Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for how can you tell if its the battery or alternator
In the dynamic world of automotive maintenance, one of the key challenges B2B buyers face is accurately diagnosing vehicle issues, particularly when determining whether the problem lies with the battery or the alternator. This guide, “How Can You Tell If It’s the Battery or Alternator,” offers a comprehensive overview tailored for international buyers, especially those operating in diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including countries like Brazil and Germany.
Understanding the distinctions between battery and alternator failures is crucial for effective procurement and service delivery. This guide delves into the signs and symptoms of both components, providing actionable insights on troubleshooting methods, maintenance tips, and the implications of each issue on vehicle performance. Additionally, it explores various types of batteries and alternators available in the market, their applications in different vehicle models, and best practices for supplier vetting.
By equipping B2B buyers with in-depth knowledge and practical strategies, this guide empowers them to make informed purchasing decisions that enhance operational efficiency and reduce downtime. Whether sourcing replacement parts or negotiating with suppliers, having a clear understanding of these critical components will enable businesses to optimize their automotive services and improve customer satisfaction.
Table Of Contents
- Top 2 How Can You Tell If Its The Battery Or Alternator Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for how can you tell if its the battery or alternator
- Understanding how can you tell if its the battery or alternator Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of how can you tell if its the battery or alternator
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘how can you tell if its the battery or alternator’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for how can you tell if its the battery or alternator
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for how can you tell if its the battery or alternator
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘how can you tell if its the battery or alternator’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for how can you tell if its the battery or alternator Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing how can you tell if its the battery or alternator With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for how can you tell if its the battery or alternator
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the how can you tell if its the battery or alternator Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of how can you tell if its the battery or alternator
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for how can you tell if its the battery or alternator
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Understanding how can you tell if its the battery or alternator Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Battery Failure Diagnosis | Slow engine start, dim lights, odd smells | Automotive repair shops, fleet management | Pros: Quick identification; Cons: May require battery replacement. |
| Alternator Performance Check | Flickering lights, frequent stalls, unusual noises | Automotive diagnostics, fleet maintenance | Pros: Helps prevent breakdowns; Cons: Complexity in diagnosing without tools. |
| Combined Systems Analysis | Evaluates battery, alternator, and starter simultaneously | Full-service garages, automotive training | Pros: Comprehensive overview; Cons: Time-consuming if issues are interlinked. |
| Environmental Impact Assessment | Evaluates effects of temperature and moisture on components | Automotive manufacturing, parts suppliers | Pros: Informs product durability; Cons: Requires specialized knowledge. |
| Corrosion and Electrical Integrity Check | Inspects terminals and wiring for corrosion and damage | Automotive repair, fleet management | Pros: Prevents future failures; Cons: Often overlooked until problems arise. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Battery Failure Diagnosis?
Battery failure diagnosis primarily revolves around symptoms such as slow engine starts, dim dashboard lights, and unusual odors like a rotten egg smell. This type of diagnosis is crucial for automotive repair shops and fleet management services, where quick identification of battery issues can minimize downtime. Buyers should consider the average lifespan of batteries, common causes of failure, and the importance of regular maintenance checks to ensure reliability.
How Can You Identify Alternator Performance Issues?
Identifying alternator performance issues involves observing signs such as flickering lights, frequent engine stalls, and unusual noises. This type of analysis is particularly relevant for automotive diagnostics and fleet maintenance, as a failing alternator can lead to significant operational disruptions. Buyers should prioritize tools that facilitate accurate diagnostics, as well as training for staff to recognize these symptoms early on.
Why Consider a Combined Systems Analysis?
A combined systems analysis evaluates the battery, alternator, and starter collectively, providing a comprehensive overview of the vehicle’s electrical system. This approach is beneficial for full-service garages and automotive training programs, as it allows for more efficient troubleshooting. Buyers should weigh the time investment required for this analysis against the potential for identifying multiple issues simultaneously, thus reducing repair times and costs.
What Is the Importance of Environmental Impact Assessment?
Environmental impact assessments focus on how external factors like temperature and moisture affect battery and alternator performance. This analysis is essential for automotive manufacturing and parts suppliers, as it informs product durability and reliability in varying climates. Buyers should consider the geographical conditions of their target markets and how these factors might influence the lifespan and performance of their products.
How Does Corrosion and Electrical Integrity Check Benefit Buyers?
Corrosion and electrical integrity checks inspect terminals and wiring for damage that could lead to failures. This type of check is vital for automotive repair and fleet management, as it helps prevent future breakdowns. Buyers should recognize the importance of these checks in their maintenance schedules, as addressing corrosion early can save significant costs and enhance vehicle reliability.
Key Industrial Applications of how can you tell if its the battery or alternator
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of how can you tell if its the battery or alternator | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive Repair | Diagnostics for vehicle electrical issues | Reduces downtime by quickly identifying the issue | Access to reliable diagnostic tools and training for technicians |
| Fleet Management | Regular maintenance checks on vehicles | Ensures operational efficiency and minimizes breakdowns | Bulk purchasing agreements for batteries and alternators |
| Agriculture Equipment | Troubleshooting power issues in farm machinery | Increases productivity by minimizing equipment failure | Availability of durable batteries suited for harsh environments |
| Construction Vehicles | Assessing power systems in heavy machinery | Enhances safety and reliability on job sites | Sourcing robust alternators and batteries that withstand heavy use |
| Transportation & Logistics | Evaluating fleet vehicle performance | Improves logistics efficiency and reduces operational costs | Long-term supplier relationships for consistent parts availability |
How is ‘how can you tell if its the battery or alternator’ applied in Automotive Repair?
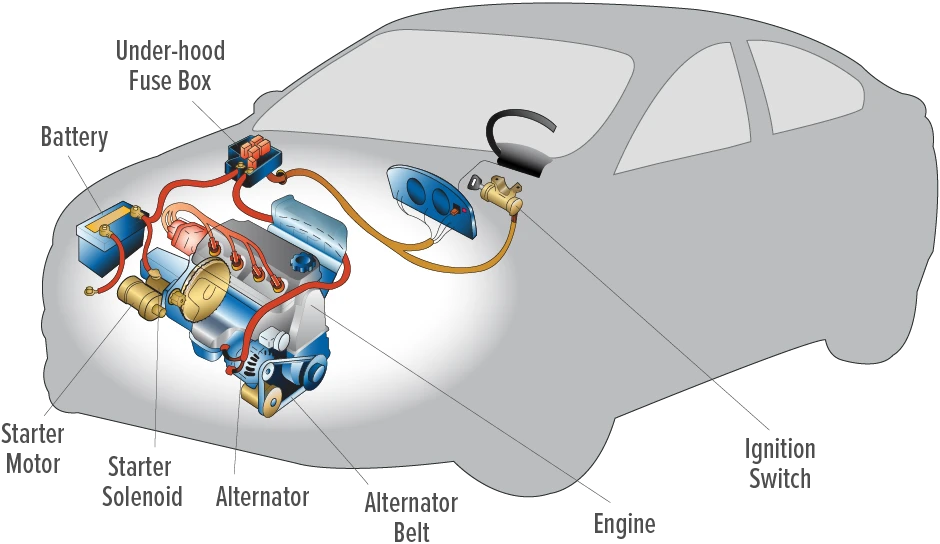
In the automotive repair sector, accurately diagnosing whether a vehicle’s starting issues stem from the battery or alternator is crucial. Repair shops utilize diagnostic tools and techniques to troubleshoot electrical problems, allowing for efficient repairs. This not only minimizes customer downtime but also enhances the shop’s reputation for reliability. B2B buyers in this sector should prioritize sourcing high-quality diagnostic equipment and training for technicians to ensure effective troubleshooting.
What role does ‘how can you tell if its the battery or alternator’ play in Fleet Management?
For fleet management, understanding the nuances of battery and alternator issues is vital for maintaining vehicle uptime. Fleet operators conduct routine inspections to identify electrical problems before they lead to significant breakdowns. This proactive approach enhances operational efficiency and reduces maintenance costs. International buyers should consider bulk purchasing agreements for batteries and alternators, ensuring they have a steady supply of reliable components to keep their fleet running smoothly.
Illustrative image related to how can you tell if its the battery or alternator
How does ‘how can you tell if its the battery or alternator’ benefit Agriculture Equipment?
In agriculture, machinery is often subjected to harsh conditions, making reliable power systems essential. Farmers and agricultural equipment dealers use diagnostic techniques to troubleshoot power issues in tractors and harvesters, ensuring that operations run without interruption. This focus on maintaining equipment reliability directly translates to increased productivity. B2B buyers should seek durable batteries designed for agricultural use, which can withstand extreme temperatures and vibrations.
Why is ‘how can you tell if its the battery or alternator’ critical for Construction Vehicles?
Construction vehicles must operate reliably in demanding environments. Assessing the power systems of heavy machinery helps prevent failures that could lead to costly delays. Construction managers utilize diagnostic methods to determine whether issues are battery-related or stem from the alternator, enhancing safety and reliability on job sites. Buyers in this industry should prioritize sourcing robust alternators and batteries that can endure rigorous use and adverse conditions.
How does ‘how can you tell if its the battery or alternator’ enhance Transportation & Logistics operations?
In the transportation and logistics sector, evaluating fleet vehicle performance is crucial for maintaining efficiency. Regular checks on battery and alternator functionality help prevent unexpected breakdowns, leading to improved logistics and reduced operational costs. B2B buyers should establish long-term relationships with suppliers to ensure consistent availability of high-quality parts, which is essential for maintaining a reliable fleet.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘how can you tell if its the battery or alternator’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Diagnosing Electrical Issues
The Problem: B2B buyers, particularly fleet managers and automotive service providers, often encounter vehicles that exhibit intermittent starting issues. They may experience prolonged cranking times or complete failure to start, leading to operational delays. This uncertainty can be frustrating, as it can stem from either a dead battery or a malfunctioning alternator. The inability to quickly and accurately diagnose the issue not only affects productivity but can also lead to unnecessary replacement costs if components are misidentified.
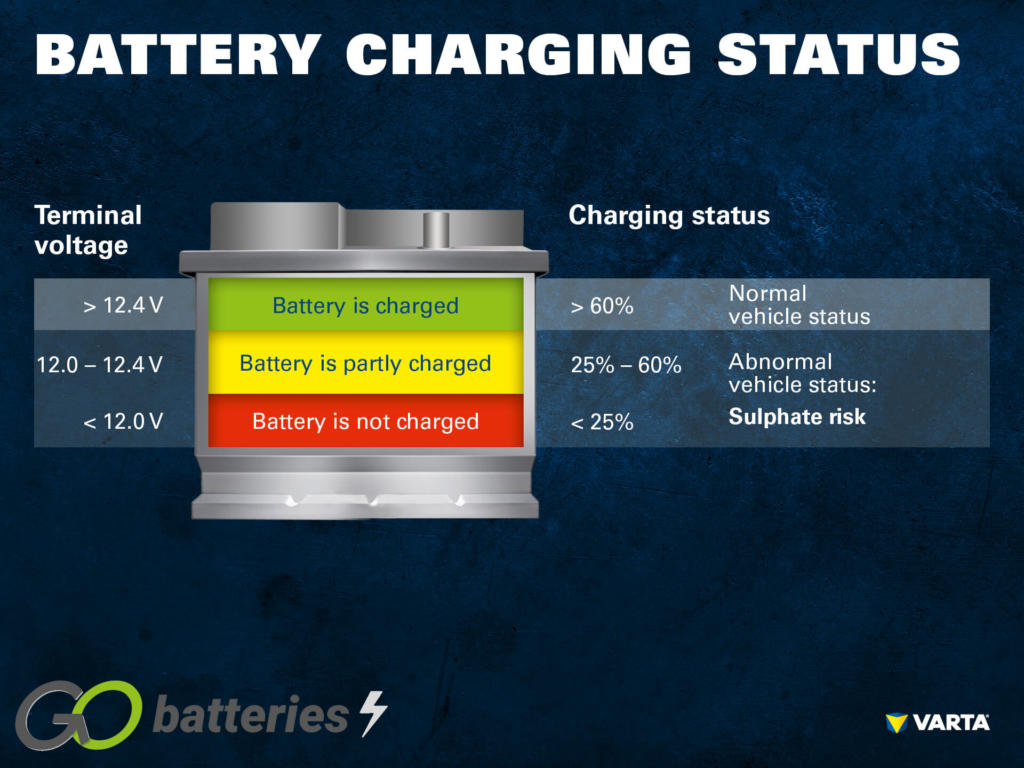
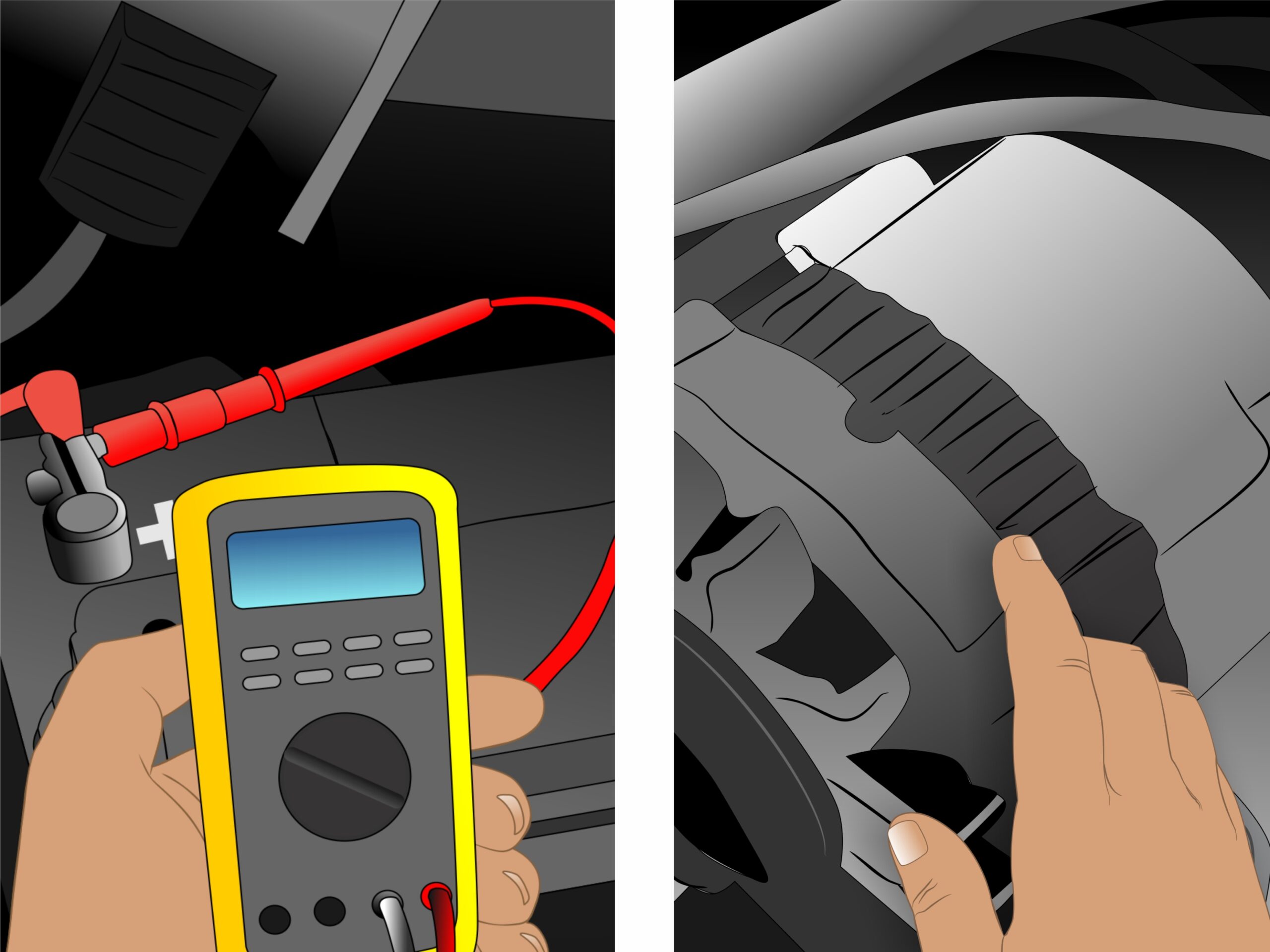
The Solution: Implement a systematic troubleshooting approach to isolate whether the problem lies with the battery or the alternator. Start by checking the battery’s health; this can be done using a multimeter to measure voltage. A healthy battery should read around 12.6 volts when fully charged. If the voltage is significantly lower, the battery may be the culprit. Next, perform a jump-start. If the vehicle runs but then stalls shortly after, the alternator is likely failing to charge the battery. Additionally, checking for dimming lights during engine revs can indicate alternator issues. By training your staff on these diagnostic procedures, you can reduce downtime and make more informed decisions on repairs, ensuring that resources are allocated efficiently.

Illustrative image related to how can you tell if its the battery or alternator
Scenario 2: Frequent Vehicle Downtime Due to Misdiagnosis
The Problem: Companies operating in sectors reliant on transportation, such as logistics and delivery services, face significant challenges when vehicles frequently break down. A common scenario involves technicians misdiagnosing a battery issue as an alternator problem, leading to unnecessary replacements and extended vehicle downtime. This misjudgment not only affects service delivery but can also inflate maintenance budgets and disrupt supply chains.
The Solution: To mitigate misdiagnosis, establish a standardized diagnostic protocol that all technicians must follow. This protocol should include a checklist of symptoms and tests. For example, if a vehicle experiences frequent stalls, check the battery connections and inspect for corrosion before concluding that the alternator is at fault. Additionally, investing in diagnostic tools, such as battery testers and alternator testers, can provide precise readings that guide decision-making. Providing ongoing training for technicians on the signs and symptoms of battery and alternator issues will enhance their diagnostic skills, reducing misdiagnosis rates and ultimately lowering maintenance costs.
Scenario 3: Inconsistent Electrical Performance Across Fleet Vehicles
The Problem: For businesses managing a fleet, inconsistent electrical performance across vehicles can lead to operational inefficiencies. Symptoms such as flickering headlights, dashboard lights dimming, or strange electrical behavior can indicate problems with either the battery or the alternator. Fleet managers often find themselves uncertain about whether to replace batteries, alternators, or both, leading to inconsistent repairs and potential waste of resources.
The Solution: Implement a robust fleet maintenance management system that includes regular electrical system checks. Schedule routine inspections that focus specifically on battery and alternator performance. During these inspections, assess battery voltage, examine terminal connections for corrosion, and check the alternator’s output while the engine runs. Documenting these checks allows fleet managers to track performance trends over time and make informed decisions about replacements. Additionally, consider leveraging predictive maintenance technologies that analyze vehicle performance data to forecast potential failures before they occur. This proactive approach can significantly enhance operational efficiency and reduce the likelihood of unexpected downtime.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for how can you tell if its the battery or alternator
When determining whether a vehicle’s starting issues stem from a battery or an alternator, the materials used in the components can significantly influence performance, durability, and overall functionality. This analysis will explore several key materials commonly used in batteries and alternators, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for international B2B buyers.
What Materials Are Commonly Used in Batteries and Alternators?
Lead-Acid
Key Properties: Lead-acid batteries are composed of lead dioxide (PbO2) and sponge lead (Pb) submerged in sulfuric acid (H2SO4). They operate effectively in a wide temperature range, typically from -20°C to 50°C.
Pros & Cons: Lead-acid batteries are cost-effective and have a high discharge current capability, making them suitable for starting applications. However, they are heavy, have a limited lifespan (usually 3-5 years), and can be sensitive to extreme temperatures. Additionally, they require maintenance to prevent sulfation.
Impact on Application: Lead-acid batteries are compatible with various vehicles, but their performance can degrade in high temperatures, which is a consideration for buyers in hot climates like parts of Africa and South America.
Illustrative image related to how can you tell if its the battery or alternator
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards such as IEC and ASTM is crucial. Buyers should also be aware of the environmental regulations regarding lead disposal, which may vary by region.
Lithium-Ion
Key Properties: Lithium-ion batteries are lightweight and have a high energy density, typically operating efficiently between -20°C and 60°C. They also exhibit low self-discharge rates.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of lithium-ion batteries is their longevity and efficiency, often lasting 8-10 years. However, they are more expensive to manufacture and can be sensitive to overcharging, which may lead to safety concerns.
Impact on Application: Their high energy density makes them suitable for electric vehicles and hybrid systems. However, their performance can be affected by extreme temperatures, particularly in regions with high heat.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers must consider compliance with safety standards such as UN 38.3 for transportation and ISO standards for quality assurance. The higher upfront cost may be a barrier for some markets.

Illustrative image related to how can you tell if its the battery or alternator
Copper
Key Properties: Copper is known for its excellent electrical conductivity and resistance to corrosion. It typically operates effectively in various environmental conditions, with a melting point of 1,984°F (1,085°C).
Pros & Cons: Copper wiring is durable and provides efficient power transfer, which is critical for alternators. However, it is relatively expensive compared to aluminum, and its weight can be a disadvantage in lightweight applications.
Impact on Application: In alternators, copper is used for windings and connections, ensuring optimal performance. Corrosion resistance is crucial in humid or coastal environments, which can affect longevity.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that copper components meet international standards like ASTM B170 for copper wire. The cost may be a consideration for budget-sensitive markets.
Aluminum
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight, has good electrical conductivity, and offers resistance to corrosion. It typically operates well in temperatures up to 1,221°F (660°C).

Illustrative image related to how can you tell if its the battery or alternator
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of aluminum is its lightweight nature, which can improve fuel efficiency in vehicles. However, it has lower conductivity than copper, which may necessitate larger wire sizes, potentially increasing manufacturing complexity.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is often used in alternator housings and some wiring applications. Its lightweight properties can be beneficial in reducing overall vehicle weight.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ISO 9001 for quality management is essential. The cost-effectiveness of aluminum makes it attractive for many markets, but buyers should consider its conductivity limitations.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for how can you tell if its the battery or alternator | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lead-Acid | Commonly used in traditional vehicle batteries | Cost-effective and high discharge | Limited lifespan and heavy | Low |
| Lithium-Ion | Increasingly used in modern electric and hybrid vehicles | Long lifespan and high energy density | Higher manufacturing cost and safety concerns | High |
| Copper | Essential for wiring and connections in alternators | Excellent conductivity | Relatively expensive and heavy | Med |
| Aluminum | Used in alternator housings and lightweight applications | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Lower conductivity than copper | Med |
This analysis provides a comprehensive overview of the materials involved in battery and alternator applications, offering valuable insights for international B2B buyers navigating the complexities of material selection and compliance in diverse markets.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for how can you tell if its the battery or alternator
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Processes for Batteries and Alternators?
Understanding the manufacturing processes behind batteries and alternators is crucial for B2B buyers looking to ensure quality and reliability in their supply chains. The production of these components typically involves several key stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How Is Material Prepared for Battery and Alternator Manufacturing?
The manufacturing process begins with material preparation, which includes the selection and treatment of raw materials. For batteries, this often involves lead, sulfuric acid, and plastic components, while alternators require copper windings, steel casings, and various electrical components.
The quality of raw materials is critical; for example, lead must be sourced from reputable suppliers to avoid contamination and ensure longevity. Materials undergo rigorous testing to check for impurities and compliance with international standards, such as ISO 9001, which guarantees consistent quality management systems.
What Techniques Are Used in the Forming Stage of Battery and Alternator Production?
The forming stage involves shaping the prepared materials into usable components. In battery manufacturing, this typically includes processes such as grid casting and paste application, where the lead is molded into grids that will hold the active material. For alternators, forming involves stamping and machining the steel casing and rotor.
Advanced techniques, such as automated stamping and CNC machining, are often employed to ensure precision. These methods help maintain tight tolerances and improve the overall quality of the finished products.
How Are Batteries and Alternators Assembled?
Assembly is a critical phase where various components are brought together to create the final product. In battery assembly, grids are filled with the active material and then sealed within the casing, ensuring that all connections are secure to prevent leaks. For alternators, the rotor is fitted into the stator, and electrical connections are made to ensure efficient power generation.
Quality control checkpoints during assembly are vital. B2B buyers should inquire about the specific assembly procedures used by suppliers, as this can significantly affect the reliability and longevity of the products.
What Finishing Processes Are Involved in Battery and Alternator Manufacturing?
Finishing processes enhance the durability and aesthetics of the products. For batteries, this may include additional coatings to prevent corrosion, while alternators might undergo surface treatments to improve their resistance to wear and environmental factors.
Post-finishing inspections ensure that each product meets the required specifications. This stage is crucial for B2B buyers who must ensure that products can withstand the rigors of their intended applications, especially in challenging environments found in regions like Africa and South America.
What Are the Key Quality Assurance Standards for Battery and Alternator Manufacturing?
Quality assurance is a cornerstone of reliable manufacturing processes, particularly for critical components like batteries and alternators. International and industry-specific standards play a significant role in ensuring product quality.
Which International Standards Should B2B Buyers Look For?
ISO 9001 is a universally recognized standard that outlines the requirements for a quality management system. Compliance with this standard indicates that a manufacturer has established processes for consistent quality and customer satisfaction. Additionally, certifications like CE (Conformité Européenne) for European markets and API (American Petroleum Institute) for specific automotive applications can also signify adherence to quality and safety standards.
What Are Common Quality Control Checkpoints During Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are integral to maintaining high standards throughout the manufacturing process. These checkpoints typically include:
Illustrative image related to how can you tell if its the battery or alternator
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Checks raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Monitors the manufacturing process at various stages to detect defects early.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Inspects finished products before they are shipped to customers.
Each checkpoint serves to minimize defects and ensure that only high-quality products reach the market.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Measures?
For B2B buyers, verifying the quality control measures of potential suppliers is essential for making informed purchasing decisions.
What Methods Can Buyers Use to Assess Supplier Quality?
-
Audits: Conducting regular audits of suppliers can provide insights into their manufacturing processes and adherence to quality standards. These audits can be scheduled or unannounced and should focus on both the manufacturing environment and specific processes.
-
Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports from suppliers can help buyers understand their QC processes. These reports should outline testing results, defect rates, and corrective actions taken.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s manufacturing processes. These services often include detailed inspections of raw materials, production processes, and finished products.
What QC and Certification Nuances Should International Buyers Consider?
International B2B buyers, especially from diverse regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, must be aware of specific certification nuances. Different markets may have varying requirements for compliance and quality assurance. For instance, European buyers might prioritize CE certification, while buyers in other regions may focus on different standards.
Illustrative image related to how can you tell if its the battery or alternator
Understanding these nuances is critical for ensuring that products not only meet local regulations but also align with the buyers’ quality expectations. Building relationships with suppliers who are knowledgeable about these requirements can facilitate smoother transactions and enhance product reliability.
Conclusion
In summary, the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for batteries and alternators are complex yet essential for ensuring product reliability. B2B buyers must pay close attention to each stage of production, from material preparation to finishing, and ensure that suppliers adhere to relevant international standards. By implementing thorough verification processes, buyers can mitigate risks and secure high-quality components for their operations. This diligence not only enhances operational efficiency but also builds trust in the supply chain across international markets.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘how can you tell if its the battery or alternator’
Introduction
Understanding whether your vehicle’s issues stem from the battery or alternator is essential for effective troubleshooting and maintenance. This guide provides a practical checklist for B2B buyers, helping you navigate the procurement process for automotive electrical components. By following these steps, you can ensure that you make informed purchasing decisions that align with your operational needs and regional standards.
Step 1: Identify Common Symptoms of Failure
Before sourcing components, familiarize yourself with the typical signs of battery and alternator problems. For instance, a slow-starting engine or dim lights often indicates a battery issue, while flickering headlights or frequent stalling may suggest alternator failure. Recognizing these symptoms allows you to specify your requirements more accurately when consulting suppliers.
Step 2: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outline the technical requirements for the batteries and alternators you intend to procure. Consider factors such as voltage, capacity, and compatibility with various vehicle models. This step is crucial for ensuring that the components you source will meet your operational needs and adhere to local regulations.

Illustrative image related to how can you tell if its the battery or alternator
- Voltage and Capacity: Ensure the specifications match the vehicle requirements.
- Type of Battery: Decide between lead-acid, lithium-ion, or other types based on performance and lifespan.
Step 3: Research Potential Suppliers
Thoroughly research potential suppliers to assess their reliability and product quality. Look for companies with a strong reputation in the automotive sector, particularly those specializing in electrical components. This can include checking online reviews, industry certifications, and business longevity.
- Industry Certifications: Verify if suppliers have relevant certifications such as ISO or SAE.
- Customer Testimonials: Seek feedback from other businesses that have purchased similar products.
Step 4: Request Product Samples
Before making large orders, request samples of the batteries and alternators. Testing these samples will allow you to evaluate their performance under real-world conditions and ensure they meet your quality standards. This step can prevent costly returns and dissatisfaction later on.
Step 5: Evaluate Warranty and Support Options
Assess the warranty and support options provided by suppliers. A robust warranty can safeguard your investment against premature failures, while reliable customer support is vital for addressing any issues that may arise post-purchase. Understanding these aspects can significantly impact your long-term satisfaction with the product.
- Warranty Duration: Look for warranties that cover a significant period, indicating supplier confidence in their product.
- After-Sales Support: Ensure the supplier offers technical support for installation and troubleshooting.
Step 6: Compare Pricing and Payment Terms
Gather quotes from multiple suppliers to compare pricing and payment terms. While the lowest price may be tempting, consider the overall value, including quality, warranty, and support. Establish clear payment terms that align with your cash flow management practices to avoid any financial strain.
Step 7: Finalize the Purchase and Logistics
Once you have selected a supplier, finalize your order and logistics arrangements. Ensure that shipping and handling methods are efficient and that delivery timelines meet your operational needs. Confirm all details in writing to mitigate any misunderstandings.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can effectively navigate the complexities of sourcing batteries and alternators, ensuring they make informed, strategic decisions that support their business operations.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for how can you tell if its the battery or alternator Sourcing
When navigating the complexities of sourcing components like batteries and alternators, understanding the cost structure and pricing dynamics is critical for B2B buyers. This section delves into the essential components influencing costs, the factors that determine pricing, and valuable insights for buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
What Are the Key Cost Components in Battery and Alternator Sourcing?
-
Materials: The primary cost drivers include the raw materials used in batteries (lead, sulfuric acid, plastic) and alternators (copper, aluminum, magnets). Fluctuations in the prices of these materials can significantly affect overall costs.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary based on the region of production. For example, manufacturers in Europe may have higher labor costs compared to those in Africa or South America due to different wage standards and labor regulations. The complexity of the assembly process for each component also plays a role in determining labor expenses.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with factory operations, utilities, and maintenance of equipment. Efficient production processes can help mitigate these costs, but inefficiencies or outdated equipment can lead to higher overhead.
-
Tooling: Initial tooling costs can be substantial, especially for custom designs or specialized components. Buyers should consider the amortization of these costs over the expected production volume to determine their impact on unit pricing.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring high-quality standards is essential, especially in automotive components. QC costs can vary depending on the certifications required (like ISO standards) and the testing processes implemented.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs can vary widely based on the distance from manufacturing sites to the buyer’s location, the mode of transport, and the chosen Incoterms. For international buyers, understanding the full scope of logistics costs is vital.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically apply a margin that reflects their operational risks and market conditions. This margin can differ based on the supplier’s reputation, reliability, and market position.
Which Price Influencers Should Buyers Consider?
-
Volume/MOQ: Minimum order quantities (MOQs) can significantly impact pricing. Higher volumes often lead to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should assess their needs carefully to optimize order sizes.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom specifications can increase costs due to the need for specialized materials or production processes. Clear communication of requirements can help manage expectations and costs.
-
Quality and Certifications: Higher quality standards and certifications can increase initial costs but may lead to lower Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) due to reduced failures and warranty claims over time.
-
Supplier Factors: The reliability and reputation of suppliers can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their track record of quality and service, while newer entrants might offer lower prices to gain market share.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the chosen Incoterms is crucial, as they determine who is responsible for shipping costs, insurance, and tariffs. This can significantly affect the total landed cost of goods.
What Buyer Tips Can Enhance Cost-Efficiency?
-
Negotiation: Effective negotiation strategies can lead to better pricing, especially for larger orders. Building a relationship with suppliers can also facilitate more favorable terms over time.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Buyers should evaluate not just the purchase price but the entire lifecycle costs associated with the product, including maintenance, potential downtime, and disposal costs.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Different regions may have varying market dynamics. For instance, buyers in Africa may encounter different logistical challenges compared to those in Europe. Understanding local market conditions and regulatory requirements can aid in making informed purchasing decisions.
-
Disclaimer for Indicative Prices: It’s essential to note that prices can fluctuate based on market conditions, supplier negotiations, and other external factors. Buyers should seek quotes and confirmations from suppliers to ensure accuracy.
By grasping these components and influences, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions when sourcing batteries and alternators, ultimately enhancing their operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing how can you tell if its the battery or alternator With Other Solutions
Introduction to Alternative Solutions for Diagnosing Electrical Issues
When faced with starting problems in vehicles, determining whether the issue lies with the battery or the alternator is critical for effective troubleshooting. While understanding the symptoms of each component is essential, exploring alternative solutions can enhance the diagnostic process. This analysis will compare the traditional method of assessing battery and alternator issues against two alternative diagnostic technologies: battery testers and multimeters.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | How Can You Tell If It’s The Battery Or Alternator | Battery Testers | Multimeters |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Effective for identifying issues based on symptoms | Provides quick battery health check | Versatile, measures voltage, current, and resistance |
| Cost | Low-cost (manual checks) | Moderate (varies by brand) | Varies widely (affordable to professional-grade) |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires basic knowledge of symptoms | User-friendly with simple instructions | Requires technical knowledge for accurate use |
| Maintenance | Minimal, mainly observational | Low, occasional battery replacement | Low, regular calibration may be needed |
| Best Use Case | General troubleshooting without tools | Quick checks for battery health | Comprehensive diagnostics for electrical systems |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Battery Testers
Battery testers are designed to assess the health of a vehicle’s battery quickly. They provide clear results regarding the battery’s charge level and overall condition. The primary advantage of using a battery tester is its ease of use; many testers are user-friendly and require minimal setup. However, they primarily focus on battery health, leaving out other potential issues related to the alternator or starter. This limitation makes them less effective for comprehensive diagnostics.
Multimeters
Multimeters are highly versatile tools capable of measuring various electrical parameters, including voltage, current, and resistance. This capability allows for a more thorough investigation of both the battery and alternator, making it easier to identify specific issues within the electrical system. The main advantages of multimeters include their broad application and the depth of information they provide. However, they require a certain level of technical knowledge to operate effectively, which might be a barrier for some users. Additionally, the cost can vary widely, with professional-grade models being significantly more expensive than basic ones.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
When deciding on the most appropriate solution for diagnosing battery and alternator issues, B2B buyers should consider their specific needs and capabilities. The traditional method of observing symptoms remains a viable option for those with basic automotive knowledge. However, for businesses looking for faster and more accurate diagnostics, investing in battery testers or multimeters can enhance operational efficiency. Battery testers are excellent for quick assessments, while multimeters offer the most comprehensive data for electrical diagnostics. Ultimately, the choice should align with the business’s technical expertise, budget constraints, and the complexity of the vehicles serviced.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for how can you tell if its the battery or alternator
What Key Specifications Should B2B Buyers Consider When Diagnosing Battery or Alternator Issues?
1. Battery Capacity (Ah)
Battery capacity, measured in ampere-hours (Ah), indicates how much energy a battery can store. This specification is crucial for B2B buyers in sectors such as automotive repair or fleet management, as it influences the battery’s longevity and performance. A higher Ah rating means the battery can supply more power over a longer period, essential for vehicles that require significant electrical demand or operate in extreme conditions.
2. Cold Cranking Amps (CCA)
Cold Cranking Amps measure a battery’s ability to start an engine in cold temperatures. This specification is particularly relevant for regions with harsh winters, as a battery with a higher CCA rating will perform better under low temperatures. B2B buyers in colder climates must prioritize CCA ratings to ensure reliable vehicle operation, reducing the likelihood of breakdowns and maintenance costs.
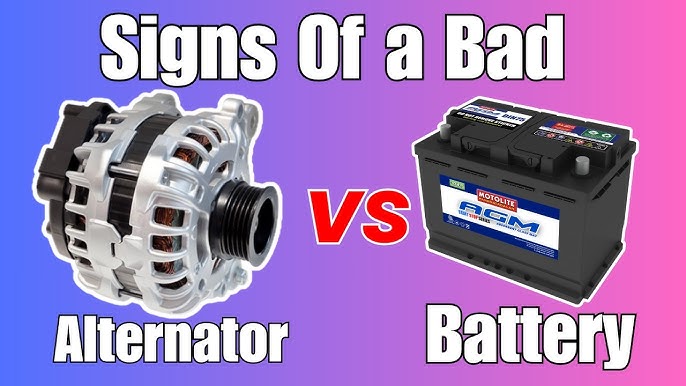
Illustrative image related to how can you tell if its the battery or alternator
3. Voltage Rating
Most automotive batteries have a standard voltage rating of 12 volts. However, understanding the voltage requirements of different vehicles is essential for B2B buyers. Selecting a battery or alternator with the correct voltage rating ensures compatibility with the vehicle’s electrical system, preventing potential electrical failures or damages.
4. Alternator Output (Amps)
The output of an alternator, measured in amps, indicates its ability to charge the battery and power electrical components while the engine runs. A higher output rating is critical for vehicles with multiple electronic systems, such as advanced infotainment or navigation systems. B2B buyers need to assess their vehicles’ electrical demands to select an alternator that can efficiently support their operations.
5. Temperature Range
Both batteries and alternators have specified operational temperature ranges. Understanding these ranges helps in selecting components that will perform reliably in various environmental conditions. For instance, batteries may freeze or overheat outside their operational range, leading to premature failure. B2B buyers should ensure that the products they procure can withstand the temperatures typical of their regions.
What Common Trade Terms Should B2B Buyers Know When Dealing with Battery and Alternator Components?
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to parts made by the original manufacturer of the vehicle. For B2B buyers, sourcing OEM parts ensures compatibility and reliability, as these components are designed specifically for the vehicle model. Understanding OEM vs. aftermarket distinctions can guide purchasing decisions and affect warranty considerations.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is significant for B2B buyers, as it impacts inventory management and cash flow. Knowing the MOQ can help businesses plan their purchases effectively, ensuring they meet their operational needs without overcommitting financially.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document that businesses send to suppliers to request pricing for specific products or services. In the context of batteries and alternators, submitting RFQs allows B2B buyers to gather competitive pricing and terms from multiple suppliers, facilitating informed purchasing decisions.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international trade, covering aspects such as shipping, insurance, and tariffs. For B2B buyers, understanding Incoterms is essential when importing batteries or alternators, as they dictate the transfer of risk and cost responsibility, impacting overall procurement strategies.
5. Wattage (W)
Wattage is a measure of electrical power and is particularly relevant for understanding how much energy a battery or alternator can deliver. For B2B buyers, wattage specifications help assess whether the components meet the electrical needs of various vehicle systems, ensuring optimal performance.
In conclusion, being well-versed in these technical specifications and trade terms equips B2B buyers with the knowledge necessary to make informed decisions regarding battery and alternator procurement, ultimately leading to improved vehicle reliability and operational efficiency.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the how can you tell if its the battery or alternator Sector
What Are the Key Market Drivers Influencing Battery and Alternator Sourcing?
In recent years, the automotive sector has experienced significant shifts due to technological advancements, regulatory changes, and evolving consumer preferences. Key drivers for international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, include the increasing adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) and hybrid models. This transition is not only reshaping the battery market but also influencing the demand for high-efficiency alternators that can support advanced electrical systems.
Additionally, the rise of smart automotive technologies is pushing manufacturers to innovate battery and alternator designs that integrate seamlessly with vehicle electronics. B2B buyers must stay attuned to emerging sourcing trends such as the preference for modular components, which offer easier replacement and upgrading, and the increasing importance of supply chain transparency to ensure reliable sourcing from reputable manufacturers.
Furthermore, fluctuating raw material prices and geopolitical factors can impact sourcing strategies. For instance, lithium and cobalt, essential for battery production, are often subject to market volatility influenced by mining regulations and environmental concerns. Buyers should consider diversifying their supplier base to mitigate risks associated with reliance on specific regions or suppliers.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact Battery and Alternator Procurement?
Sustainability is becoming a critical consideration for B2B buyers in the automotive sector. The environmental impact of battery production, particularly regarding lithium extraction, has raised concerns about water usage and ecosystem disruption. Consequently, buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers that adhere to sustainable practices and demonstrate a commitment to ethical sourcing.
The importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated. Buyers are encouraged to seek partners who hold certifications that reflect environmental responsibility, such as ISO 14001 for environmental management systems. Moreover, the adoption of recycled materials in battery manufacturing not only reduces waste but also enhances the sustainability profile of products.
As consumer awareness grows, companies that invest in green technologies and sustainable practices will likely enjoy a competitive advantage. This shift towards sustainability is also reflected in regulatory frameworks in Europe and other regions, which demand stricter compliance with environmental standards. B2B buyers should consider these factors when selecting suppliers to align with market trends and consumer expectations.
What Is the Historical Context of Battery and Alternator Development?
The evolution of batteries and alternators can be traced back to the early 20th century, when the first automotive batteries were introduced. Initially, lead-acid batteries became the standard due to their reliability and cost-effectiveness. However, as automotive technology advanced, the need for more efficient power sources led to innovations in battery chemistry and design.
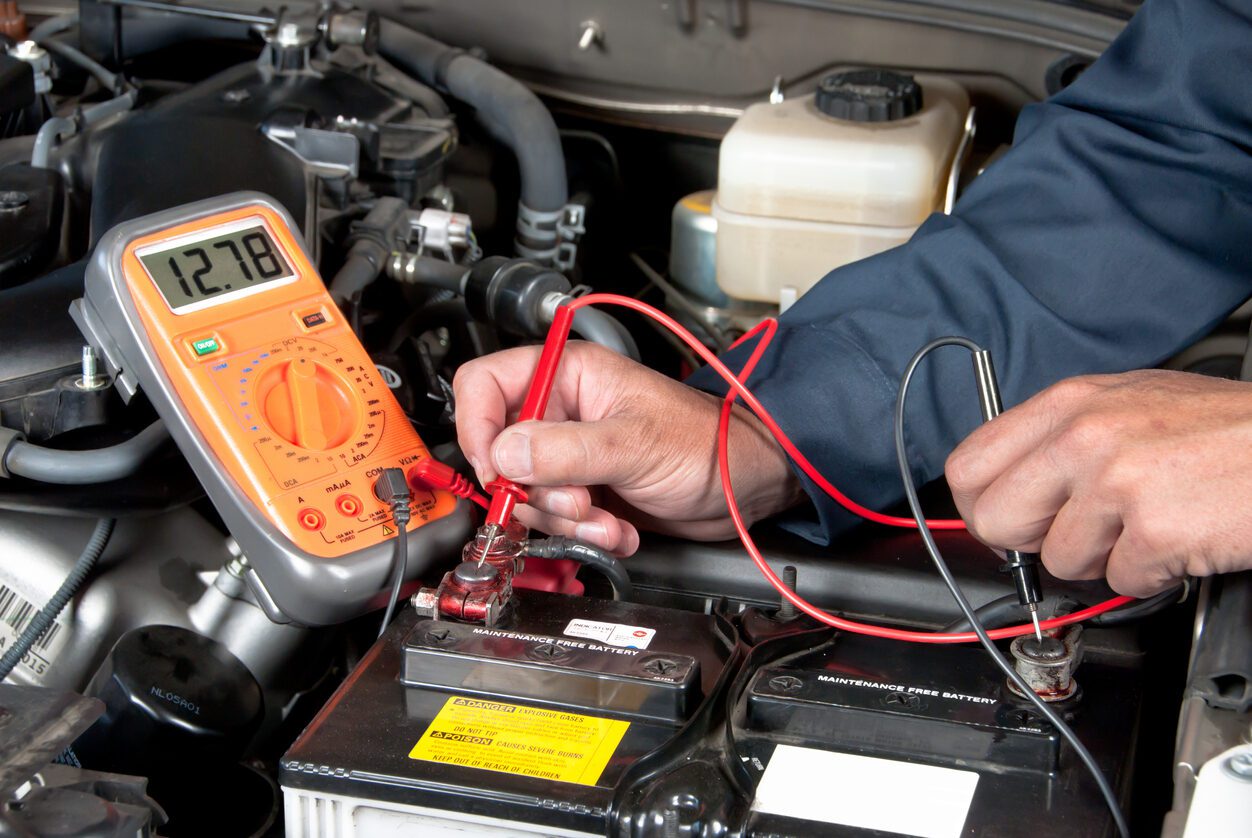

Illustrative image related to how can you tell if its the battery or alternator
The introduction of alternators in the 1960s marked a significant shift from generators, providing a more efficient means of charging batteries while powering vehicle electronics. This technological advancement paved the way for modern vehicles that rely heavily on electrical systems.
In recent decades, the push for electric and hybrid vehicles has further transformed the landscape, prompting manufacturers to innovate continuously. The development of lithium-ion batteries and advancements in alternator technology reflect the industry’s response to changing consumer demands and environmental challenges. Understanding this historical context is crucial for B2B buyers as they navigate current market dynamics and sourcing strategies.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of how can you tell if its the battery or alternator
-
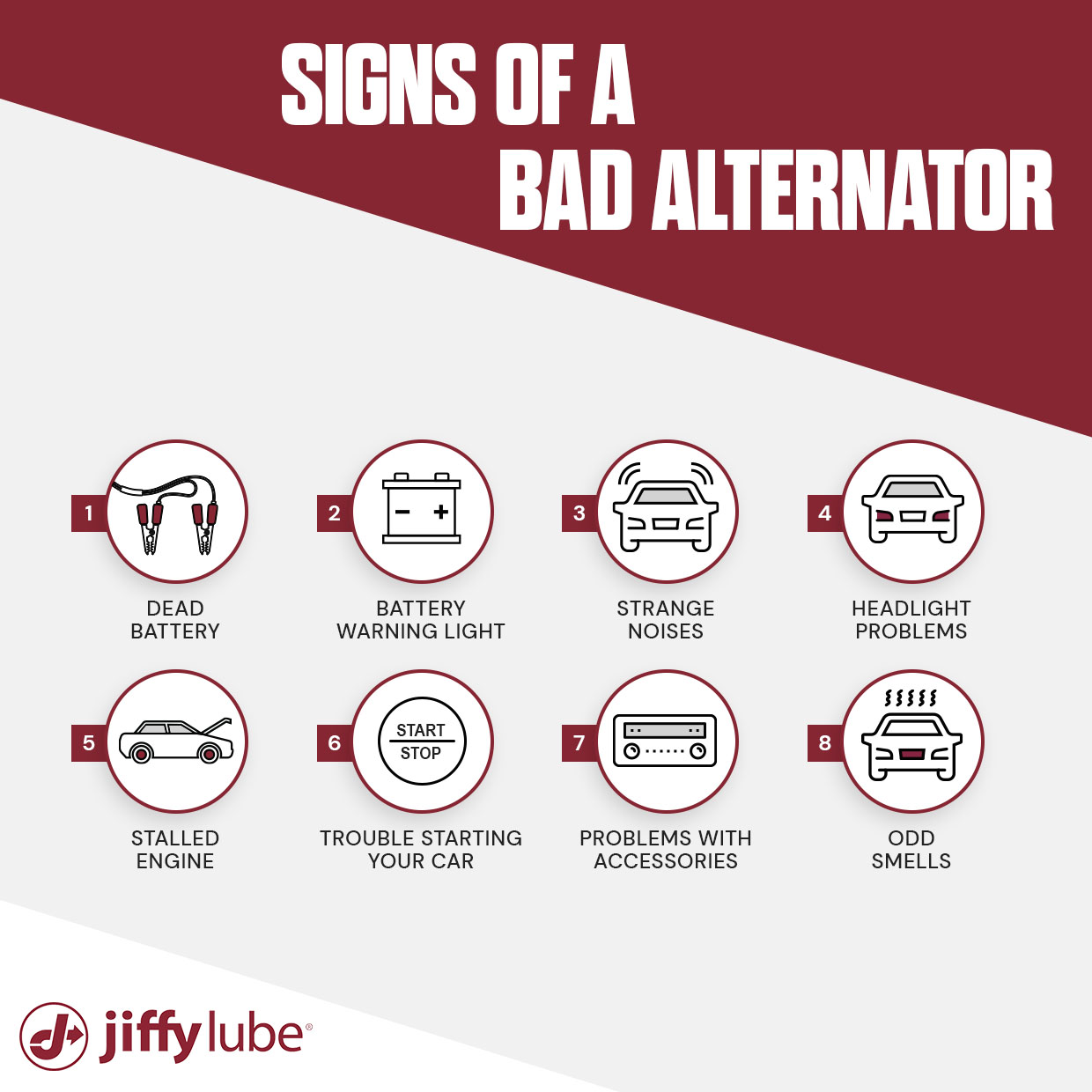
1. How do I determine if my vehicle’s issue is related to the battery or alternator?
To diagnose whether the problem lies with the battery or alternator, start by observing the vehicle’s symptoms. A slow engine start or dimming lights when the engine is off typically indicates a battery issue. Conversely, if the engine stalls shortly after a jump-start or the headlights flicker while driving, it may suggest an alternator problem. Conducting a jump-start can help confirm the diagnosis: if the vehicle runs for a while and then stalls, it points to a battery issue; if it doesn’t stay running, the alternator might be at fault. -
2. What are the common signs of a failing battery?
Common indicators of a failing battery include difficulty starting the engine, dim dashboard lights, and unusual smells like rotten eggs, which can signal leakage. Additionally, a battery that shows physical signs of swelling or corrosion at the terminals often needs replacement. Regular maintenance and monitoring can extend battery life, but if the battery is over three to five years old and shows these signs, it’s prudent to consider a replacement. -
3. What are the key symptoms of a faulty alternator?
A faulty alternator can manifest through several symptoms, such as frequent engine stalls, flickering headlights, or erratic behavior of electrical components like the stereo or power windows. If the battery is repeatedly dying even after a jump-start, this could indicate that the alternator is not charging it properly. Unusual noises, such as squealing or growling, and burning smells from the engine compartment may also signal alternator issues that require immediate attention. -
4. How can I find a reliable supplier for batteries and alternators?
When sourcing batteries and alternators, prioritize suppliers with a solid reputation and positive reviews in the industry. Look for certifications and quality assurance processes that demonstrate compliance with international standards. Engaging with suppliers that offer warranties and after-sales support can also be beneficial. Networking at industry trade shows or through online platforms can provide insights into trustworthy suppliers in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. -
5. What customization options should I consider when sourcing batteries and alternators?
Customization options can vary by supplier but may include specifications such as voltage, capacity, and physical dimensions to match specific vehicle models. Some suppliers may offer branding options or special features like enhanced performance in extreme temperatures. Discussing your requirements upfront will help ensure that the products meet your operational needs. Always inquire about the feasibility of custom orders and associated costs. -
6. What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for batteries and alternators?
Minimum order quantities for batteries and alternators can vary significantly based on the supplier and product type. Generally, larger suppliers may have higher MOQs, while smaller manufacturers might accommodate lower quantities. It’s essential to clarify these details during negotiations and consider your inventory turnover rates when placing orders. Understanding MOQ can help optimize your supply chain and reduce excess stock. -
7. What payment terms are commonly offered by suppliers in the automotive parts industry?
Payment terms can differ widely among suppliers, but common options include upfront payment, net 30 or net 60 days, and letter of credit arrangements for larger orders. Discussing payment terms early in the negotiation process is crucial to align expectations. Ensure that any agreements are documented clearly to avoid misunderstandings, and consider potential currency exchange implications when dealing with international suppliers. -
8. How do I ensure quality assurance when sourcing automotive parts?
To ensure quality assurance when sourcing batteries and alternators, request detailed specifications and certifications from suppliers, such as ISO or other industry standards. Implementing a robust quality control process, including pre-shipment inspections and sample testing, can help mitigate risks. Building a strong relationship with suppliers allows for better communication regarding quality expectations and can lead to improved product consistency over time.
Top 2 How Can You Tell If Its The Battery Or Alternator Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Nationwide – Alternator & Battery Guide
Domain: blog.nationwide.com
Registered: 1994 (31 years)
Introduction: Alternator: Powers the car when the engine is running, lasts the lifetime of the car but may require repair or replacement due to wear and tear. Signs of a bad alternator include dim interior lights, dim or overly bright headlights, growling noises, and burning smells. Battery: Stores power, starts the engine, delivers electricity to the ignition system, works with the alternator to power electron…
2. Alternator Testing – Risks of Battery Disconnection
Domain: mechanics.stackexchange.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: The text discusses a technique to test an alternator by removing a 12V battery lead while the vehicle is running. It highlights that this method is not recommended due to potential damage to the vehicle’s electronics and the alternator itself. The text emphasizes that the battery plays a crucial role in filtering spikes and transients, and disconnecting it can lead to damaging the voltage regulato…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for how can you tell if its the battery or alternator
In navigating the complexities of automotive electrical systems, understanding whether the issue lies with the battery or the alternator is crucial for efficient repairs and maintenance. Key indicators, such as dimming lights, unusual smells, or persistent stalling, can guide professionals in diagnosing the root cause of electrical failures. By leveraging strategic sourcing for high-quality batteries and alternators, B2B buyers can enhance their offerings and ensure reliable vehicle performance.
Investing in reputable suppliers not only ensures access to durable products but also strengthens supply chain resilience, particularly in diverse markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. As global automotive demands evolve, fostering relationships with trusted manufacturers will be essential for maintaining a competitive edge.
Looking ahead, businesses should prioritize proactive maintenance solutions and stock the right components to mitigate downtime. By staying informed and strategically sourcing automotive parts, international buyers can position themselves for success in an ever-changing marketplace. Engage with suppliers who understand the unique challenges of your region and collaborate for innovative solutions that meet the needs of your customers.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.