Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for is the alternator part of the engine
In today’s global automotive market, understanding whether the alternator is part of the engine is crucial for B2B buyers involved in vehicle maintenance and repair. The alternator plays a vital role in converting mechanical energy into electrical energy, ensuring that vehicles operate smoothly and efficiently. This guide serves as a comprehensive resource for international buyers, addressing key challenges such as identifying various types of alternators, their applications across different vehicle models, and strategies for vetting reliable suppliers.
Navigating the complexities of sourcing alternators can be daunting, especially for businesses operating in diverse markets like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This guide empowers buyers to make informed purchasing decisions by detailing critical factors including cost analysis, quality standards, and essential maintenance practices. By providing insights into the lifecycle of alternators—from installation to replacement—this resource ensures that buyers can optimize their procurement strategies, reduce operational downtime, and enhance overall vehicle performance.
As you explore this guide, you’ll gain access to valuable knowledge that not only clarifies the role of the alternator within the engine but also equips you with actionable strategies for successful sourcing and supplier engagement in the competitive automotive landscape. Whether you’re based in Nigeria or Saudi Arabia, this guide is designed to meet your unique business needs and foster long-term success.
Table Of Contents
- Top 4 Is The Alternator Part Of The Engine Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for is the alternator part of the engine
- Understanding is the alternator part of the engine Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of is the alternator part of the engine
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘is the alternator part of the engine’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for is the alternator part of the engine
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for is the alternator part of the engine
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘is the alternator part of the engine’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for is the alternator part of the engine Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing is the alternator part of the engine With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for is the alternator part of the engine
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the is the alternator part of the engine Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of is the alternator part of the engine
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for is the alternator part of the engine
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Understanding is the alternator part of the engine Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Conventional Alternator | Uses electromagnetic induction to generate electricity. | Automotive manufacturing, repair services | Pros: Widely available, cost-effective. Cons: Limited efficiency at low RPMs. |
| High-Output Alternator | Designed for performance vehicles with higher power demands. | Racing, aftermarket upgrades | Pros: Increased power output, better for high-performance applications. Cons: Higher cost, may require modifications. |
| Smart Alternator | Incorporates advanced electronics for energy management. | Electric and hybrid vehicle manufacturing | Pros: Improves fuel efficiency, optimizes battery life. Cons: More complex, potentially higher repair costs. |
| Diesel Alternator | Built to withstand harsh conditions, typically larger. | Heavy-duty vehicles, commercial fleets | Pros: Durable, reliable under heavy loads. Cons: Heavier, more expensive. |
| Brushless Alternator | Utilizes permanent magnets, reducing wear and tear. | Renewable energy systems, advanced vehicles | Pros: Longer lifespan, higher efficiency. Cons: Higher initial investment. |
What are the characteristics of a Conventional Alternator?
A conventional alternator is the most common type found in vehicles, utilizing electromagnetic induction to convert mechanical energy into electrical energy. It is typically mounted at the front of the engine and is driven by a serpentine belt. Ideal for standard automotive applications, it is an economical choice for manufacturers and repair services. Buyers should consider its availability and cost-effectiveness, but be aware of its limitations in efficiency at lower RPMs.
How does a High-Output Alternator serve specific markets?
High-output alternators cater to performance vehicles that require more electrical power due to added accessories or modifications. These alternators provide increased output to support high-demand electrical systems, making them ideal for racing or aftermarket upgrades. While they offer significant advantages in power delivery, buyers should factor in the higher costs and potential need for vehicle modifications when considering this option.
What advantages does a Smart Alternator offer?
Smart alternators feature advanced electronic systems that improve energy management by adjusting output based on the vehicle’s needs. This technology is particularly beneficial for electric and hybrid vehicles, enhancing fuel efficiency and prolonging battery life. B2B buyers in the automotive sector should evaluate the added complexity and potential repair costs against the long-term benefits of fuel savings and battery health.
Why are Diesel Alternators essential for heavy-duty applications?
Diesel alternators are designed for heavy-duty vehicles, providing robust performance in demanding conditions. Their construction often includes larger components to handle higher loads, making them suitable for commercial fleets and construction equipment. While they offer durability and reliability, the trade-offs include increased weight and higher costs, which buyers should consider in their procurement decisions.
What makes Brushless Alternators a modern choice?
Brushless alternators utilize permanent magnets instead of brushes, significantly reducing wear and tear while increasing efficiency. They are often found in renewable energy applications and advanced vehicles, appealing to B2B buyers focused on sustainability and long-term investment. Although the initial costs are higher, the long lifespan and efficiency gains can justify the expense, making them an attractive option for forward-thinking companies.
Key Industrial Applications of is the alternator part of the engine
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of is the alternator part of the engine | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive Manufacturing | Power generation for vehicle electrical systems | Ensures reliable vehicle operation and customer satisfaction | Quality standards, compatibility with vehicle models, cost-effectiveness |
| Transportation & Logistics | Charging systems for commercial trucks and fleets | Reduces downtime and maintenance costs | Durability under heavy loads, warranty, and service support |
| Mining & Construction | Power supply for heavy machinery and equipment | Enhances operational efficiency and equipment reliability | Environmental resistance, performance in extreme conditions, sourcing from trusted suppliers |
| Agriculture | Electrical systems for farm machinery | Improves productivity and reduces repair costs | Adaptability to various machinery types, reliability, and availability of spare parts |
| Renewable Energy | Integration in hybrid and electric vehicles | Supports sustainability goals and market competitiveness | Compliance with international standards, energy efficiency, and technology integration |
How Is the Alternator Used in Automotive Manufacturing?
In the automotive manufacturing industry, the alternator is crucial for generating electrical power necessary for vehicle systems. It converts mechanical energy from the engine into electrical energy, ensuring that batteries are charged and electrical systems function optimally. For international buyers, especially in regions like Africa and South America, sourcing alternators that meet stringent quality standards and compatibility with various vehicle models is essential. This not only ensures reliable vehicle operation but also enhances customer satisfaction, reducing warranty claims and boosting brand reputation.
What Role Does the Alternator Play in Transportation and Logistics?
In the transportation and logistics sector, particularly for commercial trucks and fleets, the alternator is vital for maintaining the electrical systems that power various components, from lighting to navigation. A well-functioning alternator reduces the risk of vehicle downtime, which can significantly impact operational efficiency and profitability. Buyers in this sector should consider the durability of alternators under heavy loads and the availability of service support to ensure long-term performance and minimal maintenance costs.
How Is the Alternator Essential for Mining and Construction Equipment?
Mining and construction industries rely on heavy machinery, where the alternator serves as a key component in powering electrical systems essential for equipment operation. A robust alternator enhances operational efficiency by ensuring that machinery remains functional even in challenging environments. For B2B buyers in these sectors, sourcing alternators that can withstand environmental stresses and provide reliable performance is crucial. Additionally, understanding the supplier’s reputation and service capabilities can mitigate risks associated with equipment failures.
What Is the Importance of Alternators in Agriculture?
In the agricultural sector, alternators are integral to the electrical systems of farm machinery, ensuring that equipment operates efficiently. This reliability directly correlates with productivity and can significantly reduce repair costs. International buyers should prioritize alternators that are adaptable to various types of agricultural machinery and have a proven track record of reliability. Access to spare parts and service support is also a key consideration to minimize downtime during critical farming seasons.
How Do Alternators Contribute to Renewable Energy Solutions?
In the renewable energy field, particularly with the rise of hybrid and electric vehicles, alternators are pivotal in integrating electrical systems that support sustainability initiatives. They help charge batteries and manage energy flow, making them essential for the efficiency of these vehicles. B2B buyers must ensure that the alternators they source comply with international energy efficiency standards and are compatible with advanced technologies. This not only supports corporate sustainability goals but also enhances market competitiveness in a rapidly evolving industry.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘is the alternator part of the engine’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Misunderstanding Alternator Functionality in Vehicle Performance
The Problem: Many B2B buyers, particularly those involved in fleet management or vehicle maintenance, often misunderstand the role of the alternator as part of the engine’s electrical system. This can lead to misdiagnosing issues, resulting in unnecessary repairs or replacements of components such as batteries or starters. For example, a fleet manager may notice that vehicles are frequently stalling or having starting issues and might assume that the battery is at fault, overlooking the alternator’s role in maintaining battery charge and overall electrical system functionality.
The Solution: To address this misunderstanding, it is crucial for buyers to invest in training for their maintenance staff. This training should cover the relationship between the alternator, battery, and starter, emphasizing how the alternator generates electrical energy to keep the battery charged while the engine is running. Additionally, equipping maintenance teams with diagnostic tools can help accurately identify alternator-related issues. By understanding the specific signs of alternator failure—such as dimming lights, battery warning lights, or unusual noises—technicians can make informed decisions and avoid unnecessary costs.
Scenario 2: Sourcing Quality Alternators for Diverse Vehicle Models
The Problem: International B2B buyers often face challenges in sourcing high-quality alternators that fit a wide range of vehicle models, especially when dealing with imports or less common brands. This can result in delays in repairs and increased downtime for vehicles, negatively impacting operational efficiency. For instance, a parts distributor in Nigeria might struggle to find reliable suppliers for alternators that are compatible with the locally prevalent vehicle models, leading to issues with inventory management and customer satisfaction.
The Solution: To overcome sourcing challenges, B2B buyers should establish relationships with multiple suppliers who specialize in various vehicle parts, including alternators. Utilizing a centralized inventory management system can also help track which alternators are frequently in demand and which suppliers provide the best quality products. It may be beneficial to attend trade shows or industry conferences to connect with reputable manufacturers and distributors. Moreover, buyers should consider sourcing from suppliers that offer warranties and guarantees on their products, ensuring that they receive quality alternators that can withstand the rigors of the local environment.
Scenario 3: Cost Management in Alternator Replacement and Repair
The Problem: Alternator replacement can represent a significant expense for businesses, especially when it comes to maintaining a fleet of vehicles. B2B buyers may find themselves facing unexpected costs if alternators fail prematurely or if they do not have a clear understanding of the pricing structure for repairs and replacements. For example, a logistics company operating in South America might experience budget overruns due to unexpected alternator failures, leading to increased operational costs.
The Solution: To manage costs effectively, B2B buyers should develop a comprehensive maintenance schedule that includes regular checks on the alternator and other electrical components. Investing in predictive maintenance technologies can help identify potential failures before they occur, allowing for planned repairs rather than emergency replacements. Additionally, negotiating bulk purchase agreements with suppliers can lower costs per unit when buying alternators. It is also advisable to educate procurement teams about the total cost of ownership, including not just the purchase price but also labor costs and downtime, to make informed purchasing decisions. By fostering a proactive maintenance culture and understanding pricing dynamics, businesses can significantly reduce the financial impact of alternator-related issues.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for is the alternator part of the engine
What Materials Are Commonly Used in Alternators?
When selecting materials for alternators, it is essential to consider their properties, performance, and suitability for various applications. The alternator, as a critical component of the engine, requires materials that can withstand mechanical stresses, electrical demands, and environmental factors. Below are analyses of four common materials used in alternators.
Aluminum: A Lightweight Option
Key Properties: Aluminum is known for its excellent strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and thermal conductivity. It can typically withstand temperatures up to 150°C and is resistant to oxidation.
Pros & Cons: The lightweight nature of aluminum makes it ideal for automotive applications, as it reduces overall vehicle weight and enhances fuel efficiency. However, it may not be as durable as other metals under high-stress conditions, making it susceptible to deformation. Manufacturing complexity is moderate, as aluminum can be easily cast or extruded.
Impact on Application: Aluminum’s corrosion resistance is beneficial for alternators operating in humid or coastal environments, as it reduces the risk of failure due to rust.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in regions like Africa and South America should ensure compliance with local standards for aluminum alloys, such as ASTM or JIS specifications, to guarantee quality and performance.
Copper: The Electrical Conductor
Key Properties: Copper boasts high electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, and ductility. It can handle high temperatures, typically up to 200°C, and has excellent corrosion resistance when coated.
Pros & Cons: Copper is the preferred material for windings in alternators due to its superior conductivity, which enhances efficiency. However, it is heavier and more expensive than aluminum, which can impact overall manufacturing costs. The complexity of processing copper is higher due to its malleability, requiring specialized techniques.
Impact on Application: The use of copper in alternators ensures optimal electrical performance, crucial for maintaining battery charge and powering electrical systems.
Considerations for International Buyers: In regions like the Middle East, where high temperatures are common, ensuring that copper components meet local electrical standards is critical for reliability.
Steel: The Structural Backbone
Key Properties: Steel is known for its high tensile strength and durability. It can withstand significant mechanical stress and is often rated for high-temperature applications.
Pros & Cons: Steel provides excellent structural integrity, making it ideal for the housing and mounting components of an alternator. However, it is heavier than aluminum and can be prone to rust if not properly coated. Manufacturing complexity can be high due to the need for precise machining.
Impact on Application: Steel’s strength is vital for protecting sensitive internal components from physical damage, especially in rugged environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in Europe should be aware of the various steel grades and their compliance with DIN standards, ensuring that they select materials that meet local regulations for safety and performance.
Plastic: The Insulator
Key Properties: Engineering plastics are lightweight, resistant to corrosion, and can withstand moderate temperatures (up to 120°C). They offer good electrical insulation properties.
Pros & Cons: Plastic components are cost-effective and can be molded into complex shapes, facilitating design flexibility. However, they may not withstand extreme temperatures or mechanical stresses as well as metals, limiting their use in high-performance applications.
Impact on Application: Plastics are often used for insulators and covers in alternators, helping to prevent electrical shorts and enhancing safety.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that the selected plastics comply with international safety and environmental standards, particularly in regions with stringent regulations.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Alternators
| Material | Typical Use Case for is the alternator part of the engine | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Housing and structural components | Lightweight, corrosion-resistant | Less durable under high stress | Medium |
| Copper | Electrical windings | Superior electrical conductivity | Heavier and more expensive | High |
| Steel | Mounting and protective components | High tensile strength | Heavier and prone to rust | Medium |
| Plastic | Insulators and covers | Cost-effective, design flexibility | Limited temperature and stress resistance | Low |
This strategic material selection guide provides valuable insights for international B2B buyers, helping them make informed decisions when sourcing components for alternators. Understanding the properties, advantages, and limitations of these materials ensures optimal performance and compliance with regional standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for is the alternator part of the engine
What Are the Key Manufacturing Processes for Alternators in Automotive Engines?
The manufacturing process of alternators involves several critical stages, each designed to ensure the final product meets stringent quality and performance standards. Understanding these processes is crucial for B2B buyers, particularly those sourcing components for automotive applications.
How Is Material Prepared for Alternators?
The first step in the manufacturing process is material preparation, which involves selecting high-quality raw materials. Common materials used in alternator production include:
- Copper Wire: Essential for windings due to its excellent electrical conductivity.
- Aluminum or Steel Casings: Provides structural integrity and protection against environmental factors.
- Magnetic Materials: Used for the rotor and stator, which are crucial for generating electrical energy.
These materials undergo thorough inspection to ensure they meet industry specifications. B2B buyers should inquire about the sourcing and certification of these materials to ensure compliance with relevant standards.
What Forming Techniques Are Used in Alternator Production?
After material preparation, the next phase is forming. This includes several techniques:
- Winding: Copper wire is wound around the stator and rotor to create electromagnetic fields. Automated winding machines are often employed to ensure precision and consistency.
- Stamping: Metal casings and other components are stamped out of sheets of aluminum or steel. This process requires high precision to ensure all parts fit together seamlessly.
- Casting: Some components may be cast, particularly those that require complex shapes. This technique is often used for rotors and housings.
Each forming technique is critical to the alternator’s performance, and B2B buyers should ensure that their suppliers use modern, automated processes to minimize human error.
How Are Alternators Assembled?
Once individual components are formed, they move to the assembly stage. This typically involves:
- Component Integration: All parts, including the rotor, stator, bearings, and casing, are assembled. This process often employs both manual and automated techniques.
- Electrical Connections: Ensuring that all electrical connections are secure and insulated is paramount to the alternator’s function.
- Quality Control Checks: After assembly, each unit undergoes initial quality checks to ensure all components are properly integrated.
B2B buyers should verify that the assembly process includes multiple checkpoints to catch any defects early, which can save significant costs down the line.
What Finishing Processes Are Important for Alternators?
The finishing stage is crucial for enhancing the alternator’s durability and performance. Key finishing processes include:
Illustrative image related to is the alternator part of the engine
- Coating: Protective coatings are applied to prevent corrosion and wear. This is particularly important in regions with harsh climates, such as parts of Africa and the Middle East.
- Balancing: Rotors are dynamically balanced to minimize vibrations during operation, which can lead to premature wear.
- Final Inspection: Each alternator undergoes a final inspection to ensure it meets all specifications and quality standards.
This stage is vital for ensuring that the alternators can withstand the rigors of daily use in various environments.
What Quality Assurance Standards Are Relevant for Alternators?
Quality assurance is a critical aspect of alternator manufacturing, especially for B2B buyers who need to ensure reliability and performance. Understanding the relevant standards can help in selecting reputable suppliers.
Which International Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
International standards such as ISO 9001 provide a framework for quality management systems. Compliance with ISO 9001 ensures that manufacturers have consistent processes in place to produce high-quality products. Additionally, industry-specific standards such as:
- CE Marking: Indicates conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards for products sold within the European Economic Area.
- API Standards: Relevant for automotive parts, ensuring that products meet performance and quality benchmarks.
B2B buyers should request documentation proving compliance with these standards, as this serves as a guarantee of quality.
What Are the Key QC Checkpoints in the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control (QC) is integrated throughout the manufacturing process, with key checkpoints including:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Inspection of raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Ongoing checks during the manufacturing process to identify defects early.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Comprehensive testing of finished products to ensure they meet performance specifications.
Each checkpoint serves as a safeguard, preventing defective products from reaching the market. B2B buyers should inquire about the specific QC processes used by their suppliers.
Illustrative image related to is the alternator part of the engine
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
Ensuring that suppliers maintain high-quality standards is essential for B2B buyers. Here are some effective strategies for verification:
What Audit and Inspection Methods Are Effective?
- Supplier Audits: Regular audits of manufacturing facilities can provide insights into the processes and QC measures employed. Buyers should consider conducting these audits themselves or hiring third-party services.
- Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports can help buyers understand a supplier’s performance over time. This includes data on defect rates and compliance with industry standards.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection agencies can provide an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s quality processes and final products.
These methods not only help verify quality but also build a foundation of trust between buyers and suppliers.
What Are the QC Considerations for International Buyers?
For international B2B buyers, particularly those from diverse regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, several QC nuances should be considered:
- Cultural Differences: Understanding local manufacturing practices and quality expectations can aid in effective communication and negotiation with suppliers.
- Logistics and Supply Chain Management: Ensuring that quality is maintained throughout the supply chain is critical, especially when components are sourced from multiple countries.
- Compliance with Local Regulations: Buyers should be aware of and comply with local regulations that may affect the quality and safety of automotive components.
By taking these factors into account, B2B buyers can enhance their procurement strategies and ensure they source high-quality alternators that meet their operational needs.
Illustrative image related to is the alternator part of the engine
In conclusion, the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for alternators are integral to ensuring their performance and reliability. By understanding these processes and maintaining rigorous quality control standards, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that benefit their businesses in the long run.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘is the alternator part of the engine’
To assist international B2B buyers in understanding the procurement of alternators and their relation to engine components, this guide provides a step-by-step checklist. By following these actionable steps, buyers can make informed decisions that ensure quality and compatibility in their sourcing processes.
Step 1: Understand the Role of the Alternator
Before initiating the procurement process, it’s essential to grasp the alternator’s function within the engine. The alternator is responsible for converting mechanical energy into electrical energy, which is crucial for charging the vehicle’s battery and powering electrical components. Understanding this role helps buyers appreciate the importance of selecting high-quality alternators that meet specific performance standards.
Step 2: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outline the technical specifications required for the alternators you need. Consider factors such as power output, size, and compatibility with existing engine models. This step ensures that the alternators sourced will not only fit but also function effectively within your vehicles, reducing the likelihood of operational issues.
Step 3: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify potential suppliers who specialize in automotive parts, particularly alternators. Look for suppliers with a proven track record and experience in your target markets, such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. A robust supplier network can provide competitive pricing and ensure timely delivery.
Step 4: Verify Supplier Certifications
Before finalizing any agreements, verify that your potential suppliers have the necessary certifications and quality assurances. Certifications such as ISO 9001 or specific automotive industry standards indicate that the supplier adheres to quality management systems. This step is crucial for ensuring that the alternators meet safety and reliability standards.
Step 5: Request Samples for Testing
Once you’ve narrowed down potential suppliers, request samples of the alternators for testing. This allows you to evaluate the quality, performance, and compatibility of the products with your vehicles. Testing samples can reveal any potential issues early in the procurement process, saving time and resources in the long run.
Illustrative image related to is the alternator part of the engine
Step 6: Assess Pricing and Terms of Sale
Evaluate the pricing structures and terms of sale offered by your shortlisted suppliers. Look for competitive pricing but also consider the total cost of ownership, including shipping, taxes, and potential tariffs. Understanding these costs upfront helps avoid unexpected expenses later on.
Step 7: Establish a Clear Communication Channel
Effective communication is vital throughout the procurement process. Establish a clear line of communication with your suppliers to discuss specifications, timelines, and any potential issues that may arise. Regular updates and feedback can enhance collaboration and ensure that both parties are aligned throughout the sourcing process.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of procuring alternators efficiently and effectively, ensuring they make well-informed decisions that support their operational needs.
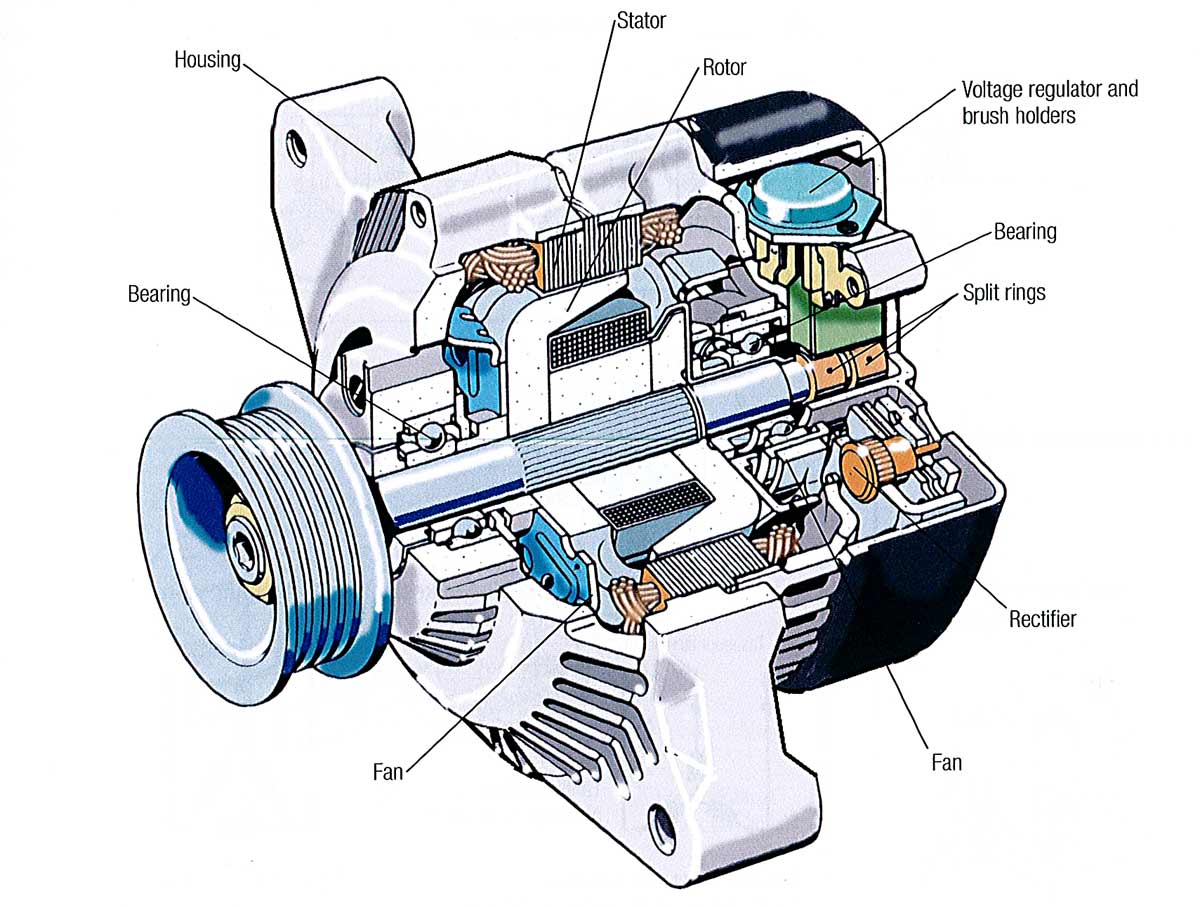
Illustrative image related to is the alternator part of the engine
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for is the alternator part of the engine Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Sourcing Alternators in Engine Applications?
When sourcing alternators as a component of engine assemblies, understanding the cost structure is crucial for effective budgeting and procurement strategies. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and margins.
Materials are the foundation of the cost structure, typically accounting for a significant portion of the total price. Common materials used in alternators include copper for wiring, aluminum or steel for the casing, and various polymers for insulation. The fluctuations in raw material prices can significantly impact overall costs, making it essential for buyers to stay informed about market trends.
Labor costs involve the workforce required to manufacture alternators. This includes assembly line workers, engineers for design and quality assurance, and maintenance personnel. Labor costs can vary greatly depending on the geographic location of the manufacturer, with regions like Europe and North America typically having higher wage structures compared to parts of Africa or South America.
Manufacturing overhead includes indirect costs related to production, such as utilities, rent, and administrative expenses. These costs are often spread across all products manufactured, influencing the pricing of each unit.
Tooling costs refer to the expenses incurred in creating molds and machinery specific to alternator production. These costs can be significant for custom or specialized alternators, which may require unique designs or adaptations.
Quality Control (QC) is another vital aspect, ensuring that the alternators meet industry standards and specifications. Implementing rigorous QC processes can increase costs but ultimately leads to higher product reliability and customer satisfaction.
Logistics costs encompass the transportation and warehousing of alternators. Factors like the distance to the buyer, shipping methods, and applicable tariffs can influence these costs. For international buyers, understanding Incoterms is essential to clarify who bears responsibility for shipping costs and risks.
Illustrative image related to is the alternator part of the engine
Margins are the final component, reflecting the profit margin set by suppliers. These can vary based on the supplier’s market positioning, brand reputation, and the perceived value of the alternators.
How Do Price Influencers Affect the Sourcing of Alternators?
Several factors influence the pricing of alternators in the B2B market. Volume and Minimum Order Quantities (MOQs) play a significant role; larger orders often lead to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should negotiate MOQs that align with their demand forecasts to maximize cost efficiency.
Specifications and customization can also affect pricing. Standard alternators may be less expensive than those requiring specific adaptations for unique engine designs. Buyers should assess their needs carefully to avoid over-specifying, which can unnecessarily inflate costs.
The quality and certifications of alternators are critical considerations, particularly for international buyers. Products that meet specific international quality standards or certifications may command higher prices but offer enhanced reliability and performance, which can lead to lower total costs over time.
Supplier factors, including their reputation, production capabilities, and delivery timelines, can significantly impact pricing. Engaging with suppliers who have a proven track record can help mitigate risks associated with delays or subpar products.
What Are the Best Negotiation Tips for B2B Buyers Sourcing Alternators?
Effective negotiation is essential for securing favorable pricing on alternators. Buyers should conduct thorough market research to understand current pricing trends and leverage this information during discussions. Building long-term relationships with suppliers can also yield better pricing terms, as trust and volume commitments often result in discounts.
Understanding the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) is crucial. This includes not just the purchase price but also potential costs related to maintenance, warranties, and performance. Buyers should evaluate the long-term value of alternators rather than focusing solely on upfront costs.
For international buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, and the Middle East, it is vital to consider pricing nuances such as import tariffs, shipping fees, and currency fluctuations. These factors can significantly affect the overall cost and should be included in the negotiation process to ensure comprehensive cost analysis.
Illustrative image related to is the alternator part of the engine
In conclusion, sourcing alternators involves a complex interplay of various cost components and pricing influencers. By understanding these elements and employing strategic negotiation techniques, B2B buyers can achieve cost-effective solutions that meet their operational needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing is the alternator part of the engine With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to ‘Is the Alternator Part of the Engine’
In the automotive sector, understanding the components that contribute to vehicle functionality is crucial for B2B buyers. The alternator is a key part of the engine, responsible for converting mechanical energy into electrical energy to charge the battery and power electrical systems. However, there are alternative technologies and methods that can achieve similar outcomes. This section compares the role of the alternator with alternative solutions, highlighting their performance, cost, ease of implementation, maintenance, and best use cases.
| Comparison Aspect | Is The Alternator Part Of The Engine | Alternative 1: Integrated Starter Generator (ISG) | Alternative 2: Battery Electric Vehicles (BEV) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Reliable energy conversion; essential for traditional combustion engines | Higher efficiency; supports engine start-stop technology | Excellent performance; no emissions during operation |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment; replacement costs can be high | Higher upfront cost; potential savings in fuel | High initial investment; savings on fuel and maintenance |
| Ease of Implementation | Standard installation in combustion engines | Requires system redesign; complex integration | Requires charging infrastructure; may need specialized training |
| Maintenance | Regular checks needed; wear and tear over time | Lower maintenance due to fewer moving parts | Minimal maintenance; battery management needed |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for traditional gasoline and diesel vehicles | Suitable for hybrid vehicles with start-stop systems | Best for urban environments with charging infrastructure |
What are the Benefits and Drawbacks of Integrated Starter Generators (ISG)?
Integrated Starter Generators (ISGs) combine the functions of a starter and alternator into one unit, making them highly efficient for hybrid and mild hybrid vehicles. They provide a seamless transition between electric and combustion power, enhancing fuel efficiency and reducing emissions. However, ISGs typically involve higher upfront costs and necessitate a redesign of the vehicle’s electrical system, which may not be feasible for all manufacturers. For businesses focused on sustainability, ISGs are a viable alternative that can significantly reduce overall vehicle operating costs over time.
How Do Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs) Compare?
Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs) represent a radical shift away from traditional combustion engines. They rely entirely on electric power stored in batteries, eliminating the need for an alternator altogether. This not only results in zero tailpipe emissions but also significantly lowers maintenance costs as BEVs have fewer moving parts. However, BEVs come with a high initial purchase price and require a robust charging infrastructure, which may be a challenge in regions with limited resources. For companies targeting eco-friendly practices and operating in urban areas, BEVs offer an innovative solution with long-term benefits.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
When deciding between the alternator and alternative technologies like ISGs or BEVs, B2B buyers must consider their specific operational requirements, budget constraints, and long-term goals. For traditional combustion engines, the alternator remains a reliable choice. However, for businesses looking to invest in more modern, efficient technologies, ISGs or BEVs may provide significant advantages. Evaluating factors such as performance, cost, maintenance, and the intended use case will guide buyers in selecting the optimal solution that aligns with their strategic objectives and market demands.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for is the alternator part of the engine
What Are the Key Technical Properties of an Alternator in an Engine?
Understanding the technical properties of an alternator is crucial for B2B buyers, particularly when sourcing components for automotive applications. Below are several critical specifications that define the quality and performance of alternators:
-
Material Grade
The materials used in alternator construction, such as high-grade aluminum for the housing and copper for the windings, significantly impact durability and efficiency. High-quality materials can withstand high temperatures and vibrations, essential for the harsh environments in which vehicles operate. B2B buyers should prioritize suppliers who adhere to stringent material standards to ensure longevity and reliability. -
Output Voltage
Alternators typically produce a voltage output ranging from 12 to 14.5 volts, essential for charging the battery and powering electrical components. Understanding the output voltage is vital for compatibility with different vehicle models. Buyers must ensure that the alternator meets the voltage requirements of the specific engine type to avoid electrical issues. -
Ampere Rating
The ampere rating indicates the maximum current an alternator can deliver. Ratings typically range from 40 to over 200 amps, depending on the vehicle’s electrical demands. Buyers must assess the total electrical load of the vehicle to select an alternator with an appropriate ampere rating, ensuring that all electrical systems function optimally without overloading the component. -
Speed Range (RPM)
The operational speed range, measured in revolutions per minute (RPM), indicates how efficiently an alternator converts mechanical energy into electrical energy. Most automotive alternators function effectively between 1,000 and 6,000 RPM. B2B buyers should consider the speed range to ensure compatibility with the engine’s performance characteristics, particularly for high-performance applications. -
Regulator Type
Alternators may feature either internal or external voltage regulators. Internal regulators are typically more compact and efficient, while external regulators can offer better performance in specific applications. Understanding the type of regulator can help buyers make informed decisions about maintenance and replacement parts, ensuring compatibility with existing systems.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Alternators?
Familiarity with industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the automotive supply chain. Here are several key terms relevant to alternators:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
This term refers to companies that produce parts that are used in the assembly of vehicles. When sourcing alternators, buyers often prefer OEM parts for their guaranteed compatibility and reliability compared to aftermarket components. Understanding this term helps in selecting quality products that meet manufacturer specifications. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ indicates the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. This is a critical consideration for B2B buyers who may need to balance inventory costs with supplier requirements. Understanding MOQ can help buyers negotiate better terms and manage their procurement strategy effectively. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing information for specific products or services. In the context of alternators, an RFQ can help buyers obtain competitive pricing and terms from various suppliers, ensuring they make informed purchasing decisions. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
These are a set of international rules that define the responsibilities of sellers and buyers in international transactions. Knowing Incoterms is crucial for B2B buyers involved in importing alternators, as they dictate shipping responsibilities, risk management, and costs associated with transportation. -
Aftermarket
The aftermarket refers to parts and accessories not made by the original manufacturer. For alternators, this includes replacement parts and performance upgrades. Buyers should evaluate the quality and compatibility of aftermarket options to ensure they meet their operational needs. -
Warranty
A warranty is a guarantee provided by the manufacturer or supplier regarding the condition of the product. Understanding warranty terms is essential for B2B buyers to assess the risk associated with purchasing alternators and to ensure they are covered against defects and failures.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing alternators, ensuring optimal performance and reliability in their applications.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the is the alternator part of the engine Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics Influencing the Alternator Sector?
The alternator sector is experiencing significant transformation driven by global market dynamics and technological advancements. One of the primary drivers is the increasing demand for electric and hybrid vehicles, particularly in regions like Europe and parts of the Middle East. As manufacturers pivot towards greener technologies, the alternator’s role in these vehicles is evolving, necessitating innovation in design and materials. Additionally, the rise of smart automotive technologies is leading to the integration of advanced electronics within alternators, enhancing efficiency and performance.
Illustrative image related to is the alternator part of the engine
In emerging markets such as Africa and South America, the demand for automotive parts, including alternators, is on the rise due to growing vehicle ownership and maintenance needs. B2B buyers in these regions are increasingly seeking reliable suppliers who can provide high-quality parts at competitive prices. Another key trend is the digital transformation in procurement processes, where B2B buyers are leveraging e-commerce platforms for sourcing automotive components, thus enhancing accessibility and transparency in the supply chain.
Furthermore, international buyers are increasingly focused on the total cost of ownership rather than just the initial purchase price. This shift is prompting suppliers to emphasize the durability and reliability of alternators, which can impact maintenance costs over the vehicle’s lifecycle. With the global market projected to grow, understanding these dynamics is essential for international B2B buyers looking to navigate sourcing trends effectively.
How Are Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Shaping the Alternator Market?
Sustainability has become a critical consideration in the alternator sector, as both manufacturers and buyers are increasingly aware of the environmental impact of automotive components. The production of alternators can involve significant energy consumption and resource extraction, which necessitates a focus on reducing carbon footprints. B2B buyers are now prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate commitment to sustainable practices, such as using recycled materials or employing energy-efficient manufacturing processes.
Ethical sourcing is also paramount, particularly for international buyers from regions like Africa and South America, where supply chain transparency can be a concern. Buyers are seeking partners who adhere to fair labor practices and can provide certifications that verify their commitment to sustainability. The use of green certifications, such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and other eco-labels, is becoming increasingly important in supplier selection.
Moreover, the demand for eco-friendly materials in the production of alternators is rising. Manufacturers that utilize biodegradable or recyclable materials in their products are likely to gain a competitive edge. By aligning with sustainability goals, B2B buyers can not only meet regulatory requirements but also enhance their brand reputation and appeal to environmentally conscious consumers.
What Is the Historical Context of the Alternator’s Evolution in Automotive Engineering?
The alternator has undergone significant evolution since its inception in the early 20th century. Initially, vehicles were equipped with generators, which were less efficient than modern alternators. The transition to alternators began in the 1960s, driven by the need for more reliable electrical systems in increasingly complex vehicles. As automotive technologies advanced, the alternator adapted, incorporating features like internal voltage regulation and improved efficiency.
By the 1980s and 1990s, the integration of electronic components and the advent of computerized vehicle systems necessitated further enhancements in alternator design. These advancements allowed alternators to manage electrical loads more effectively, ensuring that modern vehicles could support a growing array of electrical systems, from infotainment to safety features.
Today, the alternator is a vital component in both internal combustion and electric vehicles, reflecting the ongoing shifts in automotive engineering towards enhanced efficiency and sustainability. Understanding the historical context of the alternator’s development can provide valuable insights for B2B buyers looking to source components that meet the demands of modern automotive technology.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of is the alternator part of the engine
-
How do I determine if the alternator is functioning properly?
To assess the functionality of an alternator, look for signs such as dimming headlights, dashboard warning lights, or unusual noises coming from the engine compartment. Testing the alternator’s output voltage can provide a clear indication; it should typically range between 13.8 to 14.5 volts when the engine is running. For B2B buyers, ensuring that the alternator meets industry standards and specifications is critical for vehicle performance and reliability. -
What is the best alternator for commercial vehicles?
The best alternator for commercial vehicles often depends on the specific power requirements and engine type. Heavy-duty alternators with higher amperage ratings are advisable for vehicles that power multiple electrical components or accessories. When sourcing alternators, consider suppliers that offer customization options to meet specific amperage needs and ensure compliance with regional standards, particularly for markets in Africa and the Middle East. -
How do I vet suppliers for alternators in international trade?
When vetting suppliers for alternators, it’s essential to evaluate their certifications, production capabilities, and quality assurance processes. Check for industry standards compliance, such as ISO certification, and request samples to assess product quality. Additionally, consider suppliers with a proven track record in your target market, ensuring they understand local regulations and customer preferences, particularly in regions like South America and Europe. -
What are the common minimum order quantities (MOQs) for alternators?
Minimum order quantities for alternators can vary significantly based on the supplier and the customization options required. Typically, MOQs range from 50 to 500 units. For international buyers, negotiating MOQs is often possible, especially if you can demonstrate a commitment to long-term partnership or bulk purchasing potential. Understanding your inventory needs will help you navigate these discussions effectively. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing alternators?
Payment terms can vary by supplier and region, but common practices include 30% upfront payment with the balance due upon delivery or after inspection. For international transactions, consider using secure payment methods such as letters of credit or escrow services to mitigate risk. Discussing payment terms upfront can help establish a mutually beneficial relationship and ensure that both parties are comfortable with the arrangements. -
How can I ensure quality assurance for alternators sourced internationally?
To ensure quality assurance for internationally sourced alternators, establish clear specifications and standards before placing orders. Request documentation such as quality control reports and certifications from the supplier. Additionally, consider employing third-party inspection services to verify product quality before shipment, especially when dealing with suppliers in regions with varying manufacturing standards. -
What logistical considerations should I keep in mind when importing alternators?
When importing alternators, consider factors such as shipping methods, customs regulations, and import tariffs in your destination country. Partnering with a logistics provider experienced in automotive parts can streamline the process. Additionally, ensure that the alternators are packaged securely to prevent damage during transit, and factor in lead times to align with your inventory needs. -
How do I handle warranty issues for alternators sourced internationally?
Handling warranty issues for internationally sourced alternators can be complex. Ensure that the supplier provides a clear warranty policy that outlines coverage terms, duration, and procedures for claims. Familiarize yourself with local consumer protection laws that may apply. In case of defects, establish a process for returns and repairs, and consider insurance options to mitigate potential losses during the warranty period.
Top 4 Is The Alternator Part Of The Engine Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Reddit – Alternator Functionality
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: This company, Reddit – Alternator Functionality, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
2. Endurance Warranty – Alternator Insights
Domain: endurancewarranty.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: An alternator is an electrical generator in a vehicle that converts mechanical energy to electrical energy, keeping the car battery charged and the electrical system running. Signs of a bad alternator include a battery light on the dashboard, dim or flickering headlights, a dead battery, strange noises, a burning smell, slow electrical accessories, difficulty starting the car, and stalling while d…
3. Euro Car Clinic – Alternator
Domain: eurocarclinic.com
Registered: 2011 (14 years)
Introduction: The alternator is a crucial component of a car’s engine that charges the vehicle’s battery by converting mechanical energy into electricity. It consists of three basic components: an external casing for protection, wire coils for voltage generation, and a rectifier to convert AC into DC. The alternator is typically belt-driven by the car’s serpentine belt and produces around 14 volts of electricit…
4. Paulins Tire – Alternators
Domain: paulinstire.com
Registered: 2010 (15 years)
Introduction: Alternators are a part of the vehicle’s charging system, which includes the battery, voltage regulator, and alternator itself. They generate electrical currents to power various electrical components in the car, such as headlights and dashboard lights. Located at the front of the engine, alternators are powered by the engine’s serpentine belt and use the crankshaft’s power to create electrical cur…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for is the alternator part of the engine
In summary, understanding the alternator’s critical role within the engine is essential for international B2B buyers in the automotive sector. The alternator not only generates the electrical energy necessary to power vehicle systems but also plays a vital part in maintaining battery health. Recognizing the signs of alternator failure can prevent costly repairs and downtime, emphasizing the need for strategic sourcing of quality components and reliable suppliers.
Investing in high-quality alternators and ensuring effective maintenance practices can lead to enhanced vehicle reliability and customer satisfaction, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where automotive demands are rapidly evolving.
As the automotive market continues to innovate, leveraging strategic sourcing will be crucial for businesses aiming to stay competitive. Buyers should actively seek partnerships with trusted manufacturers and suppliers to ensure they are equipped with top-tier products that meet global standards. This proactive approach not only mitigates risks but also positions companies for growth in an increasingly interconnected marketplace.
Now is the time to evaluate your sourcing strategies and make informed decisions that will drive success in your automotive ventures.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.