Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for how to tell if it’s my battery or alternator
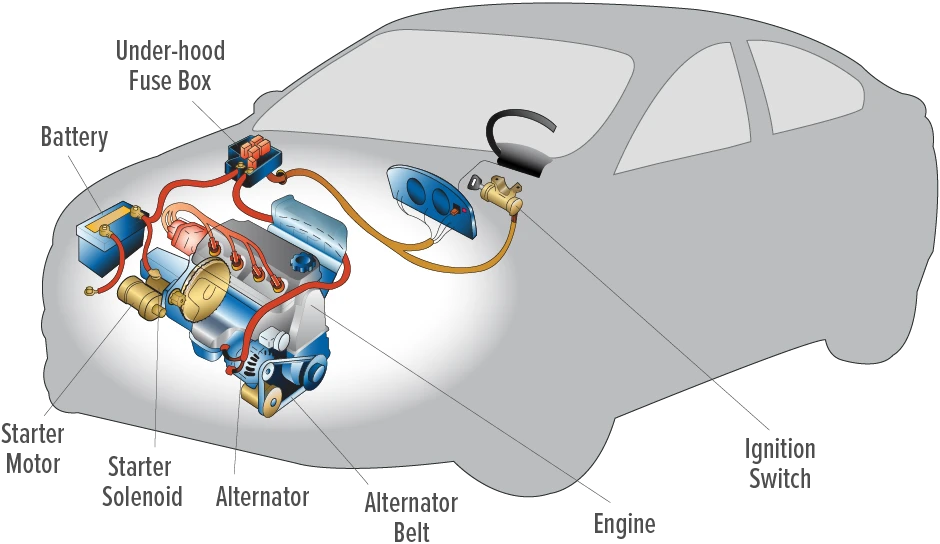
In the dynamic landscape of automotive maintenance, understanding whether the issue lies with your battery or alternator is crucial for international B2B buyers. Sourcing accurate diagnostic solutions for “how to tell if it’s my battery or alternator” can significantly impact your operational efficiency and cost management. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of battery and alternator functionality, providing essential insights into their roles, symptoms of failure, and effective testing methods.
Whether you are in Africa, South America, the Middle East, or Europe—particularly in automotive hubs like Germany and Vietnam—making informed purchasing decisions is paramount. This guide not only covers the types of batteries and alternators available in the market but also discusses their applications across various vehicle categories. Additionally, we explore supplier vetting processes, ensuring that you can confidently engage with manufacturers and distributors that meet your quality and compliance standards.
By equipping you with actionable insights into diagnostics and maintenance practices, this guide empowers your business to minimize downtime and reduce repair costs. Understanding these components will enhance your procurement strategy, enabling you to select the right products that align with your operational needs and regional market dynamics. Your journey to efficient vehicle management starts here, and we are committed to supporting you every step of the way.
Table Of Contents
- A Look at How To Tell If It’S My Battery Or Alternator Manufacturers & Suppliers
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for how to tell if it’s my battery or alternator
- Understanding how to tell if it’s my battery or alternator Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of how to tell if it’s my battery or alternator
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘how to tell if it’s my battery or alternator’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for how to tell if it’s my battery or alternator
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for how to tell if it’s my battery or alternator
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘how to tell if it’s my battery or alternator’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for how to tell if it’s my battery or alternator Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing how to tell if it’s my battery or alternator With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for how to tell if it’s my battery or alternator
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the how to tell if it’s my battery or alternator Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of how to tell if it’s my battery or alternator
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for how to tell if it’s my battery or alternator
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Understanding how to tell if it’s my battery or alternator Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Visual Inspection | Check for corrosion, leaks, and physical damage | Fleet management, vehicle maintenance | Pros: Quick and low-cost; Cons: May miss hidden issues. |
| Voltage Testing | Measuring battery and alternator voltage with a multimeter | Automotive repair shops, diagnostics | Pros: Accurate; Cons: Requires equipment and expertise. |
| Load Testing | Assessing battery performance under load conditions | Battery suppliers, automotive service | Pros: Comprehensive; Cons: Time-consuming and requires specialized tools. |
| Electrical System Diagnostics | Using advanced diagnostic tools to evaluate the entire system | Automotive manufacturers, fleet services | Pros: Detailed analysis; Cons: High initial investment. |
| Performance Monitoring | Continuous monitoring of battery and alternator performance | Commercial fleets, logistics companies | Pros: Preventive; Cons: Ongoing costs for monitoring systems. |
What are the characteristics of Visual Inspection for Battery and Alternator Issues?
Visual inspection is a straightforward method that involves checking the battery and alternator for visible signs of wear or damage. This includes looking for corrosion on battery terminals, cracks in the battery casing, or loose connections. For alternators, checking for frayed wires or unusual noises can be indicative of problems. This method is particularly suitable for fleet management, where regular maintenance checks can identify potential issues before they escalate. However, while this approach is cost-effective, it may overlook underlying electrical problems that require more sophisticated testing.
How does Voltage Testing help in diagnosing battery or alternator problems?
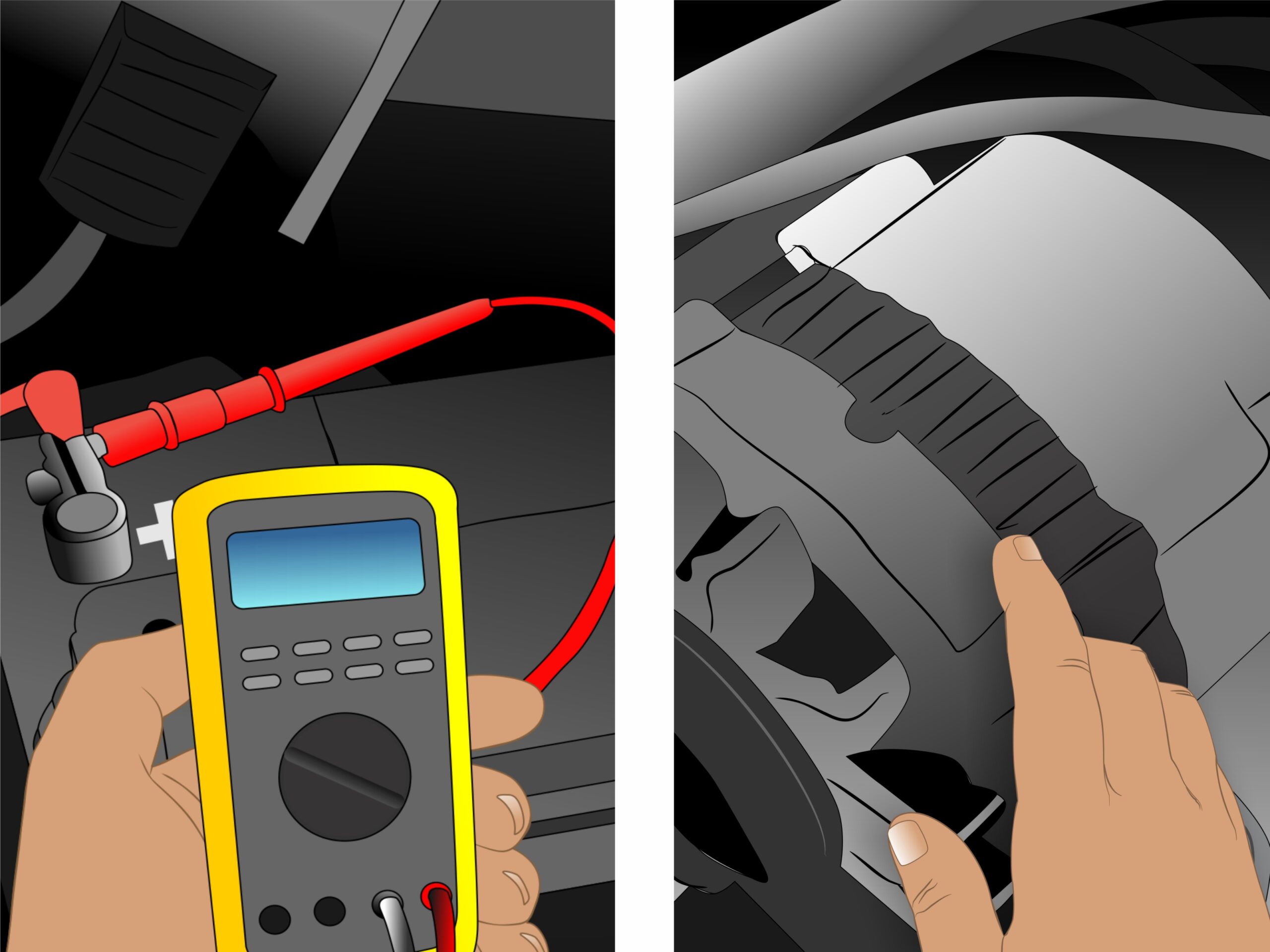
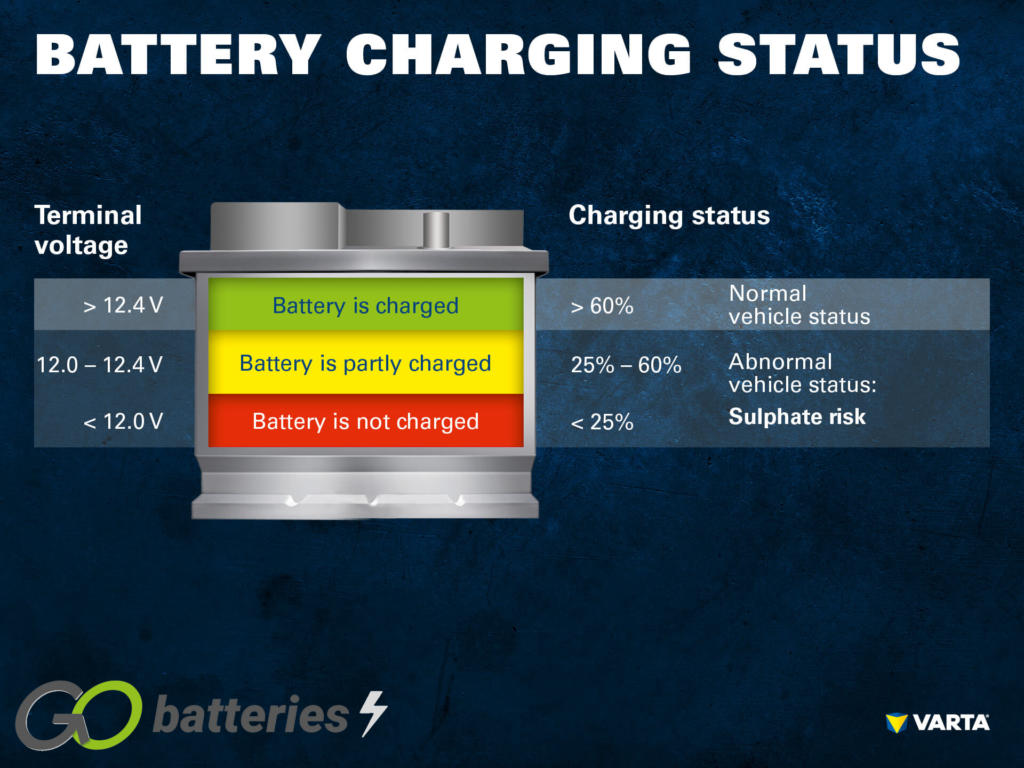
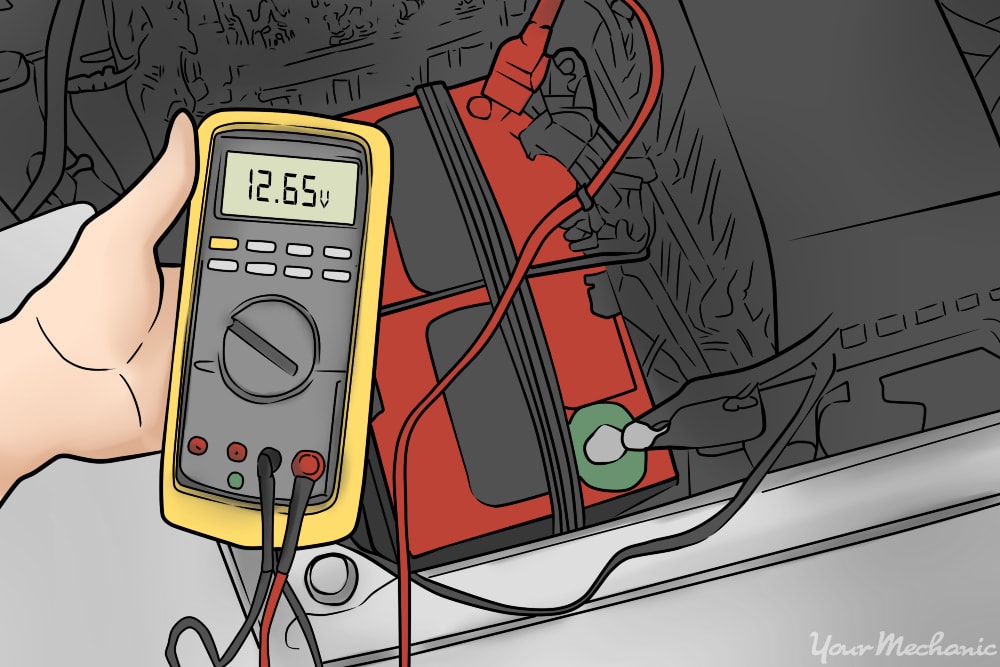
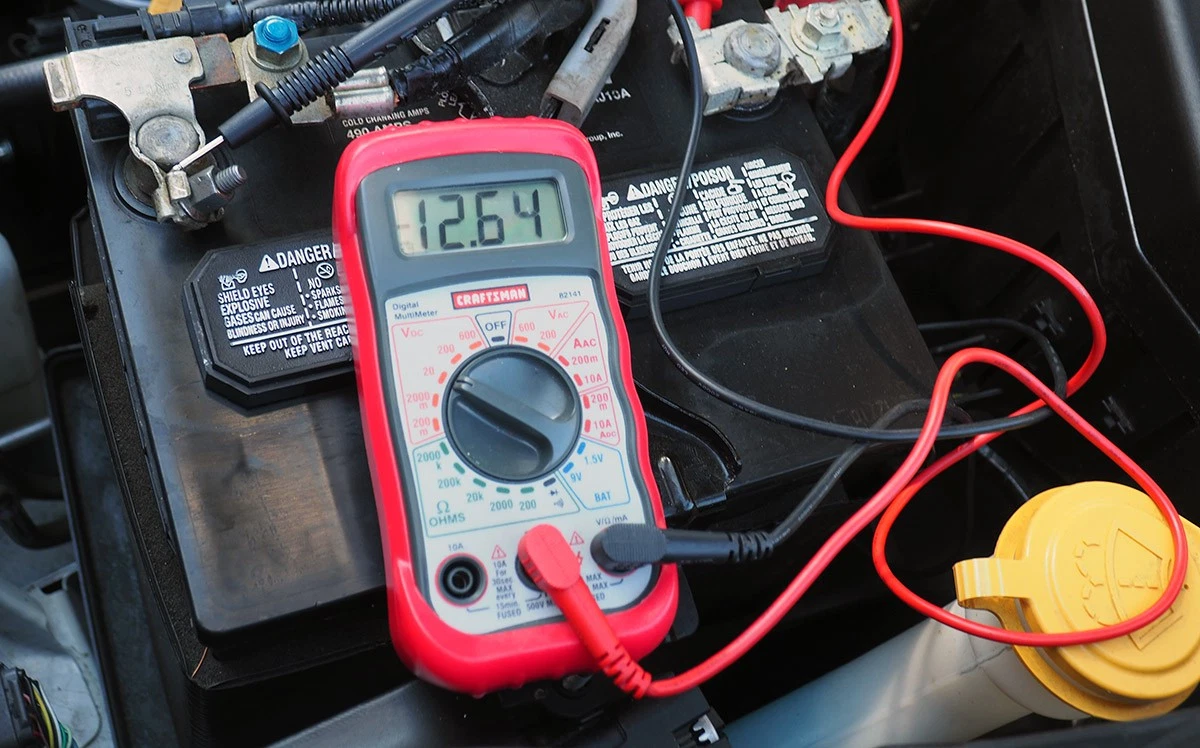
Voltage testing involves using a multimeter to measure the voltage output of both the battery and the alternator. A healthy battery should read around 12.6 volts when fully charged, while an operating alternator should provide between 13 and 14.5 volts. This method is widely used in automotive repair shops and diagnostics, providing a quick assessment of electrical health. While voltage testing is relatively accurate, it does require the appropriate tools and knowledge to interpret the results correctly.
What is Load Testing and when is it most effective?
Load testing evaluates a battery’s ability to perform under load conditions. This involves applying a specific load to the battery and measuring its voltage response. This method is essential for battery suppliers and automotive service providers to determine if a battery can hold a charge effectively. Load testing is comprehensive and provides insights into battery health, but it can be time-consuming and necessitates specialized equipment, which may not be readily available to all businesses.
What does Electrical System Diagnostics involve?
Electrical system diagnostics utilizes advanced tools to evaluate the entire electrical system of a vehicle, including the battery, alternator, and wiring. This method is prevalent among automotive manufacturers and fleet services, as it offers a detailed analysis of potential faults. While this approach yields thorough insights, it typically requires a significant initial investment in diagnostic equipment and skilled technicians, which may be a barrier for smaller operations.
How does Performance Monitoring contribute to proactive maintenance?
Performance monitoring involves the continuous tracking of battery and alternator performance through specialized systems. This method is particularly beneficial for commercial fleets and logistics companies that rely heavily on vehicle uptime. By proactively identifying issues before they lead to failures, businesses can save on costly repairs and downtime. However, this approach incurs ongoing costs for monitoring systems, which may deter some buyers from implementing it.
Key Industrial Applications of how to tell if it’s my battery or alternator
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of how to tell if it’s my battery or alternator | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive Repair | Diagnostic services for vehicles to identify battery or alternator issues | Reduces downtime and enhances customer satisfaction | Access to reliable diagnostic tools and parts suppliers |
| Transportation & Logistics | Fleet maintenance to ensure vehicle reliability and efficiency | Minimizes operational disruptions and repair costs | Availability of bulk purchasing options for parts |
| Construction Equipment | Maintenance checks on heavy machinery to ensure operational readiness | Increases equipment uptime and productivity | Partnerships with local service providers for quick repairs |
| Renewable Energy | Battery storage systems for solar or wind energy applications | Optimizes energy storage solutions and system performance | Sourcing high-quality batteries and testing equipment |
| Agriculture | Maintenance of agricultural machinery to prevent operational failures | Ensures timely farming operations and reduces losses | Access to durable and reliable parts suitable for harsh conditions |
How is “how to tell if it’s my battery or alternator” utilized in the Automotive Repair Industry?
In the automotive repair sector, businesses frequently encounter issues with vehicle electrical systems, often stemming from battery or alternator failures. By employing diagnostic tools and techniques to differentiate between these two components, repair shops can effectively address customer concerns, leading to faster repairs and increased customer trust. B2B buyers in this field must prioritize sourcing reliable diagnostic equipment and high-quality replacement parts to maintain service standards.
What role does “how to tell if it’s my battery or alternator” play in Transportation & Logistics?
In the transportation and logistics industry, fleet managers rely on efficient vehicle performance to ensure timely deliveries. Understanding whether a vehicle’s issues are related to the battery or alternator is crucial for minimizing downtime. By implementing routine diagnostic checks, companies can preemptively address potential failures, thereby reducing operational disruptions. Buyers should consider suppliers that offer bulk purchasing options for parts to optimize their maintenance budgets.
Why is “how to tell if it’s my battery or alternator” critical for Construction Equipment?
Construction equipment often operates under demanding conditions, making the reliability of its electrical systems vital. Regular diagnostics help identify whether battery or alternator issues are affecting machinery performance. This proactive approach enhances equipment uptime, directly impacting project timelines and cost efficiency. B2B buyers should establish partnerships with local service providers to ensure quick access to repairs and parts, especially in remote job sites.
How does “how to tell if it’s my battery or alternator” benefit Renewable Energy applications?
In renewable energy systems, such as solar or wind energy installations, the reliability of battery storage systems is paramount. Understanding the health of batteries versus alternators allows for better management of energy storage solutions, optimizing overall system performance. Businesses in this sector should focus on sourcing high-quality batteries and testing equipment to ensure longevity and efficiency, thus maximizing return on investment.
What is the importance of “how to tell if it’s my battery or alternator” in Agriculture?
In agriculture, machinery reliability is essential for timely planting and harvesting. Identifying whether electrical issues stem from the battery or alternator can prevent costly downtime during critical periods. Farmers and agricultural businesses should seek durable and reliable parts that can withstand harsh conditions, ensuring that their equipment remains operational when needed most. Access to local suppliers for quick repairs can significantly reduce potential losses in productivity.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘how to tell if it’s my battery or alternator’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Inconsistent Electrical Performance in Fleet Vehicles
The Problem: Fleet managers often encounter vehicles that exhibit sporadic electrical issues, leading to unreliable performance. This can manifest as dimming lights, erratic dashboard indicators, or inconsistent power to accessories. Such problems not only impact operational efficiency but can also result in increased downtime and maintenance costs. For businesses reliant on transportation, the inability to pinpoint whether the issue lies with the battery or alternator can lead to unnecessary replacements and prolonged vehicle unavailability.
The Solution: To accurately diagnose the issue, fleet managers should implement a systematic approach using diagnostic tools like multimeters. First, check the battery voltage when the vehicle is off; a healthy battery should read around 12.6 volts. Next, start the vehicle and measure the voltage across the battery terminals again. A reading between 13 and 14.5 volts indicates that the alternator is functioning properly. If the voltage fluctuates or falls below 13 volts, the alternator may need further evaluation. Establishing a regular maintenance schedule that includes these checks can prevent minor issues from escalating into significant operational disruptions. Additionally, sourcing high-quality batteries and alternators from reputable suppliers can enhance reliability across the fleet.
Illustrative image related to how to tell if it’s my battery or alternator
Scenario 2: Difficulty in Diagnosing Starting Issues in Remote Locations
The Problem: Businesses operating in remote areas often face challenges when vehicles fail to start. Without access to immediate assistance, operators may struggle to determine whether the problem is a dead battery or a malfunctioning alternator. This uncertainty can lead to costly delays, especially in industries where timely deliveries are critical, such as logistics or emergency services. Misdiagnosing the issue may result in unnecessary service calls or parts replacements, further compounding the problem.
The Solution: To streamline the diagnostic process in remote locations, companies should invest in portable battery and alternator testing kits. These kits typically include multimeters and jumper cables, allowing users to perform basic diagnostics on-site. Instructing staff on how to use these tools can empower them to assess the situation effectively. For example, if a vehicle fails to start, they can first check the battery’s voltage and attempt a jump start. If the vehicle starts but dies shortly thereafter, the alternator is likely at fault. Providing training on these procedures not only saves time but also reduces reliance on external services. Furthermore, maintaining a stock of essential spare parts can ensure quick repairs, minimizing downtime.
Scenario 3: High Replacement Costs Due to Frequent Failures
The Problem: Many companies face high costs associated with frequent battery and alternator replacements, which can be particularly burdensome for businesses with extensive vehicle fleets. Understanding the underlying issues that lead to these failures—such as improper charging practices or excessive accessory loads—is crucial. Without a clear understanding of whether the problem is with the battery or alternator, companies may repeatedly incur costs without addressing the root cause.
The Solution: To mitigate replacement costs, businesses should adopt a comprehensive monitoring and maintenance strategy. Start by analyzing driving patterns and vehicle usage; short trips can prevent batteries from fully charging, leading to premature failure. Implementing regular inspections of the electrical system, including checking for corrosion on terminals and ensuring proper belt tension for the alternator, can significantly extend the lifespan of both components. Additionally, businesses should consider investing in higher-capacity batteries and alternators designed for their specific usage conditions. Partnering with suppliers who offer warranties and guarantees can also protect against potential losses and foster long-term relationships that benefit both parties.
Illustrative image related to how to tell if it’s my battery or alternator
Strategic Material Selection Guide for how to tell if it’s my battery or alternator
When diagnosing whether an issue lies with a vehicle’s battery or alternator, the materials used in the components and tools for testing can significantly impact performance and reliability. Here, we analyze several materials relevant to this context, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international B2B buyers.
What Materials Are Commonly Used in Battery and Alternator Diagnostics?
1. Copper
Copper is widely used in electrical connections and wiring due to its excellent conductivity.
- Key Properties: High electrical conductivity (approximately 60% better than aluminum), good thermal conductivity, and resistance to corrosion when properly coated.
- Pros & Cons: Copper is highly durable and can withstand high temperatures, making it suitable for automotive applications. However, it is more expensive than aluminum and can be prone to oxidation if not treated, which may affect performance.
- Impact on Application: Copper wiring ensures efficient power transfer, crucial for accurate diagnostics. Its high conductivity is essential for tools like multimeters used to test battery and alternator performance.
- Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards such as ASTM B170 for copper wire is critical. In regions like Africa and South America, sourcing high-quality copper can be challenging due to varying local standards.
2. Aluminum
Aluminum is often used as a lightweight alternative to copper in electrical applications.
- Key Properties: Lower conductivity than copper, but still effective for many applications; lightweight and corrosion-resistant.
- Pros & Cons: Aluminum is cost-effective and lightweight, making it easier to handle and install. However, its lower conductivity can lead to higher resistance and potential voltage drops, which may complicate diagnostics.
- Impact on Application: While aluminum can be used for wiring in battery and alternator systems, it may not provide the same level of performance as copper, particularly in high-demand scenarios.
- Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with standards like DIN 17660 for aluminum. In Europe, especially in Germany, the preference may lean towards copper for critical applications.
3. Lead
Lead is primarily used in traditional lead-acid batteries, which are still prevalent in many vehicles.
- Key Properties: High density, good corrosion resistance, and ability to withstand repeated charge cycles.
- Pros & Cons: Lead batteries are reliable and have a long history of use, but they are heavy and can pose environmental hazards if not disposed of properly. Moreover, lead is increasingly facing regulatory scrutiny due to health concerns.
- Impact on Application: The use of lead in batteries is crucial for starting vehicles and supporting electrical systems. However, the environmental impact of lead disposal is a growing concern for manufacturers and users alike.
- Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with regulations like the EU’s RoHS directive is essential for buyers in Europe. In regions like the Middle East, understanding local regulations regarding lead disposal can influence sourcing decisions.
4. Plastic (Polypropylene)
Plastic is commonly used in battery casings and connectors due to its insulating properties.
- Key Properties: Lightweight, resistant to chemicals, and provides good electrical insulation.
- Pros & Cons: Plastic is cost-effective and easy to mold into various shapes, making it suitable for battery enclosures. However, it may not withstand extreme temperatures as well as metals, potentially leading to brittleness over time.
- Impact on Application: The use of plastic in battery casings protects the internal components and ensures safety during operation. However, its performance can be compromised in high-temperature environments.
- Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ISO 9001 for quality management is crucial. Buyers in regions like Africa should also consider local manufacturing capabilities for plastic components.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for how to tell if it’s my battery or alternator | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Copper | Electrical connections and wiring for battery and alternator tests | Excellent conductivity | Higher cost and oxidation potential | High |
| Aluminum | Lightweight wiring in battery and alternator systems | Cost-effective and lightweight | Lower conductivity than copper | Medium |
| Lead | Lead-acid batteries in vehicles | Reliable and long-lasting | Environmental hazards and weight | Medium |
| Plastic | Battery casings and connectors | Lightweight and chemically resistant | Limited temperature tolerance | Low |
This analysis provides a comprehensive overview of the materials involved in diagnosing battery and alternator issues, emphasizing the importance of material selection for performance and compliance in international markets.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for how to tell if it’s my battery or alternator
What are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Processes for Battery and Alternator Diagnostics?
Manufacturing processes for components related to battery and alternator diagnostics involve several key stages, each critical to ensuring product quality and reliability. Understanding these stages helps B2B buyers assess the capabilities of potential suppliers.
1. Material Preparation: What Raw Materials are Used?
The first stage in manufacturing is the preparation of raw materials. For batteries, this typically includes lead, sulfuric acid, and other chemical compounds necessary for creating lead-acid batteries. For alternators, copper, aluminum, and various plastics are essential for windings, housings, and other components. Rigorous quality control at this stage ensures that only high-grade materials are used, which can significantly affect performance and longevity.
2. Forming: How Are Components Shaped and Assembled?
In the forming stage, materials undergo processes such as stamping, casting, or machining. For instance, battery plates are stamped from lead sheets, while alternator housings may be cast or machined from aluminum. Techniques such as injection molding may also be employed for plastic components. Precision in this stage is crucial; any defects can lead to inefficiencies or failures during operation.

Illustrative image related to how to tell if it’s my battery or alternator
3. Assembly: What Techniques Are Employed for Quality Assembly?
The assembly process involves bringing together various components to create a functional unit. Automated assembly lines are commonly used for both batteries and alternators, incorporating techniques such as soldering, welding, and fastening. Quality assurance measures at this stage include visual inspections and automated checks to ensure components fit correctly and function as intended.
4. Finishing: What Final Touches Are Applied?
Finishing processes may involve surface treatments, painting, or coating to enhance durability and aesthetics. For batteries, this might include applying protective coatings to terminals, while alternators might undergo treatments to prevent corrosion. Finishing checks ensure that the final product meets specified standards for both appearance and functionality.
How is Quality Assurance Implemented in Battery and Alternator Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is paramount in the production of batteries and alternators, ensuring that products meet international and industry-specific standards. B2B buyers must be familiar with the various QA processes to ensure they partner with reputable suppliers.
Illustrative image related to how to tell if it’s my battery or alternator
1. What International Standards Govern Battery and Alternator Quality?
International standards such as ISO 9001 provide a framework for quality management systems across industries, including automotive components. Compliance with these standards is often a prerequisite for doing business in many regions. Additionally, certifications like CE (Conformité Européenne) for products sold in Europe and API (American Petroleum Institute) for oil-related products are also relevant.
2. What are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control checkpoints are integrated throughout the manufacturing process. These include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Raw materials are inspected before production begins to ensure they meet specifications.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during the manufacturing process helps catch defects early. This can involve real-time inspections and measurements.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): The finished products undergo comprehensive testing to verify they meet performance standards. This may include electrical testing for alternators and capacity testing for batteries.
3. What Common Testing Methods are Used for Quality Assurance?
Testing methods vary depending on the component but often include:
- Voltage Testing: For batteries, voltage readings are taken to ensure they hold a charge.
- Load Testing: This assesses how well a battery performs under load conditions.
- Electrical Output Testing: For alternators, output voltage and amperage are measured to confirm they meet specifications.
- Durability Testing: Components may undergo stress tests to simulate long-term use.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
B2B buyers must conduct due diligence when selecting suppliers, particularly in international markets where standards may vary. Here are actionable steps to verify quality control practices.
1. What Audit Procedures Should Buyers Implement?
Conducting audits is a critical step in verifying a supplier’s quality control practices. Buyers should consider both pre-qualification audits and regular follow-up audits. These can include:
- On-Site Inspections: Visiting the manufacturing facility to observe processes and quality checks firsthand.
- Documentation Review: Assessing quality management documents, including quality manuals, inspection reports, and compliance certificates.
2. How Can Buyers Access Quality Control Reports?
Buyers should request detailed quality control reports from suppliers. These documents should outline testing methods, results, and any corrective actions taken in the event of failures. Transparency in reporting is a good indicator of a supplier’s commitment to quality.
3. What Role Do Third-Party Inspections Play?
Utilizing third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased evaluation of a supplier’s quality control practices. These organizations can perform independent audits and testing, offering additional assurance that products meet required standards. This is particularly valuable for international buyers who may not have the resources to conduct thorough inspections themselves.
Illustrative image related to how to tell if it’s my battery or alternator
What are the QC and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers face unique challenges when it comes to quality assurance and certification, especially in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
1. How Do Regional Standards Impact Quality Control?
Different regions may have specific regulations and standards that impact manufacturing and quality control processes. Buyers should familiarize themselves with local regulations and ensure their suppliers are compliant. For example, European buyers must ensure products meet CE marking requirements, while buyers in South America might need to consider local certifications.
2. What Challenges Might Buyers Face in Ensuring Compliance?
Navigating the landscape of international standards can be complex. Language barriers, varying levels of regulatory enforcement, and differing cultural attitudes toward quality can complicate the verification process. Buyers should consider partnering with local experts or consultants who understand the nuances of the target market.
By thoroughly understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures involved in battery and alternator diagnostics, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they select suppliers that adhere to high standards of quality and reliability. This vigilance not only enhances operational efficiency but also contributes to long-term business success.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘how to tell if it’s my battery or alternator’
Introduction
This practical sourcing guide is designed to assist B2B buyers in determining whether the issues in their vehicles are related to the battery or the alternator. Understanding these components is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions, especially when selecting diagnostic tools, replacement parts, or services. This checklist will help you identify the necessary steps to accurately diagnose and address electrical system problems in vehicles.

Illustrative image related to how to tell if it’s my battery or alternator
Step 1: Identify Common Symptoms
Recognizing the symptoms of battery or alternator failure is the first step in diagnosis. A dead battery typically manifests as a failure to start the vehicle, slow cranking, or clicking sounds when turning the ignition. In contrast, alternator issues may present as dimming lights or fluctuating electrical performance. Documenting these symptoms will help you communicate effectively with suppliers and technicians.
Step 2: Conduct Basic Tests
Performing simple tests can provide immediate insights into the condition of your battery and alternator. Use a multimeter to check the battery voltage; a healthy battery should read around 12.6 volts. For the alternator, measure the voltage while the engine is running; it should be between 13 and 14.5 volts. These initial tests can guide your procurement decisions regarding parts or services needed.
Step 3: Research Diagnostic Tools
Investing in reliable diagnostic tools is essential for accurate assessment. Look for multimeters or specialized automotive diagnostic equipment that can measure voltage and amperage effectively. Ensure that the tools are compatible with the types of vehicles you service, as specifications can vary significantly across models and regions.
Step 4: Define Your Technical Specifications
When sourcing replacement batteries or alternators, clearly define the specifications needed. Consider factors such as voltage, capacity, and compatibility with existing vehicle systems. Providing precise specifications helps suppliers offer the most suitable options and avoids costly mismatches.
Step 5: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Thoroughly vet potential suppliers to ensure they meet your quality and service standards. Request company profiles, including certifications and case studies. Look for suppliers who have experience in your specific market, as they will be more familiar with regional vehicle types and requirements.
Step 6: Request Samples or Demonstrations
Before finalizing any purchase, consider requesting samples or demonstrations of the products. This step is particularly important for diagnostic tools and replacement parts. Evaluating the performance of these items firsthand can provide assurance of their quality and reliability.
Step 7: Establish a Maintenance Plan
Once you’ve diagnosed the problem and sourced the necessary parts or tools, establish a maintenance plan to prevent future issues. Regular inspections and maintenance can prolong the life of both batteries and alternators. Collaborate with suppliers who can provide ongoing support and service options tailored to your needs.
Illustrative image related to how to tell if it’s my battery or alternator
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can make informed decisions regarding battery and alternator issues, ensuring efficient vehicle operations and reducing downtime.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for how to tell if it’s my battery or alternator Sourcing
When determining whether an issue lies with a vehicle’s battery or alternator, understanding the cost structure and pricing nuances of related sourcing can be crucial for international B2B buyers. This analysis covers the key cost components involved in sourcing solutions for battery and alternator diagnostics, as well as price influencers and buyer tips that can enhance procurement strategies.
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Battery and Alternator Solutions?
-
Materials: The primary materials involved in battery and alternator diagnostics include high-quality electrical components, wiring, connectors, and diagnostic equipment like multimeters. The choice of materials can significantly affect costs, especially when considering certifications and quality standards required in different regions.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is essential for both manufacturing and diagnosing issues. Labor costs can vary widely based on geographic location, with higher costs in regions like Europe compared to South America or Africa. It is important to consider the availability of trained technicians who can perform accurate diagnostics.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses all indirect costs associated with production, including utilities, rent, and administrative expenses. Efficient manufacturing processes can help mitigate these costs, allowing for more competitive pricing.
-
Tooling: Initial investments in tooling and equipment for manufacturing diagnostic tools can be substantial. However, as production scales, these costs can be distributed over larger volumes, reducing the per-unit cost.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that diagnostic tools meet stringent quality standards is vital. This includes testing procedures to verify that equipment accurately differentiates between battery and alternator issues. QC processes can add to the overall cost but are essential for maintaining product reliability.
-
Logistics: The cost of transporting materials and finished products can vary based on distance, shipping method, and customs regulations. For international buyers, understanding Incoterms is crucial to determine who bears the costs and risks during transportation.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically mark up prices to cover costs and ensure profitability. The margin can vary based on market demand, competition, and the perceived value of the product.
What Influences Pricing for Battery and Alternator Diagnostic Tools?
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Pricing often decreases with larger orders. Buyers should assess their needs to leverage better pricing through bulk purchases.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom tools designed for specific vehicle types or diagnostic needs can incur additional costs. Buyers should evaluate whether standard solutions meet their requirements to avoid unnecessary expenses.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: High-quality materials that comply with international standards tend to be more expensive. Buyers should weigh the cost against potential long-term savings from increased durability and reliability.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reputation, reliability, and service levels can affect pricing. Building strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better terms and conditions.
-
Incoterms and Shipping Costs: Understanding Incoterms is essential for international buyers to manage shipping responsibilities and costs effectively. Different terms can significantly impact the total cost of ownership.
How Can Buyers Negotiate for Better Pricing?
To achieve cost efficiency, buyers should consider the following strategies:
-
Leverage Volume Discounts: When feasible, combine orders or collaborate with other businesses to meet minimum order quantities and secure bulk discounts.
-
Explore Alternative Suppliers: Conduct market research to identify multiple suppliers, allowing for competitive bidding and better negotiation leverage.
-
Assess Total Cost of Ownership: Consider not just the purchase price but also maintenance, durability, and potential downtime costs associated with lower-quality products.
-
Negotiate Payment Terms: Flexible payment terms can help manage cash flow and reduce immediate financial burdens.
In conclusion, understanding the cost structure, pricing influences, and negotiation strategies is vital for B2B buyers seeking solutions for battery and alternator diagnostics. By leveraging these insights, international buyers can optimize their procurement processes and achieve better financial outcomes. Always remember to conduct thorough market research and supplier assessments to inform purchasing decisions effectively.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing how to tell if it’s my battery or alternator With Other Solutions
Introduction to Alternative Solutions for Diagnosing Battery and Alternator Issues
In the automotive industry, accurately diagnosing whether a vehicle issue stems from the battery or alternator is crucial for operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness. While traditional methods of testing have their merits, exploring alternative solutions can enhance diagnostic precision and save time. This analysis compares the conventional approach of testing the battery and alternator against two alternative methods: using an onboard diagnostic (OBD-II) scanner and employing professional diagnostic services.
Illustrative image related to how to tell if it’s my battery or alternator
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | How To Tell If It’s My Battery Or Alternator | OBD-II Scanner | Professional Diagnostic Services |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Direct voltage and functionality tests | Provides error codes and data | Comprehensive diagnostics and repairs |
| Cost | Low-cost tools (multimeter) required | Moderate (typically $50-$200) | Higher (varies by service provider) |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires basic technical knowledge | User-friendly; plug-and-play | Requires scheduling and transport |
| Maintenance | Minimal; periodic checks | Software updates needed | Ongoing relationship with service provider |
| Best Use Case | Quick, at-home diagnostics | DIY enthusiasts and technicians | Complex issues needing expert analysis |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
1. OBD-II Scanner
An OBD-II scanner is a diagnostic tool that connects to the vehicle’s onboard computer system. It provides real-time data and error codes that can indicate whether the battery or alternator is malfunctioning. The primary advantage of using an OBD-II scanner is its ability to offer a broader perspective on vehicle health, including other potential issues beyond just the battery or alternator. However, the initial cost can be a barrier for some users, and interpreting the codes requires a certain level of technical knowledge.
2. Professional Diagnostic Services
Utilizing professional diagnostic services is another viable alternative for determining battery or alternator issues. These services offer in-depth analysis conducted by trained technicians who use advanced tools and methodologies. The primary benefit is the comprehensive nature of the diagnostics, which can uncover underlying issues that may not be apparent through basic testing. However, this option tends to be more expensive and requires coordination for vehicle drop-off or pick-up. Additionally, the turnaround time can vary, which may not be ideal for businesses that rely on quick vehicle servicing.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
When selecting the right method to diagnose battery and alternator issues, B2B buyers must consider factors such as budget, technical capability, and urgency of the need. For those with basic mechanical skills, a multimeter or OBD-II scanner may provide adequate insights at a lower cost. However, for businesses dealing with more complex vehicle fleets or lacking in-house expertise, investing in professional diagnostic services might be the more prudent choice. Understanding these alternatives allows buyers to make informed decisions that align with their operational requirements and financial constraints.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for how to tell if it’s my battery or alternator
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Batteries and Alternators?
When assessing whether an issue lies with a vehicle’s battery or alternator, understanding certain technical properties is essential. Here are several critical specifications to consider:
-
Voltage Output
– Definition: Batteries typically have a nominal voltage of 12 volts, while alternators provide an output voltage between 13 to 14.5 volts.
– Importance: For B2B buyers, knowing the voltage output is crucial for ensuring compatibility with various vehicle systems. A battery that consistently reads below 12.6 volts may indicate a failing unit, while an alternator that fails to maintain voltage can lead to inadequate charging and system failure. -
Ampere Rating
– Definition: The ampere rating measures the maximum current a battery or alternator can provide. Typical automotive alternators range from 130 to 200 amps, with some high-performance models exceeding 400 amps.
– Importance: Understanding ampere ratings helps businesses select the right components for specific applications, particularly when dealing with vehicles that require additional power for accessories like high-end audio systems or heavy-duty electrical components. -
Cold Cranking Amps (CCA)
– Definition: CCA is a rating used to define a battery’s ability to start an engine in cold temperatures, measuring how many amps a battery can deliver at 0°F (-18°C) for 30 seconds while maintaining at least 7.2 volts.
– Importance: This property is vital for B2B buyers in regions with extreme weather conditions, as it directly impacts vehicle reliability and performance. Ensuring the correct CCA rating can prevent operational downtime in colder climates. -
State of Charge (SOC)
– Definition: SOC is a measure of the current charge level of a battery, typically expressed as a percentage of its total capacity.
– Importance: Businesses should monitor SOC to prevent battery degradation and ensure optimal performance. A low SOC can indicate the need for recharging or replacement, making it a critical metric for fleet management and maintenance strategies. -
Cycle Life
– Definition: Cycle life refers to the number of complete charge and discharge cycles a battery can undergo before its capacity significantly diminishes.
– Importance: Understanding cycle life is crucial for B2B buyers looking to invest in batteries for electric vehicles or renewable energy storage. A longer cycle life translates to lower replacement costs and improved sustainability.
What Are the Common Trade Terms Used in Battery and Alternator Procurement?
Familiarity with industry jargon is essential for effective communication and procurement processes. Here are some common terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Definition: An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer.
– Importance: For B2B buyers, sourcing OEM parts ensures compatibility and quality assurance, which is critical for maintaining vehicle performance and reliability. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– Definition: MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell.
– Importance: Understanding MOQ helps businesses manage inventory and budget effectively. It also influences purchasing decisions, especially for smaller companies or those testing new products. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– Definition: An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting a quote for specific goods or services.
– Importance: Utilizing RFQs allows businesses to compare prices and terms from multiple suppliers, fostering competitive pricing and better purchasing decisions. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Definition: Incoterms are a series of pre-defined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce, outlining the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions.
– Importance: Knowledge of Incoterms helps B2B buyers understand shipping responsibilities, costs, and risks, which is crucial for international procurement and logistics planning. -
Warranty Period
– Definition: The warranty period is the duration during which a product is guaranteed against defects or failures.
– Importance: For B2B buyers, understanding warranty terms can significantly influence purchasing decisions, as longer warranties often reflect product quality and can reduce long-term costs associated with replacements or repairs.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terminologies, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance operational efficiency and product reliability in their vehicle fleets.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the how to tell if it’s my battery or alternator Sector
What Are the Key Drivers Shaping the Battery and Alternator Market?
The global battery and alternator market is experiencing significant transformation, driven by advancements in automotive technology, increasing demand for electric vehicles (EVs), and a rising focus on renewable energy solutions. The automotive sector is witnessing a shift toward hybrid and electric vehicles, which rely heavily on high-performance batteries and alternators. This trend is particularly pronounced in regions like Europe and parts of Asia, where regulatory frameworks are supportive of sustainable transportation solutions.
Emerging technologies such as smart batteries, which can communicate with vehicle systems to optimize performance, are becoming more prevalent. Furthermore, the integration of advanced diagnostic tools that enable users to easily differentiate between battery and alternator issues is gaining traction. This is particularly valuable for B2B buyers in markets like Africa and South America, where access to reliable automotive maintenance resources can be limited.
Another notable trend is the growing importance of digital platforms for sourcing automotive parts. International B2B buyers are increasingly leveraging online marketplaces to procure batteries and alternators, allowing for competitive pricing and streamlined supply chains. In addition, the ongoing global supply chain challenges necessitate a focus on local sourcing, which can help mitigate delays and ensure product availability.
How Is Sustainability Influencing Battery and Alternator Sourcing Decisions?
Sustainability is becoming a critical factor in the sourcing of batteries and alternators, as businesses increasingly recognize the environmental impacts associated with these products. The production of batteries, particularly lithium-ion types, can have significant ecological footprints, from resource extraction to manufacturing processes. Consequently, B2B buyers are prioritizing suppliers that adopt ethical sourcing practices and environmentally friendly production methods.
The importance of certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and adherence to guidelines set by organizations like the Responsible Minerals Initiative (RMI) is growing. These certifications assure buyers that their suppliers are committed to minimizing environmental impacts and promoting ethical labor practices throughout the supply chain.
Moreover, the demand for “green” materials is on the rise. Buyers are actively seeking alternatives to conventional batteries, such as those made from recycled materials or utilizing more sustainable components. This shift not only aligns with global sustainability goals but also meets the growing consumer expectations for environmentally responsible products.
What Is the Historical Context of Battery and Alternator Development?
The evolution of batteries and alternators can be traced back to the early days of the automobile. Initially, lead-acid batteries dominated the market due to their reliability and affordability. However, as automotive technologies advanced, there was a push for batteries that could support higher power demands and longer lifespans. This led to the development of more sophisticated battery technologies, including lithium-ion batteries, which are now standard in electric and hybrid vehicles.

Illustrative image related to how to tell if it’s my battery or alternator
Alternators, which replaced generators in vehicles during the 1960s, have also undergone significant advancements. Modern alternators are designed to be more efficient, providing better voltage regulation and improved performance under various driving conditions. This historical progression has not only enhanced vehicle reliability but has also paved the way for the current trends in battery and alternator technology that prioritize sustainability and high performance.
As the automotive industry continues to evolve, understanding these dynamics is crucial for B2B buyers seeking to navigate the complexities of sourcing batteries and alternators in a competitive marketplace.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of how to tell if it’s my battery or alternator
-
How do I determine whether my vehicle issue is related to the battery or alternator?
To identify whether the problem lies with the battery or alternator, start by observing your vehicle’s behavior. If the engine fails to start or only produces a clicking sound, it may indicate a dead battery. Conversely, if the engine starts but dies shortly after, it suggests a failing alternator. You can also use a multimeter to check the battery voltage; a healthy battery should read around 12.6 volts. If the voltage rises to between 13 and 14.5 volts while the engine is running, the alternator is likely functioning correctly. -
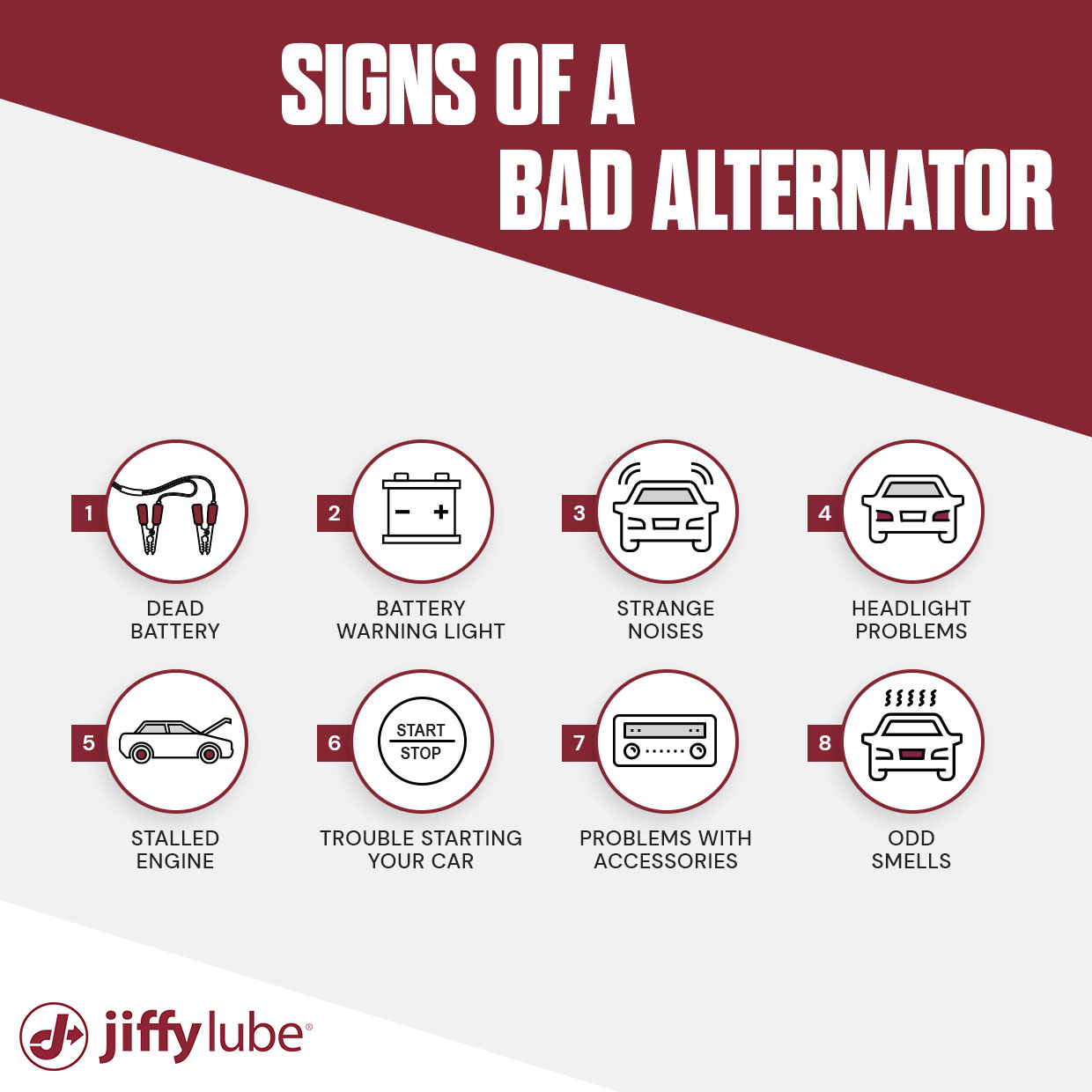
What signs indicate that the battery is failing?
Common symptoms of a failing battery include slow engine cranking, the presence of a battery warning light on the dashboard, and difficulty starting the vehicle in cold weather. Additionally, if your vehicle struggles to power electrical accessories like headlights or infotainment systems, this may also indicate battery issues. Regular testing and maintenance can help identify battery health before it fails, allowing for timely replacements. -
What should I look for to diagnose an alternator problem?
Signs of a failing alternator include dimming headlights, fluctuating dashboard lights, and electrical accessories that operate inconsistently. If your vehicle starts but dies shortly after, it may suggest that the alternator is not adequately charging the battery. Additionally, if you notice any strange noises, such as grinding or whining sounds coming from the engine compartment, it could indicate issues with the alternator’s internal components. -
What is the best battery type for commercial vehicles?
For commercial vehicles, heavy-duty lead-acid batteries are typically the best choice due to their high cranking amps and robust design. Opt for batteries with deep-cycle capabilities if your vehicles frequently use electrical accessories while idling. Depending on your region, consider temperature-resistant batteries designed to perform in extreme conditions, ensuring reliability across various climates, especially in Africa and South America. -
How can I verify the quality of batteries and alternators from suppliers?
When sourcing batteries and alternators, request certifications and quality assurance documentation from suppliers. Look for compliance with international standards such as ISO 9001, which indicates effective quality management systems. Additionally, consider suppliers who provide product warranties and detailed technical specifications, ensuring that you are investing in reliable products that meet your business requirements. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for batteries and alternators?
Minimum order quantities vary by supplier and product type. Typically, MOQs can range from a few dozen to several hundred units, particularly for batteries and alternators. When negotiating with suppliers, clarify your purchasing needs to explore potential flexibility in MOQs, especially if you are a smaller business or testing new products in your market. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing automotive parts internationally?
Payment terms can vary significantly based on the supplier’s location and policies. Common arrangements include upfront payments, letters of credit, or payment upon delivery. For international transactions, it’s advisable to discuss terms that minimize risk, such as partial payments upon order confirmation and the balance upon successful delivery. Ensure to assess the supplier’s reputation and reliability before finalizing payment agreements. -
How can I ensure timely logistics and delivery for automotive parts?
To secure timely logistics and delivery, establish clear communication with your suppliers regarding shipping methods and timelines. Opt for suppliers with robust logistics networks and those who offer tracking options. Additionally, consider working with freight forwarders who specialize in automotive parts to streamline customs clearance and ensure that your orders arrive on schedule, regardless of the shipping route.
A Look at How To Tell If It’S My Battery Or Alternator Manufacturers & Suppliers
Could not verify enough suppliers for how to tell if it’s my battery or alternator to create a list at this time.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for how to tell if it’s my battery or alternator
In navigating the complexities of automotive maintenance, understanding the distinction between battery and alternator issues is crucial for international B2B buyers. A well-functioning battery is essential for vehicle start-up and accessory power, while the alternator ensures ongoing electrical supply and battery recharging. Recognizing symptoms such as dimming lights or slow engine cranking can lead to timely interventions, reducing downtime and repair costs.
Strategic sourcing of high-quality automotive parts is vital for businesses looking to maintain operational efficiency. By partnering with reliable suppliers, companies can ensure they have access to the right components, enhancing vehicle reliability and performance. Implementing preventive measures, such as routine maintenance and proper battery care, can significantly extend the lifespan of these critical components.
As the automotive landscape continues to evolve, staying informed about advancements in battery and alternator technology will be beneficial. We encourage B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe to leverage these insights for smarter procurement decisions. Explore partnerships that align with your operational needs and invest in the future of your fleet to drive sustainable growth.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.

Illustrative image related to how to tell if it’s my battery or alternator
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.















