Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for how much does it cost to fix a starter
As global markets evolve, one pressing challenge for B2B buyers is understanding the cost implications of fixing a starter, a critical component in vehicle performance. The cost of starter replacement can vary significantly based on factors such as vehicle type, labor rates, and the quality of replacement parts. This comprehensive guide aims to demystify the complexities surrounding starter repair costs, offering insights into different types of starters, their applications, and essential supplier vetting processes.
International buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including countries such as Vietnam and Saudi Arabia—face unique considerations when sourcing automotive parts. With fluctuating prices and varying service standards, making informed decisions is paramount. This guide empowers you with the knowledge needed to navigate these challenges effectively, ensuring you choose the right suppliers and solutions that align with your operational needs.
By exploring the intricacies of starter replacement costs, from economy to high-performance options, as well as the potential additional repairs that may arise, this resource equips you to optimize your purchasing strategy. Armed with this information, you can enhance your supply chain efficiency, minimize downtime, and ultimately drive greater value for your business.
Table Of Contents
- Top 6 How Much Does It Cost To Fix A Starter Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for how much does it cost to fix a starter
- Understanding how much does it cost to fix a starter Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of how much does it cost to fix a starter
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘how much does it cost to fix a starter’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for how much does it cost to fix a starter
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for how much does it cost to fix a starter
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘how much does it cost to fix a starter’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for how much does it cost to fix a starter Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing how much does it cost to fix a starter With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for how much does it cost to fix a starter
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the how much does it cost to fix a starter Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of how much does it cost to fix a starter
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for how much does it cost to fix a starter
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Understanding how much does it cost to fix a starter Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Economy Starters | Budget-friendly, aftermarket parts, lower lifespan | Cost-sensitive markets, fleet operations | Pros: Lower initial cost; Cons: Shorter lifespan may lead to frequent replacements. |
| OEM Starters | Original parts, designed for specific vehicle models | High-end vehicle maintenance, dealerships | Pros: Guaranteed fit and performance; Cons: Higher upfront cost. |
| High-Performance Starters | Specialty parts for racing or performance vehicles | Motorsports, specialized automotive shops | Pros: Enhanced performance; Cons: Significantly higher price point. |
| Remanufactured Starters | Rebuilt from used parts, cost-effective option | Small repair shops, budget-conscious buyers | Pros: Lower price than new; Cons: Potentially shorter lifespan and reliability. |
| DIY Starter Kits | Parts sold for self-installation, varying quality | Individual mechanics, DIY enthusiasts | Pros: Cost savings on labor; Cons: Risk of improper installation and additional costs. |
What Are the Characteristics of Economy Starters?
Economy starters are primarily aftermarket parts designed to be budget-friendly. They are often used in cost-sensitive markets, such as fleet operations, where the initial investment is crucial. While they provide a lower upfront cost, these starters typically have a shorter lifespan, which can lead to frequent replacements. B2B buyers should consider the total cost of ownership, including potential replacements, when evaluating these options.
How Do OEM Starters Differ from Aftermarket Options?
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) starters are designed specifically for particular vehicle models, ensuring a perfect fit and optimal performance. They are commonly used in high-end vehicle maintenance and by dealerships that prioritize quality and reliability. The primary drawback is their higher price point, which may not be suitable for all B2B buyers, especially those in budget-sensitive sectors. However, their longevity and reliability often justify the investment.
What Is Unique About High-Performance Starters?
High-performance starters are tailored for racing or performance vehicles, offering enhanced power and durability. They are primarily utilized in motorsports and specialized automotive shops where performance is critical. While these starters provide significant benefits, their price point is considerably higher, making them less accessible for average consumers or businesses focused on cost efficiency. B2B buyers should assess whether the performance gains align with their operational needs.
Why Choose Remanufactured Starters?
Remanufactured starters are rebuilt from used parts and provide a cost-effective alternative to new units. This option is popular among small repair shops and budget-conscious buyers who seek to balance quality and price. Although they come at a lower price than new starters, the potential for a shorter lifespan and reliability issues should be carefully considered. B2B buyers must weigh the initial savings against the possibility of future replacement costs.
What Are the Benefits and Risks of DIY Starter Kits?
DIY starter kits offer parts for self-installation, appealing to individual mechanics and DIY enthusiasts looking to save on labor costs. However, while they can lead to significant savings, there is a risk of improper installation, which can result in additional costs for repairs. B2B buyers should evaluate their technical expertise and the potential risks before opting for this route, as it may not always result in the most economical solution in the long run.
Key Industrial Applications of how much does it cost to fix a starter
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of how much does it cost to fix a starter | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive Repair Shops | Estimating costs for starter repairs and replacements | Helps in providing accurate quotes to customers | Availability of OEM vs. aftermarket parts, local labor rates |
| Fleet Management | Budgeting for maintenance of vehicle fleets | Reduces downtime and enhances operational efficiency | Bulk purchasing options, warranty terms, and service agreements |
| Transportation & Logistics | Evaluating starter repair costs for logistics vehicles | Ensures reliable transport and timely deliveries | Access to reliable parts suppliers and service providers |
| Agricultural Equipment | Assessing starter repair costs for farming machinery | Minimizes equipment downtime during critical seasons | Compatibility of parts with diverse machinery models |
| Construction Industry | Cost analysis for starter replacements in heavy machinery | Maintains project timelines and productivity | Availability of specialized starters for various equipment types |
How Do Automotive Repair Shops Use Starter Cost Estimates?
Automotive repair shops rely on accurate cost estimates for starter repairs and replacements to provide competitive quotes to customers. Understanding the price range for different types of starters—OEM, aftermarket, or remanufactured—enables shops to offer tailored solutions that meet customer needs. For international B2B buyers, sourcing reliable parts and understanding local labor rates are crucial to maintaining profitability while ensuring customer satisfaction.
Why Is Budgeting Important for Fleet Management?
Fleet management companies must budget for vehicle maintenance, including starter repairs, to minimize operational disruptions. By knowing how much it costs to fix a starter, these businesses can allocate funds more effectively and schedule maintenance during off-peak hours, thereby reducing downtime. International buyers should consider bulk purchasing options and negotiate service agreements to optimize their maintenance costs across diverse vehicle models.
How Does Transportation & Logistics Benefit from Starter Cost Analysis?
In the transportation and logistics sector, evaluating starter repair costs is vital for ensuring that vehicles remain operational and can meet delivery schedules. A failing starter can lead to significant delays, impacting customer satisfaction. Companies in this sector should focus on sourcing reliable suppliers who can provide quality parts quickly and offer warranty options that protect their investments.
What Role Does Starter Cost Assessment Play in Agricultural Equipment?
Agricultural businesses depend heavily on machinery for planting and harvesting, making starter reliability essential. Assessing repair costs enables farmers to make informed decisions about whether to repair or replace starters in their equipment. Buyers in this sector must ensure that sourced parts are compatible with a wide range of machinery models, as agricultural equipment can vary significantly in specifications.
Why Is Understanding Starter Repair Costs Essential in the Construction Industry?
For the construction industry, where heavy machinery is critical, understanding the costs associated with starter replacements can directly impact project timelines and productivity. Any delays due to equipment failure can lead to increased costs and project overruns. Therefore, businesses should seek suppliers that offer specialized starters for various types of construction machinery, ensuring minimal downtime and adherence to project schedules.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘how much does it cost to fix a starter’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Cost Uncertainty for Fleet Maintenance
The Problem: For businesses operating a fleet of vehicles, understanding the costs associated with starter repairs can be daunting. Fleet managers often face uncertainty about whether to repair or replace starters, especially when dealing with varying vehicle makes and models. This uncertainty is compounded by fluctuating labor rates and the potential for hidden costs associated with additional repairs, such as wiring or battery issues. Without a clear picture of the financial implications, decision-makers may hesitate to act, risking vehicle downtime and operational efficiency.
The Solution: To mitigate cost uncertainty, fleet managers should implement a standardized procedure for assessing starter issues across their vehicles. This includes maintaining a database of historical repair costs, which can provide insights into the average expenses associated with different vehicle types. Additionally, establishing relationships with reliable automotive service providers can yield transparent pricing and expert advice on whether to repair or replace starters. Requesting detailed quotes that break down labor and parts costs allows for better budgeting and cost forecasting. Furthermore, consider negotiating bulk repair rates with service providers to lower overall expenses for fleet maintenance.
Scenario 2: Balancing Quality and Cost for Starter Replacement
The Problem: B2B buyers often grapple with the dilemma of choosing between OEM and aftermarket starter parts. While OEM parts typically promise quality and longevity, they come at a higher cost, which can strain budgets. Conversely, aftermarket options may offer significant savings but can lead to premature failures and additional costs down the line. This balancing act creates a challenge for businesses aiming to maintain their vehicles efficiently without overspending.
The Solution: To effectively balance quality and cost, businesses should conduct a thorough analysis of their vehicle usage and performance needs. For fleets that experience high mileage or demanding conditions, investing in OEM parts may ultimately save money by reducing the frequency of repairs and replacements. On the other hand, for vehicles with lighter usage, quality aftermarket parts can be a viable option. Establishing a partnership with trusted suppliers who can provide insights into part quality and performance history is crucial. Additionally, consider implementing a preventative maintenance program that includes regular inspections, allowing businesses to address starter issues before they escalate, thus optimizing both costs and vehicle reliability.
Scenario 3: Overcoming DIY Repair Pitfalls in Starter Replacement
The Problem: Some businesses may attempt to reduce costs by opting for DIY starter replacements, believing that this approach will save on labor expenses. However, this decision can lead to significant pitfalls, including improper installation, which may damage the vehicle’s electrical system and lead to more costly repairs. Additionally, the time invested in DIY repairs can detract from core business operations, ultimately negating any financial savings.
The Solution: To avoid the pitfalls of DIY repairs, businesses should first assess their internal capabilities and resources. If the team lacks the necessary expertise or tools, it is more prudent to invest in professional services. For businesses determined to handle repairs in-house, it is essential to provide adequate training and access to quality resources, such as repair manuals and instructional videos. Furthermore, businesses can minimize risks by consulting with professional mechanics before attempting repairs to gain insights into potential challenges. This collaborative approach allows for a more informed decision-making process and ensures that any repair undertaken aligns with best practices, maintaining vehicle integrity and operational efficiency.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for how much does it cost to fix a starter
What Materials Are Commonly Used in Starter Replacement?
When considering the cost to fix a starter, the selection of materials used in the starter motor and its components plays a crucial role in performance, durability, and overall cost. Here, we analyze four common materials relevant to starter replacements, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for international B2B buyers.
What Are the Key Properties of Copper in Starter Components?
Copper is widely used in electrical components due to its excellent conductivity and thermal properties. It can withstand high temperatures and pressures, making it suitable for starter motors that operate under varying conditions. Copper also offers good corrosion resistance when properly coated, which is essential for longevity in diverse environments.

Illustrative image related to how much does it cost to fix a starter
Pros: The main advantages of copper include high electrical conductivity, which ensures efficient power transfer, and excellent thermal conductivity that helps in heat dissipation.
Cons: However, copper can be prone to oxidation if not protected, which may lead to electrical failures. Additionally, copper components can be more expensive than alternatives like aluminum.
Impact on Application: In starter motors, copper wiring and contacts ensure reliable operation, particularly in high-performance vehicles where quick starts are critical.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with international standards such as ASTM B75 for copper wire. In regions like Africa and South America, where environmental conditions can vary significantly, selecting copper components with protective coatings is advisable.

Illustrative image related to how much does it cost to fix a starter
How Does Aluminum Compare as a Material for Starters?
Aluminum is another common material, often used for casings and structural components of starter motors. It is lightweight, which can contribute to overall vehicle efficiency.
Pros: Aluminum is resistant to corrosion, making it suitable for vehicles operating in humid or saline environments. Its lightweight nature also reduces the overall weight of the starter, potentially improving fuel efficiency.
Cons: On the downside, aluminum has lower electrical conductivity compared to copper, which may affect performance in high-demand situations. It is also less durable under extreme mechanical stress.

Illustrative image related to how much does it cost to fix a starter
Impact on Application: Aluminum is often used in starter housings, where weight savings are beneficial, but it may not be suitable for high-performance applications requiring maximum electrical efficiency.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards like JIS H 2000 for aluminum alloys is crucial. Buyers in the Middle East should consider the impact of high temperatures on aluminum durability.
What Role Does Steel Play in Starter Construction?
Steel is commonly used for the structural components of starters, particularly in the gear and housing assemblies. Its strength and durability make it a reliable choice.
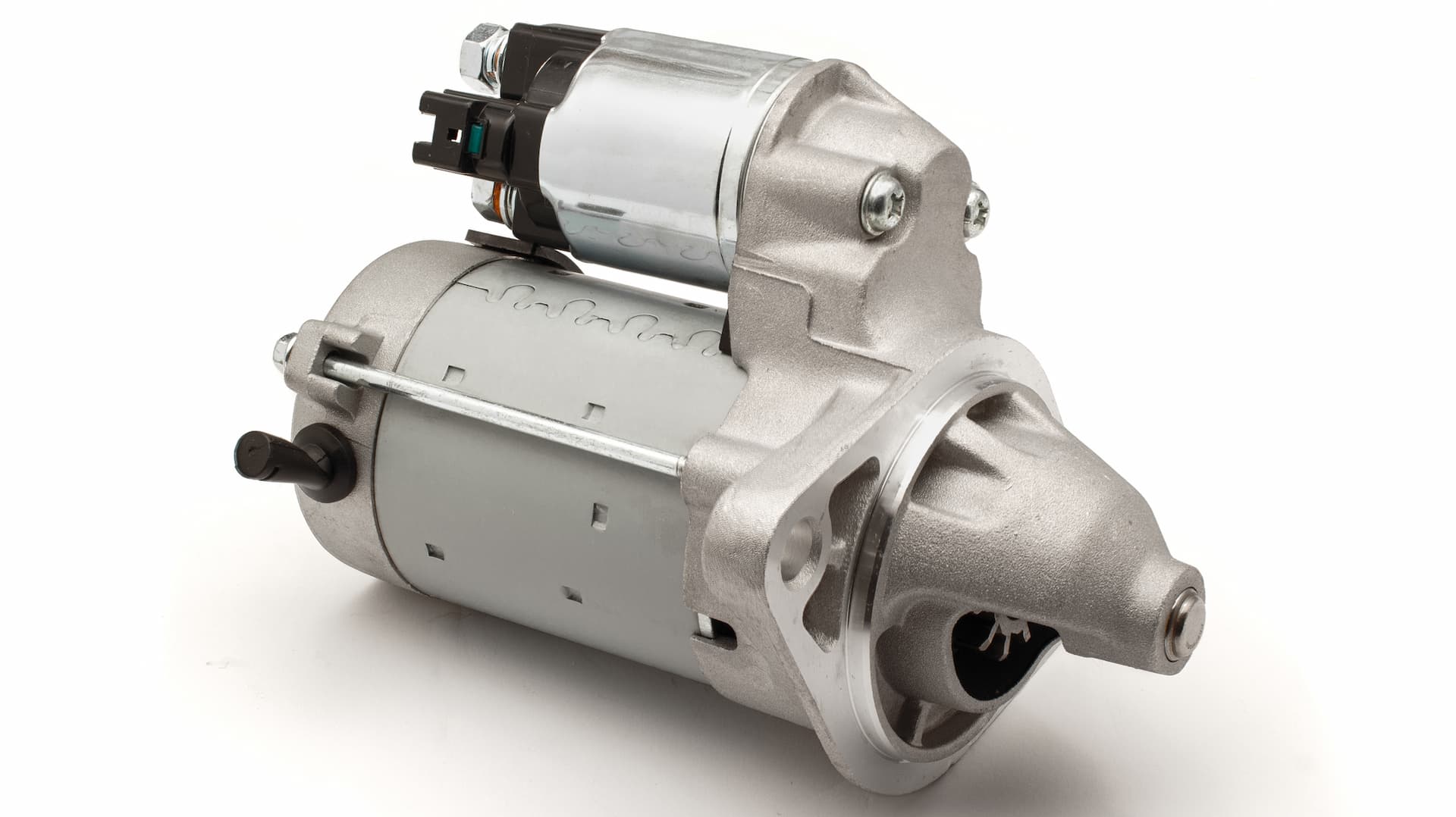
Illustrative image related to how much does it cost to fix a starter
Pros: The primary advantage of steel is its high tensile strength, which allows it to withstand significant mechanical stress without deforming. Steel components can also be treated for corrosion resistance.
Cons: However, steel is heavier than aluminum and can be prone to rust if not adequately protected. This can lead to increased maintenance costs over time.
Impact on Application: Steel is best suited for components that require strength and durability, such as the starter drive gear, which must endure repeated engagement and disengagement.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should look for steel components that meet international standards like ASTM A36. In regions with high humidity, additional corrosion protection may be necessary.
How Does Plastic Contribute to Starter Design?
Plastic is increasingly being used in starter motors for non-load-bearing components, such as insulation and covers. It offers versatility and cost savings.
Pros: Plastic is lightweight, cost-effective, and can be molded into complex shapes. It also provides excellent electrical insulation, which is vital for safety.
Cons: The main disadvantages include lower mechanical strength compared to metals and potential degradation over time due to heat or exposure to chemicals.
Impact on Application: Plastic components are suitable for parts that do not bear heavy loads but require insulation, such as covers and wiring harnesses.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards like ASTM D638 for plastics is essential. Buyers in Europe may prefer plastics that meet RoHS regulations for hazardous substances.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Starter Replacement
| Material | Typical Use Case for how much does it cost to fix a starter | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Copper | Electrical wiring and contacts in starter motors | High electrical conductivity | Prone to oxidation | High |
| Aluminum | Casings and structural components | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Lower electrical conductivity | Medium |
| Steel | Gear and housing assemblies | High tensile strength | Heavier and prone to rust | Medium |
| Plastic | Insulation and non-load-bearing components | Cost-effective and versatile | Lower mechanical strength | Low |
This analysis provides a comprehensive overview for B2B buyers considering material options for starter replacements, emphasizing the importance of material selection in cost, performance, and compliance with international standards.

Illustrative image related to how much does it cost to fix a starter
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for how much does it cost to fix a starter
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Starters?
The manufacturing process of automotive starters involves several critical stages that ensure the final product meets the required performance standards. Understanding these stages is essential for B2B buyers, as it directly impacts the cost and quality of the starter.
How Is Material Prepared for Starter Manufacturing?
The first stage in the manufacturing process is material preparation. This involves sourcing high-quality raw materials, such as copper for windings, steel for the housing, and various alloys for components like gears. Suppliers should ensure that materials meet specific industry standards, which can affect durability and performance.
Once sourced, materials undergo cleaning and inspection to eliminate any impurities that could affect functionality. This stage is crucial because the quality of raw materials significantly influences the longevity and reliability of the starter.
What Techniques Are Used in Forming Starter Components?
After material preparation, the forming stage begins. Key techniques used include:
-
Stamping: Metal sheets are stamped into shapes required for the starter components. This technique allows for high precision and repeatability, essential for fitting parts together seamlessly.
-
Machining: Components that require fine tolerances undergo machining processes. CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining is commonly used to ensure high accuracy in dimensions, particularly for the starter’s housing and gears.
-
Winding: The copper wire is wound around the starter’s rotor and stator. This process must be performed with precision to ensure optimal electromagnetic performance.
Each of these techniques requires skilled labor and specialized equipment, which can contribute to the overall cost of the starter.
How Is Assembly Conducted in Starter Manufacturing?
The assembly stage involves putting together all the formed components into a functional starter. This process typically includes:
-
Component Integration: Individual parts such as the motor, solenoid, and housing are assembled. Ensuring proper alignment and fit is critical, as misalignment can lead to performance issues.
-
Electrical Connections: Technicians connect electrical components, ensuring that all wiring is secure and insulated to prevent shorts.
-
Testing During Assembly: Many manufacturers implement in-line testing during assembly to catch defects early. This includes checking electrical connections and ensuring the motor functions correctly before moving to the next stage.
What Finishing Techniques Are Applied to Ensure Quality?
Once assembly is complete, the finishing stage enhances the starter’s durability and performance. Common techniques include:
-
Coating: Starters often undergo coating processes, such as painting or plating, to protect against corrosion. This is especially important for starters used in harsh environments.
-
Final Inspection: A thorough inspection is conducted to check for any visual defects, alignment issues, or surface irregularities. This is a critical step before the starters are packaged and shipped.
What Quality Assurance Standards Are Relevant for Starter Manufacturing?
Quality assurance is a vital aspect of the manufacturing process, particularly for automotive components like starters. Various international and industry-specific standards guide manufacturers to ensure high-quality products.
Which International Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
ISO 9001 is the most recognized international standard for quality management systems. Compliance with ISO 9001 signifies that a manufacturer has established effective processes for quality control and continuous improvement. B2B buyers should prioritize suppliers who are ISO 9001 certified, as this indicates a commitment to maintaining quality throughout the manufacturing process.

Illustrative image related to how much does it cost to fix a starter
What Industry-Specific Certifications Are Important?
In addition to ISO standards, industry-specific certifications may also be relevant, depending on the region and type of vehicle. For instance:
-
CE Marking: In Europe, products must meet safety, health, and environmental protection standards. A CE mark ensures that the starter complies with these regulations.
-
API Certification: For starters used in specific applications, such as heavy machinery, API (American Petroleum Institute) certifications may be necessary to ensure compatibility and performance.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Starter Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) is integral to ensuring that each starter meets the required standards before it reaches the market. The following checkpoints are commonly used:
How Do Incoming Quality Control (IQC) Procedures Work?
During the incoming quality control stage, raw materials are inspected upon delivery. This involves checking for compliance with specifications and testing samples for material properties. Ensuring that only high-quality materials enter the production process is crucial for the final product’s reliability.
What Is In-Process Quality Control (IPQC)?
In-process quality control involves monitoring the manufacturing process at various stages. This can include:
- Regular Inspections: Random checks of components during assembly to ensure they meet specifications.
- Performance Testing: Conducting electrical and mechanical tests during assembly to identify issues early.
Implementing IPQC helps minimize defects and reduces rework costs, which can impact overall pricing.

Illustrative image related to how much does it cost to fix a starter
What Is Final Quality Control (FQC) and Its Importance?
Final quality control is the last checkpoint before the starters are packaged for shipment. This stage involves comprehensive testing of completed units to ensure they function correctly and meet all specifications. Common tests include:
- Electrical Testing: Verifying that the starter engages and operates under load.
- Mechanical Testing: Checking for any physical defects or misalignments.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
For international B2B buyers, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is crucial to ensure the reliability of the starters being purchased. Here are some ways to conduct due diligence:
What Steps Should Buyers Take for Supplier Audits?
Conducting supplier audits can provide insights into the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures in place. Buyers should request access to quality management system documentation, inspection records, and compliance certificates during audits.
How Can Buyers Utilize Reports and Third-Party Inspections?
Buyers should also consider utilizing reports from third-party inspection agencies. These reports can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s manufacturing and quality control processes. Engaging third-party inspectors can help identify potential issues that internal audits may overlook.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International Buyers?
When dealing with suppliers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, it is essential to understand the local manufacturing practices and regulatory requirements. Each region may have its own standards that can impact quality assurance processes.
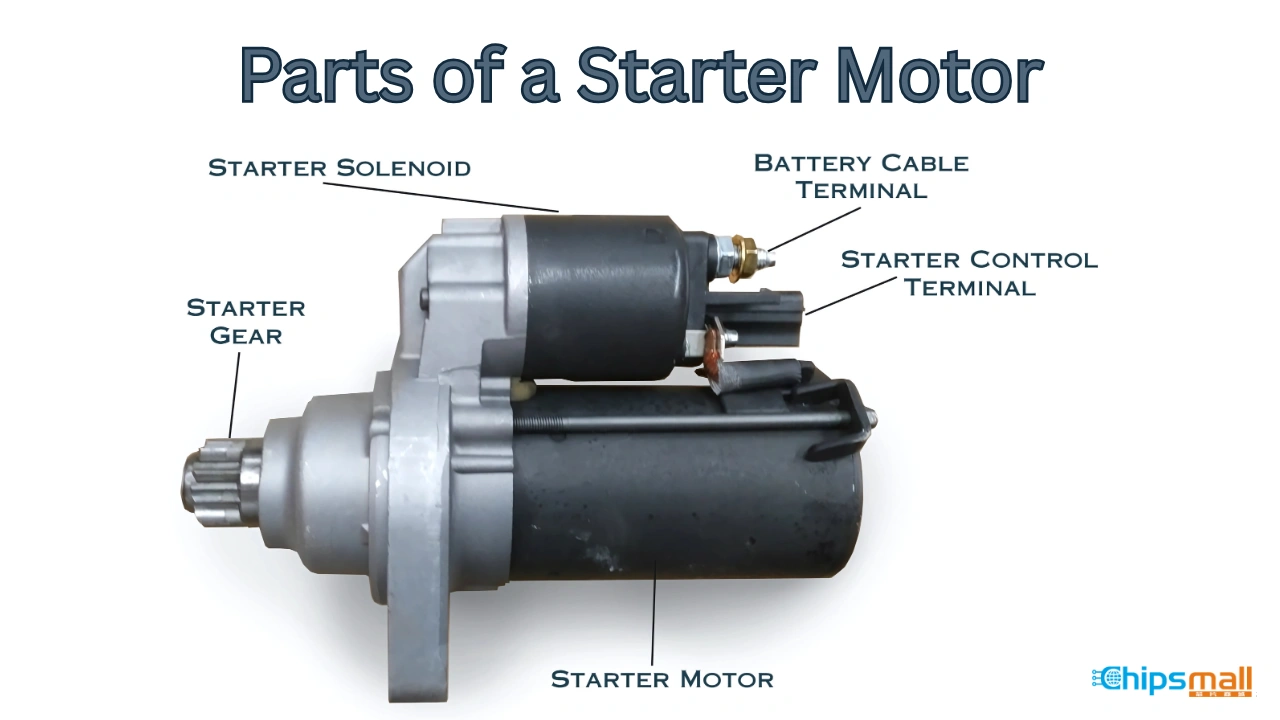
Illustrative image related to how much does it cost to fix a starter
Buyers should familiarize themselves with local certifications, common manufacturing challenges, and cultural differences in business practices. This knowledge can help in negotiating contracts and ensuring that quality expectations are met.
In conclusion, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for starters is vital for B2B buyers. By focusing on the key stages of production, relevant standards, and QC checkpoints, buyers can make informed decisions that enhance their supply chain and ensure the reliability of the starters they purchase.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘how much does it cost to fix a starter’
When considering the costs associated with fixing a starter, it’s essential for B2B buyers to have a systematic approach to sourcing. This guide provides a step-by-step checklist to ensure informed decisions when procuring starter repair services and parts.
Step 1: Assess Your Vehicle’s Requirements
Understanding your vehicle’s specific needs is crucial. Different makes and models have unique starter specifications, which directly influence repair costs. Review the vehicle manual or consult with a qualified mechanic to determine the exact starter type required.
- Considerations:
- Engine size and configuration.
- Whether the vehicle is domestic or foreign, as this affects parts availability and pricing.
Step 2: Research Replacement Options
Identifying whether to opt for a new, remanufactured, or aftermarket starter is vital. Each option has different implications for cost, longevity, and performance.
- Key Points:
- New starters offer better reliability but come at a higher price.
- Remanufactured starters are budget-friendly but may have a shorter lifespan.
- Aftermarket options can vary widely in quality, so assess the reputation of the manufacturer.
Step 3: Obtain Multiple Quotes
Gathering quotes from several suppliers or service providers helps in understanding the market rate for starter repairs. This step not only aids in cost comparison but also provides insights into service quality.
- Action Items:
- Request detailed breakdowns of parts and labor costs.
- Inquire about warranties and service guarantees.
Step 4: Evaluate Supplier Credentials
Before finalizing your choice, vet potential suppliers thoroughly. This includes checking their experience, customer reviews, and any relevant certifications.
- What to Look For:
- Industry certifications (e.g., ASE for automotive service).
- Client testimonials or case studies demonstrating past performance.
Step 5: Verify Labor Costs and Timeframes
Labor costs can vary significantly based on the complexity of the starter replacement. Understanding the expected time for repairs helps in planning and budgeting.
Illustrative image related to how much does it cost to fix a starter
- Considerations:
- Complexity of the vehicle model and accessibility of the starter.
- Average labor rates in your region to ensure competitive pricing.
Step 6: Account for Additional Repairs
Often, issues with the starter may indicate underlying problems that could require additional repairs, such as battery or wiring issues.
- Why This Matters:
- Addressing these issues promptly can prevent further damage and additional costs in the future.
- Always inquire about potential add-on repairs during initial assessments.
Step 7: Review Warranty and After-Sales Support
Finally, ensure that the parts and services come with a warranty. Reliable after-sales support can be invaluable if problems arise post-repair.
- Key Points:
- Understand the terms of the warranty and what it covers.
- Assess the supplier’s reputation for customer service and support.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can make informed decisions about sourcing starter repairs, ensuring they receive quality service at a fair price.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for how much does it cost to fix a starter Sourcing
Understanding the cost structure for fixing a starter motor is crucial for international B2B buyers, especially in markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This analysis delves into the various cost components and price influencers, offering actionable insights for negotiating and optimizing procurement strategies.

Illustrative image related to how much does it cost to fix a starter
What Are the Key Cost Components for Starter Motor Replacement?
-
Materials: The primary cost driver is the starter motor itself. Prices can vary significantly based on whether the starter is an economy model, OEM, or high-performance version. Economy starters may range from $75 to $200, while OEM parts typically cost between $150 and $400, and specialty starters can exceed $1,000.
-
Labor: Labor costs are influenced by the complexity of the vehicle model. Basic replacements can range from $100 to $250, while luxury or performance vehicles may incur labor costs of $300 to $600 due to the need for more extensive disassembly and expertise.
-
Manufacturing Overhead and Tooling: Suppliers often factor in costs related to manufacturing overhead, which includes expenses for facility maintenance, utilities, and equipment depreciation. Tooling costs can also add to the price, particularly if specialized equipment is required for certain vehicle models.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that the starter meets quality standards incurs additional costs. Suppliers must implement rigorous QC processes to minimize defects and warranty claims, which can influence the overall pricing.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs can vary based on the origin of the starter motor. International buyers should consider shipping fees, customs duties, and potential delays, which can affect the total landed cost.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a margin to cover their operating costs and profit. This margin can vary widely based on market dynamics and the competitiveness of the supplier.
How Do Price Influencers Affect the Cost of Starter Motors?
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders often lead to discounts due to economies of scale. Buyers should negotiate MOQs to benefit from lower per-unit costs.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom specifications can significantly increase costs. Buyers should evaluate whether standard parts meet their needs or if custom solutions are necessary, which can drive up prices.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher quality materials and certifications (like ISO standards) can enhance performance and longevity but also increase costs. Buyers should weigh the benefits of investing in higher quality against the budget.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation, reliability, and geographical location of suppliers can impact pricing. Local suppliers may offer lower shipping costs but might not have the same quality assurance as international manufacturers.
-
Incoterms: The choice of Incoterms can greatly influence total costs. Understanding terms like FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) is essential for international transactions to avoid unexpected charges.
What Buyer Tips Can Enhance Cost-Efficiency in Starter Motor Procurement?
-
Negotiation Strategies: Engage suppliers in discussions regarding bulk purchase discounts or long-term agreements that can lock in lower prices. Leverage competitive quotes to negotiate better terms.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): When evaluating starter motor options, consider the TCO, which includes not just the purchase price but also installation, maintenance, and potential warranty claims. This holistic view can reveal better long-term value.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Be aware of currency fluctuations and their impact on pricing. Understanding local market conditions and supplier networks can also provide leverage in negotiations.
-
Local Regulations and Compliance: Ensure that any parts sourced meet local regulations and compliance standards, as non-compliance can lead to additional costs or delays.
Disclaimer for Indicative Prices
The prices and cost components discussed herein are indicative and can vary based on specific circumstances, including geographical location, market conditions, and supplier agreements. It is advisable for buyers to conduct thorough market research and engage with multiple suppliers to obtain accurate and competitive pricing tailored to their needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing how much does it cost to fix a starter With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Starter Repair Costs
In the automotive industry, a failing starter can lead to significant inconvenience and expenses. For B2B buyers, understanding the costs associated with fixing a starter compared to alternative solutions is essential for informed decision-making. Here, we will compare the traditional method of starter repair with two alternative solutions: battery replacement and the use of a jump starter.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | How Much Does It Cost To Fix A Starter | Battery Replacement | Jump Starter |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High, restores full functionality | Moderate, only addresses battery issues | High, provides immediate power |
| Cost | $250 – $1,000+ | $100 – $300 | $50 – $150 |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires professional service | Can be DIY or professional | DIY, very user-friendly |
| Maintenance | Low, once replaced | Moderate, may need future replacements | Low, rechargeable models available |
| Best Use Case | Long-term solution for starter failure | When the battery is the issue | For emergencies or temporary fixes |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
1. Battery Replacement
Battery replacement is a common solution when starting issues arise, as a faulty battery can often mimic starter problems. The cost of replacing a battery typically ranges from $100 to $300, making it a more economical choice for businesses facing budget constraints. However, while it can resolve starting issues, it does not address underlying problems with the starter itself. This method is suitable for vehicles that experience intermittent starting problems but may lead to additional costs if the starter is ultimately the root cause of the issue.
2. Jump Starter
A jump starter provides a quick, temporary solution for starting vehicles with a dead battery. Priced between $50 and $150, jump starters are portable, easy to use, and can be a lifesaver in emergencies. However, they only offer a stopgap measure and do not fix the underlying issue of a failing starter. While they are great for immediate use, relying on a jump starter may lead to ongoing problems if the starter continues to fail. This solution is best for businesses looking for a cost-effective way to manage immediate starting issues without committing to full repairs.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Needs
When evaluating how much it costs to fix a starter versus alternative solutions, it is crucial for B2B buyers to consider their specific circumstances. If the starter is the primary issue, investing in a complete repair is often the most effective long-term solution. Conversely, if the problem lies with the battery or if immediate access to a vehicle is needed, battery replacement or a jump starter may be more appropriate. Ultimately, the decision should be guided by a thorough assessment of the vehicle’s condition, budget constraints, and operational needs.

Illustrative image related to how much does it cost to fix a starter
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for how much does it cost to fix a starter
What Are the Key Technical Properties Related to Starter Repair Costs?
Understanding the essential technical properties associated with starter repairs is crucial for B2B buyers, especially when considering costs and ensuring quality. Here are some critical specifications to keep in mind:
1. Material Grade
The material grade of a starter motor impacts its durability and performance. Common materials include high-grade steel for housing and copper for windings. Higher-grade materials generally lead to longer-lasting starters, which can reduce overall replacement costs for businesses in the long run.
2. Electrical Resistance
Electrical resistance measures how much a component opposes the flow of electric current. For starters, lower resistance indicates better efficiency. A starter with low resistance will draw less power from the battery, enhancing vehicle reliability and potentially lowering energy costs for fleet operators.
3. Torque Rating
Torque rating refers to the rotational force generated by the starter motor. It is a critical specification, especially for larger vehicles and equipment. A higher torque rating is essential for effectively cranking engines in heavy machinery or luxury vehicles, impacting the choice of starter based on the application.

Illustrative image related to how much does it cost to fix a starter
4. Temperature Tolerance
Temperature tolerance indicates the range within which a starter can operate effectively without failure. Starters subjected to extreme conditions (like high heat or cold) should have higher temperature tolerances. This property is crucial for businesses in regions with varying climates, ensuring reliability and reducing maintenance costs.
5. Lifespan and Warranty Period
The expected lifespan of a starter motor, along with its warranty period, provides insights into its durability and the manufacturer’s confidence in the product. A longer lifespan and comprehensive warranty can lead to lower total ownership costs, an essential consideration for fleet managers and service providers.
What Are Common Trade Terms in Starter Replacement Costs?
Familiarity with industry jargon can help B2B buyers navigate discussions about starter repairs and replacements more effectively. Here are several key terms:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to parts made by the original manufacturer of the vehicle. OEM starters are typically more expensive but offer guaranteed compatibility and reliability. Businesses often prefer OEM parts to maintain quality and performance standards.

Illustrative image related to how much does it cost to fix a starter
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is crucial for B2B buyers as it can influence purchasing decisions and inventory management. Businesses should assess their needs to avoid overstocking or frequent reorders.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document issued by a buyer to suppliers asking for price quotes on specific products or services. This term is vital in the procurement process, allowing businesses to compare prices and negotiate better terms for starter replacements.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are standardized trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. They clarify who is responsible for shipping, insurance, and tariffs, impacting the overall cost of starter parts when sourced globally.
5. Aftermarket Parts
Aftermarket parts are components made by manufacturers other than the OEM. They can be more affordable but may vary in quality. B2B buyers should weigh the cost savings against potential risks in performance and compatibility when considering aftermarket starters.
By understanding these technical properties and industry terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions regarding starter repairs, ensuring both quality and cost-effectiveness in their operations.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the how much does it cost to fix a starter Sector
What Are the Global Drivers Impacting the Starter Repair Market?
The global market for starter repair and replacement is shaped by several key drivers, particularly influencing B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Firstly, the increasing age of vehicles on the road necessitates more frequent repairs, including starter replacements. As vehicles age, components like starters become more prone to failure, prompting businesses to source reliable parts and services.
Another significant trend is the rise of e-commerce platforms that facilitate the procurement of automotive parts. These platforms are particularly beneficial for international buyers, offering competitive pricing and a broader selection of products. Additionally, the integration of advanced technologies such as predictive analytics and IoT in automotive diagnostics is transforming how businesses assess and address starter issues. These technologies enable precise identification of starter problems, leading to more efficient repairs and reduced downtime.
Moreover, the impact of economic factors, such as fluctuating currency exchange rates and tariffs, can significantly influence sourcing decisions. Businesses must navigate these dynamics to optimize their procurement strategies and maintain competitive pricing.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact the Starter Repair Sector?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing have become paramount concerns in the automotive parts industry, including starter repairs. As environmental regulations tighten globally, businesses are increasingly held accountable for their sourcing practices. B2B buyers are now prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to sustainability, including the use of eco-friendly materials and processes.
The environmental impact of starter production and disposal is significant. Manufacturers and suppliers are encouraged to adopt sustainable practices, such as using remanufactured starters, which can reduce waste and lower the carbon footprint associated with new part production. Additionally, certifications like ISO 14001 can help B2B buyers identify suppliers who adhere to recognized environmental management standards.

Illustrative image related to how much does it cost to fix a starter
Ethical sourcing also extends to labor practices. Buyers are increasingly scrutinizing the supply chain to ensure that components are sourced from manufacturers that uphold fair labor practices and provide safe working conditions. By prioritizing suppliers with strong sustainability and ethical standards, businesses not only contribute to environmental preservation but also enhance their brand reputation and customer loyalty.
What Is the Historical Context of Starter Replacement Costs?
The history of starter replacement costs reflects broader trends in automotive technology and consumer behavior. Initially, starters were relatively simple components, often replaced as part of routine maintenance. However, as vehicles became more sophisticated, the complexity of starters increased, leading to higher replacement costs.
In the early 2000s, the introduction of advanced electrical systems in vehicles resulted in a shift towards more expensive OEM starters, which offered better performance and longevity. This transition marked a turning point for B2B buyers, who began to weigh the costs of OEM parts against budget-friendly aftermarket options. The evolution of starter technology has also led to the emergence of remanufactured starters, providing a cost-effective alternative for buyers looking to balance quality and price.
As technology continues to advance, the starter replacement market is expected to evolve further, with innovations aimed at improving durability and efficiency. B2B buyers must stay informed about these trends to make strategic sourcing decisions that align with their operational needs and budget constraints.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of how much does it cost to fix a starter
-
How much does it typically cost to replace a starter in different regions?
The cost of replacing a starter can vary significantly based on the region. In North America, the average price ranges from $250 to $1,000, including parts and labor. In Africa and South America, costs may be lower due to reduced labor rates, generally between $150 to $600. The Middle East and Europe may see prices similar to North America, but factors such as import taxes and local market conditions can influence these rates. Always consider local supplier quotes and currency fluctuations when budgeting. -
What factors influence the cost of starter replacement?
Several key factors affect the cost of starter replacement, including the vehicle’s make and model, the quality of the replacement part (new vs. remanufactured), and labor costs. Luxury vehicles often require more expensive parts and specialized labor, which can drive up costs. Additionally, if other components are damaged, such as wiring or the battery, this can lead to additional expenses. Understanding these factors can help B2B buyers make informed purchasing decisions. -
Are there minimum order quantities (MOQs) for purchasing starters in bulk?
Many suppliers set minimum order quantities (MOQs) for bulk purchases of starters, which can range from 10 to 100 units, depending on the manufacturer and the type of starter. B2B buyers should communicate with potential suppliers to negotiate MOQs that align with their business needs. Lower MOQs might be available for remanufactured starters, offering a more economical option for smaller operations or those testing new markets. -
How can I verify the quality of starters from international suppliers?
To ensure the quality of starters from international suppliers, conduct thorough due diligence. Request certifications, quality assurance processes, and product samples before placing bulk orders. Consider suppliers with a strong reputation in the industry and positive customer reviews. Engaging third-party inspection services can also provide an additional layer of verification, ensuring that the products meet specified standards and are free from defects. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing starters internationally?
Payment terms for international purchases of starters can vary widely among suppliers. Common arrangements include upfront payment, partial payments with the balance due upon delivery, or net payment terms (e.g., net 30 or net 60 days). It’s crucial to negotiate terms that are favorable and manageable for your cash flow. Additionally, using letters of credit can provide a secure method of payment, protecting both parties in the transaction. -
What are the logistics considerations for importing starters?
When importing starters, consider logistics factors such as shipping methods, customs regulations, and potential tariffs. Air freight is faster but more expensive, while sea freight is cost-effective for bulk shipments. Ensure compliance with local import regulations to avoid delays or additional costs. It may also be beneficial to work with a freight forwarder who can handle the complexities of international shipping and customs clearance. -
Can I customize starters for specific vehicle models?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options for starters to fit specific vehicle models or performance requirements. Customization can involve adjustments to the starter’s size, power output, or connectors. B2B buyers should discuss their specific needs with suppliers to determine feasibility, lead times, and any additional costs associated with customized orders. This approach ensures that the starters meet the exact specifications required for optimal performance. -
How do I handle warranty claims for starters purchased internationally?
Handling warranty claims for starters sourced internationally can be complex. It’s essential to review the warranty policy provided by the supplier before making a purchase. Ensure that the warranty covers parts and labor and inquire about the process for filing claims. Keep detailed records of all transactions and communications with the supplier. In the event of a claim, prompt communication and adherence to the supplier’s procedures can facilitate a smoother resolution.
Top 6 How Much Does It Cost To Fix A Starter Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Reddit – Starter Replacement Services
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Starter replacement, labor charges, diagnostics, OEM starter pricing, markup on parts.
2. Facebook – Car Starter Replacement Cost
Domain: facebook.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: cost to get car to the shop and replace starter
3. Last Chance Auto Repairs – Starter Replacement Costs
Domain: lastchanceautorepairs.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: Starter Replacement Cost: Economy starters: $75 – $200, OEM starters: $150 – $400, High-performance starters: $300 – $1000+. Labor costs: Basic vehicle replacement: $100 – $250, Complex installations: $300 – $600+. Average total cost: $250 – $1,000+. Factors affecting cost: Vehicle type & model, New vs Re-Manufactured starters, Additional repairs. DIY costs: Parts only: $100 – $400, Tools & equipm…
4. Car Talk – Starter Replacement Costs
Domain: cartalk.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Cost to replace a starter: $600 to $900 for common vehicles; $900 to $1,400 for luxury models. Symptoms of a failing starter include: a click sound when starting, screeching noise, intermittent functionality. Starters can be new, remanufactured, or repaired; remanufactured starters are commonly used. Modern vehicles with stop-start systems do not experience premature starter failures.
5. AAA – Starter Replacement Costs
Domain: aaa.com
Registered: 1990 (35 years)
Introduction: Average cost to replace a starter: $700 – $1,200; Replacement part cost: $100 – $400; Labor cost: $100 – $250 per hour; Types of starters: Gear reduction (more efficient, more expensive) and Direct drive (less efficient, cheaper); Symptoms of starter issues: slow engine cranking, car won’t start, clicking or grinding sounds, starter running after engine starts, smoke from engine, dashboard warning…
6. Denso – Starter Replacement for 2007 Toyota Tundra
Domain: tundras.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Starter replacement cost: $1500 (labor: $900, part: $650). Part number: Denso 428000-4640. Vehicle: 2007 Toyota Tundra CrewMax with 174k miles.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for how much does it cost to fix a starter
In summary, understanding the costs associated with starter replacement is essential for international B2B buyers looking to optimize their automotive maintenance strategies. The total expense is influenced by several factors, including the type of vehicle, the quality of the starter, and the complexity of the installation. By strategically sourcing components—balancing between new and remanufactured parts—businesses can ensure cost-effectiveness while maintaining operational efficiency.
For buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, leveraging local suppliers and understanding regional labor rates can further enhance procurement strategies. Engaging with reputable automotive service providers not only guarantees professional installation but also offers warranties that protect your investment.
As the automotive market continues to evolve, staying informed about pricing trends and technological advancements is crucial. By prioritizing strategic sourcing and fostering strong supplier relationships, businesses can navigate the complexities of starter replacement costs effectively. We encourage you to reach out to trusted suppliers and service centers to discuss your specific needs, ensuring your fleet remains reliable and efficient for the long term.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.