Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for starter vs alternator vs battery
The interplay between the starter, alternator, and battery is crucial for the optimal functioning of any vehicle, making the task of sourcing reliable components a significant challenge for international B2B buyers. Understanding the differences and applications of these essential automotive parts is vital, especially in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where diverse environmental conditions can impact performance and lifespan. This guide provides a comprehensive analysis of starters, alternators, and batteries, covering their types, applications, maintenance needs, and common failures.
By delving into the intricacies of each component, this resource empowers businesses to make informed purchasing decisions that align with their operational demands. It includes practical insights on supplier vetting processes, ensuring that buyers can identify trustworthy partners who meet quality standards. Additionally, the guide addresses cost considerations, offering strategies to optimize budgets while maintaining high-quality procurement.
With a focus on actionable insights tailored to the unique challenges faced by B2B buyers in different markets, this guide serves as an invaluable tool. It not only clarifies the technical aspects of starters, alternators, and batteries but also equips buyers with the knowledge to navigate the global marketplace effectively, ensuring their vehicles remain reliable and efficient in any operational context.
Table Of Contents
- Top 2 Starter Vs Alternator Vs Battery Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for starter vs alternator vs battery
- Understanding starter vs alternator vs battery Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of starter vs alternator vs battery
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘starter vs alternator vs battery’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for starter vs alternator vs battery
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for starter vs alternator vs battery
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘starter vs alternator vs battery’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for starter vs alternator vs battery Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing starter vs alternator vs battery With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for starter vs alternator vs battery
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the starter vs alternator vs battery Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of starter vs alternator vs battery
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for starter vs alternator vs battery
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Understanding starter vs alternator vs battery Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lead-Acid Battery | Traditional design, available in standard and AGM types | Automotive, industrial equipment | Pros: Cost-effective, widely available. Cons: Heavier, limited lifespan in extreme conditions. |
| Lithium-Ion Battery | Lightweight, high energy density, longer cycle life | Electric vehicles, portable devices | Pros: Longer lifespan, faster charging. Cons: Higher initial cost, sensitive to temperature. |
| Starter Motor | Converts electrical energy to mechanical energy to start the engine | Automotive, marine applications | Pros: Essential for vehicle operation. Cons: Can be prone to wear, requiring timely replacement. |
| Alternator | Generates electricity while the engine runs, charges battery | Automotive, heavy machinery | Pros: Reliable power generation, longer lifespan. Cons: Can fail if not maintained, affecting battery life. |
| High-Performance Starter | Enhanced design for rapid engine cranking, often gear-reduction type | Racing, performance vehicles | Pros: Improved starting efficiency, suitable for high-demand engines. Cons: More expensive, may require modifications. |
What are the Characteristics and Suitability of Lead-Acid Batteries in B2B Applications?
Lead-acid batteries are the most common type used in automotive and industrial applications. They come in two main variations: standard flooded batteries and absorbed glass mat (AGM) batteries. Lead-acid batteries are cost-effective and readily available, making them a popular choice for businesses looking to minimize initial investment. However, they have a limited lifespan, especially in extreme temperatures, which can be a significant consideration for buyers in hotter or colder climates.
How Do Lithium-Ion Batteries Stand Out for B2B Buyers?
Lithium-ion batteries are increasingly favored for applications requiring lightweight and high energy density solutions, such as electric vehicles and portable devices. They offer a longer cycle life and quicker charging times compared to lead-acid batteries. Although the initial investment is higher, the long-term savings due to reduced maintenance and replacement costs make them an attractive option for businesses looking for efficiency and sustainability in their energy solutions.
What Should B2B Buyers Know About Starter Motors?
Starter motors are crucial components that convert electrical energy from the battery into mechanical energy to start an engine. They are essential for automotive and marine applications, ensuring reliable vehicle operation. While starter motors are generally durable, they are subject to wear and may require timely replacement to avoid unexpected downtime. B2B buyers should consider the quality and compatibility of starter motors with their specific vehicle models to ensure optimal performance.
Why is the Alternator Important for B2B Applications?
The alternator plays a vital role in generating electricity while the engine runs, powering the vehicle’s electrical systems and charging the battery. With a lifespan of 8-12 years, alternators are a reliable choice for automotive and heavy machinery applications. However, neglecting maintenance can lead to failure, which can adversely affect battery life and overall vehicle performance. B2B buyers should prioritize sourcing high-quality alternators to ensure longevity and reliability.
What are the Advantages of High-Performance Starters for Specialized Needs?
High-performance starters are designed for rapid engine cranking, making them ideal for racing and performance vehicles. These starters often feature gear-reduction technology, enhancing efficiency and power delivery. While they may come at a premium price, the benefits in terms of improved starting performance can justify the investment for businesses operating high-demand engines. Buyers should assess their specific performance needs and vehicle modifications when considering high-performance starters.
Key Industrial Applications of starter vs alternator vs battery
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of starter vs alternator vs battery | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive Manufacturing | Integration of starters, alternators, and batteries in vehicles | Enhanced vehicle performance and reliability | Quality certifications, compatibility with vehicle models, and warranty terms |
| Renewable Energy | Use of batteries for energy storage in solar and wind systems | Increased energy efficiency and reduced operational costs | Durability in harsh climates, capacity specifications, and lifecycle management |
| Heavy Equipment | Starters and batteries in construction machinery | Improved operational uptime and reduced maintenance costs | Robustness against extreme conditions, ease of installation, and service support availability |
| Transportation & Logistics | Battery systems in electric and hybrid vehicles | Lower fuel costs and reduced emissions | Compliance with international standards, battery life cycle, and recycling options |
| Marine & Aviation | Starters and batteries for aircraft and marine engines | Enhanced safety and reliability in critical operations | Weight considerations, environmental resistance, and certification for aviation/marine use |
How Are Starters, Alternators, and Batteries Used in Automotive Manufacturing?
In the automotive manufacturing sector, starters, alternators, and batteries are integral components of vehicle assembly. These parts work cohesively to ensure reliable engine ignition and electrical system functionality. Manufacturers benefit from sourcing high-quality components to enhance vehicle performance and reliability. For international buyers, particularly in Africa and South America, sourcing must consider compatibility with various vehicle models and adherence to quality certifications to ensure optimal performance in diverse environmental conditions.
What Role Do Batteries Play in Renewable Energy Applications?
Batteries are essential in renewable energy applications, particularly in solar and wind energy systems, where they store generated energy for later use. This capability allows businesses to maximize energy efficiency and reduce operational costs by utilizing stored energy during peak demand periods. Buyers in regions with fluctuating energy supplies, such as parts of the Middle East and Africa, should prioritize sourcing batteries that offer durability in harsh climates and have specifications that align with their energy storage needs.
How Do Heavy Equipment Industries Utilize Starters and Batteries?
In the heavy equipment sector, starters and batteries are vital for the operation of construction machinery. Reliable starters ensure that equipment can be quickly mobilized, while robust batteries provide the necessary power for extended use in challenging conditions. Businesses benefit from improved operational uptime and reduced maintenance costs. For international buyers, especially in regions with extreme weather, sourcing should focus on the robustness of components and the availability of service support to minimize downtime.
What Benefits Do Transportation and Logistics Companies Gain from Battery Systems?
Transportation and logistics companies increasingly rely on battery systems in electric and hybrid vehicles to lower fuel costs and reduce emissions. The integration of advanced battery technology not only enhances operational efficiency but also aligns with global sustainability goals. Buyers in Europe and the Middle East should consider compliance with international standards and lifecycle management when sourcing batteries to ensure long-term viability and performance.
How Are Starters and Batteries Critical in Marine and Aviation Industries?
In the marine and aviation sectors, starters and batteries are critical for the safe operation of engines. These components must perform reliably under varying conditions, making quality and certification essential for safety. Businesses in these industries benefit from enhanced safety and reliability during critical operations. When sourcing, international buyers should focus on weight considerations, environmental resistance, and certification for aviation or marine use to ensure compliance with stringent industry regulations.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘starter vs alternator vs battery’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Identifying the Real Culprit Behind Vehicle Start Failures
The Problem: B2B buyers in the automotive sector often face the frustrating challenge of diagnosing vehicle start failures. When a fleet vehicle fails to start, it can halt operations, leading to lost productivity and increased downtime. The interconnected nature of the starter, alternator, and battery complicates the troubleshooting process. Buyers frequently struggle to pinpoint whether the issue lies with the battery, the alternator, or the starter, resulting in unnecessary replacement costs and service delays.
The Solution: To effectively diagnose the issue, B2B buyers should implement a systematic troubleshooting approach. Start by checking the battery health, as it’s the most common failure point. Conduct a voltage test using a multimeter; a reading below 12.4 volts indicates a weak battery. If the battery is functional, move on to the alternator. Look for signs of wear, such as dimming headlights or unusual noises. A faulty alternator can be diagnosed by testing the voltage output while the engine is running; it should typically read between 13.8 to 14.4 volts. Lastly, if both the battery and alternator are functioning well, focus on the starter. A simple jump-start test can help determine if the starter is the issue. By adopting this structured approach, B2B buyers can accurately diagnose the problem and minimize unnecessary part replacements, ultimately saving time and costs.
Scenario 2: Managing the Impact of Environmental Conditions on Component Lifespan
The Problem: B2B buyers operating in regions with extreme weather conditions—such as high temperatures in parts of Africa or cold winters in Europe—often encounter premature failures of batteries, starters, and alternators. These environmental factors can lead to reduced efficiency and lifespan of these components, causing unexpected breakdowns and financial strain.
The Solution: To mitigate the impact of environmental conditions, it is essential for buyers to source high-quality, climate-appropriate components. When selecting batteries, look for those designed to withstand extreme temperatures, such as AGM (Absorbent Glass Mat) batteries, which are more resilient to heat and cold. Additionally, regular maintenance checks should be scheduled to inspect connections, clean terminals, and ensure proper installation. Implementing a preventive maintenance program can help identify wear and tear before failures occur. Educating drivers on recognizing early warning signs—such as slow cranking or flickering lights—can also empower them to report issues promptly. By proactively addressing these environmental challenges, B2B buyers can enhance the reliability of their fleet and reduce the likelihood of costly roadside repairs.
Scenario 3: Streamlining Parts Procurement for Optimal Fleet Maintenance
The Problem: For B2B buyers managing large fleets, sourcing reliable parts for starters, alternators, and batteries can be a logistical nightmare. Inconsistent supplier quality, long lead times, and lack of part compatibility can lead to inefficient operations, increased costs, and vehicle downtime.
The Solution: To streamline the procurement process, buyers should establish partnerships with reputable suppliers who specialize in automotive components. Conduct thorough research to identify suppliers that offer a comprehensive warranty and support for their products. Implementing an inventory management system can help track the usage and lifespan of components, ensuring timely replacements and minimizing emergency orders. Additionally, utilizing a centralized purchasing approach can improve negotiation power with suppliers, leading to better pricing and terms. Consider forming a consortium with other businesses to bulk order and reduce costs further. By optimizing the procurement process and establishing reliable supply chains, B2B buyers can maintain their fleets more effectively, ensuring that all vehicles are equipped with the best possible components for performance and reliability.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for starter vs alternator vs battery
What Materials Are Commonly Used in Starters, Alternators, and Batteries?
When selecting materials for starters, alternators, and batteries, it is crucial to consider their unique properties and how they affect performance. Here, we analyze common materials used in these components, focusing on their key properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for international B2B buyers.
How Does Copper Influence Performance in Starters and Alternators?
Key Properties: Copper is highly conductive, which makes it an ideal choice for electrical components. It has excellent thermal and electrical conductivity, with a melting point of approximately 1,984°F (1,085°C).

Illustrative image related to starter vs alternator vs battery
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of copper is its superior conductivity, which enhances the efficiency of starters and alternators. However, copper is prone to corrosion, especially in humid or saline environments, which can lead to reduced performance over time. Additionally, copper can be more expensive than alternatives like aluminum.
Impact on Application: In applications where high electrical efficiency is paramount, copper is preferred. However, in regions with high humidity, such as parts of Africa and South America, corrosion-resistant coatings or treatments may be necessary.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards such as ASTM B170 for copper quality is essential. Buyers should also consider the local availability of copper and its cost fluctuations in their regions.
What Role Does Aluminum Play in Starters and Alternators?
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight and has good thermal conductivity, with a melting point of around 1,221°F (660°C). It is also resistant to corrosion due to its natural oxide layer.
Pros & Cons: The lightweight nature of aluminum reduces the overall weight of the starter and alternator, which can enhance vehicle efficiency. However, aluminum’s electrical conductivity is lower than that of copper, which may affect performance in high-demand applications.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is often used in applications where weight savings are critical, such as in automotive and aerospace industries. However, its lower conductivity may necessitate larger wire gauges or additional connections.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that the aluminum used meets standards such as ASTM B221. In regions with high temperatures, such as the Middle East, the thermal properties of aluminum should be evaluated to ensure reliability.
How Does Lead Affect Battery Performance?
Key Properties: Lead is dense and has a high melting point of about 621°F (327°C). It is also highly resistant to corrosion when used in a controlled environment.
Pros & Cons: Lead-acid batteries are cost-effective and have a proven track record for reliability. However, lead is heavy, which can be a disadvantage in applications where weight is a concern. Additionally, environmental regulations regarding lead disposal can complicate its use.
Impact on Application: Lead is commonly used in automotive batteries due to its ability to provide high starting power. However, in regions with stringent environmental regulations, alternatives like lithium-ion batteries may be preferred.

Illustrative image related to starter vs alternator vs battery
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with environmental regulations such as the EU’s RoHS directive is critical. Buyers in regions like Europe and South America should be aware of local legislation regarding lead usage and disposal.
What About Plastic Materials in Battery Casings?
Key Properties: Plastics like polypropylene are lightweight, resistant to corrosion, and have good insulating properties. They can withstand a range of temperatures, typically from -40°F to 176°F (-40°C to 80°C).
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of plastic casings is their resistance to corrosion and lightweight nature, which can improve battery performance. However, plastics may not offer the same level of durability as metals in extreme conditions.
Impact on Application: Plastic is ideal for battery casings, providing insulation and protection against environmental factors. However, in high-temperature regions, the longevity of plastic materials should be assessed.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that plastic materials comply with standards such as ASTM D4101 for polypropylene. In regions with extreme temperatures, evaluating the thermal stability of plastics is essential.
Summary Table of Material Selection
| Material | Typical Use Case for starter vs alternator vs battery | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Copper | Starters and alternators | Superior electrical conductivity | Prone to corrosion | High |
| Aluminum | Starters and alternators | Lightweight | Lower conductivity than copper | Medium |
| Lead | Lead-acid batteries | Cost-effective and reliable | Heavy and environmental concerns | Low |
| Plastic | Battery casings | Corrosion-resistant and lightweight | May lack durability in extreme conditions | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide provides insights into the materials used in starters, alternators, and batteries, helping B2B buyers make informed decisions based on performance requirements and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for starter vs alternator vs battery
What Are the Key Manufacturing Processes for Starters, Alternators, and Batteries?
Understanding the manufacturing processes of starters, alternators, and batteries is essential for B2B buyers, especially when sourcing components for vehicles. Each component undergoes a series of stages that ensure quality and performance.
How Are Materials Prepared for Manufacturing Starters, Alternators, and Batteries?
The first stage in manufacturing these components involves material preparation. For starters and alternators, high-grade metals like steel and aluminum are commonly used for their durability and conductivity. For batteries, lead and sulfuric acid are the primary materials.
Manufacturers usually follow strict guidelines in selecting materials, ensuring that they meet specific industry standards. For instance, lead must be sourced responsibly to comply with environmental regulations. This stage also involves cleaning and treating materials to enhance adhesion and conductivity, which is crucial for the performance of electrical components.
What Forming Techniques Are Used in the Production of Starters, Alternators, and Batteries?
Once the materials are prepared, the next phase is forming.
-
Starters: Components such as the motor housing, armature, and pinion gear are typically manufactured through processes like die casting and machining. Die casting allows for the creation of complex shapes while ensuring dimensional accuracy.
-
Alternators: The rotor and stator are produced using winding techniques where copper wire is wound into coils. The forming of the aluminum casing often involves die casting as well, ensuring a lightweight yet robust structure.
-
Batteries: The lead plates used in batteries are formed through a process called pasting, where a paste made from lead oxide and sulfuric acid is applied to grids. These grids are then dried and cured to ensure optimal performance.
How Are Starters, Alternators, and Batteries Assembled?
The assembly process varies for each component but generally follows a systematic approach:
-
Starters: After forming, the components are assembled in a clean environment to avoid contamination. This includes fitting the armature into the housing and attaching the pinion gear.
-
Alternators: Similar to starters, alternators require precise assembly. The rotor is inserted into the stator, and the housing is secured to ensure that all electrical connections are intact.
-
Batteries: Assembly involves stacking the lead plates and connecting them with separators. The cells are then filled with electrolyte and sealed, ensuring that the casing is airtight to prevent leaks.
What Finishing Processes Are Essential for Quality Control?
Finishing processes are critical for enhancing the durability and performance of these components. Common finishing techniques include:
Illustrative image related to starter vs alternator vs battery
-
Coating: Starters and alternators may undergo coating processes to prevent corrosion. This is especially important for components exposed to harsh environments.
-
Testing: Batteries are subjected to rigorous testing for voltage and capacity. Manufacturers often use computerized systems to ensure that each battery meets performance specifications.
-
Labeling and Packaging: Proper labeling is crucial for identifying specifications and compliance with international standards. Packaging is designed to protect the components during shipping and storage.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Implemented in Manufacturing?
Quality assurance is vital in ensuring that starters, alternators, and batteries meet international standards. Here are key components of the QC process:
Which International Standards Are Relevant for Quality Assurance?
Manufacturers often adhere to international quality standards such as ISO 9001, which outlines requirements for a quality management system. Compliance with these standards is crucial for ensuring consistent product quality.
Additionally, industry-specific certifications like CE (Conformité Européenne) and API (American Petroleum Institute) ensure that products meet safety and performance criteria. These certifications are particularly relevant for B2B buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
What Are the Key QC Checkpoints During the Manufacturing Process?
Quality Control (QC) checkpoints are established at various stages of the manufacturing process, including:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial stage involves inspecting raw materials to ensure they meet specifications before production begins.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during the manufacturing process helps identify and rectify issues in real-time. This includes testing components at different assembly stages.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): A comprehensive inspection occurs before products are packaged. This includes functional testing, visual inspections, and performance evaluations.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers can take several steps to ensure that their suppliers maintain high-quality standards:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting regular audits allows buyers to assess the manufacturing processes and quality control measures in place. This includes evaluating compliance with international standards and certifications.
-
Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports can provide insights into the manufacturing process, including testing results and any issues encountered during production.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can offer an unbiased evaluation of the supplier’s quality assurance practices. These services can perform random checks and validate compliance with required standards.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers must be aware of specific nuances when dealing with suppliers from different regions.
-
Cultural Differences: Understanding local business practices and communication styles is essential for effective collaboration.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Buyers must ensure that suppliers comply with both local and international regulations, particularly concerning environmental standards and material sourcing.
-
Logistics and Supply Chain: Quality control extends beyond manufacturing; buyers should consider logistics and supply chain factors that can affect product integrity during transportation.
By understanding these manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing starters, alternators, and batteries, ultimately ensuring the reliability and performance of their vehicles.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘starter vs alternator vs battery’
When it comes to sourcing components like starters, alternators, and batteries for your automotive needs, having a structured approach can significantly streamline the procurement process. This guide aims to provide a clear checklist to help B2B buyers navigate the complexities of sourcing these essential automotive parts effectively.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Understanding the specific requirements for your vehicles is crucial before initiating the sourcing process. Identify the make, model, and year of the vehicles for which you need parts. Additionally, consider the operational environment; for example, components may need to withstand extreme temperatures or humidity in regions like Africa or the Middle East.
- Key Considerations:
- Voltage and amp ratings
- Physical dimensions and weight
- Compatibility with existing systems
Step 2: Research Reliable Suppliers
A thorough supplier search can save you time and money in the long run. Look for suppliers with a proven track record in the automotive parts industry. Utilize platforms like trade shows, industry directories, and online marketplaces to identify potential partners.
- What to Look For:
- Years of experience in the market
- Positive reviews and testimonials from other B2B buyers
- Geographic proximity to reduce shipping times and costs
Step 3: Verify Supplier Certifications
Ensuring that your suppliers meet industry standards is vital for maintaining quality and reliability. Check for certifications such as ISO 9001 or specific automotive industry certifications that indicate adherence to quality management practices.
- Why This Matters:
- Certified suppliers are more likely to provide high-quality products.
- Certifications can often streamline customs and import processes.
Step 4: Request Product Samples
Before finalizing any orders, request samples of the starters, alternators, or batteries. This allows you to assess the quality and performance of the components firsthand.
- Key Actions:
- Test samples under real operational conditions.
- Evaluate the fit and compatibility with your vehicles.
Step 5: Compare Pricing and Terms
Collect quotes from multiple suppliers to compare pricing structures. Pay attention not only to the base price but also to shipping costs, payment terms, and warranty conditions.
- Consider the Following:
- Bulk purchase discounts
- Return policies for defective parts
- Lead times for delivery
Step 6: Assess After-Sales Support
Reliable after-sales support can greatly enhance your purchasing experience. Investigate the level of customer service and technical support offered by the supplier.
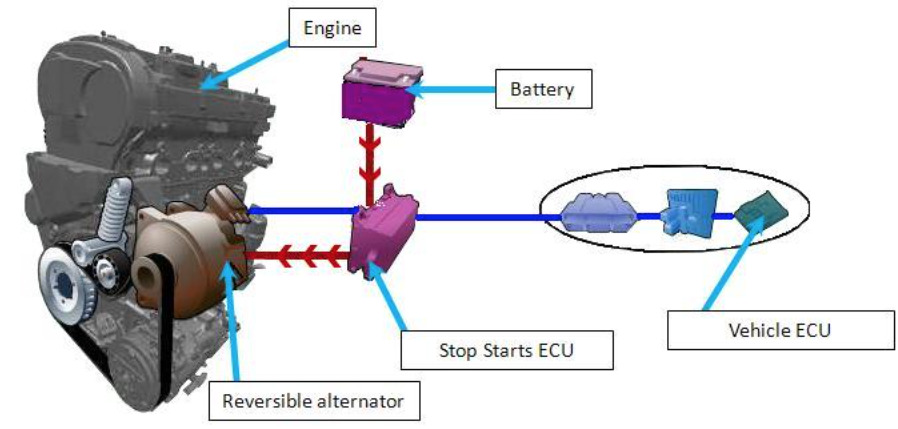
Illustrative image related to starter vs alternator vs battery
- Important Aspects:
- Availability of technical assistance for installation and troubleshooting
- Warranty and service agreements
Step 7: Finalize Your Purchase Agreement
Once you have evaluated all factors, draft a comprehensive purchase agreement. Ensure it includes all terms discussed, such as delivery schedules, payment methods, and warranties.
- Essential Elements:
- Clear specifications of the products being purchased
- Dispute resolution processes
- Confidentiality clauses, if necessary
By following this structured approach, you will be well-equipped to make informed decisions when sourcing starters, alternators, and batteries, ensuring that your procurement process is efficient and effective.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for starter vs alternator vs battery Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Starters, Alternators, and Batteries?
When sourcing starters, alternators, and batteries, understanding the cost structure is essential for effective budgeting and procurement. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and margins.
-
Materials: The raw materials used in the production of these components can vary significantly. Starters typically require steel, copper, and plastics, while alternators may involve more complex materials like magnets and specialized electrical components. Batteries primarily consist of lead, acid, and sometimes lithium for advanced models. Fluctuations in global commodity prices can directly impact the overall cost.
-
Labor: Labor costs can differ based on the manufacturing location. Regions with lower labor costs, such as parts of Africa and South America, may offer competitive pricing, but they could also face challenges related to skill levels and training. In contrast, European manufacturers may provide higher quality assurance but at elevated labor costs.
-
Manufacturing Overhead and Tooling: Overhead includes expenses related to factory operations, utilities, and maintenance. Tooling costs, which cover the equipment needed for production, can also be significant, especially for custom designs. Buyers should inquire about tooling costs when requesting quotes, particularly for specialized or high-volume orders.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring product reliability is crucial in automotive components. QC processes add to the overall cost but are essential for maintaining standards. Certifications, such as ISO or TS16949, may also influence pricing, as certified manufacturers often command higher prices due to their proven reliability.
-
Logistics: Transportation and shipping costs can vary widely based on geographical location and Incoterms. Buyers need to account for these costs when evaluating total expenses. International shipping can introduce delays and additional fees, which should be factored into the overall sourcing strategy.
-
Margin: Suppliers will include their desired profit margins in the pricing. Understanding the typical margins in your target market can help buyers negotiate better deals.
What Influences Pricing for Starters, Alternators, and Batteries?
Several factors can influence the pricing of automotive components, including volume, specifications, materials, quality certifications, supplier dynamics, and Incoterms.

Illustrative image related to starter vs alternator vs battery
-
Volume/MOQ: Minimum order quantities (MOQs) can significantly affect pricing. Higher volumes often lead to discounts, while smaller orders may incur higher per-unit costs. Establishing long-term partnerships can help secure better pricing structures.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom specifications may lead to increased costs. Buyers should be clear about their requirements to avoid unnecessary expenses. Standard products typically offer better pricing due to economies of scale.
-
Material Choices: The choice of materials can greatly affect the price. For instance, lithium batteries might be more expensive than traditional lead-acid batteries but offer longer life and better performance, leading to lower total ownership costs.
-
Quality and Certifications: Products with higher quality standards and certifications tend to be priced higher. However, investing in quality can reduce maintenance costs and enhance reliability, making it a wise long-term decision.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can also influence pricing. Established suppliers may offer better warranties and support but at a premium.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the Incoterms associated with your purchase can help mitigate unforeseen costs. Terms like FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) dictate who bears responsibility for shipping and insurance, impacting the overall cost structure.
What Are the Best Practices for Negotiating Prices in International B2B Sourcing?
Negotiating prices in international B2B sourcing requires a strategic approach to achieve cost-efficiency and value. Here are some tips:
-
Research and Benchmarking: Before entering negotiations, conduct thorough market research to understand price ranges and competitor offerings. This knowledge empowers you during discussions.
-
Focus on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Emphasize the long-term benefits of quality products over initial cost savings. Presenting TCO can be a compelling argument for investing in higher-quality components.
-
Build Relationships: Establishing strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing and terms over time. Trust and reliability often yield better negotiation outcomes.
-
Be Flexible with Terms: If a supplier cannot meet your price, consider negotiating other terms, such as payment schedules or delivery timelines, to create a more favorable overall agreement.
-
Consider Local Market Conditions: Be aware of regional economic conditions and pricing trends in your target markets. Understanding local dynamics can enhance your negotiation strategy.
In conclusion, sourcing starters, alternators, and batteries requires a comprehensive understanding of cost components and pricing influencers. By applying these insights and negotiation strategies, international B2B buyers can make informed purchasing decisions that balance quality, cost, and long-term value.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing starter vs alternator vs battery With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternative Solutions to Starter, Alternator, and Battery Systems
In the automotive industry, the traditional reliance on the starter, alternator, and battery trio is being challenged by emerging technologies. As B2B buyers consider their options, understanding these alternatives can significantly impact operational efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and overall performance.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Starter Vs Alternator Vs Battery | Fuel Cell Systems | Supercapacitors |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Essential for starting and powering vehicles | High efficiency and low emissions | Rapid charge and discharge capabilities |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment, with batteries needing regular replacement | High initial cost, but low operational costs | Moderate cost with longer lifespan |
| Ease of Implementation | Commonly understood and easy to integrate | Requires specialized knowledge and infrastructure | Simple integration in hybrid systems |
| Maintenance | Moderate; batteries require regular checks | Low, but fuel supply management is necessary | Minimal maintenance required |
| Best Use Case | Conventional vehicles and machinery | Clean energy vehicles and stationary power | Energy recovery systems and hybrid vehicles |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Fuel Cell Systems
Fuel cell technology converts chemical energy from hydrogen into electricity, providing an alternative to traditional internal combustion engines. The advantages include high efficiency and lower emissions, making them an attractive option for environmentally conscious operations. However, the high initial investment and the need for specialized infrastructure can deter some buyers. Additionally, the availability of hydrogen fueling stations remains a challenge in many regions, impacting the feasibility of widespread adoption.
Supercapacitors
Supercapacitors store energy electrostatically, allowing for rapid charging and discharging. This technology excels in applications requiring quick bursts of power, such as in hybrid vehicles or energy recovery systems. Their lifespan tends to be longer than that of conventional batteries, and they require minimal maintenance. However, their energy density is lower compared to batteries, which limits their use as standalone energy sources. They are best suited for systems that can benefit from rapid energy delivery rather than long-term energy storage.
Making the Right Choice: How to Select the Best Solution
When determining the most suitable solution for your needs, consider factors such as performance requirements, budget constraints, and operational conditions. For businesses in regions like Africa and South America, where infrastructure may be limited, the traditional starter, alternator, and battery setup might still be the most practical choice. Conversely, for companies focused on sustainability and long-term operational savings, investing in fuel cells or supercapacitors could yield significant benefits. Ultimately, aligning your choice with your operational goals and the specific demands of your industry will guide you to the best solution.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for starter vs alternator vs battery
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Starters, Alternators, and Batteries?
When dealing with automotive components such as starters, alternators, and batteries, understanding their technical specifications is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. Here are some essential properties that B2B buyers should consider:
-
Material Grade
The materials used in the construction of these components significantly affect their performance and lifespan. For instance, batteries often utilize lead-acid technology, while starters and alternators typically feature copper windings and steel housings. The quality of materials can influence corrosion resistance, thermal stability, and overall durability, directly impacting operational reliability in harsh environments. -
Voltage Rating
Most automotive batteries and alternators operate at a standard voltage of 12V, but understanding the voltage rating is critical for compatibility with specific vehicle models. Starters may require higher cranking voltages to initiate engine start-up, especially in larger vehicles or those with heavy-duty engines. Ensuring that the voltage ratings match is essential to avoid equipment failure. -
Cranking Amps (CA) and Cold Cranking Amps (CCA)
These specifications indicate the battery’s ability to start an engine under various conditions. Cranking Amps measure the battery’s performance at room temperature, while Cold Cranking Amps assess its ability to start an engine in cold conditions. For regions with extreme temperatures, such as parts of Africa and the Middle East, selecting batteries with higher CCA ratings can prevent operational issues. -
Durability and Life Cycle
Battery lifespan typically ranges from 3 to 5 years, while alternators can last 8 to 12 years. Understanding the expected life cycle of each component helps buyers assess total cost of ownership and plan for replacements. Factors such as temperature extremes, vibration, and exposure to moisture can shorten these life spans, making it essential to choose components designed for specific environmental conditions. -
Tolerance Levels
Tolerance refers to the allowable deviation in manufacturing dimensions, which is vital for ensuring proper fit and function. For starters and alternators, precise tolerances are necessary to prevent misalignment that can lead to mechanical failure. When sourcing these components, buyers should verify that manufacturers adhere to industry standards for tolerance to ensure compatibility with vehicle specifications.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Starters, Alternators, and Batteries?
Navigating the automotive parts industry requires familiarity with specific jargon. Here are some key terms that B2B buyers should understand:
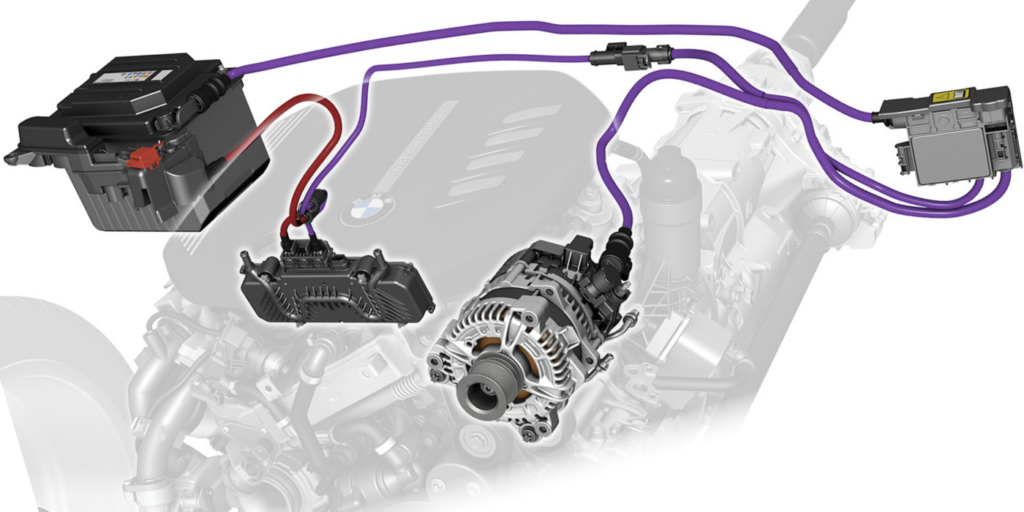
Illustrative image related to starter vs alternator vs battery
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
Refers to parts made by the same manufacturer that produced the original components for the vehicle. OEM parts are often preferred for their guaranteed compatibility and quality, making them a reliable choice for businesses looking to maintain vehicle performance. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
This term indicates the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is critical for budget-conscious buyers who need to manage inventory costs effectively, especially when sourcing components for multiple vehicles. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing information for specific components. It is essential for B2B buyers to prepare RFQs accurately to ensure they receive competitive pricing and terms that meet their operational needs. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
These are predefined international shipping terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in a transaction. Familiarity with Incoterms helps B2B buyers understand shipping costs, risks, and delivery responsibilities, which is particularly important for international procurement. -
Warranty Period
This term refers to the duration during which a manufacturer guarantees the performance of a product. Understanding warranty terms can help buyers assess the reliability of components and their long-term value, ensuring that they choose products that offer sufficient protection against defects.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions when sourcing starters, alternators, and batteries, ultimately enhancing their purchasing strategy and operational efficiency.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the starter vs alternator vs battery Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Starter, Alternator, and Battery Sector?
The global automotive sector is experiencing a significant transformation, driven by technological advancements, changing consumer preferences, and regulatory pressures. For international B2B buyers, particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these dynamics is crucial. The demand for reliable starter, alternator, and battery systems is being propelled by the increasing prevalence of electric vehicles (EVs) and hybrid technologies. As countries implement stricter emissions regulations, the push for more efficient and eco-friendly automotive components is intensifying.
Emerging technologies such as advanced battery management systems (BMS) and integrated starter-generator systems are reshaping the sourcing landscape. B2B buyers should focus on suppliers who adopt these innovations, as they can offer enhanced performance, longevity, and energy efficiency. Additionally, the rise of connected vehicles and smart technologies is leading to the development of diagnostic tools that can proactively address issues related to starters, alternators, and batteries before they lead to failures, reducing maintenance costs and enhancing vehicle reliability.
Sourcing trends are also evolving, with a shift towards local suppliers to mitigate supply chain disruptions, particularly evident during the COVID-19 pandemic. Buyers are increasingly prioritizing partnerships with manufacturers who can provide just-in-time inventory and flexible sourcing options, ensuring a steady supply of critical components. Furthermore, the growing trend of e-commerce in the automotive parts market enables buyers to access a broader range of products and suppliers, enhancing competition and driving down costs.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact the Starter, Alternator, and Battery Market?
Sustainability is becoming a fundamental consideration for B2B buyers in the automotive sector. The environmental impact of traditional battery production, particularly lead-acid batteries, raises concerns about resource depletion and pollution. Buyers are encouraged to seek manufacturers that use sustainable materials and processes, such as lithium-ion batteries made from responsibly sourced lithium and cobalt. This not only aligns with global sustainability goals but also meets the increasing consumer demand for greener products.
Ethical sourcing is another critical aspect, particularly in regions where mining and manufacturing practices may involve human rights violations. B2B buyers should prioritize suppliers who are transparent about their supply chains and adhere to ethical standards, ensuring that materials are sourced responsibly. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and adherence to the Responsible Minerals Initiative can serve as indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability.
Moreover, the adoption of circular economy principles is gaining traction. B2B buyers can benefit from engaging with suppliers who offer recycling programs for batteries and components, reducing waste and contributing to a more sustainable supply chain. By prioritizing sustainability and ethical sourcing, buyers not only enhance their brand reputation but also align with regulatory trends and consumer expectations, driving long-term business success.

Illustrative image related to starter vs alternator vs battery
What Is the Historical Evolution of Starters, Alternators, and Batteries?
The evolution of starters, alternators, and batteries dates back to the early days of the automotive industry. Initially, vehicles were equipped with hand-crank starters, which required significant manual effort. The introduction of the electric starter in the early 20th century revolutionized vehicle ignition, allowing for easier and more reliable engine starts.
As automotive technology advanced, the alternator replaced the older generator systems in the 1960s, providing a more efficient means of charging the battery and powering electrical systems. The development of lead-acid batteries became the standard for automotive applications, although the rise of electric vehicles has led to increased interest in lithium-ion batteries, which offer higher energy density and longer life.
In recent years, the focus on performance, efficiency, and sustainability has driven innovation in battery technology, including advancements in solid-state batteries and battery management systems. This evolution reflects the industry’s response to changing market demands and regulatory pressures, ultimately shaping the sourcing strategies of B2B buyers in the automotive sector. Understanding this historical context can provide valuable insights into current trends and future directions in the starter, alternator, and battery market.
Illustrative image related to starter vs alternator vs battery
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of starter vs alternator vs battery
-
How do I determine whether I need a new starter, alternator, or battery?
To identify which component is failing, start by observing the symptoms. If the engine doesn’t crank but the lights work, the starter may be at fault. If the engine cranks but dies quickly, the battery might be the issue. A failing alternator often leads to dimming lights or electrical system malfunctions while driving. Conducting a jump-start test can also help: if the vehicle starts with a jump but dies when disconnected, the alternator is likely not charging the battery. Consult with a professional technician for a definitive diagnosis. -
What is the best battery type for heavy-duty applications?
For heavy-duty applications, lead-acid batteries, particularly AGM (Absorbent Glass Mat) batteries, are often recommended due to their durability and ability to handle deep cycling. These batteries offer high cranking power and are resistant to vibrations, making them suitable for commercial vehicles or machinery in rugged environments. Lithium-ion batteries are also gaining popularity due to their lightweight and longer lifespan, but they may come at a higher cost. Evaluate your specific power needs and environmental conditions before making a selection. -
How can I vet suppliers for starters, alternators, and batteries?
When vetting suppliers, consider their reputation, experience, and certifications. Request references or case studies from previous clients, particularly those in similar markets. It’s crucial to assess their quality assurance processes and compliance with international standards. Additionally, examine their ability to provide customization options and after-sales support. Engaging in direct communication and possibly visiting their facilities can further ensure their capability to meet your requirements. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQ) for starters, alternators, and batteries?
MOQs can vary significantly based on the supplier and product type. Generally, for starters and alternators, MOQs might range from 50 to 100 units, while batteries could have a higher MOQ due to shipping constraints and packaging requirements. Always clarify MOQs during negotiations, as some suppliers may be flexible, especially for first-time buyers or bulk orders. Understanding the supplier’s inventory capacity can also provide insight into their ability to meet your demands. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing from international suppliers?
Payment terms can vary widely depending on the supplier’s policies and the buyer’s negotiation power. Common terms include upfront payment, a 30% deposit with the balance upon delivery, or net 30/60 days after receipt of goods. Letters of credit (LC) are often used in international transactions to minimize risk. It’s advisable to discuss and agree on payment terms early in the negotiation process and ensure they are clearly outlined in the purchase agreement. -
How do I ensure quality assurance for automotive components purchased internationally?
To ensure quality assurance, request detailed product specifications and certifications from your suppliers. Conduct third-party inspections before shipment, focusing on critical components like starters and alternators, which are vital for vehicle performance. Establishing a clear return policy and warranty terms can protect your investment. Additionally, consider developing a quality checklist to verify compliance with your standards upon receipt of the goods. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing automotive components?
Logistics is crucial when importing automotive components. Consider shipping methods, as air freight is faster but more expensive than sea freight. Verify that your supplier can handle customs documentation and compliance with international regulations. Evaluate the total landed cost, including tariffs and taxes, to understand the financial implications of your purchase. Additionally, ensure that your logistics partner has experience in handling sensitive automotive parts to prevent damage during transit. -
Are there specific certifications I should look for when sourcing automotive batteries and starters?
Yes, certain certifications can indicate quality and safety standards. Look for products that comply with ISO 9001 for quality management systems and ISO 14001 for environmental management. Additionally, automotive components should meet industry standards such as SAE (Society of Automotive Engineers) or IATF 16949, which is specific to the automotive sector. Certifications like CE (European Conformity) and UL (Underwriters Laboratories) may also be relevant, especially for components being sold in Europe and North America.
Top 2 Starter Vs Alternator Vs Battery Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Honda – Starter Troubleshooting
Domain: mechanics.stackexchange.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: 2006 Honda Civic EX 1.8L 4 Cylinder; symptoms include weak cranking, failure to start, single click sound when attempting to start; potential issues with starter or alternator; battery tested good; updates indicate starter was the problem; voltage drop test suggested for diagnosis.
2. Champion Auto Parts – Automotive Battery, Alternator & Starter Solutions
Domain: championautoparts.com
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
Introduction: Battery: Typically lasts 3-5 years, easiest and cheapest to replace. Symptoms of a dead battery include failure to start. Alternator: Lasts 8-12 years, charges the battery and powers the electrical system. Symptoms of a bad alternator include a dead battery. Starter: Responsible for starting the engine, draws power from the battery. Symptoms of a bad starter include failure to start the vehicle.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for starter vs alternator vs battery
In the intricate interplay between starters, alternators, and batteries, understanding their distinct roles is crucial for effective vehicle maintenance and operational efficiency. Each component not only supports the vehicle’s functionality but also contributes to the overall performance and longevity of the engine. For B2B buyers, strategic sourcing of these components can lead to significant cost savings and improved reliability, especially in markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Key takeaways include recognizing the signs of failure in each component, which can prevent costly downtimes and repairs. By investing in high-quality products and reliable suppliers, businesses can enhance fleet management and ensure optimal vehicle performance. Furthermore, the importance of regular maintenance and timely replacements cannot be overstated, as this minimizes the risk of unexpected failures.
Looking ahead, international buyers should prioritize partnerships with manufacturers and suppliers who offer comprehensive solutions and support. As the automotive landscape evolves, staying informed about advancements in battery technology, starter efficiency, and alternator performance will be essential. Engage with trusted suppliers to secure the best components for your needs and position your business for success in a competitive environment.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.