Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for cost of replacing an alternator in car
In the intricate landscape of automotive maintenance, understanding the cost of replacing an alternator in a car is paramount for international B2B buyers. Whether you’re operating a fleet of vehicles in Africa, managing logistics in South America, or overseeing maintenance operations in Europe and the Middle East, the ability to accurately assess and budget for alternator replacement can significantly impact your bottom line. With alternators being critical components responsible for powering essential vehicle systems, timely replacement not only ensures operational efficiency but also minimizes downtime.
This comprehensive guide delves into the various aspects of alternator replacement costs, including types of alternators, their applications across different vehicle models, and the nuances of supplier vetting. By exploring factors such as labor costs, geographical price variations, and the importance of sourcing quality parts, this resource equips you with the knowledge to make informed purchasing decisions. Additionally, we will examine the implications of choosing between original equipment manufacturer (OEM) parts and aftermarket options, guiding you towards cost-effective solutions without compromising on quality.
Empowering B2B buyers with actionable insights, this guide serves as your roadmap to navigating the global market for alternator replacements, ultimately enhancing your procurement strategies and fostering sustainable business practices in your automotive operations.
Table Of Contents
- Top 1 Cost Of Replacing An Alternator In Car Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for cost of replacing an alternator in car
- Understanding cost of replacing an alternator in car Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of cost of replacing an alternator in car
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘cost of replacing an alternator in car’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for cost of replacing an alternator in car
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for cost of replacing an alternator in car
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘cost of replacing an alternator in car’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for cost of replacing an alternator in car Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing cost of replacing an alternator in car With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for cost of replacing an alternator in car
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the cost of replacing an alternator in car Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of cost of replacing an alternator in car
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for cost of replacing an alternator in car
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Understanding cost of replacing an alternator in car Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| OEM Replacement | Original equipment manufacturer parts, high quality assurance. | Dealerships, high-end auto repair shops. | Pros: Guaranteed compatibility, warranty included. Cons: Higher cost, longer lead time. |
| Aftermarket Parts | Third-party manufactured parts, often at lower prices. | Independent garages, fleet maintenance services. | Pros: Cost-effective, wide availability. Cons: Variable quality, potential compatibility issues. |
| Remanufactured Alternators | Parts restored to like-new condition, often with new components. | Auto parts retailers, repair shops. | Pros: Cost savings, reliable performance. Cons: May lack warranty, quality varies by provider. |
| Used Alternators | Second-hand parts, typically the lowest cost option. | Budget repair shops, DIY mechanics. | Pros: Lowest cost, immediate availability. Cons: High risk of failure, no warranty. |
| Repair Services | Minor repairs instead of full replacement, such as cleaning. | Small auto repair shops, specialty services. | Pros: Cost-effective for minor issues, quick turnaround. Cons: Not always a long-term solution, may require future replacement. |
What are the Characteristics of OEM Replacement Alternators?
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) replacements are the gold standard for alternator replacement. These parts are produced by the same manufacturer that made the original alternator for the vehicle, ensuring perfect fit and compatibility. They are ideal for businesses that prioritize quality and reliability, such as dealerships and high-end auto repair shops. While the cost is higher, the assurance of quality and the warranty that often accompanies these parts make them a preferred choice for many B2B buyers.
How Do Aftermarket Parts Compare to OEM Options?
Aftermarket parts are produced by third-party manufacturers and can be significantly cheaper than OEM replacements. They are widely available and often used by independent garages and fleet maintenance services looking to cut costs. However, buyers must be cautious as the quality can vary greatly. While many aftermarket parts perform adequately, some may not meet the same standards as OEM parts, leading to potential issues down the line.
What are the Benefits of Choosing Remanufactured Alternators?
Remanufactured alternators are a middle-ground option, offering parts that have been restored to like-new condition, often with new internal components. This option is suitable for auto parts retailers and repair shops seeking to balance cost and reliability. They typically come at a lower price than new OEM parts while still providing a level of assurance regarding performance. However, the warranty may not be as robust as that of new parts, and buyers should verify the reputation of the remanufacturer.
Why Would Businesses Consider Used Alternators?
Used alternators represent the most economical choice, appealing to budget-conscious repair shops and DIY mechanics. While they are readily available and inexpensive, they come with significant risks, including the potential for failure and lack of warranty. Businesses considering used parts should weigh the immediate savings against the likelihood of needing further repairs or replacements shortly after installation.
When is Repair Services a Viable Option?
Repair services can be a cost-effective solution for businesses facing minor alternator issues, such as cleaning connections or replacing a belt. This option is particularly beneficial for small auto repair shops and specialty services that can diagnose and address specific problems without a full replacement. However, businesses should be prepared for the possibility of future issues, as repairs may not provide a long-term solution compared to a complete alternator replacement.
Key Industrial Applications of cost of replacing an alternator in car
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of cost of replacing an alternator in car | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive Repair Shops | Estimating repair costs for customers | Enhances customer trust and satisfaction | Quality of parts, labor costs, warranty options, local market rates |
| Fleet Management | Budgeting for vehicle maintenance expenses | Optimizes operational costs and resource allocation | Volume discounts, reliability of parts, supplier reputation |
| Car Dealerships | Offering competitive pricing on repairs | Attracts more customers and boosts service sales | OEM vs aftermarket parts, service time estimates, customer service |
| Auto Parts Suppliers | Setting pricing strategies for alternators | Increases sales and market competitiveness | Sourcing quality parts, understanding market trends, logistics |
| Insurance Companies | Evaluating claims related to vehicle repairs | Accurate claim processing and customer satisfaction | Repair cost benchmarks, relationships with repair shops, fraud detection |
How is the Cost of Replacing an Alternator Used in Automotive Repair Shops?
Automotive repair shops frequently estimate the cost of replacing an alternator to provide transparent pricing to customers. This practice not only builds trust but also enhances customer satisfaction. Shops must consider the quality of parts used, as well as labor costs and warranty options, to ensure they remain competitive. For international buyers, understanding local market rates and sourcing reliable suppliers is crucial to maintain profitability.
Why is Cost Consideration Important in Fleet Management?
For fleet management companies, budgeting for vehicle maintenance, including alternator replacement, is essential for optimizing operational costs. By accurately forecasting these expenses, businesses can allocate resources more effectively and avoid unexpected downtime. Key sourcing considerations include negotiating volume discounts with suppliers, ensuring the reliability of parts, and assessing the reputation of suppliers to minimize risks associated with vehicle repairs.
How Do Car Dealerships Leverage Repair Costs?
Car dealerships utilize the cost of replacing an alternator to create competitive pricing for their repair services. This strategy not only attracts more customers but also boosts service sales, enhancing overall profitability. Dealerships must weigh the benefits of using OEM parts against aftermarket options, as well as provide accurate service time estimates. Excellent customer service plays a pivotal role in retaining clients and encouraging repeat business.
What Role Do Auto Parts Suppliers Play in Pricing Strategies?
Auto parts suppliers analyze the costs associated with alternator replacements to set competitive pricing strategies. This approach helps increase sales and maintain market competitiveness. Suppliers must focus on sourcing quality parts and staying informed about market trends to adjust their pricing accordingly. Additionally, efficient logistics are crucial for timely delivery to meet the demands of repair shops and dealerships.
How Can Insurance Companies Benefit from Understanding Repair Costs?
Insurance companies evaluate the costs of vehicle repairs, including alternator replacements, to streamline their claims processing. Accurate cost assessments lead to improved customer satisfaction and trust. Establishing strong relationships with repair shops can help insurers gain insights into repair cost benchmarks, while also implementing strategies to detect potential fraud. This knowledge is particularly valuable for insurers operating in diverse international markets, where repair costs may vary significantly.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘cost of replacing an alternator in car’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Budget Constraints in Alternator Replacement Costs
The Problem: Many B2B buyers, particularly in emerging markets, face budget limitations when it comes to vehicle maintenance. The cost of replacing an alternator can vary widely, with estimates ranging from $350 to $900 depending on the vehicle’s make and model, labor costs, and whether OEM or aftermarket parts are used. This unpredictability can lead to financial strain, especially for businesses operating a fleet of vehicles where multiple replacements may be needed simultaneously. Buyers may feel overwhelmed by the potential costs and unsure of how to allocate resources effectively.
The Solution: To manage costs, B2B buyers should first conduct thorough market research to understand the average costs of alternator replacement in their region. Establishing relationships with multiple suppliers can provide leverage in negotiations and help secure better prices on parts and labor. Additionally, consider implementing a preventative maintenance program that includes regular inspections of alternators and related components. By identifying wear and tear early, buyers can mitigate the risk of sudden failures and avoid costly emergency replacements. Furthermore, investing in quality aftermarket parts, when backed by reputable brands, can lead to substantial savings without compromising on performance.

Illustrative image related to cost of replacing an alternator in car
Scenario 2: Quality Assurance Concerns with Aftermarket Alternators
The Problem: With the availability of cheaper aftermarket alternators, B2B buyers often grapple with the dilemma of quality versus cost. Poor-quality alternators can lead to premature failures, resulting in additional costs for replacements and potentially affecting operational efficiency. Buyers may find it challenging to discern which aftermarket options are reliable, leading to hesitation and indecision in purchasing.
The Solution: To ensure quality while keeping costs manageable, B2B buyers should focus on sourcing from established aftermarket manufacturers with positive reputations and warranties. Conducting due diligence through online reviews, testimonials, and industry forums can provide insights into the reliability of different brands. Additionally, partnering with trusted local distributors who specialize in automotive parts can facilitate access to high-quality products. Establishing a return policy for faulty parts can also provide a safety net, allowing businesses to make more confident purchasing decisions. Lastly, consider investing in remanufactured alternators, as these often meet or exceed OEM specifications at a reduced price, balancing quality and cost effectively.
Scenario 3: Understanding the Impact of Geography on Alternator Replacement Costs
The Problem: B2B buyers operating in diverse geographical locations, especially in regions like Africa and South America, often encounter variations in labor costs and part availability. This geographical disparity can lead to confusion regarding the true cost of alternator replacement, complicating budget forecasts and operational planning. Buyers may also struggle to find local technicians with the necessary expertise to perform quality replacements, which can lead to extended vehicle downtime.
The Solution: To navigate these geographical challenges, B2B buyers should conduct localized market assessments to gain a clear understanding of the prevailing costs in their specific regions. Building a network of reliable local technicians can ensure that replacement services are both efficient and effective. Additionally, exploring partnerships with international suppliers who have local distribution capabilities can streamline the procurement process, making it easier to source parts at competitive prices. Leveraging technology, such as online platforms for comparing prices and services, can also aid in decision-making. Furthermore, establishing a robust communication strategy with local service providers about expected costs and timelines can minimize surprises and enhance operational efficiency.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for cost of replacing an alternator in car
What Materials Are Commonly Used in Alternator Replacement?
When considering the cost of replacing an alternator in a car, the choice of materials plays a crucial role in determining performance, durability, and overall cost. Here, we analyze four common materials used in alternators: aluminum, copper, plastic, and steel.

Illustrative image related to cost of replacing an alternator in car
How Does Aluminum Impact Alternator Performance?
Aluminum is frequently used in the housing and components of alternators due to its lightweight nature and excellent thermal conductivity. With a temperature rating of up to 200°C, aluminum can effectively dissipate heat, which is critical for maintaining optimal performance.
Pros: Aluminum is resistant to corrosion, making it suitable for various climates, including humid or coastal environments. Its lightweight nature contributes to reduced overall vehicle weight, enhancing fuel efficiency.
Cons: While aluminum is durable, it can be more susceptible to fatigue over time compared to other metals. Additionally, the manufacturing process can be complex, leading to higher production costs.
Impact on Application: Aluminum’s compatibility with electrical components makes it an ideal choice for alternators, where efficient heat management is essential.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in regions like Europe and the Middle East should ensure compliance with standards such as DIN and ASTM for aluminum quality and performance.
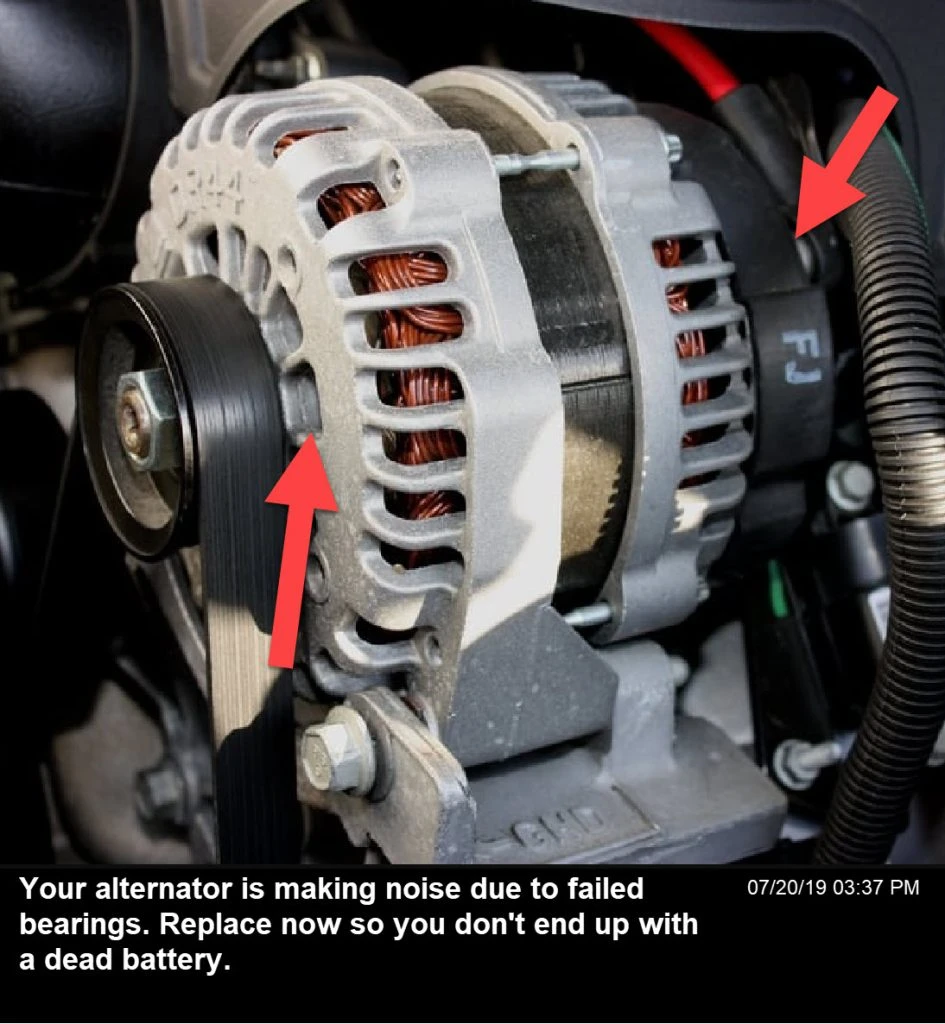
Illustrative image related to cost of replacing an alternator in car
What Role Does Copper Play in Electrical Efficiency?
Copper is primarily utilized in the windings of the alternator due to its superior electrical conductivity. This material can handle high temperatures and has a melting point of approximately 1,085°C, making it ideal for high-performance applications.
Pros: Copper’s excellent conductivity ensures efficient power generation, which is crucial for the alternator’s function. It also exhibits good resistance to corrosion when properly treated.
Cons: The primary drawback of copper is its cost, which is significantly higher than aluminum or steel. Additionally, copper’s weight can contribute to an increase in the overall weight of the alternator.
Impact on Application: Copper windings enhance the alternator’s ability to produce electricity, making it suitable for vehicles with high electrical demands.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international electrical standards is vital, especially for buyers in South America and Africa, where electrical systems may vary.
How Does Plastic Contribute to Cost-Effective Design?
Plastic is often used for non-structural components of alternators, such as covers and insulators. It is lightweight and can withstand moderate temperatures, typically up to 100°C.
Pros: The use of plastic can significantly reduce manufacturing costs and weight, making it a cost-effective choice for alternator design. It is also resistant to corrosion and can be molded into complex shapes.

Illustrative image related to cost of replacing an alternator in car
Cons: Plastic may not withstand high temperatures as effectively as metals, potentially leading to deformation or failure in extreme conditions. Its durability is also generally lower compared to metals.
Impact on Application: While plastic components can lower costs, they should be used judiciously to ensure that critical components maintain structural integrity and performance.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the specific plastic grades used, ensuring they meet local standards for automotive applications, particularly in regions with stringent regulations like Germany.
Why Is Steel Still Relevant in Alternator Construction?
Steel is sometimes used for structural components of alternators due to its strength and durability. It can withstand high temperatures and has a melting point of around 1,370°C.
Pros: Steel’s robustness makes it ideal for components that require high strength and resistance to wear. It is also relatively inexpensive compared to aluminum and copper.
Cons: Steel is heavier than aluminum and can lead to increased vehicle weight, negatively impacting fuel efficiency. Additionally, it is prone to corrosion if not properly treated.
Impact on Application: Steel is suitable for applications where strength is prioritized over weight, but care must be taken to manage its corrosion potential.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider the type of steel used and ensure it complies with international standards, particularly in regions like the Middle East where environmental conditions can be harsh.

Illustrative image related to cost of replacing an alternator in car
Summary Table of Material Selection for Alternator Replacement
| Material | Typical Use Case for cost of replacing an alternator in car | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Housing and structural components | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Susceptible to fatigue | Medium |
| Copper | Windings and electrical connections | Excellent electrical conductivity | High cost and weight | High |
| Plastic | Covers and insulators | Cost-effective and lightweight | Limited temperature resistance | Low |
| Steel | Structural components | High strength and durability | Heavier and prone to corrosion | Medium |
This analysis provides B2B buyers with essential insights into material selection for alternator replacement, helping them make informed decisions that align with performance, cost, and compliance requirements in their respective markets.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for cost of replacing an alternator in car
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing an Alternator?
The manufacturing process of an alternator involves several critical stages, each essential for ensuring the final product meets performance and quality standards. The typical stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How Is Material Prepared for Alternator Production?
Material preparation is the foundational stage where raw materials such as aluminum, copper, and steel are sourced and processed. The quality of these materials directly affects the performance and longevity of the alternator. Suppliers often conduct thorough inspections and certifications to ensure that materials meet specific standards, such as ASTM (American Society for Testing and Materials) specifications. This stage may also include machining processes to create components like the rotor and stator.
What Forming Techniques Are Used in Alternator Manufacturing?
The forming stage involves several advanced techniques such as die casting, stamping, and machining. Die casting is commonly used for aluminum components, allowing for complex shapes and high precision. Stamping is utilized for metal parts, where sheets of metal are cut and shaped into specific designs. CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining ensures that components are manufactured with high accuracy, minimizing tolerances that could lead to performance issues in the final assembly.
How Are Alternators Assembled?
Assembly is a critical stage where various components come together to form the complete alternator. This process typically involves manual and automated methods. For instance, the rotor is inserted into the stator, and the bearings are installed. Quality control checks are often integrated at this stage, where components are tested for proper fit and alignment. This helps identify any issues before the alternator moves to the finishing stage.
Illustrative image related to cost of replacing an alternator in car
What Finishing Processes Are Essential for Alternators?
Finishing processes, including painting, coating, and final inspections, are essential to enhance the durability and aesthetics of the alternator. Corrosion-resistant coatings are often applied to protect against environmental factors, especially for applications in regions with harsh climates. Final inspections include electrical testing to ensure that the alternator meets operational specifications, such as voltage output and current capacity.
What Quality Assurance Standards Should B2B Buyers Consider?
Quality assurance is paramount in alternator manufacturing, particularly for international B2B buyers. Various international standards, such as ISO 9001, ensure that manufacturers maintain effective quality management systems. These standards help facilitate consistency and reliability in production processes.
How Do International Standards Like ISO 9001 Impact Alternator Quality?
ISO 9001 certification indicates that a manufacturer adheres to internationally recognized quality management principles. This includes a strong customer focus, the involvement of top management, a process approach, and continuous improvement. For B2B buyers, sourcing from ISO-certified manufacturers can significantly reduce the risk of receiving subpar products.
What Are the Industry-Specific Quality Certifications for Alternators?
In addition to ISO 9001, certain industry-specific certifications may apply to alternators. For example, CE marking is crucial for products marketed in the European Economic Area, ensuring compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards. API (American Petroleum Institute) certifications may also be relevant for alternators used in automotive applications involving oil and gas industries. Understanding these certifications can help B2B buyers make informed sourcing decisions.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Alternator Manufacturing?
Quality control checkpoints are integral throughout the manufacturing process to ensure that products meet specified standards. Common QC checkpoints include Incoming Quality Control (IQC), In-Process Quality Control (IPQC), and Final Quality Control (FQC).
How Does Incoming Quality Control (IQC) Ensure Material Quality?
IQC is the first line of defense in quality assurance, focusing on the materials and components received from suppliers. This involves inspecting the materials against predefined specifications to ensure they meet quality standards. Non-conforming materials are rejected or returned, minimizing defects in the final product.
What Role Does In-Process Quality Control (IPQC) Play in Manufacturing?
During the assembly and forming processes, IPQC is implemented to monitor production in real-time. This includes checks for dimensional accuracy, visual inspections, and functional tests of components. IPQC helps identify issues early in the production line, reducing waste and ensuring that corrective actions can be taken promptly.
Why Is Final Quality Control (FQC) Critical Before Shipment?
FQC is conducted after assembly and finishing to ensure that the alternators meet all operational and safety standards before they are shipped to customers. This may involve electrical testing, performance assessments, and visual inspections. Only products that pass these rigorous tests are approved for shipment, which is crucial for maintaining customer satisfaction and brand reputation.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
B2B buyers can take several steps to verify a supplier’s quality control processes, ensuring they receive high-quality alternators.

Illustrative image related to cost of replacing an alternator in car
What Are the Best Practices for Conducting Supplier Audits?
Conducting supplier audits is a proactive approach to assess the manufacturer’s quality control practices. Audits can include facility inspections, review of quality management systems, and evaluation of production processes. Buyers should inquire about the frequency and scope of these audits to ensure compliance with international standards.
How Can Quality Reports Help in Supplier Assessment?
Quality reports provide insights into a manufacturer’s QC processes and product performance over time. B2B buyers should request these reports to evaluate the manufacturer’s track record in meeting quality standards. Analyzing trends in defect rates and corrective actions taken can offer a clearer picture of a supplier’s reliability.
What Role Do Third-Party Inspections Play in Ensuring Quality?
Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s manufacturing processes. These services often conduct random checks on production batches, ensuring that the products meet specified quality standards. This added layer of verification can give B2B buyers peace of mind regarding their purchasing decisions.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for B2B Buyers in Different Regions?
B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe must navigate varying quality control expectations and regulations.

Illustrative image related to cost of replacing an alternator in car
How Do Regional Differences Affect Quality Standards?
Different regions may have unique regulatory requirements that affect alternator production. For instance, European markets may have stricter environmental regulations compared to those in Africa or South America. Buyers should familiarize themselves with these regional standards to ensure compliance and avoid potential penalties.
What Should Buyers Know About Import Regulations and Certifications?
Understanding import regulations is crucial for B2B buyers, especially when sourcing from international suppliers. Certification requirements may vary by country, and products may need to be tested and certified before importation. Buyers should ensure that their suppliers are aware of and comply with these regulations to avoid delays in shipping and customs clearance.
By comprehensively understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices related to alternators, B2B buyers can make informed purchasing decisions that prioritize quality, performance, and compliance with international standards. This knowledge not only helps mitigate risks but also fosters long-term partnerships with reliable suppliers.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘cost of replacing an alternator in car’
This guide provides a structured approach for B2B buyers seeking to understand the costs associated with replacing an alternator in vehicles. Given the critical nature of the alternator in vehicle performance, it’s essential to take a methodical approach to sourcing and procurement.
Step 1: Understand the Cost Factors
Before engaging suppliers, familiarize yourself with the various cost components involved in alternator replacement. This includes labor, parts, and any additional services like diagnostic tests. Knowing the average costs—typically between $350 to $900 depending on vehicle make and model—will empower you to make informed decisions when negotiating with suppliers.
Step 2: Identify Your Vehicle’s Specifications
Different vehicles require different alternators, so it’s vital to have the specific make, model, and year of the vehicle on hand. This information will help you source the right alternator that meets OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) specifications. Pay attention to the alternator’s voltage and amperage ratings as these can vary significantly.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing, it’s crucial to vet suppliers thoroughly. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in a similar industry or region. Look for suppliers with a strong reputation in the market and positive reviews regarding their quality and service.
- Check certifications: Ensure the suppliers comply with international quality standards (e.g., ISO certifications).
- Inquire about warranty: A good warranty can indicate the supplier’s confidence in their product quality.
Step 4: Compare Pricing and Quality
Collect quotes from multiple suppliers and compare not only the prices but also the quality of the alternators. Lower-priced alternators may not always be the best choice; consider the long-term implications of quality on vehicle performance and reliability. Look for remanufactured alternators as a cost-effective yet reliable option.
Step 5: Assess After-Sales Support
After purchasing, support from the supplier can be crucial, especially if issues arise post-installation. Evaluate the level of customer service and technical support offered. Suppliers should provide clear guidance on installation, troubleshooting, and warranty claims.
Step 6: Consider Regional Variations
Costs and availability of alternators can vary by region due to factors such as import taxes, shipping costs, and local market dynamics. For buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these regional differences will enhance your sourcing strategy. Research local suppliers who may offer competitive pricing and shorter lead times.
Step 7: Plan for Future Maintenance
Lastly, consider the long-term maintenance of the vehicle when replacing the alternator. Regular checks and timely replacements can save costs down the line. Establish a relationship with a reliable supplier who can provide ongoing support for future needs, including other electrical components of the vehicle.
By following these steps, B2B buyers can streamline the procurement process for alternator replacements, ensuring they achieve the best value and reliability for their automotive needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for cost of replacing an alternator in car Sourcing
Understanding the cost structure involved in replacing an alternator is crucial for international B2B buyers, especially when sourcing automotive parts across diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Here’s a detailed breakdown of the cost components and pricing influencers, along with strategic buyer tips.
What Are the Key Cost Components in Alternator Replacement?
-
Materials: The primary material cost comes from the alternator itself, which can range from $100 to $350 depending on the make and model. This price may vary based on whether the part is OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) or aftermarket. Additionally, any supplementary components, such as serpentine belts, wiring harnesses, or connectors, may add $20 to $50 to the overall material costs.
-
Labor: Labor costs for alternator replacement typically range from $120 to $200, based on a standard 2-3 hour job. These costs can fluctuate depending on the region and labor rates in specific countries. In regions with high labor costs, such as Western Europe, buyers should expect to pay at the higher end of the spectrum.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with the production of the alternator, such as factory maintenance, utilities, and administrative expenses. The percentage of overhead can vary significantly among manufacturers, impacting the final pricing.
-
Tooling: For manufacturers producing alternators, tooling costs can be substantial, especially for custom or specialized units. These expenses are typically amortized over the production volume, meaning higher volumes can reduce the per-unit cost.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that the alternator meets safety and performance standards incurs QC costs. Buyers should inquire about certifications (e.g., ISO) to ensure quality, especially when sourcing from international suppliers.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can vary based on the Incoterms agreed upon in the contract. For instance, costs will differ significantly between Ex Works (EXW) and Cost, Insurance, and Freight (CIF) shipping methods. Additionally, longer shipping times can increase inventory holding costs.
-
Margin: Supplier margins can vary based on market dynamics, competition, and the supplier’s brand reputation. Establishing relationships with multiple suppliers can provide leverage in negotiations.
How Do Pricing Influencers Affect the Cost of Alternators?
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Bulk purchasing can significantly lower unit costs. Suppliers often provide discounts for larger orders, which is advantageous for B2B buyers looking to manage costs effectively.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom alternators or those with specific features may incur additional costs. Buyers should clearly define their specifications to avoid unexpected price increases.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: The choice between OEM and aftermarket parts can lead to price variations. While OEM parts generally come with a higher price tag, they often provide better reliability, which can reduce long-term costs.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and location of the supplier can affect pricing. Suppliers with robust quality assurance processes may charge higher prices, but they can also offer better reliability and fewer warranty claims.
-
Incoterms: The agreed shipping terms can significantly influence the total cost of ownership. Buyers should be aware of their responsibilities under different Incoterms to avoid unexpected expenses.
What Tips Should Buyers Consider for Cost-Efficiency?
-
Negotiation: Leverage multiple quotes from suppliers to negotiate better pricing. Building relationships can also lead to favorable terms and discounts.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider not just the initial purchase price but also factors like installation, maintenance, and potential downtime. Investing in higher-quality parts may yield savings in the long run.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Be aware of currency fluctuations, tariffs, and trade agreements that may impact costs when importing alternators from different regions.
-
Warranty and After-Sales Support: Always check the warranty period and the availability of after-sales support. A strong warranty can provide peace of mind and indicate the supplier’s confidence in their product.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices mentioned in this analysis are indicative and can fluctuate based on market conditions, geographic location, and specific vehicle models. Always consult with suppliers for the most accurate and up-to-date pricing information tailored to your needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing cost of replacing an alternator in car With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Replacing an Alternator in Vehicles
When faced with the need to replace an alternator, B2B buyers often seek alternatives that may offer similar benefits at different costs or operational efficiencies. Understanding the available solutions is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions that align with budget constraints and operational requirements.
| Comparison Aspect | Cost Of Replacing An Alternator In Car | Used or Rebuilt Alternator | Alternator Repair Service |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High; OEM parts ensure reliability | Varies; quality can be inconsistent | Moderate; repairs may not restore full function |
| Cost | $350 – $900 (including labor) | $100 – $250 | $150 – $300 |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires professional installation | May require professional installation | Typically quicker, may be DIY-friendly |
| Maintenance | Minimal; once installed, low upkeep | Varies; depends on part’s condition | Regular checks recommended; parts may fail again |
| Best Use Case | Long-term vehicle use, high reliability | Budget-conscious buyers, older vehicles | Minor issues, when full replacement isn’t necessary |
In-Depth Analysis of Alternatives
1. Used or Rebuilt Alternator
Opting for a used or rebuilt alternator can present a more budget-friendly solution. While prices can range from $100 to $250, the reliability of these parts can be uncertain. Used alternators often lack warranties, making them a gamble. On the other hand, rebuilt alternators undergo some refurbishment but may still retain old components. This option is best suited for buyers looking to save costs on older vehicles, but they should be cautious about potential future failures.
2. Alternator Repair Service
For minor issues, an alternator repair service may be a viable alternative. Costs typically range from $150 to $300, depending on the extent of the repairs needed. This option is beneficial for businesses that have budget constraints or for vehicles that don’t require extensive use. However, repairs may only temporarily resolve the issue, and buyers should be prepared for the possibility of future repairs. This approach is ideal for minor malfunctions but may not be cost-effective in the long term if recurring issues arise.
Making the Right Decision as a B2B Buyer
When choosing the right solution for alternator-related issues, B2B buyers should consider several factors. The cost of replacing an alternator with a new part offers the highest reliability and performance but comes at a higher price. Alternatives like used or rebuilt units or repair services may reduce upfront costs but can lead to longer-term reliability issues.
Illustrative image related to cost of replacing an alternator in car
Ultimately, the decision should align with the vehicle’s usage, the buyer’s budget, and the importance of reliability for operational efficiency. By carefully evaluating these alternatives, businesses can optimize their vehicle maintenance strategies while managing costs effectively.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for cost of replacing an alternator in car
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Alternators in Vehicle Replacement?
When evaluating the cost of replacing an alternator, several technical properties are crucial for B2B buyers to consider. Understanding these specifications not only aids in making informed purchasing decisions but also ensures compatibility and performance reliability.
1. Output Rating (Amperage)
The output rating, measured in amperes (A), indicates the maximum current the alternator can produce. It is vital for determining whether the alternator can support a vehicle’s electrical demands, especially for those with additional accessories like high-powered audio systems or aftermarket lighting. Selecting an alternator with insufficient amperage can lead to underperformance and potential damage to the vehicle’s electrical system.
2. Voltage Regulation
Voltage regulation is essential for maintaining consistent electrical output. An alternator typically operates at 12 volts, but variations can occur. A reliable voltage regulator prevents fluctuations that could damage sensitive electronic components. Understanding the voltage regulation capability ensures the longevity of both the alternator and the vehicle’s electrical system.
3. Physical Dimensions and Weight
Physical dimensions and weight affect the fitment and installation of the alternator. It is crucial for B2B buyers to ensure that the alternator matches the specifications of the vehicle’s mounting space. Incompatibility can lead to installation challenges, increased labor costs, and potential delays in service.

Illustrative image related to cost of replacing an alternator in car
4. Material Composition
The materials used in the construction of the alternator, such as aluminum or composite materials, influence its durability and performance. High-quality materials can enhance resistance to environmental factors like heat and moisture, which is particularly important in regions with extreme climates. Buyers should prioritize alternators made from materials that ensure longevity and reduce the frequency of replacements.
5. Warranty Terms
Understanding the warranty terms associated with an alternator replacement is essential for B2B buyers. A comprehensive warranty indicates the manufacturer’s confidence in the product’s quality. Warranties may cover specific issues such as defects in materials or workmanship and can vary significantly between OEM and aftermarket parts.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Alternator Replacement?
In the automotive parts industry, certain jargon and trade terms are frequently used. Familiarity with these terms can enhance communication and negotiation processes for B2B buyers.
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to parts made by the manufacturer that originally produced the vehicle’s components. These parts are often more expensive but guarantee compatibility and quality. B2B buyers may choose OEM for critical components like alternators to ensure optimal performance and reliability.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is crucial for B2B buyers as it directly impacts inventory management and procurement strategies. Buyers should negotiate MOQs that align with their operational needs to avoid excess stock.

Illustrative image related to cost of replacing an alternator in car
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal document soliciting price quotes from suppliers for specific products or services. B2B buyers should issue RFQs to multiple suppliers to compare pricing, terms, and delivery options for alternators, ensuring they get the best deal.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international shipping. These terms clarify who is responsible for shipping costs, insurance, and customs duties. Familiarity with Incoterms helps B2B buyers navigate international transactions more effectively, minimizing unexpected costs.
5. Aftermarket Parts
Aftermarket parts are components made by companies other than the OEM. They can offer cost savings but may vary in quality. B2B buyers should evaluate aftermarket options carefully, considering factors such as warranty, compatibility, and reliability, to ensure they meet their operational standards.

Illustrative image related to cost of replacing an alternator in car
Understanding these technical properties and trade terms will empower B2B buyers to make informed decisions when sourcing alternators, leading to better procurement practices and enhanced vehicle performance.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the cost of replacing an alternator in car Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends in the Alternator Replacement Sector
The global automotive alternator replacement market is influenced by a variety of factors, including vehicle longevity, the rise in electric vehicle (EV) adoption, and advancements in automotive technology. As vehicles age, the likelihood of alternator failure increases, creating a steady demand for replacement services. In regions such as Africa and South America, where older vehicles dominate the market, the demand for cost-effective solutions is particularly pronounced. In contrast, the Middle East and Europe are witnessing a growing trend towards electric and hybrid vehicles, necessitating a shift in sourcing strategies to accommodate new technology.
B2B buyers are increasingly leveraging digital platforms for sourcing parts, leading to the emergence of e-commerce solutions that facilitate easier access to quality parts at competitive prices. Additionally, the trend toward remanufactured alternators is gaining traction, as businesses seek sustainable alternatives that offer cost savings without compromising quality. This shift is particularly relevant for international buyers who must navigate varying regulations and standards in their respective markets.
Furthermore, the integration of smart technologies in automotive systems is reshaping sourcing trends. Buyers are now looking for suppliers who can provide advanced diagnostic tools and solutions that enhance the efficiency of alternator replacements, such as predictive maintenance technologies that can forecast failures before they occur.
How Can Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing Impact the Cost of Replacing an Alternator?
Sustainability is becoming a pivotal concern in the automotive parts industry, with B2B buyers increasingly prioritizing ethical sourcing practices. The environmental impact of manufacturing and disposing of alternators is significant, prompting a shift towards sustainable practices. Suppliers are now expected to demonstrate their commitment to reducing carbon footprints, which can influence purchasing decisions.
The use of ‘green’ certifications, such as ISO 14001, signifies adherence to environmental management standards, providing buyers with assurance regarding the ecological impact of their sourcing choices. Additionally, opting for remanufactured alternators can reduce waste and energy consumption compared to traditional manufacturing processes. This not only aligns with sustainability goals but can also result in lower costs for buyers, as remanufactured products often come at a fraction of the price of new components.
Moreover, the importance of transparent supply chains cannot be overstated. Buyers need to ensure that their suppliers adhere to ethical labor practices and environmental regulations. By prioritizing suppliers who uphold these standards, businesses can enhance their brand reputation while contributing positively to global sustainability efforts.
What is the Evolution of the Alternator Replacement Market?
The alternator replacement market has evolved significantly over the past few decades. Initially, alternators were primarily serviced through local auto repair shops, which limited access to quality parts and competitive pricing. However, with the advent of the internet and e-commerce, buyers now have access to a global network of suppliers, enabling them to source high-quality parts from various regions.
The rise of remanufactured alternators has also marked a shift in market dynamics, offering a cost-effective and sustainable alternative to new parts. As technology advances, manufacturers have improved the efficiency and longevity of alternators, further influencing replacement cycles. Additionally, the increasing complexity of automotive systems has led to the development of specialized diagnostic tools, enhancing the precision of replacements and repairs.
In summary, the alternator replacement sector is undergoing transformation driven by technological advancements, sustainability concerns, and changing consumer preferences. B2B buyers must stay informed about these trends to make strategic sourcing decisions that align with their business objectives.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of cost of replacing an alternator in car
-
1. How do I determine the average cost of replacing an alternator in different regions?
To gauge the average cost of alternator replacement, consider local labor rates, the price of parts, and any additional services that might be necessary. In Europe, for instance, costs can be higher due to labor expenses, often ranging from €300 to €700. In contrast, costs in regions like Africa or South America might be lower, around $200 to $500, depending on local market conditions. It’s essential to conduct market research and consult with local automotive repair shops to obtain accurate estimates tailored to specific locales. -
2. What factors influence the cost of alternator replacement?
The cost of alternator replacement can vary significantly based on several factors, including the vehicle’s make and model, the type of alternator (OEM vs. aftermarket), and the complexity of the installation process. Labor costs also play a crucial role, as some vehicles require more time to access and replace the alternator. Additionally, geographic location can affect pricing; urban areas may have higher labor costs than rural regions. Understanding these variables can help in budgeting effectively for repairs. -
3. Are there specific signs that indicate an alternator needs replacement?
Yes, there are several indicators that your alternator may need replacement. Common signs include dimming headlights, unusual noises from the engine, difficulty starting the vehicle, and illuminated warning lights on the dashboard. If you notice a rapid discharge of the battery or malfunctioning electrical components, these may also signal a failing alternator. Identifying these signs early can prevent more extensive damage and costly repairs down the line. -
4. Should I choose OEM or aftermarket alternators for replacement?
Choosing between OEM and aftermarket alternators depends on your specific needs and budget. OEM parts often come with guaranteed quality and warranty, ensuring compatibility and reliability. However, they can be more expensive. Aftermarket parts may offer cost savings, but it’s essential to vet suppliers for quality assurance. If opting for aftermarket, look for reputable brands with positive reviews and warranties. This choice will ultimately impact both performance and longevity. -
5. How can I vet suppliers for alternators in international markets?
To vet suppliers for alternators, conduct thorough research on their reputation and reliability. Check for certifications, customer reviews, and industry references. Engage in direct communication to assess responsiveness and customer service quality. Additionally, consider requesting samples to evaluate product quality firsthand. Establishing a solid relationship through transparent communication will enhance trust and facilitate smoother transactions. -
6. What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQ) for alternators when sourcing internationally?
Minimum order quantities (MOQ) for alternators can vary widely among suppliers and depend on factors like the type of alternator and the supplier’s production capabilities. Generally, MOQs may range from 10 to 100 units for aftermarket parts, while OEM suppliers might have higher MOQs due to manufacturing constraints. It’s advisable to discuss MOQs directly with suppliers to negotiate terms that align with your business needs. -
7. What payment terms should I expect when sourcing alternators internationally?
Payment terms for international sourcing can vary significantly based on supplier policies and the nature of the transaction. Common terms include upfront payments, deposits (typically 30-50%), or payment upon delivery. It’s crucial to negotiate terms that provide security and flexibility. Additionally, consider utilizing secure payment methods such as letters of credit or escrow services to protect against potential fraud and ensure safe transactions. -
8. How do logistics and shipping impact the cost of sourcing alternators?
Logistics and shipping can significantly influence the overall cost of sourcing alternators, particularly in international transactions. Factors such as shipping distance, mode of transport (air vs. sea), and customs duties must be considered. Import tariffs can add to the total cost, so it’s essential to factor these into your budget. Working with reliable logistics partners can help streamline the process, reduce costs, and ensure timely delivery of products.
Top 1 Cost Of Replacing An Alternator In Car Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Car Talk – Alternator Replacement Costs
Domain: cartalk.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: The cost to replace an alternator ranges from approximately $600 to $1,500. An alternator is a critical component that converts mechanical energy into electrical energy, powering the vehicle’s engine, lights, and charging the battery. Signs of a failing alternator include a check engine light, dimming headlights, and the need for jump-starts. Alternators can fail due to mechanical wear or electric…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for cost of replacing an alternator in car
In summary, understanding the cost dynamics associated with alternator replacement is crucial for international B2B buyers. The average expense ranges from $350 to $900, influenced by factors such as vehicle make, model, and regional labor costs. Strategic sourcing plays a pivotal role in optimizing these costs, allowing businesses to leverage quality aftermarket parts while ensuring reliability and performance.
For buyers in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, it is essential to establish strong relationships with reputable suppliers who can provide genuine OEM or high-quality remanufactured alternators. This approach not only enhances operational efficiency but also mitigates risks associated with low-quality components.
As the automotive landscape continues to evolve, proactive sourcing strategies will be key to maintaining competitiveness. Buyers should prioritize partnerships that facilitate access to innovative solutions and cost-effective alternatives. Embrace the opportunity to streamline your supply chain, ensuring that your operations remain resilient and prepared for future demands. Engage with trusted suppliers today to secure the best value for your alternator replacement needs, empowering your business for sustained success.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.

Illustrative image related to cost of replacing an alternator in car