Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for how to start a car if the starter is bad
In the dynamic landscape of the automotive industry, one prevalent challenge that international B2B buyers face is understanding how to start a car if the starter is bad. This issue not only disrupts operations but also raises concerns about maintenance costs and vehicle downtime. Our comprehensive guide delves into various methods and techniques to address this problem, ensuring buyers are well-equipped to make informed decisions.
This resource covers a wide spectrum of topics, including the identification of starter issues, potential temporary fixes, and the necessary tools for troubleshooting. Furthermore, it highlights the importance of supplier vetting and cost considerations, enabling businesses to source reliable automotive components effectively.
By leveraging this guide, B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—countries like Nigeria and Germany—can enhance their operational efficiency and minimize disruptions caused by faulty starters. Armed with actionable insights and expert recommendations, you will be empowered to navigate the complexities of automotive maintenance and make strategic purchasing decisions that align with your business objectives.
Table Of Contents
- Top 4 How To Start A Car If The Starter Is Bad Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for how to start a car if the starter is bad
- Understanding how to start a car if the starter is bad Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of how to start a car if the starter is bad
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘how to start a car if the starter is bad’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for how to start a car if the starter is bad
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for how to start a car if the starter is bad
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘how to start a car if the starter is bad’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for how to start a car if the starter is bad Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing how to start a car if the starter is bad With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for how to start a car if the starter is bad
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the how to start a car if the starter is bad Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of how to start a car if the starter is bad
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for how to start a car if the starter is bad
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Understanding how to start a car if the starter is bad Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Battery Connection Cleaning | Involves cleaning corroded battery terminals for better contact | Automotive repair shops, fleet services | Pros: Quick and low-cost; Cons: Only effective if corrosion is the issue. |
| Tapping the Starter | Gently striking the starter motor to free stuck components | Auto repair services, roadside assistance | Pros: Simple and quick; Cons: Temporary solution, risk of further damage. |
| Solenoid Inspection | Checking and cleaning solenoid connections for functionality | Automotive parts suppliers, repair shops | Pros: Identifies specific issues; Cons: Requires technical knowledge. |
| Push Start for Manual Vehicles | Using physical force to start a manual transmission vehicle | Automotive training programs, DIY workshops | Pros: No tools needed; Cons: Limited to manual vehicles, requires assistance. |
| Jump Starting | Using jumper cables to start the vehicle from another battery | Fleet management, vehicle service centers | Pros: Can resolve battery issues quickly; Cons: Ineffective if the starter is faulty. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Battery Connection Cleaning?
Battery connection cleaning is a straightforward method where corroded terminals are cleaned to improve electrical contact. This technique is particularly suitable for automotive repair shops and fleet services, as it can be performed quickly with minimal tools. Buyers should consider the cost-effectiveness of this method, especially for fleets where downtime needs to be minimized. Regular maintenance of battery connections can prevent future starter issues, making it a wise investment for businesses managing multiple vehicles.

Illustrative image related to how to start a car if the starter is bad
Why Is Tapping the Starter a Viable Option?
Tapping the starter involves striking it gently to dislodge any stuck components inside the motor. This method is particularly useful for roadside assistance and auto repair services that require quick fixes. While it is a simple and fast approach, it should be noted that this is a temporary solution and may not address underlying issues. Businesses should weigh the risk of potential damage to the starter against the urgency of getting a vehicle operational.
How Does Solenoid Inspection Benefit B2B Operations?
Inspecting the solenoid involves checking the connections and ensuring they are clean and functional. This method is essential for automotive parts suppliers and repair shops that need to diagnose specific issues with a vehicle’s starting system. While it requires a certain level of technical knowledge, the ability to pinpoint the problem can lead to efficient repairs and reduced labor costs. Businesses should consider investing in training for their technicians to enhance service quality.
What Makes Push Starting Effective for Manual Vehicles?
Push starting is a technique used exclusively for manual transmission vehicles, where physical force is applied to get the car moving and then the clutch is released to start the engine. This method is beneficial for automotive training programs and DIY workshops, as it requires no specialized tools. However, it relies on the presence of additional people to assist, making it less practical in solo scenarios. Businesses should consider this method as a last resort for manual vehicles in emergency situations.
When Is Jump Starting Most Appropriate?
Jump starting a vehicle involves using jumper cables to connect a working battery to a dead one, providing the necessary power to start the engine. This method is widely used in fleet management and vehicle service centers due to its speed and efficiency. However, it is important for buyers to understand that if the starter is the issue, jump starting will not resolve the problem. Regular training on jump-starting techniques can be beneficial for staff to enhance customer service and operational efficiency.
Key Industrial Applications of how to start a car if the starter is bad
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of how to start a car if the starter is bad | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive Repair Shops | Utilizing temporary fixes to diagnose starter issues | Reduces downtime for clients, enhancing service reputation | Availability of quality tools (e.g., wrenches, voltmeters) and training for staff on procedures |
| Fleet Management | Implementing quick-start techniques for fleet vehicles | Minimizes operational disruptions and maintains service levels | Reliable access to starter repair kits and trained personnel for maintenance |
| Transportation Services | Employing manual push-start methods for stranded vehicles | Ensures timely service delivery and customer satisfaction | Knowledge of vehicle types and manual starting techniques for various models |
| Car Rentals | Providing customers with solutions for starting issues | Enhances customer experience and reduces vehicle downtime | Training staff on troubleshooting common starter problems and providing necessary tools |
| Emergency Services | Equipping teams with tools to start vehicles in emergencies | Ensures rapid response times and operational readiness | Durable, portable tools and equipment that can withstand harsh conditions |
How Can Automotive Repair Shops Benefit from Temporary Fixes for Bad Starters?
Automotive repair shops can leverage temporary fixes to address starter issues, allowing them to quickly diagnose problems and offer immediate solutions to customers. This can include cleaning battery terminals or using a mallet to tap the starter. By minimizing vehicle downtime, repair shops enhance their service reputation, encouraging repeat business. For international B2B buyers, especially in regions with diverse vehicle models, sourcing quality diagnostic tools and ensuring staff are well-trained in these techniques is crucial.
What Advantages Do Fleet Management Companies Gain from Quick-Start Techniques?
Fleet management companies can implement quick-start techniques to keep their vehicles operational, reducing the risk of lost productivity. Techniques such as jump-starting or cleaning battery connections can quickly resolve issues without extensive downtime. This is particularly valuable in regions with unreliable infrastructure, where vehicle availability is critical. Key considerations for buyers in this sector include securing reliable starter repair kits and ensuring that maintenance staff are trained in effective troubleshooting methods.
How Do Transportation Services Ensure Timely Operations with Manual Push-Start Methods?
Transportation services can utilize manual push-start methods for vehicles that experience starter failures, enabling them to maintain service delivery even in challenging circumstances. This technique is especially useful for manual transmission vehicles and can be a lifesaver in remote areas. To maximize effectiveness, companies need to ensure their staff are knowledgeable about various vehicle models and the specific techniques for push-starting. This approach can significantly enhance customer satisfaction by ensuring timely pickups and deliveries.

Illustrative image related to how to start a car if the starter is bad
Why Is Customer Experience Critical for Car Rental Businesses Facing Starter Issues?
Car rental businesses can enhance customer experience by providing solutions for starting issues, such as offering quick-start techniques or ensuring vehicles are well-maintained to prevent starter problems. Providing customers with clear instructions on what to do if they encounter a starter issue can improve satisfaction and trust. For B2B buyers, investing in staff training and equipping rental locations with necessary tools is essential to minimizing vehicle downtime and ensuring a smooth rental process.
How Can Emergency Services Equip Teams for Vehicle Start Issues?
Emergency services can benefit from equipping their teams with tools specifically designed to address vehicle start issues, ensuring they can respond quickly in critical situations. Having portable tools like jumper cables and mallets readily available allows for immediate action, which is vital in emergencies. Buyers in this sector should focus on sourcing durable, high-quality equipment that can withstand challenging conditions, ensuring that their teams remain operationally ready at all times.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘how to start a car if the starter is bad’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Dealing with Frequent Vehicle Downtime
The Problem: B2B buyers managing fleets often face the challenge of frequent vehicle downtime due to faulty starters. This can lead to lost productivity and increased operational costs, especially in regions where transportation is critical for business success. In countries like Nigeria or Brazil, where road conditions may exacerbate vehicle issues, a non-functioning starter can bring operations to a halt. Fleet managers must ensure that vehicles are always operational, making it crucial to quickly address starter issues without incurring significant repair costs.
The Solution: One effective approach is to implement regular maintenance checks focused on the starter system. Buyers should invest in diagnostic tools that can help identify starter issues before they lead to breakdowns. For instance, using a voltmeter, they can routinely check battery voltage and connections to the starter. If a bad starter is suspected, they can apply temporary fixes such as gently tapping the starter with a mallet, which can sometimes free stuck components. Additionally, sourcing reliable starter repair kits can facilitate quick on-site repairs, reducing downtime and maintaining operational efficiency. By establishing a proactive maintenance schedule and training staff on basic troubleshooting techniques, B2B buyers can significantly minimize the impact of starter-related issues.
Scenario 2: Managing Repair Costs in Different Markets
The Problem: B2B buyers in diverse international markets often grapple with varying repair costs and parts availability, particularly when dealing with faulty starters. In regions such as the Middle East or Europe, where labor and parts may be more expensive, the financial burden of repairs can strain budgets. Furthermore, the inconsistency in parts quality can lead to repeated failures, which not only increases costs but also affects trust in local service providers.
The Solution: To navigate these challenges, buyers should develop partnerships with reputable local suppliers who can provide high-quality starter parts at competitive prices. Conducting market research to identify trusted vendors can ensure that the components sourced are reliable and durable. Additionally, negotiating bulk purchasing agreements can help lower costs. Implementing a standardized repair protocol across regions can also streamline processes and reduce the variability in repair expenses. Leveraging technology, such as fleet management software, can help track vehicle performance and alert managers to potential starter issues before they escalate, allowing for budget-friendly maintenance planning.
Scenario 3: Ensuring Safety During Emergency Repairs
The Problem: In critical situations, B2B buyers may find themselves needing to start a vehicle with a bad starter in unsafe or inconvenient locations, such as construction sites or remote areas. This can pose safety risks not only to the vehicle operators but also to others in the vicinity. If a vehicle fails to start, it can lead to delays and hazardous situations, especially in regions with limited access to immediate repair services.
The Solution: To enhance safety and efficiency, it is vital for B2B buyers to equip their vehicles with emergency starter repair kits that include essential tools such as jumper cables, a hammer, and basic cleaning supplies for battery terminals. Training personnel on how to safely execute temporary fixes, like jump-starting or using a mallet on the starter, can empower them to address issues quickly and safely. Additionally, establishing a clear protocol for emergency repairs can help ensure that all team members know how to respond effectively in such situations. Incorporating safety gear, such as gloves and goggles, into these kits can further mitigate risks during emergency repairs. By preparing for potential starter failures with the right tools and training, businesses can maintain safety and minimize disruption in their operations.

Illustrative image related to how to start a car if the starter is bad
Strategic Material Selection Guide for how to start a car if the starter is bad
What Are the Key Materials for Starting a Car with a Bad Starter?
When addressing the challenge of starting a car with a faulty starter, selecting the right materials is crucial for effective temporary solutions. Here, we analyze several common materials that can be utilized in this context, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international B2B buyers.
What Are the Key Properties of Jumper Cables?
Jumper cables are essential for jump-starting vehicles with a weak battery, which can often be mistaken for starter issues. Typically made from copper or aluminum, these cables feature high conductivity and flexibility.
- Key Properties: Jumper cables generally have a temperature rating of -40°F to 140°F and a high current capacity (often 400-600 amps).
- Pros: They are relatively inexpensive, lightweight, and easy to store. Their flexibility allows for easy maneuvering in tight spaces.
- Cons: Lower-quality cables can suffer from insulation wear over time, leading to potential electrical hazards. They may also have limited durability under extreme conditions.
- Impact on Application: Jumper cables are compatible with most vehicle batteries, but users must ensure proper gauge thickness to handle the required current.
- Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM D2273 for electrical cables is essential. Buyers in regions like Africa and South America should also consider the local climate’s impact on cable insulation.
How Do Mallets or Hammers Assist in Starting a Car?
Using a mallet or hammer to tap the starter can help free stuck components. This method is particularly useful when the brushes inside the starter motor are worn.
- Key Properties: Mallets are typically made from rubber or wood, providing a non-damaging impact, while hammers are usually steel, offering a more forceful strike.
- Pros: They are cost-effective and widely available. Tapping the starter can be a quick fix without requiring extensive mechanical knowledge.
- Cons: Overuse can lead to damage to the starter or surrounding components. It may not work if the starter is entirely non-functional.
- Impact on Application: The effectiveness of this method depends on the condition of the starter motor and the surrounding space for maneuverability.
- Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that the tools meet local safety standards and are suitable for the vehicle models prevalent in their regions.
What Role Do Wrenches Play in This Process?
Wrenches are vital for safely disconnecting and reconnecting battery terminals, which can often be the source of starting issues.
- Key Properties: Wrenches are typically made from steel or chrome vanadium, offering high tensile strength and resistance to corrosion.
- Pros: They are durable and can withstand high torque, making them suitable for various automotive applications. Their availability in various sizes makes them versatile.
- Cons: High-quality wrenches can be more expensive, and improper use can lead to rounded-off nuts and bolts.
- Impact on Application: Wrenches must be compatible with the specific bolt sizes of the vehicle’s battery and starter terminals.
- Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as DIN 3110 for wrenches is important, especially for buyers in Europe and the Middle East.
Why Is a Voltmeter Essential in Diagnosing Starter Issues?
A voltmeter is crucial for diagnosing battery health and ensuring that the starter receives adequate voltage.
- Key Properties: Digital voltmeters typically operate in a range of 0-20 volts with a high degree of accuracy.
- Pros: They provide quick diagnostics and can help identify whether the issue lies with the battery or the starter.
- Cons: They require a basic understanding of electrical systems to interpret readings accurately. Some models can be expensive.
- Impact on Application: A voltmeter is compatible with all vehicle electrical systems, but users must ensure it is calibrated correctly.
- Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should look for voltmeters that comply with IEC 61010 safety standards, especially in regions with varying electrical regulations.
Summary Table of Material Selection
| Material | Typical Use Case for how to start a car if the starter is bad | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jumper Cables | Jump-starting a vehicle with a weak battery | High conductivity and flexibility | Insulation wear over time | Low |
| Mallet or Hammer | Tapping the starter to free stuck components | Cost-effective and widely available | Risk of damaging the starter | Low |
| Wrench | Disconnecting/reconnecting battery terminals | Durable and versatile | Can be expensive if high-quality | Medium |
| Voltmeter | Diagnosing battery health | Quick diagnostics | Requires understanding of readings | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide provides valuable insights for B2B buyers looking to address starter issues effectively. By understanding the properties, advantages, and limitations of each material, businesses can make informed decisions that enhance their operational efficiency.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for how to start a car if the starter is bad
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process for Starter Motors?
The manufacturing process for starter motors involves several critical stages, each integral to ensuring the final product meets the required performance and reliability standards.
Material Preparation
The first stage of manufacturing starter motors begins with material preparation. High-quality materials such as copper for windings, steel for the casing, and various alloys for internal components are selected based on their electrical conductivity, strength, and durability.
Materials undergo rigorous testing to confirm they meet specified standards, including resistance to corrosion and heat. This step often involves sourcing raw materials from certified suppliers who adhere to international standards such as ISO 9001, ensuring that the materials are suitable for automotive applications.
Forming Techniques
Once materials are prepared, the next step involves forming components. This includes processes such as stamping, machining, and die-casting to create parts like the housing, armature, and field coils.
Advanced techniques, such as computer numerical control (CNC) machining, are commonly employed to ensure precision in manufacturing. This precision is crucial for the starter’s performance, as any deviations can lead to failures or inefficiencies.
Assembly Process
The assembly stage is where all components come together. Here, parts are meticulously fitted and secured using methods such as soldering, welding, and mechanical fastening.
Quality control checkpoints are critical during assembly to ensure that each component is correctly installed. For example, the alignment of the armature and the field coils must be precise to ensure efficient operation. This stage often involves automated assembly lines to enhance efficiency while maintaining high-quality standards.
Finishing Techniques
The final stage in the manufacturing process involves finishing techniques that enhance the starter’s durability and performance. This includes surface treatments like plating to prevent corrosion and improve conductivity.
Additionally, components may undergo testing for electrical integrity, ensuring that all connections are secure and functional. Finishing processes are vital for prolonging the lifespan of the starter motor, especially in demanding environments.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Starter Motor Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is a cornerstone of the manufacturing process for starter motors, impacting their performance and reliability significantly.
What Are the Relevant International Standards for Quality Control?
International standards such as ISO 9001 provide a framework for quality management systems, ensuring that manufacturers maintain high standards throughout their processes. Compliance with these standards is essential for companies looking to export products to various regions, including Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
In addition to ISO standards, industry-specific certifications such as CE marking (for products sold in the European Economic Area) and API (American Petroleum Institute) standards may apply to specific starter motor applications. These certifications indicate compliance with safety, health, and environmental regulations.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are implemented throughout the manufacturing process to ensure that each component and assembly meets the required standards. These checkpoints typically include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint assesses the quality of raw materials upon arrival. Only materials meeting the specified quality criteria are allowed into the production line.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, various tests and inspections are conducted to monitor quality. This includes checking dimensional tolerances, material properties, and assembly accuracy.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): The final inspection occurs after assembly, where the complete starter motor undergoes rigorous testing for functionality, electrical performance, and durability. This step ensures that the product is ready for market delivery.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used in Starter Motor Quality Control?
Testing methods play a crucial role in verifying the quality and performance of starter motors.
Common Testing Methods
-
Electrical Testing: This method checks the starter motor’s electrical performance, ensuring that it meets voltage and current specifications. Tests for insulation resistance and short circuits are also conducted.
-
Mechanical Testing: Mechanical tests assess the physical integrity of the starter motor. This includes vibration tests and torque tests to evaluate the motor’s ability to withstand operational stresses.
-
Environmental Testing: Starter motors are often subjected to temperature and humidity tests to simulate real-world operating conditions. This ensures reliability in various climates, which is particularly relevant for markets in Africa and the Middle East.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For B2B buyers, especially those in international markets, verifying the quality control processes of suppliers is essential for ensuring product reliability.
What Steps Can B2B Buyers Take?
-
Conduct Audits: Regular audits of suppliers can help verify compliance with quality standards. Buyers should inquire about the frequency of these audits and the criteria used.
-
Request Quality Reports: Suppliers should provide detailed quality assurance reports, including data on testing methods, results, and any corrective actions taken.
-
Engage Third-Party Inspections: Utilizing third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control processes. These inspectors can evaluate manufacturing practices, conduct tests, and verify compliance with international standards.
What Nuances Should International B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
International buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, and the Middle East, must navigate various nuances in quality control and certification.

Illustrative image related to how to start a car if the starter is bad
Key Considerations
-
Regulatory Compliance: Different regions have varying regulations regarding automotive components. Understanding these requirements is crucial for compliance and market access.
-
Cultural Differences: Business practices and expectations can differ significantly across regions. B2B buyers should be aware of these cultural nuances when establishing partnerships with suppliers.
-
Logistical Challenges: Importing automotive components may involve additional logistical challenges, including customs regulations and shipping delays. Buyers should account for these factors when planning procurement strategies.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices associated with starter motors, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they partner with reliable suppliers who can meet their quality and performance needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘how to start a car if the starter is bad’
To assist B2B buyers in navigating the complexities of starting a car with a faulty starter, this practical sourcing guide outlines essential steps and considerations. By following these guidelines, businesses can ensure effective solutions and minimize downtime.
Step 1: Identify Your Needs and Specifications
Understanding the specific requirements of your automotive repair operations is crucial. Determine the types of vehicles you typically service and the common issues you encounter with starters. This information will guide your sourcing decisions and help you choose the right tools and methods tailored to your needs.
Step 2: Research Available Tools and Equipment
Explore the market for tools that facilitate the process of starting a car with a bad starter. Essential tools include jumper cables, wrenches, mallets, and voltmeters. Prioritize suppliers that offer high-quality equipment designed for durability and reliability in automotive environments.
- Jumper cables: Ensure they are heavy-duty and long enough to reach various vehicle configurations.
- Voltmeters: Look for models that provide accurate readings and are easy to use in various lighting conditions.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Before engaging with suppliers, verify their industry certifications and standards. This step is important as it ensures that the tools and equipment meet safety and quality regulations. Request documentation related to their certifications, such as ISO standards, to assess their credibility.
Step 4: Assess Warranty and Support Services
A strong warranty and reliable customer support can significantly affect your purchasing decision. Evaluate the warranty terms offered by suppliers for their tools and equipment, ensuring they provide adequate coverage for defects or issues. Additionally, check if they offer technical support or guidance on using their products effectively.
Step 5: Request Samples or Demonstrations
If possible, request samples or demonstrations of the tools you are considering. This hands-on experience allows you to assess the usability and effectiveness of the equipment in real-world scenarios. It also helps to ensure that the tools fit well with your operational processes.

Illustrative image related to how to start a car if the starter is bad
Step 6: Compare Pricing and Value
Conduct a thorough comparison of pricing among different suppliers while considering the overall value offered. Cheaper tools may not always be the best choice if they compromise on quality or effectiveness. Look for suppliers that provide a good balance of cost, quality, and support.
- Bulk purchasing discounts: Inquire about bulk order options that could reduce overall costs.
- Long-term partnerships: Consider establishing long-term relationships with suppliers who provide consistent quality and service.
Step 7: Make Informed Decisions and Purchase
After completing your research and evaluation, make informed purchasing decisions based on your findings. Ensure that the chosen tools and equipment align with your operational needs and budget. Place your order with a supplier that demonstrates reliability and professionalism in their dealings.
By following this comprehensive checklist, B2B buyers can streamline the process of sourcing tools and equipment necessary for effectively starting a car with a bad starter, ultimately enhancing service delivery and operational efficiency.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for how to start a car if the starter is bad Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Starting a Car with a Bad Starter?
When analyzing the costs involved in starting a car with a bad starter, several cost components come into play. These include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margins.
Materials encompass the tools and supplies needed, such as jumper cables, wrenches, and cleaning agents. Depending on the complexity of the task and whether additional parts (like a starter relay) are needed, material costs can vary significantly.
Illustrative image related to how to start a car if the starter is bad
Labor costs are influenced by the skill level required for the task. If the job is straightforward, a basic mechanic’s assistance may suffice. However, more complex issues may require specialized technicians, thus increasing labor expenses.
Manufacturing overhead may apply if parts or tools are sourced from manufacturers. This includes indirect costs like utilities and rent associated with the production facility.
Tooling costs can arise if specialized tools are required for diagnosis or repair. For instance, a voltmeter may be essential for troubleshooting, and its cost should be factored into the overall analysis.
Quality Control (QC) measures ensure that the tools and parts function correctly and meet safety standards. This can add to the costs but is crucial for maintaining reliability and customer satisfaction.
Logistics costs involve the transportation of tools and parts, which can vary based on the geographic location of suppliers and buyers. International shipping can significantly impact these costs, especially for businesses in Africa and South America where infrastructure may be less developed.
Lastly, the margin is the profit added by suppliers or service providers, which can vary widely based on market conditions and competition.
How Do Price Influencers Impact the Cost of Starting a Car with a Bad Starter?
Several factors influence pricing in this context, including volume or minimum order quantity (MOQ), specifications and customization, material quality, certifications, supplier factors, and Incoterms.
Volume/MOQ is critical; larger orders often attract discounts. Businesses should negotiate these terms to ensure cost-efficiency.
Specifications and customization can affect costs. For example, customized tools for specific car models may be more expensive than standard options. Buyers should assess their needs carefully to avoid unnecessary expenses.
Material quality and certifications also play a role. Higher-quality components that meet international safety standards may come at a premium but can provide long-term savings through durability and reliability.

Illustrative image related to how to start a car if the starter is bad
Supplier factors, such as reputation and reliability, can impact pricing. Established suppliers might charge more due to their proven track record but often provide better support and warranty options.
Incoterms determine responsibilities for shipping and handling costs, which can affect the final price. International buyers should be aware of these terms to avoid unexpected charges.
What Are the Best Buyer Tips for Negotiating Costs in International Markets?
For international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding negotiation tactics and pricing nuances is essential for cost efficiency.
Negotiation is key. Buyers should come prepared with data on market prices, potential competitors, and volume discounts to leverage better terms.
Cost-efficiency can be maximized by considering Total Cost of Ownership (TCO). This includes not just the initial costs but also maintenance, operational costs, and potential downtime.
Pricing nuances vary by region. For example, buyers in Nigeria may face different logistical challenges compared to those in Germany. Understanding local market conditions can provide leverage in negotiations.
It is advisable to build relationships with multiple suppliers to compare offers and ensure competitive pricing.
Lastly, always request a detailed breakdown of costs from suppliers to identify areas where savings can be made, ensuring transparency and informed decision-making.
Disclaimer
The prices and cost structures discussed herein are indicative and can vary based on market conditions, supplier negotiations, and specific regional dynamics. Always conduct thorough market research and supplier assessments before making purchasing decisions.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing how to start a car if the starter is bad With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternative Methods for Starting a Car with a Faulty Starter
When faced with the challenge of starting a car with a bad starter, several alternative solutions can be considered. Each method has its unique advantages and drawbacks that can affect decision-making, particularly for B2B buyers seeking efficient solutions in automotive maintenance. This analysis compares the traditional method of starting a car with a bad starter against two viable alternatives: using a jump starter and employing a push-start technique for manual vehicles.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | How To Start A Car If The Starter Is Bad | Jump Starter | Push Start |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Varies based on the specific fix applied | High, if battery-related | Effective for manual cars |
| Cost | Low to moderate (tools and temporary fixes) | Moderate (device purchase) | Minimal (requires manpower) |
| Ease of Implementation | Moderate (requires some technical skill) | Easy (plug-and-play) | Moderate (requires assistance) |
| Maintenance | Low (temporary solutions may need repeat) | Low (one-time investment) | Low (if performed correctly) |
| Best Use Case | Temporary fix until a new starter is installed | Quick battery boost | Manual cars with a bad starter |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Jump Starter
A jump starter is a portable device designed to provide a quick boost to a car’s battery. This method is highly effective when the issue stems from a low battery rather than a faulty starter. The performance is generally high, as it can start the vehicle almost immediately if the battery is the issue. While the initial investment in a jump starter may be moderate, it offers ease of use with straightforward plug-and-play functionality. Maintenance is minimal, as it typically involves ensuring the device is charged and functional. This solution is best utilized in situations where the battery is suspected to be the primary problem.
Push Start
Push starting is a method applicable mainly to manual transmission vehicles. It involves getting the car rolling and then engaging the clutch to start the engine. This technique can be highly effective and cost-efficient, requiring only the assistance of a few individuals to push the car. Performance is contingent on the vehicle’s speed and the physical effort of those assisting. However, it can be moderately challenging to implement, as it requires coordination and a clear understanding of the vehicle’s mechanics. Maintenance is low, as it does not involve any additional tools or devices. This method is best suited for emergency situations where immediate assistance is available.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
When selecting the best method to start a car with a faulty starter, B2B buyers must consider their specific circumstances, such as the type of vehicle, the condition of the battery, and the availability of assistance. For situations where a battery-related issue is suspected, investing in a jump starter may be the most efficient solution. Conversely, for those dealing with manual transmission vehicles and immediate assistance, a push start can serve as a quick and effective workaround. Ultimately, understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each approach will empower buyers to make informed decisions that best suit their operational needs.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for how to start a car if the starter is bad
What Are the Key Technical Properties Related to Starting a Car with a Bad Starter?
When addressing the issue of starting a car with a faulty starter, several critical technical properties come into play. These properties not only influence the immediate task at hand but also have broader implications for maintenance, repairs, and the overall efficiency of automotive operations.

Illustrative image related to how to start a car if the starter is bad
-
Material Grade of Electrical Components
– The electrical components, including the starter motor and battery cables, are typically made from materials like copper for conductivity. The material grade affects the efficiency of electrical flow and the durability of connections. High-grade materials ensure less resistance, reducing heat generation and improving performance, which is crucial for international buyers who prioritize reliability and longevity in automotive parts. -
Voltage Tolerance
– Most automotive systems operate at a standard voltage of 12 volts. Understanding voltage tolerance is essential when diagnosing issues. For instance, a weak battery may register below 12 volts, indicating insufficient power to engage the starter. This knowledge helps in making informed purchasing decisions about batteries and starters, ensuring compatibility and optimal performance in various vehicle types. -
Corrosion Resistance
– Corrosion can significantly hinder electrical connections, particularly at battery terminals and starter connections. Components treated for corrosion resistance prolong the lifespan of these connections and reduce maintenance costs. B2B buyers should consider suppliers who offer corrosion-resistant products, especially in regions with high humidity or saline environments, where corrosion is more prevalent. -
Thermal Tolerance
– Starters and electrical components must withstand varying temperatures. High thermal tolerance ensures that parts do not fail under extreme conditions, which is vital for vehicles operating in diverse climates. Buyers should inquire about the thermal ratings of components, especially in markets with extreme weather conditions like Africa or the Middle East. -
Current Rating
– The current rating, measured in amperes (A), indicates how much electrical current a starter can handle. A higher current rating is beneficial for ensuring that the starter can engage even in adverse conditions, such as cold weather. B2B buyers must assess current ratings to ensure they meet the demands of their vehicle fleets.
What Are the Common Trade Terminology and Jargon in Automotive Repairs?
Understanding industry-specific terminology is crucial for effective communication and decision-making in the automotive sector, especially when dealing with international suppliers and manufacturers.
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– This term refers to companies that produce parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of starters, OEM parts are those made by the vehicle manufacturer or their approved suppliers. Using OEM parts often ensures compatibility and reliability, making them a preferred choice for many B2B buyers. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– MOQ indicates the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is vital for international buyers as it affects inventory management and cost-effectiveness. Buyers should negotiate MOQs that align with their operational needs without incurring excess costs. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to request pricing and terms for specific products or services. In the automotive sector, RFQs are essential for obtaining competitive pricing for starters and related components, enabling buyers to make informed purchasing decisions. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– These are standardized trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding Incoterms is crucial for managing logistics, costs, and risks associated with shipping automotive parts, particularly when sourcing from different continents. -
Aftermarket Parts
– Aftermarket parts are components made by manufacturers other than the OEM. While often cheaper, they may vary in quality and compatibility. B2B buyers should evaluate the trade-offs between cost and reliability when considering aftermarket options for starter replacements. -
Lead Time
– Lead time refers to the time it takes from placing an order to receiving the product. In the automotive industry, shorter lead times are crucial for maintaining operational efficiency. Buyers should assess lead times when selecting suppliers to minimize downtime in their operations.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when addressing issues related to starting a car with a faulty starter, ensuring optimal performance and reliability in their automotive fleets.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the how to start a car if the starter is bad Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in Starting a Car with a Bad Starter?
The automotive repair sector, particularly regarding issues like faulty starters, is witnessing a transformative phase driven by technological advancements and shifting consumer expectations. In regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, B2B buyers are increasingly prioritizing solutions that combine efficiency with cost-effectiveness. As vehicle ownership rises in these markets, so does the demand for reliable repair services, including methods to start cars with malfunctioning starters. Key trends include the adoption of mobile diagnostics tools that allow mechanics to quickly identify starter issues, reducing downtime and enhancing customer satisfaction.
Furthermore, the rise of e-commerce platforms has made sourcing parts and tools more accessible, enabling buyers to procure necessary items like jumper cables, voltmeters, and starter relays from a variety of suppliers. This shift towards digital marketplaces is revolutionizing traditional supply chains, allowing for real-time inventory management and improved price transparency. Importantly, as manufacturers and suppliers respond to global competition, there is a notable emphasis on developing innovative starter systems that are more durable and easier to service.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact B2B Buyers in the Automotive Sector?
Sustainability has become a pivotal consideration for B2B buyers in the automotive sector, particularly in regions with growing environmental awareness. The sourcing of materials and components used to address issues like bad starters now demands a focus on ethical supply chains. Buyers are increasingly looking for suppliers who can demonstrate environmental responsibility through certifications such as ISO 14001 or adherence to the UN Global Compact principles. These certifications not only reflect a commitment to sustainability but also enhance brand reputation and customer loyalty.
Moreover, the environmental impact of automotive repairs, including the disposal of old starters and batteries, has prompted a shift towards recycling and the use of eco-friendly materials. Buyers should prioritize partnerships with manufacturers who utilize sustainable practices and offer products that minimize environmental harm. Such considerations are crucial not only for compliance with increasingly stringent regulations but also for meeting the expectations of environmentally-conscious consumers in markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
What Is the Historical Context of Automotive Starter Issues?
The automotive starter motor has evolved significantly since its inception in the early 20th century. Originally, vehicles relied on hand cranks to start the engine, a method that was both labor-intensive and hazardous. The introduction of the electric starter motor in the 1910s revolutionized vehicle operation, making it more accessible and safer for drivers. Over the decades, advancements in starter technology have led to more reliable and efficient systems, integrating features such as solenoids and improved electrical components.
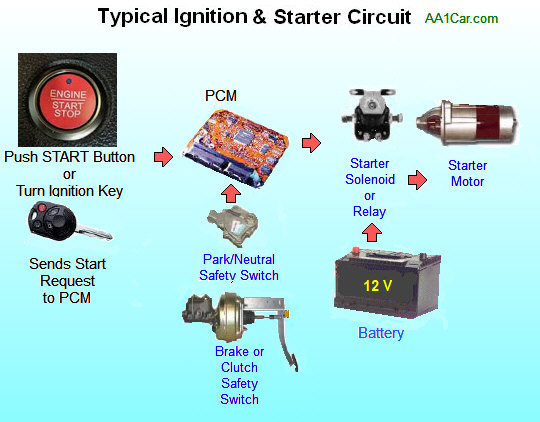
Illustrative image related to how to start a car if the starter is bad
As automotive technology continues to advance, the focus has shifted from merely starting vehicles to ensuring longevity and ease of repair. The emergence of smart automotive diagnostics is now aiding mechanics in identifying starter issues more accurately, reflecting a broader trend towards technological integration in automotive maintenance. This historical context underscores the importance of understanding starter systems for contemporary B2B buyers who are navigating a rapidly evolving market landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of how to start a car if the starter is bad
-
How do I identify a bad starter in a vehicle?
To identify a bad starter, begin by turning the ignition key. If you hear rapid clicking sounds, the issue may lie with the battery rather than the starter. If the engine turns over but fails to start, consider other components like the ignition system or fuel delivery. However, if there’s no noise or just one click when turning the key, this indicates a potential starter failure. Regular maintenance and inspections of the starter can help in early identification of issues, reducing downtime for vehicles in your fleet. -
What tools are essential for starting a car with a bad starter?
Key tools include jumper cables for testing the battery, a mallet or hammer for gentle taps on the starter, and a voltmeter to check battery voltage. A wrench is necessary for safely disconnecting and reconnecting battery terminals, while a flashlight ensures good visibility during inspection. Optional tools like starter relays and protective gear enhance safety and efficiency. Investing in these tools not only aids in immediate fixes but also supports long-term maintenance strategies for your fleet. -
Can I jump-start a car with a bad starter?
Jump-starting may temporarily help if the issue is a weak battery rather than a faulty starter. If the battery voltage is below 12V, a jump can provide the necessary power to start the vehicle. However, if the starter is indeed faulty, jump-starting will not resolve the underlying problem, and the vehicle will likely not start again. For B2B buyers, understanding the relationship between battery health and starter functionality is crucial for effective fleet management. -
What are the implications of using temporary fixes for a bad starter?
While temporary fixes like tapping the starter or jump-starting may provide immediate results, they do not address the root cause of the problem. Relying on these methods can lead to increased downtime and potential damage to the starter or other components. It’s advisable to schedule a thorough inspection and repair as soon as possible to avoid further complications and ensure the reliability of your vehicles, particularly in logistics and transportation sectors. -
How do I vet suppliers for starter repair parts?
When sourcing starter repair parts, vet suppliers by checking their reputation, customer reviews, and industry certifications. Request samples to assess quality and compatibility with your vehicles. Additionally, inquire about their supply chain reliability and lead times, especially if your operations depend on timely repairs. Establishing a solid relationship with trustworthy suppliers can greatly enhance your fleet’s operational efficiency and reduce costs associated with poor-quality parts. -
What customization options are available for starter parts?
Many suppliers offer customization options for starter parts, including different sizes, materials, and performance specifications. Customization can enhance compatibility with specific vehicle models or improve durability in challenging environments. When discussing with suppliers, clearly outline your needs and operational conditions to ensure the customized parts meet your expectations. This can lead to improved performance and longevity of the starters in your fleet. -
What minimum order quantities (MOQ) should I expect from suppliers?
Minimum order quantities (MOQ) vary widely among suppliers and depend on the type of parts and their manufacturing processes. Some suppliers may have low MOQs for common starter parts, while others may require larger orders for customized solutions. It’s essential to negotiate MOQs that align with your purchasing strategy and inventory management. Building a strong relationship with suppliers can often lead to more flexible terms and better pricing. -
How do payment terms affect my purchasing decisions?
Understanding payment terms is crucial for budgeting and cash flow management. Common terms include net 30, net 60, or even upfront payments for custom orders. Evaluate the impact of these terms on your financial planning and operational capabilities. Additionally, consider negotiating terms that allow for more favorable cash flow, such as extended payment deadlines for larger orders. Clear communication with suppliers about your payment preferences can foster better relationships and ensure smoother transactions.
Top 4 How To Start A Car If The Starter Is Bad Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Honda Accord – Starter Troubleshooting
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: 2003 Honda Accord, suspected bad starter, battery full, attempted jump start, headlights bright but do not dim when cranking, starter makes clicking noise but does not turn over, automatic transmission (cannot pop start).
2. Facebook – Community Support
Domain: facebook.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: This company, Facebook – Community Support, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
3. Car – No Start Troubleshooting
Domain: mechanics.stackexchange.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: The car has a powerful new battery (1 week old). Symptoms include: car won’t start, not even a click when trying to start, all lights are functioning and not dim. Possible issues include: loose battery connection, need for a jump start, faulty ignition switch, bad starter, bad solenoid, bad ground, or bad starter connection.
4. WikiHow – Starting a Car with a Bad Starter
Domain: wikihow.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: The article provides solutions for starting a car with a bad starter, including tapping the starter with a hammer or wood, push-starting the vehicle if it has a manual transmission, and jumping the battery to rule out battery issues. It emphasizes the importance of checking the battery first, as many starter problems are actually battery-related. The article also mentions that if the starter is da…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for how to start a car if the starter is bad
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your Automotive Maintenance Solutions?
In conclusion, understanding how to start a car with a bad starter is not just about immediate fixes; it also emphasizes the importance of strategic sourcing in the automotive sector. By leveraging quality components and reliable tools, businesses can enhance their service offerings, ensuring that they address customer needs effectively while minimizing downtime.
Key takeaways include the necessity of proper diagnostics, the importance of maintaining battery connections, and the value of having the right tools on hand. Companies should prioritize sourcing durable components, such as high-quality starters and reliable jump-start kits, to improve customer satisfaction and operational efficiency.
As international B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe explore their options, embracing strategic sourcing can lead to more robust supply chains and increased resilience against common automotive challenges. The future of automotive maintenance lies in your hands—invest in quality, build strong partnerships, and position your business for success. Engage with trusted suppliers today to elevate your service capabilities and meet the evolving demands of the market.
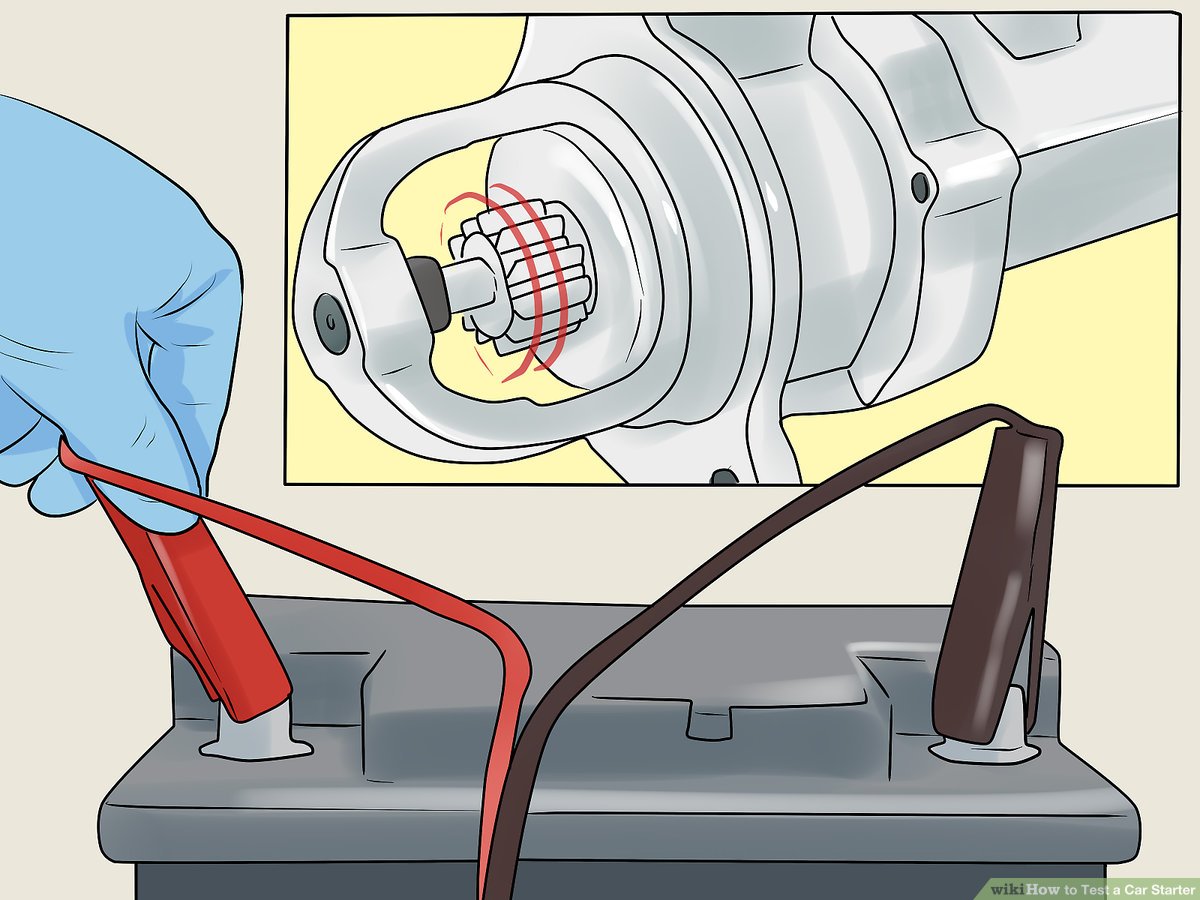
Illustrative image related to how to start a car if the starter is bad
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.