Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for how is a motor different from a generator
Understanding the distinction between electric motors and generators is crucial for B2B buyers navigating the complex landscape of industrial machinery and energy solutions. Whether you’re sourcing equipment for manufacturing plants in Africa or evaluating power generation options for infrastructure projects in Europe, knowing how a motor differs from a generator can significantly impact your purchasing decisions. This guide aims to demystify these two essential technologies by exploring their types, applications, and operational principles, while also addressing supplier vetting processes and cost considerations.
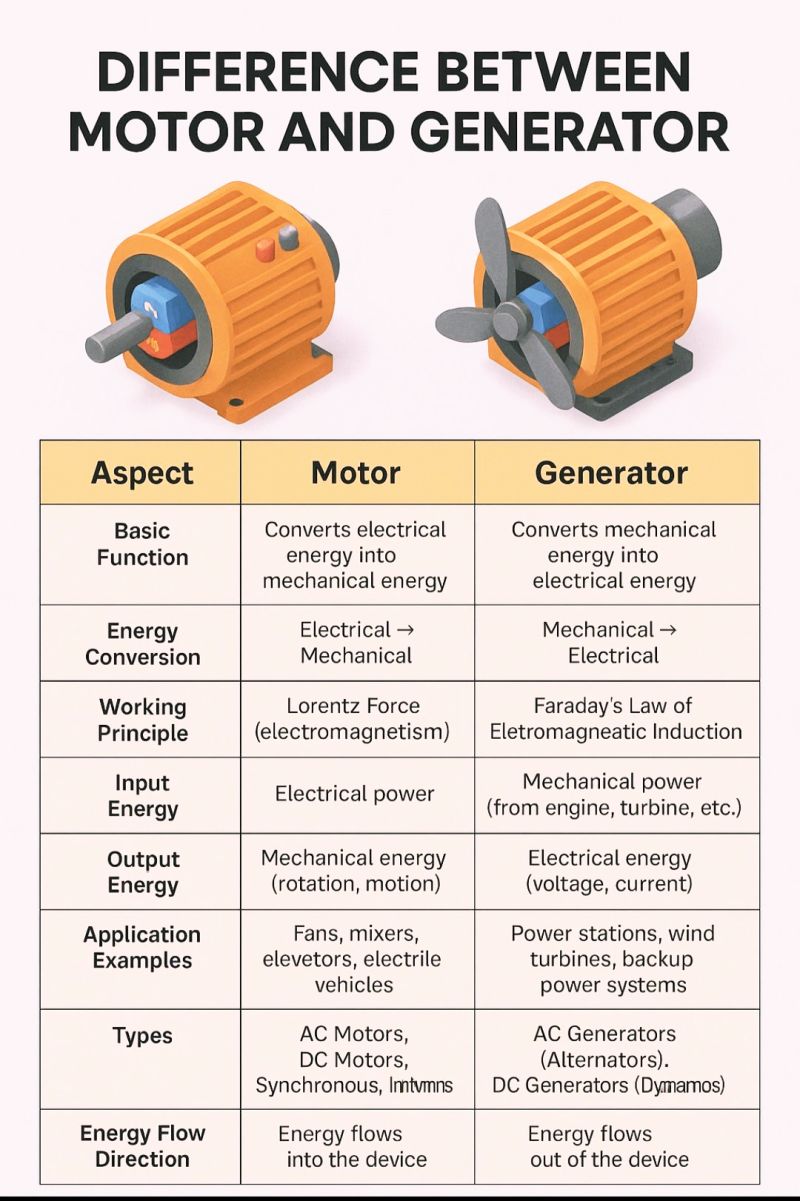
As global markets evolve, the need for reliable and efficient energy solutions becomes paramount. Electric motors convert electrical energy into mechanical energy, powering everything from conveyor belts to household appliances, while generators transform mechanical energy into electrical energy, essential for industries and power stations. By understanding these fundamental differences, international buyers can make informed choices that align with their operational needs and sustainability goals.
In this comprehensive guide, we will cover various types of motors and generators, delve into their specific applications across different sectors, and provide insights into evaluating suppliers. Additionally, we will highlight cost factors and efficiency metrics to empower you in making strategic purchasing decisions. With a focus on the unique challenges faced by businesses in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, this resource is designed to enhance your understanding and facilitate successful sourcing strategies in a competitive global market.
Table Of Contents
- Top 2 How Is A Motor Different From A Generator Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for how is a motor different from a generator
- Understanding how is a motor different from a generator Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of how is a motor different from a generator
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘how is a motor different from a generator’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for how is a motor different from a generator
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for how is a motor different from a generator
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘how is a motor different from a generator’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for how is a motor different from a generator Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing how is a motor different from a generator With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for how is a motor different from a generator
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the how is a motor different from a generator Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of how is a motor different from a generator
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for how is a motor different from a generator
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Understanding how is a motor different from a generator Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electric Motors | Converts electrical energy to mechanical energy; operates on Fleming’s left-hand rule. | Industrial machinery, HVAC systems, electric vehicles. | Pros: High efficiency, wide application range. Cons: Initial investment can be high. |
| Electric Generators | Converts mechanical energy to electrical energy; operates on Fleming’s right-hand rule. | Power generation, backup power systems, renewable energy systems. | Pros: Essential for energy supply, versatile energy sources. Cons: Maintenance can be costly. |
| Alternators | A type of generator producing alternating current; uses rotating magnetic fields. | Automotive applications, power plants, wind turbines. | Pros: Reliable power generation, efficient for large-scale use. Cons: More complex design. |
| Dynamos | A type of generator producing direct current; simpler design compared to alternators. | Small-scale power generation, battery charging. | Pros: Simple and robust; lower cost for small applications. Cons: Limited to specific applications. |
| Stepper Motors | Converts electrical pulses into distinct mechanical movements; used in precision applications. | Robotics, CNC machines, 3D printers. | Pros: High precision and control. Cons: Limited torque at high speeds. |
What are Electric Motors and Their B2B Relevance?
Electric motors are essential components in numerous B2B applications, transforming electrical energy into mechanical energy to drive machinery. Their efficiency and reliability make them a staple in industries such as manufacturing, HVAC, and automotive. Buyers should consider factors such as energy efficiency ratings, power output, and compatibility with existing systems when purchasing. Investing in high-quality electric motors can lead to long-term savings on energy costs and reduced maintenance.
How Do Electric Generators Function in Business Applications?
Electric generators play a crucial role in converting mechanical energy into electrical energy, serving industries that require consistent power supply. They are widely used in power generation plants, backup systems, and renewable energy applications. When selecting a generator, businesses should assess their power needs, fuel type (diesel, natural gas, etc.), and the generator’s efficiency. Understanding the total cost of ownership, including maintenance and fuel expenses, is vital for making informed purchasing decisions.
What Makes Alternators Suitable for Various Industries?
Alternators are specialized generators that produce alternating current (AC) and are commonly found in automotive and large-scale power generation applications. Their design allows for efficient energy conversion and reliability, making them ideal for environments where consistent power is crucial. Buyers should evaluate the alternator’s output capacity, durability, and installation requirements. Although typically more complex than other generators, their benefits often outweigh the challenges, especially in large-scale operations.
Why Choose Dynamos for Smaller Applications?
Dynamos generate direct current (DC) and are simpler in design compared to alternators. They are often used in small-scale applications like battery charging and low-power generation. Businesses focused on small power solutions may find dynamos to be cost-effective options. When considering a dynamo, buyers should weigh its output capacity against their specific energy needs and consider potential limitations in scalability.
How Do Stepper Motors Enhance Precision in Business Operations?
Stepper motors are unique in that they convert electrical pulses into precise mechanical movements, making them ideal for applications requiring high accuracy, such as robotics and CNC machinery. Their ability to maintain position without a feedback system makes them suitable for various automation tasks. When purchasing stepper motors, B2B buyers should focus on torque specifications, pulse per revolution, and compatibility with control systems to ensure optimal performance in their operations.
Key Industrial Applications of how is a motor different from a generator
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of how is a motor different from a generator | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Use of motors in conveyor systems and generators for backup power | Enhanced efficiency and reliability in production lines | Compatibility with existing systems, power capacity, and efficiency ratings |
| Renewable Energy | Wind turbines utilizing generators for electricity generation | Sustainable energy production and reduced operational costs | Type of generator (DC/AC), maintenance support, and scalability |
| Automotive | Electric motors in electric vehicles and generators for alternators | Improved vehicle performance and energy efficiency | Voltage requirements, weight considerations, and performance specs |
| Construction | Motors in heavy machinery and generators for site power supply | Increased productivity and reduced downtime on job sites | Durability, power output, and ease of integration with machinery |
| Agriculture | Motors for irrigation systems and generators for powering farm equipment | Enhanced productivity and resource management | Energy efficiency, availability of parts, and service support |
How Are Motors and Generators Used in the Manufacturing Sector?
In manufacturing, electric motors drive conveyor systems, ensuring smooth and efficient material handling. Simultaneously, generators provide backup power to maintain operations during outages. These applications are crucial for optimizing production efficiency and minimizing downtime. Buyers should consider compatibility with existing equipment, power capacity, and efficiency ratings to ensure seamless integration and operation.
What Role Do Motors and Generators Play in Renewable Energy?
In the renewable energy sector, generators are integral to wind turbines, converting mechanical energy from wind into electricity. This application promotes sustainable energy production and can significantly lower operational costs. Buyers must assess the type of generator (DC or AC), maintenance support, and scalability to meet energy demands effectively, especially in regions with varying wind conditions.
How Are Motors and Generators Transforming the Automotive Industry?
Electric vehicles (EVs) rely on electric motors for propulsion, while generators, often in the form of alternators, recharge batteries. This technology enhances vehicle performance and energy efficiency, appealing to environmentally conscious consumers. Buyers should focus on voltage requirements, weight considerations, and performance specifications to ensure optimal vehicle design and functionality.
What Is the Importance of Motors and Generators in Construction?
In construction, electric motors power heavy machinery, while generators supply electricity at job sites, particularly in remote locations. This dual application boosts productivity and minimizes downtime, which is essential for project timelines. Key sourcing considerations include durability, power output, and ease of integration with existing machinery to ensure reliability on challenging job sites.
How Do Motors and Generators Benefit the Agriculture Sector?
Agricultural operations utilize motors for irrigation systems and generators to power essential farm equipment. These applications enhance productivity and resource management, particularly in regions with limited access to grid electricity. Buyers should prioritize energy efficiency, availability of parts, and service support to maintain operations and ensure optimal performance in diverse agricultural environments.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘how is a motor different from a generator’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Misapplication Leading to Equipment Failure
The Problem: A manufacturing company in Africa recently purchased a large electric motor to power a new conveyor system. However, due to a lack of understanding about the differences between motors and generators, they mistakenly connected the motor to a mechanical system intended for a generator. This misapplication caused the motor to overheat and ultimately fail, resulting in costly downtime and repairs. The team faced frustration not only from the equipment failure but also from the financial implications of lost production time.
The Solution: To prevent such costly mistakes, B2B buyers should invest in comprehensive training for their engineering and maintenance teams regarding the fundamental differences between electric motors and generators. This training should cover the operational principles, application contexts, and the specific requirements for each device. Additionally, sourcing equipment from suppliers who offer expert consultation can provide valuable insights. Ensure that specifications are clearly outlined in procurement documents, indicating whether a motor or generator is required for the intended application. A checklist for installation and operational requirements, along with regular maintenance protocols, can further mitigate the risk of equipment misapplication.
Scenario 2: Difficulty in Selecting the Right Technology
The Problem: A renewable energy company in South America is exploring options for integrating wind power into their existing energy grid. They are confused about whether to use electric motors or generators in their systems, leading to indecision that stalls project timelines. The complexity of their technology needs and the lack of clear guidance on selecting the appropriate equipment have resulted in frustration and uncertainty among stakeholders.
The Solution: To streamline the selection process, companies should conduct a thorough needs assessment that evaluates the energy conversion requirements specific to their applications. Engaging with a technical consultant who specializes in renewable energy systems can provide tailored insights into the advantages of using generators versus motors. This consultant can help clarify that, in wind energy systems, generators are typically used to convert mechanical energy from turbine blades into electrical energy. Additionally, buyers should consider establishing partnerships with manufacturers that offer a range of solutions and can provide demonstrations or pilot programs. This practical experience can aid decision-making and ensure the chosen technology aligns with project goals.
Scenario 3: Confusion Over Operational Efficiency
The Problem: A European industrial firm is facing challenges with energy efficiency in their production line. They are unsure whether the existing motors are operating optimally or if they should consider integrating generators to enhance overall efficiency. The lack of clarity on how motors and generators impact energy consumption has led to excessive operational costs and dissatisfaction among management regarding energy waste.
The Solution: To address efficiency concerns, a detailed audit of current energy usage should be conducted, focusing on the performance metrics of existing motors. This audit should assess the load requirements and operational patterns to determine if the current motors are appropriately sized and whether they are being utilized to their full potential. For companies considering the integration of generators, it is essential to evaluate the potential for energy recovery systems that can convert excess mechanical energy back into electricity. Additionally, collaborating with energy management consultants can provide actionable insights into optimizing the existing setup. They can recommend energy-efficient motor alternatives or hybrid systems that combine motors and generators to improve the overall efficiency of the production line.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for how is a motor different from a generator
What Are the Key Materials Used in Motors and Generators?
When evaluating the differences between motors and generators, the choice of materials plays a crucial role in their performance and suitability for specific applications. Here, we analyze several common materials used in the construction of these devices from a B2B perspective, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international buyers.
1. Copper: The Preferred Conductor
Key Properties:
Copper is renowned for its excellent electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, and resistance to corrosion. It can operate effectively in a wide range of temperatures, making it suitable for various applications in motors and generators.
Pros & Cons:
Copper’s high conductivity ensures minimal energy loss, which is vital for efficiency. However, it is relatively expensive compared to alternatives like aluminum. Manufacturing complexity is moderate, as copper is easy to work with but requires careful handling to prevent damage during fabrication.
Impact on Application:
Copper is ideal for windings in both motors and generators, ensuring efficient energy transfer. Its compatibility with high-frequency applications makes it suitable for modern electric vehicles and renewable energy systems.
International Considerations:
For buyers in regions such as Africa and South America, sourcing copper may involve navigating supply chain challenges. Compliance with international standards like ASTM B170 for copper wire is essential, and buyers should consider local availability and pricing fluctuations.
2. Aluminum: A Cost-Effective Alternative
Key Properties:
Aluminum is lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and has decent electrical conductivity, though not as high as copper. It can withstand moderate temperatures and is often used in applications where weight savings are critical.
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage of aluminum is its lower cost and lighter weight, making it easier to transport and install. However, it has a higher resistivity, which can lead to energy losses in high-power applications. Manufacturing complexity is lower than copper, but care must be taken to ensure proper connections to prevent overheating.
Impact on Application:
Aluminum is often used in the construction of generator casings and motor housings, where weight reduction is beneficial. Its corrosion resistance makes it suitable for outdoor applications in humid climates.
Illustrative image related to how is a motor different from a generator
International Considerations:
B2B buyers should be aware of the varying quality standards for aluminum in different regions. Compliance with standards such as JIS H 2000 in Japan or DIN 1725 in Germany is important for ensuring product reliability.
3. Steel: Structural Integrity and Durability
Key Properties:
Steel is known for its strength, durability, and ability to withstand high mechanical stresses. It has good thermal conductivity and can be treated for corrosion resistance.
Pros & Cons:
The main advantage of steel is its structural integrity, which is essential for the frames and casings of motors and generators. However, it is heavier than aluminum and can be prone to rust if not properly treated. Manufacturing complexity is moderate, as steel requires machining and finishing processes.
Impact on Application:
Steel is commonly used in the construction of the stator and rotor assemblies in both motors and generators. Its robustness makes it suitable for heavy-duty applications in industrial settings.
International Considerations:
Buyers should ensure compliance with ASTM A36 or similar standards for structural steel. In regions with high humidity, additional treatments may be necessary to prevent corrosion, impacting overall costs.
Illustrative image related to how is a motor different from a generator
4. Insulation Materials: Ensuring Safety and Performance
Key Properties:
Insulation materials, such as thermoplastics and thermosets, are crucial for preventing electrical shorts and ensuring safety. They must withstand high temperatures and provide excellent dielectric strength.
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage of modern insulation materials is their ability to maintain performance under extreme conditions. However, they can be costly, and their manufacturing processes may involve complex chemical treatments.
Impact on Application:
Insulation materials are vital in both motors and generators, ensuring safe operation and longevity. They are particularly important in applications involving variable frequency drives or high voltages.
International Considerations:
B2B buyers must consider compliance with international insulation standards, such as IEC 60085 for thermal insulation. Regional preferences for specific insulation types may also influence sourcing decisions.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for how is a motor different from a generator | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Copper | Windings in motors and generators | Excellent electrical conductivity | Higher cost compared to aluminum | High |
| Aluminum | Motor housings and generator casings | Lightweight and cost-effective | Higher resistivity | Medium |
| Steel | Stator and rotor assemblies in motors and generators | High strength and durability | Heavier and prone to corrosion | Medium |
| Insulation Materials | Electrical insulation in motors and generators | Maintains performance under stress | Can be costly and complex to manufacture | Medium |
In summary, the selection of materials for motors and generators is pivotal in determining their efficiency, durability, and overall performance. International buyers should consider local standards, material properties, and cost implications when making purchasing decisions.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for how is a motor different from a generator
What Are the Key Manufacturing Processes for Electric Motors and Generators?
Manufacturing electric motors and generators involves several critical stages, each tailored to ensure the final product meets stringent performance and quality standards. The main stages of manufacturing typically include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How is Material Prepared for Motors and Generators?
The manufacturing process begins with the selection of high-quality raw materials. For motors, materials such as copper for windings, steel for the core, and various types of plastics or composites for housing are commonly used. Generators also utilize similar materials, with an emphasis on durability and conductivity.
Material preparation involves cutting, treating, and sometimes coating these materials to enhance performance and longevity. For instance, copper wires may undergo annealing to improve ductility, while steel components may be treated to resist corrosion. This stage is crucial as the quality of materials directly affects the efficiency and lifespan of both motors and generators.
What Techniques Are Used for Forming Components?
Forming processes include various methods like stamping, winding, and machining. For electric motors, winding techniques are particularly important. The wire is wound around the stator or rotor in a specific pattern, which is essential for effective electromagnetic interaction.
In generators, the rotor and stator are formed through similar methods but may include additional steps to ensure the alignment of magnetic fields. Techniques such as precision machining and laser cutting are often employed to ensure that components fit together correctly, which is vital for performance.
What Does the Assembly Process Look Like for Motors and Generators?
The assembly of motors and generators typically follows a systematic approach, often utilizing automated assembly lines to increase efficiency. During this phase, the various components such as the rotor, stator, and housing are meticulously assembled.
For electric motors, assembly may include integrating the stator with the rotor, ensuring that they have the correct air gap for optimal magnetic interaction. In contrast, generators require precise alignment of the rotor and stator to maximize electromagnetic induction.

Illustrative image related to how is a motor different from a generator
Quality control checkpoints are critical during assembly. These may include inspections for component integrity and functional testing to ensure that the assembly meets specified performance criteria before moving to the finishing stage.
What Finishing Processes Are Essential for Quality Motors and Generators?
The finishing stage includes processes such as painting, coating, and sometimes additional testing. This stage not only enhances the aesthetic appeal of the motors and generators but also provides protective coatings that can improve durability and resist environmental factors.
For motors, this might involve applying a layer of insulation to prevent electrical short circuits. Generators may undergo additional testing to ensure that they can withstand the mechanical stresses they will encounter during operation.
How is Quality Assurance Implemented in Motor and Generator Manufacturing?
Quality assurance is integral to manufacturing processes, especially in industries where performance and reliability are non-negotiable. International standards such as ISO 9001 provide a framework for quality management systems. Manufacturers must adhere to these standards to ensure that their products meet global quality benchmarks.
What Are the Relevant International and Industry-Specific Quality Standards?
In addition to ISO 9001, industry-specific standards such as CE marking (for safety and compliance in Europe) and API (American Petroleum Institute) standards for oil and gas applications are critical. Compliance with these standards ensures that the products are safe for use and meet the necessary regulatory requirements.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints During Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) involves several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process, including:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Inspects raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specifications.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Monitors the production process to catch defects early, ensuring that assembly and forming processes are adhering to quality standards.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Conducts thorough testing of the finished product to verify that it meets all operational specifications and safety requirements.
Common testing methods include electrical testing, thermal testing, and performance benchmarking, which help identify any potential issues before the product reaches the market.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Measures?
B2B buyers must be proactive in verifying the quality control measures of their suppliers. This can include:
- Conducting Audits: Regular audits of suppliers can help ensure compliance with quality standards. Buyers should request access to audit reports and certifications.
- Requesting Quality Reports: Suppliers should be able to provide documentation detailing their QC processes, including results from IQC, IPQC, and FQC.
- Engaging Third-Party Inspectors: Utilizing third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s quality control processes and product reliability.
What Quality Control Nuances Should International Buyers Consider?
International B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, must be aware of specific nuances in quality control. Differences in regulatory compliance, cultural approaches to quality, and logistical challenges can impact the supply chain.
It is essential for buyers to establish clear communication with suppliers regarding quality expectations and standards. Additionally, understanding local regulations and compliance requirements can help mitigate risks associated with product quality and safety.
By prioritizing these aspects of manufacturing and quality assurance, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they source reliable motors and generators that meet their operational needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘how is a motor different from a generator’
The purpose of this guide is to assist B2B buyers in understanding the essential differences between motors and generators. This knowledge is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions that align with specific operational needs. By following this checklist, you can navigate the complexities of sourcing these two critical components effectively.
Step 1: Identify Your Application Needs
Understanding the specific application for which you need a motor or generator is fundamental. Consider the operational environment, load requirements, and energy efficiency goals. For instance, if you require a motor for a manufacturing process, look for specifications that can handle continuous operation under load.
Step 2: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outline the technical requirements for your motor or generator. This includes voltage, power output, size, and type (AC or DC). Having these specifications detailed will help streamline the sourcing process and ensure that suppliers can meet your requirements without ambiguity.
Step 3: Research Motor and Generator Types
Familiarize yourself with the different types of motors and generators available in the market. Motors can be categorized into various types, such as induction, synchronous, or stepper, each serving different purposes. Similarly, generators can be classified into alternators or dynamos, depending on whether you need alternating or direct current. Understanding these distinctions will guide your selection process.
Step 4: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a supplier, it’s crucial to conduct thorough evaluations. Look for suppliers with a proven track record in your industry, and request case studies or references from similar projects. Assess their product quality, delivery timelines, and customer support to ensure they align with your expectations.
Step 5: Verify Compliance with Standards
Ensure that the motors or generators comply with international standards and regulations relevant to your industry. This may include certifications like ISO, CE, or IEC. Compliance not only ensures safety and reliability but also affects the long-term performance of the equipment.
Step 6: Request Quotes and Compare Offers
Once you have shortlisted potential suppliers, request detailed quotes that outline pricing, warranties, and lead times. Comparing offers will help you identify the best value for your investment. Take note of any hidden costs, such as shipping or installation, that may impact your budget.
Step 7: Consider After-Sales Support and Maintenance
Evaluate the level of after-sales support provided by the supplier. This includes warranty terms, availability of spare parts, and maintenance services. Reliable support is vital for minimizing downtime and ensuring the longevity of your motor or generator.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing motors and generators, ensuring that they meet their operational needs while maximizing value and efficiency.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for how is a motor different from a generator Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Motors and Generators?
When analyzing the cost structure for sourcing motors and generators, several critical components come into play. Understanding these elements can help international B2B buyers make informed purchasing decisions.
-
Materials: The cost of raw materials significantly influences the overall pricing. For motors, materials like copper for windings and high-grade steel for the rotor and stator are essential. Generators may require additional components such as magnets and more robust housing materials to withstand mechanical stress. Fluctuations in material costs, influenced by global supply chains, can impact pricing dramatically.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region and complexity of the machinery. In regions like Europe and Germany, higher labor standards may lead to increased costs, while countries in Africa or South America might offer lower labor costs but may also have varying skill levels. It’s crucial to assess the labor market in the supplier’s location to understand how it affects the final price.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses all indirect costs associated with production, including utilities, rent, and administrative expenses. Efficient manufacturing processes can reduce overhead costs, making it essential for buyers to evaluate suppliers based on their operational efficiencies.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling can represent a significant upfront cost, particularly for specialized motors or generators. Buyers seeking customized solutions should consider these costs in their total budget, as they can substantially increase initial pricing.
-
Quality Control (QC): Investing in quality control measures can increase production costs but is crucial for ensuring reliability and performance. Certifications such as ISO can also add to the cost but provide assurance of quality, which is especially important in markets with stringent regulatory standards.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can vary significantly based on the destination, Incoterms, and the size of the order. For international buyers, understanding the logistics involved in transporting motors and generators is essential. Factors such as shipping routes, customs duties, and freight insurance can impact the total cost.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a profit margin to cover their costs and ensure profitability. This margin can vary based on market competition, the supplier’s reputation, and the perceived value of the product.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Motor and Generator Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of motors and generators beyond the basic cost structure:
-
Volume/MOQ: Minimum order quantities (MOQs) can affect pricing significantly. Larger orders often lead to reduced per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should negotiate MOQs that align with their needs to optimize costs.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom specifications can increase costs due to the need for specialized materials or manufacturing processes. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid unexpected price hikes.
-
Quality/Certifications: Higher quality standards and certifications can lead to increased prices but may be necessary for compliance in certain markets. Buyers must balance the need for quality with budget constraints.
-
Supplier Factors: Established suppliers with a strong reputation may charge a premium for their products. However, they often provide better support and reliability, which can justify the higher price in the long run.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is crucial for international transactions. They dictate the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs, which can significantly influence the total cost.
What Are the Best Practices for Negotiating Prices in the International B2B Market?
For international B2B buyers, effective negotiation strategies can lead to better pricing and terms:
-
Research and Compare: Conduct thorough market research to understand average prices and supplier offerings. This knowledge empowers buyers during negotiations.
-
Focus on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider not just the purchase price but also maintenance, operational costs, and potential downtime. A slightly higher upfront cost may be justified by lower long-term expenses.
-
Build Relationships: Establishing long-term relationships with suppliers can lead to better terms and pricing. Trust and reliability often lead to negotiated discounts and priority service.
-
Be Clear and Transparent: Clearly communicate your needs and constraints to suppliers. Transparency can foster collaboration and lead to better pricing solutions.
Conclusion
Understanding the cost components and pricing influencers for motors and generators is essential for international B2B buyers. By leveraging these insights and employing strategic negotiation techniques, buyers can optimize their sourcing decisions, ensuring they achieve the best value while meeting their operational requirements. It’s important to note that prices can vary significantly based on numerous factors, and buyers should seek indicative pricing tailored to their specific needs and market conditions.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing how is a motor different from a generator With Other Solutions
Introduction to Alternatives in Electrical Energy Solutions
When evaluating the distinctions between electric motors and generators, it’s important to consider alternative technologies that fulfill similar functions. These alternatives may provide different benefits in terms of performance, cost, implementation ease, and maintenance. For international B2B buyers, particularly those in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these alternatives can lead to more informed purchasing decisions.
Comparison Table of Electric Motors and Generators vs. Alternatives
| Comparison Aspect | How Is A Motor Different From A Generator | Alternative 1 Name: Solar Inverters | Alternative 2 Name: Fuel Cells |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Converts electrical energy to mechanical energy; suited for various applications | Converts solar energy to electrical energy; high efficiency in sunny regions | Converts chemical energy into electrical energy; efficient and low emissions |
| Cost | Generally lower initial investment; operational costs vary by application | High initial setup cost; long-term savings on energy bills | Moderate to high initial cost; savings on fuel and low maintenance |
| Ease of Implementation | Relatively straightforward installation; requires electrical connections | Requires solar panel installation; permits may be necessary | Requires specialized knowledge for installation; fuel infrastructure needed |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance needed; potential wear and tear | Low maintenance after installation; occasional cleaning required | Low maintenance; periodic checks on fuel supply |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for machinery, HVAC systems, and consumer electronics | Best for renewable energy systems and off-grid applications | Suited for backup power systems and transport applications |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Solar Inverters
Solar inverters play a critical role in converting the direct current (DC) generated by solar panels into alternating current (AC), which can be used in homes and businesses. Their efficiency can be particularly high in sunny regions, making them a viable alternative for energy generation. However, the initial setup costs can be significant, and installation may require permits and specialized knowledge. Long-term savings on energy bills can offset these costs, making solar inverters an attractive option for sustainable energy needs.
Fuel Cells
Fuel cells represent an innovative technology that converts chemical energy directly into electrical energy through electrochemical reactions, typically using hydrogen and oxygen. They are known for their efficiency and low emissions, making them a cleaner alternative to traditional fossil fuel systems. While fuel cells can offer substantial benefits, the initial investment and the need for a reliable fuel supply can be barriers to widespread adoption. Additionally, specialized knowledge is often required for installation, which may complicate the implementation process.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
In selecting the right energy solution, B2B buyers should assess the specific requirements of their operations, including performance needs, budget constraints, and maintenance capabilities. Electric motors and generators serve distinct functions and are optimized for different applications, while alternatives like solar inverters and fuel cells can offer unique advantages in energy efficiency and sustainability. By carefully evaluating these options, businesses can align their energy strategies with their operational goals, ensuring optimal performance and cost-effectiveness.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for how is a motor different from a generator
What Are the Key Technical Properties that Differentiate Motors from Generators?
When comparing electric motors and generators, understanding their essential technical properties is crucial for B2B decision-makers. Here are some critical specifications that highlight their differences:
-
Energy Conversion Efficiency
– Definition: This refers to the ratio of useful mechanical or electrical energy output to the input energy.
– Importance: For buyers, selecting equipment with high energy conversion efficiency can lead to reduced operational costs and improved performance. Motors typically aim for high efficiency in converting electrical energy to mechanical energy, while generators focus on maximizing the conversion of mechanical energy into electrical energy. -
Torque Rating
– Definition: Torque is a measure of the rotational force produced by a motor or generator.
– Importance: Understanding torque ratings is essential for selecting the right equipment for specific applications. High torque ratings in motors are vital for applications requiring significant mechanical force, while generators must produce sufficient torque to generate the required electrical output. -
Voltage and Current Ratings
– Definition: These ratings define the electrical output (for generators) and input (for motors) in volts and amperes.
– Importance: Accurate voltage and current ratings ensure compatibility with existing electrical systems. For B2B buyers, mismatched ratings can lead to equipment failure or inefficiencies, emphasizing the need for careful selection based on application requirements. -
Operating Speed
– Definition: This refers to the speed at which the rotor spins, typically measured in revolutions per minute (RPM).
– Importance: Different applications require specific operating speeds. Motors are often selected based on their ability to maintain performance at varying speeds, while generators must operate within specific RPM ranges to ensure stable electricity generation. -
Insulation Class
– Definition: This classifies the thermal limits of the motor or generator’s insulation materials, indicating how well they can withstand heat.
– Importance: For international B2B buyers, understanding insulation classes is crucial for ensuring longevity and reliability in various operating environments. Equipment operating in high-temperature conditions may require higher insulation classes to prevent failure.
What Are Some Common Trade Terms Related to Motors and Generators?
Familiarity with industry terminology is vital for effective communication and negotiation in the B2B landscape. Here are some key terms relevant to motors and generators:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Definition: A company that produces parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer.
– Importance: Buyers often engage with OEMs for specific components or entire systems, ensuring compatibility and reliability in their operations. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– Definition: The smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell.
– Importance: Understanding MOQ is essential for buyers to manage inventory and cost effectively. This term impacts pricing and supply chain logistics, especially for international purchases. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– Definition: A document issued by a buyer to solicit price quotes from suppliers for specific products or services.
– Importance: An RFQ is a critical step in the procurement process, allowing buyers to compare prices, terms, and conditions from different suppliers, thus ensuring they make informed purchasing decisions. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Definition: A set of rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions.
– Importance: Knowledge of Incoterms helps B2B buyers understand shipping responsibilities, costs, and risks, facilitating smoother international transactions and reducing the potential for disputes. -
Lead Time
– Definition: The time between the initiation of an order and its completion.
– Importance: Understanding lead times is vital for planning and managing production schedules. For businesses relying on motors and generators, longer lead times can impact project timelines and operational efficiency.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions when navigating the complexities of selecting motors and generators for their specific applications.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the how is a motor different from a generator Sector
What Are the Key Market Drivers Influencing the Motor and Generator Sector?
The global market for electric motors and generators is experiencing significant growth, driven by several factors. The increasing demand for energy-efficient solutions across various sectors, including manufacturing, automotive, and renewable energy, has heightened the need for advanced electric motors and generators. In regions such as Africa and South America, the push for industrialization and infrastructure development is further driving this demand. Emerging economies are particularly focused on adopting technologies that reduce energy consumption and enhance productivity.
In the Middle East, investments in renewable energy projects are accelerating the need for efficient electric generators, particularly in solar and wind power generation. Meanwhile, Europe, particularly Germany, is at the forefront of innovation in electric motor technology, focusing on automation and smart manufacturing. The trend toward Industry 4.0 is also reshaping sourcing strategies, with companies increasingly looking for suppliers that offer integrated solutions combining motors and generators with IoT capabilities.
Furthermore, the rise of electric vehicles (EVs) is significantly impacting motor demand, leading to advancements in both design and manufacturing processes. As B2B buyers navigate these dynamics, they should focus on suppliers that can provide flexible, scalable solutions that meet the evolving needs of their industries.
How Do Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact the Motor and Generator Market?
Sustainability is becoming a critical consideration for B2B buyers in the motor and generator sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes, including energy consumption and waste generation, is prompting companies to seek out suppliers who prioritize eco-friendly practices. This includes the use of sustainable materials and adherence to environmental regulations.
Ethical sourcing is equally important, as companies are increasingly held accountable for their supply chains. Buyers should look for manufacturers that can demonstrate compliance with international labor standards and fair trade practices. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and ISO 45001 (Occupational Health and Safety) are becoming essential for suppliers aiming to showcase their commitment to sustainability.
Illustrative image related to how is a motor different from a generator
Additionally, as the market shifts toward greener technologies, the demand for electric motors and generators that utilize eco-friendly components is rising. This trend is particularly relevant for industries focused on reducing their carbon footprints. B2B buyers should prioritize partnerships with suppliers that offer ‘green’ certifications and materials, ensuring that their sourcing strategies align with their sustainability goals.
What Is the Historical Context of Motors and Generators in B2B?
The evolution of electric motors and generators can be traced back to the early 19th century, with pivotal developments in electromagnetic theory. The work of pioneers like Michael Faraday laid the foundation for both technologies. Faraday’s Law of Electromagnetic Induction, discovered in 1831, is central to the functioning of both motors and generators, enabling the conversion of energy from one form to another.
Initially, electric motors were primarily used in industrial applications, while generators were essential for power generation in burgeoning urban areas. Over the decades, advancements in materials, design, and manufacturing processes have led to the widespread use of electric motors and generators in various sectors, from household appliances to large-scale industrial machinery.
In recent years, the integration of digital technologies has transformed the landscape, enabling smarter and more efficient systems. As B2B buyers consider sourcing options, understanding the historical context can provide valuable insights into the technological advancements that have shaped the current market dynamics. This knowledge can aid in making informed decisions about investments in motors and generators that meet today’s demands while anticipating future trends.

Illustrative image related to how is a motor different from a generator
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of how is a motor different from a generator
-
How do motors and generators differ in terms of energy conversion?
Electric motors convert electrical energy into mechanical energy, allowing machinery to perform work. In contrast, electric generators convert mechanical energy into electrical energy, typically harnessed from sources like wind, water, or fossil fuels. Understanding this fundamental difference is crucial when sourcing equipment for industrial applications, as it directly impacts the choice of machinery based on the intended function. -
What applications are best suited for motors versus generators?
Electric motors are commonly used in applications requiring mechanical movement, such as conveyor systems, fans, and pumps. On the other hand, generators are essential for producing electricity in power plants, backup power systems, and renewable energy setups like wind or hydroelectric plants. When sourcing equipment, consider the specific application to ensure optimal performance and efficiency. -
What factors should I consider when sourcing motors and generators for my business?
When sourcing these devices, evaluate your specific energy needs, the type of energy available (AC or DC), efficiency ratings, and the operational environment (temperature, humidity). Additionally, assess the manufacturer’s reputation, warranty offerings, and after-sales support. Customization options may also be relevant, especially for unique industrial applications. -
How can I vet suppliers of motors and generators in international markets?
To effectively vet suppliers, research their industry experience, customer reviews, and certifications. Request references from previous clients, and consider visiting their production facilities if possible. Ensure they comply with international standards and regulations relevant to your region. Engaging in direct communication can also help gauge their responsiveness and reliability. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for motors and generators?
MOQs can vary significantly based on the supplier, product type, and customization requirements. For standard models, MOQs may range from a few units to several hundred. However, for specialized or custom-built motors and generators, suppliers might require larger orders. Always discuss MOQs during negotiations to align with your business needs and budget constraints. -
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing motors and generators internationally?
Payment terms can vary by supplier and region but typically include options like upfront payment, partial payment upon order confirmation, and balance upon delivery. It’s common to negotiate terms such as letters of credit or escrow services for larger transactions. Be sure to clarify payment methods accepted, as this can impact the overall cost and transaction security. -
How important is quality assurance (QA) in sourcing motors and generators?
Quality assurance is critical in ensuring the reliability and longevity of motors and generators. Look for suppliers that implement rigorous QA processes, including testing and certification of their products. Inquire about their compliance with international quality standards, as this can significantly affect the operational efficiency and safety of the equipment in your applications. -
What logistical considerations should I keep in mind when importing motors and generators?
Logistical considerations include shipping methods, lead times, and customs regulations in your destination country. Assess the supplier’s ability to manage logistics effectively, including packaging to prevent damage during transit. Additionally, consider potential duties and tariffs that may apply to your imports, as these can impact the overall cost and timeline of your procurement process.
Top 2 How Is A Motor Different From A Generator Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Byju’s – Motor vs Generator Explained
Domain: byjus.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: Difference between Motor and Generator: 1. Definition: Motor converts electrical energy to mechanical energy; Generator converts mechanical energy to electrical energy. 2. Rule: Motor follows Fleming’s left-hand rule; Generator follows Fleming’s right-hand rule. 3. Principle: Motor works on the principle of a current-carrying conductor in a magnetic field; Generator works on electromagnetic induct…
2. Study.com – Motors and Generators
Domain: study.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Motors transform electrical energy into mechanical energy, used in applications like electric fans, blenders, washing machines, and industrial machinery. Generators convert mechanical energy into electrical energy, functioning as backup power supplies during outages in residential and commercial buildings. Motors produce torque from a current-carrying loop in a magnetic field, while generators use…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for how is a motor different from a generator
In summary, understanding the distinctions between electric motors and generators is crucial for international B2B buyers, particularly those operating in diverse markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Electric motors convert electrical energy into mechanical energy, powering various applications from industrial machinery to household appliances. Conversely, generators transform mechanical energy into electrical energy, serving as vital components in power generation systems.
Strategic sourcing plays a pivotal role in optimizing the procurement of these essential technologies. By aligning purchasing decisions with reliable suppliers and advanced technologies, businesses can enhance operational efficiency and reduce costs.
As you consider your sourcing strategies, focus on evaluating both motors and generators based on performance, energy efficiency, and long-term reliability. The future of energy solutions lies in adopting innovative technologies that not only meet current demands but also anticipate future needs. Embrace the opportunity to leverage these insights to drive growth and sustainability in your operations. Partner with trusted suppliers to secure the best products that will empower your business in an ever-evolving marketplace.

Illustrative image related to how is a motor different from a generator
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.