Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for difference in alternator and generator
In today’s global market, understanding the difference between alternators and generators is crucial for B2B buyers looking to optimize their energy solutions. As industries across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe navigate the complexities of energy sourcing and efficiency, discerning the right technology can significantly impact operational effectiveness and cost management. This guide delves into the fundamental distinctions between these two essential devices, focusing on their types, applications, and the nuances of supplier vetting.
By exploring the technical specifications and performance characteristics of alternators and generators, this comprehensive resource empowers international buyers to make informed purchasing decisions. Key considerations such as energy efficiency, output capacity, and suitability for specific applications are dissected, providing a clear roadmap for selecting the right product for your business needs.
Moreover, we will cover critical factors such as cost implications, maintenance requirements, and the latest advancements in technology, ensuring that your procurement strategy aligns with current market trends. Whether you’re operating in a bustling Nigerian manufacturing hub or a high-tech facility in Germany, this guide is designed to equip you with the knowledge necessary to harness the full potential of your electrical energy solutions. Embrace the opportunity to enhance your energy management strategy with insights that bridge the gap between technical understanding and practical application.
Table Of Contents
- Top 4 Difference In Alternator And Generator Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for difference in alternator and generator
- Understanding difference in alternator and generator Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of difference in alternator and generator
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘difference in alternator and generator’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for difference in alternator and generator
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for difference in alternator and generator
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘difference in alternator and generator’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for difference in alternator and generator Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing difference in alternator and generator With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for difference in alternator and generator
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the difference in alternator and generator Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of difference in alternator and generator
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for difference in alternator and generator
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Understanding difference in alternator and generator Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alternator | Converts mechanical energy to AC; stationary armature; efficient energy use. | Automotive industry, renewable energy systems, backup power systems. | Pros: Higher efficiency, compact size, less maintenance. Cons: Cannot charge dead batteries, limited to AC output. |
| DC Generator | Converts mechanical energy to DC; rotating armature; requires commutator. | Industrial applications, battery charging, electric vehicles. | Pros: Suitable for battery charging, stable DC output. Cons: Larger size, more maintenance due to brush wear. |
| AC Generator | Converts mechanical energy to AC; rotating armature; used in power plants. | Large-scale electricity generation, remote locations, construction sites. | Pros: High power output, versatile applications. Cons: Requires more space, complex installation. |
| Inverter Generator | Combines generator and inverter technology; produces clean AC power. | Small business operations, outdoor events, remote work sites. | Pros: Quiet operation, portable, stable output. Cons: Limited power output, higher initial cost. |
| Synchronous Generator | Operates at constant speed; used in conjunction with grid systems. | Power plants, large industrial facilities, renewable energy integration. | Pros: High efficiency and reliability, suitable for large power needs. Cons: Complex controls, higher installation costs. |
What are the Key Characteristics of Alternators for B2B Buyers?
Alternators are devices that efficiently convert mechanical energy into alternating current (AC). They feature a stationary armature, which minimizes wear and maintenance needs, making them ideal for applications in the automotive sector and renewable energy systems. Their ability to adjust output based on load conditions allows for effective energy conservation. B2B buyers should consider their operational efficiency and size, particularly when space is limited, but should also note that they are not suitable for charging completely drained batteries.
Why Choose DC Generators for Specific Industrial Applications?
DC generators are designed to convert mechanical energy into direct current (DC) and are particularly useful in industrial applications where stable DC power is necessary, such as battery charging and powering electric vehicles. They utilize a rotating armature and require a commutator, which can lead to increased maintenance due to brush wear. Buyers should evaluate their needs for consistent DC output against the generator’s larger footprint and maintenance requirements.
How Do AC Generators Serve Large-Scale Power Needs?
AC generators are fundamental in large-scale electricity generation, commonly employed in power plants and construction sites. They convert mechanical energy into alternating current with a rotating armature, which allows for high power outputs. Their versatility makes them suitable for a range of applications, but B2B buyers must consider the space required for installation and the complexity involved in setup.
What Advantages Do Inverter Generators Offer for Small Businesses?
Inverter generators combine the functionality of traditional generators with inverter technology, producing clean, stable AC power. They are ideal for small business operations, outdoor events, and remote work sites due to their portability and quiet operation. However, B2B buyers should be aware of their limited power output and higher initial costs, making them best suited for applications where noise and space are concerns.
Why are Synchronous Generators Important for Power Plants?
Synchronous generators are critical in power generation, operating at a constant speed to maintain grid stability. They are commonly used in power plants and large industrial facilities, providing high efficiency and reliability for substantial power needs. However, their complexity in control systems and higher installation costs are important considerations for B2B buyers looking to integrate these generators into existing infrastructure.
Key Industrial Applications of difference in alternator and generator
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of difference in alternator and generator | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Use of alternators in vehicle electrical systems | Improved energy efficiency and battery longevity | Compatibility with vehicle models and voltage ratings |
| Renewable Energy | Generators in wind and hydroelectric power systems | Reliable power generation and energy independence | Output capacity, fuel type, and maintenance requirements |
| Construction | Generators for temporary power supply on job sites | Continuous power for tools and equipment | Portability, fuel efficiency, and noise levels |
| Telecommunications | Alternators in backup power systems for data centers | Enhanced reliability and reduced operational costs | Load capacity, efficiency ratings, and installation space |
| Industrial Manufacturing | Generators for emergency power in manufacturing plants | Minimization of downtime and operational disruptions | Fuel type, output capacity, and compliance with local regulations |
How Are Alternators and Generators Used in the Automotive Industry?
In the automotive sector, alternators are crucial for charging the vehicle’s battery and powering electrical systems while the engine runs. The efficiency of alternators helps prevent battery overcharging, which extends battery life and reduces maintenance costs. B2B buyers in this industry must consider the compatibility of alternators with various vehicle models and the specific voltage ratings required for optimal performance. This is particularly important for manufacturers and suppliers in regions like Germany, where automotive standards are stringent.
What Role Do Generators Play in Renewable Energy Applications?
Generators are fundamental in renewable energy sectors, particularly in wind and hydroelectric systems, where they convert mechanical energy into electrical energy. These generators provide a reliable source of power, contributing to energy independence and sustainability. For international buyers, sourcing generators involves evaluating output capacity and fuel types, as well as understanding the maintenance requirements to ensure long-term operation. This is especially relevant for countries in Africa and South America, where access to reliable electricity can be challenging.
How Are Generators Utilized in Construction Projects?
In the construction industry, generators serve as a vital power source for tools and equipment on job sites. They provide continuous energy, ensuring that work progresses without interruptions due to power outages. B2B buyers should focus on portability, fuel efficiency, and noise levels when sourcing generators for construction, as these factors can significantly impact operational efficiency. Particularly in regions with less stable power grids, like parts of the Middle East, reliable generators are essential for maintaining productivity.
Why Are Alternators Important in Telecommunications?
In telecommunications, alternators are used in backup power systems to ensure data centers remain operational during power outages. Their ability to provide efficient and reliable power helps reduce operational costs and enhances overall system reliability. For B2B buyers, key considerations include the load capacity of the alternators and their efficiency ratings, as these will directly affect the performance of critical telecommunications infrastructure across Europe.
How Do Generators Support Manufacturing Operations?
Generators are critical in manufacturing plants, providing emergency power to minimize downtime during outages. This capability helps maintain productivity and operational efficiency, which is crucial for businesses that rely on continuous production processes. When sourcing generators, companies must evaluate factors such as fuel type, output capacity, and compliance with local regulations, ensuring that they meet specific operational needs while adhering to environmental standards, especially in regions with strict industrial regulations.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘difference in alternator and generator’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Understanding Energy Efficiency for Cost Reduction
The Problem: Many B2B buyers, particularly in industries like manufacturing and construction, struggle to differentiate between alternators and generators. This confusion can lead to poor investment decisions, resulting in higher operational costs. For instance, a company might choose a generator for a project where an alternator would be more efficient, leading to unnecessary energy consumption and inflated utility bills.
The Solution: To address this challenge, it is crucial for businesses to conduct a thorough analysis of their energy needs. Buyers should focus on the efficiency ratings of both devices. Opt for alternators when the application requires high efficiency and load-dependent power generation, especially in automotive or smaller-scale applications. Conversely, if the business requires a reliable power source for larger installations, generators may be preferable. It’s advisable to consult with equipment specialists to evaluate specific operational requirements and select the right solution that balances efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Scenario 2: Dealing with Maintenance and Longevity Issues
The Problem: B2B buyers often face challenges with the maintenance and lifespan of their electrical devices. For example, organizations using generators may experience more frequent breakdowns due to the wear and tear on brushes and components, leading to increased downtime and repair costs. This situation is exacerbated when companies are unaware of the differences in design and operation between alternators and generators.
The Solution: Understanding the mechanical differences between these two devices is essential for effective maintenance planning. Alternators have stationary armatures and rotating magnetic fields, which result in less wear on brushes compared to generators. Buyers should prioritize the purchase of alternators for applications where low maintenance and durability are critical. Additionally, implementing a regular maintenance schedule that includes inspections and cleanings can help extend the life of both alternators and generators. Working closely with experienced suppliers can also provide insights into best practices for maintaining equipment longevity.
Scenario 3: Ensuring Compatibility with Existing Systems
The Problem: In sectors like construction and energy, businesses often need to integrate new power solutions into existing infrastructure. A common pain point arises when a buyer selects a generator or alternator that is incompatible with their current systems. This can lead to performance issues and additional costs for retrofitting or replacing existing equipment, causing project delays and budget overruns.
The Solution: To prevent compatibility issues, it is vital for buyers to conduct a comprehensive assessment of their current electrical systems before making a purchase. This includes evaluating voltage requirements, current types (AC or DC), and physical space constraints. Buyers should engage with suppliers who provide detailed specifications and compatibility assessments for their products. Furthermore, involving a qualified electrical engineer early in the selection process can ensure that the chosen alternator or generator aligns with existing systems, reducing the risk of unforeseen challenges and ensuring a smoother integration.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for difference in alternator and generator
What Materials Are Commonly Used in Alternators and Generators?
When selecting materials for alternators and generators, several key properties and performance factors must be considered. The choice of materials affects durability, efficiency, and overall application suitability. Below, we analyze four common materials used in the construction of these devices: copper, aluminum, steel, and composite materials.
How Does Copper Impact Performance in Alternators and Generators?
Copper is widely recognized for its excellent electrical conductivity, making it a preferred choice for windings in both alternators and generators. Its high thermal and electrical conductivity ensures efficient energy transfer, which is critical for performance. Copper also offers good corrosion resistance, particularly when coated, and can withstand high temperatures without significant degradation.
Pros and Cons: The primary advantage of copper is its superior conductivity, which leads to better efficiency and performance. However, copper is relatively expensive compared to other materials, which can increase manufacturing costs. Additionally, its weight can be a disadvantage in applications where reducing weight is crucial.
Impact on Application: Copper windings are ideal for applications requiring high efficiency and reliability, such as automotive alternators and industrial generators. Its compatibility with various media makes it versatile, but international buyers should consider the implications of sourcing copper in terms of environmental regulations and ethical sourcing.
What Role Does Aluminum Play in Alternators and Generators?
Aluminum is another common material used in the manufacturing of alternators and generators, particularly for windings and casings. It is lightweight and has decent electrical conductivity, though not as high as copper. Aluminum also provides good resistance to corrosion, especially when anodized, and is often used in applications where weight reduction is a priority.
Pros and Cons: The main advantage of aluminum is its lower cost and lighter weight, making it suitable for applications where reducing overall weight is essential. However, its lower conductivity compared to copper can lead to reduced efficiency, particularly in high-performance applications.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is often used in automotive and portable generator applications where weight and cost are critical factors. International buyers should be aware of standards related to aluminum use, such as ASTM and DIN, to ensure compliance and compatibility with local regulations.
How Does Steel Contribute to the Structural Integrity of Alternators and Generators?
Steel is commonly used for the structural components of alternators and generators, including frames, housings, and magnetic cores. Its high tensile strength and durability make it suitable for withstanding mechanical stresses and environmental conditions. Steel components can also be treated to enhance their corrosion resistance, extending their lifespan.
Pros and Cons: The primary advantage of steel is its strength and durability, which ensures long-term reliability in demanding environments. However, steel is heavier than aluminum and can be more susceptible to rust if not properly treated, which may necessitate additional protective coatings.
Impact on Application: Steel is often used in industrial generators and heavy-duty alternators where robust performance is required. Buyers from regions with high humidity or corrosive environments, such as parts of Africa and South America, should consider corrosion-resistant steel options to ensure longevity.
What Are the Benefits of Using Composite Materials in Alternators and Generators?
Composite materials, such as fiberglass or carbon fiber, are increasingly being used in alternators and generators for specific applications. These materials offer a unique combination of lightweight properties and high strength, making them suitable for specialized components like rotor housings and insulation.
Pros and Cons: The main advantage of composites is their lightweight nature and resistance to corrosion, which can enhance the overall efficiency of the device. However, composites can be more expensive to manufacture and may require specialized processes, which can complicate production.
Impact on Application: Composites are particularly beneficial in applications where weight savings are critical, such as aerospace or high-performance automotive generators. Buyers should ensure that any composite materials used meet relevant international standards for safety and performance.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Alternators and Generators
| Material | Typical Use Case for difference in alternator and generator | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Copper | Windings in alternators and generators | Superior electrical conductivity | High cost and weight | High |
| Aluminum | Windings and casings in automotive applications | Lightweight and cost-effective | Lower conductivity than copper | Medium |
| Steel | Structural components in heavy-duty generators | High strength and durability | Heavier and susceptible to rust | Medium |
| Composite | Specialized components in high-performance applications | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Higher manufacturing complexity and cost | High |
This strategic material selection guide provides B2B buyers with essential insights into the materials used in alternators and generators, helping them make informed decisions based on performance, cost, and application suitability.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for difference in alternator and generator
What Are the Key Manufacturing Processes for Alternators and Generators?
Manufacturing alternators and generators involves several stages, each crucial for ensuring the final product meets quality and performance standards. Understanding these processes allows B2B buyers to evaluate potential suppliers effectively.
Illustrative image related to difference in alternator and generator
Material Preparation: What Materials Are Used in Alternators and Generators?
The manufacturing process begins with selecting high-quality materials. Common materials include:
- Copper: Used for windings due to its excellent conductivity.
- Silicon Steel: Essential for the magnetic core, providing high magnetic permeability and low losses.
- Aluminum: Often used in the casing for its lightweight properties and corrosion resistance.
- Insulating Materials: Such as varnish and epoxies are used to prevent short circuits and enhance durability.
The material selection is critical, as the quality directly impacts the efficiency and longevity of the alternators and generators.
How Are Alternators and Generators Formed During Manufacturing?
Once materials are prepared, the next stage is forming. This typically involves:
- Stamping and Cutting: Sheets of silicon steel are stamped and cut into core shapes. This step is crucial for achieving the desired magnetic properties and reducing eddy current losses.
- Winding: Copper wire is wound around the core to create the armature or stator. The winding process can be done using automated machines to ensure precision and consistency.
- Machining: Components may require additional machining to meet specific tolerances, ensuring that parts fit together accurately during assembly.
These processes are essential for ensuring that the alternators and generators perform efficiently and reliably.
What Assembly Techniques Are Commonly Used for Alternators and Generators?
The assembly stage is where all components come together. Key techniques include:
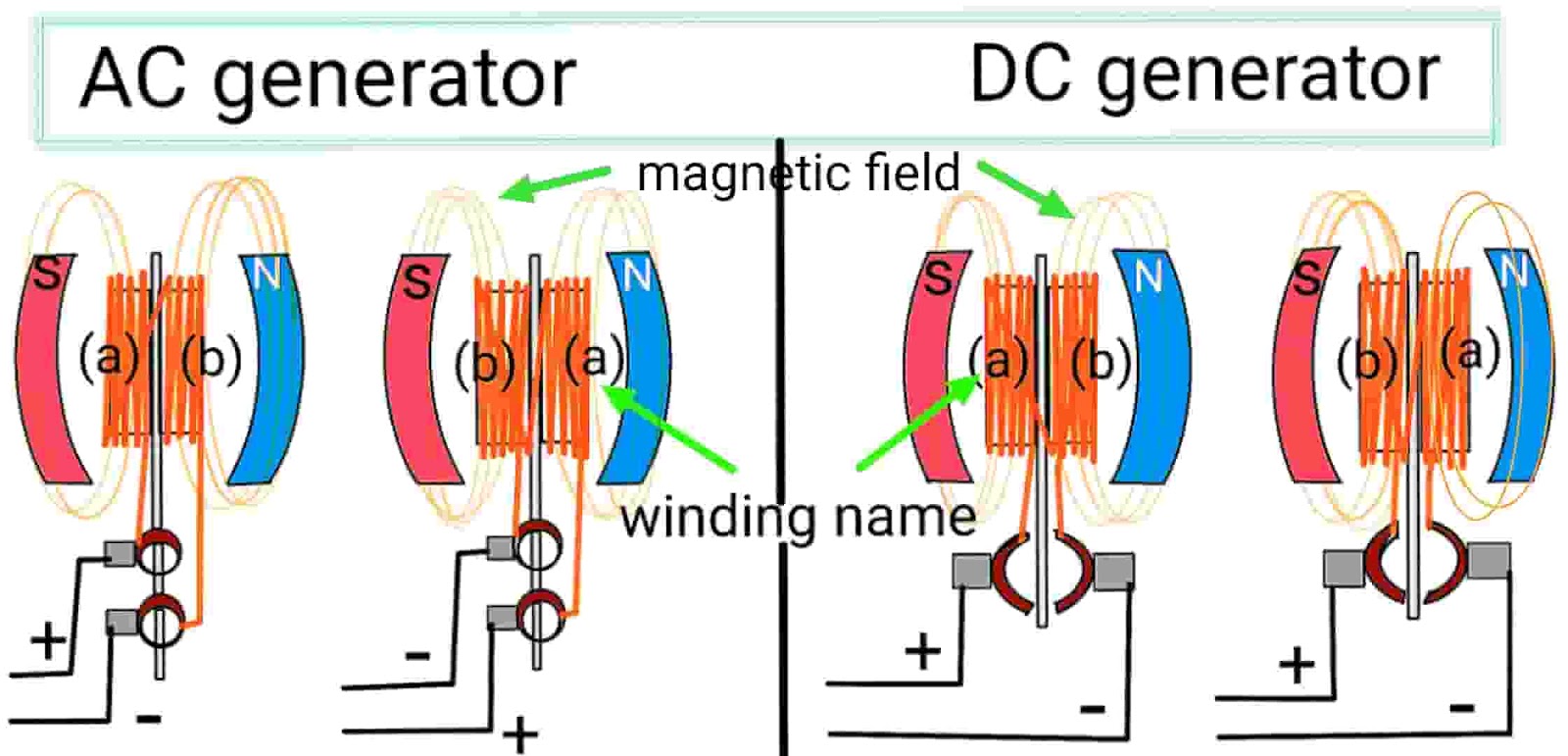
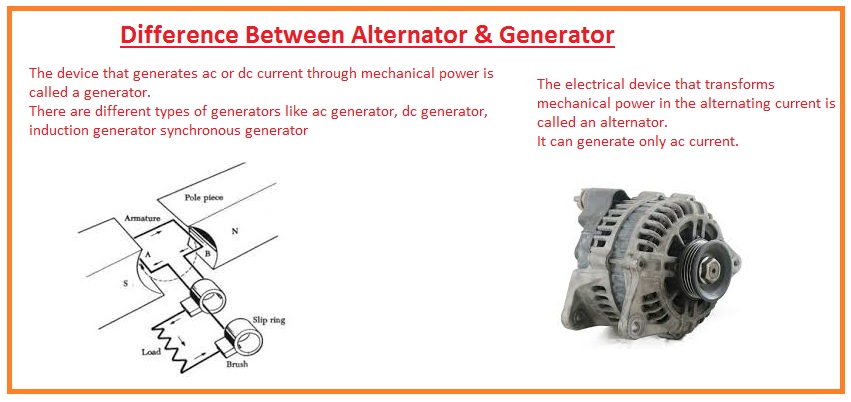
- Component Assembly: The rotor and stator are assembled, ensuring proper alignment. For alternators, the rotor is typically the rotating magnetic field, while in generators, the armature rotates within a fixed magnetic field.
- Electrical Connections: Connections are made using brushes (in alternators) or commutators (in generators) to ensure efficient electrical transfer. This stage requires precision to avoid issues such as voltage drop or excessive wear.
- Encapsulation: Many manufacturers encapsulate components with insulating materials to protect against environmental factors and improve durability.
Effective assembly techniques can significantly influence the performance and reliability of the final product.
What Finishing Processes Are Essential for Quality Alternators and Generators?
The finishing stage enhances the product’s performance and appearance. This includes:
- Surface Treatment: Coatings may be applied to prevent corrosion and improve aesthetics. Techniques like anodizing or powder coating are common.
- Quality Checks: Initial quality checks are performed before products move to final testing. This includes visual inspections and dimensional checks to ensure compliance with specifications.
Finishing processes not only enhance appearance but also contribute to the longevity and reliability of the units.
What Quality Assurance Standards Should Buyers Look For?
Quality assurance is crucial in the manufacturing of alternators and generators. International standards, such as ISO 9001, provide a framework for quality management systems. Compliance with these standards indicates that manufacturers follow best practices in production and quality control.
Illustrative image related to difference in alternator and generator
Which Industry-Specific Certifications Are Relevant for Alternators and Generators?
In addition to ISO standards, certain industry-specific certifications may be applicable:
- CE Marking: Indicates compliance with European safety and environmental standards, essential for buyers in Europe.
- API Standards: Relevant for generators used in the oil and gas sector, ensuring they meet specific operational criteria.
Certification helps buyers ascertain that the products meet necessary regulatory and performance standards.
How Do Quality Control Checkpoints Function in the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control checkpoints are integral to ensuring product quality at various stages of manufacturing:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Raw materials undergo inspection upon arrival. This ensures that only high-quality materials are used in production.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Inspections occur during the manufacturing process to detect defects early. This can include checking the dimensions of machined parts or the quality of windings.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): The final product undergoes comprehensive testing, including electrical testing and performance evaluations, to ensure it meets all specifications before shipment.
These checkpoints help minimize defects and ensure consistent product quality.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used in Quality Assurance?
Testing methods for alternators and generators can vary, but common techniques include:
- Electrical Testing: To assess voltage output, current capacity, and efficiency.
- Thermal Imaging: Identifies potential hot spots that could indicate electrical faults or inefficiencies.
- Vibration Analysis: Monitors mechanical stability and helps predict potential failures.
These testing methods are crucial for verifying that products can perform reliably in the field.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
B2B buyers can take several steps to verify a supplier’s quality control practices:
- Supplier Audits: Conducting audits of the manufacturing facility can provide insight into the quality management system and manufacturing practices.
- Reviewing Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports and testing documentation can help assess compliance with standards.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection agencies can provide an unbiased assessment of product quality before shipment.
These practices ensure that buyers can trust the quality of the products they purchase.
What Are the Nuances of Quality Control for International B2B Buyers?
International buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, must consider specific nuances in quality control:
- Regulatory Compliance: Different regions have varying standards and regulations. Understanding local requirements is essential for ensuring compliance.
- Logistical Considerations: Shipping and handling can impact product quality. Buyers should ensure that suppliers have robust packaging and transportation strategies.
- Cultural Differences: Communication styles and business practices can vary. Establishing clear expectations and maintaining regular communication is vital for successful partnerships.
By understanding these nuances, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of international procurement more effectively.
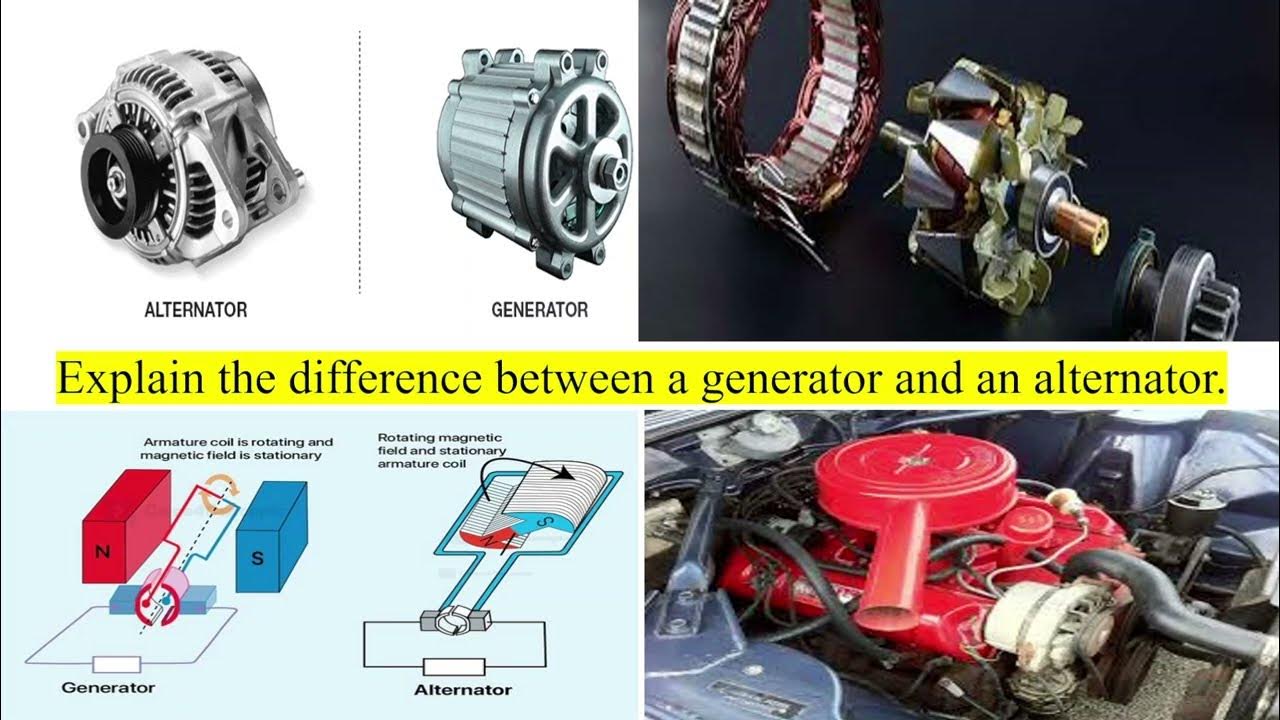
Illustrative image related to difference in alternator and generator
In conclusion, the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for alternators and generators are complex yet essential for ensuring product reliability and performance. B2B buyers must be diligent in assessing suppliers to ensure they meet their quality standards and regulatory requirements.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘difference in alternator and generator’
To assist B2B buyers in understanding the differences between alternators and generators, this practical sourcing guide provides a step-by-step checklist. It will help you make informed decisions when procuring these vital electrical devices for your operations.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establish the specific requirements for your application, including the type of electrical output needed (AC or DC), efficiency ratings, and size constraints. Clearly defining these specifications will streamline your sourcing process and ensure that you select the right equipment for your needs. Consider how the alternator or generator will integrate with existing systems and any regulatory compliance required in your region.
Step 2: Identify Your Application Needs
Different industries have unique demands when it comes to power generation. Assess whether you require an alternator for automotive applications or a generator for large-scale power production. Understanding your application will guide you in choosing the right equipment that meets operational efficiency and performance criteria.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a supplier, conduct a thorough evaluation of their capabilities. Request detailed company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in similar industries or regions. Look for suppliers who demonstrate expertise in manufacturing both alternators and generators, as this indicates a broader understanding of electrical systems.
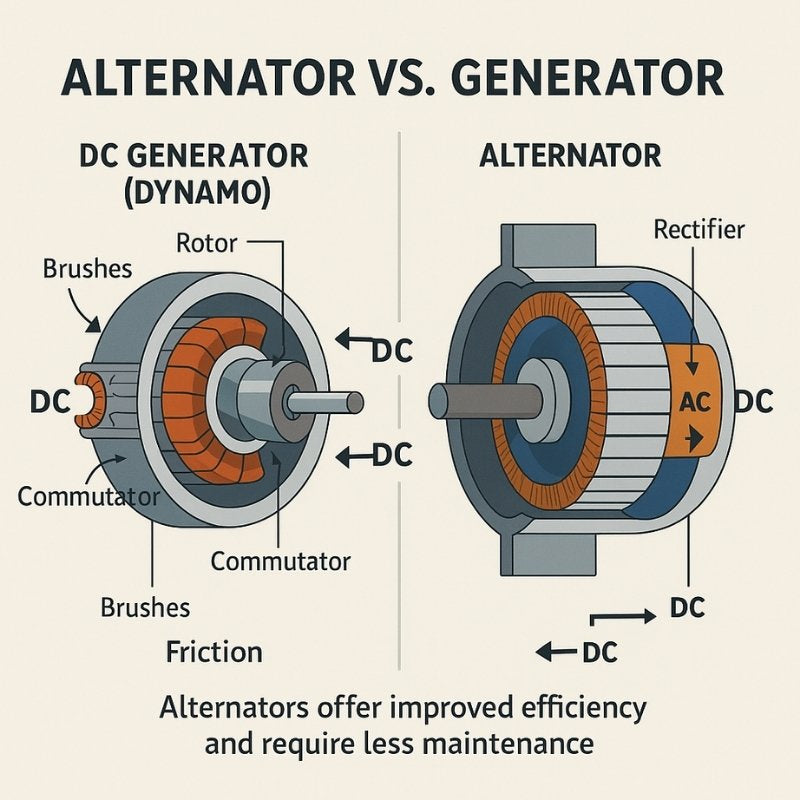
Illustrative image related to difference in alternator and generator
- Check for certifications: Ensure that suppliers comply with international standards and local regulations relevant to your industry.
- Review customer feedback: Investigate online reviews and testimonials to gauge the reliability and performance of the supplier’s products.
Step 4: Assess Product Quality and Efficiency
Quality and efficiency are crucial factors in your selection process. Compare the efficiency ratings of different models, as higher efficiency translates into lower operational costs and better performance. Look for products that have undergone rigorous testing and come with performance guarantees.
- Examine materials used: Quality materials often enhance the lifespan and reliability of the device.
- Consider warranty options: A solid warranty can provide peace of mind regarding product durability and supplier commitment.
Step 5: Review After-Sales Support and Service
Strong after-sales support is essential for maintaining operational efficiency. Inquire about the support services offered by potential suppliers, such as installation assistance, maintenance plans, and troubleshooting support. This is especially important for complex systems that may require specialized knowledge for optimal operation.
- Check for local support: Suppliers with local service centers can provide quicker response times for any issues that arise.
- Assess training offerings: Some suppliers may offer training for your staff on optimal equipment usage and maintenance.
Step 6: Compare Pricing and Total Cost of Ownership
While pricing is a key consideration, it’s important to look beyond the initial purchase cost. Assess the total cost of ownership, which includes installation, maintenance, and operational costs over the device’s lifespan. This comprehensive view will help you make a more informed financial decision.
- Get multiple quotes: Request quotes from several suppliers to compare pricing structures and included services.
- Negotiate terms: Don’t hesitate to negotiate payment terms or bulk purchase discounts, which can further reduce your overall costs.
Step 7: Make an Informed Decision
After gathering all necessary information and evaluating options, make a decision based on your research and analysis. Ensure that the chosen alternator or generator aligns with your operational needs and budget constraints. Document your decision-making process for future reference and to assist with any procurement audits.
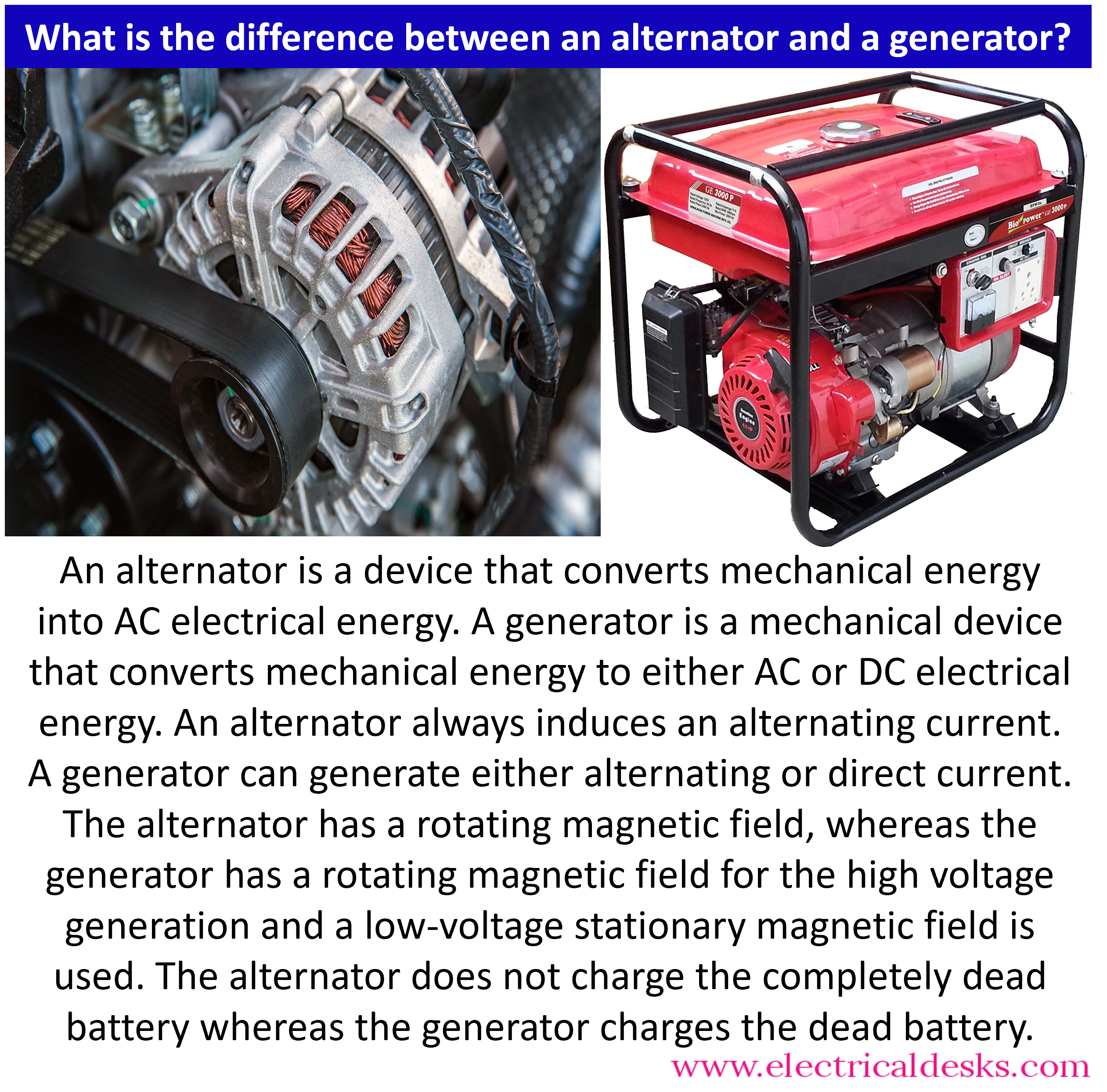
Illustrative image related to difference in alternator and generator
Following this checklist will equip B2B buyers with the necessary insights to navigate the complexities of sourcing alternators and generators, ensuring a successful procurement process.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for difference in alternator and generator Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Alternators and Generators?
When sourcing alternators and generators, understanding the cost structure is vital for B2B buyers. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margins.
-
Materials: The choice of raw materials significantly affects the cost. Alternators often use higher-quality materials for their magnetic components to improve efficiency, while generators may have more variable material costs depending on their design (AC or DC). Copper, steel, and magnets are common materials influencing costs.
-
Labor: Labor costs can vary depending on the manufacturing location. Countries with lower labor costs, such as some in Africa and South America, may offer competitive pricing. However, this may come with trade-offs in quality and consistency.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with factory operations, utilities, and equipment depreciation. In regions with advanced manufacturing capabilities, overhead can be higher, impacting overall pricing.
-
Tooling: Initial tooling costs can be substantial, especially for custom designs. These costs are typically amortized over the production volume, meaning larger orders can lead to lower per-unit costs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous QC processes are essential for ensuring reliability, especially in critical applications. These costs can vary widely based on the quality certifications required (ISO, CE, etc.) and the complexity of the products.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs, including freight and customs duties, are critical for international buyers. Understanding Incoterms can help buyers assess their responsibilities and potential additional costs.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically include a profit margin that can vary based on market conditions and competition. High-quality or highly specialized products may command higher margins.
How Do Price Influencers Affect the Cost of Alternators and Generators?
Several factors influence pricing beyond the base cost components. Key influencers include:
-
Volume/MOQ: Minimum order quantities (MOQs) can impact pricing significantly. Bulk orders often lead to reduced per-unit costs, making it more economical for larger enterprises.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized products may incur additional costs due to the need for specialized materials or designs. It’s essential to clearly define requirements to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher quality materials and certifications can increase costs but improve reliability and lifespan. Buyers should balance upfront costs with long-term benefits.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can influence pricing. Established suppliers may offer better warranties and support, which can justify higher costs.
-
Incoterms: Different Incoterms (e.g., FOB, CIF) can alter the total cost of ownership by defining responsibilities for shipping and insurance. Buyers should choose terms that align with their logistics capabilities.
What Are the Best Negotiation Strategies for International B2B Buyers?
For international buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, effective negotiation strategies can lead to better pricing and terms. Here are some tips:
-
Research Market Rates: Understanding current market prices for alternators and generators can provide leverage in negotiations.
-
Discuss Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Focus on the TCO rather than just the purchase price. Highlighting lower maintenance and operational costs can justify a higher initial investment.
-
Build Relationships: Establishing long-term relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing, terms, and service. Suppliers may be more willing to negotiate for repeat business.
-
Leverage Volume Discounts: If feasible, consolidate orders or collaborate with other buyers to meet MOQs and secure volume discounts.
-
Be Open to Alternative Solutions: Sometimes, suppliers can offer alternatives that meet your needs at a lower cost. Being flexible can lead to better deals.
Conclusion
In summary, understanding the intricate cost structure and pricing influencers of alternators and generators is essential for B2B buyers. By strategically negotiating and considering the total cost of ownership, buyers can make informed decisions that enhance their procurement processes. Always remember to approach sourcing with a clear understanding of your requirements and market dynamics to optimize costs effectively.
Illustrative image related to difference in alternator and generator
Disclaimer: Prices and costs mentioned are indicative and can vary based on market conditions, supplier negotiations, and specific project requirements.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing difference in alternator and generator With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to Alternators and Generators
When considering power generation solutions, it’s essential to evaluate not only the differences between alternators and generators but also viable alternatives that can meet specific business needs. Understanding how these technologies compare can help international B2B buyers make informed decisions based on performance, cost, and application requirements.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Difference In Alternator And Generator | Solar Power Systems | Battery Energy Storage Systems |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High efficiency, produces AC only | Variable efficiency depending on sunlight | High efficiency, delivers stored energy on demand |
| Cost | Generally higher initial cost but lower long-term maintenance | High upfront costs, incentives available | Moderate initial investment, cost-effective in long run |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires mechanical setup, less flexible | Requires space, dependent on location and weather | Easy to install, scalable solutions |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance due to stationary armature | Moderate maintenance, mainly for panels | Low maintenance, battery replacement every few years |
| Best Use Case | Automotive and small-scale applications | Ideal for renewable energy needs, remote locations | Suitable for backup power and peak demand management |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Solar Power Systems
Solar power systems harness energy from the sun through photovoltaic panels, converting sunlight directly into electricity. This renewable energy solution is particularly beneficial in regions with abundant sunlight, making it an attractive option for businesses in Africa and South America. The initial investment can be significant, but government incentives often offset costs, making it a financially viable option in the long run. However, solar energy production can be inconsistent due to weather variability, which may necessitate complementary energy sources.
Battery Energy Storage Systems
Battery energy storage systems (BESS) offer a flexible and efficient way to store electrical energy for later use. These systems are ideal for businesses looking to manage energy costs by storing energy during low-demand periods and using it during peak times. The technology has advanced significantly, allowing for scalable solutions that can be tailored to specific needs. While the initial investment may be moderate, the long-term savings on energy costs and the ability to provide backup power can make BESS a cost-effective alternative to traditional generators and alternators.
Conclusion: Making the Right Choice for Your Business
Choosing between alternators, generators, and alternative solutions like solar power and battery storage requires careful consideration of specific business needs, including performance, cost, and maintenance. For businesses in regions with abundant sunlight, solar power may provide a sustainable and cost-effective solution. Conversely, those needing reliable backup power and energy management may find battery energy storage systems more suited to their requirements. Ultimately, a thorough analysis of each option’s benefits and limitations will empower B2B buyers to select the best solution that aligns with their operational goals and budget constraints.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for difference in alternator and generator
What Are the Key Technical Properties Distinguishing Alternators from Generators?
Understanding the technical specifications of alternators and generators is crucial for B2B buyers, especially when making investment decisions for energy solutions. Here are some critical specifications that differentiate these two devices:
-
Output Current Type
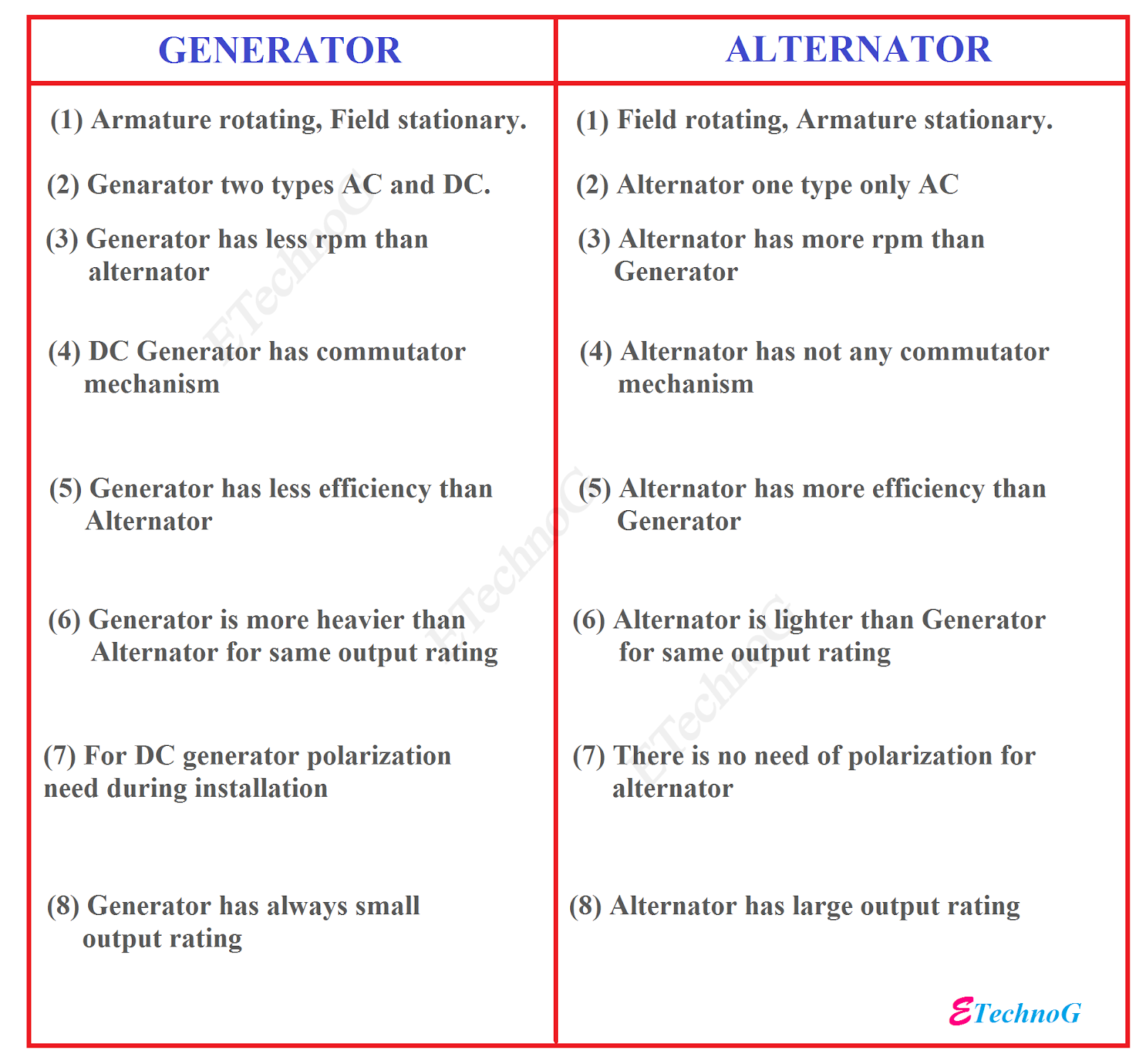
– Definition: Alternators produce alternating current (AC), while generators can produce both AC and direct current (DC).
– B2B Importance: The choice between AC and DC impacts the type of electrical systems you can support. For instance, AC is typically used for large-scale power distribution, while DC is essential for specific applications like battery charging. -
Energy Efficiency
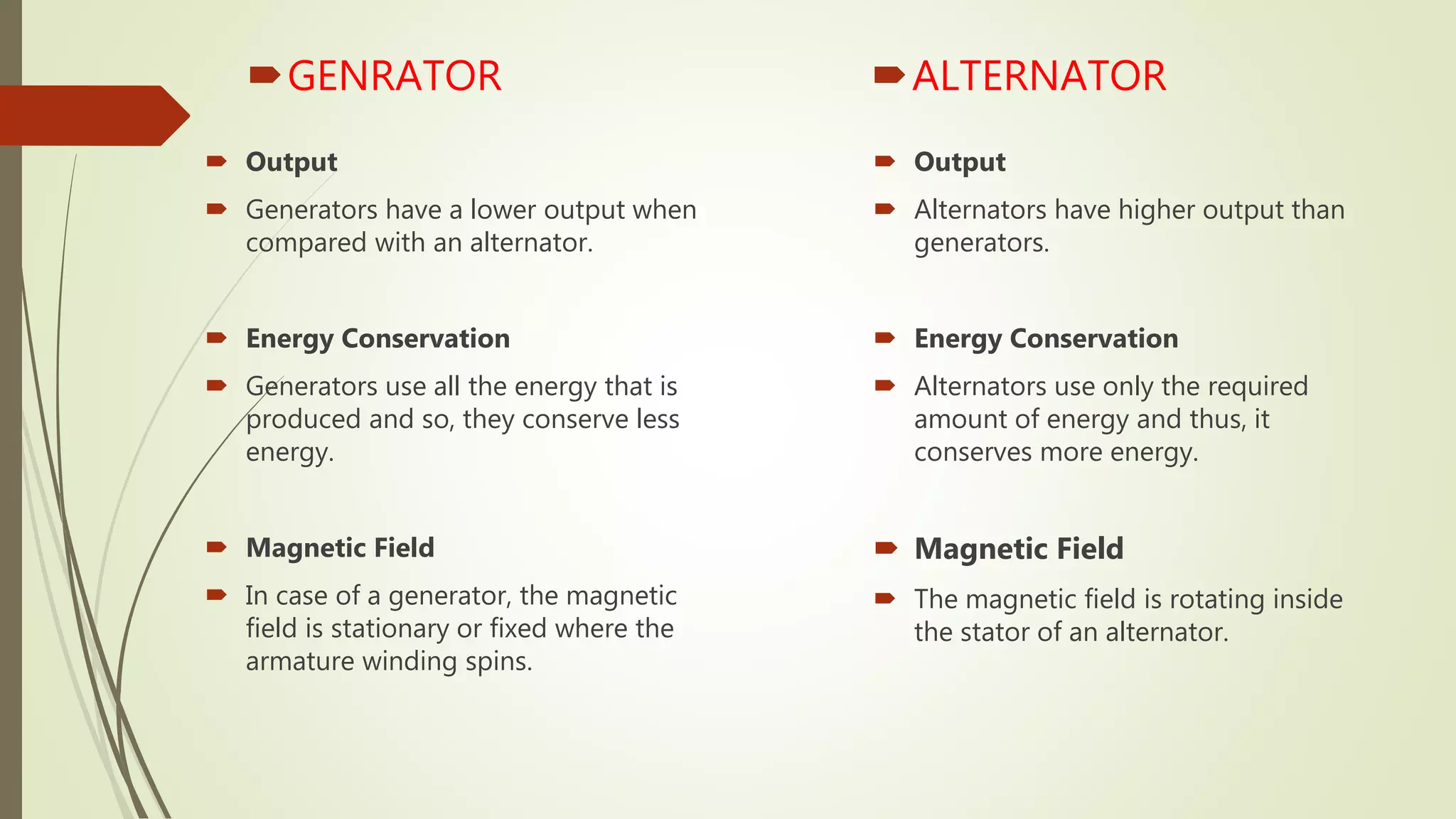
– Definition: Alternators are generally more energy-efficient than generators.
– B2B Importance: Higher efficiency translates to lower operational costs over time, a significant consideration for companies looking to minimize energy expenditures. An efficient system can also lead to reduced emissions, aligning with sustainability goals. -
Size and Weight
– Definition: Alternators are typically smaller and lighter than generators.
– B2B Importance: The compact design of alternators makes them easier to install and transport, which is advantageous for businesses with limited space or those requiring mobile energy solutions. -
Maintenance Requirements
– Definition: Alternators usually require less maintenance due to their stationary armature and longer-lasting brushes.
– B2B Importance: Reduced maintenance needs can lead to lower downtime and operational disruptions, which is crucial for businesses that rely on continuous power supply. -
Power Generation Capability
– Definition: Alternators can produce power only when needed, while generators produce power continuously.
– B2B Importance: This distinction is vital for businesses with variable energy demands. An alternator’s ability to adjust its output can help in managing energy costs effectively.
What Are the Common Trade Terms Related to Alternators and Generators?
Familiarity with industry terminology can facilitate smoother transactions and negotiations. Here are some essential terms relevant to alternators and generators:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Definition: A company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer.
– B2B Importance: Understanding OEM relationships helps businesses ensure they are sourcing quality components for their energy systems, which can affect performance and reliability. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– Definition: The smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell.
– B2B Importance: Knowing the MOQ can help businesses manage inventory effectively and understand financial commitments before placing large orders. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– Definition: A document issued by a buyer to request pricing information from suppliers.
– B2B Importance: Issuing an RFQ enables companies to gather competitive pricing and terms, aiding in budget planning and supplier selection. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Definition: A set of rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions.
– B2B Importance: Understanding Incoterms is essential for international B2B transactions to clarify shipping responsibilities, costs, and risks, ensuring smoother logistics. -
Wattage Rating
– Definition: The maximum electrical power output of an alternator or generator, measured in watts.
– B2B Importance: Knowing the wattage rating helps businesses determine the suitability of a power solution for their specific energy needs, ensuring they select the right equipment for their applications. -
Load Factor
– Definition: The ratio of the actual output of a power plant to its potential output over a specific period.
– B2B Importance: A high load factor indicates efficient use of power resources, which can be critical for businesses focused on maximizing energy efficiency and reducing costs.
Understanding these technical properties and trade terms can empower B2B buyers to make informed decisions when sourcing alternators and generators, ensuring alignment with their operational needs and strategic goals.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the difference in alternator and generator Sector
What Are the Global Drivers Influencing the Alternator and Generator Market?
The alternator and generator market is experiencing significant growth driven by increasing demand for reliable energy sources across various sectors, including automotive, construction, and renewable energy. As countries in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe face energy challenges, the need for efficient power generation technologies becomes paramount. Technological advancements, such as improved energy efficiency and the integration of digital technologies for monitoring and predictive maintenance, are reshaping the market landscape. Buyers should be aware that the shift towards renewable energy sources is also prompting a rise in hybrid systems, combining alternators and generators to optimize power generation and consumption.
Emerging trends include the growing popularity of portable generators, especially in regions prone to power outages, and the increasing use of alternators in electric vehicles (EVs) due to their efficiency in battery charging. This trend is particularly relevant for international buyers looking to source equipment that aligns with the global push for sustainability. Additionally, as industries strive for cost-effective solutions, the trend towards modular systems that allow for scalability and easy maintenance is gaining traction. B2B buyers should focus on suppliers that offer innovative solutions tailored to their specific market needs.
How Does Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact the Alternator and Generator Industry?
Sustainability has become a crucial consideration for B2B buyers in the alternator and generator sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes, including energy consumption and waste generation, necessitates a focus on sustainable practices. Buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers that adhere to environmentally friendly standards and demonstrate a commitment to reducing their carbon footprint. This includes sourcing materials that are recyclable or produced with minimal environmental impact.
Ethical supply chains are equally important, particularly in regions where labor practices may be scrutinized. B2B buyers should seek suppliers with certifications that reflect their commitment to ethical sourcing, such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and Fair Trade certifications. Moreover, the integration of green technologies in both alternators and generators is becoming a vital differentiator in the market. Products that incorporate energy-efficient designs and use sustainable materials not only reduce operational costs but also enhance brand reputation among environmentally conscious consumers.
Illustrative image related to difference in alternator and generator
What Is the Historical Context of Alternators and Generators in the B2B Landscape?
The evolution of alternators and generators dates back to the late 19th century, with significant advancements in electromagnetic theory paving the way for their development. Early generators primarily produced direct current (DC), which limited their applications. The introduction of the alternating current (AC) system by Nikola Tesla and others revolutionized the industry, leading to the widespread adoption of alternators in various applications.
In recent decades, the focus has shifted towards enhancing efficiency and reliability, spurred by global energy demands and technological innovations. The integration of microprocessors for better performance monitoring and automation reflects the industry’s response to modern energy challenges. As B2B buyers navigate this historical context, understanding the technological advancements and market shifts can inform their sourcing strategies and product selections, ensuring they remain competitive in a rapidly evolving landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of difference in alternator and generator
-
What are the key differences between alternators and generators?
Alternators convert mechanical energy into alternating current (AC), while generators can produce both alternating current (AC) and direct current (DC). Additionally, alternators are generally more efficient and have a higher output compared to generators. The magnetic field in an alternator rotates around a stationary armature, whereas in a generator, the armature rotates within a fixed magnetic field. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for selecting the right equipment for specific applications, especially in industries requiring reliable power supply solutions. -
How does efficiency impact the choice between alternators and generators?
Efficiency is a critical factor for B2B buyers, particularly in terms of operational costs and energy conservation. Alternators are designed to be more efficient, only producing energy as needed, which minimizes waste and can lead to lower operational costs over time. Generators, while versatile, typically consume more energy and may result in higher fuel costs. For businesses focused on sustainability and reducing overhead, opting for an alternator can be a more economically sound decision. -
What should I consider when sourcing alternators or generators for international trade?
When sourcing alternators or generators for international trade, consider the specific energy needs of your market. Look for suppliers with a proven track record in your region, and ensure they understand local regulations and standards. Additionally, assess their ability to provide technical support and after-sales service. It’s also important to evaluate logistics capabilities, including shipping times and costs, to ensure timely delivery of equipment to your business location. -
What customization options are typically available for alternators and generators?
Most manufacturers offer customization options for alternators and generators to meet specific operational requirements. This can include adjustments in voltage output, size, and design tailored to particular applications. When discussing customization with suppliers, ensure that they can accommodate your technical specifications and understand the unique challenges of your industry. Custom solutions can enhance performance and efficiency, aligning with your business objectives. -
How can I vet suppliers of alternators and generators?
To effectively vet suppliers, start by researching their reputation in the industry. Look for reviews, case studies, and testimonials from previous clients. Additionally, inquire about their manufacturing processes, quality assurance practices, and certifications. It’s beneficial to ask for references and conduct site visits if possible. A thorough vetting process will help ensure that you partner with reliable suppliers who can meet your quality and delivery expectations. -
What are typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for alternators and generators?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) can vary significantly among suppliers and depend on the type of equipment required. Generally, larger manufacturers may offer lower MOQs, while smaller suppliers might have higher thresholds due to production costs. When negotiating, consider your business’s demand and discuss flexible MOQs to accommodate your purchasing strategy. Understanding MOQs is essential for managing inventory and ensuring you have the right amount of equipment for your operations. -
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing from international suppliers?
Payment terms can differ widely based on the supplier’s policies and the nature of the transaction. Common arrangements include advance payments, letters of credit, or payment upon delivery. It’s crucial to clarify these terms upfront to avoid misunderstandings later. Consider negotiating terms that align with your cash flow needs and mitigate risks, such as partial payments upon shipment or performance guarantees to ensure product quality and timely delivery. -
What quality assurance measures should I look for when sourcing alternators and generators?
Quality assurance is vital when sourcing alternators and generators. Look for suppliers who adhere to international quality standards, such as ISO certifications. Inquire about their testing procedures, including performance tests and inspections conducted during production. Additionally, ask about warranty policies and after-sales support, as these can be indicators of a supplier’s commitment to quality. Ensuring robust QA measures will help you secure reliable and durable equipment for your business needs.
Top 4 Difference In Alternator And Generator Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Byju’s – Alternator
Domain: byjus.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: Alternator: A device that converts mechanical energy into AC electrical energy. It induces alternating current, is highly efficient, has a higher output than generators, conserves energy by using only the required amount, does not require polarization after installation, has a rotating magnetic field inside the stator, has a stationary armature, takes input supply from the stator, has a wide RPM r…
2. Reddit – Generators vs. Alternators
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Generators and alternators are both devices that generate electricity, but they have key differences. An alternator is a specific type of generator that produces alternating current (AC), while a generator can produce either AC or direct current (DC). Alternators are commonly used in automobiles to power electrical systems and charge the battery. They typically have more magnets than standard gene…
3. Speedway Motors – Alternators vs Generators
Domain: speedwaymotors.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Alternator vs Generator: Both convert mechanical energy into electrical energy to charge a car’s battery. Generators use a rotating armature inside static magnets, while alternators rotate the magnetic field inside the conductor. Alternators are more efficient and reliable, capable of meeting modern electrical demands. Key points for conversion: 1. Voltage regulators (internal or external) are nec…
4. Ask A CFI – Key Differences Between Generators and Alternators
Domain: askacfi.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: Key differences between a generator and an alternator include: 1. Current Creation: Generators create electricity by moving a wire armature within a fixed magnetic field, while alternators have a spinning magnetic field in a series of windings called a stator. 2. Efficiency: Alternators are more efficient due to direct wiring to output points and smoother electrical output from three separate wind…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for difference in alternator and generator
In conclusion, understanding the distinctions between alternators and generators is crucial for B2B buyers looking to optimize their energy solutions. Alternators, known for their efficiency and ability to generate AC power, are ideal for applications requiring reliable energy conservation, particularly in automotive and smaller-scale operations. Conversely, generators offer flexibility by producing both AC and DC power, making them suitable for large-scale electricity generation and emergency backup systems.
Illustrative image related to difference in alternator and generator
For international buyers, particularly those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the strategic sourcing of these devices must take into account factors such as energy needs, operational efficiency, and maintenance requirements. Leveraging these insights can lead to more informed purchasing decisions, ultimately enhancing operational performance and reducing costs.
As the global market continues to evolve, consider how advancements in technology can further influence your sourcing strategy. Engage with reputable suppliers and explore innovative solutions that align with your business objectives. By prioritizing strategic sourcing, you can position your organization for sustainable growth in an increasingly competitive landscape.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
Illustrative image related to difference in alternator and generator
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.