Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for generator vs alternator
In today’s increasingly interconnected global market, understanding the differences between generators and alternators is crucial for B2B buyers seeking reliable power solutions. Whether you’re sourcing backup power for industrial operations in Africa or equipping a fleet of vehicles in South America, the decision between these two technologies can significantly impact efficiency and operational costs. This guide delves into the intricacies of generators and alternators, offering a comprehensive analysis of their types, applications, and performance characteristics.
We will explore the advantages and disadvantages of each option, helping you navigate the complexities of sourcing the right technology for your specific needs. Additionally, this guide covers essential aspects such as supplier vetting processes, cost considerations, and maintenance requirements, tailored for international buyers from diverse regions, including the Middle East and Europe.
By arming you with actionable insights and expert recommendations, this guide empowers you to make informed purchasing decisions. Understanding the nuances of generators versus alternators will not only enhance your operational reliability but also ensure you invest wisely in your power generation needs. As you read on, you’ll find the tools necessary to select the best power solution that aligns with your business goals and regional challenges.
Table Of Contents
- Top 6 Generator Vs Alternator Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for generator vs alternator
- Understanding generator vs alternator Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of generator vs alternator
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘generator vs alternator’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for generator vs alternator
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for generator vs alternator
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘generator vs alternator’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for generator vs alternator Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing generator vs alternator With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for generator vs alternator
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the generator vs alternator Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of generator vs alternator
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for generator vs alternator
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Understanding generator vs alternator Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
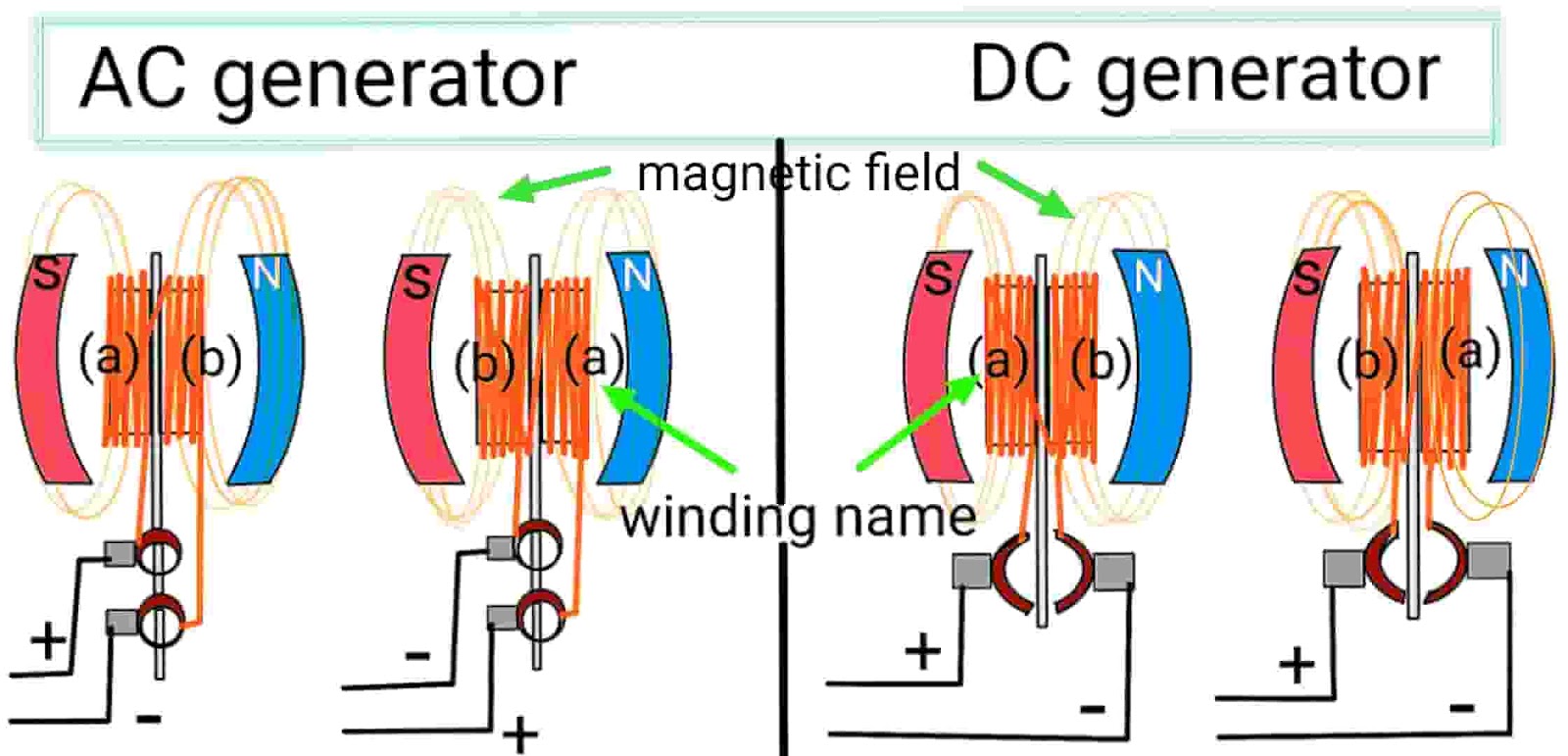
| AC Generators | Converts mechanical energy to alternating current; typically larger and heavier. | Power plants, industrial machinery | Pros: Reliable for high power output. Cons: Less efficient at low speeds. |
| DC Generators | Produces direct current; simpler design with commutator and brushes. | Automotive applications, small machinery | Pros: Good for battery charging. Cons: Requires more maintenance due to wear on brushes. |
| Alternators | Generates alternating current; lighter and more efficient at various RPMs. | Automotive, aviation, renewable energy | Pros: High efficiency, low maintenance. Cons: Sensitive to electrical surges. |
| Inverter Generators | Converts DC to AC; provides clean power with low total harmonic distortion. | Camping, outdoor events, small businesses | Pros: Quiet operation, portable. Cons: Limited power output for heavy machinery. |
| Synchronous Generators | Operates at a constant speed; used in large-scale power generation. | Utilities, large industrial facilities | Pros: Stable voltage output. Cons: More complex and expensive to install. |
What Are the Characteristics of AC Generators and Their B2B Suitability?
AC generators, often referred to as alternators in some contexts, convert mechanical energy into alternating current. They are typically larger and heavier than their DC counterparts, making them suitable for applications that demand high power output, such as power plants and industrial machinery. B2B buyers should consider the efficiency of AC generators, especially in applications requiring consistent power delivery. However, their performance can drop at low speeds, which may necessitate a careful evaluation of operational requirements.
How Do DC Generators Compare for Specific B2B Applications?
DC generators are known for their simplicity, utilizing a commutator and brushes to produce direct current. They are commonly used in automotive applications and small machinery where battery charging is essential. While they provide reliable performance, the need for regular maintenance due to brush wear can be a downside for businesses. Buyers should weigh the advantages of lower initial costs against the potential for increased maintenance expenses over time.
What Makes Alternators the Preferred Choice for Many Industries?
Alternators are widely favored due to their ability to generate alternating current efficiently across a range of RPMs. Their lightweight design and low maintenance requirements make them ideal for automotive, aviation, and renewable energy applications. However, alternators are sensitive to electrical surges, which can lead to operational challenges if not managed properly. Businesses should ensure their systems include protective measures to mitigate these risks, enhancing the reliability of their electrical systems.
Why Choose Inverter Generators for Portable Power Needs?
Inverter generators are designed to convert DC power into clean AC power, making them an excellent choice for applications like camping, outdoor events, and small businesses. They operate quietly and are portable, offering convenience for users. However, their limited power output may not support heavy machinery, which could be a critical consideration for B2B buyers needing robust power solutions. Understanding the specific power requirements is essential to ensure that an inverter generator meets operational needs effectively.
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Synchronous Generators?
Synchronous generators operate at a constant speed and are commonly used in large-scale power generation. They provide stable voltage output, making them suitable for utilities and large industrial facilities. However, their complexity and higher installation costs can be a barrier for some businesses. When considering a synchronous generator, B2B buyers should assess the long-term benefits of stable power supply against the upfront investment and operational intricacies involved in their use.
Key Industrial Applications of generator vs alternator
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of generator vs alternator | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Construction | Powering heavy machinery and tools | Ensures continuous operation at remote sites | Durability, fuel efficiency, and maintenance support |
| Agriculture | Irrigation systems and farm equipment | Enhances productivity and reduces downtime | Compatibility with existing systems and energy output needs |
| Telecommunications | Backup power for communication towers | Maintains operational integrity during outages | Reliability, ease of installation, and local service options |
| Mining | Power supply for mining operations | Facilitates uninterrupted production in remote areas | Portability, fuel type, and environmental regulations |
| Healthcare | Backup power for medical facilities | Ensures patient safety and operational continuity | Compliance with health regulations and power capacity needs |
How Are Generators and Alternators Used in Construction Projects?
In the construction industry, generators are vital for powering heavy machinery and tools, particularly at remote job sites where grid access is limited. They provide a reliable source of energy to operate equipment like cranes, excavators, and concrete mixers. Alternators, while less common, can be used in vehicles and machinery to maintain battery charge for electric tools. For international buyers, sourcing durable models that can withstand harsh conditions and offer fuel efficiency is crucial, as downtime can significantly impact project timelines and costs.
What Role Do Generators and Alternators Play in Agriculture?
In agriculture, generators are extensively used to power irrigation systems and various farm equipment, ensuring that crops receive adequate water supply and that machinery operates efficiently. Alternators are integrated into tractors and harvesters to maintain battery life, enabling the use of electronic monitoring systems that enhance operational efficiency. Buyers in regions with unstable power supply should prioritize robust generators that can handle the demands of large-scale farming while being compatible with existing equipment to minimize transition costs.
How Do Telecommunications Depend on Generators and Alternators?
Telecommunications companies rely on generators for backup power at communication towers, ensuring that services remain uninterrupted during power outages. Alternators can be found in mobile communication units, keeping batteries charged and ready for use. For B2B buyers in this sector, sourcing reliable and easy-to-install power solutions is essential to maintain operational integrity, especially in remote locations where power stability is a concern. Additionally, local service options for maintenance and support should be considered to prevent prolonged outages.
Why Are Generators and Alternators Critical in Mining Operations?
Mining operations often occur in remote areas, making generators essential for providing a consistent power supply for equipment and facilities. They help facilitate uninterrupted production, which is vital for meeting market demands. Alternators can be used in mining vehicles to ensure that electronic systems remain operational. When sourcing power solutions, companies must consider portability, fuel type, and compliance with environmental regulations to minimize operational risks and adhere to industry standards.
How Do Healthcare Facilities Utilize Generators and Alternators?
Healthcare facilities depend on generators for backup power, ensuring that critical systems remain operational during power failures. This is especially crucial for life-supporting equipment and emergency services. Alternators are used in medical transport vehicles to keep batteries charged for essential equipment. Buyers in this sector should focus on compliance with health regulations and the capacity of power systems to meet the high demands of medical technology, ensuring patient safety and operational continuity in all situations.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘generator vs alternator’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Power Reliability in Remote Operations
The Problem: In industries such as mining or agriculture, operations often take place in remote locations where access to reliable power sources is limited. B2B buyers in these sectors may face significant downtime due to power outages or equipment failure. When choosing between generators and alternators, the challenge lies in understanding which system will provide consistent power output under varying loads and conditions. For instance, traditional generators may struggle to produce adequate power at low RPMs, leading to performance issues during critical operations.
The Solution: To ensure reliable power in remote locations, B2B buyers should prioritize sourcing high-quality alternators, particularly those designed for low RPM efficiency. When specifying equipment, buyers should consider alternators with robust voltage regulators that maintain steady output across a range of operating conditions. Additionally, investing in dual systems—an alternator for consistent power needs and a generator as a backup—can mitigate risks associated with power failures. Regular maintenance and training for operational staff on load management will further enhance reliability, ensuring that power demands are met without interruption.
Scenario 2: Cost Efficiency in Long-Term Operations
The Problem: Many businesses are under pressure to reduce operational costs while maintaining productivity. In sectors like construction or manufacturing, the choice between generators and alternators can significantly impact both initial investment and long-term expenses. Generators tend to require more frequent maintenance and repairs due to their mechanical complexity, which can lead to increased downtime and costs. In contrast, alternators are often more cost-effective over time, but their sensitivity to electrical spikes can pose risks.
The Solution: B2B buyers should conduct a thorough cost-benefit analysis when selecting power systems. Opting for high-efficiency alternators that come with built-in overvoltage protection can prevent costly damage to equipment and reduce maintenance needs. Buyers should also negotiate service agreements that include regular inspections and maintenance schedules, which can prevent unexpected breakdowns and prolong equipment lifespan. By investing in training for staff to recognize early signs of electrical issues, businesses can further minimize operational disruptions, ensuring that their systems remain efficient and cost-effective.
Scenario 3: Compatibility with Modern Equipment
The Problem: In today’s tech-driven landscape, many companies utilize advanced equipment that requires stable electrical inputs for optimal performance. Industries such as aviation and telecommunications heavily rely on sophisticated electronics that can be sensitive to fluctuations in power supply. B2B buyers may struggle to determine whether to integrate traditional generators or modern alternators into their systems, especially when considering the compatibility of new technologies with existing electrical setups.
The Solution: To address compatibility issues, buyers should prioritize alternators that offer modern features such as smart voltage regulation and compatibility with digital systems. It is essential to work closely with manufacturers to understand the specifications of both the alternator and the technology it will support. Additionally, conducting a comprehensive audit of existing electrical systems can identify potential conflicts and integration challenges. Buyers should also consider future-proofing their investments by selecting equipment with scalable features, ensuring that they can adapt to evolving technological requirements without significant additional costs.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for generator vs alternator
What are the Key Materials Used in Generators and Alternators?
When selecting materials for generators and alternators, it is essential to consider properties that influence performance, durability, and cost. Here, we analyze several common materials used in these electrical devices, focusing on their key properties, advantages and disadvantages, and the implications for international buyers.
How Does Copper Influence Performance in Generators and Alternators?
Copper is a widely used conductor in both generators and alternators due to its excellent electrical conductivity. It typically has a temperature rating of up to 200°C and offers good corrosion resistance when properly treated.
Pros: Copper’s high conductivity ensures efficient energy transfer, which is critical for performance. It is also relatively easy to manufacture, allowing for intricate designs.
Cons: The primary drawback is its cost, which can be high compared to alternatives like aluminum. Additionally, copper is susceptible to oxidation, which can affect performance if not properly insulated.
Impact on Application: Copper is compatible with various media, including water and oil, making it suitable for diverse environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with international standards like ASTM B170 for copper wire. In regions like Africa and South America, where environmental conditions can vary, proper insulation and treatment against corrosion are crucial.
What Role Does Aluminum Play in Generators and Alternators?
Aluminum is increasingly used as an alternative to copper, particularly in windings and casings. It has a lower temperature rating of around 150°C and is lightweight, which can be advantageous in applications where weight is a concern.
Pros: Aluminum is less expensive than copper, making it a cost-effective option for manufacturers. Its lightweight nature can lead to reduced overall system weight.
Cons: While aluminum conducts electricity well, it is not as efficient as copper. Additionally, it is more prone to corrosion, which can lead to performance issues over time.
Illustrative image related to generator vs alternator
Impact on Application: Aluminum’s properties make it suitable for environments where weight savings are critical, but buyers must consider its lower conductivity in high-demand applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of compliance with standards such as ASTM B221 for aluminum. In regions with high humidity, like parts of the Middle East, corrosion-resistant coatings may be necessary.
How Does Steel Enhance Durability in Generators and Alternators?
Steel is often used in the structural components of generators and alternators, such as frames and casings. It offers high strength and durability, with a temperature rating typically around 300°C.
Pros: Steel’s robustness makes it ideal for heavy-duty applications, providing excellent protection against physical damage. It is also relatively inexpensive compared to other high-strength materials.
Cons: Steel is heavier than both copper and aluminum, which can be a disadvantage in applications where weight is a critical factor. Additionally, it is susceptible to rust and corrosion if not properly treated.
Impact on Application: Steel is suitable for environments where mechanical stress is a concern, but its weight may limit its use in portable applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM A36 for structural steel is essential. In regions like Europe, buyers may also need to consider local regulations regarding material sourcing and environmental impact.
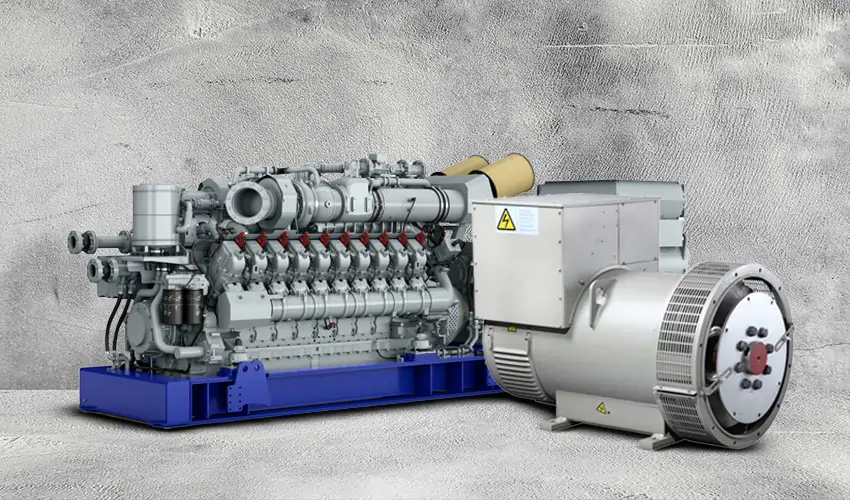
What Advantages Do Plastics Offer in Generators and Alternators?
Plastics, particularly high-performance polymers, are used for insulation and housing in generators and alternators. They can withstand temperatures up to 150°C and offer excellent corrosion resistance.
Pros: Plastics are lightweight and can be molded into complex shapes, allowing for innovative designs. They also provide good electrical insulation, reducing the risk of short circuits.
Illustrative image related to generator vs alternator
Cons: The primary limitation of plastics is their lower mechanical strength compared to metals, which can make them less suitable for structural components.
Impact on Application: Plastics are ideal for applications requiring insulation and protection against environmental factors, but they may not withstand heavy mechanical stress.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with standards like ASTM D638 for plastics. In regions with extreme temperatures, such as parts of Africa, selecting high-temperature-rated plastics is crucial.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Generators and Alternators
| Material | Typical Use Case for generator vs alternator | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Copper | Windings and connectors in both generators and alternators | High electrical conductivity | High cost and oxidation susceptibility | High |
| Aluminum | Windings and casings, especially in lightweight applications | Cost-effective and lightweight | Lower conductivity and corrosion prone | Medium |
| Steel | Structural components like frames and casings | High strength and durability | Heavier and prone to rust | Low |
| Plastics | Insulation and housing components | Lightweight and excellent insulation | Lower mechanical strength | Medium |
This analysis provides a comprehensive overview of material selection for generators and alternators, offering valuable insights for international B2B buyers. Understanding these materials’ properties and implications will enable better decision-making in sourcing and application.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for generator vs alternator
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process for Generators and Alternators?
The manufacturing processes for generators and alternators involve several key stages, each critical to ensuring that the final products meet performance and quality standards. These stages typically include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How Is Material Prepared for Generators and Alternators?
Material preparation is the foundational step in manufacturing generators and alternators. High-quality raw materials, such as copper for windings and steel for the casing, are sourced from certified suppliers. The preparation phase often involves cutting and shaping these materials into specified dimensions. This may include processes like stamping and machining to create components such as stators, rotors, and casings.
Additionally, quality checks are conducted on raw materials to ensure compliance with international standards. For B2B buyers, verifying the material specifications and certifications is essential to ensure that they are sourcing durable and reliable components.
What Forming Techniques Are Used in Generator and Alternator Manufacturing?
The forming stage is where components take shape. For generators, this often involves winding copper wire around the armature to create electromagnetic fields. In contrast, alternators use a more complex process involving the creation of three-phase windings to facilitate efficient power generation. Advanced techniques like computer numerical control (CNC) machining are commonly employed to ensure precision in component dimensions.
Illustrative image related to generator vs alternator
Magnetic cores are also manufactured during this stage, which are critical for both generators and alternators. The quality of the magnetic materials directly affects the efficiency and output of the electrical systems, making it crucial for manufacturers to adhere to strict specifications during this process.
How Are Generators and Alternators Assembled?
The assembly phase brings together all the components produced in previous stages. This step typically involves several sub-assemblies, including the rotor, stator, and housing. For generators, the assembly process may include installing carbon brushes and commutators, while alternators will integrate diodes and voltage regulators.
Quality control checkpoints are critical during assembly. Manufacturers often implement in-process quality control (IPQC) measures to monitor assembly accuracy and detect defects early. For B2B buyers, understanding the assembly process can provide insights into potential performance issues, especially if the manufacturing processes are not well-documented.
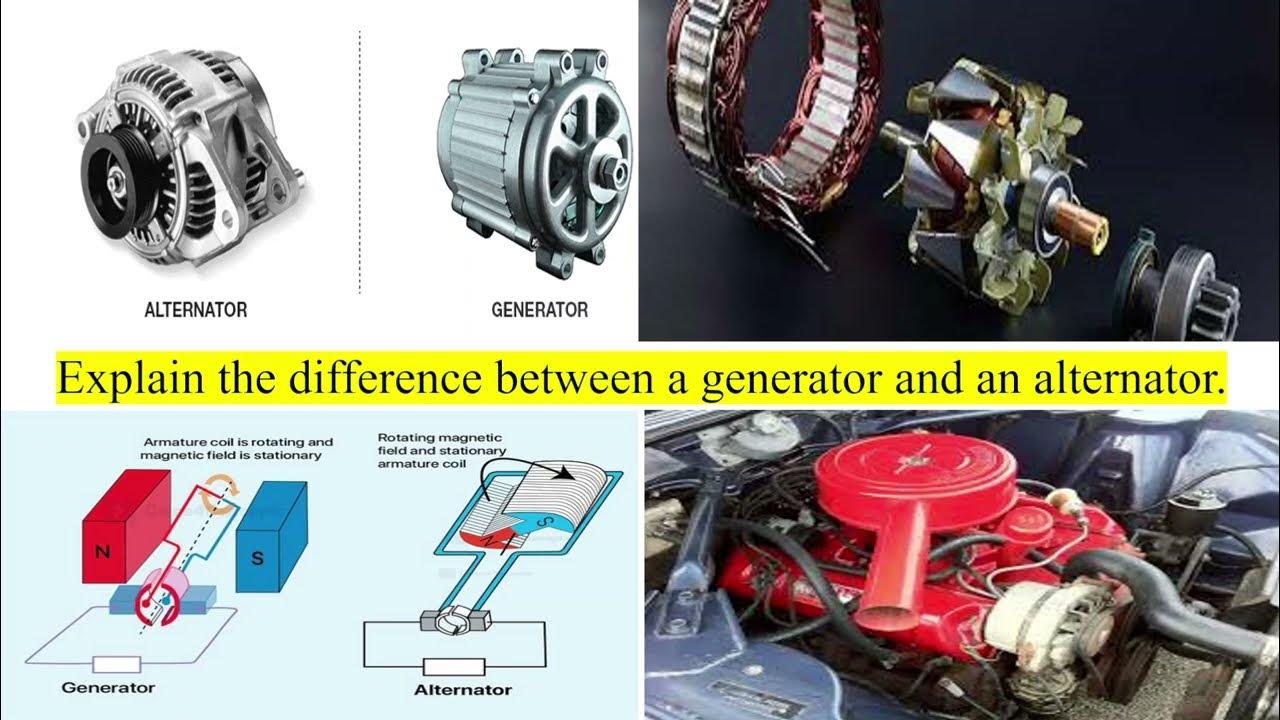
Illustrative image related to generator vs alternator
What Finishing Techniques Are Applied to Generators and Alternators?
Finishing processes play a crucial role in the durability and performance of generators and alternators. These processes may include surface treatments such as powder coating or anodizing, which protect against corrosion and wear. Additionally, manufacturers often apply insulation to windings to prevent electrical short circuits.
Final inspections are conducted to assess the aesthetic quality and functional performance of the products. This may involve testing for proper electrical output, operational noise levels, and mechanical integrity.
What Quality Assurance Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
Quality assurance is paramount in the manufacturing of generators and alternators. Buyers should be familiar with both international standards, such as ISO 9001, and industry-specific certifications like CE marking for the European market and API standards for oil and gas applications.
How Are Quality Control Checkpoints Structured?
Quality control checkpoints are integral to the manufacturing process. Typically, they include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial stage involves testing raw materials and components upon arrival to ensure they meet required specifications.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Conducted during the manufacturing process, IPQC aims to catch defects early. This can include monitoring the winding process and assembly tolerances.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): This final stage assesses the complete product, ensuring it meets all operational standards before shipping.
For B2B buyers, understanding these checkpoints can help in assessing the reliability of suppliers.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used to Ensure Quality?
Various testing methods are employed to ensure the functionality and reliability of generators and alternators. Common methods include:
-
Electrical Testing: This assesses output voltage and current under different loads to ensure compliance with specifications.
-
Thermal Testing: Evaluates the performance of components under high temperatures to identify potential overheating issues.
-
Mechanical Testing: Checks for physical integrity and durability, including vibration and shock tests.
For B2B buyers, requesting detailed testing reports can provide insights into the quality of the products they are considering.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
To ensure that suppliers maintain high-quality standards, B2B buyers can take several steps:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting audits of the manufacturing facilities can provide direct insights into the processes and quality control measures in place.
-
Requesting Quality Reports: Suppliers should be able to provide documentation of their quality assurance processes, including results from IQC, IPQC, and FQC.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party quality assurance companies can offer an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s manufacturing capabilities.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International Buyers?
International B2B buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of several nuances in quality control:
-
Regulatory Compliance: Different regions may have varying regulatory standards. Buyers should ensure that products comply with local requirements in their respective markets.
-
Cultural Differences: Understanding the cultural context in which suppliers operate can affect negotiations and expectations regarding quality.
-
Supply Chain Transparency: Establishing clear communication channels with suppliers can help mitigate risks associated with quality control, especially when sourcing from different countries.
By focusing on these manufacturing processes and quality assurance strategies, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing generators and alternators, ensuring they invest in reliable and high-quality products.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘generator vs alternator’
In the competitive landscape of power solutions, understanding the differences between generators and alternators is crucial for B2B buyers. This guide offers a practical checklist to help you make informed procurement decisions tailored to your specific needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Start by clearly outlining the technical requirements for your power system. Consider factors such as voltage output, amperage needs, and operational conditions.
– Voltage and Amperage: Determine whether you need a 12-volt or 24-volt system and the required amperage ratings based on your application.
– Operational Environment: Assess whether the equipment will operate in extreme temperatures or altitudes, which may influence your choice between a generator and an alternator.
Step 2: Evaluate Power Requirements
Conduct a comprehensive analysis of your power consumption needs. This involves estimating the total load that will be powered by the generator or alternator.
– Load Calculation: List all devices and their power ratings to ensure you select a unit that can handle peak loads.
– Future Needs: Consider potential expansions or additional equipment that may increase power requirements in the future.
Step 3: Research Reliability and Maintenance Needs
Investigate the reliability and maintenance aspects of both generators and alternators. Understanding these factors will help you choose a solution that minimizes downtime.
– Maintenance Frequency: Generators typically require more maintenance due to their mechanical components, while alternators often have a lower maintenance burden.
– Reliability Ratings: Look for user reviews and industry reports that assess the reliability of different models in your operating environment.
Step 4: Assess Supplier Credentials
Thoroughly vet potential suppliers to ensure they meet industry standards and have a solid reputation. This is critical for securing quality products and support.
– Certifications: Verify that suppliers have relevant certifications, such as ISO or other industry-specific endorsements.
– Experience: Look for suppliers with a proven track record in your industry or region, which indicates reliability and expertise.
Step 5: Request Detailed Proposals
Once you identify potential suppliers, request detailed proposals that outline specifications, pricing, and terms. This will facilitate a better comparison.
– Specifications: Ensure that proposals include exact technical specifications and compliance with your requirements.
– Cost Breakdown: Ask for a clear breakdown of costs, including potential hidden fees for shipping, installation, or maintenance.
Step 6: Evaluate After-Sales Support and Warranty
Consider the after-sales support and warranty options provided by suppliers. This can significantly impact long-term satisfaction and reliability.
– Warranty Terms: Review warranty coverage for both parts and labor to understand your protection against defects or failures.
– Support Services: Inquire about the availability of technical support, parts replacement, and maintenance services post-purchase.
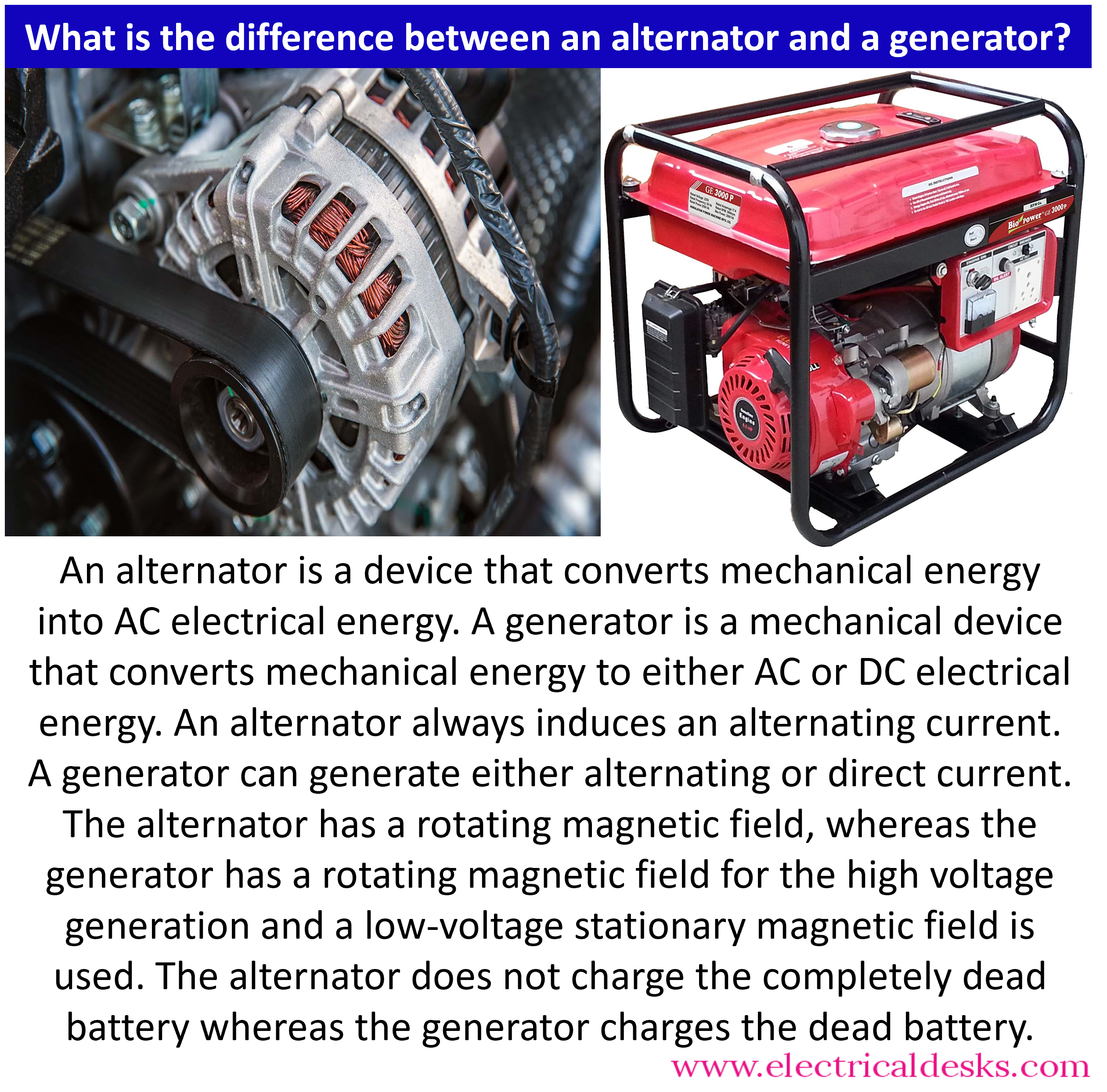
Illustrative image related to generator vs alternator
Step 7: Finalize Your Decision
After thorough evaluation and comparison, make an informed decision based on all gathered information. Ensure that the chosen solution aligns with both your immediate and long-term power needs.
– Cost vs. Value: Assess not just the initial costs but the overall value, including efficiency, lifespan, and potential savings on maintenance.
– Fit for Purpose: Confirm that the selected generator or alternator meets all operational requirements and offers the reliability your business demands.
By following these steps, B2B buyers can confidently navigate the complexities of selecting between generators and alternators, ensuring their investment aligns with their operational needs and strategic goals.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for generator vs alternator Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Generators and Alternators?
When considering sourcing generators versus alternators, understanding the cost structure is crucial for international B2B buyers. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margin.
-
Materials: The materials used in generators and alternators significantly influence cost. Generators typically require heavier components, such as copper windings and larger casings, leading to higher material costs. Alternators, on the other hand, can be produced with lighter materials, which may reduce overall costs. The choice of materials also impacts durability and performance, necessitating careful consideration.
-
Labor: Labor costs can vary by region and the complexity of the manufacturing process. Generators often require more skilled labor due to their intricate assembly and maintenance needs. Conversely, alternators, especially those manufactured using automated processes, may incur lower labor costs, which could be a factor in pricing.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to production facilities, equipment depreciation, and utilities. Generators tend to have higher overhead costs due to their larger size and more complex assembly lines. In contrast, alternators, which are generally more compact, can benefit from lower overhead.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in tooling for production can be substantial. Generators may require specialized tools for assembly and maintenance, impacting the cost structure. Alternators, while still needing tooling, might have less variability in their manufacturing processes, potentially lowering tooling costs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring the reliability and safety of electrical components is paramount. Generators often undergo rigorous testing protocols, increasing QC costs. Alternators, while still requiring quality checks, may have streamlined processes that can reduce associated costs.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs are influenced by the weight and size of the units. Generators, being heavier and bulkier, often incur higher logistics expenses than alternators. Furthermore, international shipping considerations, such as tariffs and customs duties, can significantly affect overall costs.
-
Margin: The supplier’s profit margin is also a critical factor. Margins can vary based on the supplier’s market positioning, brand reputation, and the perceived value of their products.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Generator and Alternator Sourcing?
Several factors can influence the pricing of generators and alternators, including volume, specifications, materials, quality certifications, supplier relationships, and Incoterms.
-
Volume/MOQ: Larger purchase volumes can lead to significant discounts, particularly for B2B buyers. Suppliers are often willing to negotiate better prices for minimum order quantities (MOQs) due to reduced per-unit costs.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom specifications can increase costs. Buyers seeking tailored solutions must balance their specific needs with the potential price increases associated with custom manufacturing.
-
Materials: The choice of materials directly impacts pricing. High-quality or specialty materials can lead to increased costs, while more standard materials might offer cost savings.
-
Quality/Certifications: Certifications such as ISO or CE can influence price. While certified products often come at a premium, they provide assurance of quality and compliance with international standards, which can be crucial for buyers in regulated markets.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers play a significant role in pricing. Established suppliers may charge higher prices due to their track record and quality assurance processes.
-
Incoterms: The chosen Incoterms can greatly affect total costs. Buyers should be aware of who bears responsibility for shipping, insurance, and tariffs to avoid unexpected expenses.
What Are Some Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficiency in International Sourcing?
International B2B buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, can optimize their sourcing strategies with several actionable tips:
-
Negotiation: Engage in open discussions with suppliers to explore pricing flexibility, especially for bulk orders. Building a long-term relationship can lead to better terms.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider not just the initial purchase price, but also maintenance, operational costs, and longevity. Alternators may offer lower TCO due to reduced maintenance needs.
-
Pricing Nuances: Be aware of regional price variations influenced by local market dynamics and supplier competition. Conduct market research to ensure competitive pricing.
-
Leverage Relationships: Establishing strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing, exclusive offers, and priority service.
-
Stay Informed on Market Trends: Understanding global supply chain dynamics and material costs can provide leverage in negotiations and help anticipate price fluctuations.
By carefully analyzing these cost components and influencers, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and budget constraints. It is advisable to seek multiple quotes and perform due diligence to ensure the best value in sourcing generators and alternators.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing generator vs alternator With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Generators and Alternators in Power Generation
In the world of power generation, businesses often face the challenge of choosing between traditional generators and alternators, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. However, several alternative solutions can also meet energy needs effectively. This analysis will compare generators and alternators against two viable alternatives: solar power systems and battery storage solutions.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Generator Vs Alternator | Solar Power Systems | Battery Storage Solutions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High output at higher RPMs; generators are less efficient at low RPMs. Alternators provide full output at low RPMs. | Performance depends on sunlight availability; can be unreliable in cloudy or rainy conditions. | Performance is stable; can provide consistent power but limited by battery capacity. |
| Cost | Generally lower initial cost for generators; alternators can be more expensive due to complexity. | Higher upfront costs for panels and installation; potential long-term savings on energy bills. | Costs vary based on technology; lithium-ion batteries are more expensive but offer better efficiency. |
| Ease of Implementation | Generators are relatively easy to set up; alternators require integration into existing systems. | Installation can be complex; requires adequate space and orientation for solar panels. | Installation is straightforward, but system capacity must be carefully planned. |
| Maintenance | Generators require regular maintenance and fuel; alternators are less maintenance-intensive. | Minimal maintenance; occasional cleaning of panels needed. | Low maintenance but requires monitoring of battery health and charge cycles. |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for high-demand, short-term power needs; effective in remote locations. | Best for sustainable energy needs and long-term cost savings; effective in sunny regions. | Suitable for backup power and energy storage during off-peak times; effective in combination with renewable sources. |
What Are the Pros and Cons of Solar Power Systems?
Solar power systems harness sunlight to generate electricity, making them an eco-friendly alternative. One of the main advantages is their sustainability and low operational costs after installation. They can significantly reduce energy bills and carbon footprints. However, their performance is heavily reliant on weather conditions; cloudy days can lead to reduced efficiency, making them less reliable as a standalone power source in certain regions.
How Do Battery Storage Solutions Compare?
Battery storage solutions provide a way to store energy generated from various sources, including renewable ones like solar or wind. They offer stable performance and can supply power when demand peaks or when generation is low. The main downside is the initial investment cost, particularly for advanced lithium-ion batteries. Additionally, the capacity of batteries limits how much energy can be stored, which necessitates careful planning to ensure that they meet energy demands.
Making the Right Choice for Your Business Needs
When selecting the appropriate power generation solution, B2B buyers should carefully consider their specific energy requirements, budget constraints, and the reliability of the energy source. For businesses that require high output and immediate power, generators or alternators may be the best fit. Conversely, organizations focused on sustainability and long-term savings might find solar power systems or battery storage more advantageous. Ultimately, the choice should align with operational needs, local environmental conditions, and financial goals to ensure optimal energy management.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for generator vs alternator
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Generators and Alternators?
When evaluating generators and alternators, several technical specifications play a crucial role in determining their suitability for specific applications. Here are some essential properties to consider:
-
Voltage Rating
Voltage ratings indicate the electrical output capacity of generators and alternators, commonly measured in volts (12V or 24V). For B2B buyers, understanding voltage ratings is vital as it directly impacts the compatibility with existing electrical systems. Equipment that operates at lower voltages may not be sufficient for high-demand applications, while higher voltages can provide more robust power solutions. -
Amperage Output
Amperage, measured in amps, represents the maximum current a generator or alternator can produce. This specification is crucial for businesses, especially in industries such as construction or agriculture, where high power demands are common. Knowing the amperage output helps buyers ensure they select a unit that can sustain operational loads without risking system failure. -
Efficiency Rating
Efficiency ratings, often expressed as a percentage, indicate how effectively a generator or alternator converts mechanical energy into electrical energy. Higher efficiency translates to lower fuel consumption and operational costs, making it a critical factor for B2B buyers looking to maximize return on investment. This is particularly relevant in regions where fuel costs are significant. -
Physical Dimensions and Weight
The size and weight of generators and alternators can influence transportation, installation, and operational flexibility. Buyers must consider the physical constraints of their facilities or vehicles. Compact and lightweight units may be preferable for mobile applications, while larger, heavier units may be more suitable for stationary installations. -
Durability and Material Grade
The material used in construction, such as aluminum or steel, affects both the durability and lifespan of the unit. High-grade materials can withstand harsh environmental conditions, reducing maintenance costs and downtime. For businesses operating in extreme climates, investing in robust units can lead to long-term operational efficiency. -
Noise Level
Noise levels, typically measured in decibels (dB), are an important consideration, especially in urban or residential areas. Quiet operation may be essential for compliance with local regulations or for maintaining a comfortable working environment. B2B buyers should assess the noise specifications to avoid potential disturbances or legal issues.
Which Trade Terms Are Essential for Understanding Generators and Alternators?
Familiarity with industry terminology is crucial for effective communication and negotiation in B2B transactions. Here are some key terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce components or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. For buyers, understanding OEM products is important for ensuring compatibility and quality when sourcing parts for generators and alternators. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ helps buyers plan their purchasing strategies, especially when dealing with budget constraints or inventory management. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document issued by buyers to solicit price quotes from suppliers. This process is essential for comparing costs and ensuring that buyers receive competitive pricing on generators and alternators. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding the delivery of goods, including shipping costs, risks, and insurance. Understanding these terms is crucial for international buyers to avoid unexpected expenses and ensure smooth logistics. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the duration from placing an order to delivery. For businesses, knowing lead times helps in planning operations and inventory levels, ensuring that they have the necessary equipment available when needed. -
Warranty Period
The warranty period specifies the duration for which a manufacturer guarantees the performance of their product. A longer warranty can provide peace of mind to buyers, indicating confidence in the product’s durability and reliability.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when selecting between generators and alternators, ensuring they meet their operational needs and budget constraints.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the generator vs alternator Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Generator vs. Alternator Sector?
The global generator and alternator market is witnessing significant shifts driven by technological advancements and changing consumer demands. Key trends include the increasing reliance on renewable energy sources, which is prompting manufacturers to innovate hybrid systems that combine traditional generators with alternators. This hybrid approach is particularly relevant for international B2B buyers in regions like Africa and South America, where access to reliable electricity remains a challenge.
Emerging technologies, such as IoT integration and smart monitoring systems, are also gaining traction. These technologies allow for real-time performance tracking and predictive maintenance, enhancing operational efficiency and reducing downtime. For buyers in the Middle East and Europe, the emphasis on energy efficiency and reduced operational costs is leading to a preference for high-efficiency alternators that can deliver full output even at low engine RPMs.
Market dynamics are further influenced by fluctuating raw material prices and geopolitical factors. Buyers must stay informed about regional sourcing challenges and consider diversifying their supply chains to mitigate risks. As manufacturers strive to meet the growing demand for sustainable solutions, understanding these market dynamics will be crucial for B2B buyers looking to make informed procurement decisions.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact the Generator vs. Alternator Sector?
Sustainability is becoming a cornerstone of procurement strategies in the generator and alternator sector. The environmental impact of production processes and product lifecycle is under scrutiny, prompting buyers to prioritize suppliers who adhere to sustainable practices. This includes using eco-friendly materials and implementing waste-reduction strategies throughout the manufacturing process.
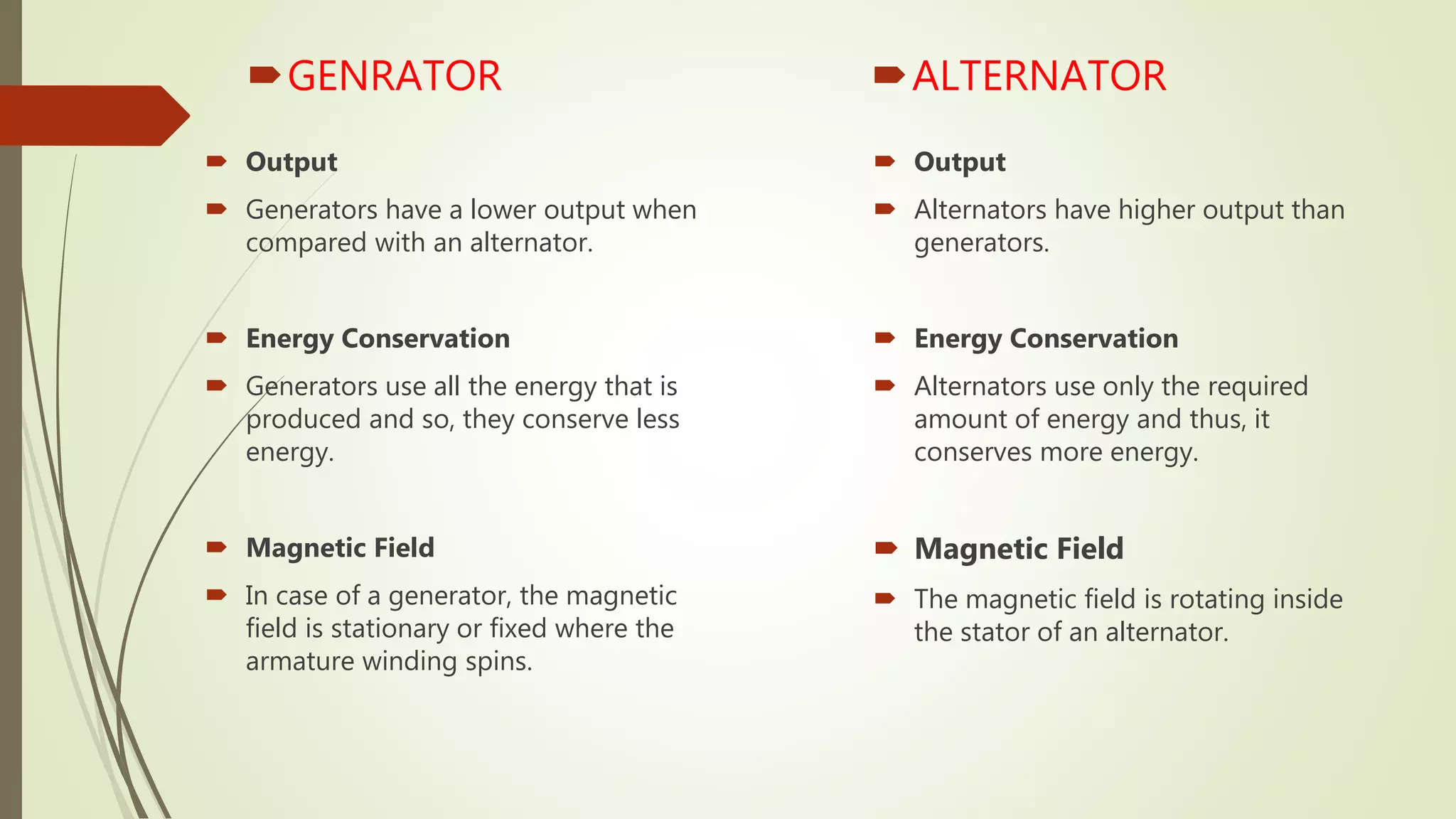
Illustrative image related to generator vs alternator
Ethical sourcing is equally important, as buyers are increasingly aware of the social implications of their procurement choices. Ensuring that suppliers comply with labor laws and environmental regulations not only aligns with corporate social responsibility goals but also enhances brand reputation. For instance, certifications like ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and ISO 45001 (Occupational Health and Safety) are becoming prerequisites for many B2B buyers when evaluating potential suppliers.
Furthermore, the rise of ‘green’ certifications for products themselves is gaining momentum. Buyers are looking for generators and alternators that meet stringent environmental standards, which can lead to reduced operational costs over time. By focusing on sustainability and ethical sourcing, businesses can drive long-term value and contribute positively to the communities in which they operate.
What Is the Brief Evolution and History of Generators and Alternators in the B2B Context?
The evolution of generators and alternators has been marked by technological advancements that have transformed their design and functionality. Initially, generators were the primary source of electrical power in various applications, including aviation and automotive. However, their limitations—such as the inability to produce full output at low RPMs—led to the development of alternators.
By the mid-20th century, alternators began to replace generators in many sectors due to their superior performance and reliability. Their ability to generate power at lower speeds and maintain efficiency made them particularly appealing for modern applications, including aviation, automotive, and industrial uses.
Today, the sector is characterized by ongoing innovations, including smart technology integration and hybrid systems, reflecting the dynamic needs of B2B buyers. Understanding this evolution is vital for international buyers who seek reliable and efficient power solutions tailored to their specific industry requirements.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of generator vs alternator
-
How do I choose between a generator and an alternator for my business needs?
Choosing between a generator and an alternator largely depends on your specific application and power requirements. Generators are typically better for applications needing consistent power output at higher RPMs, while alternators excel in scenarios requiring power at lower RPMs and offer higher efficiency. Assess your operational environment, load demands, and whether you need a backup power source or a primary power supply. Additionally, consider maintenance requirements and the potential for electrical noise that may affect other systems. -
What is the best generator or alternator for a remote location?
For remote locations, a generator is often the best choice due to its ability to produce power independently of a battery system. Diesel generators are particularly popular for their durability and long run times, making them suitable for off-grid applications. If you need to charge batteries or operate machinery at low RPMs, a high-output alternator may also be effective, especially when paired with a reliable engine. Evaluate factors like fuel availability, maintenance access, and local climate conditions to make the best selection. -
What are the common quality assurance standards for generators and alternators?
Quality assurance standards for generators and alternators often include ISO certifications, which ensure manufacturing processes meet international quality benchmarks. Additionally, look for compliance with electrical safety standards such as CE, UL, or IEC certifications, which indicate that products meet safety and performance guidelines. Partnering with suppliers who adhere to these standards can help mitigate risks associated with product reliability and safety, particularly in regions with diverse regulatory environments. -
What should I consider when vetting suppliers for generators and alternators?
When vetting suppliers, consider their industry reputation, years of experience, and customer reviews. Request references and case studies to assess their capability to meet your specific needs. Verify their certifications and compliance with international quality standards. It’s also wise to inquire about their supply chain stability, lead times, and after-sales support. Engaging in direct communication can help gauge their responsiveness and willingness to customize solutions for your business. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQ) for generators and alternators?
Minimum order quantities (MOQ) can vary significantly based on the supplier, type of equipment, and customization requirements. Many manufacturers have an MOQ ranging from 10 to 50 units for standard products. However, if you are considering customized solutions, the MOQ may increase. It’s essential to discuss your specific needs with potential suppliers to negotiate favorable terms while ensuring you receive the right quantity for your operational demands. -
What payment terms are commonly offered by suppliers of generators and alternators?
Payment terms can vary widely among suppliers but typically include options such as upfront deposits (20-50%), net 30, or net 60 payment plans. Some suppliers may offer financing options or credit terms based on your business history. It’s advisable to clarify all payment conditions upfront, including any additional fees for international transactions. Building a good relationship with your supplier can lead to more flexible terms in the future. -
How can I ensure timely logistics for generators and alternators?
To ensure timely logistics, work closely with suppliers who have established shipping protocols and partnerships with reliable freight carriers. Discuss lead times and delivery schedules during the ordering process to align expectations. Consider the logistics of customs clearance, especially when importing equipment into regions with strict regulations. Utilizing local distribution centers or warehouses may also help reduce shipping times and costs. -
What customization options are available for generators and alternators?
Customization options for generators and alternators can include modifications to voltage output, size, fuel type, and control systems. Some suppliers may also offer bespoke solutions tailored to specific industry needs, such as noise reduction features or enhanced weatherproofing for outdoor use. Engage in discussions with suppliers about your unique requirements to explore all available customization opportunities, ensuring the equipment meets your operational standards effectively.
Top 6 Generator Vs Alternator Manufacturers & Suppliers List
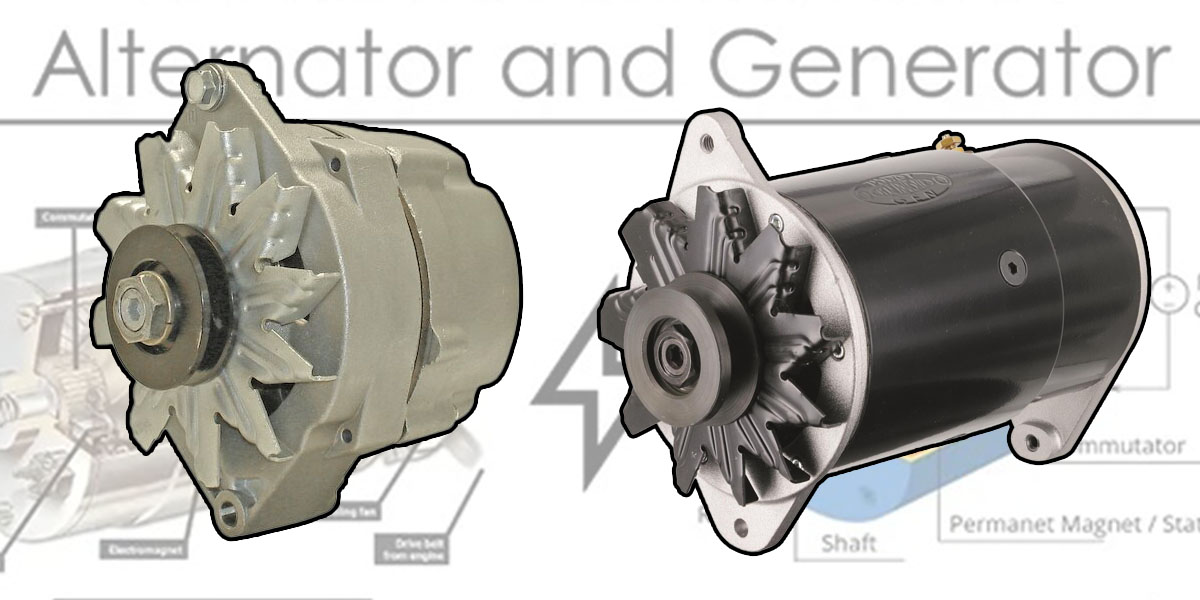
1. Reddit – Key Differences Between Generators and Alternators
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Generators and alternators are both devices that generate electricity, but they have key differences. An alternator is a specific type of generator that produces alternating current (AC), while a generator can produce either AC or direct current (DC). Alternators are commonly used in automobiles to power electrical systems and charge the battery. They typically have more magnets than standard gene…
2. Speedway Motors – High-Efficiency Alternators
Domain: speedwaymotors.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Alternators are more efficient and reliable than generators, capable of providing adequate charging for modern demands. Generators were used in early cars but struggled with current demands from modern electrical accessories. Alternators convert mechanical energy into electrical energy by rotating a magnetic field inside the conductor, producing alternating current (AC) that is then converted to d…
3. Yesterday’s Tractors – Generators vs. Alternators
Domain: forums.yesterdaystractors.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Generators and alternators are both used in tractors, with key differences highlighted in user discussions. Generators are more tolerant of reverse polarity and wrong voltage jump-starting errors, but require frequent maintenance. Alternators are noted for being virtually trouble-free, charging batteries better at lower RPMs, and supporting brighter lights. Users report that alternators recharge b…
4. Byju’s – Alternators vs. Generators
Domain: byjus.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: 1. Definition: An alternator converts mechanical energy into AC electrical energy, while a generator converts mechanical energy to either AC or DC electrical energy. 2. Output Current: Alternators induce alternating current; generators can generate either alternating or direct current. 3. Energy Efficiency: Alternators are more efficient than generators. 4. Output: Alternators have a higher output…
5. Ask A CFI – Generators vs. Alternators Explained
Domain: askacfi.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: Key differences between a generator and an alternator include: 1. Current Creation: Generators create electricity by moving a wire armature within a fixed magnetic field, while alternators have a spinning magnetic field in a series of windings called a stator. 2. Efficiency: Alternators are more efficient due to direct wiring to output points and smoother electrical output from three separate wind…
6. Facebook – Alternator vs Generator
Domain: facebook.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: This company, Facebook – Alternator vs Generator, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for generator vs alternator
What are the Key Takeaways for B2B Buyers Considering Generators vs. Alternators?
In the competitive landscape of power solutions, understanding the distinct advantages and limitations of generators and alternators is crucial for informed decision-making. Alternators offer superior efficiency, producing full-rated output at lower RPMs, making them ideal for modern applications that demand consistent electrical supply. Conversely, generators, while heavier and requiring more maintenance, can function even with a dead battery, presenting a unique advantage in specific scenarios.
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your Procurement Process?
Strategic sourcing plays a pivotal role in optimizing procurement for power generation systems. By leveraging market intelligence and supplier relationships, international buyers can secure better pricing, quality, and delivery terms. Assessing regional needs—particularly in dynamic markets like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—enables organizations to align their sourcing strategies with local operational requirements and regulatory standards.
What’s Next for International Buyers in Power Solutions?
As the demand for reliable power continues to rise globally, now is the time for B2B buyers to evaluate their sourcing strategies for generators and alternators. Investing in quality and reliability today will pay dividends in operational efficiency tomorrow. Engage with trusted suppliers, explore advanced technologies, and consider the long-term impact of your choices. The future of power solutions is bright—ensure your organization is at the forefront by making informed, strategic decisions.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.