Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for what is the car alternator
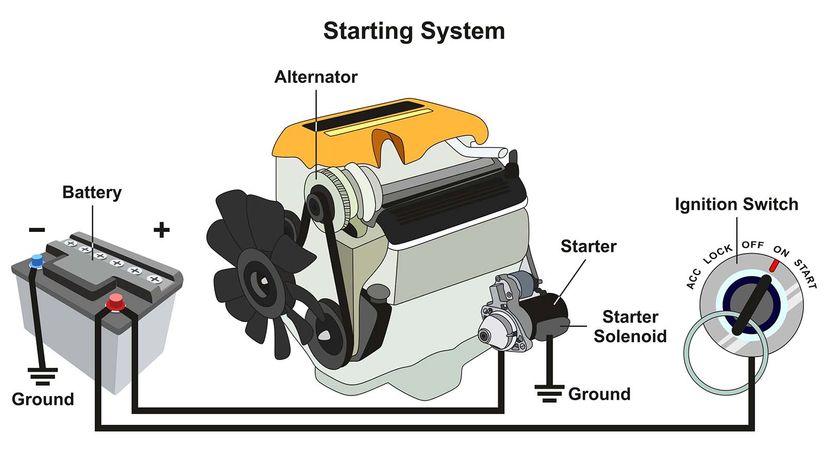
In the dynamic landscape of the global automotive market, understanding the role and functionality of the car alternator is crucial for B2B buyers seeking reliable automotive components. The alternator serves as a vital component in vehicles, converting mechanical energy into electrical energy to power essential systems such as lighting, entertainment, and charging the battery. However, sourcing high-quality alternators that meet specific regional demands can present challenges, especially for international buyers from diverse markets like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including Germany and Saudi Arabia.
This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of car alternators, exploring various types, applications, and key considerations for procurement. It will cover essential topics such as supplier vetting processes, pricing structures, and performance metrics, equipping B2B buyers with the knowledge they need to make informed purchasing decisions. By providing insights into the nuances of alternator selection, this guide empowers businesses to navigate the complexities of sourcing while ensuring the reliability and efficiency of their automotive offerings.
With the right information at their fingertips, international buyers can enhance their procurement strategies, mitigate risks, and ultimately drive success in their automotive ventures. Whether you are looking to enhance your supply chain or ensure compliance with local standards, this guide serves as your authoritative resource for understanding and sourcing car alternators in today’s global market.
Table Of Contents
- Top 3 What Is The Car Alternator Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for what is the car alternator
- Understanding what is the car alternator Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of what is the car alternator
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘what is the car alternator’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for what is the car alternator
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for what is the car alternator
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘what is the car alternator’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for what is the car alternator Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing what is the car alternator With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for what is the car alternator
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the what is the car alternator Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of what is the car alternator
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for what is the car alternator
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Understanding what is the car alternator Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Conventional Alternator | Uses electromagnetic induction to convert mechanical energy to electrical energy; typically has a rotor and stator. | Standard vehicles, commercial fleets | Pros: Reliable, widely available. Cons: Limited efficiency under extreme conditions. |
| High-Output Alternator | Designed to produce more amperage than standard alternators; often used in performance vehicles. | Performance cars, heavy-duty applications | Pros: Supports high electrical loads. Cons: Higher cost and potential overkill for standard vehicles. |
| Smart Alternator | Incorporates advanced technology for efficiency; can adjust output based on vehicle needs. | Eco-friendly vehicles, hybrids | Pros: Energy-efficient, prolongs battery life. Cons: Complex design may require specialized service. |
| Permanent Magnet Alternator | Utilizes permanent magnets instead of electromagnets for higher efficiency and smaller size. | Electric vehicles, motorcycles | Pros: Lightweight, compact, and efficient. Cons: Generally more expensive and less common. |
| Brushless Alternator | Eliminates brushes for less wear and maintenance; operates quietly and efficiently. | High-performance and industrial applications | Pros: Longer lifespan, reduced maintenance. Cons: Higher initial investment. |
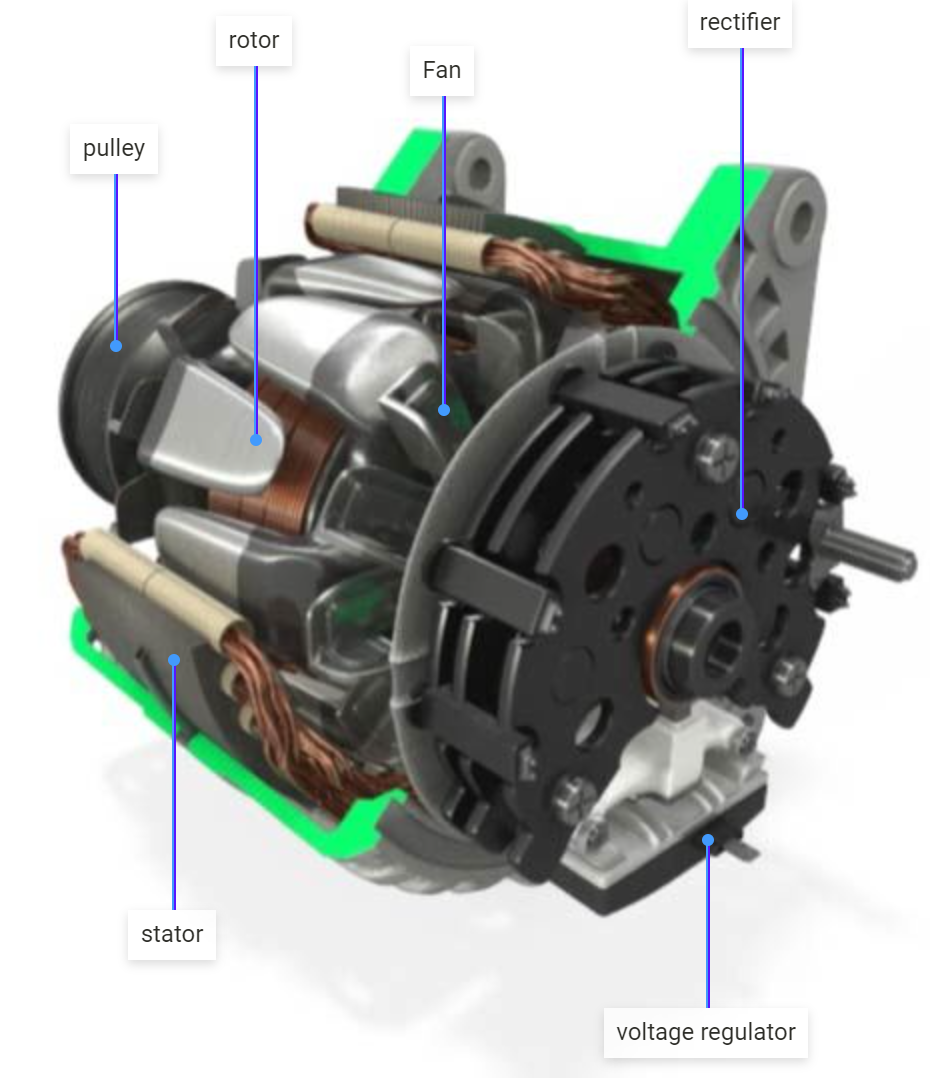
What Are the Characteristics of Conventional Alternators?
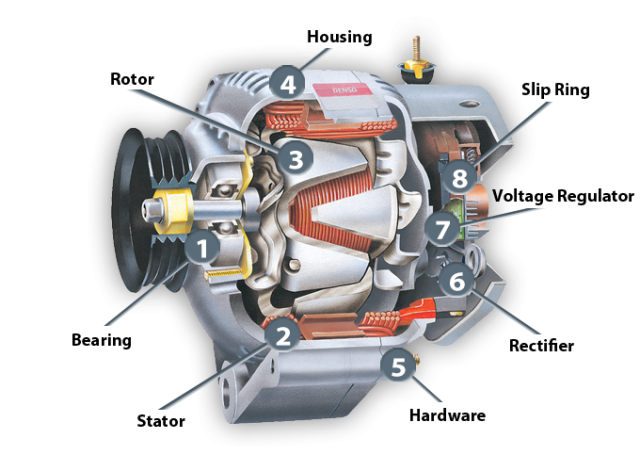
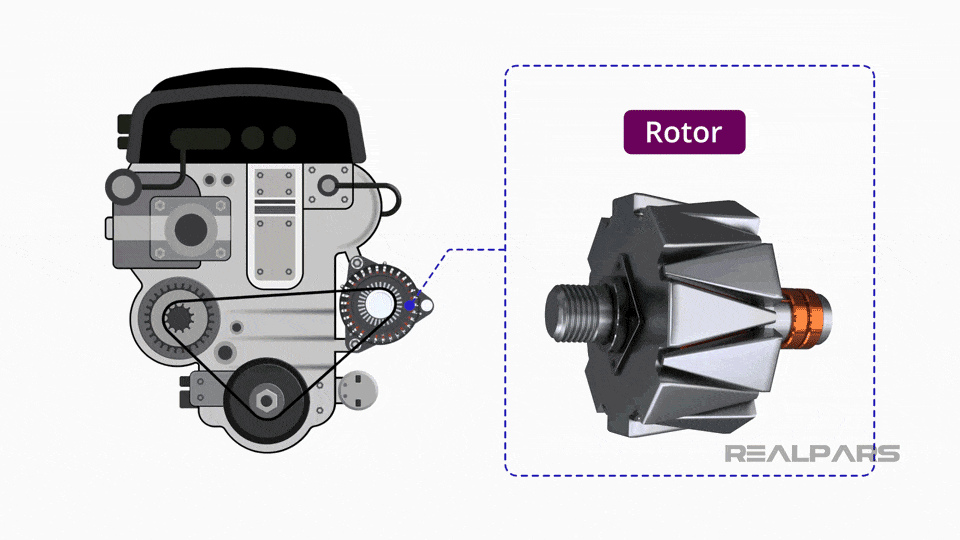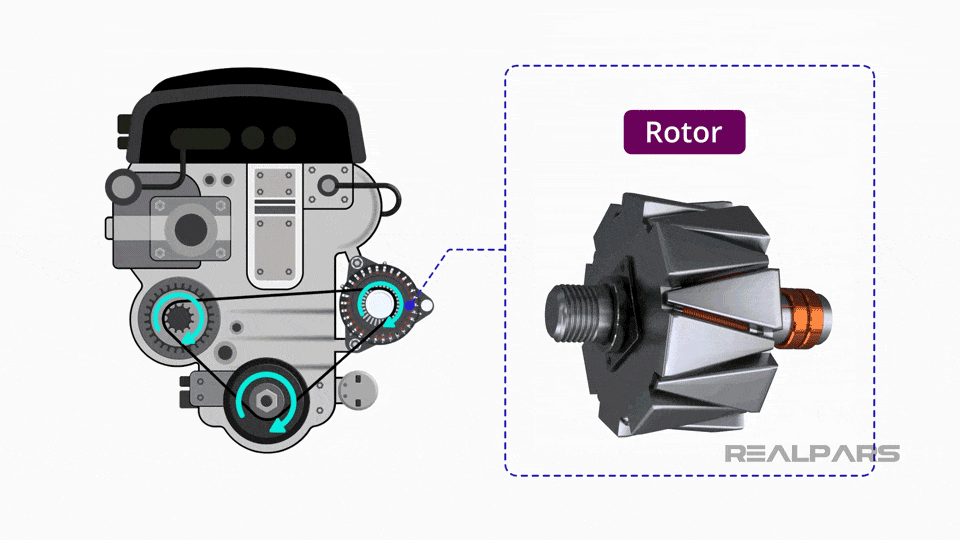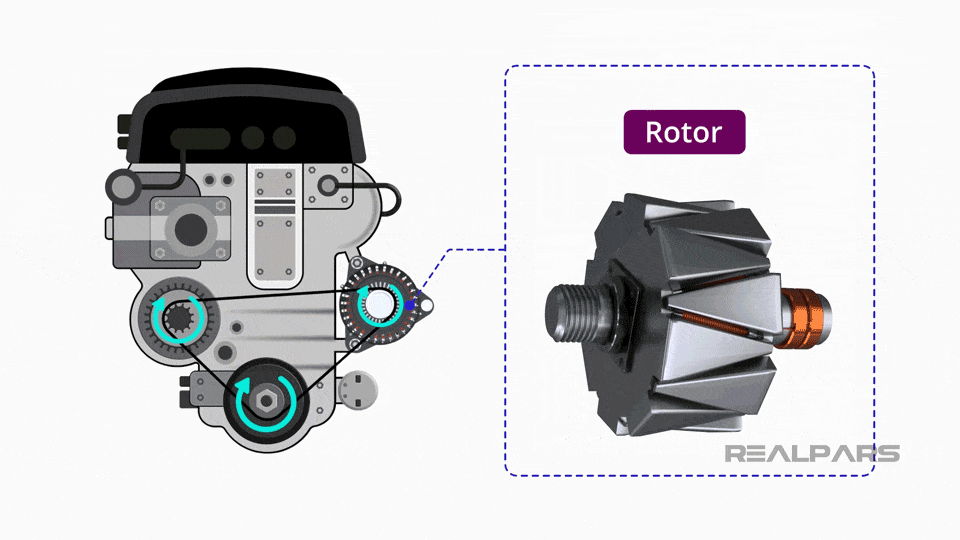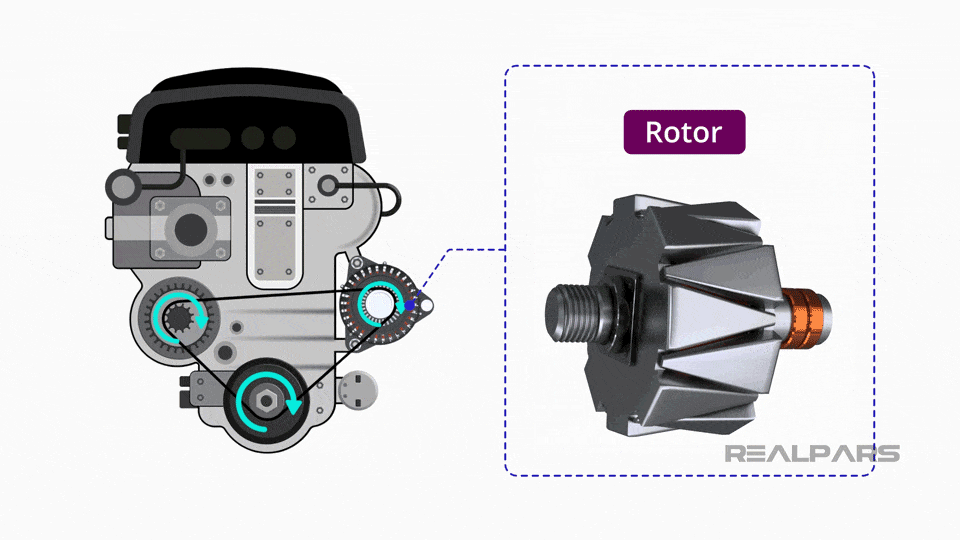
Conventional alternators are the most commonly used type in vehicles, leveraging electromagnetic induction to generate electricity. They typically consist of a rotor and stator, which work together to convert mechanical energy from the engine into electrical energy. These alternators are suitable for standard vehicles and commercial fleets, providing reliable performance. When purchasing, buyers should consider the alternator’s compatibility with their vehicle’s electrical system and its longevity, as they generally last between 60,000 to 100,000 miles.
How Do High-Output Alternators Differ from Standard Types?
High-output alternators are specifically designed to meet the demands of vehicles with extensive electrical systems, such as performance cars or heavy-duty applications. They generate significantly more amperage than conventional alternators, making them ideal for powering additional accessories like high-powered audio systems or off-road lights. B2B buyers should evaluate the electrical requirements of their applications to ensure that they select an alternator that can handle the load without compromising performance.
What Are the Advantages of Smart Alternators?
Smart alternators feature advanced technology that allows them to adjust their output based on the vehicle’s electrical demands. This capability not only improves overall efficiency but also helps prolong battery life by preventing overcharging. These alternators are particularly suitable for eco-friendly vehicles and hybrids, where energy management is critical. Buyers should consider the additional complexity of smart alternators, as they may require specialized installation and maintenance.
Why Choose Permanent Magnet Alternators?
Permanent magnet alternators utilize permanent magnets instead of electromagnets, resulting in a more compact and efficient design. These alternators are increasingly popular in electric vehicles and motorcycles due to their lightweight nature and high efficiency. However, they tend to be more expensive and less commonly found in standard vehicles. B2B buyers should weigh the benefits of efficiency and size against the higher upfront costs when considering this type.
What Makes Brushless Alternators a Good Option?
Brushless alternators eliminate the need for brushes, reducing wear and maintenance needs. They operate quietly and are highly efficient, making them suitable for high-performance and industrial applications. Their longer lifespan and reduced maintenance requirements are appealing to B2B buyers looking for durability and reliability. However, the initial investment for brushless alternators can be higher, which is an important consideration when evaluating total ownership costs.
Key Industrial Applications of what is the car alternator
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of what is the car alternator | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive Manufacturing | Production of electric vehicles (EVs) and hybrids | Enhances vehicle reliability and efficiency | Need for high-quality, durable alternators with advanced technology |
| Fleet Management | Maintenance of commercial vehicle fleets | Reduces downtime and maintenance costs | Sourcing alternators that offer warranties and easy replacement |
| Agriculture | Powering agricultural machinery and vehicles | Increases operational efficiency and reduces failures | Consideration of rugged design for harsh environments |
| Mining | Electrification of mining equipment and vehicles | Ensures consistent power supply for heavy machinery | Need for high-capacity alternators suitable for extreme conditions |
| Transportation & Logistics | Charging systems for delivery and logistics vehicles | Improves vehicle performance and reliability | Focus on sourcing alternators that meet regional compliance standards |
How is the car alternator used in automotive manufacturing, particularly for EVs and hybrids?
In the automotive manufacturing sector, particularly for electric vehicles (EVs) and hybrids, the car alternator plays a crucial role in the vehicle’s electrical system. It converts mechanical energy from the engine into electrical energy, ensuring that the battery is charged and ready to power all electrical components. This is vital for maintaining the performance and reliability of vehicles, particularly as manufacturers move towards more electric-powered systems. Buyers in this sector should focus on sourcing high-quality alternators that can handle the unique demands of EVs, such as higher voltage outputs and efficiency.
Illustrative image related to what is the car alternator
What are the applications of car alternators in fleet management?
In fleet management, car alternators are essential for maintaining the electrical systems of commercial vehicles, including delivery trucks and buses. A reliable alternator ensures that all electronic components function correctly, reducing the likelihood of vehicle downtime due to electrical failures. This reliability translates into lower maintenance costs and improved operational efficiency. Businesses should consider sourcing alternators that come with warranties and are designed for easy replacement to minimize service interruptions.
How do car alternators contribute to the agriculture sector?
In agriculture, car alternators are used to power various machinery and vehicles, such as tractors and harvesters. These vehicles often operate in challenging environments, requiring robust and reliable electrical systems to function effectively. A well-functioning alternator ensures that agricultural equipment can operate without electrical interruptions, which is critical during peak farming seasons. Buyers in this sector should prioritize sourcing alternators with rugged designs that can withstand harsh conditions and deliver consistent performance.
What role do car alternators play in mining operations?
In the mining industry, car alternators are utilized to electrify heavy machinery and vehicles that operate in extreme conditions. These machines require a reliable power supply to ensure continuous operation, particularly in remote areas where access to conventional power sources may be limited. A high-capacity alternator is essential for meeting the demanding power requirements of mining equipment. Buyers should consider sourcing alternators that are specifically designed for durability and performance under harsh mining conditions.
How do transportation and logistics benefit from car alternators?
In the transportation and logistics sector, car alternators are crucial for the charging systems of delivery vehicles, ensuring that all electrical components function optimally. This is vital for maintaining vehicle performance and reliability, particularly in urban environments where stop-and-go traffic can strain electrical systems. Businesses in this sector should focus on sourcing alternators that comply with regional standards and offer high efficiency to support the operational demands of their fleet.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘what is the car alternator’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Understanding Alternator Failure Symptoms in Fleet Vehicles
The Problem: B2B buyers managing a fleet of vehicles often struggle with diagnosing alternator issues, which can lead to unexpected downtime. For example, a logistics company operating in South America may notice that their delivery trucks are frequently stalling or experiencing electrical failures, but pinpointing the alternator as the culprit can be challenging. The inability to recognize symptoms like dimming dashboard lights or erratic electrical accessory behavior can result in costly repairs and delays in service.
The Solution: To effectively manage and mitigate these risks, fleet managers should implement a proactive maintenance schedule that includes regular diagnostics of the alternator and associated electrical systems. Investing in training for maintenance staff on the signs of alternator failure can empower them to conduct timely inspections. Additionally, utilizing diagnostic tools that can read error codes from the vehicle’s onboard computer will help identify alternator issues early. Collaborating with reliable suppliers for high-quality alternators and parts ensures that replacements are durable and suited for heavy-duty use, minimizing the risk of future failures.
Scenario 2: Sourcing Quality Alternators for Diverse Vehicle Types
The Problem: B2B buyers often face challenges when sourcing alternators for a diverse fleet, especially when dealing with multiple vehicle brands and models. A construction company in Europe, for example, may require alternators for various vehicles ranging from heavy machinery to light trucks. The difficulty in finding compatible and reliable parts can lead to operational inefficiencies and increased costs due to improper sourcing.
The Solution: To streamline the sourcing process, buyers should establish relationships with reputable suppliers who specialize in automotive electrical components and understand the nuances of different vehicle types. Creating a detailed inventory management system that categorizes vehicles by make, model, and alternator specifications can aid in quickly identifying the right parts when replacements are needed. Furthermore, engaging with suppliers that offer warranties or guarantees on their products can provide additional peace of mind, ensuring that the components will withstand the rigors of daily use in demanding environments.
Scenario 3: Cost Management Related to Alternator Repairs and Replacements
The Problem: Many B2B buyers are concerned about the long-term costs associated with alternator repairs and replacements, especially in sectors where vehicle reliability is crucial. For instance, a transportation firm in Africa might be faced with escalating costs due to frequent alternator failures, impacting their profit margins and service reliability.
The Solution: To manage and reduce these costs, it is essential to implement a comprehensive maintenance strategy that includes regular inspections and preventive measures. Establishing partnerships with certified automotive service providers can ensure that vehicles are serviced correctly, minimizing the likelihood of premature alternator failure. Additionally, investing in high-quality, OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) alternators can prove more economical in the long run, as they often last longer and come with better performance guarantees. Lastly, tracking the performance and lifespan of alternators through data analysis can help identify patterns and inform purchasing decisions, allowing buyers to optimize their fleets effectively.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for what is the car alternator
What Materials Are Commonly Used in Car Alternators?
When selecting materials for car alternators, several factors come into play, including performance, durability, cost, and compliance with international standards. This section analyzes four common materials used in the construction of alternators: aluminum, copper, steel, and plastic. Each material has unique properties that influence its suitability for various applications.
How Does Aluminum Perform in Car Alternators?
Aluminum is widely used in car alternators due to its lightweight nature and excellent thermal conductivity. Key properties include a temperature rating of up to 150°C and good corrosion resistance, making it suitable for automotive applications.
Pros: Aluminum is durable, lightweight, and cost-effective, which enhances fuel efficiency in vehicles. Its ease of manufacturing allows for complex shapes and designs, making it a preferred choice for many automotive components.
Cons: While aluminum is resistant to corrosion, it can be susceptible to fatigue and stress fractures under extreme conditions. This may lead to a shorter lifespan in high-demand applications.
Impact on Application: Aluminum’s lightweight nature contributes to better vehicle performance and fuel efficiency. However, its mechanical properties must be considered, especially in regions with extreme temperatures.
International Considerations: Buyers should ensure compliance with standards such as ASTM B221 for aluminum extrusions. In regions like Europe, adherence to DIN standards is crucial for quality assurance.
What Role Does Copper Play in Alternator Construction?
Copper is primarily used in the windings of alternators due to its excellent electrical conductivity, which is vital for efficient power generation. It can handle temperatures up to 200°C and offers good corrosion resistance.
Pros: Copper’s high conductivity results in lower energy loss, improving the overall efficiency of the alternator. It also has a long lifespan, making it a reliable choice for electrical components.
Cons: The primary drawback of copper is its cost, which can be significantly higher than other materials. Additionally, it is heavier than aluminum, which may affect vehicle weight.
Impact on Application: The use of copper enhances the performance of alternators, especially in high-demand electrical systems. However, its weight can be a consideration for manufacturers focused on reducing vehicle mass.
International Considerations: Compliance with standards such as ASTM B170 for copper wire is essential. Buyers in South America and Africa should also consider local regulations regarding material sourcing and recycling.
Why Is Steel Used in Alternator Components?
Steel is often used for structural components of alternators, such as the casing and mounting brackets. It offers high strength and durability, with a typical temperature rating of around 300°C.
Pros: Steel provides excellent mechanical strength and resistance to wear and tear, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications. It is also relatively inexpensive compared to other metals.
Cons: Steel is prone to corrosion if not properly treated, which can lead to premature failure. Its weight can also be a disadvantage in terms of overall vehicle efficiency.
Illustrative image related to what is the car alternator
Impact on Application: Steel’s durability makes it ideal for structural components, but its weight and corrosion susceptibility must be managed, especially in humid or coastal environments.
International Considerations: Buyers should ensure compliance with standards such as ASTM A36 for structural steel. In regions like Germany and Saudi Arabia, adherence to local standards for corrosion resistance is critical.
How Is Plastic Utilized in Alternators?
Plastic materials are often used in alternator housings and insulative components. They can withstand temperatures up to 120°C and provide good electrical insulation.
Illustrative image related to what is the car alternator
Pros: Plastics are lightweight, cost-effective, and resistant to corrosion, which enhances the longevity of the alternator. They also allow for complex designs and shapes.
Cons: The primary limitation of plastic is its lower mechanical strength compared to metals, which may affect durability under high-stress conditions.
Impact on Application: Plastic components can reduce overall weight and improve fuel efficiency. However, their mechanical properties must be carefully evaluated for specific applications.
International Considerations: Compliance with standards such as ISO 9001 for quality management systems is vital. Buyers should also consider local regulations regarding plastic use and recycling.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Car Alternators
| Material | Typical Use Case for what is the car alternator | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Housing, brackets | Lightweight, good thermal conductivity | Susceptible to fatigue | Medium |
| Copper | Windings | Excellent electrical conductivity | Higher cost, heavier | High |
| Steel | Structural components | High strength and durability | Prone to corrosion, heavier | Low |
| Plastic | Housings, insulative parts | Lightweight, corrosion-resistant | Lower mechanical strength | Low |
This analysis provides valuable insights for international B2B buyers looking to make informed decisions about material selection for car alternators. Understanding the properties, advantages, and limitations of each material is crucial for optimizing performance and ensuring compliance with regional standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for what is the car alternator
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing a Car Alternator?
The manufacturing of car alternators involves a series of precise stages that ensure the final product meets both performance and quality standards. Understanding these stages is crucial for B2B buyers who are looking to procure high-quality alternators for their automotive needs.
1. Material Preparation: What Materials Are Used in Alternator Manufacturing?
The first stage in manufacturing alternators is material preparation. Key components typically include:
- Copper Wire: Used for the stator windings, copper is chosen for its excellent conductivity.
- Silicon Steel: This material is used for the stator and rotor cores to enhance magnetic performance.
- Aluminum or Magnesium Housing: Lightweight yet durable, these materials protect internal components and facilitate efficient heat dissipation.
- Diodes and Voltage Regulators: These electronic components are critical for converting AC to DC and managing power output.
The selection of high-quality materials is essential as it directly impacts the alternator’s efficiency, durability, and performance.
2. Forming: How Are Alternator Components Shaped?
The forming process involves shaping the prepared materials into the necessary components. Techniques include:
- Stamping: Used to create the stator and rotor cores from silicon steel sheets. Precision stamping ensures that the dimensions are exact, which is critical for the performance of the magnetic field.
- Winding: The copper wire is wound around the stator core to form the windings. This is often done using automated machines that guarantee consistency and precision.
- Casting: For housings made of aluminum or magnesium, casting techniques are employed. Die casting is common, allowing for complex shapes while maintaining tight tolerances.
These forming techniques are vital to achieving the desired specifications and ensuring the alternator functions correctly.
3. Assembly: What Steps Are Involved in Assembling an Alternator?
Once the components are formed, the assembly process begins. This stage typically involves:
- Component Integration: The rotor is placed within the stator, and the windings are connected to the diodes and voltage regulator.
- Mechanical Fastening: Various components are secured using screws, bolts, or rivets, ensuring that everything is tightly held together.
- Quality Inspections: At this stage, initial inspections are performed to check for any visible defects or misalignments.
Effective assembly is crucial as it determines the alternator’s reliability and operational efficiency.
4. Finishing: What Are the Final Steps in Alternator Manufacturing?
The finishing stage includes several key processes that enhance the alternator’s performance and appearance:
Illustrative image related to what is the car alternator
- Coating: Protective coatings may be applied to prevent corrosion and wear. This is particularly important for alternators used in harsh environments.
- Final Assembly: Additional components, such as cooling fans, are installed.
- Testing: Each alternator undergoes rigorous testing to ensure it meets performance specifications before leaving the factory.
The finishing processes not only improve the product’s durability but also ensure compliance with industry standards.
What Are the Key Quality Assurance Measures in Alternator Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is critical in alternator manufacturing, as it ensures that the products meet both international and industry-specific standards. B2B buyers should be aware of the following QA measures.
1. What International Standards Govern Alternator Quality?
Manufacturers often adhere to international quality standards, such as:
- ISO 9001: This standard sets criteria for a quality management system and is essential for ensuring consistency in production and service delivery.
- CE Marking: Required for products sold in the European Economic Area, CE marking indicates compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: While more common in oil and gas, some manufacturers may comply with API standards relevant to automotive applications.
Understanding these standards helps B2B buyers gauge a supplier’s commitment to quality.
2. What Quality Control Checkpoints Are Critical in the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are strategically placed throughout the manufacturing process. Key checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Raw materials and components are inspected upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Inspections during the manufacturing process help identify defects early, reducing the risk of faulty products.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): The finished alternators undergo comprehensive testing to verify that they meet all performance and safety standards.
Implementing these checkpoints minimizes defects and ensures that only high-quality products reach the market.
3. What Common Testing Methods Are Employed for Alternators?
Manufacturers employ various testing methods to ensure performance and reliability:
- Electrical Testing: Measures output voltage and current to confirm that the alternator meets specified electrical performance criteria.
- Thermal Testing: Assesses how the alternator performs under high-temperature conditions.
- Vibration Testing: Ensures that the alternator can withstand the operational vibrations experienced in a vehicle.
These testing methods are essential for verifying product quality and reliability.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Assurance Practices?
B2B buyers looking to procure alternators should consider the following methods to verify a supplier’s quality assurance practices:
1. What Audit Processes Are Available for Supplier Verification?
Conducting audits is a critical step in verifying a supplier’s quality processes. Buyers can:
- Request Supplier Audits: Engage third-party auditors to evaluate the supplier’s manufacturing and quality assurance processes.
- Perform On-Site Visits: If feasible, visiting the manufacturing facility allows buyers to observe processes and quality measures firsthand.
2. What Documentation Should Buyers Request from Suppliers?
Buyers should request comprehensive documentation, including:
- Quality Management System Certification: Proof of ISO 9001 or other relevant certifications.
- Testing Reports: Documentation of the testing methods and results for the alternators being supplied.
- Compliance Certificates: Evidence of compliance with industry-specific standards, such as CE marking.
These documents provide transparency and assurance of quality.
3. What Role Do Third-Party Inspections Play in Quality Assurance?
Third-party inspections can serve as an additional layer of quality assurance. Engaging independent inspection agencies can:
- Provide Objective Assessments: These agencies can evaluate the quality of the products without bias.
- Enhance Buyer Confidence: Third-party validation can instill greater confidence in the quality of the alternators being procured.
By considering these QA measures, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when selecting suppliers for car alternators, ensuring they receive high-quality products that meet international standards.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘what is the car alternator’
To assist B2B buyers in the procurement of car alternators, this practical sourcing guide outlines essential steps that ensure a smooth purchasing process. By following this checklist, businesses can confidently select high-quality alternators that meet their operational needs while minimizing risks.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Understanding the specific requirements for your alternators is crucial. Consider factors such as vehicle compatibility, power output (measured in amps), and physical dimensions. This clarity not only helps in narrowing down potential suppliers but also ensures that the alternators will function optimally in your vehicles.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify suppliers with a strong track record in the automotive industry. Look for companies that specialize in alternators and have experience serving clients in your region, particularly in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Pay attention to customer reviews and ratings to gauge their reputation.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Before proceeding with a supplier, verify their certifications and industry standards compliance. Certifications such as ISO 9001 or other relevant automotive quality standards indicate a commitment to quality and reliability. This step is essential to ensure that the alternators meet international safety and performance criteria.
Step 4: Request Product Samples
Whenever possible, request samples of the alternators you intend to purchase. Testing samples allows you to evaluate quality, performance, and compatibility with your vehicles. This practical approach helps identify any potential issues before placing a large order, reducing the risk of costly returns or replacements.
Step 5: Assess Warranty and After-Sales Support
Investigate the warranty terms offered by the supplier. A robust warranty indicates confidence in the product’s durability and performance. Additionally, inquire about after-sales support, including availability of spare parts and technical assistance, to ensure long-term operational efficiency.
Illustrative image related to what is the car alternator
Step 6: Compare Pricing Structures
Gather and compare pricing from multiple suppliers to ensure competitive rates. Be mindful of the total cost of ownership, which includes not just the purchase price but also shipping, handling, and potential installation costs. Consider negotiating terms that could lead to better pricing or bulk purchase discounts.
Step 7: Finalize Your Order and Logistics
Once you have selected a supplier, finalize your order details, including quantities and delivery timelines. Ensure clear communication regarding shipping methods and expected delivery dates. This step is critical to maintaining your supply chain and minimizing downtime in your operations.
By following this structured approach, B2B buyers can effectively navigate the complexities of sourcing car alternators, ensuring they make informed decisions that align with their business needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for what is the car alternator Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Car Alternators?
When sourcing car alternators, B2B buyers must consider various cost components that contribute to the total expense. The primary components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and the supplier’s margin.
-
Materials: The primary materials for alternators include copper for windings, aluminum for the housing, and various metals for internal components like rotors and stators. Prices for these materials can fluctuate based on global supply chain dynamics, impacting the overall cost.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary significantly by region. In countries with lower labor costs, such as parts of South America and Africa, sourcing might be cheaper. However, higher labor costs in Europe, particularly Germany, may reflect in the pricing.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses indirect costs associated with the manufacturing process, including utilities, depreciation, and salaries of support staff. Efficient manufacturing processes can help reduce these costs.
-
Tooling: This refers to the cost of molds and tools required for production. Customization or unique specifications can increase tooling costs significantly, which is essential for buyers looking for specific alternator features.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that alternators meet specific quality standards can incur additional costs. Buyers should consider suppliers with robust QC processes, as this can prevent costly returns and warranty claims in the future.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs can vary depending on the shipping method, distance, and Incoterms agreed upon. For international buyers, understanding these logistics costs is crucial for accurate budgeting.
-
Margin: The supplier’s profit margin is a final component of the cost structure. Buyers should assess the market to ensure they are getting a fair margin based on quality and service.
What Influences Pricing for Car Alternators?
Several factors can influence the pricing of car alternators, making it essential for B2B buyers to understand these nuances.
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Suppliers often provide discounts for bulk purchases. Establishing a consistent order volume can lead to significant cost savings.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom alternators tailored to specific vehicle types or performance requirements may come at a premium. Buyers should weigh the necessity of customization against potential cost increases.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: The choice of materials, along with certifications (like ISO or other industry standards), impacts both price and quality. Higher-quality materials often lead to longer-lasting products, which can reduce the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO).
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reputation, reliability, and after-sales support can influence pricing. Established suppliers with a good track record may command higher prices, but the assurance of quality and service can justify the cost.
-
Incoterms: The terms of shipping and delivery can significantly affect the final cost. Familiarity with Incoterms (e.g., FOB, CIF) is vital for understanding who bears the risk and costs at various points in the shipping process.
What Are the Best Negotiation Strategies for B2B Buyers?
For international buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, effective negotiation can lead to substantial savings.
-
Research and Benchmarking: Understanding market rates and competitor pricing can provide leverage during negotiations. Buyers should gather data on average costs for similar products.
-
Build Relationships: Developing a solid relationship with suppliers can facilitate better pricing and terms. Trust can lead to more favorable negotiations and potential future discounts.
-
Focus on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Highlighting the long-term value of quality over initial price can shift the focus of negotiations. Emphasizing durability and reliability can justify a higher upfront cost.
-
Flexibility in Orders: Being flexible with order quantities or timelines can sometimes yield better pricing or terms. Suppliers appreciate buyers who can accommodate their production schedules.
What Should B2B Buyers Keep in Mind Regarding Pricing Nuances?
It’s essential for B2B buyers to be aware of pricing nuances that can affect their sourcing decisions. Currency fluctuations, trade tariffs, and local regulations can impact costs significantly, particularly for international transactions. Additionally, buyers should be prepared for variations in lead times and availability based on market conditions.
Disclaimer: Prices are indicative and can vary based on market conditions, supplier negotiations, and order specifics. Always conduct thorough research and consult with multiple suppliers to ensure competitive pricing.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing what is the car alternator With Other Solutions
When considering power generation solutions for automotive applications, it’s essential to evaluate the traditional car alternator against emerging technologies. Each solution has its unique advantages and challenges that can impact performance, cost, and usability in various contexts. Below, we compare the car alternator with two viable alternatives: the DC generator and hybrid systems that combine solar panels with battery storage.
| Comparison Aspect | What Is The Car Alternator | DC Generator | Hybrid Systems (Solar + Battery) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Converts mechanical energy to electrical energy efficiently, supports all electrical components. | Provides stable DC output but less efficient at variable speeds. | Offers renewable energy, can reduce reliance on the alternator for power. |
| Cost | Generally low initial cost; replacement costs can vary significantly. | Typically higher upfront costs, but fewer components to replace. | High initial investment; savings on fuel and electricity over time. |
| Ease of Implementation | Standard in most vehicles, easy to install and replace. | Requires specialized installation; may need modifications to vehicle systems. | Complex installation; requires space for solar panels and batteries. |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; usually lasts 7-10 years. | Moderate; brushes and commutators may need replacement over time. | Low to moderate, depending on battery life and solar efficiency. |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for conventional combustion engine vehicles. | Suitable for specific applications where constant DC power is needed. | Best for eco-conscious consumers or off-grid applications. |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of a DC Generator Compared to a Car Alternator?
DC generators have been traditionally used for power generation, especially in older vehicles and specific industrial applications. They provide a stable DC output, making them suitable for certain electrical systems. However, they are less efficient at variable speeds compared to alternators, which can lead to inconsistent performance. Additionally, while DC generators can be more straightforward in terms of fewer components, they often require more frequent maintenance, particularly concerning brushes and commutators.
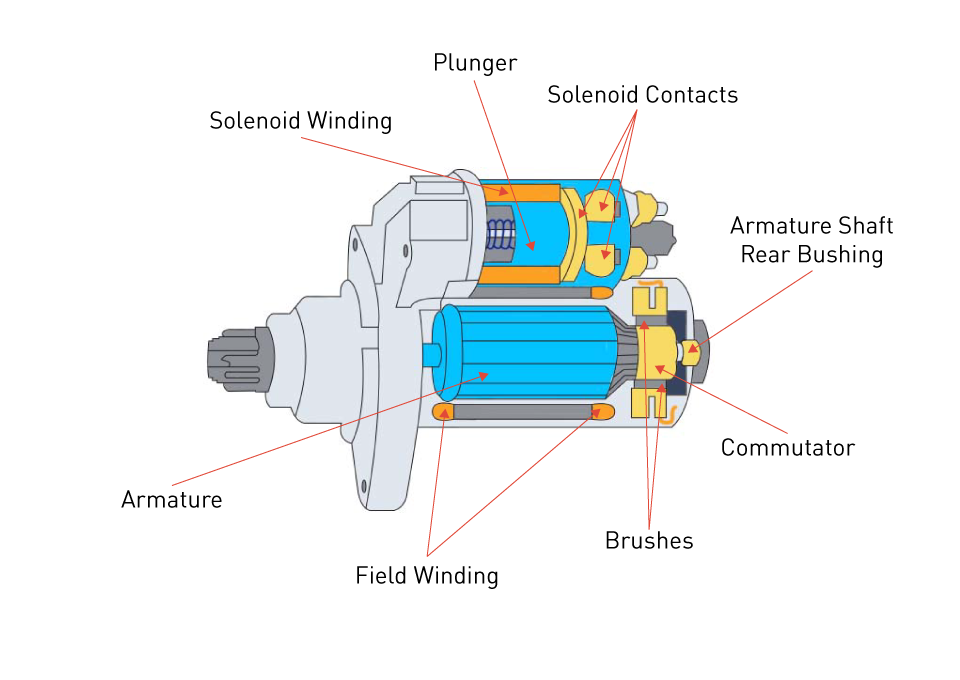
Illustrative image related to what is the car alternator
How Do Hybrid Systems Integrating Solar Panels and Batteries Compare to Car Alternators?
Hybrid systems that utilize solar panels combined with battery storage present a modern alternative to traditional alternators. These systems can significantly reduce reliance on fossil fuels, aligning with global sustainability trends. However, they come with a high initial investment and require more complex installation processes. The performance can also be affected by geographical conditions, as solar efficiency varies with climate. While they offer long-term savings on fuel and electricity, the upfront costs and installation challenges may deter some buyers.
How Can B2B Buyers Make Informed Decisions About Power Generation Solutions?
When choosing between a car alternator and its alternatives, B2B buyers should assess their specific needs, including vehicle type, operational environment, and budget constraints. For conventional vehicles, the car alternator remains a reliable and cost-effective choice. In contrast, for businesses looking to invest in sustainable technology, hybrid systems may offer long-term benefits despite their initial costs. Understanding the performance, cost implications, and maintenance requirements of each solution will empower buyers to select the most suitable option that aligns with their operational goals and environmental commitments.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for what is the car alternator
What Are the Key Technical Properties of a Car Alternator?
When evaluating car alternators for procurement, several critical specifications should be taken into account. Understanding these properties is essential for ensuring compatibility and performance in various vehicles.
1. Output Voltage
The output voltage of an alternator typically ranges from 12 to 14.5 volts. This specification is crucial as it determines the electrical power supplied to the vehicle’s battery and accessories. For B2B buyers, ensuring that the alternator meets the required voltage standards of different vehicle models is vital for maintaining electrical system integrity.
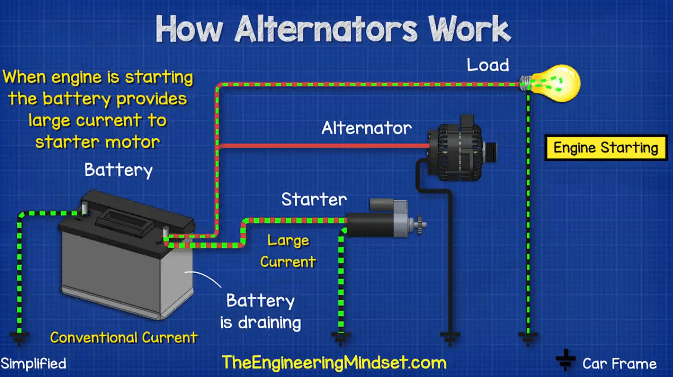
Illustrative image related to what is the car alternator
2. Amperage Rating
Amperage rating indicates the maximum current the alternator can supply, usually expressed in amps (A). Common ratings range from 60A to over 200A for high-performance vehicles. A higher amperage rating allows for the operation of more electrical accessories, such as advanced infotainment systems or additional lighting. For businesses, selecting an alternator with the appropriate amperage can prevent electrical failures and ensure reliable vehicle operation.
3. Material Composition
Alternators are typically constructed from materials like aluminum and copper. Aluminum is favored for its lightweight properties, while copper is essential for efficient electrical conduction. Understanding material grades can help B2B buyers assess the durability and performance of alternators, especially in demanding environments, which is particularly relevant for buyers in regions with extreme weather conditions.
4. Cooling Mechanism
Most alternators are equipped with a cooling fan to dissipate heat generated during operation. The efficiency of this cooling mechanism is vital for preventing overheating, which can lead to premature failure. Buyers should consider the design and effectiveness of the cooling system when selecting alternators, as it directly affects longevity and reliability.
5. Mounting Type
The mounting type of an alternator—whether it is a bolt-on or slide-on type—affects installation compatibility with different engine configurations. Understanding these mounting specifications is crucial for B2B buyers to ensure seamless integration into various vehicle models, minimizing installation time and costs.
What Are the Common Trade Terminology and Jargon Related to Car Alternators?
Navigating the automotive parts industry requires familiarity with specific terminology that can influence purchasing decisions and negotiations.
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to components made by the same manufacturer that produced the original parts for a vehicle. B2B buyers often prefer OEM parts for their guaranteed compatibility and performance, which can help in maintaining warranty conditions and achieving optimal vehicle performance.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ indicates the smallest number of units that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding the MOQ is crucial for B2B buyers as it affects inventory management and purchasing costs. Buyers should negotiate MOQs to align with their inventory needs and sales forecasts.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal process where a buyer requests pricing and terms from suppliers for specific products. This is an essential step in B2B transactions, enabling buyers to compare offers and negotiate better terms. Crafting a clear and detailed RFQ can lead to more accurate and competitive responses from suppliers.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international trade, including shipping, insurance, and delivery. Familiarity with these terms is vital for B2B buyers involved in cross-border procurement, as they clarify who bears the risk and cost at various stages of the shipping process.
Illustrative image related to what is the car alternator
5. Warranty Period
The warranty period is the timeframe during which a manufacturer guarantees the alternator’s performance and will cover repairs or replacements. Understanding warranty terms is essential for B2B buyers to assess the risk associated with their investment and to ensure that they have recourse in case of product failure.
By familiarizing themselves with these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing car alternators, ensuring they meet both performance requirements and budget constraints.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the what is the car alternator Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics and Trends in the Car Alternator Sector?
The global automotive alternator market is witnessing significant growth, driven by several key factors. The increasing production of vehicles, particularly in emerging markets such as Africa and South America, is propelling demand for alternators. Additionally, the shift towards electric vehicles (EVs) is creating a unique dynamic in the market. Although traditional combustion engine vehicles still dominate, the rise of hybrid and electric vehicles is influencing alternator design and technology, necessitating a shift in sourcing strategies for international buyers.
In regions like Europe and the Middle East, regulatory frameworks aimed at reducing emissions are pushing manufacturers towards more efficient alternator solutions. Innovations such as smart alternators, which can adjust their output based on vehicle demands, are becoming increasingly prevalent. B2B buyers are encouraged to look for suppliers who are investing in cutting-edge technology, as this can enhance vehicle performance and fuel efficiency.
Emerging trends in digitalization, such as the integration of IoT technologies, are also changing how alternators are sourced and manufactured. Buyers should be aware of suppliers offering advanced diagnostics and monitoring capabilities, as these can significantly improve maintenance and performance management. Engaging with suppliers who embrace these technological advancements will be crucial for businesses aiming to remain competitive in the evolving automotive landscape.
Illustrative image related to what is the car alternator
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact the Car Alternator Supply Chain?
Sustainability is becoming an essential factor in the sourcing of automotive components, including alternators. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes and the materials used in alternators cannot be overlooked. B2B buyers should prioritize suppliers who adopt environmentally friendly practices, such as reducing waste and utilizing recycled materials.
The importance of ethical supply chains is also gaining traction. Buyers are increasingly scrutinizing their suppliers for adherence to labor laws and fair working conditions. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and ISO 45001 for occupational health and safety can serve as indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability and ethical practices.
Moreover, the push for ‘green’ materials in automotive manufacturing is reshaping the alternator sector. Suppliers that can demonstrate the use of sustainable materials, such as eco-friendly composites or low-impact manufacturing processes, will likely be favored in the market. B2B buyers must be proactive in seeking out these suppliers to align with global sustainability goals and consumer expectations.
What Is the Brief Evolution of the Car Alternator and Its Relevance for B2B Buyers?
The car alternator has evolved significantly since its inception in the early 20th century. Originally designed to power the electrical systems of vehicles, alternators have transformed from simple mechanical devices to complex electronic units capable of meeting the growing energy demands of modern automobiles.
The introduction of the first alternator in the 1960s marked a pivotal change in automotive technology. Over the decades, advancements in materials and engineering have led to lighter, more efficient, and longer-lasting alternators. Today, with the increasing focus on performance and efficiency, alternators are equipped with advanced features such as voltage regulation and smart charging systems.
For B2B buyers, understanding this evolution is crucial. It highlights the importance of sourcing from manufacturers who not only have a historical understanding of the product but also a forward-thinking approach to innovation. Engaging with suppliers who stay ahead of industry trends ensures access to the latest technology, ultimately benefiting the end-users of their products.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of what is the car alternator
-
How do I identify when an alternator is failing?
Recognizing a failing alternator is crucial to avoid vehicle breakdowns. Common signs include dimming dashboard lights, difficulty starting the engine, or the battery warning light illuminating. Additionally, if electrical accessories like power windows or seats operate sluggishly, it may indicate insufficient power from the alternator. Regular inspections can help identify these issues early, allowing for timely replacement or repair, ensuring uninterrupted vehicle operation and minimizing downtime. -
What is the best alternator for commercial vehicles?
The best alternator for commercial vehicles often depends on the specific power requirements and load conditions. Look for high-output alternators that can handle additional electrical loads typical in commercial applications, such as lighting and communication systems. Brands like Bosch and Denso are renowned for their reliability and performance. Be sure to consider factors like durability, warranty, and compatibility with your vehicle’s engine specifications when making a selection. -
What factors should I consider when sourcing alternators internationally?
When sourcing alternators from international suppliers, consider the supplier’s reputation, quality certifications, and production capabilities. Assess their ability to provide products that meet your specific electrical requirements and local regulations. Additionally, evaluate logistics, shipping times, and customs procedures to avoid delays. Establishing clear communication regarding pricing, lead times, and after-sales support will also facilitate a smoother procurement process. -
How can I vet suppliers for alternators?
Vetting suppliers for alternators involves a multi-step process. Start by checking their business credentials, such as ISO certifications and industry experience. Request references from previous clients and assess their customer service responsiveness. It’s also beneficial to visit their manufacturing facilities if possible or to use third-party inspection services. Finally, ensure they offer warranties and quality assurance policies to protect your investment. -
What are the typical payment terms for purchasing alternators?
Payment terms can vary widely among suppliers. Common arrangements include upfront payments, partial payments (e.g., 30% upfront, 70% upon delivery), or net terms (e.g., net 30 or net 60). It’s essential to negotiate terms that align with your cash flow and procurement strategy. Additionally, consider using secure payment methods such as letters of credit or escrow services to mitigate risks in international transactions. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for alternators?
Minimum order quantities for alternators depend on the supplier and the specific product line. Some manufacturers may have MOQs as low as 10 units, while others may require orders of 100 or more for certain types. Understanding the MOQ is crucial for planning your inventory and cash flow. If MOQs are too high, consider negotiating smaller trial orders or exploring alternative suppliers that can accommodate your needs. -
How can I ensure the quality of the alternators I source?
To ensure the quality of sourced alternators, request detailed product specifications, certifications, and test reports from suppliers. Consider conducting quality audits or inspections before shipment. Establishing a quality assurance process, including sampling and testing upon arrival, can help identify defects early. Collaborating with suppliers who have established quality control systems will further enhance the reliability of your purchases. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing alternators?
Logistics is a critical aspect of importing alternators. Consider shipping methods (air vs. sea), transit times, and costs associated with each. Ensure compliance with import regulations and tariffs in your destination country. Partnering with a reliable freight forwarder can streamline the process and mitigate potential delays. Additionally, plan for customs clearance procedures and potential duties to avoid unexpected expenses.
Top 3 What Is The Car Alternator Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Kia – Alternator Solutions
Domain: kia.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: An alternator is an integral part of every combustion engine vehicle, responsible for converting chemical energy to electrical energy to charge and replenish the battery and other electrical components. The vehicle’s charging system consists of a car battery, voltage regulator, and alternator. The alternator converts mechanical energy to electrical energy with alternating current (AC), which is th…
2. Nationwide – Alternator Overview
Domain: blog.nationwide.com
Registered: 1994 (31 years)
Introduction: The alternator is a generator that distributes electricity to the car and recharges the battery. It is about the size of a coconut and is mounted to the front of the engine with a belt running around it. Key components include: 1. Rotor and Stator: The rotor spins inside the stator, producing electricity through the movement of magnets over conductive copper wiring. 2. Voltage Regulator: Oversees …
3. Matthews Tire – Electrical System Check
Domain: matthewstire.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: Matthews Tire offers a complete electrical system check for $39.95. They provide services related to battery maintenance, including wiring a battery tender to keep the battery charged. The average life of a battery is 4-5 years, and customers are advised to keep track of when they last changed their battery.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for what is the car alternator
Why Is Strategic Sourcing Essential for Car Alternators?
In today’s competitive automotive market, understanding the intricacies of the car alternator is vital for international B2B buyers. This crucial component not only generates electrical power but also ensures the longevity and efficiency of vehicles. By sourcing high-quality alternators, businesses can reduce operational risks associated with vehicle downtime and enhance customer satisfaction.
Strategic sourcing enables companies to align with reliable suppliers who provide durable and efficient alternators, ultimately driving cost savings and operational efficiency. Buyers should prioritize partnerships with manufacturers that emphasize quality control, innovative designs, and compliance with international standards. This approach not only fosters trust but also positions businesses to adapt to changing market demands effectively.
Looking ahead, as the automotive industry evolves towards electric and hybrid vehicles, the role of the alternator will continue to transform. B2B buyers must stay informed and agile, ready to embrace new technologies and supplier relationships that support sustainable practices. Engage with suppliers who can provide insights and solutions tailored to your unique market needs, ensuring your business remains competitive in the global landscape.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.