Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for alternator car function
In the dynamic landscape of automotive manufacturing, understanding the function of the alternator in vehicles is crucial for B2B buyers looking to source reliable components. As the cornerstone of a vehicle’s electrical system, the alternator plays a pivotal role in converting mechanical energy into electrical energy, ensuring that batteries remain charged and electrical components function seamlessly. However, sourcing high-quality alternators can present challenges, particularly for international buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where market variations and supplier reliability can impact operational efficiency.
This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of alternator car function, exploring various types of alternators, their applications across different vehicle models, and the critical factors to consider when vetting suppliers. We will also address cost considerations, helping you navigate pricing structures and negotiate effectively. By equipping you with essential insights and actionable strategies, this guide empowers you to make informed purchasing decisions that enhance the performance and reliability of your automotive offerings. With a focus on global sourcing, we aim to bridge the gap between regional supply challenges and the need for quality components, ultimately supporting your business’s growth in a competitive market.
Table Of Contents
- Top 2 Alternator Car Function Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for alternator car function
- Understanding alternator car function Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of alternator car function
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘alternator car function’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for alternator car function
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for alternator car function
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘alternator car function’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for alternator car function Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing alternator car function With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for alternator car function
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the alternator car function Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of alternator car function
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for alternator car function
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Understanding alternator car function Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Conventional Alternator | Uses electromagnetic induction; generates AC power. | Standard vehicles, fleet management. | Pros: Reliable, cost-effective. Cons: Limited efficiency at low RPMs. |
| High-Output Alternator | Provides increased power output for high-demand systems. | Performance vehicles, heavy-duty applications. | Pros: Supports advanced electronics. Cons: Higher cost and potential overheating. |
| Smart Alternator | Features advanced voltage regulation and monitoring. | Electric vehicles, hybrid cars. | Pros: Optimizes battery life, enhances fuel efficiency. Cons: Complex technology may increase repair costs. |
| Brushless Alternator | Utilizes a permanent magnet for energy generation. | Marine applications, off-road vehicles. | Pros: Higher efficiency, longer lifespan. Cons: More expensive and may require specialized installation. |
| Dual-Voltage Alternator | Offers both standard and high voltage outputs. | Commercial vehicles, specialized machinery. | Pros: Versatile for varied electrical needs. Cons: Complexity in wiring and installation. |
What Are the Characteristics of Conventional Alternators and Their Suitability for B2B Buyers?
Conventional alternators are the most commonly used type in standard combustion engine vehicles. They operate on the principle of electromagnetic induction, converting mechanical energy into alternating current (AC) electrical energy. These alternators are well-suited for businesses managing fleets of vehicles due to their reliability and cost-effectiveness. B2B buyers should consider their performance in terms of power output and maintenance needs, as lower RPM efficiency can be a drawback in certain operational scenarios.
How Do High-Output Alternators Meet the Demands of Performance Vehicles?
High-output alternators are designed to meet the increased electrical demands of performance vehicles and heavy-duty applications. They provide greater power output, making them ideal for businesses involved in motorsports or those that rely on advanced electronic systems in their vehicles. While they support modern electrical accessories effectively, B2B buyers should weigh the higher costs and potential for overheating against their specific power requirements.
What Advantages Do Smart Alternators Offer for Electric and Hybrid Vehicles?
Smart alternators incorporate advanced technology for voltage regulation and monitoring, making them particularly beneficial for electric and hybrid vehicles. They optimize battery life and enhance fuel efficiency by adjusting power output based on real-time demand. For businesses investing in sustainable transportation solutions, these alternators present a forward-thinking choice. However, the complexity of their systems may lead to higher repair costs, which should be factored into purchasing decisions.
Why Are Brushless Alternators Considered More Efficient for Specific Applications?
Brushless alternators utilize permanent magnets to generate electricity, offering higher efficiency and a longer lifespan compared to traditional designs. They are particularly advantageous for marine and off-road applications where reliability is paramount. B2B buyers should consider the initial investment and the need for specialized installation, as these alternators can be more expensive upfront but often result in lower maintenance costs over time.
How Do Dual-Voltage Alternators Cater to Varied Electrical Needs in Commercial Vehicles?
Dual-voltage alternators provide both standard and high voltage outputs, making them versatile for a range of electrical needs, particularly in commercial vehicles and specialized machinery. This adaptability allows businesses to use a single alternator for multiple applications, reducing inventory costs. However, the complexity of wiring and installation may require specialized knowledge, so B2B buyers should ensure they have access to qualified technicians for proper installation and maintenance.
Key Industrial Applications of alternator car function
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of alternator car function | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive Manufacturing | Integration in vehicle assembly lines | Ensures reliable power supply for assembly tools and equipment, enhancing production efficiency. | Quality standards for alternators, compatibility with various vehicle models, and after-sales support. |
| Transportation & Logistics | Fleet maintenance and operations | Reduces downtime by ensuring vehicles are always operational, improving service reliability. | Bulk purchasing options, warranty terms, and performance ratings under different conditions. |
| Renewable Energy Vehicles | Power management in electric and hybrid vehicles | Enhances battery life and efficiency, contributing to sustainability goals and reduced carbon footprint. | Technology compatibility with existing systems, capacity for energy output, and supplier reliability. |
| Mining & Heavy Equipment | Power supply for auxiliary systems in vehicles | Ensures all electrical systems function optimally, reducing the risk of operational failures in harsh environments. | Durability under extreme conditions, ease of maintenance, and availability of spare parts. |
| Emergency Services | Emergency response vehicle operations | Provides uninterrupted power for critical equipment, ensuring readiness and reliability during emergencies. | Compliance with safety standards, rapid delivery options, and robust technical support. |
How is the alternator used in automotive manufacturing applications?
In automotive manufacturing, alternators are integrated into assembly lines to provide a consistent power supply for various tools and equipment. This is crucial for the seamless operation of machinery, ensuring that production does not face interruptions due to power shortages. For international buyers, especially from regions like Africa and South America, understanding the quality standards and compatibility of alternators with different vehicle models is essential. They must consider the after-sales support offered by suppliers to ensure long-term operational efficiency.
What role does the alternator play in transportation and logistics?
In the transportation and logistics sector, the alternator’s role is vital for fleet maintenance and operations. A well-functioning alternator helps maintain the reliability of vehicles by ensuring that all electrical systems are powered, thereby reducing the risk of unexpected breakdowns. This is particularly important for businesses operating in regions like the Middle East and Europe, where logistical efficiency is paramount. Buyers should seek bulk purchasing options and favorable warranty terms to maximize their investment in fleet maintenance.
Why is the alternator important for renewable energy vehicles?
For renewable energy vehicles, such as hybrids and electric cars, the alternator is essential for effective power management. It helps enhance battery life by providing a steady charge, which is crucial for achieving sustainability goals and reducing the carbon footprint. B2B buyers from emerging markets like Brazil and Vietnam need to assess the technology compatibility of alternators with existing systems to ensure optimal performance. Additionally, evaluating the energy output capacity is critical for meeting the demands of modern electric vehicles.
How does the alternator support mining and heavy equipment operations?
In the mining industry, alternators are crucial for powering auxiliary systems in heavy vehicles, ensuring that all electrical components function optimally. Given the harsh environments in which mining operations occur, durability is a key requirement. Buyers must consider the alternator’s ability to withstand extreme conditions and the ease of maintenance, as well as the availability of spare parts. This ensures that equipment remains operational, minimizing downtime and maximizing productivity.
What is the significance of alternators in emergency services?
In emergency services, the alternator provides the necessary power for critical equipment in response vehicles, ensuring they remain operational during emergencies. This reliability is paramount for maintaining readiness and effectiveness in crisis situations. Buyers in this sector should focus on compliance with safety standards and rapid delivery options from suppliers to ensure that their vehicles are equipped with reliable alternators. Robust technical support is also essential to address any issues that may arise swiftly.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘alternator car function’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Sourcing Reliable Alternators for Diverse Markets
The Problem: B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, often struggle to find reliable suppliers of alternators that meet the specific needs of their local automotive markets. Many suppliers may offer generic products that do not consider the unique environmental conditions, vehicle models, and electrical demands prevalent in these areas. This can lead to compatibility issues, increased failure rates, and ultimately, dissatisfied customers.
The Solution: To address this issue, buyers should conduct thorough market research to identify local suppliers who specialize in alternators suited for specific vehicles and regional conditions. Engaging with manufacturers who have a proven track record in diverse markets can also provide insights into the best products for particular environmental challenges, such as extreme temperatures or high humidity. Furthermore, establishing a partnership with suppliers that offer comprehensive warranties and after-sales support can ensure long-term reliability. Investing in a robust quality assurance process that includes testing alternators for compatibility with local vehicles can further mitigate risks.
Scenario 2: Managing Increased Returns Due to Alternator Failures
The Problem: A common pain point for B2B buyers is managing returns stemming from alternator failures. This not only affects profitability but also impacts customer trust and brand reputation. Issues such as overcharging or undercharging batteries due to faulty alternators can lead to frequent complaints and returns, particularly if the products fail before the expected lifespan.
The Solution: To reduce return rates, buyers should focus on quality control when sourcing alternators. Collaborating with manufacturers that adhere to strict quality standards and offer detailed product specifications can significantly enhance reliability. Additionally, implementing a robust training program for technicians on proper installation and diagnostics can help identify potential issues early. Buyers should also consider investing in diagnostic tools that can assess the health of the alternator and battery system, allowing for proactive maintenance and reducing the risk of failure.
Scenario 3: Difficulty in Educating End Users About Alternator Maintenance
The Problem: Many B2B buyers find it challenging to educate their customers—whether they are auto repair shops or end-users—about the importance of alternator maintenance. A lack of understanding can lead to neglect, resulting in premature failures and costly repairs, which can hurt the buyer’s business through increased warranty claims and customer dissatisfaction.
The Solution: To effectively educate end users, B2B buyers should develop comprehensive training materials and resources that highlight the importance of alternator maintenance. This can include informative guides, videos, and workshops tailored to various audiences. Additionally, creating a digital platform or app that provides maintenance reminders and troubleshooting tips can empower users to take better care of their vehicles. Partnering with automotive experts to conduct seminars or online webinars can also enhance credibility and ensure that both buyers and end-users are well-informed about the critical role of alternators in vehicle performance. By fostering an educated customer base, buyers can reduce maintenance-related issues and enhance customer loyalty.
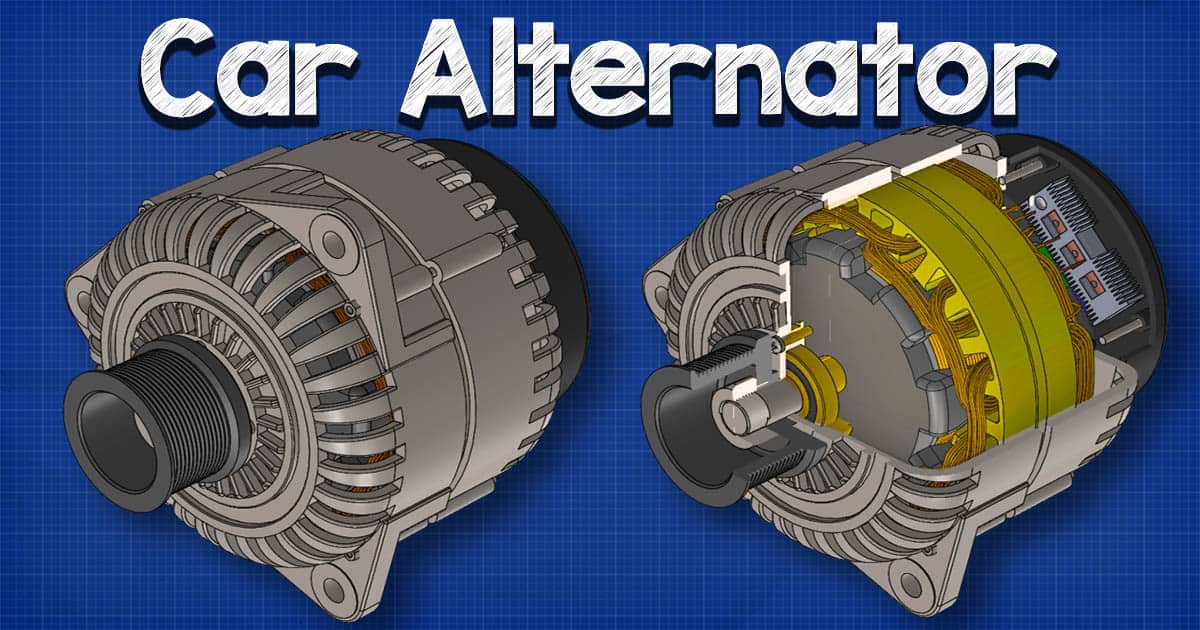
Strategic Material Selection Guide for alternator car function
When selecting materials for alternators in automotive applications, it is crucial to consider several common materials that significantly impact performance, durability, and cost. This analysis focuses on aluminum, copper, steel, and composites, examining their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international B2B buyers.
What Are the Key Properties of Aluminum in Alternators?
Aluminum is a prevalent choice for alternator housings and components due to its lightweight nature and excellent thermal conductivity. It typically has a temperature rating of up to 150°C and offers good corrosion resistance, especially when anodized. This makes aluminum suitable for environments where moisture and salt exposure are common, such as coastal regions.
Pros and Cons of Using Aluminum
The primary advantage of aluminum is its low weight, which contributes to improved fuel efficiency in vehicles. Additionally, it is relatively easy to manufacture and can be cast into complex shapes. However, aluminum may not offer the same strength as steel, making it less suitable for high-stress applications. Its cost is generally moderate, but it can be higher than some steel options.
How Does Copper Enhance Alternator Performance?
Copper is often used in the windings of alternators due to its excellent electrical conductivity, which is crucial for efficient energy transfer. It can handle high temperatures (up to 200°C) and has good corrosion resistance when properly treated.
Pros and Cons of Copper
The key advantage of copper is its superior conductivity, which enhances the overall efficiency of the alternator. However, copper is heavier than aluminum and can be more expensive, impacting the overall cost of the alternator. Additionally, its susceptibility to corrosion in certain environments can be a drawback unless protective coatings are applied.
What Role Does Steel Play in Alternator Manufacturing?
Steel is commonly used for the structural components of alternators, such as the rotor and stator cores. It provides high strength and durability, with temperature ratings often exceeding 300°C. However, steel is prone to rust if not adequately protected.
Illustrative image related to alternator car function
Pros and Cons of Steel
Steel’s primary advantage is its strength, which allows it to withstand mechanical stresses and impacts. The material is also cost-effective, making it a popular choice for manufacturers. On the downside, its weight can negatively affect vehicle performance and fuel efficiency. Additionally, corrosion resistance must be addressed through coatings or galvanization, particularly in humid environments.
Are Composites a Viable Option for Alternators?
Composites, such as fiberglass-reinforced plastics, are increasingly being explored for non-structural components in alternators. They offer excellent resistance to corrosion and can withstand a wide range of temperatures.
Pros and Cons of Composites
The main advantage of composites is their lightweight nature and resistance to corrosion, making them ideal for various environmental conditions. They can also be molded into complex shapes, allowing for innovative designs. However, composites can be more expensive to manufacture and may not provide the same mechanical strength as metals, limiting their use to non-load-bearing parts.

Illustrative image related to alternator car function
Considerations for International B2B Buyers
International buyers, especially from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should consider compliance with local standards such as ASTM, DIN, or JIS when selecting materials. Additionally, understanding the regional preferences for materials based on climate and environmental conditions is crucial. For instance, buyers in coastal areas may prioritize corrosion-resistant materials, while those in high-temperature regions may focus on thermal stability.
| Material | Typical Use Case for alternator car function | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Housings and non-load-bearing components | Lightweight and good thermal conductivity | Lower strength compared to steel | Medium |
| Copper | Windings and electrical connections | Superior electrical conductivity | Heavier and more expensive | High |
| Steel | Structural components (rotor, stator) | High strength and durability | Prone to corrosion without treatment | Low |
| Composites | Non-structural components | Corrosion resistance and lightweight | Higher manufacturing costs | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide provides valuable insights for B2B buyers, helping them make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and regional considerations.
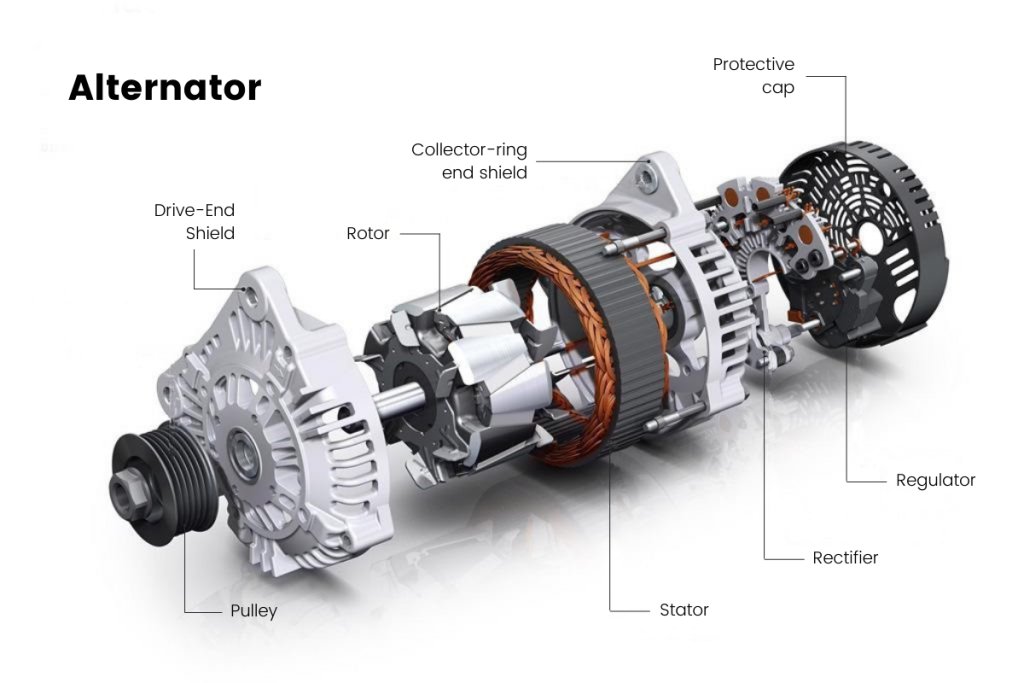
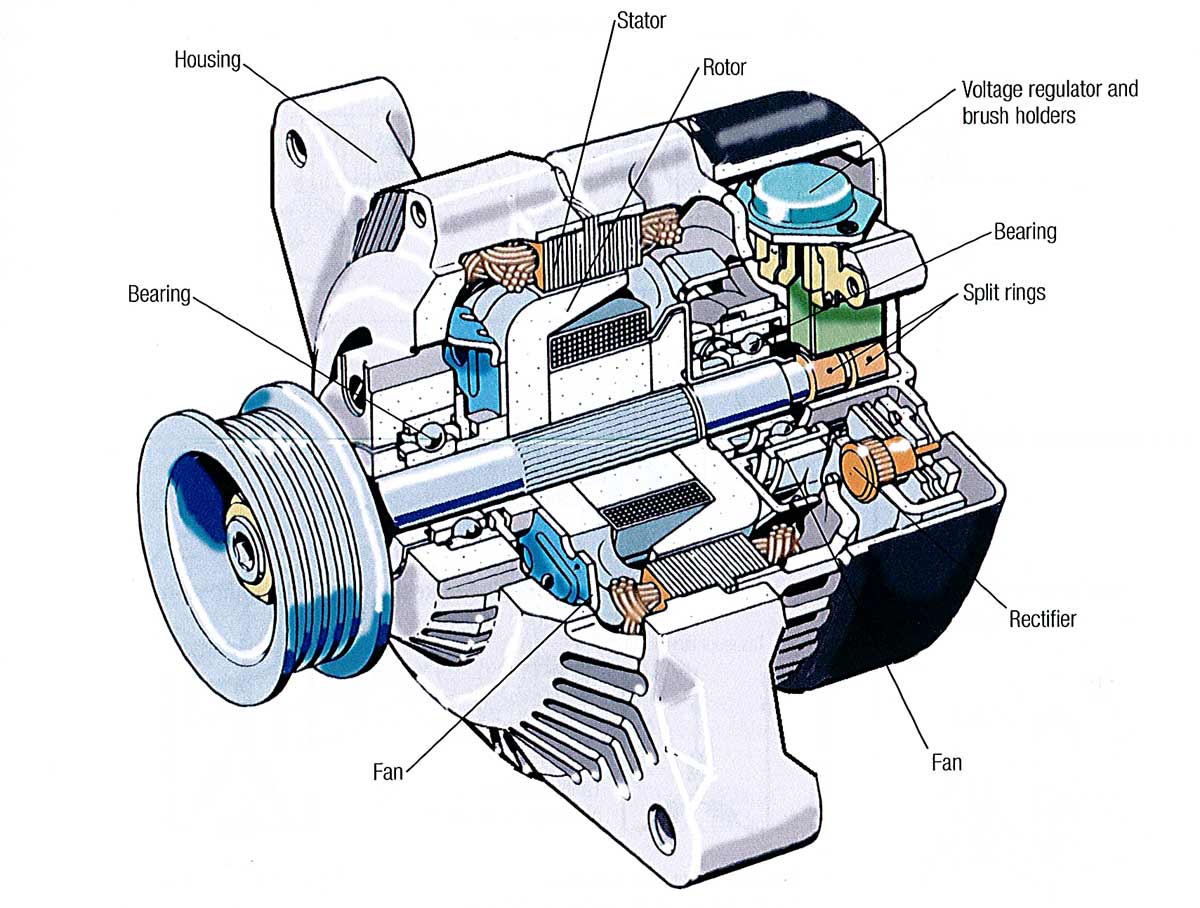
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for alternator car function
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing an Alternator?
The manufacturing process for car alternators involves several critical stages, each designed to ensure high performance and reliability. The main stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How Are Materials Prepared for Alternator Manufacturing?
The first stage is material preparation, where raw materials such as aluminum, copper, and various alloys are sourced. These materials are selected based on their electrical conductivity, thermal properties, and mechanical strength. Quality suppliers often adhere to international standards to guarantee the integrity of these materials.
Once sourced, materials undergo rigorous testing to assess their suitability. For instance, metallurgical analysis ensures that the alloys meet specific composition standards. This stage is crucial as it lays the foundation for the durability and efficiency of the final product.
What Techniques Are Used in the Forming Stage?
In the forming stage, advanced techniques such as die casting and stamping are employed to create components of the alternator, including the housing, rotor, and stator. Die casting allows for the production of complex shapes with high precision, while stamping is used for flat components like the end plates.
These techniques are complemented by CNC machining, which offers high precision in producing parts that fit together seamlessly. The use of automated machinery enhances efficiency, reduces human error, and ensures consistent quality across production batches.
How Is the Assembly Process Conducted for Alternators?
The assembly stage is where the alternator components come together. This process typically involves several steps:
- Component Inspection: Before assembly, each part undergoes inspection to ensure it meets specified tolerances and quality standards.
- Assembly of Core Components: The rotor and stator are assembled, ensuring proper alignment and secure fitting. This is critical for optimal electromagnetic performance.
- Integration of Electrical Components: The voltage regulator and rectifier are integrated into the assembly. These components are vital for converting AC to DC and regulating the voltage output.
- Final Assembly: The alternator casing is fitted, and all parts are secured. This stage may involve the use of robotic arms to enhance efficiency and reduce the risk of damage during assembly.
What Finishing Processes Are Important for Alternators?
Finishing processes are essential for enhancing the durability and performance of the alternator. Common finishing techniques include:
- Surface Treatment: Processes like anodizing or powder coating are applied to protect against corrosion and wear.
- Quality Testing: Each finished alternator undergoes functional testing to verify performance parameters, such as output voltage and current. This ensures that the product meets industry standards and customer expectations.
What International Standards Guide Quality Assurance in Alternator Manufacturing?
Quality assurance is critical in the production of alternators, with various international standards guiding the process. ISO 9001 is a widely recognized standard that outlines requirements for a quality management system. It ensures that manufacturers consistently meet customer and regulatory requirements while enhancing customer satisfaction.
In addition to ISO standards, industry-specific certifications like CE (Conformité Européenne) for European markets and API (American Petroleum Institute) standards for certain automotive applications may apply. These certifications ensure that the alternators comply with safety and performance regulations.
How Are Quality Control Checkpoints Established During Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are integral to maintaining high standards throughout the manufacturing process. Key QC checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This step involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet quality specifications.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing stages, continuous monitoring is conducted to detect any deviations from quality standards. This may include measuring tolerances and checking component integrity.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): After assembly, a comprehensive inspection and functional testing are performed. This ensures that the alternator operates within specified parameters before it is shipped to customers.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used for Alternators?
Several testing methods are employed to ensure the performance and reliability of alternators. Common methods include:
- Electrical Testing: This checks the voltage and current output to confirm that the alternator meets specifications.
- Load Testing: The alternator is subjected to load conditions to evaluate its performance under typical operational scenarios.
- Vibration Testing: This assesses the structural integrity of the alternator under dynamic conditions, ensuring it can withstand the vibrations experienced during vehicle operation.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
For B2B buyers, verifying the quality control practices of suppliers is essential for ensuring product reliability. Here are several strategies:
- Audits: Conducting regular audits of suppliers’ manufacturing facilities can provide insights into their quality management systems and adherence to international standards.
- Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports, including defect rates and testing outcomes, can help buyers assess the supplier’s commitment to quality.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased evaluation of the supplier’s production processes and product quality.
What QC and Certification Nuances Should International B2B Buyers Consider?
International buyers, especially from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of specific nuances in quality control and certification:
- Regulatory Compliance: Different regions may have varying regulatory requirements. Buyers should ensure that their suppliers comply with local laws and standards.
- Cultural Differences: Understanding the cultural context of suppliers can facilitate better communication regarding quality expectations and practices.
- Supply Chain Transparency: Buyers should seek suppliers who provide transparency in their supply chain processes, including sourcing materials and production methods.
By focusing on these aspects, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing alternators, ensuring they partner with manufacturers who prioritize quality and compliance in their production processes.

Illustrative image related to alternator car function
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘alternator car function’
This guide aims to assist B2B buyers in the automotive sector who are looking to procure alternators for vehicles. Understanding the function and importance of the alternator is crucial for ensuring the quality and reliability of automotive electrical systems. Here’s a step-by-step checklist to streamline your sourcing process.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is vital for selecting the right alternator. Consider factors such as voltage output, amperage, and compatibility with various vehicle models. Additionally, assess the operating environment, including temperature ranges and humidity levels, which can affect performance.
Step 2: Research Supplier Reputation
Before engaging with suppliers, conduct thorough research on their market reputation. Look for reviews, testimonials, and case studies from existing clients, particularly those within your industry or region. A reputable supplier is more likely to provide reliable products and support.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing, it’s crucial to vet suppliers thoroughly. Request company profiles, certifications, and references from buyers in a similar industry or region. Evaluate their experience in manufacturing alternators and any relevant technological advancements they offer.
Illustrative image related to alternator car function
- Check Certifications: Ensure that the supplier adheres to international standards such as ISO or other relevant quality certifications.
- Assess Production Capabilities: Inquire about their production processes and capacity to meet your demand.
Step 4: Request Samples for Testing
Once you have shortlisted potential suppliers, request samples of the alternators for testing. This step allows you to assess the quality, performance, and compatibility of the product with your vehicles. Ensure that the samples meet your specifications and perform well under expected conditions.
Step 5: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Engage in discussions about pricing, payment terms, and delivery schedules. Clear negotiations can help prevent misunderstandings later in the procurement process. Ensure that the terms are favorable and align with your budget while also considering the supplier’s capabilities.
- Discuss Warranty and Support: Inquire about warranty periods and after-sales support to ensure you are covered in case of defects or performance issues.
Step 6: Conduct a Risk Assessment
Before finalizing your order, conduct a risk assessment. Analyze potential risks associated with the supplier, such as delivery delays, quality issues, or geopolitical factors that may affect supply chains. Having contingency plans in place can help mitigate these risks.
Step 7: Finalize the Purchase Agreement
Once all evaluations are complete, finalize the purchase agreement. Ensure that all terms discussed are documented clearly in the contract. Include details about product specifications, delivery timelines, payment schedules, and after-sales support to avoid any future disputes.
Following this checklist can facilitate a smoother procurement process for alternators, ensuring that you source high-quality products that meet your operational needs effectively.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for alternator car function Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Alternator Manufacturing?
When sourcing alternators, international B2B buyers must understand the various cost components involved in manufacturing. The primary cost elements include:
-
Materials: The cost of raw materials such as copper wire, magnets, steel, and aluminum significantly impacts overall pricing. Fluctuations in commodity prices can lead to varying costs, so buyers should consider sourcing materials from stable regions or suppliers to mitigate risks.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region and can be influenced by local wage rates and the skill level required for assembly and production. In regions with lower labor costs, such as some parts of South America and Africa, manufacturers may offer competitive pricing.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with factory operations, utilities, and administrative expenses. Efficient manufacturing processes can reduce overhead, impacting the final price.
-
Tooling: Initial setup and tooling costs can be significant, especially for custom designs. Buyers should inquire about tooling costs when requesting quotes, as they can affect the overall price structure.
-
Quality Control (QC): Robust quality assurance processes ensure that alternators meet industry standards and specifications. However, these processes come at a cost, which should be factored into the pricing.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs are crucial, especially for international transactions. Factors such as distance, mode of transport, and customs duties can influence the overall logistics costs.
-
Margin: Suppliers will add a profit margin to their costs, which varies based on market competition and perceived value. Understanding market dynamics can help buyers gauge reasonable margins.
How Do Volume and Specifications Influence Alternator Pricing?
The pricing of alternators is often influenced by several key factors, including:
-
Volume/Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders typically result in lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should negotiate MOQs that align with their needs while considering the potential for bulk discounts.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom alternators designed for specific applications or vehicles may incur higher costs due to specialized materials or design processes. Buyers should clearly define their specifications to avoid unexpected costs.
-
Materials: The choice of materials can significantly affect pricing. High-performance alternators may utilize premium materials that enhance durability and efficiency, thus increasing costs.
-
Quality Certifications: Certifications such as ISO or IATF can indicate higher quality standards but may come with additional costs. Buyers should weigh the importance of certifications against their budget and quality requirements.
-
Supplier Factors: The reliability and reputation of suppliers can impact pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium, while new entrants might offer lower prices to gain market share.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the terms of shipping and delivery can help buyers anticipate additional costs. For instance, choosing Ex Works (EXW) may require buyers to manage shipping, potentially increasing total costs.
What Are the Best Negotiation and Cost-Efficiency Strategies for B2B Buyers?
B2B buyers can employ various strategies to secure favorable pricing and ensure cost efficiency:
-
Conduct Thorough Market Research: Understanding current market trends and price benchmarks can provide leverage during negotiations. Buyers should stay informed about material costs and supplier pricing strategies.
-
Leverage Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider the long-term costs associated with alternators, including maintenance, performance, and durability. A slightly higher initial investment may lead to lower overall costs over time.
-
Negotiate Payment Terms: Flexible payment terms can improve cash flow and reduce financial strain. Buyers should discuss options such as staggered payments or extended payment periods.
-
Build Long-term Relationships with Suppliers: Establishing partnerships with reliable suppliers can lead to better pricing and priority access to products. Trust and reliability can translate into cost savings over time.
-
Be Aware of Pricing Nuances for International Transactions: Buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should be mindful of currency fluctuations, import taxes, and tariffs that can affect total costs.
Conclusion: What Should Buyers Keep in Mind When Sourcing Alternators?
While sourcing alternators, it is crucial for international B2B buyers to consider the comprehensive cost structure and pricing influencers discussed above. By understanding these elements and employing effective negotiation strategies, buyers can achieve cost-effective solutions that meet their operational needs. Always seek detailed quotes and consider the total cost of ownership to make informed purchasing decisions.
Disclaimer: The prices and cost components mentioned herein are indicative and may vary based on market conditions, supplier negotiations, and specific buyer requirements.
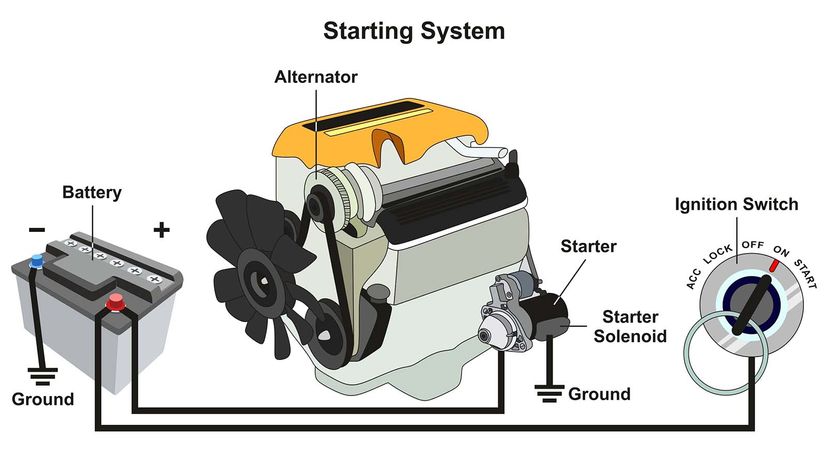
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing alternator car function With Other Solutions
In the automotive industry, the alternator plays a critical role in converting mechanical energy into electrical energy, powering a vehicle’s electrical systems and recharging its battery. However, as technological advancements continue to evolve, there are alternative solutions available that can serve similar functions. Understanding these alternatives can help B2B buyers make informed decisions based on performance, cost, and maintenance considerations.
Illustrative image related to alternator car function
Comparison Table of Alternator Car Function and Alternatives
| Comparison Aspect | Alternator Car Function | Alternative 1: Integrated Starter Generator (ISG) | Alternative 2: Battery Electric Vehicle (BEV) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High efficiency in energy conversion and reliability | Moderate efficiency; supports start-stop technology | High efficiency; relies solely on electric power |
| Cost | Generally low initial cost; maintenance required | Higher initial cost; fewer moving parts reduce maintenance | High initial cost; potential long-term savings on fuel |
| Ease of Implementation | Standard in combustion engine vehicles; easy to replace | Requires integration with advanced engine systems | Requires complete vehicle redesign; not retrofittable |
| Maintenance | Needs periodic checks; lifespan of 7-10 years | Low maintenance; fewer components lead to reliability | Minimal maintenance but battery replacement can be costly |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for traditional combustion engine vehicles | Best for hybrid vehicles aiming to improve fuel efficiency | Optimal for all-electric vehicles with charging infrastructure |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Integrated Starter Generator (ISG)
The ISG combines the functionalities of a starter motor and an alternator into a single unit, enabling the vehicle to start and generate electricity simultaneously. This technology is particularly beneficial for hybrid vehicles, where it supports start-stop systems that enhance fuel efficiency. While ISGs come with a higher initial cost, they require less maintenance due to fewer moving parts. However, their integration into existing combustion engine systems can be complex and may necessitate additional engineering considerations.
Battery Electric Vehicle (BEV)
BEVs represent a significant shift from traditional vehicles by relying entirely on electric power. They utilize large battery packs to provide energy for propulsion, eliminating the need for an alternator altogether. While BEVs offer high efficiency and reduced emissions, they come with a substantial upfront cost and require an extensive charging infrastructure. Maintenance is typically minimal, but battery replacement can be a significant expense over the vehicle’s lifespan. BEVs are best suited for markets with established charging networks and growing consumer demand for sustainable transport solutions.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
For B2B buyers in the automotive sector, the choice between an alternator, ISG, or BEV hinges on several factors, including vehicle type, intended application, and budget constraints. If the focus is on enhancing existing combustion engine vehicles, an alternator remains a reliable and cost-effective solution. However, for companies looking to innovate and meet sustainability goals, exploring ISGs or transitioning to BEVs could provide a competitive edge in a rapidly evolving market. Each option presents unique advantages and challenges, so thorough evaluation based on specific operational needs is essential.
Illustrative image related to alternator car function
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for alternator car function
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Alternators in Automotive Applications?
Understanding the technical properties of alternators is essential for B2B buyers looking to procure reliable automotive components. Here are some critical specifications that influence the performance and reliability of alternators:
-
Output Voltage
Alternators typically produce an output voltage between 12V to 14.5V, which is essential for charging the battery and powering electrical components. A stable output voltage is crucial for the proper functioning of automotive electronics. B2B buyers should ensure that the alternators meet the voltage requirements of the vehicles they service, as variations can lead to undercharging or overcharging of batteries. -
Current Rating (Amperage)
The current rating, measured in amperes (A), indicates the maximum amount of electrical current an alternator can provide. Common ratings range from 40A to over 200A depending on the vehicle’s electrical load. Higher current ratings are essential for vehicles with numerous electronic features, such as advanced infotainment systems and electric windows. Buyers should assess the current demands of the vehicles in their market to select the appropriate alternator. -
Efficiency Rating
Efficiency in alternators is defined by how effectively they convert mechanical energy into electrical energy. A higher efficiency rating means less wasted energy, resulting in better fuel economy and lower emissions. For B2B buyers, selecting high-efficiency alternators can lead to reduced operational costs and enhanced vehicle performance, which can be a competitive advantage in the marketplace. -
Material Grade and Construction
The materials used in alternator construction, such as aluminum for housings and high-grade copper for windings, significantly affect durability and performance. High-quality materials ensure resistance to corrosion and wear, extending the alternator’s lifespan. For buyers, understanding the material specifications helps in evaluating the longevity and reliability of the alternators they procure. -
Regulator Type
The type of voltage regulator (internal vs. external) influences how the alternator manages output voltage. Internal regulators are more common in modern vehicles, providing compact design and reliability. Buyers should consider the vehicle types they deal with to ensure compatibility with the regulator type used in their alternators. -
Weight and Size
The dimensions and weight of an alternator can impact installation and overall vehicle performance. Lighter and more compact designs are often preferred in modern vehicles to enhance fuel efficiency. B2B buyers should factor in these specifications, especially when dealing with performance or electric vehicles that may have stringent weight restrictions.
What Are the Common Trade Terms Used in the Alternator Industry?
Familiarity with industry jargon is vital for effective communication and negotiation in the automotive components market. Here are several key terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
Refers to companies that produce parts that are used in the assembly of new vehicles. OEM alternators are typically preferred for their guaranteed compatibility and quality, making them highly sought after by B2B buyers looking to maintain vehicle integrity. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
The smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is essential for B2B buyers to manage inventory and cash flow effectively. Buyers should negotiate MOQs to align with their sales forecasts and storage capabilities. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
A formal process where buyers request price quotes from suppliers for specific products or services. RFQs are crucial for B2B transactions as they help in comparing prices and terms from different vendors, allowing buyers to make informed purchasing decisions. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
A set of internationally recognized rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping and freight transactions. Knowledge of Incoterms is vital for B2B buyers to understand shipping costs, risks, and obligations, especially when sourcing alternators from international suppliers. -
Aftermarket
Refers to parts and accessories sold for vehicles after the original sale. Aftermarket alternators can offer cost-effective alternatives to OEM parts, but buyers must ensure quality and compatibility to avoid potential issues. -
Lead Time
The time it takes from placing an order to receiving the product. Understanding lead times is critical for B2B buyers to plan inventory and manage customer expectations effectively, especially in regions with longer shipping durations.
By grasping these technical specifications and trade terminologies, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions regarding alternator procurement, ultimately leading to better product offerings and enhanced customer satisfaction.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the alternator car function Sector
What Are the Key Market Trends Shaping the Alternator Car Function Sector?
The alternator car function sector is experiencing significant transformation driven by various global factors. Increasing vehicle electrification, particularly with the rise of hybrid and electric vehicles (EVs), is reshaping demand for alternators. As manufacturers adapt to changing technologies, there is a notable shift toward more efficient and lightweight alternators, which contribute to improved vehicle performance and fuel efficiency. Additionally, the growing focus on sustainability is prompting the use of recyclable materials and energy-efficient manufacturing processes.

Illustrative image related to alternator car function
In emerging markets like Africa and South America, the demand for reliable automotive components is surging, fueled by rising disposable incomes and increased vehicle ownership. B2B buyers in these regions are increasingly looking for suppliers that can provide high-quality alternators that meet international standards. Moreover, the Middle East and Europe are witnessing a trend towards digital sourcing platforms that streamline procurement processes, enabling buyers to easily compare products and manufacturers across borders.
Furthermore, the influence of Industry 4.0 is becoming apparent, with smart manufacturing and IoT integration enhancing production efficiencies. These technologies not only optimize supply chain management but also enable real-time monitoring of product quality and performance, which is crucial for international buyers seeking reliable components.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impacting the Alternator Car Function Sector?
Sustainability is increasingly becoming a priority in the alternator car function sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes, coupled with stricter regulations on emissions and waste, has led to a growing emphasis on ethical sourcing and sustainable practices. B2B buyers are now more inclined to partner with suppliers who prioritize eco-friendly materials and production methods.

Illustrative image related to alternator car function
Incorporating green certifications, such as ISO 14001, can significantly enhance a supplier’s appeal in the global marketplace. Buyers are seeking alternatives that utilize recyclable materials in alternator production, thereby reducing the carbon footprint associated with automotive components. Additionally, ethical sourcing ensures that raw materials are procured from responsible suppliers, reducing the risk of human rights violations and promoting fair labor practices.
As the demand for sustainable products rises, companies that align their sourcing strategies with environmental and social governance (ESG) principles are likely to gain a competitive edge. For B2B buyers, understanding a supplier’s sustainability credentials and ethical sourcing practices is essential for making informed purchasing decisions that align with their corporate responsibility goals.
What Historical Context Is Important for Understanding the Alternator Car Function Sector?
The alternator has evolved significantly since its inception in the early 20th century. Initially developed to replace the less efficient generator systems, modern alternators have been refined to enhance their performance and reliability. The transition from mechanical to electronic voltage regulation in the 1970s marked a pivotal moment, allowing for improved efficiency and reduced maintenance needs.
Today, alternators are integral to the functioning of combustion engines and increasingly complex electrical systems in vehicles. The shift towards hybrid and electric vehicles has prompted manufacturers to innovate further, leading to the development of alternators that can efficiently support the unique power demands of these technologies. Understanding this evolution is crucial for B2B buyers as they navigate sourcing decisions in a rapidly changing automotive landscape, ensuring they are equipped with the latest advancements and technologies.
In summary, awareness of market dynamics, sustainability trends, and historical context is essential for B2B buyers in the alternator car function sector. By leveraging this knowledge, they can make informed sourcing decisions that align with industry advancements and consumer expectations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of alternator car function
-
How do I identify a failing alternator in a vehicle?
To identify a failing alternator, look for common symptoms such as dimming headlights, difficulty starting the vehicle, or unusual sounds from the engine compartment. If the battery frequently requires a jump start or if electrical accessories are malfunctioning or operating slowly, these could indicate an alternator issue. Regular vehicle inspections and diagnostics at reputable service centers can help catch these problems early, ensuring your fleet remains operational and minimizes downtime. -
What is the best alternator type for commercial vehicles?
The best alternator type for commercial vehicles typically depends on the specific electrical demands of the vehicle. High-output alternators are ideal for vehicles with numerous electrical accessories, such as those used in construction or emergency services. Consider factors like voltage output, durability under heavy loads, and efficiency. It’s advisable to consult with manufacturers or suppliers specializing in commercial vehicle parts to ensure you select an alternator that meets your operational needs. -
How can I vet suppliers for automotive alternators?
When vetting suppliers for automotive alternators, consider their reputation, experience in the industry, and compliance with international standards. Request references and review customer feedback to gauge their reliability. Additionally, assess their production capabilities, quality control processes, and ability to provide warranties. Engaging in site visits or virtual meetings can also help establish trust and ensure the supplier aligns with your business requirements. -
What customization options are available for alternators?
Many manufacturers offer customization options for alternators, including specific voltage outputs, housing materials, and connectors suited to particular vehicle models. Customization may also extend to performance enhancements for specialized applications. Discuss your specific requirements with potential suppliers to explore available options and ensure the alternators meet the unique demands of your fleet. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for automotive alternators?
The minimum order quantity (MOQ) for automotive alternators varies by supplier and can depend on factors such as the type of alternator and customization requests. Generally, MOQs can range from a few units to several hundred. It’s essential to communicate your needs clearly with suppliers and negotiate terms that are beneficial for both parties, particularly if you are testing a new product line or entering a new market. -
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing alternators internationally?
Payment terms for international purchases of alternators typically include options such as advance payment, letters of credit, or payment upon delivery. It’s crucial to negotiate favorable terms that align with your cash flow needs. Ensure to clarify details regarding currency, payment methods, and any additional fees that may apply, such as transaction fees or taxes, to avoid surprises during the procurement process. -
How do I ensure quality assurance for alternators sourced internationally?
To ensure quality assurance for internationally sourced alternators, request samples for testing before placing larger orders. Establish clear quality control standards and ask suppliers about their testing processes. Certifications such as ISO or compliance with local regulations can also indicate quality. Regular audits and inspections during production can further guarantee that the alternators meet your specifications and performance standards. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing alternators?
When importing alternators, consider logistics factors such as shipping methods, lead times, and customs regulations in your country. Collaborate with experienced logistics providers to navigate import duties, tariffs, and documentation requirements efficiently. Additionally, factor in the potential for delays in shipping and customs clearance, and plan your inventory management accordingly to ensure a steady supply of alternators for your operations.
Top 2 Alternator Car Function Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Kia – Alternators
Domain: kia.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: An alternator is an integral part of every combustion engine vehicle, responsible for converting chemical energy to electrical energy to charge and replenish the battery and power other electrical components. It works as part of the vehicle’s charging system, which includes a car battery, voltage regulator, and the alternator itself. The alternator converts mechanical energy to electrical energy u…
2. Matthews Tire – Electrical System Check
Domain: matthewstire.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: Matthews Tire offers a complete electrical system check for just $39.95. They provide services related to battery and alternator maintenance, including wiring a battery tender to keep the battery charged. The average life of a battery is 4-5 years, and they advise customers to keep track of battery changes and ensure it stays charged.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for alternator car function
In conclusion, the strategic sourcing of alternators is essential for ensuring the reliable performance of vehicles across diverse markets. By understanding the critical role alternators play in converting mechanical energy into electrical energy, international B2B buyers can appreciate their importance in maintaining vehicle functionality. The symbiotic relationship between the alternator and battery underscores the need for quality sourcing to prevent operational disruptions and enhance vehicle longevity.
As global demand for reliable automotive components continues to grow, particularly in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, strategic sourcing becomes a pivotal factor in maintaining competitive advantage. Buyers should prioritize partnerships with reputable suppliers who offer high-quality, durable alternators that meet stringent industry standards.
Looking ahead, the shift towards electric and hybrid vehicles presents new opportunities for innovation in alternator technology. B2B buyers are encouraged to stay informed about emerging trends and advancements in alternator design to ensure they are equipped to meet the evolving needs of their markets. By investing in quality sourcing now, businesses can position themselves for future growth and success in the automotive sector.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.

















