Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for generator and alternator
In the ever-evolving landscape of global commerce, sourcing reliable generators and alternators presents a significant challenge for B2B buyers. These critical devices are essential for a myriad of applications, from powering remote construction sites in Africa to supporting industrial operations in Germany. Understanding the differences between generators and alternators, along with their specific applications, is vital for making informed purchasing decisions.
This comprehensive guide delves into the various types of generators and alternators, their operational efficiencies, and the unique requirements of different markets, including those in South America and the Middle East. We explore essential factors such as supplier vetting, cost analysis, and maintenance considerations, equipping you with the knowledge needed to navigate this complex market landscape.
By highlighting the nuances of AC and DC outputs, energy efficiency, and application-specific requirements, this guide empowers international B2B buyers to make strategic choices that optimize operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness. Whether you are in Brazil seeking robust solutions for power generation or in Europe looking for energy-efficient alternatives, this resource will help you confidently approach your procurement strategy, ensuring that you select the best generator or alternator to meet your business needs.
Table Of Contents
- Top 2 Generator And Alternator Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for generator and alternator
- Understanding generator and alternator Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of generator and alternator
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘generator and alternator’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for generator and alternator
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for generator and alternator
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘generator and alternator’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for generator and alternator Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing generator and alternator With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for generator and alternator
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the generator and alternator Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of generator and alternator
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for generator and alternator
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Understanding generator and alternator Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC Alternator | Converts mechanical energy to AC; stationary armature. | Automotive, industrial power generation. | Pros: Efficient, compact, low maintenance. Cons: Not suitable for charging dead batteries. |
| DC Generator | Converts mechanical energy to DC; rotating armature. | Battery charging, electroplating, welding. | Pros: Can charge dead batteries, stable output. Cons: Less efficient, larger size. |
| Synchronous Generator | Operates at a constant speed; produces AC. | Power plants, renewable energy systems. | Pros: High efficiency, stable voltage output. Cons: Requires precise speed control. |
| Induction Generator | Relies on rotor speed exceeding synchronous speed. | Wind turbines, small-scale power generation. | Pros: Simple design, cost-effective. Cons: Limited to specific applications, lower output. |
| Portable Generator | Compact, fuel-powered; designed for mobility. | Construction sites, outdoor events, emergency power. | Pros: Versatile, easy to transport. Cons: Limited run time, fuel dependency. |
What are the Characteristics of AC Alternators and Their Suitability for B2B Buyers?
AC alternators are vital in industries requiring reliable and efficient power generation. They convert mechanical energy into alternating current, utilizing a stationary armature, which minimizes wear and maintenance. Commonly used in automotive applications, they are ideal for businesses focused on efficiency and energy conservation. When purchasing, buyers should consider output capacity, efficiency ratings, and compatibility with existing systems.
How Do DC Generators Function and What Are Their Key B2B Applications?
DC generators are designed to convert mechanical energy into direct current, making them suitable for applications like battery charging and electroplating. They feature a rotating armature, which allows for a stable output. Businesses in sectors such as construction or automotive repair will find DC generators particularly useful for charging batteries and providing power for tools. When selecting a DC generator, factors like output voltage, size, and maintenance requirements should be prioritized.
What Makes Synchronous Generators a Preferred Choice in Power Plants?
Synchronous generators operate at a constant speed and are primarily used in large-scale power generation, such as in power plants. They provide stable voltage and high efficiency, making them ideal for renewable energy systems. For B2B buyers, the key considerations when investing in synchronous generators include installation costs, the need for precise speed control, and the capacity to integrate with grid systems, ensuring reliable energy delivery.
Why Are Induction Generators Gaining Popularity in Renewable Energy?
Induction generators are characterized by their ability to operate when the rotor speed exceeds synchronous speed, making them suitable for wind turbines and small-scale power generation. Their simple design and cost-effectiveness appeal to businesses looking to invest in renewable energy solutions. Buyers should assess the generator’s power output capabilities and its adaptability to varying wind conditions, ensuring it meets their operational needs.
What Are the Benefits and Limitations of Portable Generators for B2B Use?
Portable generators are designed for mobility and convenience, making them ideal for construction sites, outdoor events, and emergency power needs. They typically run on fuel and can be easily transported, providing versatility for various applications. However, buyers should consider the limited run time and fuel dependency when selecting a portable generator, as these factors can impact operational efficiency during extended use.
Key Industrial Applications of generator and alternator
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of generator and alternator | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Construction | Portable power generation for tools and machinery | Ensures uninterrupted work on-site, enhancing productivity | Reliability, fuel efficiency, and noise levels are critical. |
| Agriculture | Backup power for irrigation systems and farm operations | Reduces downtime during critical planting and harvesting periods | Compatibility with existing systems and maintenance support. |
| Telecommunications | Power supply for cell towers and data centers | Maintains network reliability and service continuity | Sourcing durable units with remote monitoring capabilities. |
| Mining | Power for remote mining operations and equipment | Supports operations in off-grid locations, improving operational efficiency | Consideration for environmental regulations and ruggedness. |
| Healthcare | Emergency power for hospitals and clinics | Ensures patient safety and operational continuity during outages | Compliance with health regulations and ease of maintenance. |
How Are Generators and Alternators Used in the Construction Industry?
In the construction sector, generators provide portable power for tools and heavy machinery, ensuring that work can continue without interruption. This is particularly vital in remote locations where access to the electrical grid may be limited or non-existent. Buyers should prioritize reliability and fuel efficiency when sourcing generators, as these factors directly impact operational costs and project timelines. Additionally, noise levels are a concern, especially in residential areas, making quieter models preferable.
What Role Do Generators and Alternators Play in Agriculture?
Generators and alternators are crucial in agriculture, particularly for irrigation systems and other farming operations that require reliable power. During critical planting and harvesting periods, any downtime can lead to significant financial losses. International buyers should look for generators that can seamlessly integrate with existing agricultural systems and provide robust maintenance support. The ability to operate efficiently in diverse environmental conditions is also a key consideration.
How Are Generators and Alternators Essential for Telecommunications?
In telecommunications, generators are used to ensure a constant power supply for cell towers and data centers, which is vital for maintaining network reliability. Any power disruption can lead to service outages, affecting customer satisfaction and business revenue. Companies sourcing these systems should consider durability and remote monitoring capabilities, allowing for proactive maintenance and reduced downtime. Compliance with local regulations regarding emissions and noise is also essential.
Why Are Generators and Alternators Important in Mining?
Mining operations often take place in remote areas where traditional power sources are unavailable. Generators provide the necessary electricity for equipment and facilities, enhancing operational efficiency. Buyers in this sector should consider the ruggedness of the units and their compliance with environmental regulations, as mining activities can be heavily scrutinized. Ensuring that the generator can withstand harsh conditions and provide consistent power is crucial for uninterrupted operations.
How Do Generators and Alternators Support Healthcare Facilities?
In healthcare, generators are vital for providing emergency power to hospitals and clinics, ensuring that critical medical equipment remains operational during outages. This capability directly impacts patient safety and the overall effectiveness of healthcare services. When sourcing generators for this sector, compliance with health regulations is paramount, along with ease of maintenance to ensure readiness during emergencies. Reliability and quick response times are key attributes that buyers should prioritize.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘generator and alternator’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Inconsistent Power Supply Disrupting Operations
The Problem: Many businesses in regions with unstable electricity supply face frequent power outages, leading to production halts and financial losses. For instance, manufacturing plants in Africa may experience daily interruptions, which can affect everything from machinery operation to lighting. This inconsistency not only disrupts workflow but can also damage sensitive equipment that relies on a steady power supply. B2B buyers are often caught between the need for reliable energy sources and the high costs of alternative solutions.
The Solution: To mitigate this issue, B2B buyers should consider investing in high-capacity generators that can be tailored to specific operational needs. When selecting a generator, it’s crucial to conduct a thorough load analysis to determine the total power requirements of the facility. Buyers should look for generators with features such as automatic voltage regulation (AVR) to ensure stable output and avoid equipment damage. Additionally, establishing a regular maintenance schedule can enhance the longevity and reliability of the generator, ensuring it performs optimally during critical times. Partnering with suppliers who provide comprehensive after-sales support and service can further secure a reliable power solution.
Scenario 2: High Operating Costs Due to Inefficient Energy Use
The Problem: Businesses relying on traditional generators often face high operational costs due to fuel inefficiency. This is especially prevalent in industries like construction or agriculture, where equipment must run for extended periods. For instance, a construction firm in Brazil may find that their older generator consumes excessive diesel, leading to significant monthly fuel expenditures. This inefficiency can erode profit margins and complicate budget forecasts.
The Solution: Transitioning to modern, energy-efficient alternators can significantly reduce operating costs. B2B buyers should look for alternators that feature advanced energy management systems, which optimize power output based on real-time demand. Choosing an alternator with a high efficiency rating not only conserves energy but also minimizes fuel consumption. Additionally, implementing a monitoring system that tracks energy usage can help identify patterns and further reduce waste. Collaborating with suppliers who offer insights into energy-efficient models and best practices can help organizations make informed purchasing decisions that align with their long-term financial goals.
Scenario 3: Difficulty in Sourcing Reliable Parts and Support
The Problem: Sourcing reliable components and support for generators and alternators can be a significant challenge for B2B buyers, particularly in remote locations. Companies may find themselves struggling with downtime due to the unavailability of replacement parts or inadequate technical support. For example, a mining operation in the Middle East could experience significant delays if a generator part fails, and local suppliers are unable to provide quick replacements or repairs.
The Solution: To address this pain point, businesses should establish relationships with reputable suppliers that offer comprehensive service packages, including parts availability and technical support. It is advisable for buyers to engage with suppliers who have a proven track record in the region and can provide rapid response times for repairs and maintenance. Additionally, investing in a stock of critical spare parts can significantly reduce downtime during failures. Buyers should also consider participating in training programs offered by manufacturers to ensure their staff can perform basic maintenance and troubleshooting, which can further minimize reliance on external support. By prioritizing suppliers who understand the unique challenges of their industry, businesses can enhance their operational resilience and ensure sustained productivity.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for generator and alternator
What Are the Common Materials Used in Generators and Alternators?
When selecting materials for generators and alternators, it is crucial to consider their properties, performance, and suitability for specific applications. Here, we analyze four common materials: copper, aluminum, steel, and composite materials, focusing on their key properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for international B2B buyers.
How Does Copper Perform in Generators and Alternators?
Copper is widely recognized for its excellent electrical conductivity, making it a preferred choice for windings in both generators and alternators. Its thermal conductivity allows for efficient heat dissipation, which is critical in high-performance applications.
Pros: Copper’s high durability and resistance to corrosion enhance the longevity of electrical components. It is also relatively easy to manufacture into various forms, including wires and coils.
Cons: The primary drawback of copper is its cost, which is significantly higher than alternatives like aluminum. Additionally, its weight can be a disadvantage in applications where weight reduction is crucial.
Impact on Application: Copper is compatible with a variety of media, including oils and coolants, which are often used in generator and alternator systems.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM B170 (for copper wire) is essential. Buyers from regions like Europe may also need to consider RoHS compliance for environmental regulations.
What Role Does Aluminum Play in Generators and Alternators?
Aluminum is a lightweight alternative to copper, often used in windings and housing components. Its lower density makes it an attractive option for applications where weight savings are critical.
Pros: Aluminum is less expensive than copper and offers good conductivity, albeit lower than copper. It is also resistant to corrosion, particularly when anodized.
Cons: The main limitations of aluminum include its lower mechanical strength compared to copper and its tendency to oxidize, which can affect conductivity if not properly treated.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is suitable for environments with moderate temperatures and pressures but may not perform as well under extreme conditions.

Illustrative image related to generator and alternator
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that aluminum components meet relevant standards, such as DIN EN 573 for aluminum alloys, and consider the implications of material sourcing in terms of sustainability.
How Does Steel Contribute to Generator and Alternator Performance?
Steel is commonly used for structural components, including frames and housings, due to its high strength and durability.
Pros: Steel provides excellent mechanical strength and can withstand high temperatures and pressures. It is also relatively cost-effective compared to non-ferrous metals.
Cons: Steel is prone to corrosion if not properly coated or treated, which can lead to failure in harsh environments. Additionally, its weight can be a disadvantage in portable applications.
Impact on Application: Steel is suitable for applications where structural integrity is paramount, but care must be taken to protect against environmental factors.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM A36 for structural steel is essential. Buyers from regions with high humidity, like parts of Africa and South America, should prioritize corrosion-resistant coatings.
What Are the Advantages of Composite Materials in Generators and Alternators?
Composite materials, including fiberglass and carbon fiber, are increasingly used in generator and alternator applications due to their unique properties.
Pros: Composites are lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and can be engineered for specific performance characteristics. They also offer excellent thermal stability.
Cons: The primary drawback is the higher manufacturing complexity and cost associated with composites. Additionally, they may not provide the same level of electrical conductivity as metals.
Impact on Application: Composites are particularly beneficial in applications requiring weight reduction and resistance to environmental degradation.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with relevant standards, such as ASTM D3039 for composite materials, and consider the implications of sourcing and manufacturing in their regions.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Generators and Alternators
| Material | Typical Use Case for generator and alternator | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Copper | Windings and electrical connections | Excellent electrical conductivity | High cost | High |
| Aluminum | Windings and lightweight components | Cost-effective and lightweight | Lower strength and oxidation risk | Medium |
| Steel | Structural components and housings | High strength and durability | Prone to corrosion | Medium |
| Composite | Housing and specialized components | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Higher manufacturing complexity | High |
This strategic material selection guide provides a comprehensive overview of the materials used in generators and alternators, enabling B2B buyers to make informed decisions based on performance, cost, and compliance considerations relevant to their specific markets.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for generator and alternator
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Generators and Alternators?
The manufacturing processes for generators and alternators encompass several critical stages, ensuring that the final product meets the required performance and safety standards. Here are the primary stages involved:
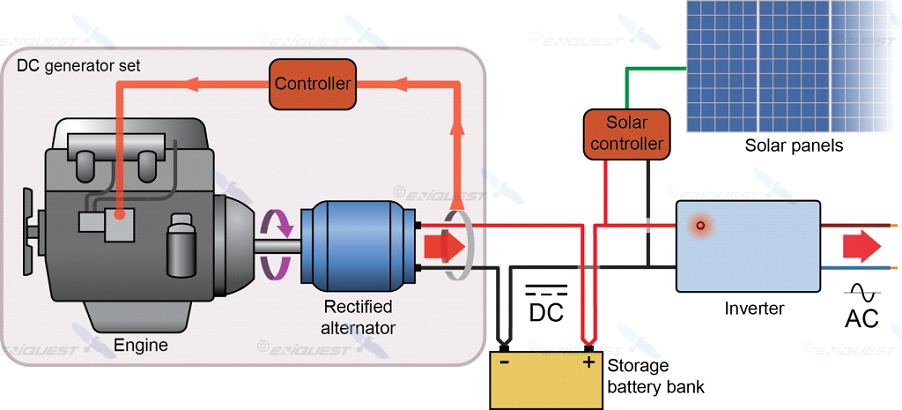
Illustrative image related to generator and alternator
Material Preparation: What Materials Are Used in Generators and Alternators?
The manufacturing journey begins with the careful selection of materials. Key components include:
- Copper and Aluminum: Used for windings due to their excellent electrical conductivity.
- Steel and Iron: Employed for the stator and rotor cores, which need to withstand high magnetic fields.
- Insulating Materials: Such as varnishes and resins, are crucial for electrical insulation and thermal stability.
These materials are often sourced based on international quality standards to ensure durability and performance.
How Are Generators and Alternators Formed?
The forming process involves several techniques to shape the raw materials into functional components:
- Winding: Conductors are wound into coils, either by hand or using automated winding machines. Precision in this step is vital for electrical performance.
- Stamping: Steel sheets are stamped into the required shapes for the stator and rotor. This process often utilizes CNC machines for accuracy and repeatability.
- Casting: For certain components, such as the frame or housing, casting techniques may be employed to create robust structures.
Each forming method is designed to ensure the integrity of the parts, which is critical for the overall efficiency and reliability of the generator or alternator.
What Is the Assembly Process for Generators and Alternators?
The assembly stage integrates all individual components into a cohesive unit. This process typically follows these steps:
- Component Assembly: The stator and rotor are assembled, ensuring that all windings and magnetic parts are correctly positioned.
- Electrical Connections: Connections are made using soldering or crimping techniques to ensure reliable electrical conductivity.
- Final Assembly: The assembled components are housed within the outer casing, which protects them from environmental factors.
Quality checks at this stage help detect issues before moving on to the finishing processes.
What Finishing Techniques Are Applied in Manufacturing Generators and Alternators?
Finishing processes enhance the functionality and aesthetic appeal of generators and alternators. Common techniques include:
- Painting and Coating: Protective coatings are applied to prevent corrosion and wear. This is especially crucial for outdoor units exposed to harsh environments.
- Balancing: Rotors are dynamically balanced to reduce vibration during operation, which can lead to premature wear or failure.
- Testing: Each unit undergoes rigorous testing to ensure it meets performance specifications.
These finishing touches contribute to the longevity and reliability of the products, making them suitable for diverse applications.
What Are the Quality Assurance Standards for Generators and Alternators?
Quality assurance (QA) in the manufacturing of generators and alternators is critical to ensure that products meet international and industry-specific standards. Key standards include:
- ISO 9001: A globally recognized standard for quality management systems that ensures consistent quality across production.
- CE Marking: Indicates compliance with EU safety, health, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: Relevant for generators and alternators used in the oil and gas industry, ensuring they meet specific operational requirements.
Adhering to these standards not only assures product quality but also enhances marketability in international markets.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) is integral to maintaining product standards throughout the manufacturing process. Common QC checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Raw materials and components are inspected upon arrival to ensure they meet specified criteria.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Ongoing inspections during manufacturing help identify defects early, preventing costly rework.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): The finished product undergoes comprehensive testing to verify that it meets all specifications before shipment.
Implementing these QC checkpoints is essential for maintaining the integrity of the manufacturing process and ensuring customer satisfaction.

Illustrative image related to generator and alternator
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used for Generators and Alternators?
Various testing methods are employed to validate the performance and safety of generators and alternators:
- Electrical Testing: This includes insulation resistance tests, continuity tests, and load tests to ensure electrical integrity.
- Mechanical Testing: Vibration analysis and thermal imaging can identify potential issues in the physical structure and operational efficiency.
- Performance Testing: Units are tested under simulated operating conditions to evaluate their output and efficiency.
These tests provide critical data that can be used to make necessary adjustments before the product reaches the market.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international B2B buyers, particularly in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying supplier quality control is paramount. Buyers can adopt several strategies:
- Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to assess the manufacturing processes, quality control measures, and adherence to standards firsthand.
- Requesting Quality Reports: Suppliers should provide detailed reports on their QC processes, including results from testing and compliance with international standards.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent inspection agencies can provide unbiased assessments of the supplier’s quality control practices.
These verification methods not only build trust but also ensure that the products received meet the expected standards.
What Quality Control Nuances Should International Buyers Consider?
International buyers must be aware of specific nuances when dealing with quality control in different regions:
- Regulatory Differences: Compliance requirements can vary significantly between countries. Understanding local regulations is crucial for ensuring that products meet all necessary standards.
- Cultural Variations: Attitudes toward quality and compliance may differ. Building strong relationships with suppliers can enhance communication and cooperation regarding quality expectations.
- Logistical Challenges: Shipping and customs can impact the delivery of quality products. Buyers should work closely with suppliers to ensure timely and compliant shipments.
By considering these factors, B2B buyers can effectively navigate the complexities of international sourcing, ensuring they receive high-quality generators and alternators tailored to their needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘generator and alternator’
In the competitive landscape of B2B procurement, sourcing generators and alternators requires a structured approach to ensure you acquire the right equipment for your operational needs. This checklist is designed to guide you through the essential steps, helping you make informed decisions and establish successful supplier relationships.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outline the technical requirements for the generators or alternators you need. Consider factors such as power output (measured in kW or kVA), fuel type (diesel, gasoline, or renewable sources), and whether you require AC or DC output. This clarity will help you communicate effectively with suppliers and ensure you receive equipment that meets your operational demands.
Step 2: Research Market Trends and Innovations
Stay informed about the latest trends and technological advancements in the generator and alternator market. Understanding innovations, such as energy-efficient designs or smart technology integration, can influence your purchasing decisions. This knowledge will also enable you to assess whether potential suppliers are aligned with contemporary industry standards.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before making any commitments, conduct thorough evaluations of potential suppliers. Review their company profiles, request case studies, and seek references from other businesses in your industry or region. Pay attention to their reputation in the market, customer service quality, and after-sales support, as these factors can significantly impact your long-term satisfaction.
Step 4: Verify Supplier Certifications and Compliance
Ensure that the suppliers you consider hold relevant certifications and comply with international standards. Look for ISO certifications, safety compliance (like CE or UL), and environmental standards (such as ISO 14001). Compliance not only reflects the quality of their products but also assures you that they adhere to safety and environmental regulations.
Step 5: Request Detailed Quotations
Once you have shortlisted potential suppliers, request detailed quotations. These should include pricing, warranty terms, delivery timelines, and payment options. Comparing these details will help you identify the best value proposition and negotiate better terms. Be sure to clarify any hidden costs or additional fees that might arise during the procurement process.
Step 6: Assess Technical Support and Maintenance Services
Investigate the level of technical support and maintenance services offered by your potential suppliers. This is crucial, as reliable support can minimize downtime and extend the lifespan of your equipment. Ensure they provide comprehensive service packages, including installation, routine maintenance, and emergency repairs.
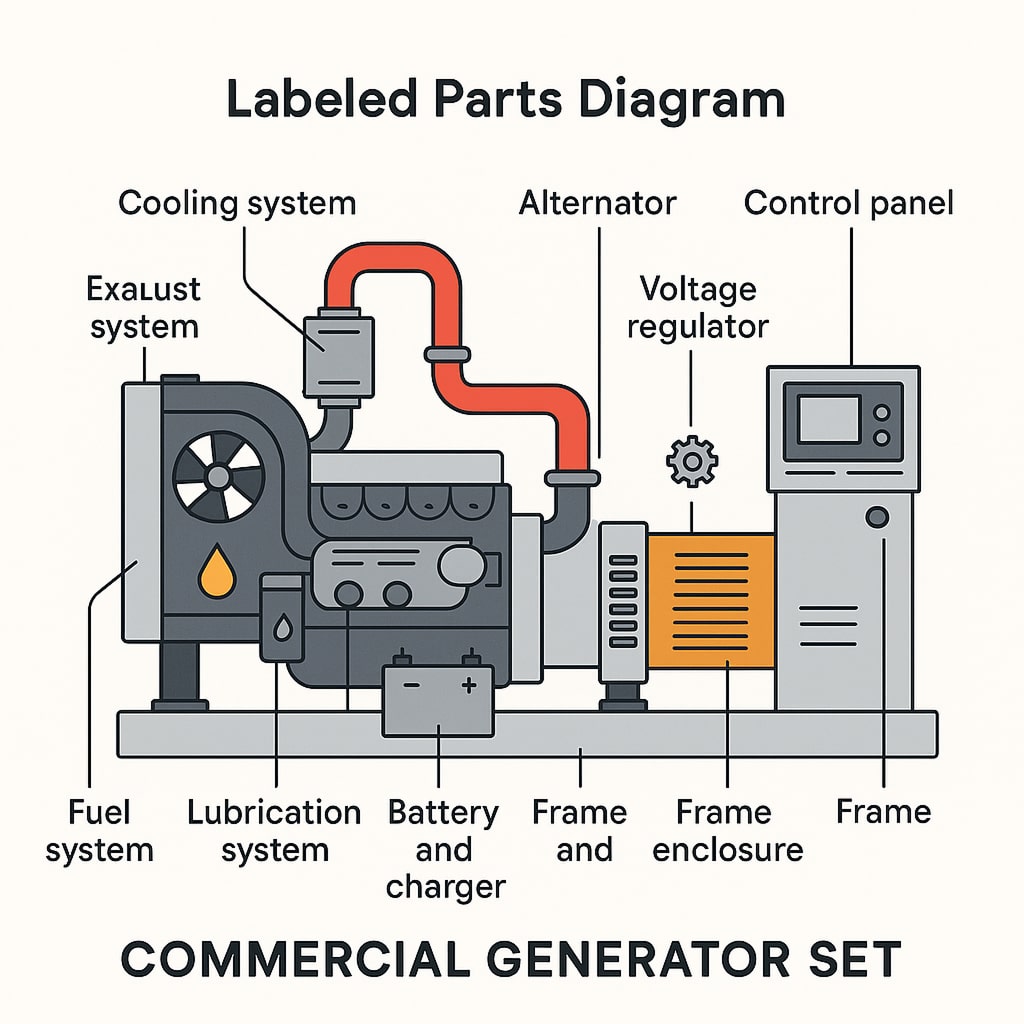
Illustrative image related to generator and alternator
Step 7: Finalize the Contract and Terms of Agreement
Before concluding your purchase, review the contract thoroughly. Ensure all terms and conditions are clear, including delivery schedules, payment terms, warranties, and liability clauses. A well-structured agreement protects both parties and sets the foundation for a successful business relationship.
By following this practical sourcing checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of procuring generators and alternators effectively, ensuring they select the right equipment to meet their operational needs while fostering strong supplier partnerships.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for generator and alternator Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components Involved in Sourcing Generators and Alternators?
When sourcing generators and alternators, understanding the detailed cost structure is essential for international B2B buyers. The main cost components include:
-
Materials: The quality and type of materials significantly influence costs. For alternators, high-grade copper and aluminum are commonly used in windings, while generators may require durable steel for the casing. Prices can fluctuate based on global commodity markets.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is crucial for assembly and quality assurance. Regions with lower labor costs, such as parts of Africa and South America, may offer competitive pricing, but buyers must ensure that quality standards are met.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to factory operations, utilities, and administrative expenses. Efficient manufacturing processes can reduce overhead, impacting overall pricing.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling may be necessary for specialized designs or larger orders. Initial tooling costs can be significant but may be amortized over higher volume orders.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous QC processes are vital to ensure reliability and efficiency. The costs associated with testing and compliance certification should not be overlooked, especially for markets with stringent regulations.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs vary depending on the origin of the products and the destination. Incoterms play a critical role in determining who bears these costs and risks during transport.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a margin to cover costs and generate profit. Understanding the typical margin in the industry can help buyers assess whether they are receiving competitive pricing.
How Do Volume and Customization Affect Generator and Alternator Pricing?
Volume and customization are significant price influencers in the B2B landscape.
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Larger orders often lead to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should negotiate MOQs to leverage bulk purchasing advantages, especially when sourcing for large projects or tenders.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom specifications can lead to increased costs due to unique tooling or material requirements. However, customization can also provide significant value by ensuring that the product meets specific operational needs, which may justify a higher price.
What Quality and Certification Factors Should International Buyers Consider?
Quality and certifications are critical when sourcing generators and alternators, particularly in regions with stringent compliance requirements.
-
Materials and Quality Standards: Buyers should ensure that suppliers adhere to international quality standards, such as ISO certifications. This is particularly important for buyers in Europe and the Middle East, where compliance with safety and performance standards is mandatory.
-
Supplier Reputation: Evaluating supplier reputation and track record is crucial. Reliable suppliers often have established quality assurance processes and can provide certifications that attest to their product’s performance.
What Tips Can Help B2B Buyers Negotiate Better Pricing for Generators and Alternators?
Effective negotiation strategies can lead to better pricing and terms:
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Focus on the TCO rather than just the initial purchase price. Consider maintenance, energy efficiency, and lifespan, as these factors can significantly affect long-term costs.
-
Leverage Competitive Quotes: Obtain multiple quotes from different suppliers to understand market pricing. This can provide leverage in negotiations.
-
Be Aware of Pricing Nuances for International Markets: Currency fluctuations, import tariffs, and local market conditions can impact pricing. Buyers in regions like Africa and South America should be particularly mindful of these factors when negotiating contracts.
What Should Buyers Keep in Mind Regarding Pricing Disclaimers?
It’s important to recognize that prices quoted for generators and alternators may vary significantly based on market conditions, exchange rates, and specific supplier factors. Therefore, always seek updated quotes and verify all pricing details before making purchasing decisions. By understanding the complexities of cost components and pricing influencers, B2B buyers can make informed choices that align with their operational needs and budgetary constraints.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing generator and alternator With Other Solutions
In the landscape of power generation, businesses often seek alternatives to traditional generators and alternators. These alternatives can offer varied performance, cost efficiency, and ease of implementation, thereby influencing the decision-making process for B2B buyers. Below, we compare generators and alternators against two viable alternative solutions: solar power systems and battery storage systems.
| Comparison Aspect | Generator And Alternator | Solar Power Systems | Battery Storage Systems |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High output, efficient for large-scale electricity | Variable output based on sunlight availability | Consistent output, dependent on charge levels |
| Cost | High initial investment, ongoing fuel and maintenance costs | High initial setup costs, low operational costs | Moderate to high initial investment, low maintenance costs |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires significant space and installation expertise | Requires space for panels, installation can be complex | Easier to implement with modular designs, but needs space for charging |
| Maintenance | Requires regular maintenance and fuel supply | Low maintenance, occasional cleaning of panels | Minimal maintenance, monitoring of charge cycles needed |
| Best Use Case | Industrial settings needing reliable power | Remote locations, eco-conscious businesses, and grid-tied systems | Backup power for homes and businesses, integration with renewable sources |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Solar Power Systems?
Solar power systems harness sunlight to generate electricity, providing a renewable and eco-friendly alternative to traditional generators and alternators. One of the main advantages of solar power is its low operational cost once installed, as it relies on free sunlight. However, the performance can be variable, heavily dependent on weather conditions and time of day, which may not suit industries requiring consistent power supply. The initial investment for solar panels can be high, but government incentives may alleviate some of these costs.
How Do Battery Storage Systems Compare?
Battery storage systems store electricity for later use, providing a reliable backup power source. They are particularly beneficial for businesses that experience power interruptions or require off-grid solutions. The modular nature of battery systems allows for flexible installation, making them easier to implement in various settings. While the initial costs can be moderate to high, operational expenses are typically low, as maintenance is minimal. However, battery systems may not provide the same high output as generators and alternators, especially for large-scale energy needs.
Conclusion: How Should B2B Buyers Choose the Right Power Solution?
When selecting between generators, alternators, and their alternatives, B2B buyers must assess their specific needs, including performance requirements, budget constraints, and space availability. For industries that demand consistent and high-output power, traditional generators or alternators may be the best fit. Conversely, businesses focused on sustainability or those operating in remote areas may find solar power systems to be a more suitable option. Battery storage systems offer flexibility and reliability, making them ideal for backup solutions. Ultimately, understanding the unique advantages and limitations of each option will enable buyers to make informed decisions that align with their operational goals and environmental considerations.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for generator and alternator
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Generators and Alternators?
When considering generators and alternators for procurement, understanding their technical properties is essential for making informed decisions. Here are some critical specifications that B2B buyers should consider:
-
Output Voltage and Current Rating
– Definition: This specification indicates the voltage (typically in volts) and current (in amperes) that the device can produce.
– Importance: Selecting equipment with the correct output ratings is crucial for ensuring compatibility with existing systems. Over- or under-rated equipment can lead to inefficiencies or equipment failures. -
Efficiency Rating
– Definition: This measures how effectively a generator or alternator converts mechanical energy into electrical energy, usually expressed as a percentage.
– Importance: Higher efficiency means lower fuel consumption and operational costs, making it a key consideration for businesses aiming to minimize expenses while maximizing output. -
Size and Weight
– Definition: The physical dimensions and weight of the generator or alternator.
– Importance: Understanding the size and weight is vital for logistical planning, installation, and determining whether the unit will fit within existing infrastructure. Space constraints can significantly impact operational choices. -
Noise Level
– Definition: Measured in decibels (dB), this indicates the sound produced during operation.
– Importance: For businesses operating in noise-sensitive environments, such as residential areas or hospitals, selecting a quieter model can be essential for regulatory compliance and maintaining good community relations. -
Durability and Material Grade
– Definition: The materials used in the construction of the generator or alternator, often indicated by grades such as steel or aluminum.
– Importance: Higher-grade materials typically offer better resistance to wear and tear, which is crucial for longevity and reducing maintenance costs. This is particularly important in industrial applications where equipment is subjected to harsh conditions. -
RPM (Revolutions Per Minute) Range
– Definition: The operating speed of the generator or alternator, indicating how fast the rotor spins.
– Importance: Different applications require different RPM ranges. Understanding this property helps in selecting a unit that meets specific operational requirements without compromising performance.
What Are the Common Trade Terms in the Generator and Alternator Industry?
Familiarity with industry terminology can streamline communication and negotiation processes. Here are some essential trade terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Definition: A company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer.
– Importance: Identifying OEMs can help buyers ensure they are sourcing high-quality components that meet industry standards, which is crucial for reliability and performance. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– Definition: The smallest number of units that a supplier is willing to sell.
– Importance: Understanding MOQ is vital for inventory management and budgeting. It helps businesses plan their purchases and avoid excess stock or supply shortages. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– Definition: A document sent to suppliers to solicit price and terms for specific products or services.
– Importance: An RFQ is a critical step in the procurement process, allowing buyers to compare offers and make informed purchasing decisions based on price, terms, and capabilities. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Definition: A set of predefined international trade terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC).
– Importance: Familiarity with Incoterms helps businesses understand their responsibilities regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs, which is essential for international transactions and risk management. -
Lead Time
– Definition: The time it takes from placing an order until the product is delivered.
– Importance: Knowing lead times is essential for project planning and ensuring that equipment is available when needed, helping avoid delays in operations. -
Warranty Period
– Definition: The duration during which a manufacturer guarantees the performance of their product.
– Importance: A robust warranty can significantly affect the total cost of ownership. Buyers should consider warranty terms to ensure long-term reliability and support for their investment.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when purchasing generators and alternators, ensuring they select equipment that meets their operational needs while optimizing costs and efficiency.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the generator and alternator Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends in the Generator and Alternator Sector
The generator and alternator market is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing demand for reliable power supply across various sectors. Key global drivers include rapid urbanization, industrialization, and the rising need for continuous electricity supply in regions with unstable grid systems. For international B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these dynamics is essential for effective sourcing strategies.
Emerging technologies such as smart generators and advanced alternators are reshaping the landscape. These devices incorporate IoT (Internet of Things) capabilities, enabling remote monitoring and predictive maintenance. This trend is particularly relevant for businesses looking to enhance operational efficiency and minimize downtime. Furthermore, the shift toward renewable energy sources is driving the development of hybrid generators that combine traditional fossil fuels with solar or wind energy, appealing to eco-conscious buyers.
The competitive landscape is also evolving, with manufacturers increasingly focusing on customization and scalability to meet diverse customer needs. B2B buyers are advised to seek suppliers who offer flexible solutions tailored to specific operational requirements, whether for construction, mining, or agriculture. As competition intensifies, establishing long-term partnerships with reliable manufacturers will be crucial for securing favorable pricing and ensuring timely delivery.
How is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Important in the Generator and Alternator Market?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing are becoming integral to the generator and alternator sector, as businesses recognize the environmental impact of their operations. With increasing scrutiny from consumers and regulatory bodies, B2B buyers must prioritize suppliers committed to sustainable practices. This includes sourcing materials from suppliers that adhere to responsible mining and manufacturing processes, thereby reducing the carbon footprint associated with production.
Moreover, certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and the use of green materials are becoming essential criteria for evaluating suppliers. Buyers should consider partnering with manufacturers who invest in sustainable technologies, such as energy-efficient motors and recyclable materials, which not only reduce waste but also enhance the overall efficiency of the products.
In addition, the adoption of circular economy principles within the generator and alternator market encourages manufacturers to design products that are easier to repair, recycle, or upgrade. B2B buyers can leverage these sustainable practices to enhance their corporate social responsibility (CSR) initiatives, thus appealing to environmentally conscious stakeholders and customers.
How Has the Generator and Alternator Sector Evolved Over Time?
The evolution of generators and alternators can be traced back to the late 19th century when the first electrical generators were developed. Initially, these machines were large and inefficient, primarily used in industrial applications. Over the decades, advancements in technology led to the development of smaller, more efficient models, facilitating their use in residential and commercial sectors.
The introduction of the alternator in the early 20th century marked a significant milestone, as it allowed for more efficient conversion of mechanical energy into electrical energy. This innovation paved the way for widespread applications, particularly in the automotive industry, where alternators replaced generators due to their superior efficiency and reliability.
Today, the focus is on integrating digital technologies and sustainability into generator and alternator design. As the market continues to evolve, B2B buyers must remain informed about technological advancements and shifts in consumer preferences, ensuring they select products that not only meet current demands but also anticipate future trends.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of generator and alternator
-
How do I choose between a generator and an alternator for my business needs?
Choosing between a generator and an alternator depends on your specific energy requirements. If you need a reliable source of electrical energy for large-scale applications, such as powering an entire facility, a generator is ideal as it can produce both AC and DC output. Conversely, if you require a compact and efficient power supply for smaller applications, like automotive or backup systems, an alternator is preferable due to its higher efficiency and ability to generate AC power. Consider factors like load demands, energy efficiency, and space constraints when making your decision. -
What are the key factors to consider when sourcing generators and alternators internationally?
When sourcing generators and alternators from international suppliers, key factors include quality certifications, compliance with local regulations, and warranty terms. Assess the supplier’s reputation by checking reviews and references from other B2B buyers. Additionally, evaluate their ability to provide customization options, as well as the availability of spare parts and technical support. It’s also crucial to understand shipping and delivery timelines, as well as any potential tariffs or duties that could affect overall costs. -
What customization options are available for generators and alternators?
Many manufacturers offer customization options to suit your specific operational needs. Customizations can include voltage output, power capacity, size, and design features such as noise reduction or fuel type. Some suppliers may also provide tailored solutions for unique applications, such as marine or industrial use. When discussing customization, ensure clear communication of your requirements and confirm lead times for production and delivery to avoid delays. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for generators and alternators?
Minimum order quantities can vary significantly between suppliers and depend on factors such as product type and manufacturing capabilities. Typically, larger manufacturers may have higher MOQs, while smaller companies or those focused on niche markets might accommodate smaller orders. When negotiating, clarify the MOQ upfront to ensure it aligns with your purchasing strategy and budget. Additionally, inquire about flexibility for future orders as your needs grow. -
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing generators and alternators?
Payment terms can vary widely among suppliers and may include options such as upfront payment, net 30/60/90 days, or letter of credit. It’s essential to discuss and negotiate these terms before finalizing any agreements. Consider your cash flow and financing options when assessing payment terms. Additionally, ensure that the chosen payment method is secure and offers adequate protection against potential disputes or delivery issues. -
How do I ensure quality assurance when sourcing generators and alternators?
To ensure quality assurance, request samples or prototypes from suppliers before placing a bulk order. Verify that the manufacturer holds relevant certifications, such as ISO or CE, which indicate compliance with international quality standards. Additionally, consider conducting factory audits or inspections to evaluate production processes. Establish a clear quality control agreement outlining the criteria for acceptance, testing procedures, and the process for addressing defects or non-conformance. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing generators and alternators?
Logistics plays a crucial role in importing generators and alternators. Consider factors such as shipping methods, transit times, and costs associated with freight forwarding. Evaluate the supplier’s experience in international shipping and their ability to handle customs clearance. It’s also important to factor in local regulations, potential tariffs, and delivery to your final destination. Collaborating with a reliable logistics partner can streamline the process and minimize potential delays. -
What are common challenges faced when sourcing generators and alternators, and how can I mitigate them?
Common challenges include communication barriers, cultural differences, and varying quality standards. To mitigate these issues, engage with suppliers who have a proven track record in international trade and are familiar with your market. Establish clear and consistent communication channels to address any misunderstandings promptly. Additionally, consider using local representatives or intermediaries who understand both the supplier’s and buyer’s cultures and can facilitate smoother transactions.
Top 2 Generator And Alternator Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Byju’s – Alternators vs Generators
Domain: byjus.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: 1. Definition: An alternator converts mechanical energy into AC electrical energy, while a generator converts mechanical energy to either AC or DC electrical energy.
2. Output Current: Alternators induce alternating current; generators can generate either alternating or direct current.
3. Energy Efficiency: Alternators are more efficient than generators.
4. Output: Alternators have a higher output…
2. Speedway Motors – Alternators and Generators
Domain: speedwaymotors.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Alternators and generators are devices that convert mechanical energy into electrical energy for charging a car’s battery. Key differences include:
– Generators use a rotating armature inside static magnets, while alternators rotate the magnetic field inside the conductor.
– Generators are less efficient and struggle to provide adequate current for modern electrical demands, especially at low sp…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for generator and alternator
In the evolving landscape of energy solutions, understanding the nuances between generators and alternators is vital for strategic sourcing. Both devices serve critical roles in energy production, yet their applications, efficiency, and operational characteristics differ significantly. Generators provide flexibility by delivering both AC and DC power, making them suitable for diverse applications, while alternators excel in efficiency and energy conservation, particularly in automotive and renewable energy sectors.
B2B buyers must prioritize sourcing strategies that align with their specific energy needs and operational contexts. This includes evaluating supplier capabilities, understanding regional energy demands, and considering the total cost of ownership, which encompasses maintenance and efficiency factors. As markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe continue to expand, the ability to source the right technology will be key to enhancing operational reliability and sustainability.
Looking ahead, companies should embrace innovation and seek partnerships with reliable manufacturers who can provide cutting-edge solutions. By doing so, they will not only meet current energy demands but also position themselves for future growth in an increasingly competitive global marketplace. Engage with suppliers today to secure a robust energy strategy for tomorrow.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.