Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for how much to fix a starter on car
In today’s global automotive market, understanding the intricacies of how much to fix a starter on a car is essential for B2B buyers, especially in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. The challenge lies not only in sourcing reliable components but also in navigating a landscape filled with varying labor costs, parts availability, and regional pricing dynamics. This comprehensive guide aims to demystify the starter replacement process by outlining essential factors such as types of starters, their applications across different vehicle models, and critical supplier vetting processes.
By providing detailed insights into cost estimations, including labor and parts breakdowns, this guide empowers international buyers to make informed purchasing decisions. Understanding the average costs—ranging from $531 to $773 for typical replacements—enables businesses to budget effectively and negotiate better deals with suppliers. Furthermore, we delve into regional considerations, ensuring that buyers from diverse markets, including Brazil and Nigeria, can identify the best practices for their specific contexts.
With actionable strategies for assessing quality and reliability, this guide serves as a vital resource for those looking to optimize their automotive repair operations. Whether you are a repair shop owner or a fleet manager, gaining clarity on the factors influencing starter repair costs will enhance your decision-making process and ultimately improve your bottom line.
Table Of Contents
- Top 6 How Much To Fix A Starter On Car Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for how much to fix a starter on car
- Understanding how much to fix a starter on car Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of how much to fix a starter on car
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘how much to fix a starter on car’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for how much to fix a starter on car
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for how much to fix a starter on car
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘how much to fix a starter on car’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for how much to fix a starter on car Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing how much to fix a starter on car With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for how much to fix a starter on car
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the how much to fix a starter on car Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of how much to fix a starter on car
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for how much to fix a starter on car
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
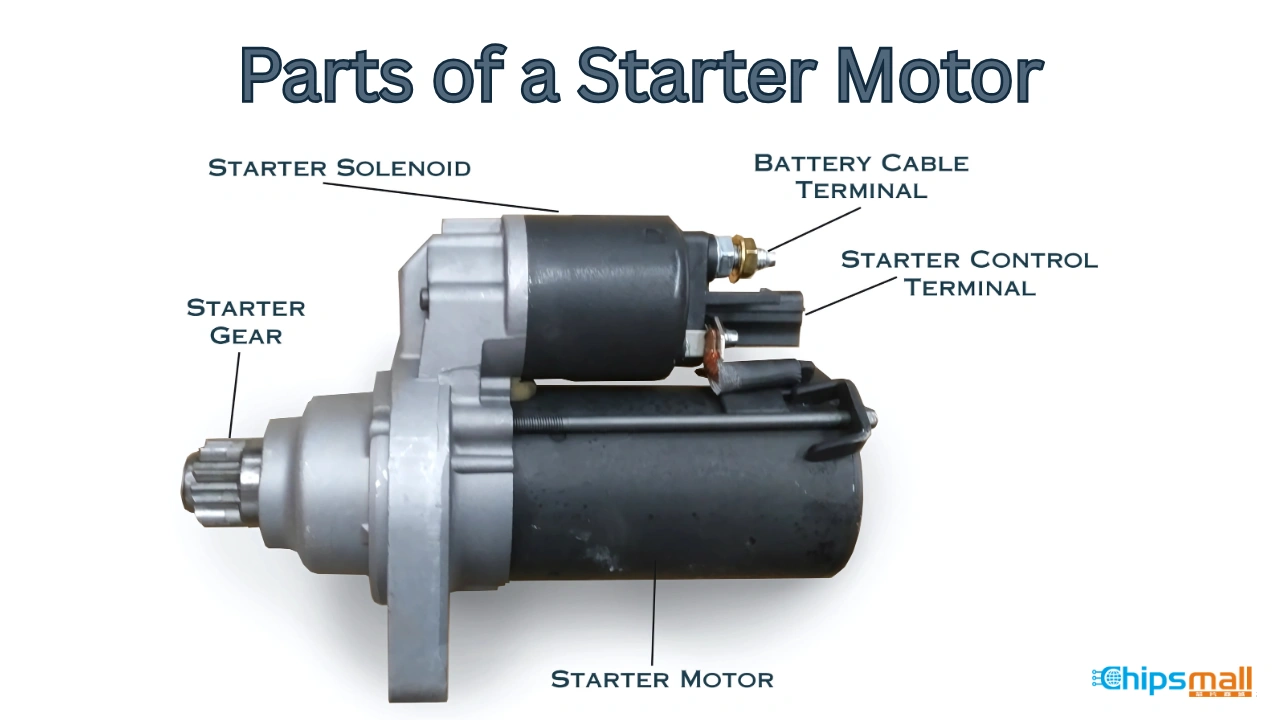
Understanding how much to fix a starter on car Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| OEM Starter Replacement | Original equipment manufacturer (OEM) parts, high reliability | Automotive repair shops, dealerships | Pros: Guaranteed fit and performance; Cons: Higher cost compared to aftermarket parts. |
| Aftermarket Starter Replacement | Non-OEM parts, varying quality and price points | Independent repair shops, budget-conscious buyers | Pros: Cost-effective; Cons: Potential quality variance; may not fit all models. |
| Remanufactured Starters | Rebuilt starters from used components, often tested for quality | Fleet services, budget repair shops | Pros: Lower cost than new; Cons: May have a shorter lifespan than new parts. |
| High-Performance Starters | Designed for enhanced performance, often lighter and more powerful | Racing teams, performance vehicle shops | Pros: Improved starting power; Cons: Higher price and may not suit everyday vehicles. |
| DIY Starter Kits | Kits that include necessary tools and parts for self-installation | DIY enthusiasts, small repair shops | Pros: Cost savings; Cons: Requires technical skill and can be time-consuming. |
What are the Characteristics of OEM Starter Replacements?
OEM starter replacements are manufactured by the original vehicle maker, ensuring a perfect fit and optimal performance. These starters often come with warranties that guarantee their longevity and reliability. B2B buyers, particularly automotive repair shops and dealerships, benefit from using OEM parts as they reduce the likelihood of repeat repairs and enhance customer satisfaction. However, the higher price point may deter budget-conscious buyers.
How Do Aftermarket Starters Differ from OEM Options?
Aftermarket starters are produced by third-party manufacturers and come in a range of quality and price options. They are typically less expensive than OEM parts, making them attractive to independent repair shops and budget-focused buyers. However, the quality can vary significantly, which may lead to compatibility issues or shorter lifespans. B2B buyers should conduct thorough research on suppliers to ensure they are getting reliable aftermarket options.
What are the Benefits of Choosing Remanufactured Starters?
Remanufactured starters are created from used components that have been restored to like-new condition. They are a cost-effective solution for fleet services and budget repair shops looking to manage expenses without sacrificing quality. While these starters can provide significant savings, buyers should be aware that they might not last as long as new starters, making it essential to consider warranty options when purchasing.
Why Consider High-Performance Starters for Specific Applications?
High-performance starters are engineered for vehicles requiring increased starting power, such as racing cars or modified vehicles. These starters are often lighter and more efficient, providing faster engine cranking. B2B buyers in the performance automotive sector will find these starters beneficial for enhancing vehicle performance. However, the premium price and specialized nature mean they may not be suitable for standard vehicles.
What Should DIY Enthusiasts Know About Starter Kits?
DIY starter kits include all necessary components and tools for replacing a starter, appealing to DIY enthusiasts and small repair shops. These kits offer significant cost savings but require a certain level of technical skill and time investment. B2B buyers should evaluate the complexity of installation and the potential for errors, as improper installation can lead to further issues and additional costs.
Key Industrial Applications of how much to fix a starter on car
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of how much to fix a starter on car | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive Repair Shops | Estimating costs for starter replacements | Improved customer trust through transparent pricing | Access to reliable parts suppliers and competitive pricing |
| Fleet Management | Budgeting for maintenance of vehicle starters | Cost control and optimized operational budgets | Volume purchasing agreements for parts and services |
| Car Rental Services | Predicting repair costs for fleet vehicles | Enhanced customer satisfaction and retention | Evaluation of local repair services and turnaround times |
| Insurance Companies | Assessing repair costs for claims related to starter issues | Accurate claims processing and customer service | Partnerships with certified auto repair shops |
| Auto Parts Distributors | Pricing strategies for starter components | Competitive advantage in the market | Supplier reliability and quality assurance |
How Do Automotive Repair Shops Benefit from Knowing Starter Repair Costs?
Automotive repair shops can leverage the knowledge of starter replacement costs to provide accurate estimates to their customers. By understanding the average labor and parts costs, shops can build trust and transparency, which are critical for customer retention. Repair shops should focus on sourcing high-quality OEM parts to enhance their service offerings, ensuring that they are competitive in pricing while maintaining quality.
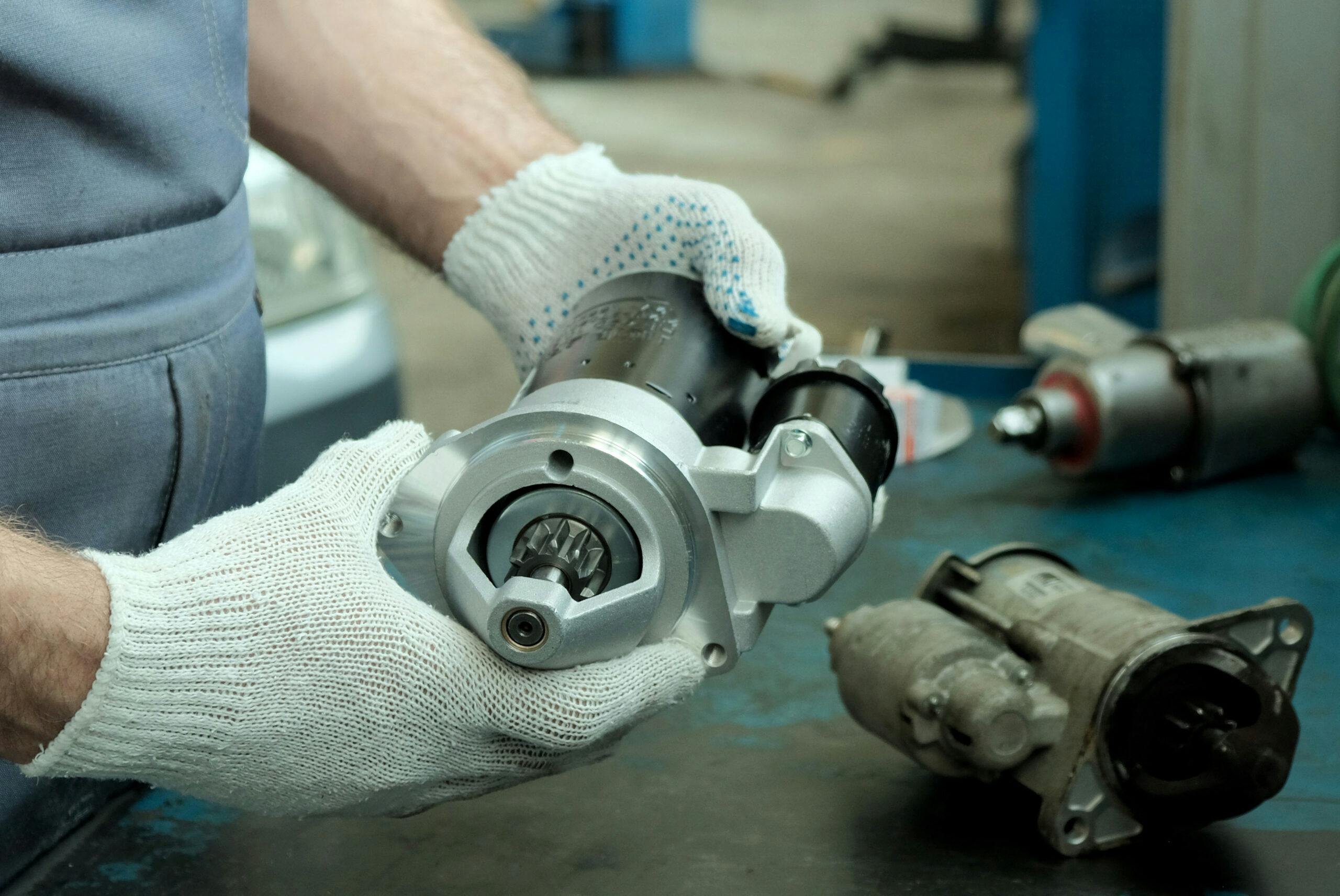

Illustrative image related to how much to fix a starter on car
Why Is Cost Awareness Important for Fleet Management?
For fleet management companies, being aware of starter repair costs is essential for budgeting maintenance and minimizing downtime. Accurate cost assessments help in planning for repairs and replacements, thus optimizing operational budgets. Fleet managers should consider establishing relationships with parts suppliers to negotiate bulk pricing and ensure timely access to components, which can significantly reduce repair lead times.
How Can Car Rental Services Use Starter Repair Cost Estimates?
Car rental services can utilize starter repair cost estimates to predict potential maintenance costs for their fleet. By understanding these costs, they can set competitive rental prices while ensuring their vehicles are reliable for customers. It’s crucial for rental companies to evaluate local repair shops for their service quality and turnaround times to minimize vehicle downtime and enhance customer satisfaction.
What Role Do Insurance Companies Play in Assessing Starter Repair Costs?
Insurance companies benefit from having a clear understanding of starter repair costs to facilitate accurate claims processing. When customers report starter-related issues, insurers can quickly assess the situation and provide timely resolutions. Establishing partnerships with certified auto repair shops can enhance service quality and ensure that repairs are done to industry standards, ultimately improving customer service.

Illustrative image related to how much to fix a starter on car
How Do Auto Parts Distributors Leverage Knowledge of Starter Repair Costs?
Auto parts distributors can use insights into starter repair costs to develop competitive pricing strategies for their components. By understanding the market demand and customer needs, they can position themselves advantageously against competitors. Reliability in sourcing high-quality parts is essential, as it builds brand reputation and fosters long-term relationships with automotive repair shops and other B2B clients.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘how much to fix a starter on car’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Unexpected High Costs from Starter Replacement
The Problem: B2B buyers often face unexpected costs when it comes to starter replacements for their fleets or service vehicles. A typical scenario occurs when a company operates a diverse range of vehicle models, leading to significant variations in parts and labor costs. For instance, a buyer might budget for an average starter replacement cost of $600, only to discover that a particular luxury model requires a starter that costs over $1,400 due to its complex installation process. This discrepancy can strain budgets and disrupt financial planning, especially when multiple vehicles require servicing simultaneously.
The Solution: To mitigate unexpected costs, B2B buyers should implement a proactive vehicle maintenance strategy that includes regular diagnostics and thorough assessments of vehicle health. Utilizing a reliable service platform that provides detailed estimates based on vehicle make and model can help buyers make informed decisions. Additionally, establishing relationships with trusted mechanics or auto repair shops that specialize in fleet services can lead to negotiated rates and better pricing on parts. Regular training for in-house maintenance teams on how to accurately diagnose starter issues can also prevent premature replacements and reduce costs.
Scenario 2: Difficulty in Finding Quality Replacement Parts
The Problem: Another common pain point for B2B buyers involves sourcing quality replacement starters that meet the specific needs of their vehicles. In regions like Africa and South America, where supply chains may be less stable, buyers often struggle to find OEM parts or high-quality alternatives. This can lead to delays in vehicle repairs, resulting in downtime and lost productivity. Additionally, using subpar parts can lead to further complications, requiring additional repairs and ultimately increasing long-term costs.
The Solution: To address these challenges, B2B buyers should leverage online marketplaces and networks that specialize in automotive parts to ensure access to quality starters. Conducting thorough research to identify reputable suppliers, including those that offer warranties or guarantees on their products, is crucial. Establishing partnerships with local distributors who understand the regional market can also enhance supply chain reliability. Buyers should prioritize OEM parts whenever possible to ensure compatibility and performance. Implementing a standard operating procedure for sourcing parts, including checks for quality certifications, can further streamline the procurement process.

Illustrative image related to how much to fix a starter on car
Scenario 3: Misdiagnosis Leading to Unnecessary Repairs
The Problem: Misdiagnosis is a prevalent issue in the automotive repair industry that can lead to unnecessary starter replacements. A common scenario involves technicians mistakenly identifying the starter as the culprit when the actual issue lies with the battery, ignition switch, or wiring. For B2B buyers managing fleets, this misdiagnosis not only results in wasted repair costs but also contributes to vehicle downtime, which can severely impact operational efficiency.
The Solution: To combat misdiagnosis, B2B buyers should invest in comprehensive training for their mechanics or service partners, emphasizing the importance of thorough diagnostic procedures. Utilizing advanced diagnostic tools that can accurately assess the starting and charging systems will help ensure that issues are correctly identified before replacement decisions are made. Additionally, implementing a protocol for systematic troubleshooting can reduce the likelihood of overlooking potential problems. Encouraging regular communication between technicians and fleet managers about vehicle performance and symptoms can foster a culture of accuracy and efficiency, ultimately reducing unnecessary repairs.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for how much to fix a starter on car
What Materials Are Commonly Used in Starter Components?
When considering the costs associated with fixing a starter on a car, the materials used in the starter assembly play a crucial role. The selection of materials impacts not only the performance and durability of the starter but also the overall repair costs. Here, we analyze four common materials used in starter components, focusing on their key properties, advantages, disadvantages, and specific considerations for international B2B buyers.
What Are the Key Properties of Copper in Starters?
Copper is widely used in electrical components due to its excellent conductivity and thermal properties. It has a high melting point of about 1,984°F (1,085°C) and is resistant to corrosion, making it ideal for automotive applications where exposure to moisture and varying temperatures is common.
Pros: Copper’s high conductivity ensures efficient electrical flow, which is vital for starter performance. It is also relatively easy to work with during manufacturing.
Cons: The primary drawback of copper is its cost, which can be higher than other conductive materials. Additionally, copper can be prone to oxidation if not properly coated, which could affect performance over time.
Impact on Application: Copper is essential for components like electrical windings and connectors in starters, ensuring efficient operation.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards such as ASTM B187 for copper wire is essential. Buyers in regions like Africa and South America should consider the local availability of high-quality copper to avoid performance issues.
How Does Steel Contribute to Starter Durability?
Steel is often used in the housing and structural components of starters. It offers excellent strength and durability, with a tensile strength of around 60,000 psi (pounds per square inch) or higher, depending on the grade.
Pros: Steel is cost-effective and provides robust protection against physical damage, making it suitable for harsh automotive environments.
Cons: While steel is strong, it is susceptible to rust and corrosion if not treated or coated properly. This can lead to premature failure in environments with high humidity or exposure to road salt.
Impact on Application: Steel’s durability allows it to withstand the mechanical stresses encountered during starter operation, but corrosion resistance must be considered in design.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as DIN 17100 for structural steel is crucial. Buyers in the Middle East, where humidity can be high, should prioritize corrosion-resistant coatings.
What Role Does Aluminum Play in Starter Design?
Aluminum is increasingly used in starter components due to its lightweight nature and good corrosion resistance. With a melting point of around 1,221°F (660°C), aluminum can withstand moderate temperatures without deforming.

Illustrative image related to how much to fix a starter on car
Pros: The lightweight characteristic of aluminum reduces the overall weight of the starter, which can improve fuel efficiency in vehicles. It is also resistant to corrosion, making it suitable for various climates.
Cons: Aluminum has lower tensile strength compared to steel, which may limit its use in high-stress applications unless alloyed with other metals.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is often used in housings and covers where weight savings are critical, but its strength limitations must be considered in high-stress areas.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that aluminum components meet standards such as ASTM B221 for aluminum extrusions. In regions like Europe, adherence to environmental regulations regarding aluminum production is also important.
How Important Is Plastic in Starter Components?
Plastic is often used in non-structural components of starters, such as housings and insulators. It offers excellent electrical insulation properties and can withstand moderate temperatures.
Pros: Plastic is lightweight and can be molded into complex shapes, making it versatile for various applications. It is also generally less expensive than metals.
Cons: The main limitation of plastic is its susceptibility to degradation from heat and UV exposure, which can lead to failure over time.
Impact on Application: Plastic components can reduce weight and manufacturing complexity, but their long-term durability must be assessed, especially in high-heat environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ISO 9001 for quality management systems is important. Buyers should also consider the availability of high-quality plastics that can withstand environmental factors prevalent in regions like Africa and South America.
Summary Table of Material Properties for Starters
| Material | Typical Use Case for how much to fix a starter on car | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Copper | Electrical windings and connectors | Excellent conductivity | Higher cost, oxidation risk | High |
| Steel | Structural components and housing | Strong and durable | Susceptible to rust without coating | Medium |
| Aluminum | Housings and covers | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Lower tensile strength | Medium |
| Plastic | Non-structural components (insulators, housings) | Versatile and cost-effective | Susceptible to heat and UV degradation | Low |
This analysis provides a comprehensive overview of the materials involved in starter assemblies, helping B2B buyers make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and regional conditions.
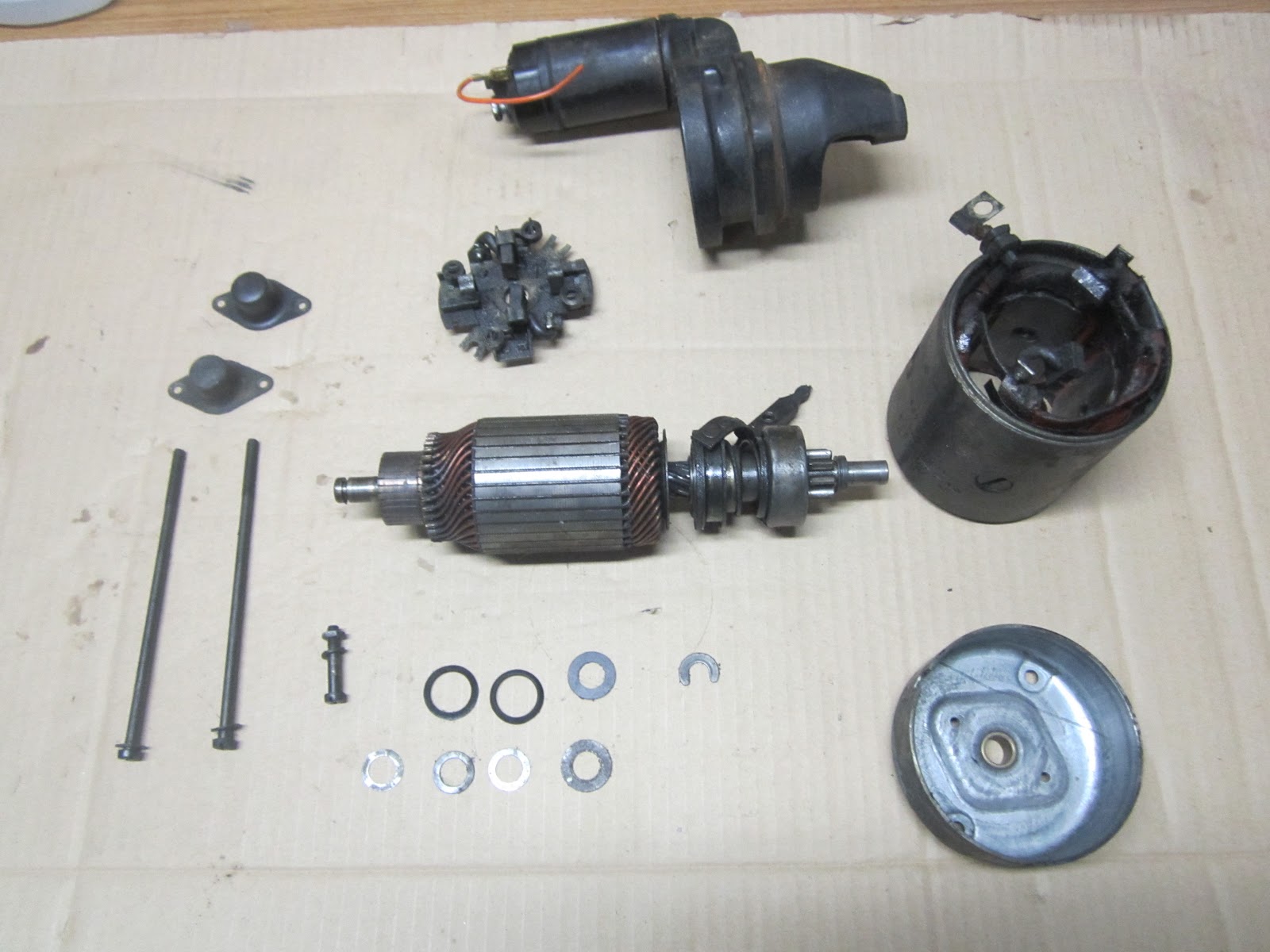
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for how much to fix a starter on car
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing a Car Starter?
The manufacturing of car starters involves several critical stages, each designed to ensure the final product meets rigorous performance and quality standards. The primary stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How Is Material Prepared for Starter Manufacturing?
Material preparation begins with sourcing high-quality components, including steel, copper, and various plastics. The selection of materials is crucial as they must withstand the demanding conditions of automotive applications.
- Material Inspection: Incoming materials undergo an Incoming Quality Control (IQC) process, where they are inspected for defects, dimensional accuracy, and compliance with specifications. This step ensures that only the best materials are used in production.
What Forming Techniques Are Used in Starter Production?
The forming stage involves shaping the prepared materials into the necessary components of the starter motor. Common techniques include:
- Stamping: Metal sheets are stamped into various shapes, including the starter housing and end plates. This process is efficient and allows for high-volume production.
- Machining: Components like the armature and rotor are machined to precise tolerances. CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines are often employed for their accuracy.
- Injection Molding: Plastic parts, such as the housing and connectors, are created using injection molding. This method ensures uniformity and allows for complex designs.
How Is the Assembly Process Structured for Starters?
Once the components are formed, they move to the assembly stage. Here, each part is carefully integrated to create the complete starter motor.
- Automated Assembly Lines: Many manufacturers utilize automated assembly lines that enhance efficiency and reduce human error. Robotics may be employed to handle repetitive tasks, such as inserting brushes or connecting wires.
- Manual Assembly: Certain delicate components may still require skilled labor to ensure proper assembly. Technicians conduct visual inspections during this process to catch any potential issues early.
What Finishing Techniques Are Applied to Ensure Quality?
The final stage, finishing, involves several processes to enhance the durability and performance of the starter.
- Surface Treatment: Components may undergo surface treatments like galvanizing or powder coating to prevent corrosion and improve wear resistance.
- Final Inspections: Before packaging, starters are subjected to rigorous quality checks, ensuring they meet all specifications and performance criteria.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Starter Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is a fundamental aspect of the manufacturing process, ensuring that the finished products are reliable and safe for use. International standards and specific industry practices guide these QA processes.

Illustrative image related to how much to fix a starter on car
What International Standards Are Relevant to Starter Manufacturing?
Many manufacturers adhere to international quality standards such as ISO 9001, which outlines a framework for quality management systems. Compliance with these standards indicates a commitment to consistent quality and continual improvement.
- ISO 9001: This standard focuses on quality management principles, including strong customer focus, the involvement of top management, a process approach, and continual improvement.
In addition to ISO standards, industry-specific certifications such as CE (Conformité Européenne) and API (American Petroleum Institute) may also apply, depending on the geographical market and application of the starters.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Starter Production?
Quality Control (QC) is embedded at various stages of the manufacturing process, ensuring that potential defects are identified and rectified promptly. Key checkpoints include:

Illustrative image related to how much to fix a starter on car
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial inspection checks raw materials against specifications.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During production, ongoing inspections occur to monitor the manufacturing process and detect any deviations from quality standards.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): After assembly, the finished starters undergo comprehensive testing, including electrical performance tests and durability assessments.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used for Starters?
Testing methods for starters often include:
- Bench Testing: Each starter is tested under controlled conditions to verify its functionality and performance.
- Vibration and Shock Testing: This assesses the starter’s ability to withstand real-world conditions, simulating the stresses it will encounter in a vehicle.
- Thermal Testing: Starters may be exposed to extreme temperatures to ensure they can operate effectively in various climates.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
When sourcing starters, especially from international suppliers, B2B buyers must ensure that they partner with manufacturers who maintain robust quality control systems.
What Are Effective Strategies for Auditing Supplier Quality?
- Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to evaluate the manufacturer’s quality control processes firsthand. This includes reviewing documentation, inspecting facilities, and assessing compliance with relevant standards.
- Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports can provide insights into a supplier’s quality performance over time, including defect rates and corrective actions taken.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can add an extra layer of assurance. These organizations can conduct independent evaluations of a supplier’s quality practices and product performance.
What Are the QC Considerations for International B2B Buyers?
For international buyers, particularly those in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, several nuances must be considered:
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensure that the supplier’s products meet local regulations and standards, as these can vary significantly between regions.
- Cultural Differences: Understand that manufacturing practices and quality perceptions may differ across cultures. Building strong relationships with suppliers can facilitate better communication and quality assurance.
- Logistics and Supply Chain Factors: Consider how transportation and logistics may affect product quality. For example, improper handling during shipping can lead to damage, negating the benefits of high-quality manufacturing.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures in starter production, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they procure reliable and durable components for their automotive needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘how much to fix a starter on car’
To assist B2B buyers in navigating the complexities of procuring starter repairs for vehicles, this guide offers a practical checklist. By following these steps, businesses can ensure they make informed decisions regarding the cost and quality of starter replacements.

Illustrative image related to how much to fix a starter on car
Step 1: Assess the Vehicle Requirements
Understanding the specific vehicles in your fleet is crucial. Different makes and models have varying starter specifications and costs associated with repairs. Evaluate the age, model, and condition of each vehicle to determine the most common starter issues you may face and plan your budget accordingly.
Step 2: Research Average Repair Costs
Before initiating contact with suppliers or service providers, familiarize yourself with the typical costs associated with starter replacements. Generally, the cost ranges from $531 to $773, depending on the vehicle. Knowing these figures helps you set realistic budgets and negotiate effectively with service providers.
Step 3: Identify and Verify Suppliers
It’s essential to compile a list of potential repair shops or suppliers that specialize in starter replacements. Look for businesses with a strong reputation in the industry, ideally those that have experience with the specific vehicle types in your fleet. Verify their credentials, including certifications and customer reviews, to ensure reliability and quality of service.
- Consider local suppliers: This can reduce shipping costs and turnaround times.
- Check for warranty offerings: A warranty can indicate confidence in the product or service.
Step 4: Evaluate Supplier Experience and Expertise
Investigate the experience of your shortlisted suppliers in handling starter replacements. Suppliers with extensive experience are more likely to provide high-quality repairs and accurate diagnostics. Request case studies or references from other businesses within your industry to gauge their reliability.
Step 5: Request Detailed Quotes
Once you have identified potential suppliers, request detailed quotes that outline labor and parts costs. Ensure that the quotes include all potential fees, such as diagnostics or additional repairs that may be necessary. This transparency allows you to compare prices effectively and avoid unexpected costs down the line.

Illustrative image related to how much to fix a starter on car
Step 6: Inquire About Parts Quality
When it comes to starter replacements, the quality of parts used can significantly affect the longevity and performance of the repair. Ask suppliers about the brands of starters they use, favoring OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) parts for better reliability. Discuss warranties on parts to further safeguard your investment.
Step 7: Establish a Maintenance Plan
To minimize future starter issues, consider establishing a regular maintenance schedule with your chosen supplier. Regular check-ups can help identify potential problems before they lead to complete failures, thus saving costs in the long run. This proactive approach can enhance the longevity of your fleet and improve overall operational efficiency.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can make informed decisions regarding starter repairs, ensuring they achieve the best value and quality for their investment.
Illustrative image related to how much to fix a starter on car
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for how much to fix a starter on car Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Fixing a Car Starter?
When assessing the costs associated with fixing a car starter, several key components contribute to the overall pricing structure. The primary cost elements include:
-
Materials: The starter motor itself is the most significant material cost, typically ranging from $356 to $516, depending on the vehicle make and model. Additional materials may include wiring, connectors, and any necessary mounting hardware.
-
Labor: Labor costs can vary widely based on geographic location and the complexity of the repair. Expect to pay between $175 and $257 for labor, influenced by the mechanic’s hourly rate and the estimated time required for the job.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to the production of the starter, such as utilities, rent, and salaries of factory workers. These costs are typically factored into the pricing of the starter itself.
-
Tooling and Equipment: Specialized tools are often required for starter installation and diagnosis. The cost of these tools can be significant, especially for independent repair shops.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that the starters meet specific performance and safety standards incurs additional costs. High-quality starters may undergo rigorous testing, impacting their price.
-
Logistics: Transportation and distribution of parts from manufacturers to repair shops also contribute to the cost. This includes shipping fees and handling charges, which can vary based on the distance and mode of transport.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a markup to cover their expenses and profit margin. This can vary significantly based on the supplier’s business model and market conditions.
What Influences the Pricing of Car Starter Repairs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of starter repairs, particularly for international B2B buyers:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Bulk purchasing can lead to significant discounts. Negotiating a favorable MOQ can reduce per-unit costs.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom specifications or modifications can lead to higher costs due to the need for specialized production processes or materials.
-
Quality and Certifications: Higher-quality starters often come with warranties and certifications, which can justify a higher price. Buyers should consider the long-term benefits of investing in quality.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can impact pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their proven track record and quality assurance.
-
Incoterms: The choice of Incoterms can affect the final cost. Terms such as FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) determine who is responsible for shipping costs and risks.
What Are the Essential Tips for B2B Buyers When Sourcing Starter Repairs?
International B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should consider the following tips:
Illustrative image related to how much to fix a starter on car
-
Negotiation Strategies: Always negotiate pricing and terms. Building a long-term relationship with suppliers can lead to better deals over time.
-
Focus on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate not just the initial costs but also the long-term costs associated with repairs and replacements. Investing in higher-quality starters may reduce future maintenance expenses.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances: Be aware that pricing can fluctuate based on local demand, economic conditions, and currency exchange rates. Keeping abreast of these factors can aid in timing your purchases effectively.
-
Leverage Local Resources: Utilize local suppliers when possible to reduce shipping costs and lead times. This can be particularly advantageous in regions with limited access to imported parts.
-
Research and Compare: Always compare multiple suppliers and repair options to ensure you are receiving competitive pricing. Online platforms and industry forums can provide valuable insights into pricing trends and supplier reliability.
Disclaimer
The prices mentioned are indicative and may vary based on location, vehicle type, and specific circumstances. Always consult with local repair professionals for precise estimates tailored to your needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing how much to fix a starter on car With Other Solutions
Introduction to Alternative Solutions for Starter Issues
In the automotive industry, addressing starter issues can be a significant concern for businesses that rely on vehicle efficiency and reliability. While fixing a starter is a common solution, exploring alternatives can provide B2B buyers with cost-effective and efficient options. This analysis compares the cost and effectiveness of fixing a starter with two alternative solutions: starter repair and battery replacement. Each method has unique advantages and disadvantages that can influence decision-making.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | How Much To Fix A Starter On Car | Starter Repair | Battery Replacement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Restores vehicle functionality; average lifespan of 5-10 years | Can extend the life of the existing starter, but may not be permanent | Provides immediate power restoration for starting the vehicle |
| Cost | $531 – $773 | $150 – $300 | $100 – $300 |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires professional installation; may involve multiple components | Can be done by a skilled technician; less invasive | Usually straightforward; many users can DIY |
| Maintenance | Minimal post-repair maintenance; occasional checks recommended | Ongoing checks needed; not always a long-term solution | Regular battery checks; batteries may need replacement every 3-5 years |
| Best Use Case | When starter failure is confirmed | When starter shows signs of wear but isn’t completely failed | When vehicle won’t start, and battery is suspected as the issue |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
1. Starter Repair
Starter repair involves diagnosing and fixing specific issues within the starter motor, such as replacing worn-out components. This option can be less expensive than a full replacement, typically ranging from $150 to $300. The main advantage is cost savings while potentially extending the life of the existing starter. However, this method may not provide a permanent solution, as further issues could arise later. For businesses operating in regions where labor costs are lower, this option might be particularly appealing.
2. Battery Replacement
Replacing the battery can often resolve starting issues, especially if the battery is old or has been underperforming. The cost for a new battery typically ranges from $100 to $300. Battery replacements are usually easy to implement, with many vehicle owners opting to do this themselves. However, while this solution can temporarily restore functionality, it does not address underlying starter problems and may lead to further issues if the starter is, in fact, the primary concern. It is best used when the vehicle shows signs of battery failure, such as slow cranking or electrical issues.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
For B2B buyers evaluating how to address starter issues, the decision should be based on the specific context of the vehicle’s performance and the financial implications of each option. If the starter is confirmed to be faulty, investing in a new starter may be the best long-term solution despite the higher upfront cost. On the other hand, if the vehicle shows signs that point to battery issues, a battery replacement may offer a quick and cost-effective fix. Starter repair can serve as a middle ground, offering a temporary solution that can extend the life of the starter. Ultimately, careful diagnosis and an understanding of the vehicle’s condition will guide the best choice for operational efficiency and cost management.

Illustrative image related to how much to fix a starter on car
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for how much to fix a starter on car
What Are the Key Technical Properties to Consider When Fixing a Starter on a Car?
Understanding the essential technical properties of a starter motor is crucial for B2B buyers involved in the automotive repair industry. Here are several critical specifications that should be considered:
-
Material Grade
The material used in starter construction typically includes high-grade metals such as copper for windings and steel for housing. High-quality materials ensure durability and efficient performance. B2B buyers should prioritize sourcing starters made from superior materials to minimize replacement frequency and enhance customer satisfaction. -
Torque Rating
Torque rating indicates the amount of rotational force the starter can generate to crank the engine. This specification is vital for ensuring compatibility with various engine sizes and types. Buyers should assess torque ratings against their vehicle models to guarantee optimal functionality and avoid potential engine damage. -
Voltage Compatibility
Most starters operate at a standard voltage of 12V, but some vehicles may require different voltages. Understanding the voltage compatibility is essential for ensuring the starter will function correctly within a specific vehicle. B2B buyers should confirm voltage specifications to prevent mismatches that could lead to electrical failures. -
Current Draw
This specification indicates how much current the starter draws during operation, typically measured in amps. A higher current draw could signify a more powerful starter but may also indicate inefficiency. Buyers need to consider the current draw to ensure their battery can handle the load without depleting too quickly. -
Temperature Tolerance
Starters must operate effectively within a range of temperatures. Understanding the temperature tolerance can help in selecting starters for vehicles operating in extreme climates. Buyers should look for starters that can withstand higher temperatures to ensure reliability and performance in various environmental conditions.
Which Trade Terms Are Commonly Used in Starter Replacement?
Familiarity with industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the automotive sector. Here are several common terms related to starter replacement:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM parts are components made by the original manufacturer of the vehicle. These parts are usually more reliable and come with a warranty. B2B buyers often prefer OEM starters to ensure compatibility and performance, despite a potentially higher cost compared to aftermarket options. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the minimum number of units a supplier is willing to sell in a single order. Understanding MOQ is crucial for B2B buyers as it impacts inventory management and cash flow. Buyers should negotiate MOQs that align with their sales projections to maintain cost-effectiveness. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to solicit price quotes for specific products or services. B2B buyers utilize RFQs to compare prices and terms from different suppliers, ensuring they secure the best deal for starter replacements. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a series of pre-defined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC). They clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding these terms helps B2B buyers navigate shipping and delivery logistics when sourcing starters from overseas suppliers. -
Aftermarket Parts
Aftermarket parts are replacements produced by companies other than the original manufacturer. These parts can vary in quality and price. B2B buyers should assess the benefits and risks associated with using aftermarket starters, balancing cost savings with potential quality issues.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing and purchasing starters, ensuring they meet the needs of their customers while optimizing operational efficiency.

Illustrative image related to how much to fix a starter on car
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the how much to fix a starter on car Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends: What Drives the Starter Replacement Sector?
The global market for automotive starter replacements is influenced by various factors, including rising vehicle ownership, increasing average vehicle age, and advancements in automotive technology. As more consumers retain older vehicles, the demand for starter replacements rises, especially in emerging markets like Africa and South America, where vehicle maintenance is often prioritized over new purchases.
In the B2B space, international buyers are increasingly utilizing technology to streamline sourcing processes. Digital platforms for parts procurement and repair services are becoming more popular, allowing buyers to compare prices and quality across different suppliers. Additionally, the trend towards e-commerce in automotive parts is growing, making it easier for businesses to access a wider range of products from global suppliers.
Moreover, the rise of electric vehicles (EVs) is reshaping the starter market. While traditional starter motors are still in demand, the transition to EVs necessitates new sourcing strategies for parts that comply with the latest technologies. Buyers must remain adaptable, keeping an eye on market dynamics such as fluctuating part prices and changing regulations regarding emissions and vehicle safety.
How Can B2B Buyers Ensure Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in Starter Replacement?
As environmental concerns gain prominence, B2B buyers must consider the sustainability of their sourcing practices for automotive parts, including starters. The automotive industry is under pressure to reduce its carbon footprint, prompting suppliers to adopt greener manufacturing processes. Buyers should prioritize partnerships with manufacturers that utilize sustainable materials and adhere to eco-friendly practices, such as recycling and waste reduction.
Ethical sourcing is equally important. Buyers should ensure their suppliers maintain transparent supply chains, free from labor exploitation and environmental harm. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) or ISO 26000 (Social Responsibility) can serve as indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability and ethical practices.
Furthermore, investing in high-quality, durable starter components can also contribute to sustainability goals. By reducing the frequency of replacements and extending product lifespans, businesses can minimize waste and resource consumption. This strategic approach to sourcing not only aligns with global sustainability goals but also enhances brand reputation among environmentally conscious consumers.
What is the Evolution of the Starter Replacement Market?
The starter replacement market has evolved significantly over the decades, driven by advancements in automotive technology and changes in consumer behavior. Initially, starter motors were simple mechanical devices that operated on direct electrical connections. However, as vehicles became more complex, so did the starters, incorporating sophisticated electronic components and solenoids.
The introduction of more efficient and compact starter designs, such as gear reduction starters, has enhanced performance and reliability. This evolution has led to a shift in the aftermarket landscape, with a growing demand for OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) parts that ensure compatibility and longevity.

Illustrative image related to how much to fix a starter on car
In recent years, the emergence of electric and hybrid vehicles has introduced new challenges and opportunities in the starter market. Manufacturers are now focusing on developing starters that can handle the unique requirements of these vehicles, paving the way for innovation and growth in the sector. B2B buyers must stay informed about these trends to make strategic sourcing decisions that align with the future of automotive technology.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of how much to fix a starter on car
-
How do I determine the cost to fix a starter on a car?
To estimate the cost of fixing a starter, first consider the vehicle’s make and model, as this significantly influences parts pricing and labor costs. Generally, starter replacement can range from $531 to $773, with labor costs between $175 and $257 and parts ranging from $356 to $516. It’s advisable to obtain multiple quotes from local mechanics or suppliers, especially those familiar with your specific vehicle type, to ensure competitive pricing. -
What factors influence the starter replacement cost?
Several factors can affect the cost of starter replacement, including the vehicle’s age, model, and the complexity of the installation. Luxury or high-performance vehicles often incur higher labor charges due to the need for specialized tools or knowledge. Additionally, regional labor rates and availability of parts in your market can lead to price variations, so it’s essential to conduct thorough market research. -
How can I identify a reliable supplier for starter parts?
To find a reliable supplier, evaluate their reputation through customer reviews and industry certifications. Consider suppliers who provide warranties on their products and offer transparent pricing. Networking within industry forums or attending trade shows can also help identify trusted suppliers. Establishing a relationship with suppliers who understand local market dynamics can provide better pricing and support. -
What are the typical payment terms when sourcing automotive parts internationally?
Payment terms can vary widely based on the supplier and the buyer’s relationship. Common options include upfront payments, letters of credit, or payment on delivery. For international transactions, it’s crucial to negotiate terms that protect both parties and ensure compliance with local regulations. Consider using escrow services for larger transactions to mitigate risks. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for starter parts?
Minimum order quantities vary by supplier and can depend on the type of starter parts you require. Many suppliers offer flexibility for first-time buyers or smaller businesses, while established distributors may have stricter MOQs. It’s beneficial to discuss your specific needs with suppliers to find a solution that aligns with your purchasing strategy and inventory management. -
How can I ensure quality assurance (QA) when sourcing starters?
To ensure quality assurance, request samples before placing large orders and verify that the parts meet industry standards. Establish clear quality criteria and inspections during production. Utilizing third-party inspection services can also help verify product quality before shipment. Additionally, maintaining open communication with suppliers about quality expectations is crucial for long-term partnerships. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing starter parts?
When importing starter parts, consider shipping costs, delivery times, and customs regulations in your country. Work with logistics providers experienced in automotive parts to streamline the process. It’s also essential to understand duty rates and tariffs that may apply to automotive components, which can significantly affect your overall cost. -
How do I handle warranty claims for defective starter parts?
To manage warranty claims effectively, ensure you have clear documentation of the purchase, including invoices and warranty terms. Communicate promptly with the supplier regarding the issue, providing detailed information about the defect. Many suppliers will require the return of the defective part for assessment before issuing a replacement or refund, so be prepared for this process.
Top 6 How Much To Fix A Starter On Car Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Starter Replacement – Cost Breakdown
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Starter replacement, labor charges, part pricing, dealership vs. independent shop pricing, diagnostics fees, OEM parts, markup on parts.
2. Facebook – Car Repair Cost Guide
Domain: facebook.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: cost to get car to the shop and replace starter
3. CarTalk – Starter Replacement Guide
Domain: cartalk.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Cost to replace a starter: $600 to $900 for common vehicles; $900 to $1,400 for luxury models. Symptoms of a bad starter include clicking sounds, screeching, and intermittent functionality. Repairing a starter is often not cost-effective compared to replacement. New starters are rare; remanufactured starters are commonly used and come with warranties. Modern vehicles with stop-start systems have s…
4. Last Chance Auto Repairs – Starter Replacement Costs
Domain: lastchanceautorepairs.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: Starter Replacement Cost: Economy starters: $75 – $200, OEM starters: $150 – $400, High-performance starters: $300 – $1000+. Labor costs: Basic vehicle starter replacement: $100 – $250, Complex installations: $300 – $600+. Average total cost: $250 – $1,000+. Factors affecting cost: Vehicle type & model, New vs Re-Manufactured starters, Additional repairs. DIY costs: Parts only: $100 – $400, Tools …
5. CarBuzz – Starter Motor Replacement Costs
Domain: carbuzz.com
Registered: 2003 (22 years)
Introduction: Starter motor replacement cost ranges from $450 to $600 on average. For specific models, the Toyota Tundra (2000-2005) V8 starter replacement costs between $650 and $900, while the Honda Civic costs between $490 and $760. Labor time for most replacements is 1.5 to 2.5 hours, but can be up to four hours for certain engine configurations. Aftermarket starters cost $120 to $200, while OEM starters ar…
6. AAA – Car Starter Replacement Costs
Domain: aaa.com
Registered: 1990 (35 years)
Introduction: The average cost to replace a car starter ranges from $700 to $1,200, influenced by factors such as make and model, labor hours, and type of starter. The list price for the starter part alone ranges from under $100 to over $400. Labor rates within the AAA network range from $100 to $250 per hour. Common signs of a faulty starter include slow cranking, failure to start, strange noises, continuous r…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for how much to fix a starter on car
In navigating the complexities of starter replacement costs, B2B buyers must prioritize strategic sourcing to optimize procurement and maintenance expenses. The average cost for replacing a starter ranges from $531 to $773, with labor and parts contributing significantly to this figure. Buyers should consider the varying costs based on vehicle make and model, ensuring they engage suppliers that offer OEM parts to mitigate future failures.
Additionally, understanding the common symptoms of starter issues—such as clicking sounds or intermittent starting—can aid in timely diagnosis and procurement decisions. For businesses operating in diverse markets like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, establishing relationships with reliable local suppliers is crucial for minimizing downtime and enhancing operational efficiency.
Looking ahead, the global automotive parts market is poised for growth, driven by advancements in technology and increasing vehicle ownership. B2B buyers should leverage this momentum by investing in quality components and fostering partnerships that ensure consistent supply. By doing so, they can not only reduce repair costs but also enhance their service offerings, ultimately leading to greater customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.