Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for parts of automobiles
In the ever-evolving landscape of the automotive industry, sourcing high-quality automobile parts presents a formidable challenge for international B2B buyers. From the heart of the engine to the intricate transmission systems, understanding the diverse array of components is crucial for maintaining vehicle performance and compliance with safety standards. This comprehensive guide delves into the various types of automobile parts, their specific applications, and the intricacies of supplier vetting. It also addresses critical cost considerations that impact procurement strategies, ensuring that buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs.
As international buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe navigate this complex market, they face unique hurdles, including varying regulations, fluctuating supply chains, and differing quality standards. This guide empowers these buyers by providing actionable insights and a structured approach to sourcing automobile parts. By understanding the nuances of the market, including the latest trends in component technology and supplier capabilities, buyers can enhance their procurement processes and foster long-term partnerships with reliable suppliers. Whether you are sourcing parts for manufacturing or aftermarket services, this guide is designed to equip you with the knowledge necessary to thrive in a competitive global marketplace.
Table Of Contents
- Top 1 Parts Of Automobiles Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for parts of automobiles
- Understanding parts of automobiles Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of parts of automobiles
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘parts of automobiles’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for parts of automobiles
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for parts of automobiles
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘parts of automobiles’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for parts of automobiles Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing parts of automobiles With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for parts of automobiles
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the parts of automobiles Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of parts of automobiles
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for parts of automobiles
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Understanding parts of automobiles Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Internal Combustion Engine | Comprises cylinder block, pistons, crankshaft, and camshaft. | Engine manufacturing and repair | Pros: High power output; widely available parts. Cons: Requires regular maintenance; emissions regulations. |
| Transmission Systems | Includes automatic, manual, and CVT types for gear shifting. | Vehicle assembly and aftermarket | Pros: Various options for driving preferences; enhances vehicle performance. Cons: Complexity can lead to higher repair costs. |
| Suspension Systems | Composed of shocks, struts, and control arms for stability. | Automotive repair and aftermarket | Pros: Improves ride quality; essential for safety. Cons: Can wear out over time; may need frequent replacements. |
| Electrical Systems | Encompasses battery, alternator, and wiring harnesses. | Electrical component suppliers | Pros: Critical for vehicle functionality; diverse aftermarket options. Cons: Vulnerable to corrosion; may require specialized tools for installation. |
| Exhaust Systems | Includes catalytic converters, mufflers, and tailpipes. | Emission control and vehicle repair | Pros: Reduces harmful emissions; enhances engine efficiency. Cons: Can be expensive; installation may require professional help. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Internal Combustion Engines?
Internal combustion engines are the powerhouse of most vehicles, converting fuel into mechanical energy through a series of controlled explosions. The primary components include the cylinder block, pistons, crankshaft, and camshaft, all intricately designed to maximize efficiency and power output. For B2B buyers, understanding the specific engine types, such as V6 or V8, is crucial for selecting the appropriate parts or engines for various applications, including commercial vehicles and machinery. Additionally, compliance with emissions regulations is a key consideration for manufacturers and distributors in different regions.
How Do Transmission Systems Affect Vehicle Performance?
Transmission systems, which include automatic, manual, and continuously variable transmissions (CVT), are essential for controlling vehicle speed and direction. Each type has unique features: automatic transmissions provide ease of use, manual transmissions offer driver engagement, and CVTs optimize fuel efficiency. B2B buyers should consider the specific needs of their customer base when sourcing transmission parts or systems, as different markets may prefer certain types based on driving conditions and preferences. Additionally, understanding the maintenance requirements and potential repair costs can influence purchasing decisions.
Why Are Suspension Systems Vital for Vehicle Safety?
Suspension systems play a crucial role in vehicle stability and ride quality. They consist of components such as shocks, struts, and control arms that work together to absorb road imperfections and enhance handling. For B2B buyers in the automotive repair sector, sourcing high-quality suspension parts is essential for ensuring vehicle safety and customer satisfaction. It’s also important to consider the lifespan of these components and the frequency of replacement, as this can affect inventory management and customer service.
What Role Do Electrical Systems Play in Modern Vehicles?
Electrical systems are integral to vehicle operation, encompassing the battery, alternator, and various wiring harnesses. These components are critical for starting the engine and powering electrical accessories. For B2B buyers, understanding the compatibility of electrical parts with different vehicle models is essential to ensure efficient supply chain management and customer satisfaction. Additionally, the growing trend towards electric vehicles underscores the importance of sourcing advanced electrical components, which may require specialized knowledge and partnerships with manufacturers.
How Do Exhaust Systems Contribute to Environmental Compliance?
Exhaust systems, including catalytic converters, mufflers, and tailpipes, are designed to reduce harmful emissions and enhance engine performance. B2B buyers must navigate the complexities of sourcing exhaust components that meet varying regional emissions standards, particularly in markets with strict environmental regulations. Understanding the technological advancements in exhaust systems can also provide a competitive edge, as buyers seek products that offer improved efficiency and compliance.
Key Industrial Applications of parts of automobiles
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of parts of automobiles | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive Manufacturing | Engine components (pistons, crankshafts) | Enhances performance and efficiency of vehicles | Quality certifications, compatibility with existing models |
| Transportation & Logistics | Suspension systems (shocks, struts) | Improves safety and ride quality for commercial fleets | Durability under heavy loads, local availability of parts |
| Automotive Repair Shops | Brake systems (pads, calipers) | Ensures vehicle safety and compliance with regulations | Availability of OEM vs aftermarket parts, warranty options |
| Renewable Energy Vehicles | Battery systems and electric drivetrains | Supports the shift towards sustainable transportation | Supplier reliability, technology compatibility |
| Export & Import Trade | Fuel tanks and exhaust systems | Compliance with international emissions standards | Understanding local regulations, sourcing from certified suppliers |
How Are Engine Components Used in Automotive Manufacturing?
In the automotive manufacturing sector, engine components such as pistons and crankshafts are critical for building high-performance vehicles. These parts are engineered to withstand high temperatures and pressures, ensuring optimal combustion efficiency. Manufacturers must consider sourcing components that meet stringent quality standards to enhance vehicle performance and reliability. For international buyers, understanding the compatibility of these parts with various engine models is vital, especially when dealing with diverse automotive markets in regions like Africa and South America.
What Role Do Suspension Systems Play in Transportation & Logistics?
Suspension systems, including shocks and struts, are essential in the transportation and logistics industry for maintaining vehicle stability and ride comfort, particularly in commercial fleets. These systems help absorb road shocks, ensuring smoother rides over long distances and reducing wear on cargo. For B2B buyers in regions with challenging terrains, sourcing durable suspension components that can handle heavy loads while offering reliability is crucial. Local availability of these parts can also significantly reduce downtime during maintenance.
Why Are Brake Systems Important for Automotive Repair Shops?
Brake systems, comprising pads and calipers, are paramount for automotive repair shops to ensure vehicle safety. These components must meet regulatory compliance to prevent accidents and liabilities. Repair shops need to source reliable parts, balancing between OEM and aftermarket options based on customer needs and budget considerations. For international buyers, understanding warranty options and the availability of technical support can enhance their procurement decisions, especially in markets with varying safety standards.
How Do Battery Systems Support Renewable Energy Vehicles?
In the growing market for renewable energy vehicles, battery systems and electric drivetrains play a pivotal role in transitioning towards sustainable transportation. These components must be sourced from reliable suppliers to ensure performance and longevity, meeting the increasing demand for electric vehicles (EVs). International buyers should consider technology compatibility and supplier reliability, particularly in regions like Europe, where EV adoption is accelerating, and infrastructure is evolving rapidly.
What Compliance Considerations Are There for Fuel Tanks and Exhaust Systems in Export & Import Trade?
Fuel tanks and exhaust systems are critical for compliance with international emissions standards, making them essential in the export and import trade of automotive parts. Sourcing these components requires a deep understanding of local regulations to avoid penalties and ensure market access. For international buyers, collaborating with certified suppliers who understand the regulatory landscape can streamline the procurement process and enhance competitiveness in regions like the Middle East and Africa, where emissions regulations are tightening.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘parts of automobiles’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Sourcing Quality Parts in a Competitive Market
The Problem: B2B buyers often face challenges in sourcing quality automobile parts amid fierce competition. In regions like Africa and South America, where the automotive supply chain may be less established, buyers can struggle with counterfeit products or subpar components that jeopardize vehicle performance and safety. This can lead to costly downtime, reputational damage, and potential legal liabilities if faulty parts lead to accidents.
The Solution: To mitigate these risks, B2B buyers should establish relationships with reputable suppliers who have a proven track record in the industry. Conduct thorough due diligence by verifying the supplier’s certifications, product reviews, and industry reputation. Utilize platforms that specialize in automotive parts to access verified suppliers. Additionally, implementing a quality assurance protocol, including inspections and testing of parts upon arrival, can ensure that only top-quality components are utilized in repairs or manufacturing processes. Establishing long-term partnerships with trusted suppliers can also lead to better pricing and priority service, enhancing reliability in the supply chain.
Scenario 2: Navigating Complex Compliance Regulations
The Problem: B2B buyers are often overwhelmed by the myriad of compliance regulations related to automobile parts, especially in diverse markets across Europe and the Middle East. Different countries have varying standards for emissions, safety, and performance, which can complicate the procurement process. Failure to comply with these regulations can result in heavy fines, product recalls, and damage to a company’s reputation.
The Solution: To navigate this complex landscape, buyers should invest time in understanding the specific regulations that apply to their target markets. Collaborating with legal experts or compliance consultants can provide valuable insights into the necessary certifications and testing required for automobile parts. Additionally, buyers should prioritize suppliers who are well-versed in international compliance standards and can provide documentation proving their products meet these requirements. Creating a compliance checklist tailored to each market can further streamline the procurement process, ensuring all parts sourced are compliant before they reach the assembly line or end-user.
Scenario 3: Managing Inventory and Supply Chain Disruptions
The Problem: Inventory management is a critical pain point for B2B buyers in the automotive industry. Fluctuations in demand, unexpected supply chain disruptions, or delays in shipping can lead to either excess inventory or shortages. This imbalance can strain financial resources and impact customer satisfaction, especially in regions where timely access to parts is essential for maintaining vehicle operations.
The Solution: Implementing a robust inventory management system that utilizes real-time data analytics can significantly improve supply chain efficiency. Buyers should consider adopting just-in-time (JIT) inventory practices to reduce excess stock while ensuring that critical components are always on hand. Establishing a network of alternative suppliers can also provide a buffer against disruptions, allowing for swift adjustments in sourcing when necessary. Regularly reviewing inventory levels and sales forecasts can help identify trends and prepare for seasonal fluctuations, ensuring that the supply chain remains responsive and agile. Utilizing software solutions that integrate supply chain logistics can provide insights into lead times and inventory turnover rates, ultimately leading to more informed decision-making.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for parts of automobiles
What Are the Key Materials Used in Automobile Parts?
When selecting materials for automobile parts, understanding the properties, advantages, and limitations of each material is crucial for B2B buyers. This guide analyzes four common materials used in the automotive industry, focusing on their performance characteristics and implications for international buyers, particularly in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
How Does Steel Perform in Automotive Applications?
Steel is one of the most widely used materials in automobile manufacturing due to its excellent strength-to-weight ratio. It can withstand high temperatures and pressures, making it suitable for critical components like the chassis and engine blocks. Steel’s inherent corrosion resistance can be enhanced through galvanization or coatings, which is essential for parts exposed to harsh environments.
Pros: Steel is durable and cost-effective, making it a preferred choice for mass production. Its mechanical properties can be tailored through various alloying techniques, allowing for customized performance.
Cons: While steel is strong, it can be heavier than alternative materials, potentially impacting fuel efficiency. Manufacturing processes for steel can be complex and energy-intensive, affecting overall production costs.
Impact on Application: Steel’s compatibility with various automotive fluids and its ability to endure mechanical stress make it ideal for structural components.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards such as ASTM and DIN is crucial. Buyers should also consider local regulations regarding emissions and recycling, particularly in regions like Brazil and Nigeria, where environmental concerns are increasingly prioritized.
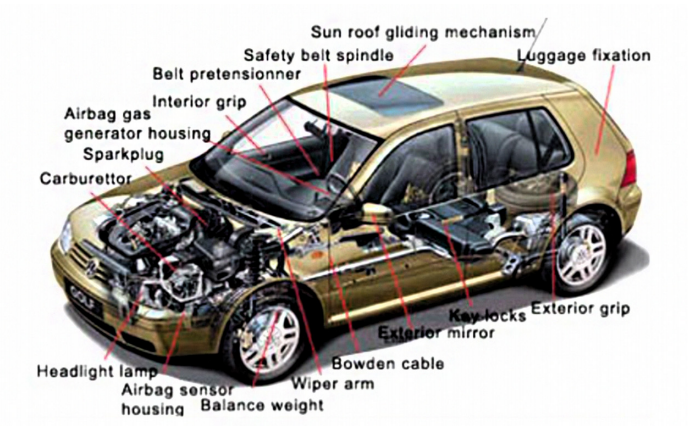
Illustrative image related to parts of automobiles
What Role Does Aluminum Play in the Automotive Industry?
Aluminum is gaining popularity in the automotive sector due to its lightweight nature and excellent corrosion resistance. It is commonly used in components such as wheels, engine blocks, and body panels, where weight reduction is critical for improving fuel efficiency.
Pros: Aluminum’s low density contributes to overall vehicle weight reduction, enhancing performance and fuel economy. It also offers good thermal conductivity, making it suitable for heat exchangers.
Cons: The primary drawback is its higher cost compared to steel, which can be a limiting factor for budget-sensitive projects. Additionally, aluminum can be less durable under certain stress conditions, necessitating careful design considerations.
Impact on Application: Aluminum’s compatibility with various automotive fluids and resistance to corrosion makes it suitable for both structural and aesthetic applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the varying standards for aluminum alloys, such as JIS and EN. Understanding local market preferences for lightweight vehicles can also influence material selection.

Illustrative image related to parts of automobiles
How Does Plastic Contribute to Automotive Parts Manufacturing?
Plastics are increasingly used in automotive applications due to their versatility and ability to be molded into complex shapes. Common uses include interior components, bumpers, and various housings.
Pros: Plastics are lightweight, cost-effective, and resistant to corrosion and chemical exposure. They also offer design flexibility, allowing for innovative shapes and features.
Cons: While plastics are durable, they may not withstand high temperatures as effectively as metals. Some plastics can degrade under UV exposure, which is a consideration for exterior components.
Impact on Application: The chemical compatibility of plastics with automotive fluids is generally favorable, but specific grades must be chosen to ensure performance under varying conditions.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with safety and environmental regulations, particularly in markets with stringent standards like Europe. Understanding the local preferences for materials can also guide selection.
What Benefits Does Composite Material Offer in Automotive Parts?
Composite materials, particularly fiber-reinforced polymers, are increasingly utilized in high-performance automotive applications. They are known for their high strength-to-weight ratio and excellent fatigue resistance.
Pros: Composites are lightweight and can be engineered for specific performance characteristics, making them ideal for high-performance vehicles. They also offer superior corrosion resistance.
Cons: The primary limitations include higher costs and more complex manufacturing processes. Repairing composite materials can also be more challenging compared to metals.
Impact on Application: Composites are particularly suitable for components exposed to high stress and fatigue, such as structural reinforcements and body panels.

Illustrative image related to parts of automobiles
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be familiar with specific standards for composite materials and their applications. Additionally, understanding the local market demand for high-performance vehicles can influence the decision to use composites.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Automotive Parts
| Material | Typical Use Case for parts of automobiles | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Chassis, engine blocks | Excellent strength-to-weight ratio | Heavier than alternatives | Medium |
| Aluminum | Wheels, engine blocks, body panels | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Higher cost | High |
| Plastic | Interior components, bumpers | Lightweight and cost-effective | May degrade under UV exposure | Low |
| Composite | High-performance vehicle components | High strength-to-weight ratio | Higher costs and complex repairs | High |
This analysis provides B2B buyers with critical insights into material selection, helping them make informed decisions tailored to their specific regional and application needs.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for parts of automobiles
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Automobile Parts?
The manufacturing of automobile parts is a complex process that typically involves several key stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Each stage is crucial in ensuring that the final product meets the high standards of quality and performance required in the automotive industry.
How Is Material Prepared for Automobile Parts Manufacturing?
Material preparation involves selecting and processing raw materials to ensure they meet specific requirements for strength, durability, and performance. Common materials used include steel, aluminum, plastic, and composites.
The process often begins with the sourcing of high-quality raw materials from reputable suppliers. These materials undergo various treatments, such as heat treatment or surface finishing, to enhance their properties. B2B buyers should ensure that suppliers provide material certifications that comply with international standards, such as ASTM or ISO specifications.

Illustrative image related to parts of automobiles
What Forming Techniques Are Commonly Used in Automobile Parts Manufacturing?
Forming is the next critical stage, where raw materials are transformed into specific shapes and sizes using various techniques. Common methods include:
-
Stamping: This involves using high-pressure machines to shape sheet metal into parts like body panels or brackets. Stamping is efficient for producing large volumes of parts with high precision.
-
Casting: This process involves pouring molten metal into molds to create complex shapes, such as engine blocks or transmission housings. It allows for the production of intricate designs but requires careful control of cooling rates to prevent defects.
-
Machining: Machining processes, such as turning, milling, and drilling, are used to achieve precise dimensions and surface finishes. This stage is crucial for parts that require tight tolerances, such as crankshafts or gears.
Understanding these techniques can help B2B buyers assess the capabilities of potential suppliers and their ability to meet specific part requirements.
How Are Automobile Parts Assembled?
The assembly stage brings together various components to form complete parts or systems. This stage often involves both manual and automated processes. For example, automated assembly lines may be used for high-volume parts, while complex assemblies may require skilled labor for precision fitting.
Key considerations during assembly include:
-
Workforce Training: Ensuring that assembly workers are adequately trained in quality control measures and assembly techniques is vital for maintaining high standards.
-
Use of Jigs and Fixtures: These tools help ensure consistent alignment and positioning of parts during assembly, reducing variability and defects.
B2B buyers should inquire about a supplier’s assembly processes and workforce training programs to ensure consistent quality.
What Finishing Processes Are Essential for Automobile Parts?
Finishing processes are the final steps in the manufacturing journey, where parts are treated to enhance their appearance and performance. Common finishing techniques include:
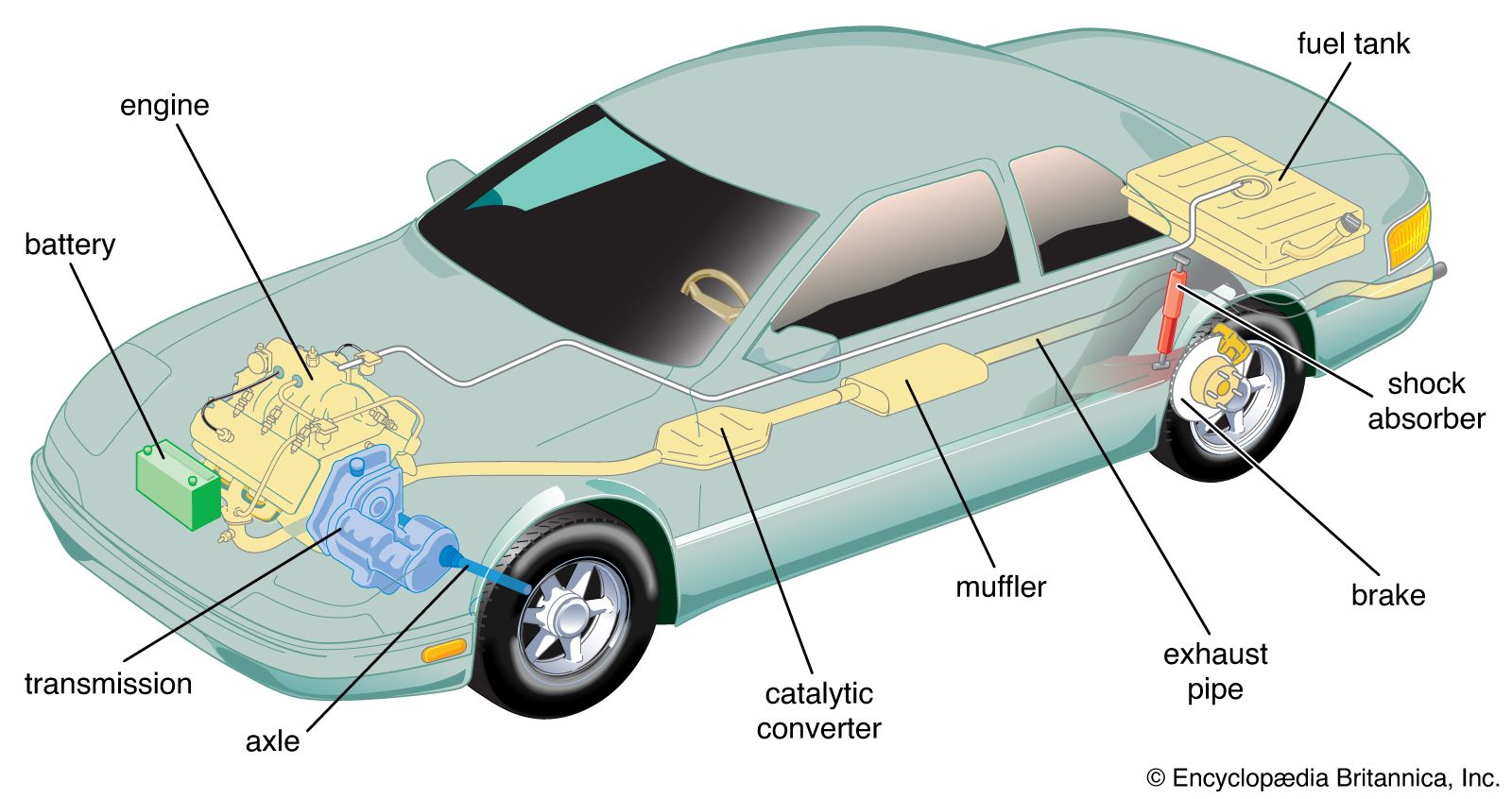
Illustrative image related to parts of automobiles
-
Painting and Coating: Protective coatings are applied to prevent corrosion and wear, while paint provides aesthetic appeal. It is essential to use environmentally friendly processes to comply with international regulations.
-
Surface Treatment: Techniques such as anodizing, galvanizing, or polishing improve surface properties and enhance durability.
Buyers should verify that suppliers adhere to relevant environmental and quality standards, especially when sourcing from regions with stricter regulations.
What Quality Assurance Standards Should B2B Buyers Consider?
Quality assurance (QA) is critical in the automotive industry to ensure that parts meet safety and performance standards. B2B buyers should be familiar with international standards, such as ISO 9001, which outlines requirements for a quality management system. Additionally, industry-specific certifications, such as CE marking for European markets or API standards for automotive components, are essential for compliance.
How Are QC Checkpoints Implemented in the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are integrated throughout the manufacturing process to identify defects early and ensure compliance with specifications. Key checkpoints include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This phase involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to verify that they meet specified standards.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During production, samples are taken at various stages to ensure that processes are functioning correctly and that parts meet quality standards.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): The final inspection of completed parts assesses their performance against established criteria before they are shipped to customers.
Implementing these checkpoints helps suppliers maintain high standards and provides assurance to B2B buyers regarding product quality.
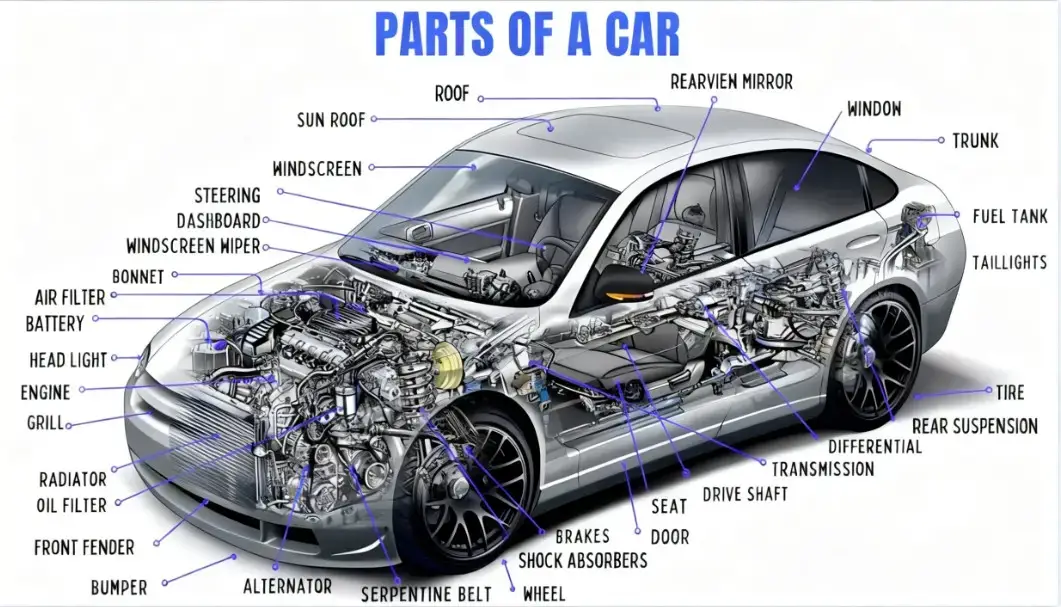
Illustrative image related to parts of automobiles
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used in Quality Assurance for Automobile Parts?
Various testing methods are employed to assess the quality and performance of automobile parts. Common methods include:
-
Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Techniques such as ultrasonic testing, radiography, and magnetic particle inspection allow for the evaluation of materials without causing damage.
-
Mechanical Testing: Tensile, compression, and fatigue tests assess the mechanical properties of materials to ensure they can withstand operational stresses.
-
Dimensional Inspection: This involves using precision measuring tools to verify that parts meet specified dimensions and tolerances.
B2B buyers should request information on the testing methods used by suppliers to ensure that products meet the required standards.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers should adopt a proactive approach to verify the quality control practices of their suppliers. Key strategies include:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting regular audits of suppliers helps assess their compliance with quality standards and manufacturing processes. This can include reviewing documentation, inspecting facilities, and observing production methods.
-
Requesting Quality Reports: Suppliers should provide detailed quality reports that include data on defect rates, inspection results, and corrective actions taken.
-
Engaging Third-Party Inspectors: Utilizing independent inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s quality control processes.
By implementing these strategies, B2B buyers can mitigate risks and ensure that they source high-quality automobile parts.
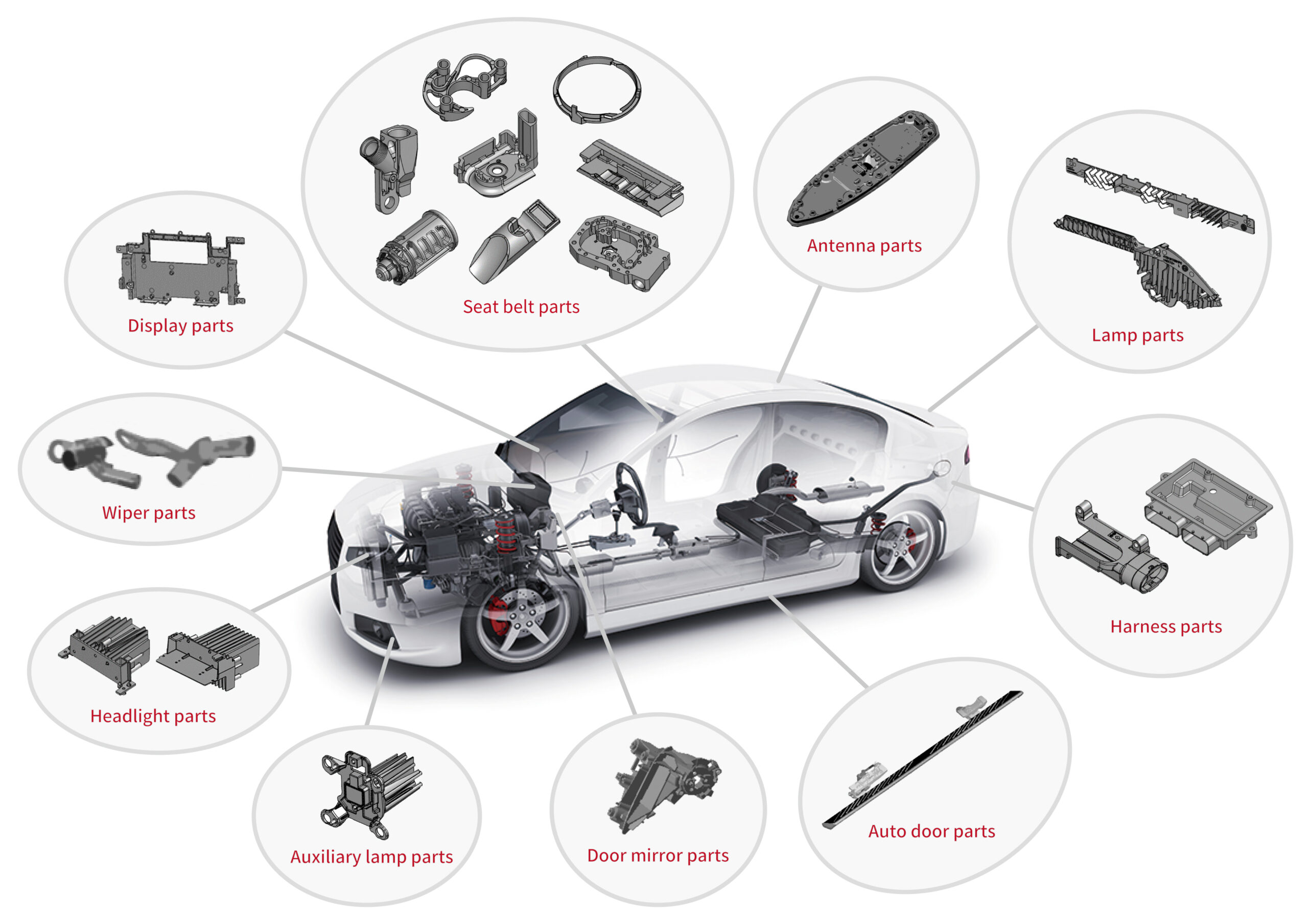
Illustrative image related to parts of automobiles
What Are the Nuances of Quality Control for International B2B Buyers?
For international B2B buyers, particularly those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of quality control is essential. Factors to consider include:
-
Regional Standards: Different regions may have varying quality standards and regulations. Buyers should familiarize themselves with local requirements and ensure that suppliers comply with them.
-
Cultural Differences: Business practices and communication styles can vary significantly across cultures. Building strong relationships with suppliers can enhance collaboration and ensure that quality expectations are met.
-
Logistics and Transportation: Consideration should be given to how transportation and logistics may affect the quality of parts. Proper handling and storage during transit are crucial to maintaining product integrity.
By keeping these factors in mind, international B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing automobile parts and ensure that they receive high-quality products that meet their specific needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘parts of automobiles’
To assist B2B buyers in the procurement of automobile parts, this practical guide outlines essential steps to ensure a successful sourcing process. Understanding the intricacies of automobile components and their suppliers can lead to better purchasing decisions, cost savings, and enhanced operational efficiency.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Begin by clearly outlining the specifications for the automobile parts you require. This includes understanding the make, model, and year of the vehicle, as well as the specific part numbers and features. Accurate specifications help prevent errors and ensure compatibility, which is crucial for smooth operations and customer satisfaction.
- Key Considerations:
- Identify the exact part numbers and any unique features.
- Consider the materials and standards required for durability and performance.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify suppliers that specialize in the automobile parts you need. Look for companies with a proven track record in quality and reliability. Using online marketplaces, trade directories, and industry-specific forums can provide valuable insights into potential vendors.

Illustrative image related to parts of automobiles
- Key Considerations:
- Review supplier ratings and customer feedback.
- Check their experience in your specific market region, such as Africa or South America.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Before engaging with suppliers, verify their certifications and compliance with industry standards. Certifications such as ISO 9001 or local automotive quality standards are indicators of a supplier’s commitment to quality and reliability.
- Key Considerations:
- Ensure they adhere to international safety and quality standards.
- Request copies of their certifications for your records.
Step 4: Request Samples or Prototypes
To ensure the quality and fit of the parts, request samples or prototypes from your shortlisted suppliers. This step is essential for assessing the physical attributes of the parts and confirming that they meet your specifications.
- Key Considerations:
- Evaluate the sample for quality, durability, and compatibility.
- Use the opportunity to gauge the supplier’s responsiveness and support.
Step 5: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Once you have selected a supplier, engage in negotiations to establish favorable terms and conditions. Discuss pricing, payment terms, delivery schedules, and warranty provisions. Clear agreements can prevent misunderstandings and foster a long-term partnership.
- Key Considerations:
- Ensure all terms are documented in a formal contract.
- Be clear about penalties for delays or quality issues.
Step 6: Plan for Logistics and Distribution
Consider the logistics involved in shipping and receiving the automobile parts. This includes understanding shipping costs, delivery timelines, and customs regulations, especially when dealing with international suppliers.
- Key Considerations:
- Assess the supplier’s logistics capabilities and their experience with cross-border shipments.
- Plan for potential delays and establish a buffer in your inventory levels.
Step 7: Establish Ongoing Quality Control
After procurement, implement a quality control process to monitor the parts received. Regular inspections can help identify any defects early and ensure that the parts maintain their required standards throughout their lifecycle.
- Key Considerations:
- Set up a schedule for periodic inspections and audits.
- Collect feedback from your team on the performance of the parts in real-world applications.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing automobile parts more effectively, minimizing risks and maximizing the value of their investments.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for parts of automobiles Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Automobile Parts?
When sourcing automobile parts, understanding the cost structure is crucial for international B2B buyers. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margins.
-
Materials: The cost of raw materials varies significantly based on type and quality. For instance, high-performance components often require specialized materials that can increase costs. Buyers should consider sourcing materials locally to mitigate import duties and transportation costs.
-
Labor: Labor costs are influenced by the region where manufacturing occurs. Countries with lower labor costs, such as those in parts of Africa and South America, may provide more competitive pricing. However, it’s essential to balance cost with the skill level and expertise of the workforce.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses indirect costs associated with production, such as utilities and equipment maintenance. Understanding the overhead structure of a supplier can provide insight into their pricing strategy.
-
Tooling: Tooling costs can be substantial, especially for custom parts. Buyers should consider whether the supplier has the necessary tooling in place or if they will incur additional charges for new tooling.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring the quality of parts is non-negotiable. QC processes add to the cost but are essential for maintaining standards. Buyers should evaluate suppliers based on their certifications and quality assurance practices.
-
Logistics: Transportation and handling fees can significantly impact total costs. International buyers need to factor in shipping methods, freight charges, and potential delays, especially when sourcing from overseas suppliers.
-
Margin: Supplier profit margins can vary widely. Understanding a supplier’s pricing strategy can help buyers negotiate better deals and identify areas for potential savings.
How Do Pricing Influencers Impact Automobile Parts Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of automobile parts:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Higher order volumes often lead to lower unit prices due to economies of scale. Buyers should assess their needs carefully to optimize order sizes.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom parts generally come at a premium. Clearly defining specifications upfront can help avoid costly adjustments later.
-
Materials: The choice of materials directly affects pricing. Premium materials enhance performance but can also elevate costs. Buyers should evaluate the trade-offs between cost and performance.
-
Quality/Certifications: Parts that meet international standards or possess industry certifications may be priced higher but offer greater reliability and safety. It is crucial to consider long-term value rather than just upfront costs.
-
Supplier Factors: A supplier’s reputation, reliability, and historical performance can affect pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their proven track record.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) is vital for cost management. They dictate responsibilities for shipping, insurance, and tariffs, which can significantly influence the total landed cost.
What Negotiation Tips Can Help Buyers Achieve Cost-Efficiency?
International B2B buyers should adopt strategic approaches to negotiations for better pricing:
-
Build Relationships: Establishing strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing and terms. A collaborative approach often yields more favorable outcomes.
-
Leverage Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Instead of focusing solely on initial costs, consider TCO, which includes maintenance and operational costs over the part’s lifespan. This perspective can justify higher upfront costs for better quality parts.
-
Conduct Market Research: Being informed about market trends and competitor pricing can empower buyers during negotiations. Knowledge of alternative suppliers can also create leverage.
-
Be Flexible: Consider alternative materials or specifications that may reduce costs without compromising quality.
What Should International Buyers Be Aware of Regarding Pricing Nuances?
For buyers in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, several pricing nuances are essential to understand:

Illustrative image related to parts of automobiles
-
Currency Fluctuations: Exchange rates can impact costs, particularly when sourcing from different countries. It’s advisable to negotiate prices in a stable currency.
-
Import Duties and Tariffs: Be aware of local regulations that may impose additional costs on imported parts. These can significantly affect the total cost.
-
Cultural Considerations: Understanding cultural differences in business practices can facilitate smoother negotiations and build trust.
-
Disclaimer on Prices: Prices can fluctuate based on market conditions, supplier changes, and raw material availability. It’s essential to confirm prices with suppliers regularly and consider them as indicative rather than fixed.
By comprehensively analyzing these aspects, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that optimize their sourcing strategies for automobile parts.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing parts of automobiles With Other Solutions
Introduction: Understanding Alternatives to Automobile Parts
In the automotive sector, the traditional parts of automobiles have been the backbone of vehicle functionality and performance. However, with technological advancements, alternative solutions are emerging that could potentially enhance efficiency, reduce costs, or simplify maintenance. This section explores viable alternatives to conventional automobile parts, enabling B2B buyers to make informed decisions based on their operational needs and strategic goals.
Comparison Table of Automobile Parts and Alternatives
| Comparison Aspect | Parts Of Automobiles | Electric Vehicles (EV) | Autonomous Vehicle Systems |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Reliable performance with mechanical parts; efficiency varies by vehicle type. | High torque delivery, instant acceleration; efficient energy use. | Enhanced performance through advanced sensors and AI for optimal driving. |
| Cost | Initial cost varies; ongoing maintenance and replacement parts can be expensive. | Higher upfront cost; lower long-term fuel and maintenance costs. | High initial investment; potential for cost savings through reduced accidents and insurance. |
| Ease of Implementation | Established supply chains; familiar to mechanics and technicians. | Requires specific charging infrastructure; may need specialized training. | Complex integration with existing systems; significant training required. |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance needed; parts wear out over time. | Lower maintenance due to fewer moving parts; battery replacement is key. | Requires constant software updates and system checks; maintenance costs can be unpredictable. |
| Best Use Case | Conventional vehicles for varied applications (personal, commercial). | Urban environments with charging infrastructure; environmentally conscious buyers. | Logistics and transport sectors needing automation; high safety and efficiency focus. |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Electric Vehicles (EV)
Electric vehicles are gaining traction as a sustainable alternative to traditional internal combustion engine vehicles. They offer high torque and instant acceleration, which can enhance performance in urban settings. While the initial investment may be higher, EVs often yield lower long-term costs due to reduced fuel expenses and maintenance requirements. However, the need for a charging infrastructure and potential range limitations can pose challenges, particularly in regions with less developed energy networks.
Autonomous Vehicle Systems
Autonomous vehicles represent a cutting-edge alternative that leverages advanced technologies like AI and machine learning. These systems enhance performance through optimized routing and driving patterns, significantly reducing the risk of human error. However, the implementation of autonomous systems can be costly and complex, requiring substantial investment in technology and infrastructure. Maintenance can also be unpredictable, as it involves both hardware and software components that must be regularly updated to ensure safety and efficiency. These systems are best suited for sectors focused on logistics and transportation, where automation can lead to significant operational improvements.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
When selecting between traditional automobile parts and alternative solutions like electric vehicles or autonomous systems, B2B buyers must consider several factors including performance requirements, cost implications, ease of implementation, and maintenance needs. Understanding the unique advantages and challenges associated with each option will empower buyers to make strategic decisions that align with their operational goals and market demands. Ultimately, the right choice will depend on the specific context of use, available resources, and long-term business objectives.
Illustrative image related to parts of automobiles
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for parts of automobiles
Understanding the technical specifications and trade terminology associated with automobile parts is crucial for international B2B buyers. This knowledge not only streamlines procurement processes but also enhances decision-making and negotiation capabilities.
What are the Critical Technical Specifications for Automobile Parts?
-
Material Grade
Material grade refers to the classification of materials based on their chemical composition and physical properties. Common grades in automotive parts include steel (e.g., SAE 1010, SAE 1045) and aluminum alloys (e.g., 6061, 7075). Understanding material grades is essential for buyers to ensure that parts meet industry standards for durability, strength, and corrosion resistance, ultimately affecting the longevity and performance of the vehicle. -
Tolerance
Tolerance specifies the allowable deviation from a specified dimension in a part. It is crucial for ensuring proper fit and function between components. For example, a tolerance of ±0.01 mm might be specified for critical engine components. Accurate tolerances are vital for minimizing wear and tear, enhancing safety, and ensuring that parts are interchangeable, which is particularly important for OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) and aftermarket applications. -
Surface Finish
Surface finish describes the texture of a part’s surface, often specified in terms of roughness (measured in micrometers). A smoother finish can reduce friction and wear, which is vital for parts like bearings and gears. Buyers should consider surface finish specifications to ensure optimal performance and longevity, especially in high-stress applications. -
Load Rating
Load rating is the maximum load a part can safely support without failure. For example, brake components have specific load ratings that must be adhered to for safety and performance. This specification is crucial for buyers to ensure that parts are suitable for the intended application, helping to prevent potential failures that could lead to costly downtime or accidents. -
Temperature Range
This specification indicates the temperature extremes within which a part can operate effectively. For instance, engine components may need to withstand high temperatures, while electrical parts must tolerate lower temperatures. Knowing the temperature range is essential for ensuring that parts perform reliably under various operating conditions, especially in regions with extreme climates.
What are Common Trade Terms in the Automotive Parts Industry?
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce parts that are used in the manufacturing of new vehicles. Parts supplied by OEMs are typically held to higher quality standards and are designed to fit specific vehicle models. B2B buyers often prefer OEM parts for their reliability and compatibility, especially in repair and replacement scenarios. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is crucial for buyers to manage inventory costs and ensure that they can meet demand without overstocking. This term can significantly impact purchasing strategies, particularly for smaller businesses. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and availability for specific parts. This process allows buyers to compare offers from multiple suppliers, aiding in cost-effective decision-making. Clarity in RFQs can also expedite procurement processes and enhance supplier relationships. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are standardized trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. They clarify issues like shipping responsibilities, insurance, and risk transfer. Familiarity with Incoterms helps buyers navigate global logistics and avoid misunderstandings, especially when sourcing parts from different continents. -
Aftermarket Parts
Aftermarket parts are components made by third-party manufacturers that are not supplied by the OEM. These parts can often be less expensive and offer greater variety. Understanding the differences between OEM and aftermarket parts can help buyers make informed decisions based on quality, cost, and specific needs.
By grasping these technical properties and industry terms, B2B buyers can enhance their procurement strategies, ensuring they source the right parts efficiently and effectively.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the parts of automobiles Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics Affecting the Parts of Automobiles Sector?
The global automotive parts market is experiencing significant transformation driven by technological advancements, changing consumer preferences, and regulatory pressures. Key trends include the shift towards electric vehicles (EVs), which is reshaping the types of components needed, particularly in battery systems and electronic control units. As international B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe navigate this evolving landscape, understanding the implications of these trends is crucial.
Emerging technologies, such as the Internet of Things (IoT) and artificial intelligence (AI), are enhancing supply chain efficiency and predictive maintenance capabilities. IoT devices are increasingly integrated into automotive parts, allowing for real-time data collection and analysis, which can lead to improved performance and customer satisfaction. Furthermore, the rise of e-commerce platforms tailored for B2B transactions is simplifying procurement processes, enabling buyers in diverse markets to source parts more efficiently and competitively.
International buyers must also be aware of regional market dynamics. For instance, Africa’s automotive market is growing rapidly, driven by urbanization and an expanding middle class, while South America faces challenges related to economic volatility and import tariffs. Understanding these localized factors is essential for making informed sourcing decisions.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact B2B in the Parts of Automobiles Sector?
Sustainability has become a pivotal concern within the automotive parts sector, prompting buyers to consider the environmental impact of their sourcing decisions. The automotive industry is under pressure to reduce carbon footprints, and this is reflected in the increasing demand for parts made from recycled materials or those that comply with stringent environmental regulations. B2B buyers should prioritize suppliers that demonstrate a commitment to sustainability through certifications such as ISO 14001 or the use of eco-friendly materials.
Ethical sourcing practices are equally important, as consumers and businesses alike are becoming more conscious of the social implications of their purchases. Buyers should seek partnerships with manufacturers that uphold fair labor practices and transparency in their supply chains. This not only helps in mitigating risks associated with unethical practices but also enhances brand reputation, particularly in markets like Europe where consumer awareness is high.
Furthermore, integrating sustainability into procurement strategies can lead to long-term cost savings and operational efficiencies. As the regulatory landscape evolves, suppliers who are proactive in adopting sustainable practices will likely have a competitive advantage, making them more attractive to discerning B2B buyers.
What Is the Historical Context Behind the Automotive Parts Sector’s Evolution?
The automotive parts sector has evolved significantly since the inception of the automobile in the late 19th century. Initially characterized by a focus on mechanical simplicity, the industry rapidly advanced with the introduction of assembly line production in the early 20th century, which revolutionized the manufacturing process and made cars more accessible.
As the decades progressed, technological innovations led to the integration of electronic components, improving vehicle performance and safety. The rise of globalization in the late 20th century further transformed the landscape, allowing for the outsourcing of parts production to regions with lower labor costs. This has created a complex web of supply chains that B2B buyers must navigate today.

Illustrative image related to parts of automobiles
In recent years, the push towards electrification and connectivity has ushered in a new era for the automotive parts sector, with a growing emphasis on software, electronics, and sustainable materials. Understanding this historical context is essential for B2B buyers to appreciate the current dynamics and anticipate future trends within the industry.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of parts of automobiles
-
How do I choose the right supplier for automobile parts?
Selecting the right supplier for automobile parts involves evaluating several key factors. Start by verifying the supplier’s credentials, including industry certifications and customer reviews. Consider their experience in the specific parts you need, as well as their ability to meet international standards. Request samples to assess quality and ensure they can provide parts that comply with regulations in your target market. Establish clear communication channels and inquire about their capacity to fulfill orders on time, which is crucial for maintaining your supply chain efficiency. -
What is the best way to ensure quality assurance for automobile parts?
To ensure quality assurance for automobile parts, implement a multi-faceted approach. Begin by partnering with suppliers who have established quality control processes and certifications like ISO 9001. Regularly conduct audits and inspections of their facilities and production lines. Additionally, request detailed documentation of the parts, including material specifications and testing results. Consider establishing a third-party inspection service to verify compliance with your standards before shipment, ensuring that the parts meet your expectations upon arrival. -
What are the common payment terms in B2B transactions for automobile parts?
Common payment terms in B2B transactions for automobile parts vary by supplier but typically include options like net 30, net 60, or upfront deposits. Negotiating terms that suit both parties is essential; some suppliers may require a partial payment before production, especially for custom orders. Utilizing secure payment methods such as letters of credit or escrow services can mitigate risks for both buyers and sellers. Always clarify the terms in the contract to avoid misunderstandings and ensure timely payments. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for automobile parts?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for automobile parts can differ significantly based on the supplier and the type of parts required. Generally, MOQs are set to ensure cost-effectiveness for the supplier and can range from a few units for standard parts to hundreds or thousands for specialized components. When sourcing, inquire about MOQs upfront and evaluate if they align with your inventory needs. Some suppliers may offer flexibility for new customers or bulk orders, so it’s worth discussing potential adjustments based on your purchasing plans. -
How can I manage logistics for importing automobile parts?
Effective logistics management for importing automobile parts involves careful planning and coordination. Start by choosing a reliable freight forwarder with experience in handling automotive components. They can assist with customs documentation and compliance with international trade regulations. Evaluate shipping options based on cost, speed, and reliability, and consider using a mix of air and sea freight depending on urgency. Additionally, maintain clear communication with suppliers regarding shipping schedules and track shipments to address any issues proactively. -
What are the key factors to consider when customizing automobile parts?
When customizing automobile parts, key factors include compatibility with existing systems, material selection, and regulatory compliance. Collaborate closely with your supplier to define specifications that meet your performance and safety requirements. Consider lead times and the cost implications of customization, as these can affect your overall budget and delivery schedule. Additionally, ensure that all modifications are thoroughly tested and validated to avoid issues once the parts are integrated into vehicles. -
How do I address discrepancies in received automobile parts?
Addressing discrepancies in received automobile parts requires a systematic approach. First, document any issues with photographs and detailed descriptions. Contact the supplier immediately to report the discrepancies and provide supporting evidence. Review your contract to understand the terms regarding returns, exchanges, or refunds. Maintain open lines of communication to resolve the issue quickly, and consider establishing a formal process for handling discrepancies to streamline future interactions and minimize disruptions. -
What is the importance of understanding international trade regulations for automobile parts?
Understanding international trade regulations is crucial for sourcing automobile parts, as non-compliance can lead to delays, fines, and even confiscation of goods. Familiarize yourself with the import/export regulations specific to your target markets, including tariffs, quotas, and documentation requirements. Collaborate with customs brokers or legal experts to navigate complex regulations effectively. Ensuring compliance not only facilitates smooth transactions but also enhances your reputation and reliability as a B2B buyer in the automotive sector.
Top 1 Parts Of Automobiles Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Moog – Car Parts
Domain: moogparts.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Parts of a Car include: Steering Wheel, Engine (with components like timing chain, camshaft, crankshaft, spark plugs, cylinder heads, valves, pistons), Transmission, Battery, Alternator, Radiator, Front Axle, Front Steering and Suspension (including shocks/struts, ball joints, tie rod ends, rack and pinion steering system, idler/pitman arms), Brakes (disc brakes with brake pads and calipers, drum …
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for parts of automobiles
In the dynamic landscape of automotive parts sourcing, understanding the intricate components of vehicles—from engines to braking systems—is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. As international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, it is crucial to prioritize strategic sourcing that aligns with both quality and sustainability. By leveraging strong supplier relationships and investing in advanced technology, businesses can enhance their operational efficiency and reduce costs.
Moreover, staying abreast of industry trends and innovations will empower buyers to anticipate market shifts and adapt accordingly. The growing emphasis on electric vehicles and eco-friendly components presents significant opportunities for forward-thinking companies willing to diversify their sourcing strategies.
As you navigate the complexities of the automotive parts market, consider the potential of strategic partnerships and localized sourcing. Embrace a proactive approach to procurement that not only meets current demands but also positions your business for future growth. Together, let’s drive toward a more sustainable and efficient automotive industry that benefits all stakeholders involved. Explore opportunities today and ensure your supply chain is robust and ready for tomorrow’s challenges.
Illustrative image related to parts of automobiles
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.