations. Choose between air or sea freight based on urgency and cost. Ensure you understand the import duties and taxes applicable in your country. Work with a freight forwarder familiar with your industry to navigate customs clearance smoothly. Proper documentation, including invoices and certificates of origin, is essential to avoid delays and fines. -
How can I customize starter relays for specific applications?
Customizing starter relays involves working closely with your supplier to define your specifications, such as voltage, current rating, and physical dimensions. Discuss any unique requirements, such as environmental resistance or integration with existing systems. Many manufacturers offer design services or modifications to existing products. Ensure that you have a clear understanding of the cost implications and lead times for custom orders, and request prototypes to verify that the customization meets your needs before full-scale production.
Top 4 How A Starter Relay Works Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Hackster – Starter Relay
Domain: hackster.io
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: The starter relay is an electrical component that serves as a circuit completer or circuit breaker between the vehicle’s battery and the starter motor. It increases the battery’s current to allow the ignition switch to send a large current to the starter motor, which is necessary for starting the vehicle. The starter relay is crucial for the starting process, as it transmits small electric power t…
2. Reddit – Starter Relay
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Starter relay is used in cars to manage high current to the starter motor without burning up the key switch. It allows the key switch to energize the relay with a small current, which then closes high current contacts to send power to the starter motor. This design also facilitates easier integration of anti-theft protection.
3. Alion Timer – Essential Relay Solutions
Domain: aliontimer.com
Registered: 2016 (9 years)
Introduction: Protection Relay – Critical Components of Electrical Power Grid; Floatless Relay – Automatic Water Supply and Drainage Control; Modular Timer Relay – Essential Part of Motor Control; Multifunction Timer Relay – Multi-range Timer Delay Relay.
4. Facebook – Relay System
Domain: facebook.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: This company, Facebook – Relay System, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for how a starter relay works
In conclusion, understanding the mechanics of a starter relay is essential for B2B buyers involved in automotive and machinery procurement. This component plays a crucial role in initiating engine operations by facilitating the flow of electricity from the battery to the starter motor. Recognizing the importance of reliable starter relays can significantly influence vehicle performance and longevity, making them vital for maintenance and replacement strategies.
Strategic sourcing of starter relays not only ensures quality and reliability but also optimizes supply chain efficiency. Buyers should consider factors such as supplier reputation, product specifications, and compatibility with various vehicle models when making purchasing decisions. By partnering with trusted suppliers who offer high-quality components, businesses can reduce downtime and enhance operational efficiency.
Looking ahead, international buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe have a unique opportunity to tap into global supply networks. As the automotive industry continues to evolve, investing in high-quality starter relays will remain a cornerstone for ensuring optimal performance. Engage with reliable suppliers today to secure the components that will drive your business forward.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.

Illustrative image related to how a starter relay works
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.