Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for car starter vs alternator
In the increasingly complex landscape of automotive components, understanding the distinction between car starters and alternators is crucial for international B2B buyers seeking reliable automotive parts. These two essential components serve distinct functions: the starter ignites the engine, while the alternator generates electrical power to recharge the battery and run various vehicle systems. As global markets expand, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, sourcing quality automotive parts such as starters and alternators can pose significant challenges, including supplier reliability, cost fluctuations, and varying technical specifications.
This comprehensive guide delves into the nuances of car starters and alternators, covering key topics such as their types, applications, and common signs of failure. We will provide insights into supplier vetting processes, ensuring that buyers can identify trustworthy sources that meet their quality and budget requirements. Additionally, we’ll explore cost considerations and market trends that influence purchasing decisions, equipping B2B buyers with the knowledge needed to make informed choices.
By empowering decision-makers with actionable insights and expert recommendations, this guide aims to facilitate effective sourcing strategies that enhance operational efficiency and product reliability in a competitive global market. Whether you are in Vietnam or Brazil, understanding these components will enable you to navigate the automotive parts landscape with confidence.
Table Of Contents
- Top 2 Car Starter Vs Alternator Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for car starter vs alternator
- Understanding car starter vs alternator Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of car starter vs alternator
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘car starter vs alternator’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for car starter vs alternator
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for car starter vs alternator
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘car starter vs alternator’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for car starter vs alternator Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing car starter vs alternator With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for car starter vs alternator
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the car starter vs alternator Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of car starter vs alternator
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for car starter vs alternator
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Understanding car starter vs alternator Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Starter | Traditional design; uses a solenoid to engage. | Automotive repair shops, vehicle manufacturers | Pros: Widely available, cost-effective. Cons: Limited efficiency, shorter lifespan. |
| Gear Reduction Starter | Smaller and lighter; uses gear reduction for torque. | Racing vehicles, high-performance cars | Pros: High torque output, lightweight. Cons: Higher cost, may require specific installation. |
| Permanent Magnet Alternator | Uses permanent magnets for power generation. | Electric vehicles, hybrid cars | Pros: Lightweight, efficient at low speeds. Cons: Limited output at high RPMs. |
| Brushless Alternator | No brushes; reduces wear and increases lifespan. | Commercial vehicles, heavy machinery | Pros: Longer lifespan, lower maintenance. Cons: Higher initial investment. |
| Smart Alternator | Features advanced electronics for energy management. | Luxury cars, fleet vehicles | Pros: Optimizes battery life, improves fuel efficiency. Cons: Complexity may lead to higher repair costs. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Standard Starters?
Standard starters are the most commonly used type in vehicles. They operate using a solenoid that engages the starter motor when the ignition is turned on. This design is well-established, making it easy to source and replace, which is crucial for B2B buyers in regions with high vehicle turnover. However, they tend to have a shorter lifespan due to wear and tear, making it essential for businesses to consider the long-term costs of replacement and maintenance.
How Do Gear Reduction Starters Stand Out?
Gear reduction starters are engineered for high-torque applications, making them ideal for racing and performance vehicles. They utilize gears to amplify the torque generated, which is particularly beneficial in high-performance scenarios. While they are more expensive than standard starters, their lightweight design and efficiency can justify the investment for businesses focused on performance-oriented vehicles. Buyers should evaluate their specific needs and the potential for higher performance against the initial costs.
What Makes Permanent Magnet Alternators a Smart Choice?
Permanent magnet alternators are increasingly popular in electric and hybrid vehicles. They employ permanent magnets to generate electricity, making them lightweight and efficient, especially at lower speeds. This feature is particularly appealing to B2B buyers in the growing electric vehicle market. However, their output can be limited at higher RPMs, so businesses should ensure compatibility with their vehicle types and consider the trade-offs between efficiency and performance.
Why Are Brushless Alternators Considered Advanced?
Brushless alternators eliminate the need for brushes, resulting in reduced wear and a longer lifespan. They are especially suited for commercial vehicles and heavy machinery where reliability is paramount. While the initial investment may be higher, the lower maintenance costs can lead to significant savings over time. B2B buyers should weigh the upfront costs against the long-term benefits of durability and reduced service needs.
What Are the Advantages of Smart Alternators?
Smart alternators feature advanced electronics that manage energy more effectively, optimizing battery life and improving fuel efficiency. These are particularly suitable for luxury and fleet vehicles where operational efficiency is critical. The complexity of smart alternators may lead to higher repair costs, so businesses should consider their technical capabilities and the potential need for specialized service when investing in this technology.
Key Industrial Applications of car starter vs alternator
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of car starter vs alternator | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive Manufacturing | Production of vehicles and automotive parts | Ensures reliable vehicle assembly and performance reliability | Quality certifications, compatibility with various vehicle models, and after-sales support. |
| Transportation | Fleet management for commercial vehicles | Enhances operational efficiency and reduces downtime | Durability, cost-effectiveness, and availability of spare parts. |
| Agriculture | Agricultural machinery and equipment | Improves reliability in remote operations and productivity | Resistance to environmental conditions and ease of maintenance. |
| Construction | Heavy machinery and equipment | Ensures uninterrupted operations on job sites | Robustness, compliance with safety standards, and performance under load. |
| Renewable Energy | Electric vehicle charging stations | Supports the transition to sustainable transport solutions | Integration with renewable energy sources and scalability options. |
How Are Car Starters and Alternators Used in Automotive Manufacturing?
In the automotive manufacturing sector, car starters and alternators are critical components in the assembly of vehicles. The starter is responsible for initiating the engine, while the alternator maintains the battery charge and powers electrical systems during operation. For manufacturers, ensuring the reliability of these components is essential to prevent assembly line delays and guarantee vehicle performance. International buyers should prioritize sourcing from suppliers that offer high-quality, certified parts compatible with various vehicle models to maintain assembly efficiency.
What Role Do Car Starters and Alternators Play in Transportation?
In the transportation industry, particularly for fleet management, the reliability of car starters and alternators is crucial. Fleets rely on these components to ensure their vehicles start promptly and operate efficiently, minimizing downtime. Businesses benefit from investing in durable starters and alternators that can withstand extensive use and varying environmental conditions. When sourcing, companies should consider the cost-effectiveness of components and the availability of spare parts to ensure seamless operations.

Illustrative image related to car starter vs alternator
How Are Car Starters and Alternators Applied in Agriculture?
Agricultural machinery, such as tractors and harvesters, relies heavily on functional starters and alternators to operate efficiently, especially in remote areas. A reliable starter ensures that machinery can start quickly, while the alternator keeps electrical systems running for lights and other equipment. For B2B buyers in agriculture, sourcing components that can withstand harsh weather conditions and require minimal maintenance is essential for maximizing productivity during critical farming periods.
Why Are Car Starters and Alternators Important in Construction?
In the construction sector, heavy machinery such as excavators and bulldozers depends on effective starters and alternators for reliable operation. These components are vital for ensuring that equipment can start quickly and operate under demanding conditions. Buyers in this industry should focus on sourcing robust starters and alternators that comply with safety standards and can handle the rigorous demands of construction sites, thus preventing costly downtime.
What Is the Significance of Car Starters and Alternators in Renewable Energy?
As the world transitions to renewable energy, electric vehicle (EV) charging stations increasingly rely on efficient alternators and starters. These components are essential for the effective operation of charging systems, ensuring that vehicles can start and run on sustainable energy. B2B buyers in this sector should prioritize sourcing components that integrate seamlessly with renewable energy sources and offer scalability for future growth, supporting the broader shift towards sustainable transportation solutions.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘car starter vs alternator’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Misdiagnosing Electrical Failures in Fleet Vehicles
The Problem: Many B2B buyers managing fleets, especially in regions with fluctuating climates like the Middle East or South America, often encounter misdiagnosis of electrical issues. For instance, a fleet manager might receive reports of vehicles failing to start or experiencing electrical malfunctions. With both the starter and alternator playing crucial roles in a vehicle’s electrical system, it can be challenging to pinpoint which component is at fault. This uncertainty can lead to unnecessary repairs, wasted time, and increased operational costs.
The Solution: To mitigate this issue, fleet managers should implement a systematic diagnostic approach. Start by training your maintenance team on the distinct functions of the starter and alternator. Utilize diagnostic tools that can analyze voltage output and component performance. For example, if a vehicle won’t start, a simple jump-start test can help identify if the battery is dead or if the starter is malfunctioning. Establishing a checklist for each vehicle can streamline this process, helping technicians determine the root cause quickly. Partnering with reliable suppliers for high-quality starters and alternators will also ensure that replacements are durable and compatible, reducing the likelihood of future failures.
Scenario 2: Costly Downtime Due to Component Failures
The Problem: Businesses in sectors such as logistics or construction often face significant financial losses due to vehicle downtime caused by starter or alternator failures. When a vehicle is out of commission, not only does it delay project timelines, but it also leads to additional costs in terms of repairs and lost productivity. Moreover, the lack of immediate access to replacement parts can exacerbate these issues, especially in remote areas.
Illustrative image related to car starter vs alternator
The Solution: To minimize downtime, establish a proactive maintenance schedule that includes regular inspections of both starters and alternators. Educate your team on the common signs of failure, such as unusual noises or dimming lights, which can indicate a failing alternator. Additionally, forming partnerships with local suppliers ensures that you have quick access to critical components when needed. Consider investing in a mobile maintenance unit that can conduct on-site repairs and diagnostics, reducing the time vehicles spend off the road. This strategic approach not only saves costs but also enhances operational efficiency.
Scenario 3: Challenges in Sourcing Quality Replacement Parts
The Problem: For international B2B buyers, especially those in developing regions like Africa or South America, sourcing quality replacement parts for starters and alternators can be a daunting task. Many suppliers offer subpar components that may not withstand local driving conditions, leading to frequent failures and repairs. This inconsistency can damage business reputations and erode customer trust.
The Solution: To ensure the procurement of high-quality parts, buyers should conduct thorough research on potential suppliers, focusing on their reputation and product quality. Look for suppliers who provide detailed specifications and warranties for their products. Engaging in trade shows and automotive expos can also facilitate direct connections with reputable manufacturers. Furthermore, consider forming cooperative purchasing agreements with other businesses in your region to increase your buying power and secure better terms from suppliers. By prioritizing quality over price, you can reduce the frequency of failures and enhance the reliability of your fleet, ultimately leading to a more satisfied customer base.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for car starter vs alternator
What Materials Are Commonly Used in Car Starters and Alternators?
When selecting materials for car starters and alternators, it’s essential to consider various factors such as performance, durability, cost, and regional compliance. Here, we analyze four common materials used in these automotive components: aluminum, copper, steel, and plastic.
How Does Aluminum Benefit Car Starters and Alternators?
Aluminum is frequently used in the housing of starters and alternators due to its lightweight nature and excellent corrosion resistance. It can withstand moderate temperatures, making it suitable for automotive applications where heat is generated.

Illustrative image related to car starter vs alternator
Pros: Aluminum is durable yet lightweight, which contributes to overall vehicle efficiency. Its resistance to corrosion extends the lifespan of components, particularly in humid or saline environments.
Cons: While aluminum is generally cost-effective, high-quality grades can be more expensive. Additionally, aluminum’s lower tensile strength compared to steel can be a limitation in high-stress applications.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is compatible with various automotive fluids and can handle the thermal cycling typical in engine environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should ensure compliance with local standards, such as ASTM for material specifications, and consider the availability of aluminum grades that meet these standards.
What Role Does Copper Play in Electrical Conductivity?
Copper is a critical material used in the windings of both starters and alternators due to its exceptional electrical conductivity. This property ensures efficient power transfer, which is vital for the performance of these components.
Pros: Copper’s high conductivity allows for smaller gauge wires, reducing weight and space requirements. It is also highly ductile, making it easy to work with during manufacturing.
Cons: Copper is more expensive than aluminum and can be prone to corrosion if not properly insulated. In humid environments, oxidation can lead to increased electrical resistance.
Impact on Application: Copper’s compatibility with electrical systems is crucial, as it effectively transmits the high currents required for starting engines.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with electrical standards (e.g., IEC) is essential, particularly in regions like the Middle East and Europe, where electrical safety regulations are stringent.
Why Is Steel a Common Choice for Structural Components?
Steel is often used for the structural components of starters and alternators due to its high strength and durability. It is particularly favored for parts that experience significant mechanical stress.
Pros: Steel’s high tensile strength makes it suitable for high-load applications, and it is generally less expensive than aluminum and copper.
Cons: Steel is heavier than aluminum and can corrode if not properly treated or coated. Its weight can negatively impact vehicle efficiency.
Impact on Application: Steel components are well-suited for environments where mechanical durability is paramount, but they may require protective coatings to prevent rust and corrosion.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider local manufacturing capabilities and standards for steel, such as JIS in Japan or EN in Europe, to ensure compliance and quality.
How Does Plastic Contribute to Component Design?
Plastic is increasingly used in various non-structural components of starters and alternators, such as housings and insulation parts. Its lightweight nature and resistance to corrosion make it an attractive choice.
Pros: Plastic is cost-effective and can be molded into complex shapes, allowing for innovative designs that can save space and weight.
Cons: Plastic may not withstand high temperatures as effectively as metals and can degrade over time when exposed to certain automotive fluids.
Impact on Application: While plastic is suitable for non-load-bearing applications, its limitations in high-temperature environments must be considered.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with environmental regulations regarding plastic use, such as REACH in Europe, is crucial for manufacturers and suppliers.
Illustrative image related to car starter vs alternator
Summary Table of Material Selection for Car Starters vs. Alternators
| Material | Typical Use Case for car starter vs alternator | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Housing and structural components | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Lower tensile strength compared to steel | Medium |
| Copper | Electrical windings | Excellent electrical conductivity | Prone to corrosion if not insulated | High |
| Steel | Structural components | High tensile strength and durability | Heavier and prone to corrosion | Low |
| Plastic | Non-structural components and insulation | Cost-effective and moldable | Limited high-temperature resistance | Low |
This analysis provides B2B buyers with actionable insights into material selection for car starters and alternators, highlighting the importance of balancing performance, cost, and compliance with regional standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for car starter vs alternator
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Car Starters and Alternators?
Manufacturing car starters and alternators involves several critical stages that ensure the final products meet performance standards and reliability. The process typically includes material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
-
Material Preparation: The manufacturing process begins with selecting high-quality raw materials, including copper, aluminum, and various plastics. These materials must meet specific standards for conductivity, durability, and thermal resistance. Suppliers often provide material certifications to ensure compliance with international quality standards.
-
Forming: In this stage, raw materials are shaped into components. For starters, this includes creating the housing, armature, and field coils, while alternators require the production of stators, rotors, and voltage regulators. Techniques such as stamping, forging, and machining are commonly used to achieve precise dimensions and tolerances. Advanced methods like injection molding may also be employed for plastic components.
-
Assembly: After forming, the individual components are assembled. This process often includes the integration of electrical connections, the installation of bearings, and the application of lubricants. Automated assembly lines are frequently used to enhance efficiency and reduce human error. The assembly process must ensure that all parts fit correctly and function together seamlessly.
-
Finishing: The final stage involves applying protective coatings and conducting surface treatments to enhance corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal. This may include anodizing aluminum parts for alternators or applying paint to starter housings. Quality checks during this phase ensure that all components meet the required specifications and are free from defects.
What Quality Assurance Standards Should B2B Buyers Expect for Starters and Alternators?
Quality assurance (QA) is paramount in the manufacturing of car starters and alternators, as failures can lead to significant safety concerns and operational issues. Buyers should be aware of both international and industry-specific standards that govern the manufacturing process.
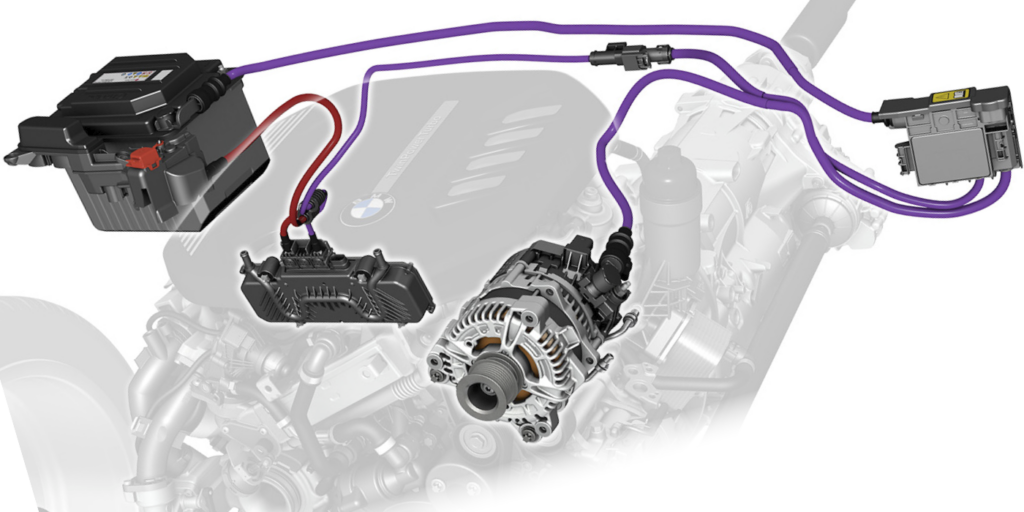
Illustrative image related to car starter vs alternator
-
International Standards: ISO 9001 is a widely recognized quality management system that outlines requirements for consistent quality in manufacturing. Compliance with ISO standards ensures that manufacturers maintain effective processes and continuously improve their operations. B2B buyers should inquire about a supplier’s ISO certification as a baseline for quality assurance.
-
Industry-Specific Certifications: In addition to ISO 9001, automotive components may need to comply with standards such as ISO/TS 16949, which specifically applies to the automotive sector. Other relevant certifications include CE marking for products sold in Europe and API standards for automotive components.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Manufacturing Starters and Alternators?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are critical at various stages of the manufacturing process to catch defects early and ensure product reliability.
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This checkpoint occurs when raw materials arrive at the facility. Suppliers must provide documentation that materials meet specified standards, and random sampling may be performed to test for quality.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, ongoing inspections are conducted at various stages to ensure that components are being produced according to specifications. This may include dimensional checks, electrical testing, and visual inspections.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once the product is fully assembled, final inspections are performed. This includes comprehensive testing of electrical components, functionality tests, and endurance testing to simulate real-world conditions. Products that pass this stage are typically marked for shipment.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
For international B2B buyers, especially those from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is crucial for ensuring product reliability.
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits of potential suppliers can provide insights into their manufacturing processes and quality control practices. During an audit, buyers can review documentation, observe manufacturing practices, and assess compliance with quality standards.
-
Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports from suppliers can help buyers understand their QC processes. These reports should include information about testing methods, failure rates, and corrective actions taken in response to any quality issues.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection agencies can provide an unbiased evaluation of a supplier’s quality control measures. These agencies can perform random inspections and testing, ensuring that the products meet the required standards before shipment.
What Are the Common Testing Methods Used in Quality Assurance for Starters and Alternators?
Testing methods for starters and alternators are designed to validate the performance and reliability of these components. Common testing techniques include:
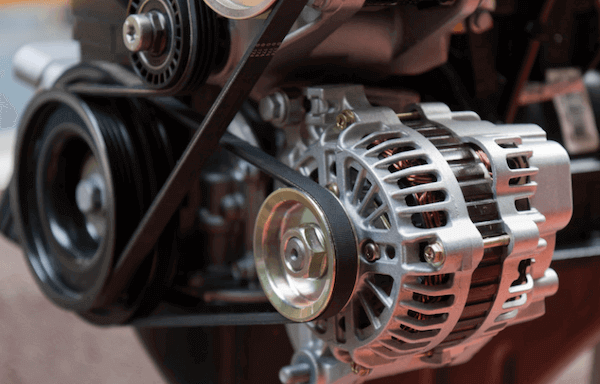
Illustrative image related to car starter vs alternator
-
Electrical Testing: This includes testing the electrical resistance, output voltage, and current draw of starters and alternators. These tests help ensure that components function correctly under load conditions.
-
Durability Testing: Products are subjected to rigorous testing to simulate long-term usage. This may involve running alternators at high temperatures and loads for extended periods to assess their ability to withstand real-world conditions.
-
Vibration and Shock Testing: Given that automotive components are often subjected to vibrations and shocks during operation, testing for these factors is critical. Components may be exposed to vibration cycles to ensure they maintain structural integrity.
What Are the Unique Quality Control Challenges for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers often face unique challenges when it comes to quality control in sourcing car starters and alternators. These challenges include:
-
Regulatory Compliance: Different countries have varying regulations regarding automotive components. Buyers must ensure that products comply with local laws and standards, which can complicate sourcing from international suppliers.
-
Communication Barriers: Language differences and cultural nuances can lead to misunderstandings regarding quality expectations. Establishing clear communication channels and documentation practices is essential.
-
Supply Chain Variability: The global supply chain can introduce variability in component quality, especially if materials are sourced from multiple suppliers. Buyers should work closely with manufacturers to ensure consistent quality across all components.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance standards for car starters and alternators, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they source reliable and high-quality automotive components that meet their operational needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘car starter vs alternator’
Introduction
This sourcing guide is designed to assist B2B buyers in making informed decisions when procuring car starters and alternators. Understanding the critical differences between these components and their respective roles in vehicle operation is essential for effective sourcing. This checklist will provide actionable steps to help you identify the right products and suppliers for your business needs.

Illustrative image related to car starter vs alternator
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Understanding the technical requirements for car starters and alternators is the first step in sourcing. This includes knowing the make and model of the vehicles you service, as well as specific power requirements and compatibility. Be sure to document voltage ratings, dimensions, and any unique features such as high-efficiency models or lightweight designs.
- Consider Environmental Factors: If you operate in extreme climates, factor in temperature tolerances and moisture resistance.
- Assess Application Needs: Identify whether you need starters and alternators for standard vehicles, luxury models, or heavy-duty applications.
Step 2: Research Market Trends and Innovations
Staying informed about the latest market trends and technological advancements can give you a competitive edge. For instance, advancements in energy efficiency and smart technology in starters and alternators are becoming more common.
- Monitor Industry Reports: Utilize industry publications and reports to understand emerging trends.
- Engage with Professional Networks: Participate in automotive forums or trade associations to gather insights from peers.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a supplier, it’s essential to conduct thorough evaluations. Request detailed company profiles and product catalogs, and ask for case studies or references from other clients in your region or industry.
- Examine Supplier Certifications: Check for relevant certifications that ensure quality, such as ISO or TS certifications.
- Review Warranty Terms: Understand the warranty offerings for the products to assess the supplier’s confidence in their quality.
Step 4: Verify Product Quality and Compliance
Quality is paramount when sourcing automotive components. Ensure that the starters and alternators meet international quality standards and local regulatory requirements.
- Request Sample Products: If possible, obtain samples to evaluate the build quality and performance.
- Check Compliance Documentation: Ensure all necessary certifications and compliance documents are available, particularly for international shipments.
Step 5: Assess After-Sales Support and Service
After-sales support can significantly impact your operations. A reliable supplier should offer robust customer service, including technical support and easy access to replacement parts.
- Inquire About Technical Assistance: Ask if the supplier provides installation support or technical guidance.
- Evaluate Return Policies: Understand the supplier’s return and replacement policies in case of defects or incompatibility.
Step 6: Consider Pricing and Payment Terms
Pricing is a critical factor in your sourcing decision. Gather quotes from multiple suppliers to compare pricing structures and terms.
- Analyze Total Cost of Ownership: Look beyond initial pricing to consider shipping costs, potential tariffs, and long-term durability.
- Negotiate Payment Terms: Discuss flexible payment options that align with your cash flow requirements.
Step 7: Finalize Your Procurement Decision
After completing your evaluations and comparisons, it’s time to make your final decision. Compile all your findings and ensure that the selected supplier aligns with your technical needs, budget, and service expectations.
- Document Your Decision: Keep a record of why you selected a particular supplier for future reference.
- Plan for Future Needs: Consider how this partnership could evolve, including potential volume discounts or exclusive arrangements.
This structured approach will streamline your sourcing process, ensuring that you choose the best car starters and alternators for your business requirements.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for car starter vs alternator Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Sourcing Car Starters and Alternators?
When evaluating the cost structure for sourcing car starters and alternators, several key components must be considered.
-
Materials: The primary materials for starters and alternators include metals like copper and aluminum, as well as plastic and rubber components. The quality and source of these materials can significantly affect pricing. For example, premium-grade copper for windings can enhance performance but also increase costs.
-
Labor: Labor costs can vary based on the location of manufacturing. Regions with higher labor costs may lead to increased prices for both starters and alternators. Outsourcing production to countries with lower labor costs can offer savings, but may introduce risks related to quality control.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses costs related to facilities, equipment maintenance, and utilities. A well-optimized manufacturing process can reduce overhead and, consequently, the final price of the components.
-
Tooling: The setup and maintenance of tooling for production can be a significant upfront cost. For custom or specialized components, this can lead to higher prices. Buyers should inquire about the tooling costs during negotiations.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing rigorous QC processes ensures reliability and performance. However, extensive testing and inspection can add to the overall cost of production. Certifications (like ISO) also contribute to pricing but enhance product credibility.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can vary widely depending on the distance, mode of transport, and customs regulations. For international buyers, understanding the logistics landscape is crucial to avoid unexpected charges.
-
Margin: Supplier margins will vary based on market competition and the perceived value of the product. Buyers should seek multiple quotations to understand the range of margins applied.
What Influences the Pricing of Car Starters and Alternators?
Pricing for starters and alternators is influenced by various factors:
-
Volume/MOQ: Larger orders typically result in lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should negotiate minimum order quantities (MOQ) that align with their needs to optimize pricing.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom-built components tailored to specific vehicles or performance standards may incur additional costs. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid unexpected price increases.
-
Materials: The choice of materials can drastically affect pricing. Higher-quality materials may improve durability and efficiency but will increase costs. Buyers should assess the trade-off between cost and performance.
-
Quality and Certifications: Products that meet higher quality standards or possess certifications will generally command higher prices. For international buyers, understanding the certification landscape in their region can be beneficial.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation, reliability, and service level of suppliers can affect pricing. Well-established suppliers may charge a premium for their products but often provide better support and warranty options.
-
Incoterms: The terms of shipping (Incoterms) can significantly influence the total landed cost. Buyers must understand their responsibilities concerning shipping costs, insurance, and tariffs to make informed purchasing decisions.
What Tips Can Help Buyers Negotiate Better Prices for Starters and Alternators?
-
Conduct Market Research: Understanding the market landscape and pricing trends for starters and alternators will empower buyers during negotiations. Knowledge of competitor pricing can provide leverage.
-
Negotiate for Volume Discounts: If feasible, consolidate purchases to increase order volume. Suppliers are often more willing to offer discounts for larger orders.
-
Consider Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): While the initial price is important, buyers should evaluate the TCO, which includes maintenance, performance, and longevity. Investing in higher-quality components may yield cost savings over time.
-
Evaluate Supplier Relationships: Building long-term relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing and service. Regular communication and feedback can enhance trust and negotiation outcomes.
-
Be Aware of Regional Pricing Nuances: Pricing can vary significantly based on geography. Buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should understand local market conditions and sourcing challenges to negotiate effectively.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for car starters and alternators can fluctuate based on market conditions, supply chain dynamics, and geopolitical factors. It is advisable for buyers to obtain updated quotations and conduct thorough due diligence before finalizing any sourcing decisions.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing car starter vs alternator With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives in Automotive Power Systems
In the automotive industry, the functionality and reliability of essential components like car starters and alternators are critical for vehicle performance. However, as technology evolves, several alternative solutions have emerged that serve similar purposes. This section will compare the traditional car starter and alternator against alternatives like hybrid battery systems and advanced starter-generator systems, providing B2B buyers with insights to make informed decisions.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Car Starter Vs Alternator | Hybrid Battery System | Advanced Starter-Generator System |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High starting torque; charges battery | Efficient energy use; longer life | Quick engine start; regenerative capabilities |
| Cost | Moderate initial cost; replacement can be expensive | Higher upfront investment | Higher initial cost; potential savings in fuel and maintenance |
| Ease of Implementation | Standard installation; common in most vehicles | More complex; requires integration | Requires specific vehicle design; more advanced |
| Maintenance | Regular checks needed; typically easy to replace | Low maintenance; long lifespan | Minimal maintenance; can be complex if issues arise |
| Best Use Case | Conventional vehicles; cost-sensitive applications | Electric and hybrid vehicles | Performance-oriented vehicles; improved fuel efficiency |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Hybrid Battery System
Hybrid battery systems are designed to power vehicles that utilize both an internal combustion engine and electric propulsion. These systems offer significant advantages in terms of fuel efficiency and reduced emissions. However, they come with a higher initial cost and require more complex integration into vehicle designs. B2B buyers should consider this option for fleets aiming to enhance sustainability and reduce operational costs in the long run. The longevity of hybrid batteries can lead to lower overall maintenance costs, making them an attractive investment for environmentally conscious businesses.
Advanced Starter-Generator System
Advanced starter-generator systems combine the functions of a starter and alternator into a single unit, often found in modern vehicles. They provide quick engine starts and can regenerate energy during braking, feeding it back into the vehicle’s electrical system. This system reduces the load on the battery and enhances fuel efficiency. While the initial investment is higher, the potential for savings in fuel costs and reduced maintenance makes this a viable option for performance-oriented fleets. However, the complexity of these systems can lead to challenges in diagnosis and repair, which should be considered by B2B buyers when evaluating their fleet’s needs.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution
When selecting between car starters, alternators, and alternative power solutions, B2B buyers must assess their specific operational requirements, budget constraints, and long-term goals. Factors such as performance, ease of implementation, and maintenance should guide the decision-making process. For companies in regions with developing automotive markets, understanding the balance between cost and technological advancement is crucial. Ultimately, investing in the right technology can enhance vehicle reliability, operational efficiency, and align with sustainability goals, ensuring that businesses remain competitive in an evolving landscape.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for car starter vs alternator
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Car Starters and Alternators?
Understanding the essential technical properties of car starters and alternators is crucial for B2B buyers, especially when sourcing components for automotive manufacturing or repair. Here are some critical specifications that should be considered:

Illustrative image related to car starter vs alternator
1. Material Grade
The materials used in starters and alternators significantly affect their durability and performance. Common materials include high-grade steel for casings and copper or aluminum for windings. High-quality materials ensure better conductivity, resistance to corrosion, and overall longevity, making them essential for reliable operation in various climates, particularly in regions like Africa and South America where conditions can be extreme.
2. Voltage Rating
The standard voltage for automotive starters and alternators is typically 12V. However, high-performance vehicles may require 24V systems. Understanding voltage ratings is critical for compatibility with existing electrical systems in vehicles. B2B buyers should ensure that the voltage specifications align with their target markets to avoid operational failures.
3. Current Draw (Amperage)
Starters can draw between 150 to 200 amps during operation, while alternators usually output between 40 to 120 amps. This specification is vital when assessing the power requirements and ensuring that the vehicle’s battery and electrical system can support these components. Buyers should consider the amperage to prevent overloads that could lead to component failure.
4. Tolerance Levels
Tolerance refers to the permissible limits of variation in a physical dimension or measured value. For starters and alternators, tight tolerances on components like bearings and gears are crucial for ensuring efficient operation and minimizing wear. Understanding tolerance levels helps buyers ensure that components fit precisely during assembly, reducing the risk of malfunction.
5. Weight
The weight of starters and alternators can affect vehicle performance and fuel efficiency. Lighter components can contribute to better overall vehicle dynamics. B2B buyers should consider the balance between weight and durability, especially in markets where fuel efficiency is a key selling point.
Illustrative image related to car starter vs alternator
6. Operating Temperature Range
The ability of starters and alternators to function in varying temperatures is a vital property, especially in regions with extreme weather conditions. Components should be designed to operate efficiently in both hot and cold environments, ensuring reliability regardless of geographic location.
What Are the Common Trade Terms Related to Starters and Alternators?
Familiarity with industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the automotive parts market. Here are some key terms relevant to starters and alternators:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
This term refers to parts made by the original manufacturer of the vehicle. OEM parts are often preferred for their guaranteed compatibility and quality. B2B buyers should assess whether to source OEM components or consider aftermarket alternatives based on their market needs.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ indicates the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is crucial for managing inventory and cash flow, especially for buyers looking to minimize excess stock while ensuring they meet demand.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for specific quantities of products. It’s a standard practice in procurement that helps buyers compare offers and negotiate better deals.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
These are internationally recognized rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping goods. Key terms include FOB (Free on Board) and CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight), which clarify who bears shipping costs and risks. Knowledge of Incoterms is vital for B2B buyers to avoid misunderstandings in international trade.
5. Aftermarket
Refers to parts and accessories made by companies other than the original manufacturer. Aftermarket products can offer cost-effective alternatives to OEM parts, but buyers must evaluate quality and compatibility.

Illustrative image related to car starter vs alternator
6. Lead Time
This term indicates the time taken from placing an order to receiving the goods. Understanding lead times is essential for B2B buyers to manage their supply chain effectively, especially in regions with longer shipping durations.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance their procurement strategies and improve operational efficiency in the automotive sector.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the car starter vs alternator Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Car Starter vs Alternator Sector?
The global automotive industry is undergoing significant transformation, driven by advancements in technology, sustainability initiatives, and changing consumer preferences. For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these dynamics is crucial for strategic sourcing.
One of the primary drivers in the car starter and alternator market is the increasing demand for electric and hybrid vehicles. As manufacturers shift towards more sustainable models, the need for efficient starters and alternators that can support electric powertrains is growing. This trend is particularly evident in Europe and parts of South America, where regulatory pressures and consumer demand for greener options are reshaping product offerings.

Illustrative image related to car starter vs alternator
Another emerging trend is the integration of advanced technology into starters and alternators. Features such as smart sensors and connectivity options are being developed to enhance performance and reliability. B2B buyers should look for suppliers who are investing in R&D to develop these innovative components, as they will likely offer a competitive edge in the marketplace.
Furthermore, globalization is influencing sourcing strategies. With a diverse supplier base spanning multiple continents, buyers can leverage competitive pricing and quality by sourcing from different regions. However, this also necessitates a keen understanding of local regulations and standards, especially in emerging markets where compliance can vary significantly.
How Are Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impacting the Car Starter vs Alternator Industry?
Sustainability has become a focal point in the automotive sector, affecting not only vehicle design but also the sourcing of components like starters and alternators. B2B buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to environmentally friendly practices. This includes sourcing materials responsibly and minimizing waste throughout the production process.
The environmental impact of traditional automotive components can be significant, prompting buyers to seek alternatives that align with sustainability goals. For instance, manufacturers are exploring the use of recycled materials and eco-friendly manufacturing processes to produce starters and alternators. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management systems can serve as indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability.

Illustrative image related to car starter vs alternator
Moreover, ethical sourcing practices are essential in today’s market. Buyers should ensure that their suppliers adhere to fair labor practices and have transparent supply chains. This not only fosters corporate social responsibility but also builds trust with consumers who are increasingly aware of the ethical implications of their purchases.
As sustainability becomes more integrated into the automotive supply chain, buyers who prioritize “green” certifications and materials will be better positioned to meet market demands and regulatory requirements.
What Is the Historical Context of Car Starters and Alternators for B2B Buyers?
The evolution of starters and alternators dates back to the early 20th century, when the first electric starters replaced hand-crank mechanisms, revolutionizing vehicle operation. Initially, these components were relatively simple, but as automotive technology advanced, so did the complexity and functionality of starters and alternators.
By the mid-20th century, the introduction of alternators improved the efficiency of electrical systems in vehicles, allowing for better battery management and the powering of additional components. Today, starters and alternators are critical to vehicle performance, particularly with the rise of advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) and electric vehicles.
For B2B buyers, understanding this historical context is vital for recognizing the importance of innovation and reliability in sourcing decisions. As the industry continues to evolve, staying informed about the latest developments will enable buyers to make strategic choices that align with their operational needs and market trends.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of car starter vs alternator
-
How do I determine whether to source a starter or an alternator for my vehicle?
To decide between a starter and an alternator, consider the symptoms your vehicle exhibits. If the engine doesn’t crank or makes a clicking sound but dashboard lights are functional, the starter may be the issue. Conversely, if the vehicle starts but electrical components fail or headlights dim while running, the alternator is likely the culprit. Conduct thorough diagnostics and consult with a trusted technician to ensure accurate identification, allowing you to source the correct part efficiently. -
What is the best way to evaluate suppliers for car starters and alternators?
When evaluating suppliers, focus on their reputation, product quality, and compliance with international standards. Request references from previous clients and assess their experience in your target market, particularly in regions like Africa or South America. Examine their certifications, such as ISO or TS16949, to ensure they meet quality assurance standards. Additionally, consider suppliers who offer comprehensive warranties and after-sales support, as these factors can significantly impact your business’s reliability and customer satisfaction. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for starters and alternators?
MOQs can vary significantly based on the supplier and the specific components you’re sourcing. Generally, MOQs for automotive parts like starters and alternators may range from 50 to 200 units. However, some suppliers may offer flexibility for first-time buyers or smaller businesses. Always discuss your needs upfront, and negotiate terms that align with your inventory strategies and cash flow management, especially if you’re entering a new market. -
How can I ensure quality assurance when sourcing starters and alternators?
To guarantee quality, request detailed product specifications and certifications from suppliers. Implement a quality control process that includes pre-shipment inspections and testing of samples before bulk orders. Consider partnering with suppliers who have established quality management systems and are willing to provide documented evidence of compliance. Additionally, establishing a clear return policy for defective parts can safeguard your investments. -
What payment terms should I negotiate with suppliers for automotive parts?
Payment terms can vary based on the supplier’s policies and your negotiation power. Common arrangements include upfront payments, letters of credit, or payment upon delivery. Aim for terms that balance cash flow with security; for example, negotiating a 30% deposit with the remaining 70% upon delivery can mitigate risk. Additionally, explore options for early payment discounts, which can enhance your profitability in the long run. -
What logistics considerations should I account for when importing starters and alternators?
When importing, consider shipping methods, customs regulations, and delivery timelines. Air freight is faster but more expensive, while sea freight is cost-effective for larger shipments but may take longer. Understand the import duties and taxes in your country, as these can impact overall costs. Additionally, establishing a reliable logistics partner familiar with automotive parts can streamline the import process and reduce delays. -
How do climate conditions affect the performance of starters and alternators?
Extreme temperatures can significantly impact the lifespan and efficiency of starters and alternators. High heat can lead to overheating and premature failure, while cold temperatures can cause batteries to lose charge quickly, affecting the starter’s performance. When sourcing parts for regions with harsh climates, consider components specifically designed to withstand these conditions. Communicating your specific environmental requirements to suppliers can ensure they provide the most suitable products. -
What customizations are available for starters and alternators?
Many suppliers offer customization options for starters and alternators, such as specific voltage ratings, gear ratios, or housing colors to fit unique vehicle specifications. Discuss your requirements with potential suppliers and inquire about their capabilities for custom designs. Customization can be beneficial for niche markets or brands looking to differentiate their products. Be sure to factor in potential lead times and costs associated with custom orders in your sourcing strategy.
Top 2 Car Starter Vs Alternator Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Reddit – Automotive Battery Basics
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: The battery provides power to all electronics on board, including the starter. The alternator charges the battery when the engine is running. The starter uses power from the battery to turn over the engine. A dead battery is indicated by no power at all, while a failing alternator may show a battery light on the dash when the engine is running.
2. Honda – Starter Troubleshooting
Domain: mechanics.stackexchange.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: 2006 Honda Civic EX 1.8L 4 Cylinder; symptoms include weak cranking, inability to start, single click sound when attempting to start; potential issues with starter or alternator; new battery installed; previous battery tested good; starter failure when hot; voltage drop test suggested for diagnosis.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for car starter vs alternator
What Are the Key Takeaways for B2B Buyers on Car Starters and Alternators?
Understanding the distinct roles and functionalities of car starters and alternators is crucial for international B2B buyers seeking to optimize their supply chains. Starters are essential for initiating engine operation, while alternators play a pivotal role in maintaining battery charge and powering electrical systems. Recognizing the symptoms of failure in these components—such as unusual noises, dimming lights, or starting issues—can lead to timely interventions and prevent costly downtimes.
Why Is Strategic Sourcing Important in the Automotive Component Market?
Strategic sourcing allows businesses to identify reliable suppliers who can provide high-quality starters and alternators, ensuring that operational efficiency is maintained. By leveraging data and market insights, B2B buyers can negotiate better terms and align their procurement strategies with the evolving automotive landscape, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
What’s Next for International Buyers in the Automotive Sector?
As the automotive industry continues to evolve, staying ahead of technological advancements and market trends is vital. B2B buyers should actively seek partnerships with suppliers who prioritize innovation and quality. Engage in discussions with potential vendors, explore emerging technologies in automotive components, and consider the long-term benefits of sustainable sourcing practices. Take proactive steps now to secure your supply chain and ensure your business thrives in a competitive market.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.