Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for alternator components diagram
In today’s global marketplace, sourcing alternator components diagram can pose significant challenges for B2B buyers, especially those operating in diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. As the demand for reliable automotive parts grows, understanding the intricate details of alternator components becomes crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. This comprehensive guide delves into the essential components of alternators, their applications across various industries, and critical aspects of supplier vetting, ensuring that buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing effectively.
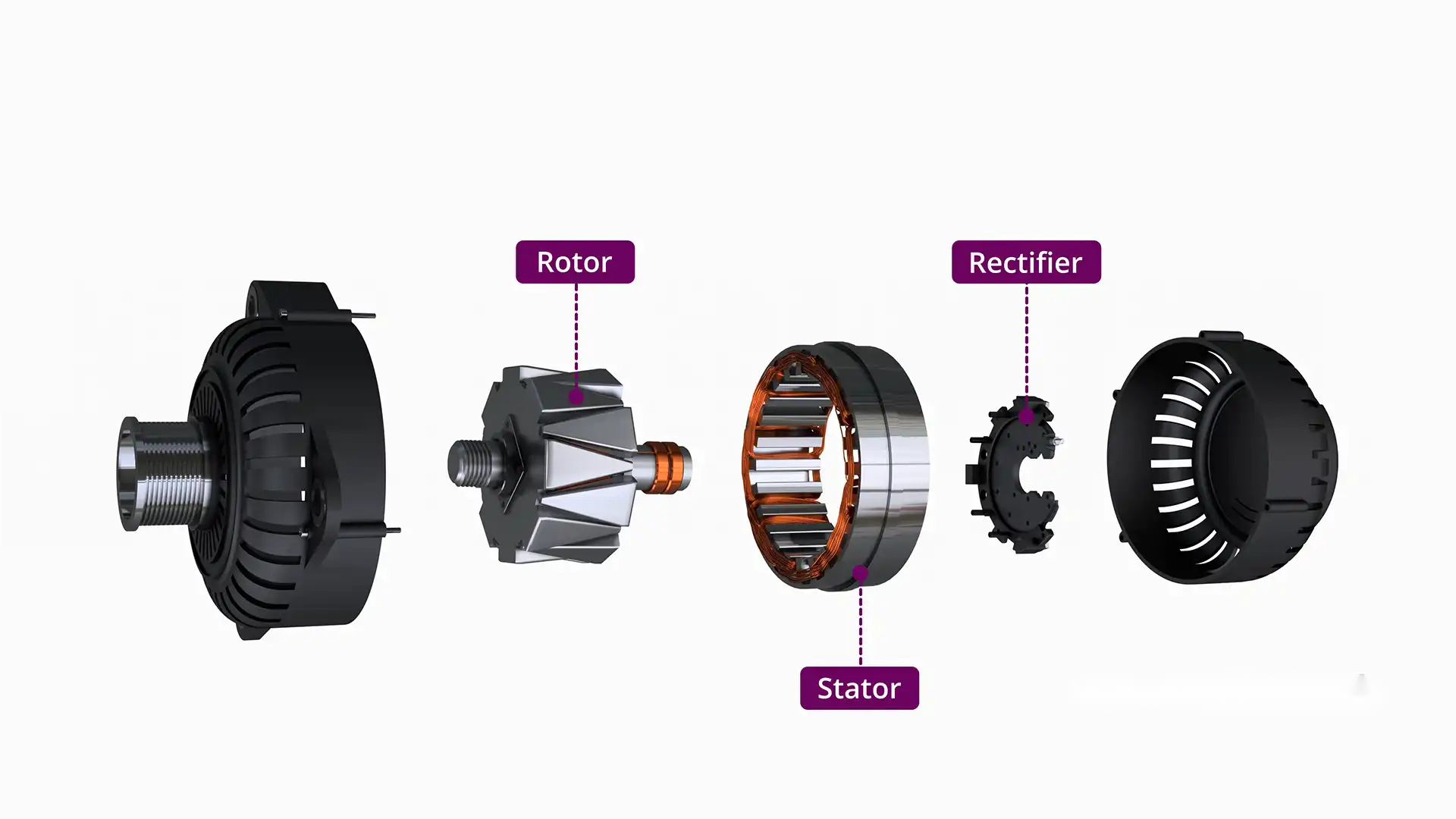
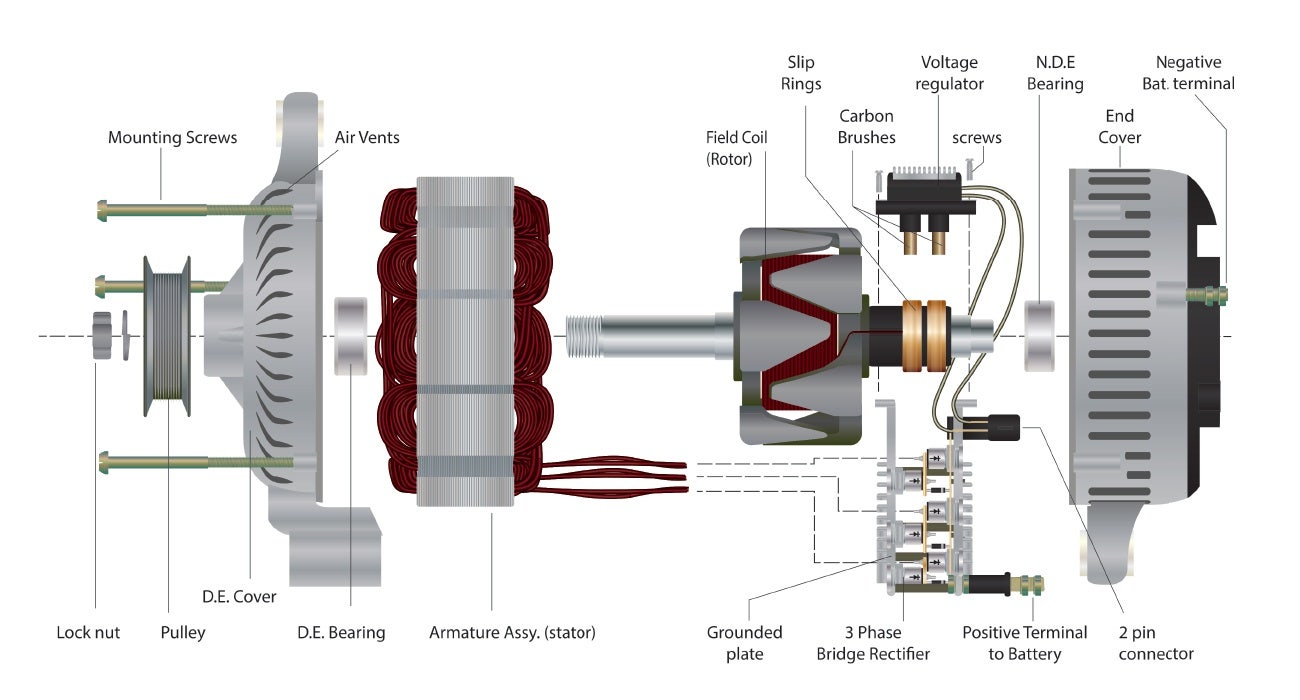
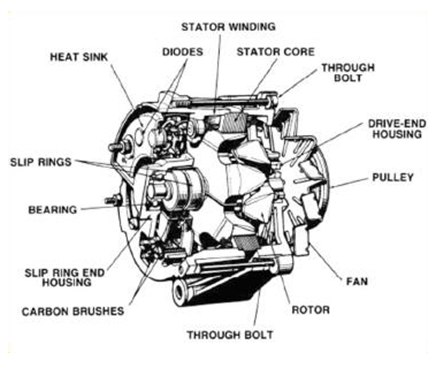
The guide covers a wide range of topics, including the primary components of alternators—such as the rotor, stator, rectifier, and voltage regulator—and how they interact to generate electrical power. Additionally, it provides insights into the varying quality standards across different markets, cost considerations, and the importance of establishing strong relationships with reputable suppliers. By equipping international B2B buyers with actionable knowledge and best practices, this resource empowers them to make strategic decisions that enhance operational efficiency and profitability.
Ultimately, understanding the alternator components diagram is not just about acquiring parts; it’s about ensuring the reliability and performance of vehicles and equipment in an increasingly competitive landscape. This guide is designed to serve as a vital tool for businesses aiming to thrive in the global automotive supply chain.
Table Of Contents
- Top 6 Alternator Components Diagram Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for alternator components diagram
- Understanding alternator components diagram Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of alternator components diagram
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘alternator components diagram’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for alternator components diagram
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for alternator components diagram
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘alternator components diagram’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for alternator components diagram Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing alternator components diagram With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for alternator components diagram
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the alternator components diagram Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of alternator components diagram
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for alternator components diagram
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Understanding alternator components diagram Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Schematic Diagram | Simplified representation of electrical connections and flow. | Educational tools, Training manuals | Pros: Easy to understand; Cons: Lacks detail. |
| Functional Block Diagram | Shows the functional relationships between components. | System design, Engineering analysis | Pros: Highlights interactions; Cons: Can be abstract. |
| Detailed Technical Diagram | Comprehensive view with dimensions and specifications. | Manufacturing, Technical specifications | Pros: High accuracy; Cons: Complex and time-consuming to interpret. |
| 3D Model Diagram | Visual 3D representation of the alternator and its components. | Product design, Prototyping | Pros: Intuitive visualization; Cons: Requires software for viewing. |
| Electrical Wiring Diagram | Focused on the wiring and electrical connections within the alternator. | Repair and maintenance, Electrical engineering | Pros: Essential for troubleshooting; Cons: Can be overwhelming for novices. |
What are the Characteristics of Schematic Diagrams and Their B2B Relevance?
Schematic diagrams are essential for illustrating the basic electrical connections and flow within an alternator. They are particularly useful in educational settings, enabling trainers to convey complex concepts simply. B2B buyers in the automotive training sector often prefer these diagrams for their clarity. However, while they are beneficial for foundational understanding, they may lack the detailed information required for in-depth technical work.
How Do Functional Block Diagrams Aid in System Design?
Functional block diagrams depict the relationships and interactions between various components of an alternator, making them invaluable in system design and engineering analysis. These diagrams help B2B buyers involved in product development visualize how each part contributes to the overall function. The main drawback is their abstract nature, which can make them less useful for those needing detailed specifications.
What Benefits Do Detailed Technical Diagrams Offer to Manufacturers?
Detailed technical diagrams provide an exhaustive view of an alternator, including dimensions, specifications, and material properties. This level of detail is crucial for manufacturers and engineers who require precision in production processes. While these diagrams enhance accuracy and provide comprehensive data, they can be complex, requiring significant time and expertise to interpret effectively.
Why Are 3D Model Diagrams Valuable for Product Design?
3D model diagrams offer a visual representation of the alternator and its components, facilitating intuitive understanding among engineers and designers. They are particularly beneficial in product design and prototyping, allowing teams to visualize spatial relationships and mechanical interactions. However, accessing and manipulating these models often requires specialized software, which may pose a barrier for some buyers.
How Do Electrical Wiring Diagrams Support Repair and Maintenance?
Electrical wiring diagrams focus on the specific wiring and electrical connections within the alternator, making them essential for repair and maintenance professionals. These diagrams are crucial for troubleshooting issues and ensuring proper installation. While they provide vital information for skilled technicians, they can be overwhelming for those less familiar with electrical systems, necessitating a certain level of expertise for effective use.
Key Industrial Applications of alternator components diagram
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of alternator components diagram | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive Manufacturing | Design and assembly of vehicle alternators | Enhances reliability and performance of vehicles | Quality standards, compatibility with existing systems, local regulations |
| Renewable Energy | Integration in wind and solar energy systems | Provides stable power generation and storage | Durability under varying environmental conditions, efficiency ratings |
| Marine Engineering | Power generation for boats and ships | Ensures reliable electrical supply for navigation | Corrosion resistance, size and weight considerations, maintenance support |
| Heavy Equipment | Powering machinery in construction and mining | Increases operational efficiency and reduces downtime | Customization options, ruggedness for harsh conditions, service availability |
| Telecommunications | Backup power for communication towers | Ensures continuous operation of communication systems | Voltage regulation capabilities, size constraints, local service support |
How is the alternator components diagram used in automotive manufacturing?
In automotive manufacturing, the alternator components diagram is essential for the design and assembly of vehicle alternators. This diagram provides a clear visual representation of the components and their functions, aiding engineers in optimizing alternator performance and reliability. By understanding the interactions between parts such as the rotor, stator, and rectifier, manufacturers can ensure that the alternators meet industry standards for efficiency and durability. International buyers from regions like Europe and the Middle East should consider sourcing components that adhere to their specific regulations and quality benchmarks.
What role does the alternator components diagram play in renewable energy systems?
In the renewable energy sector, particularly in wind and solar applications, the alternator components diagram is used to integrate alternators into energy systems. It helps engineers design systems that convert mechanical energy into electrical energy efficiently, ensuring stable power generation and storage. This is crucial for maintaining energy supply consistency. Buyers from Africa and South America should prioritize sourcing alternators that can withstand local environmental conditions, including humidity and temperature fluctuations, to ensure long-term operation.
How does the alternator components diagram benefit marine engineering?
Marine engineering relies heavily on the alternator components diagram for the design and maintenance of power generation systems on boats and ships. The diagram helps in understanding how alternators provide a reliable electrical supply necessary for navigation and onboard systems. Given the corrosive nature of marine environments, international buyers should focus on sourcing alternators with corrosion-resistant materials and robust cooling systems to enhance longevity and performance in harsh conditions.
In what way is the alternator components diagram utilized in heavy equipment?
In the heavy equipment industry, the alternator components diagram is crucial for powering machinery used in construction and mining. It assists engineers in ensuring that the electrical systems of these machines operate efficiently, reducing downtime and enhancing productivity. Buyers should consider customization options for alternators that can handle the rigorous demands of heavy machinery, including size and ruggedness, to ensure compatibility with existing equipment and operational efficiency.
How does the alternator components diagram support telecommunications?
In telecommunications, the alternator components diagram is vital for implementing backup power systems in communication towers. It ensures that these towers maintain operational integrity during power outages. The diagram aids engineers in selecting alternators with appropriate voltage regulation capabilities that meet the specific power needs of these systems. Buyers, especially in regions with unstable power supplies, should consider sourcing alternators that offer compact designs and local service support to ensure quick maintenance and repairs.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘alternator components diagram’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty Understanding Technical Diagrams
The Problem: B2B buyers often face challenges when interpreting alternator components diagrams, especially those who may not have a strong technical background. This can lead to confusion regarding the function and interrelation of each component, such as the rotor, stator, and rectifier. Misunderstanding these diagrams can result in improper installation or maintenance, which could lead to costly repairs or system failures.
The Solution: To overcome this challenge, B2B buyers should seek comprehensive educational resources tailored to their level of understanding. This can include detailed guides that break down each component of the alternator and its role within the system. Suppliers should provide annotated diagrams that highlight key parts and their functions, accompanied by explainer videos or webinars that offer visual and auditory learning. Furthermore, engaging with technical support teams for personalized explanations can help demystify complex diagrams. Buyers should also consider investing in training programs for their staff to enhance technical literacy, ensuring that everyone involved in the installation and maintenance processes can accurately interpret the diagrams.
Scenario 2: Sourcing Quality Components Based on Diagrams
The Problem: When B2B buyers refer to alternator components diagrams for sourcing parts, they often struggle to find high-quality components that match the specifications indicated in the diagrams. This is particularly challenging for international buyers who may face discrepancies in part numbers and specifications due to varying regional standards. This can lead to delays in production and increased costs if the wrong components are ordered.
The Solution: To effectively source quality components, buyers should establish partnerships with reputable suppliers who have a robust understanding of international standards and compatibility issues. Before placing orders, buyers can request detailed specifications and certifications for each component to ensure they meet the required standards. Additionally, utilizing digital platforms that provide part compatibility checks based on the alternator diagrams can streamline the sourcing process. Buyers should also consider leveraging supplier networks that specialize in automotive components to gain access to a broader range of verified options, ultimately reducing the risk of ordering incorrect parts.
Scenario 3: Ensuring Accurate Integration of Components
The Problem: B2B buyers often face difficulties ensuring that the alternator components integrate seamlessly with existing systems, particularly in complex automotive setups. Misalignment in voltage regulation or incorrect configurations can lead to performance issues or even damage to electrical systems, resulting in costly downtime for businesses.
The Solution: To ensure accurate integration, buyers should adopt a systematic approach that includes comprehensive testing and validation of each component against the alternator diagram. Engaging in a thorough review process that includes simulations or prototype testing can help identify potential integration issues before full-scale implementation. Collaborating with engineers or technical consultants who can provide insights into compatibility and performance can also be invaluable. Furthermore, buyers should maintain an open line of communication with component manufacturers to clarify any uncertainties regarding integration specifications. This proactive approach will help mitigate risks and ensure that all components work harmoniously within the overall system.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for alternator components diagram
What Are the Key Materials Used in Alternator Components?
When selecting materials for alternator components, it is essential to consider the specific properties and performance requirements of each material. Below are analyses of four common materials used in alternators, focusing on their key properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for international B2B buyers.
Aluminum: The Lightweight Champion
Aluminum is widely used for the outer housing of alternators due to its lightweight and non-magnetic properties. It effectively dissipates heat generated during operation, which is crucial for maintaining performance and longevity.
Pros: Aluminum is durable, resistant to corrosion, and relatively easy to machine. Its lightweight nature reduces the overall weight of the vehicle, improving fuel efficiency.
Cons: While aluminum is strong, it can be more expensive than some other materials like steel. Its manufacturing processes may require more energy, impacting overall costs.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is suitable for automotive applications where weight and heat dissipation are critical. However, it may not perform well in extreme environments without additional coatings.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in regions like Africa and South America should consider the availability of aluminum and its cost implications. Compliance with standards such as ASTM for aluminum alloys is crucial for ensuring quality and performance.
Steel: The Sturdy Workhorse
Steel is often utilized for components like the rotor and stator due to its high strength and durability. It can withstand significant mechanical stress and is often more cost-effective than aluminum.
Pros: Steel offers excellent tensile strength and is highly durable, making it suitable for high-stress applications. It is also relatively inexpensive compared to aluminum.
Cons: Steel is heavier than aluminum, which can affect vehicle performance. Additionally, it is prone to corrosion, requiring protective coatings or treatments.
Impact on Application: Steel components are ideal for applications where strength is paramount. However, they may require additional maintenance in corrosive environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in Europe, particularly Germany, should ensure compliance with DIN standards for steel grades. In regions with high humidity, corrosion resistance becomes a significant factor.
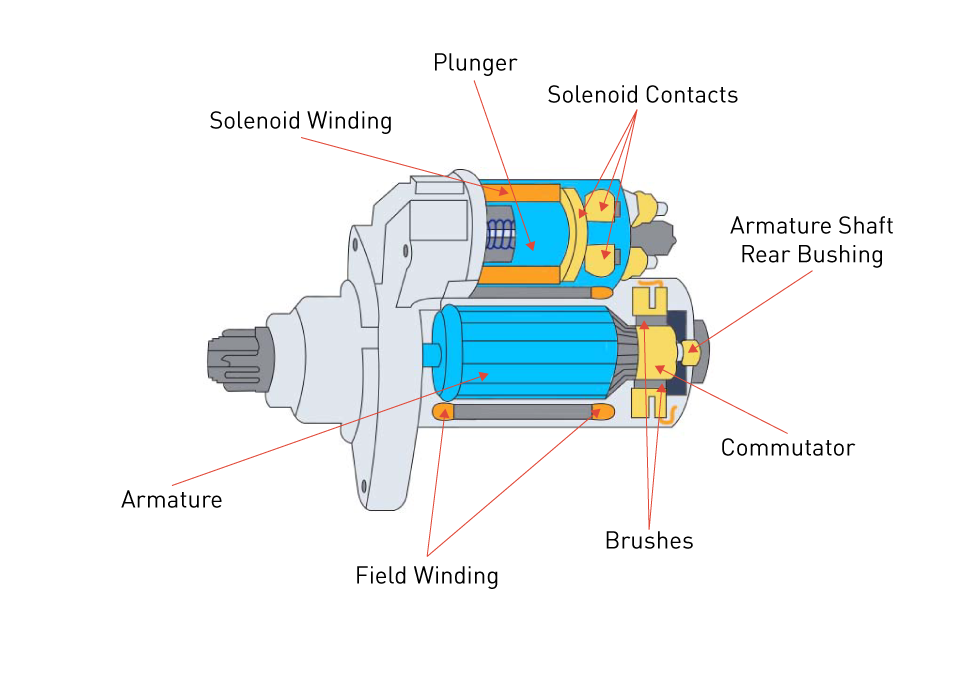
Illustrative image related to alternator components diagram
Copper: The Electrical Conductor
Copper is commonly used for windings and electrical connections within alternators due to its excellent electrical conductivity.
Pros: Copper has the highest electrical conductivity of all metals, ensuring efficient power transfer. It is also resistant to corrosion, particularly when coated.
Cons: Copper is more expensive than aluminum and can add weight to the alternator. Its availability may also vary by region, impacting procurement.
Impact on Application: Copper is essential for applications requiring efficient electrical performance. However, its weight may be a consideration in lightweight vehicle designs.
Illustrative image related to alternator components diagram
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the fluctuating copper prices and ensure compliance with international standards for electrical components, such as IEC standards.
Plastic Composites: The Innovative Alternative
Plastic composites are increasingly being used for non-structural components like covers and housings due to their lightweight and corrosion-resistant properties.
Pros: These materials are lightweight, can be molded into complex shapes, and are resistant to various chemicals. They also offer good insulation properties.
Cons: Plastic composites may not withstand high temperatures as well as metals and can be less durable under mechanical stress.
Impact on Application: Plastic composites are suitable for applications where weight savings are critical, but they may not be appropriate for high-stress components.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that the selected plastic composites meet relevant standards for automotive applications, such as ISO standards, and consider the implications of temperature variations in different regions.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Alternator Components
| Material | Typical Use Case for alternator components diagram | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Outer housing, cooling fins | Lightweight and excellent heat dissipation | Higher cost than steel | Medium |
| Steel | Rotor, stator | High strength and durability | Heavier and prone to corrosion | Low |
| Copper | Electrical windings and connections | Best electrical conductivity | Expensive and adds weight | High |
| Plastic Composites | Non-structural components like covers | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Less durable under mechanical stress | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide provides actionable insights for B2B buyers, aiding in the decision-making process for sourcing alternator components that meet both performance and regulatory requirements across various international markets.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for alternator components diagram
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Alternator Components?
The manufacturing process for alternator components is intricate, requiring precision and adherence to international standards to ensure performance and reliability. The process generally consists of four main stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
-
Material Preparation
The initial stage involves selecting high-quality raw materials. Common materials include aluminum for the housing, copper for windings, and steel for various internal components. Each material is subjected to rigorous testing to verify its mechanical and electrical properties. Suppliers should provide material certifications to ensure compliance with industry standards. -
Forming Techniques
In this stage, raw materials undergo various forming techniques. Aluminum housings are typically produced through die casting, which allows for complex shapes with minimal waste. For components like the rotor and stator, processes such as stamping and machining are used. Advanced techniques like CNC machining can enhance precision, particularly for the slip rings and brushes, which require tight tolerances. -
Assembly Procedures
Once components are formed, they move to the assembly stage. This involves the integration of various parts, including the rotor, stator, rectifier, and voltage regulator. Automated assembly lines are common, utilizing robotics for tasks such as inserting diodes and securing connections. Each assembly line should be equipped with sensors to monitor alignment and fit, ensuring that components meet specifications before proceeding. -
Finishing Processes
The final stage includes surface treatments and quality checks. Components may undergo anodizing or powder coating to enhance corrosion resistance and aesthetics. Additionally, finishing processes may involve balancing the rotor to reduce vibrations during operation. Quality checkpoints at this stage are crucial to ensure that the alternator meets performance standards.
What Quality Assurance Standards Should B2B Buyers Consider?
Quality assurance is critical in the manufacturing of alternator components, particularly for international buyers. Adherence to recognized standards ensures that products meet specific quality and safety criteria.
-
International Standards
ISO 9001 is the leading standard for quality management systems. Manufacturers should be certified to this standard, which focuses on continuous improvement and customer satisfaction. Buyers can request ISO certificates as part of their supplier verification process. -
Industry-Specific Standards
Depending on the market, additional certifications may be relevant. For example, CE marking is essential for products sold in the European Economic Area, indicating compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards. In regions like Africa and South America, local certifications may also apply, depending on regulatory requirements. -
Quality Control Checkpoints
A comprehensive quality control system should include several checkpoints:
– Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This stage verifies the quality of raw materials upon receipt.
– In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during production helps catch defects early.
– Final Quality Control (FQC): A thorough inspection of finished products ensures they meet all specifications before shipment.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers should implement several strategies to ensure their suppliers maintain high-quality standards.
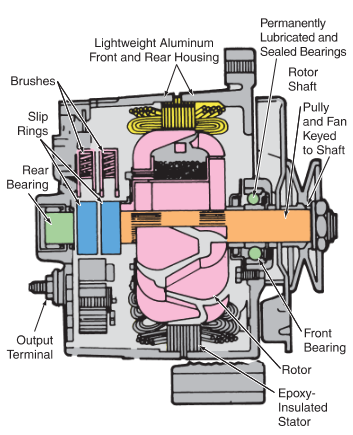
Illustrative image related to alternator components diagram
-
Conducting Audits
Regular audits of suppliers can provide insights into their quality control processes. Buyers should assess how well suppliers adhere to ISO standards and their internal QC procedures. Audits can also identify areas for improvement and foster stronger relationships. -
Requesting Quality Reports
Suppliers should provide detailed quality reports that outline testing methods, results, and corrective actions taken for any non-conformities. These reports can serve as a crucial tool for evaluating the supplier’s commitment to quality. -
Utilizing Third-Party Inspection Services
Engaging third-party inspection services can add an additional layer of assurance. These independent organizations can conduct inspections at various stages of the manufacturing process, providing unbiased assessments of product quality and compliance with specifications.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used in Quality Assurance?
Quality assurance for alternator components involves several testing methods to ensure reliability and performance.
-
Electrical Testing
Electrical tests measure the output voltage, current, and efficiency of alternators. These tests are crucial to validate the functionality of components like rectifiers and voltage regulators. -
Mechanical Testing
Mechanical tests assess the durability and strength of components. This includes tests for tensile strength, fatigue, and vibration resistance, ensuring that the alternator can withstand operational stresses. -
Thermal Testing
Since alternators generate heat during operation, thermal testing is essential. This includes evaluating the cooling efficiency of the alternator and ensuring that temperature limits are not exceeded. -
Environmental Testing
Components may undergo environmental testing to ensure they can operate under various conditions, such as extreme temperatures, humidity, and exposure to corrosive elements. This is particularly relevant for international buyers in diverse climatic regions.
What Are the Quality Control and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers must navigate various quality control and certification nuances that can differ significantly across regions.
-
Regional Compliance Requirements
Different countries have specific compliance requirements that may affect the certification process. For instance, products sold in Europe must meet CE standards, while products in the U.S. may require compliance with the Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standards (FMVSS). -
Cultural Considerations
Understanding cultural differences in business practices can influence supplier relationships. Buyers should be aware of negotiation styles, communication preferences, and the importance of building trust, especially in regions like Africa and South America. -
Documentation and Traceability
Buyers should ensure that suppliers maintain comprehensive documentation for all quality control processes. This includes records of inspections, test results, and certifications. Traceability is crucial for addressing any quality issues that may arise post-purchase.
By understanding these manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing alternator components, ensuring they select suppliers who meet their quality and performance expectations.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘alternator components diagram’
Introduction
This practical sourcing guide aims to assist B2B buyers in effectively procuring alternator components diagrams. Understanding the intricate details of these diagrams is essential for ensuring compatibility, enhancing operational efficiency, and facilitating communication with suppliers. This checklist will provide actionable steps to streamline the sourcing process and ensure you make informed decisions.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before engaging with suppliers, it is vital to articulate your technical requirements for the alternator components diagram. This includes understanding the specific components needed, such as the rotor, stator, rectifier, and voltage regulator. Clearly defined specifications help minimize misunderstandings and ensure you receive products that meet your operational needs.
- Considerations: Identify the power requirements, voltage specifications, and any specific industry standards applicable to your region.
Step 2: Research and Identify Reputable Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to compile a list of potential suppliers that specialize in alternator components. Look for companies with a proven track record in your target markets, such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
- Evaluation Criteria: Prioritize suppliers with positive reviews, industry certifications, and a portfolio showcasing their expertise in alternator components.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Verifying supplier certifications is crucial in ensuring that the products you source comply with industry standards and regulations. This step helps mitigate risks associated with low-quality components.
- Focus Areas: Look for ISO certifications, compliance with regional automotive standards, and any relevant safety certifications that demonstrate product reliability.
Step 4: Request Detailed Product Information
Once you have shortlisted potential suppliers, request comprehensive product information, including detailed diagrams of the alternator components. This information should clarify how each component interacts within the system.
- Documentation: Ensure that you receive technical datasheets, installation guides, and electrical diagrams that provide insights into product functionality and integration.
Step 5: Assess Quality Control Processes
Understanding the quality control measures implemented by your suppliers is essential. Reliable suppliers will have robust quality assurance processes to ensure that each component meets the required specifications before shipping.
- Key Questions: Inquire about their testing protocols, inspection processes, and how they handle defective products. Look for suppliers who offer warranties or guarantees on their components.
Step 6: Discuss Lead Times and Delivery Options
Timely delivery is critical in maintaining project schedules. Discuss lead times with potential suppliers to ensure they can meet your timelines. Inquire about their logistics capabilities, especially if you are sourcing from international suppliers.
- Delivery Considerations: Assess their shipping methods, costs, and any potential customs issues that could affect delivery times.
Step 7: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Finally, before finalizing your order, negotiate terms and conditions that align with your business needs. This includes pricing, payment terms, and return policies.
- Negotiation Tips: Be clear about your expectations and seek mutually beneficial agreements. Document all terms to avoid misunderstandings later in the procurement process.
By following this step-by-step checklist, B2B buyers can ensure a streamlined and effective sourcing process for alternator components diagrams, ultimately enhancing operational efficiency and product quality.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for alternator components diagram Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Alternator Components?
When evaluating the costs associated with sourcing alternator components, several key cost components must be considered. These include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and supplier margin.
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts the cost. Alternators typically utilize lightweight aluminum for housing, copper for windings, and various plastics for insulation. The market price fluctuations of these raw materials can affect overall costs, so buyers should monitor trends in commodities.
-
Labor: Labor costs are influenced by the geographic location of the manufacturing facility. Regions with higher wages, such as Western Europe, may present higher labor costs compared to countries in Africa or South America, where labor may be more affordable.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to the factory environment, utilities, and administrative expenses. Efficient manufacturing processes can lower overhead, making it crucial to evaluate suppliers’ operational efficiency.
-
Tooling: The initial setup costs for tooling can be substantial, especially for custom components. Buyers should assess whether the supplier’s tooling is already established for standard components or if new tooling is required, which can add to upfront costs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring the reliability and performance of alternator components requires rigorous QC processes. While robust QC can increase costs, it ultimately reduces the risk of product failures, which can be more expensive in the long run.
-
Logistics: Transportation and shipping costs vary significantly based on distance, mode of transport, and logistics infrastructure. International buyers must account for import duties and taxes, which can add to the total cost.
-
Margin: Suppliers will typically include a profit margin in their pricing. Understanding the competitive landscape and the value proposition of different suppliers can help buyers negotiate better terms.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Sourcing Decisions for Alternator Components?
Several factors can influence the pricing of alternator components, particularly for international B2B buyers.
-
Volume/MOQ: Purchasing in larger quantities often results in lower per-unit costs. Buyers should negotiate minimum order quantities (MOQs) that align with their inventory and cash flow capabilities.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom components tailored to specific applications can incur higher costs due to additional design and manufacturing processes. Buyers need to balance the necessity of customization with cost implications.
-
Materials: The selection of premium materials can enhance performance but also increase costs. Buyers must evaluate the trade-off between material quality and pricing to find an optimal solution.
-
Quality and Certifications: Components that meet specific industry standards or certifications may command higher prices. Buyers should consider the long-term benefits of quality assurance against the initial investment.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, reliability, and customer service can significantly influence pricing. Establishing a long-term partnership with a trustworthy supplier may yield better pricing and service terms over time.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is crucial for international transactions. These terms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs, which can impact the total landed cost.
What Are Effective Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficient Sourcing of Alternator Components?
To maximize cost efficiency in sourcing alternator components, international buyers should consider the following strategies:
-
Negotiation: Engage in negotiations with suppliers to secure better pricing, especially for larger orders. Building strong relationships can facilitate more favorable terms.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate the total cost of ownership, which includes initial purchase price, maintenance, and potential failure costs. This holistic view can help identify the most cost-effective options.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Be aware of currency fluctuations, import duties, and regional economic conditions that may affect pricing. Establishing contracts in stable currencies can mitigate risks.
-
Market Research: Conduct thorough market research to understand pricing trends and alternative suppliers. This knowledge can empower buyers during negotiations and sourcing decisions.
-
Supplier Audits: Regularly audit suppliers for quality and efficiency. This practice can uncover potential areas for cost savings and ensure compliance with standards.
By considering these cost components, pricing influencers, and strategic tips, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing alternator components, ultimately enhancing their supply chain efficiency and profitability.

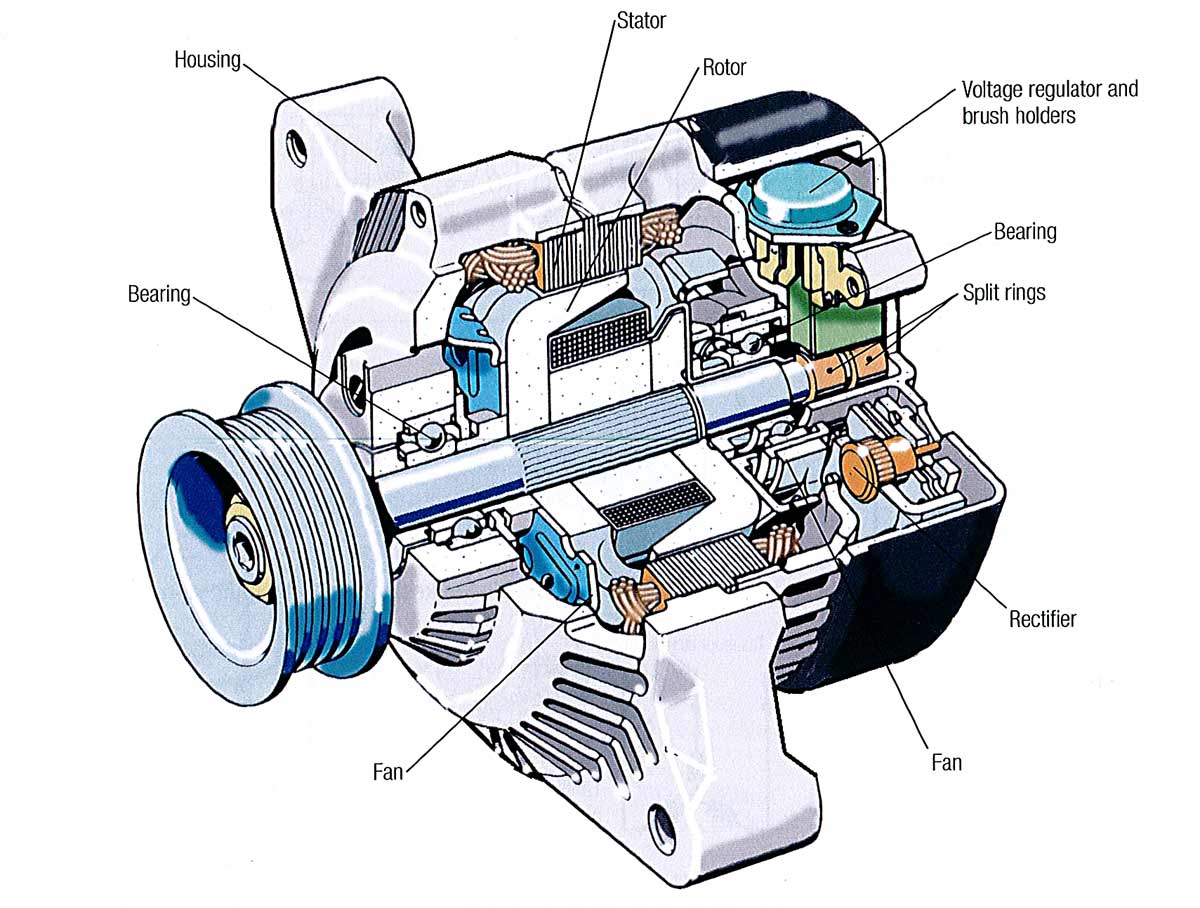
Illustrative image related to alternator components diagram
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing alternator components diagram With Other Solutions
Introduction: Exploring Alternatives in Alternator Solutions
In the automotive and industrial sectors, understanding the workings of alternators is crucial for optimizing power generation and ensuring reliability. While the ‘alternator components diagram’ serves as a valuable tool for visualizing the intricate parts and functions of an alternator, several alternative solutions exist that can also achieve similar objectives. This analysis will compare the ‘alternator components diagram’ against two viable alternatives: the ‘Alternator Simulation Software’ and the ‘Manual Troubleshooting Guide.’ Each option has its unique benefits and challenges, making it important for B2B buyers to carefully consider which solution best meets their operational needs.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Alternator Components Diagram | Alternator Simulation Software | Manual Troubleshooting Guide |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High for educational purposes | High for practical application | Moderate, depends on user skill |
| Cost | Low (often free or low-cost) | Moderate to high (software licensing) | Low (print or digital format) |
| Ease of Implementation | Easy to integrate in training | Requires software setup and training | Simple, but requires technical knowledge |
| Maintenance | No maintenance required | Regular updates needed | No maintenance, but may become outdated |
| Best Use Case | Educational settings | Training and diagnostic purposes | On-site troubleshooting and repairs |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Alternator Simulation Software
This software provides a virtual environment to simulate the functioning of alternators, allowing users to manipulate various parameters and observe outcomes in real time. One of the significant advantages of this solution is its ability to provide a hands-on learning experience without the risk of damaging physical components. However, the software can be relatively costly, requiring licensing fees, and may necessitate ongoing updates to remain relevant. Additionally, users must undergo training to navigate the software effectively, which can be a barrier for some organizations.
Manual Troubleshooting Guide
A manual troubleshooting guide is a practical resource that outlines common issues, symptoms, and solutions related to alternators. This solution excels in cost-effectiveness, as it is often available in print or digital formats at low costs. It provides quick reference points for technicians in the field, aiding in on-site repairs. However, its effectiveness largely depends on the skill level of the user; inexperienced technicians may struggle to diagnose problems accurately. Furthermore, the information may become outdated, necessitating periodic revisions to remain useful.
Conclusion: Selecting the Right Solution for Your Needs
When choosing between the ‘alternator components diagram,’ ‘alternator simulation software,’ and ‘manual troubleshooting guide,’ B2B buyers should assess their specific requirements, budget constraints, and the technical skill level of their teams. The diagram is ideal for educational settings and foundational understanding, while simulation software offers interactive learning and diagnostic capabilities. Conversely, a troubleshooting guide serves well for immediate, hands-on applications in the field. By evaluating these factors, businesses can select the most effective solution to enhance their understanding and maintenance of alternator systems, ultimately leading to improved operational efficiency.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for alternator components diagram
What are the Key Technical Properties of Alternator Components?
When considering the procurement of alternator components, understanding specific technical properties is essential for ensuring compatibility and performance in various applications. Here are some critical specifications that B2B buyers should be aware of:
1. Material Grade
The outer housing of alternators is primarily made from aluminum due to its lightweight and non-magnetizing properties. This material choice is crucial for heat dissipation and durability. For buyers, specifying material grades ensures that components meet industry standards, which can significantly impact the longevity and reliability of the alternator in automotive applications.
2. Tolerance Levels
Tolerance levels refer to the acceptable variations in dimensions and specifications of the alternator components. Tight tolerances are essential for components like the rotor and stator to ensure they fit correctly and operate efficiently. In B2B transactions, establishing clear tolerance requirements helps prevent manufacturing defects and ensures that the components perform optimally in real-world conditions.
3. Voltage Rating
The voltage rating of an alternator indicates the maximum electrical output it can provide. This is particularly important for applications that require specific voltage levels for compatibility with various electronic systems. Buyers must assess the voltage requirements of their applications to ensure that the alternator will provide sufficient power without risking damage to sensitive electronics.
Illustrative image related to alternator components diagram
4. Current Rating
Current ratings indicate the amount of electrical current an alternator can handle. This specification is critical for applications that demand higher power outputs, such as commercial vehicles or industrial machinery. Understanding current ratings allows buyers to select alternators that can support their operational needs without overloading the system.
5. Cooling Efficiency
Alternators generate significant heat during operation, and cooling efficiency is a key property. Modern alternators often incorporate internal cooling fans, while older models may feature external fans. For B2B buyers, understanding the cooling mechanism is crucial for ensuring that the alternator can maintain performance under high load conditions, thus extending its lifespan.
What are Common Trade Terms Used in Alternator Component Transactions?
Navigating the procurement landscape for alternator components requires familiarity with specific industry jargon. Here are some common terms that B2B buyers should understand:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that manufacture products that are used as components in another company’s product. In the context of alternators, OEM parts are those made by the same manufacturer as the original parts in a vehicle. Buyers often prefer OEM components for their guaranteed compatibility and quality.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is vital for buyers to manage inventory costs effectively. It helps in negotiating bulk purchases, which can lead to cost savings and ensures that procurement meets operational needs without overstocking.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting a quote for specific products or services. In the context of alternator components, an RFQ allows buyers to compare prices, lead times, and terms from multiple suppliers. This process is essential for making informed purchasing decisions.
4. Incoterms
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international trade. They cover aspects like shipping costs, insurance, and risk transfer. Familiarity with Incoterms is crucial for B2B buyers engaging with international suppliers to avoid misunderstandings regarding shipping and delivery responsibilities.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time it takes from placing an order to receiving the product. Understanding lead times is essential for B2B buyers to plan their inventory and production schedules effectively. It helps ensure that they have the necessary components available when needed, minimizing downtime in operations.
Illustrative image related to alternator components diagram
By grasping these essential technical properties and trade terminology, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing alternator components, ultimately leading to more efficient and reliable operations.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the alternator components diagram Sector
What Are the Key Trends Influencing the Alternator Components Diagram Market?
The global alternator components market is experiencing significant transformations driven by advancements in technology, increasing vehicle electrification, and a heightened focus on energy efficiency. As international B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe seek to enhance their supply chains, understanding these dynamics is crucial. Notably, the rise of electric and hybrid vehicles is reshaping the demand for alternators, prompting manufacturers to innovate and adapt their components accordingly.
In addition, the integration of smart technologies, such as intelligent voltage regulators, is becoming a standard feature. These advancements not only optimize performance but also facilitate better communication between the alternator and the vehicle’s management systems, thereby enhancing efficiency and reducing energy waste. Furthermore, the trend towards modular designs allows for easier replacement and upgrades, appealing to buyers looking for flexibility in sourcing components.
Emerging markets are also seeing a shift in sourcing strategies as companies aim to reduce lead times and costs. This is leading to an increased focus on local suppliers, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, where establishing a robust manufacturing base can mitigate supply chain disruptions. As international buyers navigate these trends, they must prioritize partnerships with suppliers who are not only technologically advanced but also capable of meeting the specific regulatory and operational requirements of their respective regions.
How Is Sustainability Shaping Ethical Sourcing Practices in the Alternator Components Market?
Sustainability has become a cornerstone of modern B2B sourcing, particularly in the alternator components sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes is under scrutiny, with buyers increasingly favoring suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to sustainable practices. This includes the use of eco-friendly materials and manufacturing techniques that minimize waste and reduce carbon footprints.
Ethical sourcing is gaining traction as businesses recognize the importance of maintaining transparent supply chains. Buyers are encouraged to seek suppliers that adhere to sustainability certifications, such as ISO 14001, which signifies a commitment to effective environmental management. The use of recycled materials in alternator components not only meets regulatory requirements but also appeals to environmentally conscious consumers, thereby enhancing brand reputation.
Moreover, the push for greener alternatives is leading to the development of innovative materials that reduce the overall environmental impact of alternators. For instance, manufacturers are exploring lightweight and recyclable materials for housing components, which can significantly lower emissions during production and use. By prioritizing ethical sourcing and sustainability, B2B buyers can contribute to a more responsible and future-proof automotive industry while ensuring compliance with increasing regulatory demands.
What Is the Historical Context of the Alternator Components Market?
The alternator has undergone significant evolution since its inception in the early 20th century. Initially, vehicles relied on simple dynamo systems for electrical generation, which were limited in efficiency and output. The transition to alternators in the 1960s marked a pivotal moment, as these devices provided a more reliable and efficient means of converting mechanical energy into electrical energy.
As automotive technology advanced, the design and functionality of alternators improved dramatically. The introduction of components like the rectifier and voltage regulator allowed for better voltage control and energy management, accommodating the growing electrical demands of modern vehicles. This evolution has been crucial for international B2B buyers, who now have access to a diverse range of high-performance alternator components designed to meet stringent regulatory standards and consumer expectations.
Understanding the historical context of alternators not only informs current sourcing decisions but also highlights the importance of innovation in maintaining competitive advantages in the ever-evolving automotive market. As the industry continues to evolve, B2B buyers must remain vigilant to emerging trends and technologies to ensure their supply chains are resilient and future-ready.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of alternator components diagram
-
How do I identify high-quality alternator components?
To identify high-quality alternator components, start by reviewing the supplier’s certifications and industry standards they adhere to, such as ISO or TS certifications. Request samples to evaluate the build quality and performance. Additionally, examine the materials used—aluminum housings are preferred for their heat dissipation properties. It’s also beneficial to seek feedback from previous customers regarding the supplier’s reliability and the longevity of their components. Conducting a thorough supplier audit can further ensure you’re sourcing from reputable manufacturers. -
What is the best way to obtain alternator components diagrams?
The best way to obtain alternator components diagrams is to directly request them from your suppliers. Many manufacturers provide detailed technical documentation, including diagrams, upon inquiry. Additionally, industry publications, technical manuals, and online databases can be excellent resources. Ensure that the diagrams are up-to-date and correspond with the specific alternator model you are sourcing. Participating in trade shows or industry conferences can also facilitate connections with suppliers who can provide these diagrams. -
How can I ensure compliance with international trade regulations when sourcing alternator components?
To ensure compliance with international trade regulations, familiarize yourself with the import/export laws of your country and the country of the supplier. Check for any trade agreements that may affect tariffs and duties. It’s advisable to work with a logistics partner or customs broker who understands the regulations involved in shipping alternator components. Additionally, ensure that the components meet safety and environmental standards required in your target market to avoid any compliance issues. -
What are the common payment terms in B2B transactions for alternator components?
Common payment terms in B2B transactions for alternator components typically include options like net 30, net 60, or payment upfront. Many suppliers may also accept letters of credit or escrow services to secure the transaction. It’s essential to negotiate terms that protect both parties and reflect the trust established during the sourcing process. Be sure to clarify any additional fees, such as transaction costs or currency conversion fees, as these can impact the overall pricing. -
What should I consider when discussing Minimum Order Quantities (MOQ) with suppliers?
When discussing Minimum Order Quantities (MOQ) with suppliers, consider your current inventory levels and demand forecasts. Ensure that the MOQ aligns with your production needs and cash flow capabilities. It’s also wise to inquire about potential discounts for larger orders, as many suppliers are open to negotiation. Additionally, assess the supplier’s flexibility in terms of adjusting the MOQ based on future orders or trial orders, which can help establish a long-term partnership. -
How do I vet suppliers for alternator components?
To vet suppliers for alternator components, conduct a thorough background check, including their business history, market reputation, and financial stability. Request references from previous clients and verify their quality control processes. Evaluate their production capabilities by visiting their facilities if possible or arranging virtual tours. Additionally, ensure they have proper certifications and adhere to industry standards. Engaging in small trial orders can also help assess their reliability before committing to larger purchases. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing alternator components?
When importing alternator components, consider the shipping methods, lead times, and associated costs. Evaluate whether air freight or sea freight is more suitable based on your urgency and budget. Ensure that you account for customs clearance processes, including necessary documentation like bills of lading and commercial invoices. It’s also beneficial to work with a logistics provider experienced in handling automotive components to mitigate risks and streamline the import process. -
How can I ensure quality assurance for alternator components?
To ensure quality assurance for alternator components, establish clear quality criteria with your supplier before production. Request detailed quality control plans and regular updates during the manufacturing process. Implement a system for incoming inspections upon delivery to verify that the components meet the agreed specifications. Consider third-party quality audits or certifications to validate the supplier’s compliance with international quality standards. Establishing a robust feedback loop can also help address any issues promptly.
Top 6 Alternator Components Diagram Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Electude – Alternator
Domain: electude.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: An alternator is a crucial automotive component that converts mechanical energy into electrical energy, generating power for the vehicle’s electrical consumer units and battery. Key components include:
– Pulley: Transfers mechanical energy from the engine to the alternator.
– Rotor: Creates the magnetic field for generating alternating current.
– Stator: The static part where voltage is generated…
2. HowStuffWorks – Alternators
Domain: auto.howstuffworks.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Alternators are small and lightweight, roughly the size of a coconut, constructed with an aluminum outer housing for heat dissipation. Key components include:
– Drive pulley attached to the rotor shaft, converting mechanical energy to electrical power.
– Terminals: S terminal (senses battery voltage), IG terminal (ignition switch), L terminal (warning lamp circuit), B terminal (main output to ba…
3. Facebook – Car Alternator Diagram
Domain: facebook.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: A detailed diagram showing the internal structure of a car alternator, with labeled components such as the rotor, stator windings, brushes, rectifier.
4. Pinterest – Car Alternator Diagrams
Domain: pinterest.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: This company, Pinterest – Car Alternator Diagrams, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
5. AutoElectro – Alternator Components
Domain: autoelectro.co.uk
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Alternator components and their functions include:
1. Regulator: Controls the power distribution from the alternator to the battery for charging.
2. Rectifier: Converts alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC) during charging.
3. Rotor: The spinning mass inside the alternator that acts as a spinning electromagnet.
4. Slip Rings: Provide direct current and power to the rotor.
5. Slip Ri…
6. Scribd – Automotive Alternator Parts
Domain: scribd.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: The document discusses the main parts and functions of an automotive alternator, describing 8 key parts: 1) Pulley – rotates the rotor assembly via the engine belt, 2) Housing – protects internal components, 3) Bearings – allow the rotor to spin freely, 4) Rotor Assembly – generates a magnetic field, 5) Stator Assembly – uses the magnetic field to generate electricity, 6) Rectifier – converts alte…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for alternator components diagram
In conclusion, understanding the intricacies of alternator components is essential for B2B buyers looking to optimize their sourcing strategies. Key components such as the rotor, stator, rectifier, and voltage regulator play pivotal roles in the efficiency and functionality of alternators. By investing in high-quality parts and reliable suppliers, businesses can ensure the longevity and performance of their electrical systems, ultimately reducing operational costs and enhancing customer satisfaction.
Strategic sourcing not only mitigates risks associated with supply chain disruptions but also fosters relationships with manufacturers who prioritize innovation and quality. For international buyers from diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, this is an opportunity to leverage regional suppliers who understand local demands and compliance standards.
Illustrative image related to alternator components diagram
Looking ahead, as the automotive industry increasingly shifts towards electrification and advanced technologies, staying ahead of sourcing trends will be crucial. We encourage businesses to engage with trusted suppliers, invest in advanced alternator technologies, and explore collaborative opportunities that can drive growth and sustainability. Empower your procurement strategy today and secure your competitive edge in the evolving marketplace.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.