Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for starter relay vs solenoid
In the global automotive landscape, sourcing the right components like starter relays and solenoids can present significant challenges for international B2B buyers. Understanding the intricate differences between these two crucial electromagnetic switches is essential for ensuring optimal vehicle performance and reliability. This guide delves into the nuances of starter relays versus solenoids, providing a comprehensive overview that includes their types, applications, and the critical factors to consider when selecting suppliers.
By navigating through this resource, buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—particularly in markets such as Germany and Saudi Arabia—will gain valuable insights into the operational functionalities of these components. The guide will also address key considerations for vetting suppliers, evaluating costs, and understanding the implications of each choice on overall vehicle performance. With this knowledge, B2B buyers can make informed purchasing decisions that not only enhance their product offerings but also ensure compliance with regional standards and customer expectations.
Empowering your sourcing strategy with the right information is crucial in a competitive market, and this guide serves as a critical tool in achieving that goal. Whether you are looking to optimize your inventory or enhance the reliability of your automotive solutions, understanding the dynamics of starter relays and solenoids is a key step towards success.
Table Of Contents
- Top 3 Starter Relay Vs Solenoid Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for starter relay vs solenoid
- Understanding starter relay vs solenoid Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of starter relay vs solenoid
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘starter relay vs solenoid’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for starter relay vs solenoid
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for starter relay vs solenoid
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘starter relay vs solenoid’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for starter relay vs solenoid Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing starter relay vs solenoid With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for starter relay vs solenoid
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the starter relay vs solenoid Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of starter relay vs solenoid
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for starter relay vs solenoid
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Understanding starter relay vs solenoid Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electromechanical Relay | Uses electromagnetic coils to open or close circuits. | Automotive, Industrial Equipment | Pros: Cost-effective, reliable; Cons: Limited current handling compared to solenoids. |
| Starter Solenoid | Directly mounted on the starter, engages high current. | Automotive, Heavy Machinery | Pros: Handles high current loads; Cons: More prone to wear and tear. |
| Remote Relay | Operated from a distance, often used in complex systems. | Automotive, Security Systems | Pros: Flexibility in installation; Cons: May require additional wiring and setup. |
| Solid State Relay | Utilizes semiconductor technology for switching. | Automation, HVAC Systems | Pros: Longer lifespan, faster switching; Cons: Higher initial cost. |
| Latching Relay | Maintains its position without continuous power. | Industrial Controls, Home Automation | Pros: Energy-efficient; Cons: More complex circuitry. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Electromechanical Relays?
Electromechanical relays are widely used due to their simplicity and cost-effectiveness. They consist of an electromagnetic coil that, when energized, opens or closes a circuit. This type is suitable for applications requiring low to moderate current handling. B2B buyers should consider the relay’s current rating and switching speed, especially in automotive or industrial environments where reliability is crucial.
How Do Starter Solenoids Differ from Other Types?
Starter solenoids are specifically designed to engage the starter motor by handling high currents directly. They are typically mounted on the starter itself, making them integral to automotive applications. Buyers should assess the solenoid’s compatibility with their engine type and the potential need for replacement parts, as solenoids may wear out faster than relays.
Why Choose Remote Relays for Complex Systems?
Remote relays are advantageous for complex installations where control is needed from a distance. They are commonly used in automotive and security systems, allowing for flexible placement. When purchasing, buyers should evaluate the relay’s range and compatibility with existing systems, as well as the potential need for additional wiring.
What Advantages Do Solid State Relays Offer?
Solid state relays utilize semiconductor technology, offering superior longevity and faster switching capabilities compared to traditional relays. They are ideal for automation and HVAC applications where rapid response times are essential. Buyers should weigh the initial investment against the long-term savings in maintenance and replacement costs.
When Are Latching Relays Most Beneficial?
Latching relays are designed to maintain their state without continuous power, making them energy-efficient for applications in industrial controls and home automation. Their complexity can be a drawback, but they provide significant energy savings. B2B buyers should consider the application requirements and the relay’s ability to maintain its state under varying conditions.
Key Industrial Applications of starter relay vs solenoid
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of starter relay vs solenoid | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive Manufacturing | Engine start systems in vehicles | Ensures reliable engine ignition and performance | Quality standards, compatibility with various vehicle models, lead time for delivery |
| Heavy Machinery | Starter systems in construction and agricultural equipment | Enhances operational efficiency and reduces downtime | Durability under harsh conditions, voltage and current ratings, availability of spare parts |
| Renewable Energy | Solar inverter systems | Facilitates efficient energy conversion and reliability | Compliance with international standards, environmental resilience, supplier reliability |
| Marine Engineering | Starter systems for ships and vessels | Guarantees dependable engine start in critical applications | Saltwater corrosion resistance, vibration durability, global supply chain support |
| Industrial Automation | Control systems for machinery and equipment | Improves automation reliability and safety | Customization options, integration with existing systems, after-sales support |
How Are Starter Relays and Solenoids Used in Automotive Manufacturing?
In automotive manufacturing, starter relays and solenoids play a critical role in engine start systems. These components enable the ignition switch to activate the starter motor without overwhelming the vehicle’s electrical system. By ensuring reliable engine ignition, they enhance vehicle performance and safety. Buyers in this sector should prioritize quality standards and ensure compatibility with various vehicle models, especially when sourcing components from international suppliers.
What Role Do Starter Relays and Solenoids Play in Heavy Machinery?
In heavy machinery, such as construction and agricultural equipment, starter relays and solenoids are essential for initiating engine operation. These devices help to improve operational efficiency and minimize downtime, which is vital in industries where time is money. Buyers should consider the durability of these components under harsh conditions, their voltage and current ratings, and the availability of spare parts to ensure long-term reliability.
How Are Starter Relays and Solenoids Integrated into Renewable Energy Systems?
Starter relays and solenoids are increasingly used in renewable energy applications, particularly in solar inverter systems. They facilitate the efficient conversion of solar energy into usable electricity by managing the high-power signals required for system operation. For international buyers, it is crucial to source components that comply with international standards and exhibit environmental resilience, ensuring consistent performance in varying climates.
What Importance Do Starter Relays and Solenoids Have in Marine Engineering?
In marine engineering, starter relays and solenoids are vital for the reliable starting of engines on ships and vessels. Given the critical nature of maritime operations, these components must guarantee dependable engine starts, even in adverse conditions. Buyers should focus on sourcing parts that offer saltwater corrosion resistance and vibration durability, as well as support from a global supply chain to ensure timely availability.
How Do Starter Relays and Solenoids Enhance Industrial Automation?
In industrial automation, starter relays and solenoids are integral to control systems for various machinery and equipment. They improve reliability and safety by enabling precise control over high-power circuits with low-power signals. Businesses in this sector should seek customization options that fit their specific operational needs, integration capabilities with existing systems, and robust after-sales support to maintain seamless operations.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘starter relay vs solenoid’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Confusion Over Component Identification
The Problem:
B2B buyers often face challenges in distinguishing between starter relays and solenoids, leading to incorrect purchases and operational inefficiencies. For example, an automotive parts supplier in Europe might receive an order for a starter solenoid, but due to the buyer’s misunderstanding, they end up sending a relay instead. This can lead to delays in repairs, increased costs, and dissatisfied customers. The confusion is compounded by the fact that many manufacturers use the terms interchangeably, further muddling the waters.
The Solution:
To mitigate this issue, buyers should invest in comprehensive training for their procurement teams regarding the technical specifications and functionalities of both components. Creating detailed product guides that include clear diagrams, application scenarios, and specifications can significantly enhance understanding. Additionally, implementing a robust inventory management system that categorizes parts accurately can prevent mix-ups. Buyers should also engage directly with suppliers to clarify any uncertainties before placing orders, ensuring they specify the correct component.
Scenario 2: Frequent Component Failures Leading to Downtime
The Problem:
Manufacturers in South America may experience frequent failures of either starter relays or solenoids, resulting in significant operational downtime. For instance, a construction equipment rental company could face multiple equipment failures on job sites due to faulty solenoids, causing delays in project timelines and increased rental costs. Understanding the root cause of these failures can be complex, as both components are integral to the starting system and may show similar symptoms when they malfunction.
The Solution:
Implementing a proactive maintenance strategy can help reduce the frequency of component failures. This involves conducting regular diagnostic checks on vehicles and machinery to identify early signs of wear or malfunction. Establishing partnerships with reliable suppliers who can provide high-quality components is crucial; opting for OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) parts can often reduce the likelihood of early failures. Additionally, offering training for technicians on how to properly install and troubleshoot these components can prevent installation errors that lead to premature failure.
Scenario 3: Difficulty in Sourcing Quality Parts at Competitive Prices
The Problem:
International buyers, particularly in the Middle East, often struggle to source high-quality starter relays and solenoids at competitive prices. Fluctuations in shipping costs, varying quality standards among manufacturers, and the challenge of navigating different regulatory environments can complicate procurement processes. A buyer looking to equip a fleet of vehicles may find it difficult to balance cost with quality, risking the reliability of their operations.
The Solution:
Developing a multi-supplier strategy can help buyers mitigate these sourcing challenges. By building relationships with multiple manufacturers across different regions, buyers can ensure competitive pricing while maintaining quality standards. Additionally, leveraging technology, such as procurement platforms, can provide access to a broader range of suppliers and streamline the comparison of products and prices. Engaging in bulk purchasing agreements or long-term contracts with trusted suppliers can also secure better pricing and ensure a steady supply of quality components. Lastly, conducting thorough quality assessments and audits of suppliers can help ensure that the parts meet the necessary specifications and reliability standards, ultimately leading to improved operational efficiency.
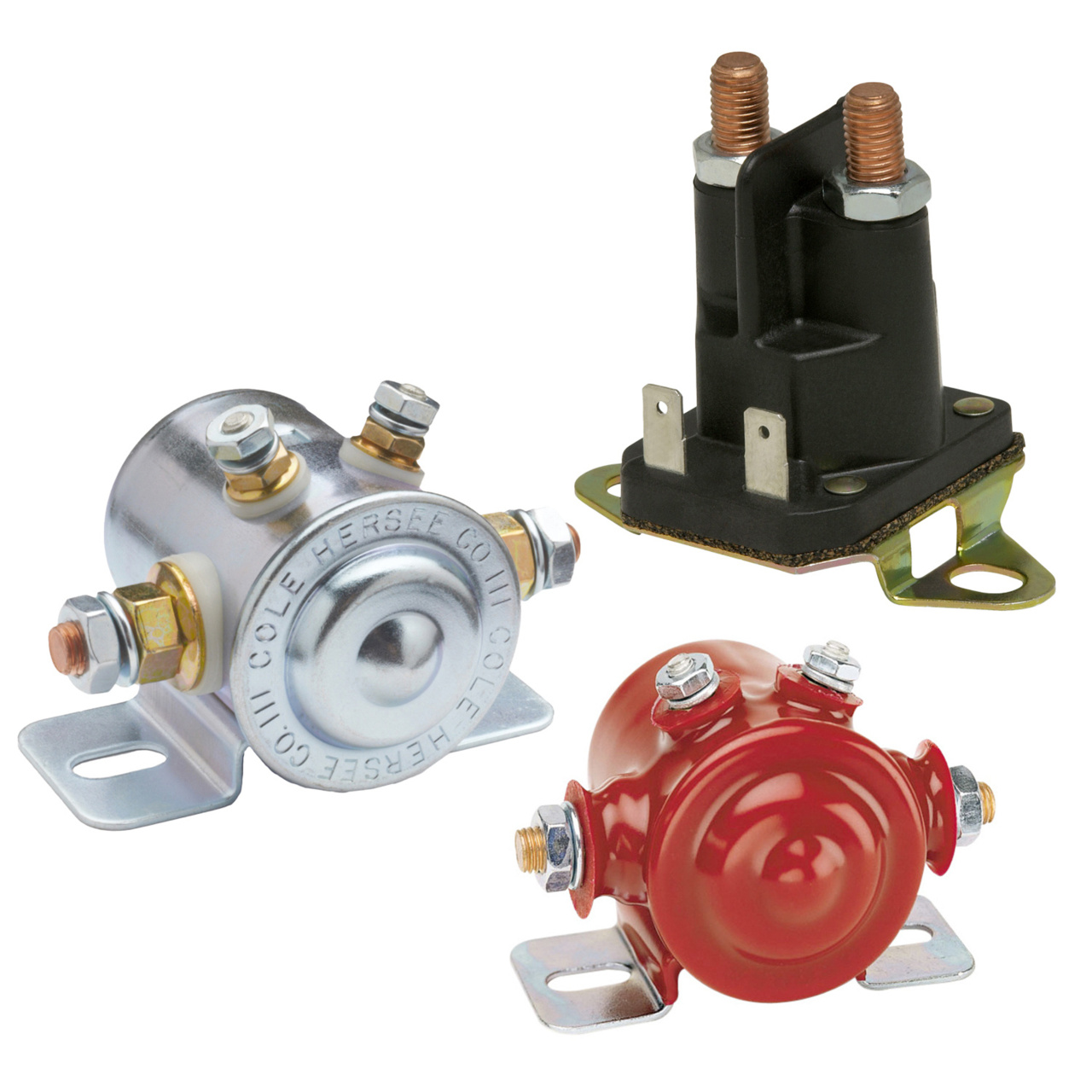
Strategic Material Selection Guide for starter relay vs solenoid
What Are the Common Materials Used in Starter Relays and Solenoids?
When selecting materials for starter relays and solenoids, understanding the properties and performance characteristics of each material is crucial. Here, we analyze four common materials: copper, aluminum, plastic, and steel, focusing on their relevance to product performance and suitability for international B2B buyers.
How Does Copper Perform in Starter Relays and Solenoids?
Copper is widely used in electrical components due to its excellent conductivity. It has a high-temperature rating, allowing it to perform well under various thermal conditions. The corrosion resistance of copper is moderate, which can be enhanced through coatings.
Pros: Copper’s high electrical conductivity ensures efficient performance in starter relays and solenoids, leading to quicker response times. It is also relatively easy to manufacture and form into complex shapes.
Cons: The main drawback is its cost, as copper is generally more expensive than aluminum. Additionally, copper can corrode over time if not properly treated, which may affect longevity in harsh environments.
Impact on Application: Copper is compatible with various media, making it suitable for diverse automotive and industrial applications. However, its weight may be a consideration in lightweight vehicle designs.

Illustrative image related to starter relay vs solenoid
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in regions like Europe and the Middle East should ensure compliance with standards such as DIN and ASTM for electrical components, as well as consider local sourcing options to mitigate costs.
What Advantages Does Aluminum Offer for Starter Components?
Aluminum is another popular choice due to its lightweight nature and good conductivity, though it is less conductive than copper. It has excellent corrosion resistance, particularly when anodized, making it suitable for outdoor applications.
Pros: The lightweight nature of aluminum can contribute to overall vehicle efficiency, and its corrosion resistance extends the lifespan of components in challenging environments.

Illustrative image related to starter relay vs solenoid
Cons: While cheaper than copper, aluminum’s lower conductivity can lead to higher energy losses, which may affect performance in high-demand applications. Manufacturing complexity can also be higher due to the need for specialized techniques.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is particularly effective in applications where weight savings are critical, such as in electric vehicles.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from Africa and South America may find aluminum components more accessible due to lower shipping costs, but they should ensure compliance with local standards to avoid quality issues.
Why Is Plastic Used in Starter Relays and Solenoids?
Plastic, often used for housings and insulation, offers excellent electrical insulation properties. It is lightweight and resistant to corrosion, making it a common choice for non-conductive parts.
Pros: The low cost of plastic makes it an attractive option for manufacturers. Its versatility allows for a wide range of designs and applications.
Cons: Plastic may not withstand high temperatures or mechanical stress as well as metals, which can limit its use in high-performance applications.
Impact on Application: Plastic is suitable for applications where electrical insulation is critical, but its limitations in temperature and pressure ratings may restrict its use in high-load scenarios.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international plastic standards, such as ASTM for materials, is essential, especially in Europe where regulations are stringent.

Illustrative image related to starter relay vs solenoid
How Does Steel Compare in Terms of Performance and Durability?
Steel is often used in solenoid housings and components that require high strength and durability. It offers excellent mechanical properties and can withstand high temperatures and pressures.
Pros: Steel’s strength and durability make it ideal for heavy-duty applications, ensuring reliability in demanding environments.
Cons: The weight of steel can be a disadvantage in automotive applications where weight reduction is a priority. Additionally, steel is prone to corrosion unless properly treated.
Impact on Application: Steel is best suited for applications requiring robust mechanical strength, particularly in industrial settings.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider the cost implications of steel, especially in regions with high shipping costs. Compliance with local standards for steel quality is also crucial to ensure performance.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Starter Relays and Solenoids
| Material | Typical Use Case for starter relay vs solenoid | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Copper | Electrical contacts in relays and solenoids | Excellent conductivity | Higher cost and potential corrosion | High |
| Aluminum | Lightweight components in automotive applications | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Lower conductivity than copper | Medium |
| Plastic | Insulation and housing for electrical components | Low cost and versatile design | Limited temperature and pressure resistance | Low |
| Steel | Structural components in solenoids | High strength and durability | Heavy and prone to corrosion | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide provides valuable insights for international B2B buyers, helping them make informed decisions when sourcing starter relays and solenoids. Understanding the properties, advantages, and limitations of each material is essential for optimizing performance and ensuring compliance with regional standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for starter relay vs solenoid
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Starter Relays and Solenoids?
The manufacturing processes for starter relays and solenoids involve several critical stages, each ensuring that the final product meets performance and reliability standards. The main stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
Material Preparation: What Materials Are Used in Starter Relays and Solenoids?
The production of starter relays and solenoids begins with the careful selection and preparation of raw materials. Common materials include high-quality metals for electrical contacts and coils, such as copper and aluminum, as well as durable plastics for housing components. Manufacturers often use specialized alloys to enhance conductivity and resistance to wear and corrosion. Quality assurance starts at this stage, as the material must meet specific standards to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
How Are Starter Relays and Solenoids Formed?
Forming is a crucial step that involves shaping the raw materials into components. Techniques such as stamping, machining, and molding are commonly employed. For instance, metal contacts are often stamped from sheets of copper, while plastic housings may be produced using injection molding. Each technique has its own set of quality checks to ensure that dimensions and tolerances are within acceptable limits. This stage is particularly critical as any deviation in size or shape can lead to malfunctioning units.
What Assembly Techniques Are Used for Relays and Solenoids?
Assembly is where the individual components come together to form the complete relay or solenoid. This process can involve manual labor or automated systems, depending on the scale of production. Key techniques include soldering for electrical connections and mechanical fastening for structural integrity. Quality control measures during assembly may include visual inspections and automated testing to ensure that all parts are correctly positioned and securely attached.
How Is the Finishing Process Conducted for Quality Assurance?
The finishing stage involves applying protective coatings and conducting final inspections. Coatings, such as epoxy or zinc plating, are often applied to enhance corrosion resistance and durability. After coating, each unit undergoes rigorous testing to ensure it meets performance standards. This may include functional tests to verify that the relay or solenoid operates correctly under simulated conditions.
What International Standards and Quality Control Measures Are Relevant?
Quality assurance in the manufacturing of starter relays and solenoids is vital for maintaining performance and reliability. International standards such as ISO 9001 provide a framework for quality management systems, ensuring that manufacturing processes are consistently monitored and improved.

Illustrative image related to starter relay vs solenoid
Which Industry-Specific Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
In addition to ISO 9001, industry-specific certifications, such as CE marking for products sold in Europe and API standards for automotive components, can be crucial. These certifications demonstrate compliance with safety and performance regulations and are often required for entry into specific markets.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) is integrated throughout the manufacturing process, typically at three main checkpoints: Incoming Quality Control (IQC), In-Process Quality Control (IPQC), and Final Quality Control (FQC).
How Do IQC, IPQC, and FQC Function in the Manufacturing Process?
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint ensures that all incoming materials meet specified standards. Suppliers must provide certification for raw materials, and random sampling may be conducted to verify compliance.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, various checks are performed to monitor the production line. This includes dimensional checks, functional tests, and process audits to ensure that operations adhere to quality standards.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): At this stage, finished products undergo comprehensive testing to verify that they meet design specifications. This can include electrical testing, functional testing, and environmental simulations to assess durability.
What Common Testing Methods Are Employed for Quality Assurance?
Testing methods are critical for verifying the functionality and reliability of starter relays and solenoids. Common methods include:
- Electrical Testing: This involves checking the electrical resistance, current draw, and overall functionality of the units.
- Mechanical Testing: Stress and strain tests may be conducted to ensure that the components can withstand operational pressures.
- Environmental Testing: Products are subjected to extreme temperatures, humidity, and vibration to simulate real-world conditions and assess durability.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
For B2B buyers, ensuring that suppliers adhere to stringent quality control measures is essential. This can be achieved through several methods:
What Audits and Reports Can Buyers Request from Suppliers?
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits of suppliers can provide insight into their manufacturing processes and quality control systems. Buyers should look for evidence of compliance with international standards and industry-specific certifications.
-
Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports from suppliers can help verify that products meet necessary standards. This includes documentation of testing results, inspection records, and any corrective actions taken for non-conformance.
How Can Third-Party Inspections Enhance Buyer Confidence?
Engaging third-party inspection services can further validate the quality of the products being sourced. These independent entities can conduct audits and tests, providing an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s capabilities and product quality.
What QC and Certification Nuances Should International Buyers Consider?
When sourcing from international suppliers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, buyers should be aware of various nuances:
-
Compliance with Local Regulations: Different countries may have unique certification requirements. Understanding these regulations is crucial for successful market entry.
-
Cultural Differences in Quality Standards: Quality expectations may vary across regions, necessitating clear communication and alignment with suppliers on quality benchmarks.
By understanding these manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing starter relays and solenoids, ensuring they acquire reliable and high-quality components for their operations.

Illustrative image related to starter relay vs solenoid
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘starter relay vs solenoid’
Introduction
When sourcing components like starter relays and solenoids, B2B buyers must navigate technical specifications, supplier reliability, and regional considerations. This guide provides a structured checklist to ensure you make informed procurement decisions, minimizing risks and maximizing efficiency in your supply chain.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before engaging suppliers, it’s essential to clarify the technical requirements for the starter relay or solenoid. Consider factors such as voltage ratings, current capacity, and compatibility with existing systems.
– Voltage and Current Ratings: Ensure that the components meet the electrical specifications of your machinery.
– Compatibility: Verify that the relay or solenoid fits seamlessly into your current systems to avoid costly modifications.
Step 2: Research Supplier Reputation
Identifying reputable suppliers is critical for ensuring quality and reliability. Conduct thorough research to assess their track record in the industry.
– Customer Reviews and Testimonials: Look for feedback from previous clients, particularly those in similar markets or industries.
– Market Presence: Suppliers with a strong presence in your target regions—such as Africa or Europe—are likely more attuned to local needs and standards.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing, it’s crucial to vet suppliers thoroughly. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in a similar industry or region.
– Certifications: Check for industry certifications that indicate adherence to quality standards, such as ISO or specific automotive standards.
– Product Range: A supplier with a diverse range of products may offer better solutions or alternatives in case of supply chain disruptions.
Step 4: Request Samples and Test Products
Once you’ve narrowed down potential suppliers, request samples of the starter relays or solenoids for evaluation. Testing the products ensures they meet your specifications and quality standards.
– Functionality Tests: Conduct tests to confirm that the components operate correctly under expected conditions.
– Durability Assessments: Evaluate how well the products withstand environmental factors relevant to your operations.
Step 5: Understand Pricing Structures and Terms
Pricing can vary significantly between suppliers, so it’s important to understand their pricing models and terms of sale.
– Bulk Discounts: Inquire about pricing breaks for larger orders, which can lead to significant savings.
– Payment Terms: Clarify payment terms, including deposit requirements, payment methods, and any financing options available.
Step 6: Assess After-Sales Support and Warranty Policies
Reliable after-sales support can be invaluable, especially for complex components like starter relays and solenoids. Ensure that suppliers offer robust support and warranty options.
– Technical Support Availability: Confirm that the supplier provides accessible technical support to address any issues that may arise post-purchase.
– Warranty Terms: Understand the warranty policy, including coverage duration and conditions, to safeguard your investment.
Step 7: Finalize Contracts and Agreements
Once you’ve selected a supplier, draft and finalize contracts that clearly outline the terms of the agreement. Ensure all aspects discussed, including pricing, delivery timelines, and support services, are documented.
– Legal Review: Consider having legal counsel review contracts to ensure compliance and protect your interests.
– Clear Communication: Maintain open lines of communication with the supplier to facilitate a smooth procurement process.
By following these steps, B2B buyers can confidently procure starter relays and solenoids, ensuring they meet technical requirements and supplier reliability while optimizing their supply chain operations.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for starter relay vs solenoid Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Starter Relays and Solenoids?
When evaluating the cost structure for starter relays and solenoids, several key components should be considered. These include:
-
Materials: The primary materials used in the manufacturing of relays and solenoids—such as copper for wiring, plastic for housings, and steel for contacts—significantly influence costs. Prices for raw materials can fluctuate based on market conditions, affecting overall sourcing costs.
-
Labor: Labor costs can vary depending on the manufacturing location. Regions with lower labor costs may offer more competitive pricing, but this should be weighed against the potential impact on quality.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes utilities, factory maintenance, and administrative expenses associated with production. Overhead costs can vary widely based on the efficiency of the manufacturing process and facility location.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling for specific designs can be a considerable upfront investment. If a buyer opts for bespoke solutions, these costs should be factored into the overall pricing strategy.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that components meet quality standards is crucial, particularly for automotive applications. Rigorous QC processes can add to costs but ultimately reduce the risk of failures.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs, including freight and handling, can greatly influence the final price, especially for international transactions. The choice of Incoterms will also affect who bears these costs.
-
Margin: The profit margin that suppliers add to their pricing can vary based on market competition and perceived value. Understanding typical margins in the industry can aid in negotiation.
How Do Price Influencers Impact Sourcing Decisions for International Buyers?
Several factors can influence pricing dynamics in sourcing starter relays and solenoids:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Suppliers often offer discounts for bulk orders. Buyers should assess their needs and negotiate MOQs that align with their purchasing strategies to optimize costs.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom specifications can lead to higher costs due to the need for specialized tooling and materials. Buyers should evaluate whether standard components can meet their needs to keep costs down.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher-quality materials may incur increased costs but can provide durability and reliability, especially in harsh environments. Certifications for quality and safety can also impact pricing.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reputation, reliability, and geographic location can all influence pricing. Engaging with multiple suppliers can provide leverage in negotiations and ensure competitive pricing.
-
Incoterms: The choice of Incoterms affects shipping responsibilities and costs. Buyers should carefully consider their terms to avoid unexpected expenses.
What Are the Best Negotiation and Cost-Efficiency Tips for International Buyers?
To maximize value in sourcing starter relays and solenoids, buyers should consider the following strategies:
-
Negotiate Terms: Always negotiate pricing, payment terms, and lead times. Suppliers may have flexibility that can lead to better overall costs.
-
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Beyond initial purchase price, consider the TCO, which includes maintenance, potential failure costs, and logistics. A lower initial price may not always lead to overall savings.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances for International Transactions: Currency fluctuations, tariffs, and import duties can impact costs. Buyers should factor these into their budgets to avoid surprises.
-
Research Market Trends: Stay informed about market conditions and material costs. Knowledge of current trends can provide leverage in negotiations.
-
Build Relationships: Establish long-term relationships with suppliers to secure better pricing and terms over time. Trust can lead to preferential treatment and access to new products.
Disclaimer
The prices indicated in this analysis are for illustrative purposes only and may vary based on specific circumstances, including supplier capabilities, market conditions, and geographic factors. Buyers are encouraged to conduct thorough market research and obtain multiple quotes to ensure competitive pricing.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing starter relay vs solenoid With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Starter Relay and Solenoid Solutions
In the automotive and machinery sectors, ensuring reliable engine ignition systems is vital for operational efficiency. While starter relays and solenoids are commonly used components to facilitate this process, various alternatives exist that can also meet ignition and power management needs. This section compares starter relays and solenoids against two viable alternatives: Solid State Relays (SSRs) and Electronic Control Units (ECUs).
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Starter Relay Vs Solenoid | Solid State Relay (SSR) | Electronic Control Unit (ECU) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Reliable but may struggle under high current | High performance with rapid switching | Complex control with multiple functions |
| Cost | Generally low-cost | Moderate cost | Higher cost due to complexity |
| Ease of Implementation | Straightforward installation | Requires heat dissipation management | Complex integration with existing systems |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance required | Minimal maintenance, long lifespan | May require software updates and diagnostics |
| Best Use Case | Standard vehicle ignition systems | High-frequency applications | Advanced engine management and diagnostics |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
What Are the Benefits and Drawbacks of Solid State Relays (SSRs)?
Solid State Relays (SSRs) offer several advantages over traditional starter relays and solenoids, primarily in performance and longevity. SSRs provide faster switching speeds, which can enhance system responsiveness. They also generate less heat and are less susceptible to mechanical wear, making them a more durable option. However, they come at a moderate cost and require careful thermal management, which may complicate installation in some applications. Their best use case is in environments where rapid cycling and high reliability are critical, such as in industrial automation systems.
How Do Electronic Control Units (ECUs) Compare?
Electronic Control Units (ECUs) represent a more sophisticated alternative that integrates multiple functionalities beyond ignition control. They can manage fuel injection, ignition timing, and even diagnostics, providing a comprehensive solution for modern vehicles. While ECUs can greatly enhance performance and efficiency, they come with a higher price tag and the need for more complex installation and integration. Additionally, they may require software updates and diagnostics, adding to the maintenance considerations. ECUs are best suited for advanced engine management systems in contemporary vehicles and machinery where precision and adaptability are paramount.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Needs
Selecting the appropriate ignition control solution depends largely on your specific operational requirements and budget constraints. For straightforward applications, starter relays and solenoids may suffice due to their reliability and cost-effectiveness. However, if your needs lean towards high-frequency operations or integrated management systems, considering alternatives like Solid State Relays or Electronic Control Units could be beneficial. B2B buyers should assess their operational environments, performance needs, and maintenance capabilities to make an informed decision that aligns with their strategic objectives.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for starter relay vs solenoid
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Starter Relays and Solenoids?
Understanding the essential technical properties of starter relays and solenoids is crucial for B2B buyers, especially those involved in automotive manufacturing and repair. Here are some critical specifications to consider:

Illustrative image related to starter relay vs solenoid
-
Material Grade
– Definition: The materials used in the construction of relays and solenoids, commonly copper for electrical contacts and high-grade plastics for housings.
– B2B Importance: Higher-grade materials can enhance conductivity and durability, which leads to improved performance and longevity. This is particularly important for buyers in regions with extreme weather conditions. -
Coil Resistance
– Definition: Measured in ohms, coil resistance indicates how much electrical resistance the solenoid or relay presents to the current.
– B2B Importance: Knowing the correct coil resistance is vital for ensuring compatibility with vehicle electrical systems. A mismatch can lead to inadequate performance or even damage. -
Current Rating
– Definition: The maximum current (measured in amperes) that the relay or solenoid can safely handle.
– B2B Importance: This specification is critical for ensuring that the component can handle the demands of modern vehicles, which often require more power. Buyers must match this rating with the starter motor’s requirements. -
Activation Voltage
– Definition: The voltage required to activate the relay or solenoid, typically found in 12V or 24V configurations.
– B2B Importance: Understanding the activation voltage helps buyers select components that are compatible with their specific vehicle systems, especially in diverse international markets. -
Tolerance Levels
– Definition: The acceptable range of variation in measurements and performance specifications.
– B2B Importance: Tolerance levels ensure that components function correctly under various operating conditions. Buyers should prioritize suppliers who adhere to strict tolerance standards for reliability. -
Operating Temperature Range
– Definition: The temperature range within which the relay or solenoid can operate effectively.
– B2B Importance: Components must withstand varying temperatures, particularly in regions with extreme climates. This specification impacts the longevity and reliability of the product.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Starter Relays and Solenoids?
Familiarity with trade terminology is essential for smooth transactions and effective communication in the B2B marketplace. Here are several key terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Definition: A company that produces parts that are sold directly to the vehicle manufacturer.
– Importance: OEM components are often preferred for their guaranteed compatibility and performance, essential for maintaining vehicle warranty. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– Definition: The smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell.
– Importance: Understanding MOQ helps buyers assess inventory needs and manage costs, especially for bulk orders. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– Definition: A document sent to suppliers to request pricing and terms for specific products.
– Importance: RFQs are critical for negotiating prices and understanding supplier capabilities, enabling informed purchasing decisions. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Definition: A set of rules that define the responsibilities of sellers and buyers in international transactions.
– Importance: Knowledge of Incoterms helps buyers understand shipping costs, risks, and responsibilities, which is particularly important for international sourcing. -
Lead Time
– Definition: The amount of time it takes from placing an order to delivery.
– Importance: Knowing lead times is essential for planning production schedules and inventory management, particularly in industries with tight deadlines. -
Certification Standards
– Definition: Compliance with industry standards and regulations, such as ISO or SAE.
– Importance: Certifications ensure product quality and reliability, which are critical for maintaining safety and performance standards in automotive applications.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terms, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they select the right starter relays and solenoids for their needs.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the starter relay vs solenoid Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics and Trends in the Starter Relay vs Solenoid Sector?
The global market for starter relays and solenoids is influenced by several dynamic factors. As automotive technology continues to evolve, the demand for reliable and efficient starter components is rising. Key drivers include the increasing production of electric and hybrid vehicles, which utilize advanced electronic systems requiring high-performance relays and solenoids. Furthermore, as countries like Germany and Saudi Arabia invest heavily in automotive manufacturing, the demand for quality components is expected to surge, particularly among B2B buyers looking for reliable suppliers.
Emerging technologies, such as IoT (Internet of Things) and smart automotive systems, are also reshaping sourcing trends. Manufacturers are now focusing on integrating advanced diagnostics into their components, enhancing performance and reliability. This trend is particularly relevant for international buyers who seek not only quality products but also innovative solutions that can improve vehicle longevity and efficiency. Additionally, the demand for customized solutions tailored to specific vehicle models is on the rise, encouraging suppliers to adopt flexible manufacturing processes.
How Are Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Addressed in the Starter Relay vs Solenoid Market?
Sustainability is becoming a critical concern for B2B buyers in the automotive sector, including those sourcing starter relays and solenoids. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes and materials used in these components is under increasing scrutiny. Companies are now prioritizing ethical sourcing practices, ensuring that their supply chains adhere to environmental standards and labor regulations. This shift not only mitigates risks associated with reputational damage but also aligns with global sustainability goals.
Buyers are increasingly looking for suppliers that can provide ‘green’ certifications, such as ISO 14001 for environmental management, and are utilizing eco-friendly materials in their products. The use of recyclable materials in the production of starter relays and solenoids is gaining traction, contributing to a circular economy. This not only appeals to environmentally conscious consumers but also positions suppliers favorably in competitive markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
What Is the Historical Context of Starter Relays and Solenoids in Automotive Applications?
The evolution of starter relays and solenoids has been closely tied to advancements in automotive technology. Initially, these components served a basic function—acting as switches to engage the starter motor using low-power signals. Over the decades, as vehicles became more sophisticated, so too did these devices. The introduction of electronic ignition systems and computerized engine management necessitated more reliable and efficient components.
Historically, solenoids were favored for their ability to handle higher currents compared to relays, leading to their widespread use in modern vehicles. As manufacturers transitioned to electric and hybrid models, the role of starter relays and solenoids expanded, adapting to new technologies and performance demands. This historical context is crucial for B2B buyers, as it highlights the ongoing innovation and the importance of sourcing from suppliers who understand the complexities of modern automotive systems. Understanding this evolution allows buyers to make informed decisions about the components they procure, ensuring compatibility with current and future vehicle technologies.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of starter relay vs solenoid
-
How do I determine whether to choose a starter relay or a solenoid for my application?
To decide between a starter relay and a solenoid, consider the power requirements of your application. Solenoids typically handle higher currents and are often used for direct connections to starters, while relays are suited for lower-power signals. Assess the electrical specifications of your system, including voltage and current ratings. If you’re unsure, consult with a technical expert from your supplier who can provide insights based on your specific needs and vehicle type. -
What are the common signs of a failing starter relay or solenoid?
Common symptoms of a failing starter relay include the engine not starting, a single click when turning the ignition, or intermittent starting issues. For solenoids, signs can include a clicking sound without engine engagement, engine starting without the key, or failure to disengage. Regular maintenance and timely diagnostics can help prevent complete failure and ensure reliability in your operations. -
How can I source high-quality starter relays and solenoids for my business?
To source quality starter relays and solenoids, research reputable manufacturers with established certifications and positive customer reviews. Attend trade shows and industry events to network and evaluate suppliers. Request samples to assess quality before placing bulk orders. Additionally, ensure that suppliers comply with international standards relevant to your region, enhancing reliability and performance in your applications. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for starter relays and solenoids?
MOQs can vary significantly between suppliers and depend on factors like manufacturing capacity and customization requirements. Typically, MOQs for starter relays and solenoids range from 100 to 1,000 units. When negotiating, inquire about flexibility in MOQs, especially if you are a new buyer or if you are testing a new market segment. Discuss bulk pricing options to optimize your purchasing strategy. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing starter relays and solenoids internationally?
Payment terms can differ by supplier and region but typically include options such as advance payment, letter of credit, or net 30/60 days after delivery. For international transactions, consider using secure payment methods like PayPal or escrow services to mitigate risks. Negotiate terms that align with your cash flow needs while ensuring the supplier’s confidence in your ability to fulfill payment obligations. -
How do I ensure quality assurance (QA) for the starter relay and solenoid I purchase?
To ensure quality assurance, establish clear specifications and standards before placing an order. Request quality certifications from your supplier, such as ISO 9001, and inquire about their QA processes. Conduct factory audits if feasible, or engage third-party inspection services to verify product quality before shipment. Implement a robust receiving inspection process upon arrival to catch any defects early. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing starter relays and solenoids?
When importing, consider shipping methods, lead times, and customs regulations that apply to your country. Choose a reliable logistics partner familiar with the automotive parts supply chain and international shipping. Factor in costs such as tariffs, duties, and insurance to your overall budget. Also, ensure that all documentation is accurate to prevent delays in customs clearance. -
Can I customize starter relays and solenoids for my specific applications?
Yes, many manufacturers offer customization options for starter relays and solenoids, allowing you to tailor products to your specific needs. Customizations can include different voltage ratings, mounting configurations, and wiring harnesses. When discussing your requirements, provide detailed specifications and performance criteria. This ensures that the final product meets your operational demands while maintaining quality and reliability.
Top 3 Starter Relay Vs Solenoid Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Ford Trucks – Starter Relay and Solenoid
Domain: ford-trucks.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Starter Relay and Starter Solenoid are terms often used interchangeably but refer to different components in automotive systems. A starter relay is an electrical switch that connects the high current required by the starter, typically mounted on the firewall or inner fender. In contrast, a starter solenoid is an electrically controlled device that activates the starter motor and is mounted directl…
2. Dotheton – Relays and Solenoids
Domain: dotheton.com
Registered: 2007 (18 years)
Introduction: Relay: An electrically controlled switch, typically handling 10A to 50A. Solenoid: An electrically controlled plunger, capable of handling higher currents, often exceeding 600A in automotive applications. Starter solenoids are designed to handle large current draws (around 150A for motorcycles) and are sometimes referred to as starter relays. Both devices use electromagnetic principles to operate,…
3. Overland Bound – Relay and Solenoid Solutions
Domain: overlandbound.com
Registered: 2011 (14 years)
Introduction: Relay: 120 amp capacity, used for low current applications like fog lights and horns. Solenoid: Generally used for higher current applications (40a and above), such as winches; can handle higher amperage (e.g., 250 amp or 500 amp solenoids for dual battery setups). Smart solenoids are recommended for better battery management, preventing dead aux battery from drawing from the main battery during i…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for starter relay vs solenoid
What Are the Key B2B Insights on Sourcing Starter Relays and Solenoids?
In the competitive landscape of automotive components, understanding the differences between starter relays and solenoids is crucial for informed procurement decisions. Both devices serve as vital electromagnetic switches, yet they differ in construction and operational capacity. Relays typically manage lower currents, while solenoids can handle more significant power demands. This distinction is essential when sourcing components that can ensure reliable engine performance and longevity.
Strategic sourcing of these components not only enhances operational efficiency but also mitigates risks associated with equipment failures. As international B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe (including Germany and Saudi Arabia) navigate their procurement strategies, prioritizing suppliers with expertise in both starter relays and solenoids will be beneficial.
Looking ahead, the automotive industry is poised for innovation, with advancements in technology potentially affecting the design and functionality of these components. Buyers should stay informed and agile, ready to adapt their sourcing strategies to capitalize on emerging trends. Engage with reputable suppliers who can provide not just products, but also insights into future developments in automotive technology.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.