Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for main car parts
In the rapidly evolving automotive industry, effectively sourcing main car parts can be a daunting challenge for B2B buyers, particularly those operating in diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. With varying regulations, quality standards, and supply chain complexities, navigating the global market requires not just knowledge but also strategic insights. This comprehensive guide aims to demystify the process by providing an in-depth exploration of the key components of vehicles, their applications, and the critical factors to consider when sourcing these parts.
Within these pages, you will find detailed information about various types of car parts—including engines, transmissions, braking systems, and more—alongside guidance on evaluating suppliers, understanding pricing structures, and assessing quality control measures. Each section is designed to empower international B2B buyers with the knowledge necessary to make informed purchasing decisions that align with their operational needs and market demands.
By leveraging the insights offered in this guide, businesses can streamline their procurement processes, mitigate risks associated with international sourcing, and ultimately enhance their competitive edge in the automotive sector. Whether you are based in Brazil or Vietnam, this resource is tailored to equip you with the tools to successfully navigate the complexities of the global car parts market.
Table Of Contents
- Top 2 Main Car Parts Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for main car parts
- Understanding main car parts Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of main car parts
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘main car parts’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for main car parts
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for main car parts
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘main car parts’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for main car parts Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing main car parts With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for main car parts
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the main car parts Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of main car parts
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for main car parts
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Understanding main car parts Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Engine | Internal combustion, components include pistons, crankshaft, camshaft | OEM replacements, performance upgrades | Pros: Central to vehicle operation; wide range of aftermarket options. Cons: High cost for advanced models; complexity may require specialized knowledge. |
| Transmission | Types include automatic, manual, CVT; manages power delivery | Fleet management, repair services | Pros: Essential for vehicle control; varied options for different driving styles. Cons: Complexity can lead to higher repair costs; specific models may limit compatibility. |
| Suspension System | Composed of shocks, springs, and linkages; enhances ride quality | Automotive repair, aftermarket enhancements | Pros: Improves safety and handling; diverse options for performance tuning. Cons: Installation can be labor-intensive; some parts may wear out quickly under heavy use. |
| Braking System | Includes disc and drum brakes; critical for safety | Fleet maintenance, parts replacement | Pros: Essential for vehicle safety; various types available for different applications. Cons: Performance can degrade over time; higher-performance options can be costly. |
| Electrical System | Comprises battery, alternator, wiring; powers vehicle electronics | OEM parts supply, electrical upgrades | Pros: Vital for modern vehicle functionality; numerous aftermarket enhancements available. Cons: Electrical issues can be challenging to diagnose; compatibility issues with older vehicles. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Engine Types?
The engine serves as the heart of any vehicle, responsible for converting fuel into mechanical energy. B2B buyers should consider the engine type (e.g., gasoline, diesel, hybrid) based on the vehicle’s application, such as commercial transport or personal use. The complexity of engine components, including pistons and crankshafts, means that sourcing OEM parts ensures compatibility and reliability. Additionally, performance upgrades may be beneficial for businesses seeking to enhance fuel efficiency or power output.
How Do Different Transmission Types Impact Vehicle Performance?
Transmission types, including automatic, manual, and continuously variable (CVT), significantly influence vehicle performance and driving experience. For fleet operators, understanding the advantages of each type is crucial; automatic transmissions offer ease of use, while manual options can provide better control and fuel efficiency. When purchasing, B2B buyers should assess the specific needs of their operations, including maintenance costs and driver preferences, to choose the most suitable transmission type.
Why Is the Suspension System Important for Vehicle Handling?
The suspension system plays a critical role in vehicle handling, comfort, and safety. Comprising components like shocks and springs, it absorbs road irregularities and maintains tire contact with the road. B2B buyers, particularly in the automotive repair sector, should focus on high-quality suspension parts to ensure optimal vehicle performance and safety. The choice of suspension system can also affect ride height and handling characteristics, which are essential for specific applications, such as off-road vehicles or performance cars.
What Should B2B Buyers Know About Braking Systems?
Braking systems, consisting of either disc or drum brakes, are fundamental to vehicle safety. They are designed to provide reliable stopping power under various conditions. B2B buyers must consider the type of braking system that best fits their fleet’s needs, as different systems may offer varying levels of performance and maintenance requirements. Understanding the pros and cons of each system can help businesses make informed purchasing decisions, particularly in terms of safety compliance and overall vehicle reliability.
How Does the Electrical System Support Modern Vehicles?
The electrical system of a vehicle includes essential components such as the battery, alternator, and wiring, which power everything from ignition to infotainment systems. For B2B buyers, sourcing high-quality electrical parts is crucial for maintaining vehicle functionality and efficiency. Given the increasing reliance on electronic systems in modern vehicles, businesses should prioritize compatibility and reliability when selecting electrical components, especially for older models that may require specific upgrades or replacements.
Key Industrial Applications of main car parts
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of main car parts | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive Manufacturing | Engine components supply for assembly lines | Streamlined production processes and reduced lead times | Quality certifications, local sourcing options, and bulk pricing |
| Fleet Management | Replacement parts for maintenance of commercial vehicles | Reduced downtime and increased vehicle lifespan | Reliability of suppliers, availability of parts, and warranty terms |
| Transportation & Logistics | Fuel systems and transmission parts for heavy-duty trucks | Enhanced fuel efficiency and operational reliability | Compliance with local regulations, part compatibility, and cost |
| Aftermarket Parts Retail | Distribution of brake systems and suspension components | Increased customer satisfaction and repeat business | Inventory management, sourcing from reputable manufacturers, and pricing strategies |
| Electric Vehicle Development | Battery management systems and electric drivetrains | Meeting growing demand for sustainable transport solutions | Technological advancements, supplier innovation, and integration capabilities |
How are Engine Components Used in Automotive Manufacturing?
Engine components, such as pistons, crankshafts, and camshafts, are essential for automotive manufacturing, particularly in assembly lines. These parts are produced in bulk and must meet stringent quality standards to ensure the reliability and performance of the vehicles. For B2B buyers in regions like Africa and South America, sourcing high-quality engine components can significantly reduce production delays and enhance vehicle performance. Companies should focus on suppliers that offer quality certifications and can provide competitive pricing for bulk orders.
What Role Do Replacement Parts Play in Fleet Management?
In fleet management, replacement parts for maintenance, including brake systems and transmission components, are crucial for minimizing downtime and extending the lifespan of commercial vehicles. Regular maintenance using quality parts ensures that vehicles remain operational, which is vital for logistics and transportation companies. For international buyers, especially in the Middle East and Europe, it’s important to consider suppliers with a strong reputation for reliability and availability of parts, as well as favorable warranty terms to protect investments.
How Do Fuel Systems Impact Transportation & Logistics?
Fuel systems and transmission parts are pivotal for heavy-duty trucks in the transportation and logistics sector. These components directly influence fuel efficiency and the overall reliability of vehicles, which can lead to significant cost savings. For B2B buyers, understanding local regulations and ensuring part compatibility with existing vehicle models is essential. Additionally, sourcing from suppliers who can provide technical support and have a track record of innovation can enhance operational efficiency.
Why Are Brake Systems Important for Aftermarket Parts Retail?
Aftermarket parts retail relies heavily on the distribution of brake systems and suspension components. These parts not only improve vehicle safety but also boost customer satisfaction and loyalty. B2B buyers in this sector must focus on inventory management and partner with reputable manufacturers to ensure a steady supply of high-quality parts. Competitive pricing strategies are also crucial, as they can attract a larger customer base and increase market share.
What Innovations Are Driving Electric Vehicle Development?
In the burgeoning electric vehicle (EV) market, battery management systems and electric drivetrains are at the forefront of innovation. These components are critical for developing sustainable transport solutions that meet the increasing consumer demand for eco-friendly vehicles. For international B2B buyers, sourcing cutting-edge technology from suppliers who invest in research and development is essential. Buyers must also consider the integration capabilities of these parts with existing vehicle platforms to ensure seamless transitions in production.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘main car parts’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Sourcing Quality Parts Amid Supply Chain Disruptions
The Problem: In recent years, many B2B buyers in the automotive sector have faced significant challenges in sourcing quality car parts due to global supply chain disruptions. These disruptions can lead to delays, increased costs, and even a compromise in the quality of parts received. For buyers in regions such as Africa or South America, where local suppliers may be limited, the stakes are even higher. They often find themselves juggling multiple suppliers and dealing with inconsistencies in product quality, which ultimately affects their business operations and customer satisfaction.
The Solution: To navigate these challenges, B2B buyers should adopt a multi-sourcing strategy that includes both local and international suppliers. Building relationships with reputable suppliers that offer a strong track record for quality and reliability is crucial. Conducting thorough due diligence by checking references, reviewing product certifications, and requesting samples can help ensure that you are sourcing the best parts. Utilizing technology platforms for real-time inventory tracking can also provide insights into availability and lead times, allowing buyers to make informed decisions quickly. Additionally, establishing agreements with suppliers that include clauses for quality assurance and timely delivery can mitigate risks associated with supply chain disruptions.
Scenario 2: Understanding Technical Specifications for Compatibility
The Problem: A common pain point for B2B buyers is the complexity of understanding technical specifications and compatibility of car parts. This issue is particularly prevalent when dealing with diverse vehicle models and brands. Buyers often struggle to ensure that the parts they order are compatible with the specific vehicles in their fleet, which can lead to costly returns and wasted time. This is exacerbated in international markets where different regions may have unique vehicle specifications.
The Solution: To address compatibility issues, buyers should invest in training for their procurement teams focused on understanding vehicle specifications and part compatibility. Utilizing advanced software tools that provide comprehensive databases of parts and their corresponding vehicle applications can streamline the selection process. These tools can be integrated with existing inventory management systems for greater efficiency. Additionally, collaborating with manufacturers who offer technical support and detailed product documentation can help clarify specifications. Creating a standardized checklist for verifying compatibility before placing orders can also minimize errors and enhance overall procurement efficiency.
Scenario 3: Managing Costs Without Sacrificing Quality
The Problem: Cost management is a critical concern for B2B buyers, especially in competitive markets. Buyers often find themselves under pressure to reduce expenses while still needing to maintain high-quality standards for car parts. The challenge lies in balancing cost-cutting measures with the risk of sourcing cheaper, lower-quality parts that could lead to increased failure rates and customer dissatisfaction.
The Solution: B2B buyers can effectively manage costs by implementing a value-based procurement strategy. This involves assessing the total cost of ownership (TCO) rather than just the initial purchase price. Buyers should focus on long-term savings associated with quality parts that reduce maintenance and replacement costs over time. Establishing partnerships with manufacturers that offer bulk purchasing discounts or loyalty programs can also enhance cost-effectiveness. Furthermore, conducting regular performance evaluations of the parts used can help identify any cost-benefit discrepancies, allowing buyers to make informed decisions about switching suppliers or negotiating better terms based on performance data. Emphasizing quality over quantity will ultimately lead to improved customer satisfaction and lower operational costs in the long run.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for main car parts
What Are the Key Materials Used in Main Car Parts?
Understanding the materials used in automotive manufacturing is crucial for international B2B buyers, especially when considering performance, compliance, and cost. Below, we analyze four common materials used in the production of main car parts, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and specific considerations for buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
How Does Steel Perform in Automotive Applications?
Steel is one of the most widely used materials in automotive manufacturing due to its excellent strength-to-weight ratio and durability. Key properties include high tensile strength, good fatigue resistance, and the ability to withstand high temperatures and pressures. Steel components, such as chassis and suspension parts, can endure significant stress and are often treated for corrosion resistance.
Pros: Steel is relatively low-cost and can be easily formed and welded, making it suitable for mass production. Its durability ensures a long lifespan, reducing the frequency of replacements.
Cons: While steel is strong, it is also heavier than alternatives like aluminum, which can impact fuel efficiency. Additionally, untreated steel is prone to rust, necessitating protective coatings.
Impact on Application: Steel is compatible with various automotive fluids and environments but requires careful consideration regarding corrosion resistance in humid or coastal regions.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM A36 or DIN 17100 is essential. Buyers should also consider local availability and the cost implications of importing steel versus sourcing locally.
What Role Does Aluminum Play in Car Manufacturing?
Aluminum is increasingly favored in the automotive industry for its lightweight properties and resistance to corrosion. Key properties include a low density, high strength-to-weight ratio, and excellent thermal conductivity, making it ideal for engine components and body panels.
Pros: The lightweight nature of aluminum contributes to improved fuel efficiency and performance. Its resistance to corrosion reduces maintenance costs over time.
Cons: Aluminum can be more expensive than steel, and its manufacturing processes can be complex, requiring specialized techniques like welding and machining.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is compatible with most automotive fluids and environments, but its thermal expansion properties must be considered during design.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of compliance with standards such as ASTM B221 or JIS H4000. Regional preferences may also dictate the use of aluminum in specific applications, particularly in markets focused on fuel efficiency.
How Does Plastic Contribute to Automotive Parts?
Plastics, particularly engineering plastics, are widely used in automotive applications due to their versatility and lightweight characteristics. Key properties include resistance to chemicals, low density, and the ability to be molded into complex shapes.
Pros: Plastics are cost-effective and can be produced in large volumes. They offer excellent resistance to corrosion and can reduce overall vehicle weight.
Cons: While durable, plastics may not withstand high temperatures as well as metals, and their mechanical properties can vary significantly based on the type of plastic used.
Impact on Application: Plastics are suitable for interior components, dashboards, and non-structural parts but may require careful selection for high-temperature areas.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards like ASTM D638 or ISO 527 is crucial. Buyers should also consider the environmental impact of plastics and local regulations regarding their use.
What Advantages Does Composite Material Offer in Automotive Parts?
Composite materials, such as carbon fiber and fiberglass, are becoming increasingly popular for high-performance automotive applications. Key properties include exceptional strength-to-weight ratios and resistance to fatigue and corrosion.
Pros: Composites can significantly reduce vehicle weight, enhancing performance and fuel efficiency. They also offer design flexibility, allowing for complex shapes and aesthetics.
Cons: The cost of composites is generally high, and the manufacturing processes can be complex, requiring specialized skills and equipment.
Impact on Application: Composites are often used in high-performance parts, such as body panels and structural components, but their compatibility with traditional automotive manufacturing processes must be evaluated.
Illustrative image related to main car parts
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with standards like ASTM D7264 or ISO 527. Additionally, the availability of composite materials may vary by region, impacting sourcing decisions.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Main Car Parts
| Material | Typical Use Case for main car parts | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Chassis, suspension components | High strength and durability | Heavier than alternatives | Low |
| Aluminum | Engine components, body panels | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Higher cost, complex manufacturing | Medium |
| Plastic | Interior components, dashboards | Cost-effective and versatile | Temperature sensitivity | Low |
| Composite | High-performance parts, body panels | Exceptional strength-to-weight ratio | High cost, complex processing | High |
This strategic material selection guide provides a comprehensive overview for B2B buyers in the automotive industry, enabling informed decisions that align with performance, compliance, and cost considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for main car parts
What Are the Key Stages in Manufacturing Main Car Parts?
The manufacturing process for main car parts is a complex sequence that involves several critical stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Each stage employs specific techniques tailored to the unique requirements of automotive components.
How Is Material Prepared for Car Parts Manufacturing?
Material preparation is the first step in the manufacturing process. High-quality raw materials, such as steel, aluminum, and plastic composites, are sourced based on the specifications of the car parts being produced. This stage often involves the following:

Illustrative image related to main car parts
- Material Inspection: Incoming materials undergo rigorous inspection to ensure compliance with industry standards. Suppliers must provide material certificates that detail the chemical composition and mechanical properties.
- Cutting and Shaping: Depending on the part, raw materials are cut into specific dimensions using techniques such as laser cutting or water jet cutting. This precision is vital for ensuring that the components fit together seamlessly during assembly.
What Forming Techniques Are Commonly Used in Automotive Manufacturing?
Once the materials are prepared, forming techniques are utilized to create the desired shapes and structures of car parts. Common methods include:
- Stamping: This process involves pressing metal sheets into molds to create components like body panels and brackets. Stamping is efficient for high-volume production and ensures consistent part dimensions.
- Casting: Used for complex shapes, casting involves pouring molten metal into molds. This method is prevalent for engine blocks and cylinder heads, where intricate designs are necessary.
- Injection Molding: For plastic components, injection molding is widely used. This technique involves injecting heated plastic into a mold, allowing for high precision and the production of complex shapes.
How Are Car Parts Assembled During Manufacturing?
The assembly stage is where various components come together to form the final product. This stage typically includes:
- Sub-Assembly: Smaller groups of parts, such as the engine assembly or suspension components, are pre-assembled. This practice helps streamline the final assembly process.
- Main Assembly Line: The main assembly line is where the car parts are put together. This process often utilizes automation and robotics for efficiency and precision. Workers are trained to follow strict assembly protocols to ensure that every component meets quality standards.
What Finishing Processes Are Essential for Car Parts?
Finishing processes are critical for enhancing the durability and appearance of car parts. These processes may include:
- Surface Treatment: Techniques such as anodizing, powder coating, or galvanizing are employed to protect metal parts from corrosion and wear. These treatments also improve aesthetics and provide a uniform finish.
- Quality Inspection: After finishing, parts undergo a final quality inspection to ensure they meet specifications. This may involve visual inspections and measurements using advanced tools like coordinate measuring machines (CMM).
What International Standards Govern Quality Assurance in Car Parts Manufacturing?
Quality assurance is a cornerstone of automotive manufacturing, ensuring that parts meet safety and performance standards. Several international standards are crucial for B2B buyers:
- ISO 9001: This standard outlines the requirements for a quality management system (QMS). Manufacturers adhering to ISO 9001 demonstrate their commitment to quality and continuous improvement.
- ISO/TS 16949: Specifically tailored for the automotive industry, this standard integrates ISO 9001 with additional requirements focused on defect prevention, waste reduction, and continuous improvement.
- CE Marking: In Europe, CE marking indicates compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards. It is essential for manufacturers looking to sell in the European market.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Car Parts Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) is implemented at various checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process to ensure that defects are identified and rectified early. Key QC checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial inspection checks the quality of raw materials before they enter production. Any materials that do not meet specifications are rejected.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Throughout the manufacturing process, regular inspections are conducted to monitor the production line and ensure that parts are being produced correctly. This may include real-time measurements and visual inspections.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Once the parts are completed, they undergo final inspections to verify that they meet all specifications and quality standards before shipping.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used to Ensure Car Parts Quality?
Testing methods play a vital role in validating the quality of car parts. Common methods include:
- Functional Testing: This ensures that the parts perform as intended under operational conditions. For instance, brake components may undergo stress testing to assess their performance under extreme conditions.
- Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Techniques such as ultrasonic testing and magnetic particle inspection are used to detect internal defects without damaging the parts.
- Dimensional Inspection: Parts are measured against specifications using precision instruments to ensure they are within tolerance levels.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For B2B buyers, especially those from diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying supplier quality control is crucial. Here are effective strategies:
- Supplier Audits: Conducting regular audits of suppliers’ manufacturing facilities can provide insights into their processes and adherence to quality standards. This can include assessments of their QMS and production capabilities.
- Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports, including inspection and testing results, can help buyers understand how suppliers maintain their quality standards.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection agencies to evaluate suppliers can offer an unbiased perspective on their quality control processes. This is particularly beneficial for international transactions, ensuring compliance with local regulations and standards.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
B2B buyers operating across different regions must navigate various quality control nuances:
- Regulatory Differences: Different countries have varying regulations and standards for automotive parts. Understanding these local requirements is crucial for compliance.
- Cultural Considerations: Cultural differences can impact communication and expectations around quality. Establishing clear guidelines and open communication with suppliers can mitigate misunderstandings.
- Logistical Challenges: Shipping car parts internationally can present challenges related to quality assurance. Ensuring proper handling and storage during transport is vital to maintaining part integrity.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols for main car parts, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that ensure they source high-quality components for their automotive needs.

Illustrative image related to main car parts
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘main car parts’
Introduction
Sourcing main car parts can be a complex process, particularly for B2B buyers navigating international markets. This guide provides a practical checklist to streamline your procurement strategy, ensuring you acquire high-quality components while minimizing risks. By following these steps, you will enhance your sourcing effectiveness, build strong supplier relationships, and ensure compliance with industry standards.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before initiating the sourcing process, it’s vital to clearly define the technical specifications of the car parts you need. This includes understanding the exact dimensions, materials, performance standards, and compatibility with existing systems.
– Importance: Clear specifications help avoid costly mistakes and ensure that the parts meet your operational requirements.
– What to look for: Consider the manufacturer’s standards and any industry regulations that apply in your region.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify potential suppliers who specialize in the car parts you need. Use online platforms, trade shows, and industry publications to compile a list of qualified vendors.
– Importance: A well-researched list of suppliers increases your chances of finding reliable partners who can meet your needs.
– What to look for: Check for supplier reputation, market presence, and customer reviews to gauge reliability and service quality.

Illustrative image related to main car parts
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Before finalizing a supplier, verify their certifications and compliance with relevant industry standards, such as ISO or local automotive regulations.
– Importance: Certifications indicate that the supplier adheres to quality management practices, which is crucial for maintaining safety and performance.
– What to look for: Request documentation of certifications and inquire about the processes they follow to maintain compliance.
Step 4: Request Samples for Quality Assurance
Once you have shortlisted suppliers, request samples of the car parts to evaluate their quality firsthand. This step is essential to ensure that the products meet your specifications and performance expectations.
– Importance: Assessing samples helps prevent future issues with defective parts that could impact your operations.
– What to look for: Inspect the samples for craftsmanship, materials used, and overall finish.
Step 5: Negotiate Terms and Pricing
Engage in negotiations with your selected suppliers to agree on pricing, payment terms, and delivery schedules. Be prepared to discuss bulk pricing and any additional services they may offer, such as warranty or after-sales support.
– Importance: Effective negotiation can lead to cost savings and better terms that enhance your overall procurement strategy.
– What to look for: Ensure that the terms are transparent and fair, and consider the total cost of ownership rather than just the initial price.
Step 6: Establish Clear Communication Channels
Once you’ve selected a supplier, establish clear communication channels to facilitate smooth collaboration. Define points of contact, preferred communication methods, and regular check-in intervals.
– Importance: Strong communication helps address any issues promptly and fosters a collaborative relationship.
– What to look for: Ensure that the supplier is responsive and that they provide timely updates on production and delivery.
Step 7: Monitor Supplier Performance
After procurement, continuously monitor the supplier’s performance regarding quality, delivery, and support. Establish key performance indicators (KPIs) to evaluate their effectiveness.
– Importance: Ongoing assessment ensures that suppliers maintain the expected standards and allows you to make informed decisions about future orders.
– What to look for: Track metrics such as on-time delivery rates, defect rates, and responsiveness to inquiries or issues.

Illustrative image related to main car parts
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing main car parts effectively, ensuring quality and reliability in their supply chain.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for main car parts Sourcing
To navigate the complexities of sourcing main car parts in the B2B market, understanding the cost structure and pricing dynamics is crucial. This analysis will delve into the core components of costs, the factors influencing pricing, and practical tips for buyers, particularly those from diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
What Are the Key Cost Components in Car Parts Manufacturing?
When evaluating the total cost of car parts, several components must be considered:
-
Materials: The choice of raw materials significantly impacts overall costs. Metals such as steel, aluminum, and composites are common, and their prices can fluctuate based on global market trends. Buyers should focus on sourcing from reliable suppliers who can offer competitive pricing for high-quality materials.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary widely depending on the region and the skill level required for production. In developing markets, lower labor costs can be advantageous, but it’s essential to ensure that quality standards are met.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with factory operations, such as utilities, rent, and maintenance. Efficient manufacturing processes can help mitigate these costs, making it essential for suppliers to maintain operational efficiency.
-
Tooling: Initial tooling costs can be significant, especially for custom parts. Investment in advanced tooling can lead to cost savings over time by enhancing production efficiency and quality.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing rigorous QC measures is vital to ensure that parts meet industry standards. While this adds to the upfront costs, it can prevent costly recalls and enhance the supplier’s reputation.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling can affect the final price significantly, especially for international transactions. Understanding the logistics involved, including potential tariffs and shipping times, is critical for accurate budgeting.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically include a margin to cover risks and profit. The margin can vary based on market competition, demand, and the supplier’s positioning.
How Do Pricing Influencers Affect Car Parts Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of car parts:
-
Volume/MOQ: Purchasing in larger quantities often leads to discounts. Understanding the supplier’s minimum order quantity (MOQ) can help buyers negotiate better prices.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom parts with specific design requirements generally incur higher costs. Clear communication of specifications can minimize misunderstandings and additional charges.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Premium materials and certifications (e.g., ISO, IATF) can increase costs but may be necessary for certain markets or applications. Buyers should weigh the importance of certifications against their budget constraints.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation, location, and production capabilities of suppliers can all impact pricing. Building long-term relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing and reliability.
-
Incoterms: Understanding International Commercial Terms (Incoterms) is essential for determining responsibilities related to shipping, insurance, and tariffs. This knowledge can prevent unexpected costs during international transactions.
What Negotiation Strategies Can International Buyers Use?
When sourcing car parts, particularly in international markets, employing effective negotiation strategies can yield significant benefits:
-
Research and Benchmarking: Understand market rates by comparing prices from multiple suppliers. This knowledge empowers buyers during negotiations.
-
Focus on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Rather than just the initial purchase price, consider the TCO, including maintenance, durability, and potential downtime costs. This perspective can justify higher upfront costs for superior parts.
-
Leverage Relationships: Building rapport with suppliers can facilitate better pricing and terms. Consider long-term partnerships that benefit both parties.
-
Be Flexible on Specifications: If possible, being open to alternative materials or specifications can lead to cost savings without compromising quality.
Conclusion: Navigating Pricing Nuances for Effective Sourcing
For B2B buyers in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the comprehensive cost structure and pricing nuances is essential for successful sourcing of car parts. While prices can fluctuate based on various factors, strategic negotiation and informed decision-making can lead to more cost-effective purchasing outcomes. Always remember that indicative prices may vary, and it is prudent to conduct thorough research before finalizing any agreements.

Illustrative image related to main car parts
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing main car parts With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternative Solutions to Main Car Parts
In the automotive industry, main car parts are essential for the functionality and performance of vehicles. However, businesses may find themselves evaluating alternative solutions that can either complement or replace traditional components. This analysis explores various alternatives, comparing them based on critical factors such as performance, cost, ease of implementation, maintenance, and best use cases.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Main Car Parts | Electric Vehicle Components | Aftermarket Upgrades |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Proven reliability and efficiency | High efficiency, quick torque | Enhanced performance metrics |
| Cost | Moderate to high initial investment | Generally higher upfront costs | Varies widely based on brand |
| Ease of Implementation | Standard installation procedures | Requires specialized knowledge | Simple to complex, depending on parts |
| Maintenance | Routine checks and replacements | Lower maintenance needs | Ongoing adjustments and tuning |
| Best Use Case | Traditional combustion vehicles | Electric vehicles and hybrids | Performance-focused upgrades |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Electric Vehicle Components
Electric vehicle (EV) components, such as electric motors and battery systems, offer a modern alternative to traditional car parts. EVs often provide superior performance through instant torque delivery, making them ideal for urban driving and environmentally conscious consumers. However, the initial investment in EV technology can be substantial, and the specialized knowledge required for installation and maintenance can be a barrier for some businesses. Furthermore, while EVs typically require less maintenance than combustion engines, the technology’s rapid evolution can necessitate frequent updates.
Aftermarket Upgrades
Aftermarket upgrades encompass a broad range of enhancements available for traditional vehicles. These parts can include performance chips, upgraded exhaust systems, and enhanced suspension components. The appeal of aftermarket parts lies in their potential to improve vehicle performance and aesthetics at a relatively lower cost compared to OEM parts. However, the complexity of installation can vary significantly, and businesses must consider the long-term implications of warranty voiding and potential compatibility issues with existing systems.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Needs
When selecting the right solution for vehicle parts, B2B buyers must consider their specific requirements, including the type of vehicle, budget constraints, and intended application. Main car parts are essential for reliable performance in traditional vehicles, while electric vehicle components may be better suited for businesses looking to invest in sustainable technology. Aftermarket upgrades present a flexible option for enhancing existing vehicles but may require careful consideration regarding installation and compatibility. Ultimately, the choice will depend on the balance between performance needs, cost, and the long-term vision for the vehicle fleet.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for main car parts
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Main Car Parts in B2B Transactions?
Understanding the technical properties of car parts is essential for B2B buyers. Here are critical specifications that influence purchasing decisions and product compatibility:
1. Material Grade
Material grade refers to the specific composition and properties of the materials used in car parts, such as steel, aluminum, or plastics. Different grades possess varying strength, durability, and corrosion resistance, which are vital for safety and longevity. Buyers must ensure that the materials meet the required standards for specific applications, especially in regions with harsh environmental conditions, like Africa and South America.
2. Tolerance
Tolerance indicates the allowable variation in dimensions of a car part. It is critical for ensuring that parts fit together properly and function as intended. Tight tolerances are often essential in components like engines and transmissions where precision affects performance. In a B2B context, understanding tolerance specifications helps buyers avoid costly rework or failures in the supply chain.
3. Load Capacity
Load capacity defines the maximum weight or force a part can safely bear without failure. This specification is particularly important for structural components like axles and suspension parts. Buyers need to assess the load capacity to ensure that parts can withstand the stresses encountered during use, which is crucial for maintaining vehicle safety and performance.
4. Finish Type
Finish type refers to the surface treatment applied to car parts, such as galvanizing, painting, or anodizing. The finish affects corrosion resistance, aesthetic appeal, and friction properties. B2B buyers should consider the finish type to align with their market requirements and ensure durability in various environmental conditions.
5. Compatibility Standards
Compatibility standards ensure that car parts can be integrated seamlessly with existing systems or vehicles. Buyers must verify that parts comply with industry standards (e.g., ISO, SAE) to avoid issues related to fit and function. This is especially relevant when sourcing parts from different regions or manufacturers.
6. Lifecycle Expectancy
Lifecycle expectancy indicates the anticipated lifespan of a car part under normal operating conditions. Understanding this property helps buyers assess the long-term value of their investments. Parts with longer lifecycles can reduce replacement frequency and lower overall maintenance costs, which is a significant consideration for fleet operators.
What Are Common Trade Terms Used in the Car Parts Industry?
Familiarity with industry terminology is crucial for effective communication and negotiation in B2B transactions. Here are several essential terms:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that manufacture parts that are used in the original assembly of vehicles. In B2B transactions, sourcing OEM parts often assures buyers of quality and compatibility, as these parts are designed to meet the specifications set by the vehicle manufacturers.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of products a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is essential for buyers to manage inventory costs and ensure they are purchasing enough to meet their demand while avoiding excess stock.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent by buyers to suppliers requesting pricing and other relevant information for specific products. This process helps streamline procurement, allowing buyers to compare options and negotiate terms effectively.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are internationally recognized rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, risk, and costs associated with the transportation of goods. Familiarity with these terms helps buyers understand their obligations and avoid disputes in cross-border transactions.
5. Lead Time
Lead time is the amount of time it takes from placing an order until the goods are received. Understanding lead times is critical for inventory planning and ensuring that production schedules are met, particularly in industries with tight deadlines.
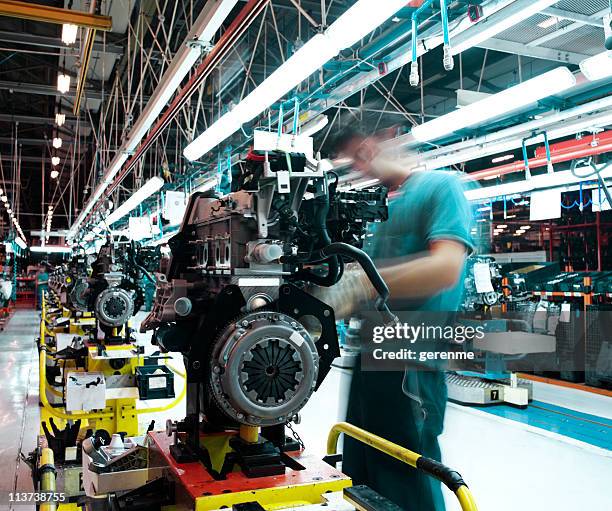

Illustrative image related to main car parts
6. Warranty Period
The warranty period is the duration during which a supplier guarantees the performance of a part. Knowing the warranty terms helps buyers evaluate the risk associated with their purchases and can influence decision-making regarding suppliers.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and market requirements.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the main car parts Sector
What are the Current Market Dynamics in the Car Parts Sector for International Buyers?
The global car parts market is experiencing dynamic shifts driven by various factors, notably technological advancements, changing consumer preferences, and economic fluctuations. International B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of the growing trend towards electric vehicles (EVs) and hybrid models, which are reshaping the demand for specific components. As countries implement stricter emission regulations, the focus on high-efficiency parts, such as advanced batteries and electric drivetrains, is increasing.
Additionally, the rise of Industry 4.0 technologies, such as IoT and AI, is revolutionizing sourcing strategies. These technologies facilitate real-time data analysis, enabling better inventory management and predictive maintenance, thereby enhancing operational efficiency. Buyers are encouraged to leverage digital platforms for sourcing, which provide access to a broader range of suppliers and allow for more competitive pricing.
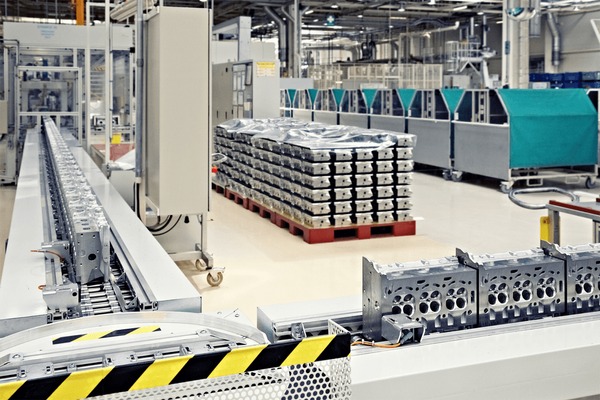

Illustrative image related to main car parts
Moreover, the ongoing impacts of global supply chain disruptions highlight the importance of diversification in sourcing strategies. Companies that previously relied on single-source suppliers are now considering multiple suppliers across different regions to mitigate risks. This shift not only enhances supply chain resilience but also opens up opportunities for international buyers to engage with emerging markets.
How Can B2B Buyers Address Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing in Car Parts?
Sustainability is becoming a critical factor in the car parts sector, especially as consumers and businesses increasingly prioritize environmentally friendly practices. The automotive industry is under pressure to reduce its carbon footprint, prompting manufacturers to adopt sustainable practices in sourcing materials. B2B buyers should prioritize suppliers that demonstrate commitment to sustainability through certifications such as ISO 14001, which denotes effective environmental management systems.
Ethical sourcing is equally important, as it encompasses fair labor practices and responsible sourcing of raw materials. Buyers should conduct due diligence to ensure that their suppliers adhere to ethical labor standards and do not engage in exploitative practices. Utilizing materials with lower environmental impact, such as recycled metals and bioplastics, can also contribute to a more sustainable supply chain.
Investing in ‘green’ technologies and materials not only meets regulatory requirements but also enhances brand reputation. Buyers who can demonstrate their commitment to sustainability can differentiate themselves in the marketplace, appealing to a growing segment of environmentally conscious consumers.
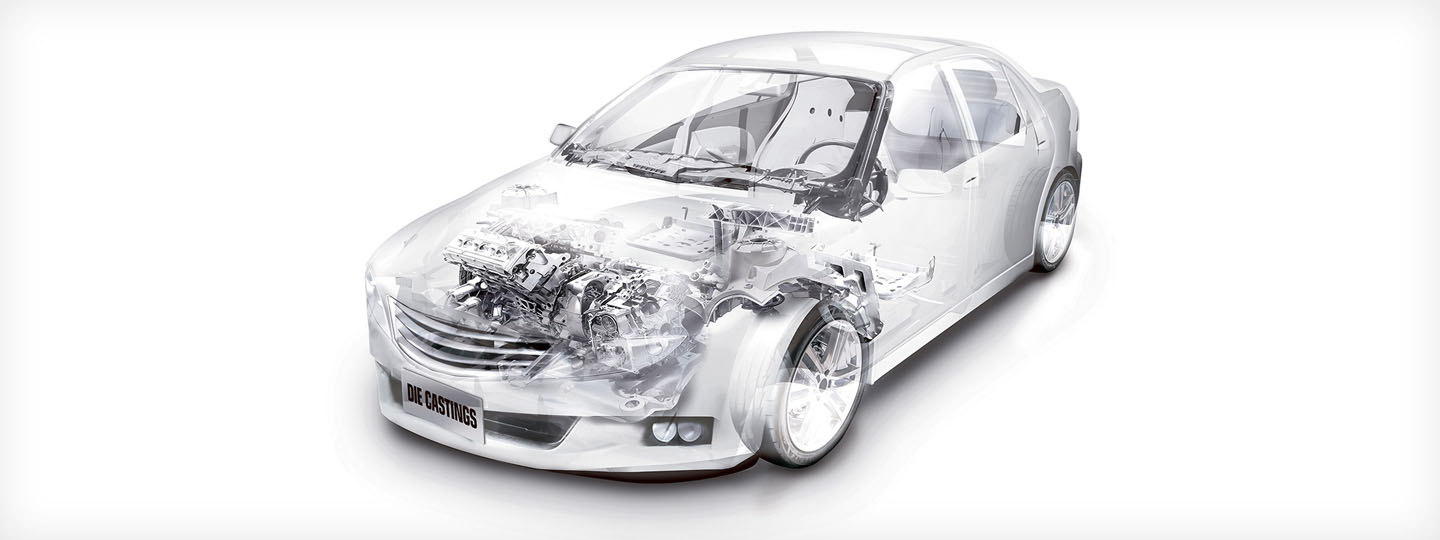

Illustrative image related to main car parts
What is the Evolution of the Car Parts Industry Relevant to B2B Buyers?
The car parts industry has evolved significantly over the past few decades, transitioning from a focus on mechanical parts to a more integrated approach that includes electronics and software. Initially dominated by traditional manufacturers, the market has seen an influx of technology-driven companies that specialize in electronic components, sensors, and software solutions.
This evolution is crucial for B2B buyers as it highlights the importance of understanding the complete vehicle ecosystem. As vehicles become more interconnected and automated, sourcing decisions must consider not only the quality of mechanical parts but also the compatibility and integration of electronic systems. This shift underscores the need for buyers to stay informed about technological advancements and to engage with suppliers who can provide cutting-edge solutions that meet the demands of modern automotive engineering.
By recognizing these trends and adapting sourcing strategies accordingly, international B2B buyers can position themselves for success in a rapidly changing market landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of main car parts
1. How do I ensure the quality of car parts when sourcing internationally?
To ensure the quality of car parts when sourcing internationally, it’s crucial to conduct thorough research on suppliers. Look for manufacturers with industry certifications such as ISO 9001, which indicates a commitment to quality management. Request samples before placing larger orders, and consider third-party inspections for quality assurance. Building a strong relationship with your suppliers can also facilitate better communication about quality standards and expectations. Lastly, reviewing customer feedback and testimonials can provide insights into the reliability of the supplier.
2. What are the best practices for vetting car parts suppliers?
When vetting car parts suppliers, start by verifying their business credentials and operational history. Check for relevant certifications and compliance with international standards. Conduct background checks and ask for references from previous clients to gauge their reliability. Attend trade shows or industry events to meet suppliers in person and assess their product offerings. Additionally, evaluate their communication responsiveness and willingness to provide detailed product information, as these factors can indicate their professionalism and customer service approach.
3. What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for car parts?
Minimum order quantities (MOQ) for car parts vary by supplier and product type. Some suppliers may have a low MOQ for standard parts, while custom or specialized components might require larger orders. It’s essential to discuss MOQs with your supplier before finalizing any agreement. If your needs do not meet their MOQ, consider negotiating or exploring alternative suppliers that offer lower MOQs. This flexibility can be crucial for small businesses or those entering new markets.
4. What payment terms should I expect when sourcing car parts internationally?
Payment terms for international car parts sourcing typically vary by supplier and transaction size. Common options include advance payment, letters of credit, and payment upon delivery. Ensure you clarify payment terms in your contract to avoid misunderstandings. Using secure payment methods, such as escrow services, can help protect your investment. Additionally, consider negotiating favorable terms based on your relationship with the supplier, such as extended payment periods for larger orders.
5. How can I customize car parts to meet specific needs?
Customizing car parts involves collaborating closely with your supplier to communicate your specific requirements. Start by providing detailed specifications, including materials, dimensions, and performance standards. Many suppliers offer customization options, but it’s essential to discuss lead times, costs, and any potential impacts on MOQs. Request prototypes to evaluate the design before mass production. Building a strong partnership with your supplier can facilitate effective communication throughout the customization process.
6. What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing car parts?
When importing car parts, consider factors such as shipping methods, customs regulations, and lead times. Choose between air freight for speed or sea freight for cost efficiency based on your urgency and budget. Understand the import duties and tariffs applicable to your goods in your country to avoid unexpected costs. Work with experienced logistics partners who can help navigate customs procedures and ensure timely delivery. Proper packaging is also crucial to prevent damage during transit.
7. How do I handle warranty and return issues for car parts?
Handling warranty and return issues begins with understanding the supplier’s policies before placing an order. Ensure that the warranty terms are clearly outlined in your agreement, including the duration and coverage for defects. If you encounter issues, maintain clear documentation of the problem, including photographs and correspondence. Promptly communicate with your supplier to initiate the return process, and be aware of any timelines or conditions that may apply. Establishing a good relationship with your supplier can facilitate smoother resolutions.
8. What are the key factors influencing car parts pricing in international markets?
Several factors influence car parts pricing in international markets, including raw material costs, manufacturing processes, and local economic conditions. Exchange rates can also impact pricing, especially for international transactions. Additionally, tariffs and import duties may affect the final cost of parts. Supplier reputation, quality standards, and the complexity of the parts can further drive prices. Conducting market research can help you understand pricing trends and make informed purchasing decisions.
Top 2 Main Car Parts Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Moog – Steering and Suspension Parts
Domain: moogparts.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Parts of a Car include: Steering (Center Drag Links, Idler Arms, Pitman Arms, Steering Stabilizers, Complete Pre-Assembled Steering Linkage, Tie Rods), Suspension (Solid Sway Bar Kits, Alignment Parts, Bushings, Coil Springs, Control Arms, Sway Bar Links, Ball Joints), Driveline (PTO/AG, Universal Joints, Couplers, Constant Velocity Axles), Wheel End (Complete Knuckle Assembly, Hub Assemblies). Ot…
2. Reddit – Car Parts & Mechanics Guide
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: A 19-year-old seeking to learn about car parts and mechanics to perform maintenance and repairs on their first car.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for main car parts
In navigating the complex landscape of automotive parts sourcing, understanding the intricacies of key components—from engines to braking systems—is essential for B2B buyers. Strategic sourcing allows businesses to optimize their supply chains, reduce costs, and enhance product quality. By fostering strong relationships with reliable suppliers, companies can ensure timely access to critical car parts, which is especially important in emerging markets like Africa and South America, where demand is rapidly growing.
As buyers evaluate their sourcing strategies, they should prioritize suppliers who offer not only competitive pricing but also transparency in their operations and adherence to quality standards. Leveraging technology and data analytics can further refine sourcing decisions, enabling businesses to predict trends and manage inventory more efficiently.
Looking ahead, the automotive industry is on the brink of significant transformation, driven by advancements in electric vehicles and sustainability initiatives. International buyers are encouraged to remain agile, embracing innovations that can enhance their operations and meet evolving consumer demands. By positioning themselves strategically in this dynamic market, businesses can unlock new opportunities for growth and success.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.