Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for how much to fix starter
In today’s dynamic automotive landscape, understanding how much to fix a starter is crucial for B2B buyers looking to maintain fleet vehicles or manage repair shops effectively. The challenge lies in navigating a plethora of options, from different types of starters to the varying costs associated with their replacement. This guide delves into the intricacies of starter replacement, covering essential aspects such as the different types of starters available, their applications across various vehicle models, and the critical process of supplier vetting.
For international B2B buyers, particularly those operating in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including key markets like Germany and Brazil—making informed purchasing decisions is vital. With fluctuating labor costs, diverse vehicle specifications, and varying quality standards across regions, it can be overwhelming to determine the most cost-effective solutions for starter replacements.
This comprehensive guide empowers businesses by providing actionable insights into the factors influencing starter costs, including labor rates and part availability. By equipping B2B buyers with the knowledge to evaluate their options critically, we aim to facilitate smarter procurement strategies that enhance operational efficiency and reduce unexpected repair expenses. Whether you are managing a fleet or running an auto repair business, understanding the nuances of starter replacement will enable you to optimize your investment and ensure reliable vehicle performance.
Table Of Contents
- Top 6 How Much To Fix Starter Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for how much to fix starter
- Understanding how much to fix starter Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of how much to fix starter
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘how much to fix starter’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for how much to fix starter
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for how much to fix starter
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘how much to fix starter’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for how much to fix starter Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing how much to fix starter With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for how much to fix starter
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the how much to fix starter Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of how much to fix starter
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for how much to fix starter
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Understanding how much to fix starter Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Starter | Basic design, typically less expensive, widely available. | General automotive repair shops, fleet services. | Pros: Cost-effective; Cons: May lack advanced features. |
| Gear Reduction Starter | More efficient, smaller, and lighter; draws less battery power. | Performance vehicles, specialized automotive applications. | Pros: Better efficiency; Cons: Higher initial cost. |
| Direct Drive Starter | Larger motor, operates at lower speeds, generally cheaper. | Commercial vehicles, older model cars. | Pros: Lower replacement cost; Cons: Less efficient. |
| High-Performance Starter | Designed for racing or heavy-duty applications; high durability. | Motorsport teams, heavy machinery. | Pros: Superior performance; Cons: Expensive and niche. |
| Remanufactured Starter | Rebuilt from used parts, often cheaper than new. | Cost-sensitive buyers, eco-conscious fleets. | Pros: Affordable; Cons: Potential reliability issues. |
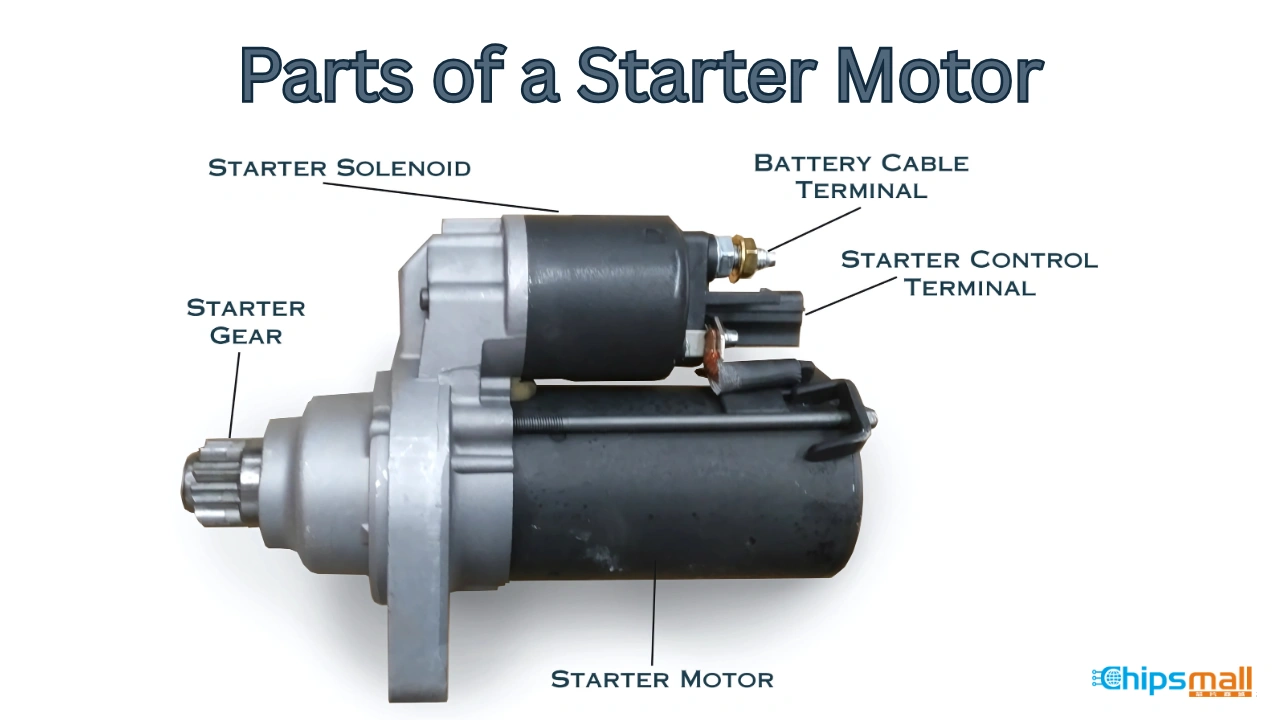
What Are the Characteristics of a Standard Starter?
Standard starters are the most commonly used type, characterized by their straightforward design and affordability. They are suitable for a wide range of vehicles, making them a go-to choice for general automotive repair shops and fleet services. When considering a standard starter, B2B buyers should focus on the vehicle make and model compatibility, as well as the warranty terms offered by suppliers. While they provide a cost-effective solution, buyers should be aware that they may not include advanced features found in more specialized starters.
How Do Gear Reduction Starters Differ from Standard Starters?
Gear reduction starters are engineered for efficiency, featuring a compact design that reduces battery draw while providing reliable performance. They are ideal for performance vehicles and specialized automotive applications where weight and power consumption are critical. B2B buyers in sectors such as racing or high-performance automotive repair should evaluate the cost-benefit ratio of these starters, as they typically come at a higher price point. The initial investment may be justified by the long-term savings on battery life and improved vehicle performance.
What Makes Direct Drive Starters a Common Choice?
Direct drive starters utilize a larger motor operating at lower speeds, making them a cost-effective option for commercial vehicles and older model cars. Their simplicity and lower replacement costs appeal to businesses looking to maintain older fleets without incurring high repair expenses. However, B2B buyers should consider the efficiency trade-offs, as direct drive starters may not perform as well under demanding conditions. Their suitability largely depends on the specific requirements of the vehicles in question.
Why Choose High-Performance Starters for Specialized Applications?
High-performance starters are crafted for racing or heavy-duty applications, emphasizing durability and reliability under extreme conditions. These starters are essential for motorsport teams and heavy machinery operators who require uncompromised performance. B2B buyers should assess the specific performance needs and operational environments when considering these starters, as they often come with a premium price tag. The investment in high-performance options can yield significant returns in terms of reliability and efficiency.
What Are the Benefits and Drawbacks of Remanufactured Starters?
Remanufactured starters are rebuilt from used components and sold at a lower price than new models, making them an attractive option for cost-sensitive buyers and eco-conscious fleets. They offer a balance of affordability and functionality, but potential reliability issues may arise due to the nature of the rebuilding process. B2B buyers should carefully evaluate the remanufacturing process and warranty coverage, ensuring that they are getting a reliable product that meets their operational needs.
Key Industrial Applications of how much to fix starter
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of how much to fix starter | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive Repair | Estimating costs for starter replacements in vehicle maintenance | Helps businesses manage repair budgets and enhance customer satisfaction | Availability of parts, labor rates, and expertise in starter systems |
| Fleet Management | Budgeting for starter repairs across vehicle fleets | Reduces downtime and operational costs through effective maintenance planning | Bulk purchasing options, reliability of parts, and service contracts |
| Construction Equipment | Assessing starter replacement costs for heavy machinery | Ensures equipment reliability, minimizing project delays due to mechanical failures | Compatibility with various machinery brands and models, sourcing quality components |
| Public Transportation | Calculating starter repair costs for buses and transit vehicles | Improves service reliability and reduces unexpected repair expenses | Access to specialized parts and efficient repair services |
| Agricultural Machinery | Evaluating starter repair expenses for farming equipment | Enhances productivity by ensuring machinery is always operational | Supplier relationships, seasonal demand considerations, and technical support |
How Can Automotive Repair Shops Use ‘How Much to Fix Starter’ to Enhance Service Offerings?
Automotive repair shops can utilize the information on starter replacement costs to provide transparent and accurate estimates to their customers. By understanding the average costs associated with different vehicle makes and models, shops can build trust and improve customer relationships. This knowledge is particularly beneficial for international buyers in regions like Europe and South America, where labor rates and parts availability can vary significantly. Repair shops should also consider sourcing quality parts that align with local regulations and standards.
What Role Does Cost Estimation Play in Fleet Management?
For fleet management companies, accurately estimating starter repair costs is crucial for maintaining operational efficiency. By budgeting for these repairs, fleet managers can minimize vehicle downtime, ensuring that transportation services remain uninterrupted. This is especially important in regions like Africa and the Middle East, where logistics and transport reliability are paramount. Fleet managers should focus on establishing relationships with suppliers who can provide bulk purchasing options and reliable service contracts to streamline maintenance processes.
Why Is Cost Assessment Important for Construction Equipment?
In the construction industry, assessing starter replacement costs for heavy machinery is essential to avoid project delays. Heavy machinery often operates under challenging conditions, making it susceptible to mechanical failures. Understanding the costs associated with repairs allows construction firms to plan their budgets effectively and ensure equipment reliability. Buyers in this sector should prioritize sourcing parts that are compatible with various machinery brands and models, as well as seek suppliers that offer technical support and quick turnaround times.
How Do Public Transportation Services Benefit from Cost Analysis?
Public transportation services can greatly benefit from a detailed analysis of starter repair costs. By budgeting for these repairs, transit authorities can improve service reliability and reduce unexpected expenses that may arise from sudden vehicle breakdowns. This is particularly relevant in European markets, where public transport systems are heavily relied upon. Authorities should ensure access to specialized parts and efficient repair services to maintain their fleets and meet the demands of commuters.
What Are the Considerations for Agricultural Machinery?
In agriculture, evaluating starter repair expenses for farming equipment is vital for maintaining productivity during critical planting and harvesting seasons. Delays caused by machinery failures can lead to significant financial losses. International buyers in this sector should focus on establishing strong supplier relationships to ensure timely access to quality components and technical support, especially during peak seasons when demand for machinery is high.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘how much to fix starter’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Understanding the True Cost of Starter Replacement for Fleet Vehicles
The Problem: Many B2B buyers managing fleet vehicles face the challenge of accurately estimating the total cost of starter replacement. Fleet managers often struggle with balancing budget constraints while ensuring their vehicles remain operational. The hidden costs associated with labor, parts, and potential downtime can lead to unexpected expenses. Additionally, varying vehicle makes and models complicate the estimation process, making it difficult to create a comprehensive financial plan for maintenance and repairs.
The Solution: To effectively manage the costs of starter replacements, fleet managers should adopt a standardized approach for all vehicles in their fleet. Begin by cataloging the specifications of each vehicle, including make, model, and year, to understand the average starter replacement costs. Use industry benchmarks, such as the average labor rates and part prices, to create a detailed cost breakdown. Consider partnering with a reliable automotive service provider that specializes in fleet management; they can offer insights into potential bulk discounts and preferred rates. Additionally, implement a proactive maintenance schedule that includes regular inspections of the starter system to prevent unexpected failures and minimize downtime. This approach not only helps manage costs but also extends the lifespan of fleet vehicles, ultimately leading to better financial outcomes.
Scenario 2: Sourcing Quality Starters Amid Supply Chain Challenges
The Problem: B2B buyers, particularly those in regions like Africa and South America, often encounter significant challenges in sourcing quality replacement starters. Supply chain disruptions can lead to delays in obtaining parts, resulting in prolonged vehicle downtime. Additionally, the risk of receiving counterfeit or subpar components increases when buyers are forced to source from less reputable suppliers. This situation can have a cascading effect on businesses that rely heavily on their vehicles for operations, leading to lost revenue and diminished customer trust.
The Solution: To navigate these sourcing challenges, businesses should establish relationships with reputable suppliers who have a proven track record of providing quality automotive parts. Conduct thorough research to identify distributors that specialize in starter motors and have access to reliable brands. Consider utilizing online marketplaces that vet their suppliers, ensuring quality and authenticity. Additionally, implement a just-in-time inventory strategy to keep essential parts on hand, reducing reliance on external suppliers during critical repair times. Building a network of multiple suppliers can also provide backup options in case of shortages or delays, ensuring that your operations remain smooth and efficient.
Scenario 3: Deciding Between Repairing or Replacing a Starter
The Problem: B2B buyers often grapple with the decision of whether to repair or replace a faulty starter. This dilemma can be particularly challenging for businesses that operate under tight budgets. Repairing a starter may seem like a cost-effective solution at first, but it may lead to recurring issues and further expenses in the long run. Conversely, the upfront cost of a new starter can strain finances, especially if the decision isn’t backed by thorough analysis.
The Solution: To make an informed decision between repairing or replacing a starter, B2B buyers should conduct a comprehensive assessment of the starter’s condition, including its age and the extent of the damage. If the starter has already undergone multiple repairs or shows signs of significant wear, replacement is likely the more prudent choice. Engage with a trusted automotive technician who can provide a detailed diagnostic report, helping to determine the long-term viability of a repair. Additionally, consider the warranty options available for new starters, which can provide peace of mind and potential savings on future repairs. Implementing a regular maintenance program can also help detect early signs of starter failure, allowing for timely interventions that minimize costs and extend the life of the vehicle components.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for how much to fix starter
What Are the Common Materials Used in Starter Components?
When considering how much to fix a starter, the choice of materials plays a critical role in determining the overall performance, durability, and cost-effectiveness of the repair. Below, we analyze four common materials used in starter components, focusing on their key properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for international B2B buyers.
What Are the Key Properties of Copper in Starter Components?
Copper is widely used in electrical components of starters due to its excellent conductivity. It has a high melting point (1,984°F or 1,085°C) and offers good corrosion resistance, making it suitable for various automotive environments.
Pros & Cons:
Copper’s high conductivity ensures efficient electrical flow, which is crucial for starter performance. However, it is more expensive than other metals like aluminum and can be prone to corrosion if not properly treated. The manufacturing process for copper components can be complex, involving precise machining and finishing to maintain conductivity.
Impact on Application:
Copper is compatible with all automotive electrical systems, but its cost may be a concern for budget-sensitive projects, especially in regions where raw material prices fluctuate.
Considerations for International Buyers:
In regions like Africa and South America, where cost efficiency is vital, the higher price of copper may deter its use. Compliance with international standards such as ASTM B75 for copper tubes is also essential for ensuring quality and safety.
How Does Aluminum Compare as a Material for Starters?
Aluminum is another common material used in starter construction, particularly for housings and casings. It has a lower density than copper, making it lighter and easier to handle.
Pros & Cons:
Aluminum is cost-effective and offers good corrosion resistance, especially when anodized. However, its lower electrical conductivity compared to copper can affect performance in high-demand applications. Manufacturing complexity is moderate, as aluminum can be easily cast or extruded.
Impact on Application:
Aluminum is suitable for various automotive applications but may not be ideal for high-performance starters where conductivity is paramount.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Aluminum is widely accepted in global markets, and compliance with standards such as DIN EN 573 for aluminum alloys is crucial. In Europe, especially in Germany, there is a strong preference for lightweight materials, making aluminum an attractive option.
What Role Does Steel Play in Starter Manufacturing?
Steel is often used for structural components within starters, such as the drive gear and mounting brackets. It offers high strength and durability, which are essential for components that undergo significant mechanical stress.
Pros & Cons:
Steel’s strength makes it suitable for high-load applications, but it is heavier than aluminum and copper, which may affect overall vehicle weight. Corrosion resistance can be a concern unless treated with coatings or galvanization, which adds to manufacturing complexity.
Impact on Application:
Steel components are critical for the mechanical integrity of starters, but their weight may be a disadvantage in performance-focused vehicles.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Steel is universally recognized and complies with various standards like ASTM A36. However, buyers in regions with high humidity, such as parts of Africa and the Middle East, should prioritize corrosion-resistant treatments.
How Is Plastic Used in Starter Components?
Plastic is increasingly used in starter components, particularly for insulation and housing elements. It provides excellent electrical insulation and is lightweight.
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage of plastic is its low cost and weight. However, it may not withstand high temperatures as effectively as metals, and its mechanical strength is lower, making it less suitable for load-bearing applications.
Impact on Application:
Plastic components are ideal for insulation but should be used cautiously in high-stress areas.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Compliance with international plastic standards, such as ISO 9001 for quality management, is essential. In markets like Europe, buyers may prefer plastics that are recyclable or have lower environmental impact.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Starter Components
| Material | Typical Use Case for how much to fix starter | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Copper | Electrical connections and wiring | Excellent conductivity | Higher cost and corrosion risk | High |
| Aluminum | Casings and housings | Lightweight and cost-effective | Lower conductivity than copper | Medium |
| Steel | Structural components (e.g., drive gear) | High strength and durability | Heavier and potential corrosion | Medium |
| Plastic | Insulation and housing elements | Low cost and lightweight | Lower temperature tolerance | Low |
This analysis provides a comprehensive overview of material options for starter repairs, helping international B2B buyers make informed decisions based on performance, cost, and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for how much to fix starter
What Are the Key Stages of Starter Manufacturing Processes?
Manufacturing a car starter involves a series of well-defined stages that ensure the final product meets performance standards and durability requirements. Understanding these stages is crucial for B2B buyers looking to source reliable components.
Material Preparation: How Are Raw Materials Selected and Processed?
The first stage involves selecting high-quality raw materials, primarily metals such as steel, copper, and aluminum. These materials are sourced based on their mechanical properties, electrical conductivity, and resistance to corrosion. Once selected, materials undergo processes like cutting, forging, and machining to create specific components, such as the armature, solenoid, and housing.
Additionally, suppliers often perform material tests to ensure compliance with international standards, which may include tensile strength and conductivity assessments. This initial step is critical, as the quality of the raw materials directly impacts the longevity and reliability of the starter.
What Techniques Are Used in the Forming Stage?
In the forming stage, components are shaped through various techniques, including die casting, stamping, and injection molding. Die casting is typically used for creating the starter housing, while injection molding can be utilized for the plastic components.
Precision is key during this phase, as any deviations can affect the assembly and performance of the starter. Advanced technologies, such as CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining, are often employed to achieve tight tolerances. This level of precision is especially important for B2B buyers who require components that fit seamlessly into their systems.
How Is the Assembly Process Conducted?
The assembly of the starter typically involves combining several key components: the armature, solenoid, and drive gear. This stage can be performed either manually or through automation, depending on the manufacturer’s capabilities and production volume.
Quality control during assembly is critical, as improper assembly can lead to failures in the field. Technicians often follow standardized assembly procedures and checklists to ensure that all components are installed correctly and function as intended. For B2B buyers, it is essential to confirm that suppliers adhere to robust assembly protocols to minimize the risk of defects.
What Finishing Techniques Are Applied to Starters?
Once assembled, starters undergo finishing processes, which may include painting, coating, or plating. These techniques enhance the component’s resistance to environmental factors, such as moisture and corrosion.
Finishing processes also contribute to the product’s aesthetics, an aspect that may be more relevant for consumer-facing applications. For B2B buyers, verifying that suppliers use high-quality finishing techniques can enhance the reliability and longevity of the products in various operating conditions.

Illustrative image related to how much to fix starter
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Starter Production?
Quality assurance (QA) is a vital aspect of the manufacturing process, ensuring that each starter meets both industry standards and customer specifications.
What International and Industry-Specific Standards Are Relevant?
Manufacturers often comply with international standards such as ISO 9001, which sets the criteria for a quality management system. Additionally, industry-specific certifications, such as CE marking in Europe or API standards for automotive parts, may be required. These certifications demonstrate that products meet safety, health, and environmental protection requirements.
For B2B buyers, understanding these standards is crucial when evaluating suppliers. Compliance with recognized standards can serve as an indicator of a manufacturer’s commitment to quality and reliability.
Which Quality Control Checkpoints Are Typically In Place?
Quality control is typically divided into several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This step involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified requirements before production begins.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, random inspections are conducted to monitor the production process and identify any deviations from quality standards.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once production is complete, finished products undergo rigorous testing to ensure they function correctly and meet all specifications.
These checkpoints help identify defects early in the process, allowing manufacturers to address issues before they reach the customer.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used for Starters?
Several testing methods are employed to validate the performance and durability of starters:
-
Electrical Testing: This includes checking the starter’s voltage, current draw, and resistance to ensure it operates within specified parameters.
-
Durability Testing: Starters may undergo simulated wear tests to assess their performance under various conditions, mimicking real-world usage.
-
Environmental Testing: Products are exposed to extreme temperatures, humidity, and other environmental factors to verify their resilience.
B2B buyers can request test reports and certifications from suppliers to ensure that products meet necessary performance standards.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international buyers, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is essential for ensuring product reliability. Here are several strategies:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to review a supplier’s manufacturing processes, quality control measures, and compliance with international standards.
-
Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports and certifications can provide insights into a supplier’s commitment to quality assurance.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Utilizing third-party inspection services can offer an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s quality control practices. These services can conduct random inspections and testing to ensure compliance with standards.
What Are the QC and Certification Nuances for International Buyers?
International buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, must navigate various certification requirements. Each market may have different standards for automotive components, which can affect sourcing decisions.
Understanding local regulations, import duties, and compliance requirements can help buyers mitigate risks associated with sourcing from international suppliers. Additionally, maintaining clear communication with suppliers regarding quality expectations and certifications can foster stronger business relationships and ensure product quality.
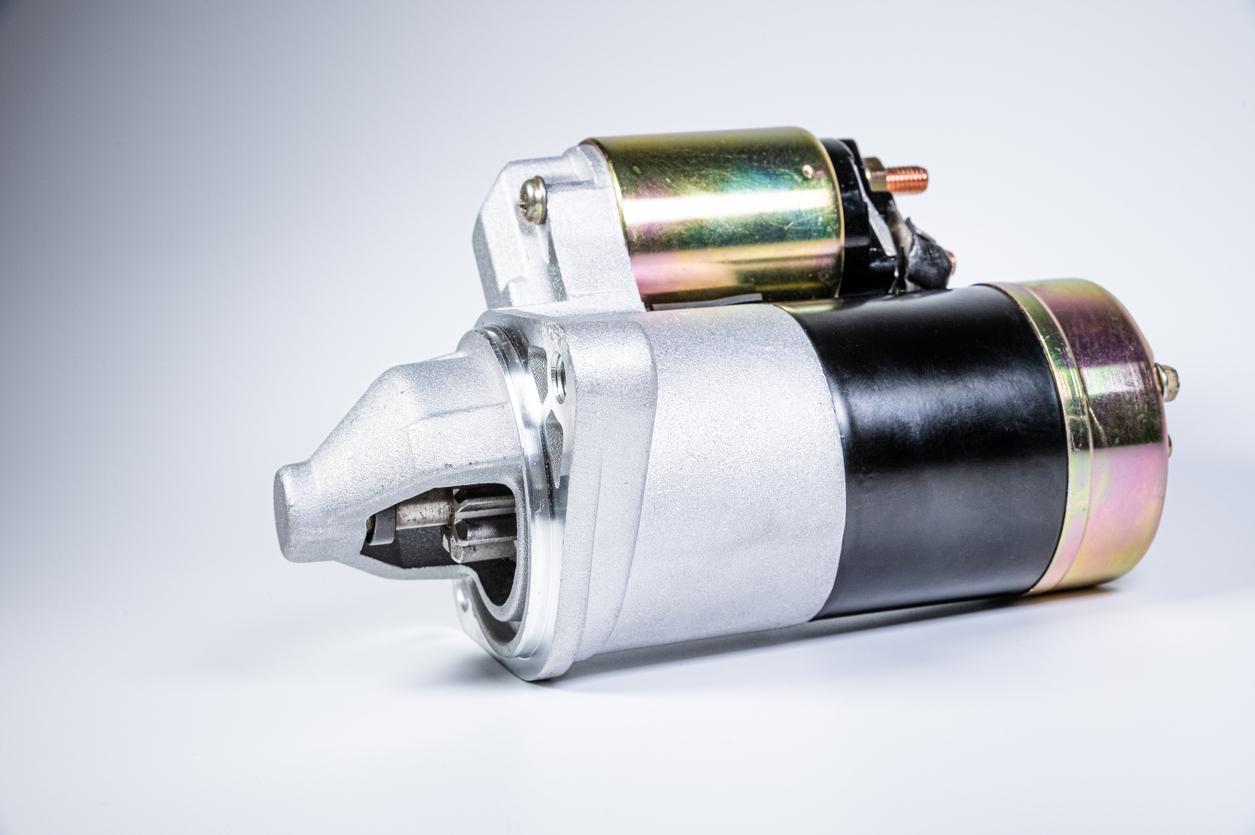

Illustrative image related to how much to fix starter
By focusing on the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures outlined above, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing starters, ensuring they receive high-quality products that meet their operational needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘how much to fix starter’
Introduction
This sourcing guide serves as a practical checklist for B2B buyers looking to procure services related to starter repair and replacement. Understanding the costs and processes involved is essential for making informed purchasing decisions, especially when engaging with suppliers in diverse international markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Step 1: Assess Your Vehicle’s Needs
Before seeking suppliers, determine the specific requirements of your vehicle’s starter system. This includes identifying the make and model, as well as any symptoms indicating a faulty starter. Knowing these details will help you communicate effectively with suppliers and ensure you receive accurate quotes.
- Key Considerations:
- Look for common issues associated with your vehicle’s starter type.
- Document the signs of malfunction, such as unusual noises or starting difficulties.
Step 2: Research Replacement Costs
Understanding the average costs associated with starter replacements is crucial for budget planning. Typically, the overall expense ranges from $700 to $1,200, influenced by labor rates and part prices.
- Cost Breakdown:
- Investigate labor rates in your region, which can vary significantly.
- Compare prices for starter parts based on your vehicle’s specifications.
Step 3: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outline the technical specifications required for the starter replacement. This includes part types (gear reduction vs. direct drive), compatibility with your vehicle, and any additional features that may be necessary.

Illustrative image related to how much to fix starter
- Why It Matters:
- Accurate specifications prevent costly errors and ensure the right components are sourced.
- They facilitate better communication with suppliers, reducing misunderstandings.
Step 4: Identify and Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Search for reputable suppliers who specialize in automotive parts and services. Evaluate their experience, reliability, and the range of products they offer.
- Supplier Vetting:
- Request company profiles and case studies to gauge their expertise.
- Look for customer testimonials and industry certifications to verify credibility.
Step 5: Request Detailed Quotations
Once you’ve narrowed down potential suppliers, request detailed quotations that break down costs for parts, labor, and any additional services. This transparency allows for accurate budget comparisons.
- What to Include:
- Ensure quotes cover the full scope of work, including any warranty or service guarantees.
- Ask about timelines for parts availability and installation.
Step 6: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Engage in discussions regarding payment terms, warranties, and return policies. Clear agreements help protect your investment and establish expectations.

Illustrative image related to how much to fix starter
- Negotiation Tips:
- Be upfront about your budget constraints and seek flexibility where possible.
- Ensure that warranties cover both parts and labor for a specified duration.
Step 7: Finalize Your Procurement
After selecting a supplier and agreeing on terms, finalize your procurement process. Ensure all agreements are documented and confirm timelines for delivery and installation.
- Final Checklist:
- Review the contract for any hidden fees or clauses.
- Confirm the installation schedule and any follow-up service agreements.
By following these steps, B2B buyers can effectively navigate the complexities of sourcing starter repair services, ensuring a smooth procurement process and optimal outcomes for their vehicle maintenance needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for how much to fix starter Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components of Starter Repair and Replacement?
When considering the costs associated with fixing or replacing a starter, several components contribute to the overall price. The primary cost elements include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and margin.
-
Materials: The price of starter motors varies significantly based on the type and brand. On average, a starter can range from $100 to $400. Higher-end vehicles, such as luxury brands, often have starters that cost between $250 and $1,000.
-
Labor: Labor costs can be substantial, often making up the majority of the total repair bill. Rates can range from $100 to $250 per hour, depending on the region and the expertise required. The complexity of accessing the starter also affects labor time; for instance, some vehicles require the removal of other components, increasing labor hours.
-
Manufacturing Overhead and Tooling: These costs include the expenses related to the production of starters, such as factory operations and the equipment used in manufacturing. High-volume production often reduces per-unit costs due to economies of scale.
-
Quality Control: Ensuring the reliability and safety of starters involves rigorous testing and quality assurance processes. This aspect may add to the cost but is crucial for maintaining product integrity, especially in high-stakes industries like automotive.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs for getting starters from manufacturers to distributors or directly to repair facilities can also influence the final pricing. Factors such as distance, shipping methods, and customs duties (for international transactions) should be considered.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a margin to cover their operational costs and profit. This margin can vary based on market demand and competition.
How Do Pricing Influencers Impact Starter Repair Costs?
Several factors influence the pricing of starter repairs and replacements, particularly for international B2B buyers.
Illustrative image related to how much to fix starter
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Bulk purchases often lead to discounted rates. Buyers should consider negotiating MOQs with suppliers to benefit from lower unit prices.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom starters designed for specific vehicles may incur additional costs due to unique manufacturing requirements. Buyers need to assess whether customization is necessary for their needs.
-
Quality and Certifications: Products that meet specific industry standards or certifications may carry a higher price tag. However, investing in quality can lead to long-term savings by reducing failure rates and maintenance costs.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can significantly affect pricing. Established suppliers may offer warranties or better support, which can justify higher prices.
-
Incoterms: The terms of sale (such as FOB, CIF, etc.) dictate who is responsible for shipping costs and risks. Understanding these terms is vital for accurate cost assessments in international transactions.
What Tips Can Help Buyers Achieve Cost-Efficiency in Starter Repairs?
International B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should consider the following strategies to optimize costs related to starter repairs:
-
Negotiate Terms: Always negotiate pricing and terms with suppliers. This can include discounts for bulk orders or better payment terms.
-
Assess Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate not just the upfront costs but also long-term expenses, including maintenance, warranty claims, and potential downtime. A slightly higher initial investment in a quality starter may save money over time.
-
Understand Regional Pricing Nuances: Be aware of regional pricing differences influenced by local market conditions, import tariffs, and currency fluctuations. Buyers from Europe may find different pricing structures compared to those in Africa or South America.
-
Research Supplier Reliability: Choose suppliers with a proven track record. Investing in reliable products can minimize the risk of early failure and additional costs.
Conclusion
Understanding the cost structure and pricing influencers for starter repairs and replacements is crucial for B2B buyers. By analyzing each component and strategically negotiating with suppliers, buyers can achieve a more cost-effective solution while ensuring the reliability and performance of their vehicle’s starter system. Always keep in mind that indicative prices may fluctuate based on market conditions and specific vehicle requirements.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing how much to fix starter With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternative Solutions for Starter Issues
When faced with a faulty starter, B2B buyers have several options to consider beyond the traditional replacement method. Understanding the costs, benefits, and potential drawbacks of these alternatives can help inform a more strategic decision. Below, we compare the typical costs and features of fixing a starter against two alternative solutions: starter repair and utilizing a jump starter or battery charger.

Illustrative image related to how much to fix starter
| Comparison Aspect | How Much To Fix Starter | Starter Repair | Jump Starter / Battery Charger |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Full functionality restored | Partial functionality, may not last | Provides temporary starting power |
| Cost | $700 – $1,200 | $150 – $400 | $50 – $150 |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires professional help | Can be DIY or professional | Very easy, often user-operated |
| Maintenance | Low (new part) | Medium (may require future repairs) | Low (recharge as needed) |
| Best Use Case | Long-term reliability | Budget-friendly, short-term fix | Quick solution for emergencies |
What Are the Pros and Cons of Starter Repair?
Starter repair is a viable alternative to complete replacement, often involving the replacement of specific components such as the solenoid or brushes. The primary advantage is cost savings, typically ranging from $150 to $400, which can be appealing for businesses looking to manage expenses. However, repairs may not offer the same reliability as a full replacement, and there is a risk of recurring issues, particularly in older vehicles. Additionally, the complexity of the repair can vary significantly based on the vehicle make and model, potentially requiring professional assistance.
How Effective Are Jump Starters or Battery Chargers?
Using a jump starter or battery charger can be an immediate solution to a starter problem, especially in emergency situations. These devices provide a temporary boost to the battery, allowing the vehicle to start without needing to replace or repair the starter. The cost is relatively low, typically between $50 and $150, making it an attractive option for businesses with limited budgets. However, this solution is not sustainable long-term, as it does not address the underlying issue with the starter itself. It is best suited for situations where immediate access to the vehicle is necessary, but it should not be relied upon as a permanent fix.
How Can B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution?
In conclusion, selecting the right solution for starter issues depends on various factors, including budget, urgency, and the desired longevity of the fix. For businesses that prioritize reliability and can invest in a full replacement, addressing the root cause with a complete starter replacement is often the best choice. Conversely, if immediate functionality is needed and the budget is tight, starter repair or utilizing a jump starter may serve as effective temporary solutions. Assessing the specific needs of the business and considering the potential for future repairs will guide B2B buyers toward the most suitable option for their circumstances.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for how much to fix starter
What Are the Key Technical Properties to Consider When Fixing a Starter?
When evaluating the cost to fix a starter, several technical properties are essential for B2B buyers to consider. These properties not only influence the repair cost but also the overall quality and reliability of the starter.
1. Material Grade
The material used in a starter significantly affects its durability and performance. Common materials include aluminum and high-grade steel, which offer resistance to wear and corrosion. In B2B transactions, understanding material grades can help buyers assess the longevity of the product and ensure they are sourcing components that meet industry standards.
2. Electrical Resistance
Electrical resistance is critical for starters, as it affects their efficiency and performance. A starter with low electrical resistance will draw less power, thereby reducing strain on the vehicle’s battery. In a B2B context, assessing this property can lead to better energy efficiency and lower operational costs for businesses that rely on fleet vehicles.
3. Tolerance Levels
Tolerance levels refer to the allowable deviations in the dimensions of starter components. Precise tolerances ensure that parts fit together correctly, which is essential for optimal performance. In B2B transactions, knowing the tolerance levels helps businesses avoid costly errors due to improper fits, leading to delays and additional repair expenses.
4. Heat Resistance
Starters operate under high temperatures, especially during engine cranking. Heat resistance indicates how well a starter can withstand elevated temperatures without degrading. For B2B buyers, particularly those in hot climates or industries requiring heavy machinery, selecting starters with high heat resistance can prevent premature failures and reduce downtime.
5. Start-Up Torque
Start-up torque is the initial force required to start the engine. Different vehicles may require varying torque levels, depending on their engine size and type. Understanding the required start-up torque helps businesses select the right starter for their fleet, ensuring reliable performance and reducing the likelihood of engine start failures.

Illustrative image related to how much to fix starter
What Are the Common Trade Terms Related to Starter Fixing Costs?
In addition to technical properties, familiarity with industry terminology is crucial for effective communication and decision-making in B2B transactions.
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to parts made by the manufacturer of the original vehicle. Using OEM starters ensures compatibility and reliability, as they meet the original specifications. In B2B purchasing, opting for OEM parts can prevent issues related to fit and performance, ultimately reducing long-term costs.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. For businesses, understanding MOQ can help in budgeting and inventory management. It’s essential for B2B buyers to negotiate MOQ to avoid overstocking or understocking parts, especially when dealing with components like starters that may have varying demand.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers asking for price estimates on specific items or services. It allows buyers to compare costs and negotiate better terms. In the context of starter repairs, issuing an RFQ can help businesses secure competitive pricing and ensure they are making informed purchasing decisions.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are internationally recognized rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping goods. Understanding Incoterms is vital for B2B transactions, as they clarify who bears the risk and costs at various points in the shipping process. This knowledge can prevent misunderstandings and financial losses in the procurement of starters.
Illustrative image related to how much to fix starter
5. Warranty Period
The warranty period is the time frame during which a product is covered for defects or failures. A longer warranty period often indicates higher confidence in product quality. For B2B buyers, evaluating warranty terms can provide insights into the expected lifespan of starters and the potential costs associated with future repairs.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions regarding starter repairs, ensuring they secure quality components at competitive prices.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the how much to fix starter Sector
What are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Starter Replacement Sector?
The global automotive starter replacement market is experiencing significant growth, driven by several key factors. Increased vehicle ownership in emerging markets, particularly in Africa and South America, coupled with a surge in the aging vehicle population in Europe and the Middle East, is propelling demand. In regions like Germany and Brazil, where automotive manufacturing is robust, the need for reliable starter replacements is heightened by strict regulatory standards on vehicle maintenance and safety.
B2B technology trends are reshaping sourcing strategies in this sector. Digital platforms facilitating real-time inventory management and advanced analytics for demand forecasting are becoming increasingly popular among suppliers and buyers alike. These technologies enable businesses to optimize their supply chains, reduce lead times, and enhance customer satisfaction. Additionally, there’s a growing trend toward direct sourcing from manufacturers, bypassing intermediaries to reduce costs and improve profit margins.
International buyers are also becoming more discerning, seeking suppliers who can provide not only competitive pricing but also transparency in sourcing and product quality. This shift is prompting manufacturers to invest in better customer relationship management systems and to adopt integrated supply chain solutions that can cater to the specific needs of various markets.
How is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impacting the Starter Replacement Market?
Sustainability is becoming a critical consideration in the automotive sector, including the starter replacement market. The environmental impact of manufacturing and disposing of automotive parts is significant, prompting businesses to adopt more sustainable practices. This includes using recycled materials in starter production and implementing energy-efficient manufacturing processes to reduce carbon footprints.
Ethical sourcing is equally important, with buyers increasingly demanding that suppliers adhere to responsible sourcing practices. This encompasses ensuring that raw materials are sourced from suppliers who prioritize environmental stewardship and fair labor practices. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and Fair Trade can enhance a supplier’s reputation and appeal to ethically-conscious buyers.
As sustainability becomes a focal point, businesses are also exploring the potential for ‘green’ certifications and materials in the starter replacement sector. For instance, the development of eco-friendly starter motors that use less energy and are made from sustainable materials is gaining traction. By prioritizing sustainability and ethical sourcing, companies can not only meet regulatory requirements but also cater to a growing consumer base that values environmental responsibility.
What is the Historical Context of the Starter Replacement Sector?
The evolution of the starter replacement sector dates back to the early 20th century when the first electric starters were introduced, revolutionizing vehicle ignition systems. Initially, these systems were complex and costly, limiting their adoption to high-end vehicles. However, as automotive technology advanced and mass production techniques improved, electric starters became standard in most vehicles.
Over the decades, the design and efficiency of starters have evolved significantly, with modern starters being more compact and energy-efficient. The introduction of gear reduction starters marked a pivotal shift, as they offered improved performance and reduced battery drain. Today, the starter replacement market is characterized by a diverse range of products catering to various vehicle makes and models, influenced by ongoing technological advancements and changing consumer preferences.

Illustrative image related to how much to fix starter
In summary, understanding the market dynamics, embracing sustainability, and recognizing the historical evolution of the starter replacement sector are crucial for international B2B buyers. This knowledge enables them to make informed sourcing decisions that align with current trends and future demands.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of how much to fix starter
-
How do I determine the cost of fixing a starter motor?
To estimate the cost of fixing a starter motor, consider factors such as the make and model of the vehicle, the type of starter, and labor costs in your region. Typically, the price for parts ranges from $100 to over $400, while labor can range from $100 to $250 per hour, depending on accessibility and expertise required. Gathering quotes from multiple suppliers or service centers can provide a clearer picture of potential costs. Additionally, assessing the overall condition of the vehicle may influence whether repair or replacement is more cost-effective. -
What factors influence the price of starter motor repairs?
The price of starter motor repairs can be influenced by several factors, including the vehicle’s make and model, the complexity of the repair, and the geographical location of the service provider. For instance, vehicles that require extensive disassembly to access the starter will incur higher labor costs. Additionally, the type of starter—gear reduction or direct drive—can also affect the price. Ensure to evaluate the total cost of ownership, including potential future repairs, when deciding on repairs or replacements. -
How can I find reliable suppliers for starter parts?
To find reliable suppliers for starter parts, start by researching manufacturers and distributors with a proven track record in the automotive industry. Check for certifications and customer reviews to gauge reliability. Engaging in industry trade shows or networking events can also help you connect with reputable suppliers. Additionally, consider leveraging online platforms that specialize in B2B transactions to access a broader range of options, ensuring you evaluate potential partners based on quality, pricing, and delivery timelines. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for starter parts?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for starter parts can vary significantly between suppliers. Typically, they range from a single unit for smaller suppliers to hundreds or thousands for larger manufacturers. When negotiating with suppliers, be clear about your needs and discuss potential flexibility in MOQs, especially if you are a new buyer or testing a new product line. Establishing a strong relationship with suppliers may also provide opportunities for better terms in the future. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing starter parts internationally?
Payment terms for international purchases can vary, but common arrangements include advance payment, letters of credit, or payment upon delivery. It’s essential to negotiate terms that provide security for both parties. Consider using escrow services or trade finance solutions to mitigate risks associated with international transactions. Always ensure that the payment terms align with your cash flow management strategy, and review any additional costs such as shipping, taxes, and tariffs that may affect the overall price. -
How do I ensure quality assurance for starter parts?
To ensure quality assurance for starter parts, request samples before placing a large order and conduct thorough inspections upon receipt. Look for suppliers who adhere to international quality standards, such as ISO certifications. Implementing a quality control process, including regular audits and checks, can help maintain product integrity. Additionally, consider establishing clear specifications and performance criteria in your contracts to hold suppliers accountable for quality. -
What are the logistics considerations for importing starter parts?
When importing starter parts, logistics considerations include shipping methods, customs regulations, and delivery timelines. Choose a reliable freight forwarder who understands the intricacies of international shipping and can assist with documentation and customs clearance. Be aware of any import duties and taxes that may apply in your region. Additionally, consider the impact of shipping times on your supply chain and factor in buffer periods for potential delays, ensuring you maintain adequate stock levels. -
How can I customize starter parts to meet specific needs?
Customizing starter parts typically involves collaboration with manufacturers who can modify designs or specifications based on your requirements. Engage with suppliers early in the design process to discuss your specific needs, such as performance enhancements or compatibility with unique vehicle models. Be prepared to provide detailed technical specifications, and understand that customization may affect lead times and pricing. Establishing a strong partnership with your supplier can facilitate smoother customization processes and ensure you receive the desired results.
Top 6 How Much To Fix Starter Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Reddit – Starter Replacement Guide
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Starter replacement, labor charges, part price, dealership pricing, diagnostic fees, OEM starter pricing.
2. Facebook – Car Repair Costs
Domain: facebook.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: cost to get car to the shop and replace starter
3. AAA – Car Starter Replacement Costs
Domain: aaa.com
Registered: 1990 (35 years)
Introduction: The average cost to replace a car starter ranges from $700 to $1,200, depending on the make and model of the vehicle and labor hours required. The list price for the starter part itself ranges from under $100 to over $400. Labor rates within the AAA Approved Auto Repair network range from $100 to $250 per hour. Factors influencing the cost include the car’s make and model, the type of starter (gea…
4. CarTalk – Starter Replacement Guide
Domain: cartalk.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Cost of replacing a starter: $600 to $900 for common vehicles; $900 to $1,400 for luxury models. Symptoms of a bad starter include clicking sounds, screeching, and intermittent functionality. Repairing a starter is often not cost-effective; replacement is preferred. Most starters used are remanufactured, not entirely new. Modern vehicles with stop-start systems have starters designed to last despi…
5. Last Chance Auto Repairs – Starter Replacement Cost Guide
Domain: lastchanceautorepairs.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: Starter Replacement Cost: Economy starters: $75 – $200, OEM starters: $150 – $400, High-performance starters: $300 – $1000+. Labor costs: Basic vehicle starter replacement: $100 – $250, Complex installations: $300 – $600+. Factors affecting cost: Vehicle type & model, New vs Re-Manufactured starters, Additional repairs. DIY costs: Parts only: $100 – $400, Time investment: 2-6 hours. Professional b…
6. Tundras – Starter Replacement
Domain: tundras.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Starter replacement for a 2007 Toyota Tundra, quoted cost: $1500 (labor: $900, part: $650). Part number for replacement: Denso 428000-4640. Vehicle mileage: 174,000. Discussion includes varying opinions on cost and difficulty of replacement.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for how much to fix starter
In conclusion, understanding the cost dynamics associated with starter replacement is crucial for B2B buyers in the automotive sector. The total replacement cost typically ranges from $700 to $1,200, heavily influenced by factors such as vehicle make and model, labor rates, and the type of starter required. Strategic sourcing plays a vital role in ensuring that businesses can acquire high-quality parts at competitive prices while also considering the long-term reliability of repairs versus replacements.
For international buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, leveraging local supplier relationships and understanding regional labor costs can lead to significant savings and better service delivery. It is essential to evaluate not only the upfront costs but also the potential for future repairs and replacements.
As the automotive industry evolves, staying informed about sourcing options and cost-effective solutions will empower businesses to make smarter purchasing decisions. Embrace the opportunity to optimize your sourcing strategy and ensure your operations remain efficient and cost-effective. Consider engaging with trusted suppliers who can provide the expertise and support necessary for your automotive needs.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.

Illustrative image related to how much to fix starter
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.