Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for starter vs alternator vs battery
Navigating the complexities of sourcing essential components like starters, alternators, and batteries can be a daunting task for international B2B buyers. Each of these components plays a crucial role in vehicle functionality, and understanding their distinctions, applications, and maintenance requirements is vital for making informed purchasing decisions. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricate interplay between starters, alternators, and batteries, offering insights into their types, applications, and common challenges faced in various global markets.
By examining common issues such as component failures and their symptoms, this guide equips buyers with the knowledge to identify potential problems before they escalate. It also covers the critical aspects of supplier vetting, ensuring that buyers can source reliable and high-quality products tailored to their regional needs.
Particularly for businesses operating in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—regions that often face unique logistical and market challenges—understanding the nuances of these components is essential. This guide aims to empower B2B buyers with actionable insights, enabling them to navigate the global market confidently, optimize their procurement processes, and ultimately ensure the longevity and reliability of their vehicles. Whether you are looking to enhance your supply chain or simply need to make smarter purchasing decisions, this guide serves as an invaluable resource in your journey.
Table Of Contents
- Top 2 Starter Vs Alternator Vs Battery Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for starter vs alternator vs battery
- Understanding starter vs alternator vs battery Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of starter vs alternator vs battery
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘starter vs alternator vs battery’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for starter vs alternator vs battery
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for starter vs alternator vs battery
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘starter vs alternator vs battery’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for starter vs alternator vs battery Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing starter vs alternator vs battery With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for starter vs alternator vs battery
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the starter vs alternator vs battery Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of starter vs alternator vs battery
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for starter vs alternator vs battery
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Understanding starter vs alternator vs battery Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lead-Acid Battery | Traditional design, high power output, cost-effective | Automotive, heavy machinery, backup power systems | Pros: Affordable, widely available. Cons: Heavier, limited lifespan (3-5 years). |
| Lithium-Ion Battery | Lightweight, longer life, fast charging capabilities | Electric vehicles, portable electronics | Pros: Higher energy density, longer life. Cons: Higher initial cost, sensitive to temperature. |
| Standard Starter | Electromechanical device, engages engine with gear | Automotive, marine applications | Pros: Reliable performance, easy to replace. Cons: Mechanical wear over time, can be noisy. |
| High-Torque Starter | Enhanced torque for larger engines, compact design | Heavy-duty vehicles, performance racing | Pros: Better starting power, compact size. Cons: More expensive, specific to certain applications. |
| Alternator (Standard) | Converts mechanical energy to electrical, charges battery | Automotive, generators, industrial equipment | Pros: Durable, less maintenance. Cons: Limited output in extreme conditions, can fail without warning. |
What are the characteristics of Lead-Acid Batteries and their B2B suitability?
Lead-acid batteries are the most common type used in vehicles and various industrial applications. They are characterized by their ability to deliver high surge currents, making them ideal for starting engines. With a lifespan of 3-5 years, they are cost-effective but relatively heavy. B2B buyers should consider their applications in automotive and heavy machinery sectors, where reliability and cost are critical. However, the limited lifespan and weight may be drawbacks for industries focused on efficiency and portability.
How do Lithium-Ion Batteries differ and where are they applied?
Lithium-ion batteries are known for their lightweight construction and superior energy density, allowing for longer usage times and faster charging. These batteries are increasingly used in electric vehicles and portable electronics due to their longevity (up to 10 years) and efficiency. For B2B buyers, the initial investment is higher, but the long-term savings and reduced maintenance make them an attractive option. Industries looking to invest in sustainable energy solutions or advanced technology products will find lithium-ion batteries particularly suitable.
What distinguishes Standard Starters from High-Torque Starters?
Standard starters are reliable electromechanical devices designed for everyday vehicles, providing sufficient power to crank engines. They are easy to replace and have a straightforward installation process. Conversely, high-torque starters are engineered for larger engines and performance applications, offering enhanced torque in a compact design. While standard starters are suitable for most automotive needs, high-torque variants are ideal for heavy-duty vehicles and racing applications. B2B buyers should consider the specific requirements of their vehicles when choosing between the two, balancing cost with performance needs.
What are the advantages and limitations of Standard Alternators in B2B applications?
Standard alternators are vital components that convert mechanical energy from the engine into electrical energy, charging the battery and powering electrical systems. They are known for their durability and require minimal maintenance. However, they can struggle to deliver adequate power in extreme conditions, leading to potential failures. For B2B buyers, understanding the output capabilities and environmental factors is crucial when selecting alternators for automotive or industrial applications. The reliability and efficiency of standard alternators make them a staple in many sectors, but awareness of their limitations is essential for long-term performance.
Key Industrial Applications of starter vs alternator vs battery
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of starter vs alternator vs battery | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive Manufacturing | Assembly lines for vehicle production | Ensures reliable engine starts and operational efficiency | Quality certifications, compatibility with various vehicle models |
| Transportation & Logistics | Fleet vehicles for goods transport | Minimizes downtime and maintenance costs, enhancing productivity | Availability of spare parts, local support for servicing |
| Agriculture | Tractors and heavy machinery | Reliable power for starting engines in remote locations | Durability in harsh environments, capacity to handle heavy loads |
| Mining | Equipment for mineral extraction | Reduces operational disruptions and enhances productivity | Resistance to extreme conditions, sourcing from trusted suppliers |
| Renewable Energy | Energy storage systems for solar and wind projects | Efficient energy management and backup power solutions | Compliance with local regulations, sustainability of sourcing |
How Are Starters, Alternators, and Batteries Used in Automotive Manufacturing?
In automotive manufacturing, the starter, alternator, and battery are essential components in the assembly lines. Starters are used to initiate engine operations, while alternators ensure that the battery remains charged during production. This synergy is crucial for maintaining the efficiency of assembly lines, as any failure could lead to significant downtime. Buyers in this sector should consider sourcing components that are compatible with various vehicle models and adhere to quality certifications to ensure reliability and performance.
What Role Do Starters, Alternators, and Batteries Play in Transportation and Logistics?
In the transportation and logistics industry, fleet vehicles depend heavily on reliable starters, alternators, and batteries for uninterrupted service. These components are vital for minimizing vehicle downtime, which directly impacts productivity and profitability. Businesses must focus on sourcing high-quality parts that offer longevity and reliability, as well as ensuring the availability of spare parts and local support for servicing to maintain operational efficiency.
Why Are Starters, Alternators, and Batteries Critical in Agriculture?
Agricultural machinery, such as tractors and harvesters, relies on robust starters, alternators, and batteries to function effectively, especially in remote areas. These components provide the necessary power to start engines and operate essential machinery, ensuring that farming activities can proceed without interruptions. Buyers in this sector should prioritize sourcing durable components capable of withstanding harsh environmental conditions while also having the capacity to handle heavy loads.
How Do Starters, Alternators, and Batteries Impact Mining Operations?
In the mining industry, equipment used for mineral extraction requires reliable starters, alternators, and batteries to minimize operational disruptions. These components are crucial for starting heavy machinery, which often operates under extreme conditions. Businesses must ensure that they source equipment that meets high durability standards and can withstand the rigors of mining environments. Trustworthy suppliers with proven track records are essential for maintaining continuous operations.
What Is the Importance of Starters, Alternators, and Batteries in Renewable Energy Projects?
In renewable energy sectors, such as solar and wind, starters, alternators, and batteries are integral for energy storage systems. They help manage energy efficiently and provide backup power when needed. This is particularly important in regions with inconsistent energy supply. Buyers should focus on sourcing components that comply with local regulations and emphasize sustainability, ensuring that their energy solutions are both effective and environmentally friendly.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘starter vs alternator vs battery’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Identifying the Root Cause of Electrical Failures
The Problem: B2B buyers, especially those in automotive fleet management or repair shops, often face the challenge of diagnosing electrical failures in vehicles. When a vehicle won’t start, it can be difficult to determine whether the issue lies with the battery, alternator, or starter. This uncertainty can lead to wasted time and resources, as technicians may replace components without accurately identifying the underlying problem. Furthermore, incorrect diagnosis can result in repeated failures, leaving businesses frustrated and affecting their operational efficiency.
The Solution: Implement a systematic troubleshooting process. Start by conducting a thorough assessment of the battery’s health, as it is often the most common culprit for starting issues. Use a multimeter to check the voltage; a healthy battery should read around 12.6 volts when fully charged. If the battery is functioning correctly, move on to the alternator. Check for signs of wear, such as unusual noises or dimming lights, and use the multimeter to test the voltage output while the engine is running—ideally between 13.7 to 14.7 volts. Finally, if both the battery and alternator are in good condition, inspect the starter. Look for symptoms like unusual clicking sounds or failure to engage. By following this methodical approach, businesses can minimize unnecessary replacements, saving both time and costs.
Scenario 2: Ensuring Component Longevity in Harsh Environments
The Problem: In regions with extreme weather conditions, such as the heat of the Middle East or the humidity of South America, the lifespan of batteries, starters, and alternators can be significantly reduced. Buyers must contend with the increased likelihood of component failures, which can lead to unexpected downtimes and repair costs. The challenge is to source components that can withstand harsh environmental conditions while maintaining performance.
The Solution: When procuring batteries, starters, and alternators, focus on components specifically designed for high-performance in extreme conditions. Look for batteries with higher cold cranking amps (CCA) for cold climates and those with better heat resistance for hotter regions. For alternators, select models with robust housing and weather-resistant seals to protect against moisture and dust. Additionally, prioritize suppliers who provide warranties or guarantees that reflect the durability of their products. Regular maintenance is crucial; establish a routine inspection schedule to check for corrosion and ensure all connections are secure. By investing in high-quality components and implementing a proactive maintenance plan, businesses can enhance the longevity of their electrical systems and reduce overall costs.
Scenario 3: Managing Inventory and Supply Chain Challenges
The Problem: B2B buyers often face difficulties in managing inventory for starters, alternators, and batteries, particularly when they have to deal with varying demand across different regions. Fluctuations in demand can lead to overstocking or stockouts, both of which can be costly. Additionally, long lead times from suppliers can exacerbate these issues, causing delays in repairs and impacting customer satisfaction.
The Solution: Implement an inventory management system that utilizes data analytics to predict demand trends based on historical usage and seasonal variations. This approach allows businesses to maintain optimal stock levels of starters, alternators, and batteries. Establish relationships with multiple suppliers to diversify your supply chain, ensuring you have access to components even during peak demand periods or supply disruptions. Consider adopting just-in-time (JIT) inventory practices, which can reduce holding costs and improve cash flow. By combining data-driven inventory management with strategic supplier partnerships, businesses can enhance their responsiveness to market changes and improve service delivery.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for starter vs alternator vs battery
What Materials are Commonly Used in Starters, Alternators, and Batteries?
When selecting materials for automotive starters, alternators, and batteries, it’s crucial to consider their specific properties and how they impact performance. Here, we analyze four common materials: lead, copper, aluminum, and plastic. Each material has unique characteristics that influence durability, cost, and suitability for various applications.
How Does Lead Affect Battery Performance?
Lead is primarily used in lead-acid batteries, which are the most common type in automotive applications. Key properties include high density and excellent conductivity, making it effective for energy storage. Lead’s corrosion resistance is moderate, but it can degrade in extreme conditions.
Pros: Lead-acid batteries are relatively low-cost and have a well-established manufacturing process. They provide reliable performance and are recyclable, which is a significant advantage in sustainability-focused markets.
Cons: The weight of lead can be a disadvantage in applications where reducing weight is critical. Additionally, lead-acid batteries have a limited lifespan (typically 3-5 years) and can be sensitive to temperature extremes, which is particularly relevant for buyers in hotter climates like parts of Africa and the Middle East.
What Role Does Copper Play in Starters and Alternators?
Copper is widely used in electrical wiring and components within starters and alternators due to its excellent electrical conductivity and thermal properties. It has a high melting point, making it suitable for high-temperature environments.
Pros: Copper’s conductivity ensures efficient power transfer, which is essential for the quick engagement of starters and the effective charging of batteries. It is also relatively durable and resistant to corrosion when properly insulated.
Cons: The primary disadvantage of copper is its cost, which can be higher than alternatives like aluminum. Additionally, copper components can be heavier, impacting overall vehicle weight.

Illustrative image related to starter vs alternator vs battery
How Does Aluminum Compare for Alternators?
Aluminum is often used in the construction of alternator housings and some internal components. It is lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and has good thermal conductivity, making it suitable for automotive applications.
Pros: The lightweight nature of aluminum can improve fuel efficiency in vehicles. It also offers good resistance to corrosion, which is beneficial in humid or coastal environments, common in regions like South America and parts of Europe.
Cons: While aluminum is generally less expensive than copper, it is not as conductive, which can lead to efficiency losses in electrical applications. Additionally, aluminum can be more susceptible to mechanical wear over time.
What Is the Importance of Plastic in Battery Casings?
Plastic is commonly used for battery casings and some components in starters and alternators. Key properties include lightweight, corrosion resistance, and electrical insulation.
Pros: Plastic casings are cost-effective and can be molded into complex shapes, allowing for design flexibility. They also provide excellent insulation, which is crucial for safety in automotive applications.
Cons: Plastic may not withstand high temperatures as well as metals, potentially leading to degradation over time. Additionally, certain plastics may not be as environmentally friendly, which is a consideration for buyers focused on sustainability.
Summary of Material Selection Insights
The choice of materials for starters, alternators, and batteries significantly impacts performance, durability, and cost. Buyers should consider the specific applications and environmental conditions relevant to their regions, particularly in diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Compliance with international standards (like ASTM, DIN, and JIS) is also critical in ensuring product reliability and safety.
| Material | Typical Use Case for starter vs alternator vs battery | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lead | Lead-acid batteries | Low cost, recyclable | Heavy, limited lifespan | Low |
| Copper | Wiring in starters and alternators | Excellent conductivity | High cost, heavy | High |
| Aluminum | Alternator housings | Lightweight, corrosion-resistant | Less conductive than copper | Medium |
| Plastic | Battery casings and components | Cost-effective, design flexibility | Less heat resistant | Low |
This table encapsulates the essential considerations for B2B buyers when selecting materials for automotive electrical components, ensuring informed decisions that align with their operational needs and market conditions.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for starter vs alternator vs battery
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Starters, Alternators, and Batteries?
The manufacturing processes for starters, alternators, and batteries share some common elements but also have distinct stages tailored to their specific functions. Understanding these processes is essential for B2B buyers looking to evaluate suppliers and ensure quality.

Illustrative image related to starter vs alternator vs battery
Material Preparation: What Materials Are Used?
For starters and alternators, high-quality materials are crucial for durability and performance. Common materials include:
- Copper: Used for windings due to its excellent electrical conductivity.
- Steel: Utilized for housing and structural components for strength.
- Plastic: Often used for insulation and housing, providing lightweight and corrosion-resistant properties.
- Lead-acid compounds: For batteries, lead and sulfuric acid are the primary materials, chosen for their energy storage capabilities.
Before manufacturing begins, these materials undergo rigorous inspections to ensure they meet specified standards.
How Are Starters and Alternators Formed?
The forming stage involves several key techniques:
- Stamping: This process shapes the metal components, such as the casing and internal brackets, using high-pressure machines to ensure precision.
- Winding: For alternators and starters, copper wire is wound into coils, which are critical for generating magnetic fields and electrical current.
- Casting: In some instances, components like the housing are cast in molds to achieve complex shapes and enhance strength.
What Assembly Processes Are Involved?
Assembly is a critical phase where all components come together:
- Component Integration: Individual components, including the rotor, stator, and brushes, are assembled into the main unit. This often requires specialized fixtures to maintain alignment.
- Electrical Connections: Connections are soldered or crimped to ensure a reliable electrical pathway, crucial for performance.
- Testing and Calibration: Each unit undergoes initial testing to verify that it meets operational specifications before proceeding to the finishing stage.
What Finishing Techniques Are Used for Starters, Alternators, and Batteries?
Finishing processes enhance the product’s durability and performance:
- Coating: Components may receive protective coatings to resist corrosion and wear, especially important in harsh environments.
- Quality Inspections: Final quality checks are conducted to ensure that all specifications are met. This includes visual inspections for defects, dimensional checks, and functional tests.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is critical to ensuring that starters, alternators, and batteries meet international standards and customer expectations.
What International Standards Are Relevant for B2B Buyers?
B2B buyers should be familiar with several international quality standards:
- ISO 9001: This standard focuses on quality management systems and is applicable across manufacturing sectors. Compliance indicates a commitment to quality control and continuous improvement.
- CE Marking: Particularly relevant in Europe, CE marking signifies that a product meets EU safety, health, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: For certain automotive parts, API (American Petroleum Institute) certifications can indicate quality in lubrication and performance.
What Are the Common QC Checkpoints in Manufacturing?
Quality control checkpoints are strategically placed throughout the manufacturing process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial stage involves inspecting raw materials for compliance with specifications before they enter the production line.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During assembly, various checkpoints ensure that components are correctly aligned, and electrical connections are secure.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): The final inspection includes functional testing, performance assessments, and visual inspections to ensure the product is free from defects.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international B2B buyers, ensuring supplier quality is paramount:
- Supplier Audits: Conduct regular audits of suppliers to verify their compliance with quality standards and manufacturing processes. This may involve on-site visits or third-party assessments.
- Quality Reports: Request detailed quality control reports that outline testing results, inspections, and any corrective actions taken during the manufacturing process.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engage independent third-party inspection agencies to evaluate the manufacturing processes and final products. This adds an extra layer of assurance regarding quality.
What Are the QC and Certification Nuances for International Buyers?
When sourcing from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, B2B buyers should consider:
- Cultural Differences: Understand the regional manufacturing practices and how they impact quality. This may include variations in workforce skills, availability of materials, and adherence to international standards.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensure that suppliers comply with local regulations and international standards that may differ from country to country.
- Language Barriers: Communication can be a challenge. Ensure that all quality documentation is available in a language that all stakeholders understand to avoid misinterpretations.
Conclusion: Why Is Understanding Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance Essential for B2B Buyers?
For B2B buyers, particularly those operating in diverse and complex markets, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for starters, alternators, and batteries is vital. This knowledge enables informed decision-making, ensuring that the products sourced meet the required standards for performance, reliability, and safety. By engaging with suppliers who prioritize quality and adhere to international standards, buyers can enhance their supply chain’s effectiveness and reduce potential risks associated with product failures.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘starter vs alternator vs battery’
This guide serves as a comprehensive checklist for B2B buyers seeking to procure starters, alternators, and batteries. Understanding the distinct roles, specifications, and quality indicators of these components is vital for making informed purchasing decisions that ensure vehicle reliability and performance.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is the foundation of your sourcing process. Identify the specific requirements for the starters, alternators, and batteries you need, including voltage, capacity, and compatibility with existing systems. This will help you narrow down potential suppliers and ensure the components meet your operational needs.
Illustrative image related to starter vs alternator vs battery
Step 2: Research Market Trends and Innovations
Stay informed about the latest market trends and technological advancements in automotive components. Researching innovations such as advanced battery technologies or high-efficiency alternators can provide insights into the best options available. This knowledge can also help you identify suppliers who offer cutting-edge products that align with market demands.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a supplier, thorough evaluation is crucial. Look for suppliers with a strong track record in your industry, and request documentation such as company profiles, case studies, and references from other businesses. Consider suppliers that operate within your region to reduce shipping times and costs, and ensure their products meet international quality standards.
Step 4: Verify Product Quality and Certifications
Quality assurance is paramount when sourcing automotive components. Check for certifications such as ISO or IATF 16949, which indicate adherence to industry quality standards. Additionally, assess product warranties and return policies to mitigate risks associated with defective components.
Step 5: Request Sample Products for Testing
Before finalizing your order, request samples of the starters, alternators, and batteries you are considering. Testing these samples in real-world conditions can help you verify their performance and compatibility with your vehicles. This step is essential to avoid costly mistakes and ensure that you are investing in reliable components.
Step 6: Negotiate Pricing and Terms
Once you have identified suitable suppliers and verified product quality, it’s time to negotiate pricing and terms. Discuss bulk purchasing discounts, payment terms, and delivery schedules to optimize your procurement costs. Ensure that you have a clear understanding of any additional fees, such as shipping or customs duties, especially when dealing with international suppliers.
Step 7: Establish a Long-term Relationship with Suppliers
Building a long-term partnership with reliable suppliers can lead to better pricing, priority service, and access to new products. Keep communication lines open, provide feedback on product performance, and stay engaged with your suppliers to foster a mutually beneficial relationship. This strategic approach can enhance your supply chain resilience and adaptability in the automotive market.
By following these steps, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing starters, alternators, and batteries, ultimately leading to improved vehicle performance and customer satisfaction.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for starter vs alternator vs battery Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Starters, Alternators, and Batteries?
When sourcing starters, alternators, and batteries for B2B applications, understanding the cost structure is crucial. The primary components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margins.
-
Materials: The cost of raw materials can vary significantly. For starters and alternators, the key materials are copper, steel, and magnets, while batteries primarily rely on lead, plastic, and acid. Fluctuations in global commodity prices can directly impact sourcing costs.
-
Labor: Labor costs will differ based on geographical location and production methods. Countries with lower labor costs may reduce overall expenses but could affect quality and consistency.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses all indirect costs associated with production, including factory utilities and indirect labor. Efficient manufacturing processes can help reduce overhead, ultimately lowering prices.
-
Tooling: Initial tooling costs can be high, especially for customized components. However, these costs can be amortized over larger production runs, making bulk orders more economical.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring product quality can incur additional costs, particularly for components that require rigorous testing and certification. However, investing in QC can reduce long-term warranty claims and enhance buyer satisfaction.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can vary widely based on the Incoterms used, transportation mode, and distances involved. For international buyers, understanding these costs is vital for calculating the total landed cost.
-
Margin: Supplier profit margins can vary based on competition, market demand, and perceived value. Buyers should be aware that higher quality and certified products may come with a premium price.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Sourcing Decisions for Starters, Alternators, and Batteries?
Several factors can influence the pricing of starters, alternators, and batteries.
-
Volume/MOQ: Minimum order quantities (MOQs) can affect pricing. Larger orders often lead to reduced per-unit costs due to economies of scale.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom specifications can drive up costs. Standardized products are typically more affordable, so buyers should assess whether customization is necessary.
-
Materials: The quality and type of materials used can significantly affect pricing. Premium materials may enhance product longevity but also increase initial costs.
-
Quality and Certifications: Products that meet international quality standards or possess certifications (e.g., ISO, CE) usually command higher prices. These certifications can also be advantageous in competitive markets.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reliability and reputation can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their proven track record, while new entrants may offer lower prices to gain market share.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the Incoterms chosen can clarify who bears responsibility for shipping costs and risks, impacting the total cost for the buyer.
What Buyer Tips Can Enhance Cost Efficiency in Sourcing?
B2B buyers should consider several strategies to enhance cost efficiency when sourcing starters, alternators, and batteries.
-
Negotiation: Effective negotiation can lead to better pricing. Building long-term relationships with suppliers may yield favorable terms, especially for repeat orders.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Buyers should evaluate the TCO, which includes purchase price, maintenance, and potential warranty costs. Focusing solely on upfront costs can lead to higher expenses in the long run.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should be aware of currency fluctuations, import duties, and local regulations that could impact costs. Conducting thorough market research can help mitigate these risks.
-
Supplier Audits: Regularly assessing suppliers for quality, reliability, and compliance can help ensure that the products meet expectations and reduce the risk of costly failures.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for starters, alternators, and batteries can vary significantly based on the factors discussed above. It is advisable for buyers to conduct thorough market research and engage directly with suppliers to obtain accurate and current pricing information tailored to their specific needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing starter vs alternator vs battery With Other Solutions
Introduction: Exploring Alternatives for Automotive Power Solutions
In the automotive sector, the interplay between starters, alternators, and batteries is crucial for vehicle functionality. However, as technology evolves, alternative solutions also emerge, providing options that can enhance performance, reduce costs, or simplify maintenance. In this analysis, we will compare these traditional components with two viable alternatives: lithium-ion battery systems and hybrid electric vehicle (HEV) technology. Understanding these alternatives is essential for B2B buyers looking to make informed decisions about automotive solutions.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Starter Vs Alternator Vs Battery | Lithium-Ion Battery Systems | Hybrid Electric Vehicle (HEV) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Reliable for starting engines and powering accessories | High energy density, fast charging | Combines internal combustion and electric power for efficiency |
| Cost | Moderate initial cost; replacement needed every 3-5 years | Higher initial investment; long-term savings | Higher upfront cost; potential fuel savings |
| Ease of Implementation | Standard installation in most vehicles | Requires compatible systems and installation | Complex integration; may need specialized knowledge |
| Maintenance | Minimal; periodic checks recommended | Low; longer lifespan with fewer replacements | Moderate; battery maintenance and system checks required |
| Best Use Case | Conventional vehicles needing reliable ignition | High-performance electric vehicles, renewable energy applications | Urban driving with mixed usage for better fuel economy |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Lithium-Ion Battery Systems
Lithium-ion battery systems represent a significant advancement in energy storage technology. They offer a higher energy density compared to traditional lead-acid batteries, enabling faster charging and longer lifespans. While the initial investment is higher, these systems can provide substantial savings over time due to lower maintenance needs and extended life cycles. However, they require compatible charging systems and may not be suitable for all vehicle types, particularly older models.
Hybrid Electric Vehicle (HEV) Technology
HEV technology combines conventional internal combustion engines with electric propulsion systems. This hybrid approach increases fuel efficiency and reduces emissions, making it an attractive option for urban environments. While HEVs come with a higher upfront cost due to their complex systems, they can lead to significant fuel savings in the long run. However, their installation may require specialized knowledge, and maintenance can be more involved compared to traditional vehicles, as both the electric and combustion systems must be managed effectively.

Illustrative image related to starter vs alternator vs battery
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
When selecting the best automotive power solution, B2B buyers must consider their specific operational requirements, budget constraints, and maintenance capabilities. Traditional starters, alternators, and batteries offer reliable performance for conventional vehicles, while lithium-ion systems and hybrid technologies provide advanced alternatives that can enhance efficiency and reduce long-term costs. Understanding the unique advantages and disadvantages of each option will empower buyers to make informed decisions tailored to their business needs, ensuring optimal performance and reliability in their automotive applications.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for starter vs alternator vs battery
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Starters, Alternators, and Batteries?
Understanding the technical properties of starters, alternators, and batteries is essential for B2B buyers in the automotive sector. Here are some critical specifications to consider:
-
Material Grade
The quality of materials used in these components affects their durability and performance. For instance, starters often use high-grade steel for the housing and copper for electrical connections, while batteries may utilize lead-acid or lithium-ion technology. Selecting components made from superior materials ensures longevity and reliability, reducing the frequency of replacements and associated costs. -
Current Rating (Amperage)
This specification defines the maximum amount of current that the battery or starter can provide. For batteries, this is often measured in Cold Cranking Amps (CCA), which indicates the battery’s ability to start an engine in cold conditions. A higher CCA rating is crucial for regions with extreme weather, impacting operational efficiency and customer satisfaction. -
Voltage Rating
Most automotive batteries operate at 12 volts, but understanding the voltage requirements of starters and alternators is crucial for compatibility. Mismatched voltage can lead to inefficiencies or component failure. Ensuring that all components in the system share the same voltage rating helps maintain optimal performance. -
Service Life
The expected lifespan of a battery (typically 3-5 years), alternator (8-12 years), and starter (around 5-10 years) can significantly influence purchasing decisions. Understanding the service life helps businesses assess long-term costs and plan for replacements, which is particularly important for fleet operators and businesses managing multiple vehicles. -
Tolerance Levels
Tolerance specifications indicate how much deviation from the standard can be accepted during manufacturing. For instance, the gap between the starter gear and flywheel should be within a specific tolerance to ensure proper engagement. Components manufactured within strict tolerances minimize wear and tear, enhancing overall system efficiency. -
Charging Capacity
For alternators, the charging capacity (measured in amps) indicates how much current it can generate to recharge the battery and power the vehicle’s electrical system. A higher capacity ensures that the battery remains charged even under heavy electrical loads, which is essential for vehicles with numerous electronic features.
What Are the Common Trade Terms Related to Starters, Alternators, and Batteries?
Familiarity with industry terminology is vital for effective communication and negotiation in the B2B marketplace. Here are some key terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
Refers to companies that produce parts that are used in the manufacturing of a vehicle. B2B buyers often prefer OEM parts for their reliability and compatibility with existing systems, ensuring optimal performance and warranty coverage. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
This term signifies the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is crucial for buyers as it influences inventory management and cash flow. Setting a reasonable MOQ can help suppliers meet production demands without excess inventory. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document that buyers send to suppliers to solicit price quotations for specific products. It serves as a formal way to initiate the purchasing process and allows buyers to compare pricing, terms, and conditions across multiple suppliers. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
These are standardized terms used in international trade to define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers. Familiarity with Incoterms such as FOB (Free On Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) helps buyers understand shipping costs, risks, and delivery responsibilities. -
Warranty Period
This term refers to the duration during which a manufacturer guarantees the performance of a product. A longer warranty period often indicates higher quality and reliability, making it an important consideration for B2B buyers looking to minimize risk. -
Lead Time
Lead time is the period between placing an order and receiving the goods. Understanding lead times is crucial for inventory management and production planning, especially for businesses that rely on just-in-time manufacturing processes.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance operational efficiency and product reliability in their automotive supply chains.

Illustrative image related to starter vs alternator vs battery
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the starter vs alternator vs battery Sector
What Are the Global Drivers Influencing the Starter, Alternator, and Battery Market?
The starter, alternator, and battery market is witnessing significant changes driven by technological advancements, regulatory pressures, and shifting consumer preferences. One primary global driver is the increasing demand for electric and hybrid vehicles, which necessitates advanced battery technologies and efficient electrical systems. The push for sustainability is also reshaping market dynamics, as manufacturers are compelled to innovate and produce more environmentally friendly components. In regions like Africa and South America, where access to reliable electricity is a challenge, robust batteries and alternators are crucial for powering not just vehicles but also renewable energy systems.
Additionally, the advent of smart technologies is influencing sourcing trends. B2B buyers are increasingly looking for components that incorporate smart features, such as battery management systems and predictive maintenance capabilities. These technologies can optimize performance and extend the lifespan of batteries and starters, providing long-term cost savings. Moreover, the rise of e-commerce platforms for automotive parts is enabling international buyers to source products more efficiently, reducing lead times and increasing competitiveness in various markets, including Brazil and Vietnam.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impacting the Starter, Alternator, and Battery Sector?
Sustainability is becoming a critical factor in the sourcing decisions of international B2B buyers in the starter, alternator, and battery sectors. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes and raw material extraction has prompted a shift towards more sustainable practices. Buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to reducing their carbon footprint and utilizing recycled materials. This trend is particularly relevant in Europe, where regulations are becoming more stringent regarding waste management and emissions.
Ethical sourcing is also gaining traction, as businesses recognize the importance of transparent supply chains. Buyers are looking for manufacturers that adhere to ethical labor practices and have certifications that validate their sustainability claims. Green certifications, such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and various eco-labels, are becoming essential for suppliers aiming to compete in the global marketplace. By choosing ethically sourced materials, businesses not only mitigate risks associated with reputational damage but also align themselves with the growing consumer demand for responsible products.
How Has the Starter, Alternator, and Battery Market Evolved Over Time?
The evolution of the starter, alternator, and battery market has been marked by significant technological advancements and changing consumer needs. Initially, automotive batteries were simple lead-acid designs, primarily used for starting engines. However, the rise of the automotive industry and the growing complexity of vehicles necessitated more sophisticated solutions. The introduction of the alternator in the 1960s allowed for more efficient charging of batteries, leading to longer-lasting performance and reduced maintenance.
In recent years, the shift towards electric vehicles has further transformed the market. Modern batteries now incorporate advanced chemistries, such as lithium-ion, which offer higher energy densities and faster charging capabilities. This evolution is not just limited to vehicle applications; batteries are increasingly being used in renewable energy storage systems, illustrating their versatility and importance in modern energy solutions. As the market continues to evolve, B2B buyers must stay informed about these trends to ensure they are sourcing the most effective and sustainable components for their needs.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of starter vs alternator vs battery
-
How do I determine if the starter, alternator, or battery is causing my vehicle’s issues?
To identify the faulty component, start with a systematic approach. Check the battery first, as it typically fails more frequently. Look for symptoms like slow engine cranking or dim lights. If the battery appears fine, inspect the alternator for signs such as flickering headlights or unusual noises. Finally, assess the starter by listening for clicking sounds when attempting to start the engine. If you’re unsure, consider consulting a professional technician for a thorough diagnosis. -
What is the best battery type for commercial vehicles?
The best battery for commercial vehicles often depends on the specific requirements of the vehicle and its operating conditions. Lead-acid batteries are common due to their reliability and cost-effectiveness. However, AGM (Absorbent Glass Mat) batteries offer superior performance in extreme conditions and longer service life. Always consider factors like climate, vehicle usage, and energy demands when selecting a battery to ensure optimal performance and longevity. -
What are the common signs of a failing alternator?
A failing alternator can manifest through various symptoms. Look for dimming headlights, a flickering dashboard warning light, or a dead battery. Additionally, unusual noises such as grinding or squealing can indicate wear on the alternator’s bearings. If you notice any of these signs, it’s crucial to have the alternator inspected promptly to avoid being stranded or causing further damage to the vehicle’s electrical system. -
How can I vet suppliers for automotive batteries, starters, and alternators?
When vetting suppliers, prioritize those with a solid reputation and relevant certifications. Check for customer reviews, industry affiliations, and their experience in the market. Request references from previous clients and assess their communication responsiveness. Additionally, inquire about their production capacity, quality assurance processes, and compliance with international standards to ensure reliability and product quality. -
What are typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for automotive components?
Minimum order quantities for automotive components can vary significantly by supplier and product type. Generally, MOQs for batteries, starters, and alternators range from 50 to 500 units. Larger manufacturers might offer lower MOQs, while specialized or custom products may require higher quantities. Always discuss your needs with potential suppliers to negotiate terms that suit your business strategy. -
What payment terms are common for international B2B transactions in automotive parts?
Common payment terms for international transactions typically include a mix of advance payment, letters of credit, or net 30/60/90 days after delivery. Some suppliers may offer discounts for early payments or larger orders. It’s crucial to clarify payment terms upfront and ensure they align with your cash flow capabilities while also protecting your interests through trade agreements. -
How should I handle logistics for importing automotive parts?
Efficient logistics management is vital when importing automotive parts. Start by selecting a reliable freight forwarder who understands the complexities of international shipping. Ensure proper documentation, including invoices, packing lists, and customs declarations, to avoid delays. Additionally, consider insurance for your shipments and familiarize yourself with local regulations regarding the importation of automotive components to ensure compliance. -
What quality assurance practices should I expect from suppliers?
Reputable suppliers should implement rigorous quality assurance practices, including regular inspections and testing of their products. Look for suppliers who follow industry standards such as ISO certifications or have in-house testing facilities. Ask about their quality control processes, warranty policies, and how they handle defective products. A transparent quality assurance approach can significantly reduce the risk of receiving subpar components.
Top 2 Starter Vs Alternator Vs Battery Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Honda Civic – Starter Diagnosis
Domain: mechanics.stackexchange.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: 2006 Honda Civic EX 1.8L 4 Cylinder; Symptoms: car won’t start, weak cranking, single click sound; Possible issues: bad starter, bad alternator, battery issues; Updates: new battery installed, fully charged battery tested good; Diagnosis: starter was identified as the problem.
2. Champion Auto Parts – Battery and Alternator Essentials
Domain: championautoparts.com
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
Introduction: Battery: Typically lasts 3-5 years; easiest and cheapest to replace; essential for starter function. Symptoms of a dead battery include inability to start the car. Alternator: Lasts 8-12 years; charges the battery and powers the electrical system; a dead battery can indicate alternator issues. Symptoms of a bad alternator include battery not holding charge. Starter: Responsible for starting the en…
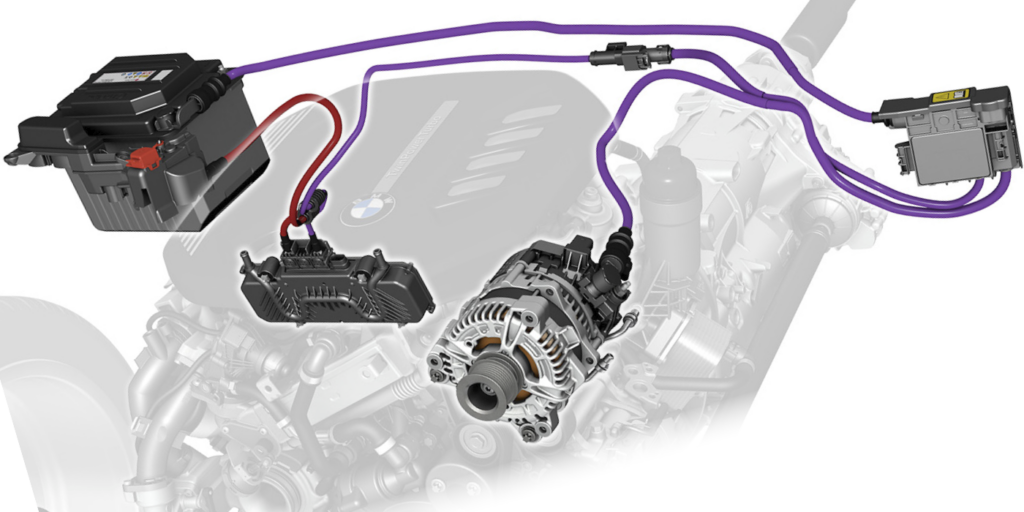
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for starter vs alternator vs battery
In the intricate ecosystem of automotive components, understanding the interplay between starters, alternators, and batteries is essential for effective strategic sourcing. Each component plays a vital role in vehicle functionality, and recognizing their individual strengths and weaknesses can lead to more informed purchasing decisions. For international B2B buyers, particularly in diverse markets like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, sourcing high-quality parts can significantly impact operational efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Key takeaways emphasize the importance of proactive maintenance and timely replacements to prevent costly downtimes. Buyers should prioritize suppliers who offer comprehensive product information, reliable warranties, and exceptional customer support. This ensures that they can swiftly address any issues that arise from component failures, maintaining a smooth supply chain.
Looking ahead, the automotive landscape is evolving with advancements in technology and sustainability. By embracing strategic sourcing practices now, businesses can position themselves advantageously for future developments. Engage with trusted suppliers who are aligned with your operational goals and stay ahead of the competition. Your commitment to sourcing excellence today will yield dividends in reliability and performance tomorrow.
Illustrative image related to starter vs alternator vs battery
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.